Exonuclease III Can Efficiently Cleave Linear Single-Stranded DNA: Reshaping Its Experimental Applications in Biosensors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
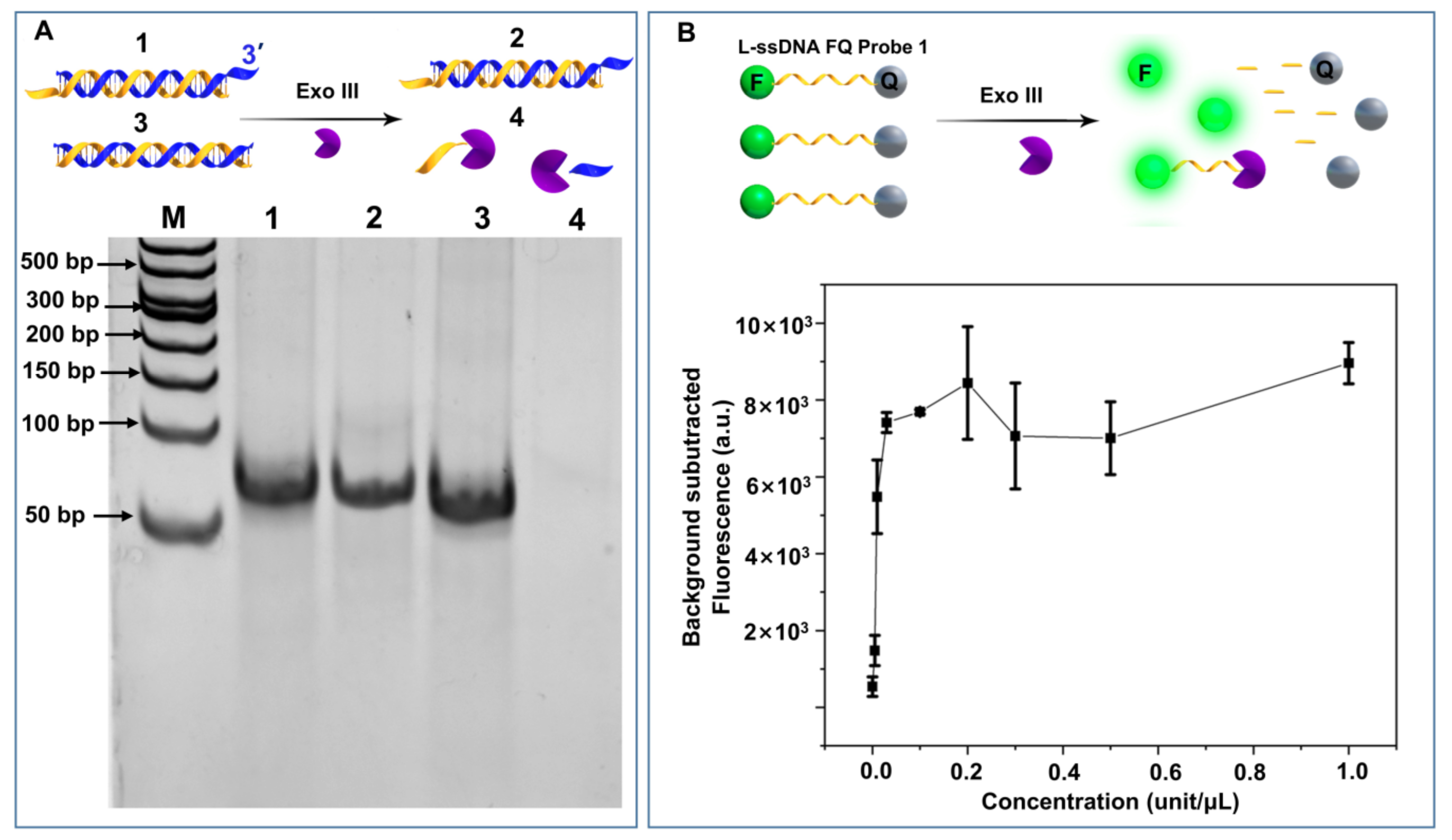
2.2. Fluorescence Detection of ssDNA FQ Reporter Digestion by Exonuclease III
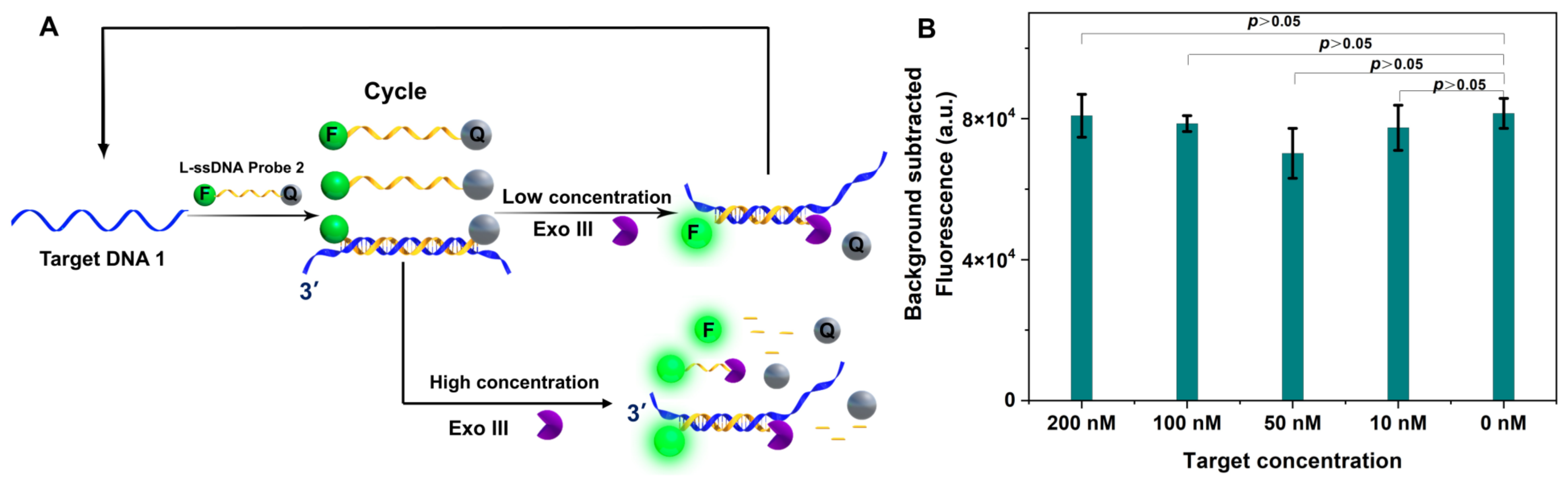
2.3. Exo III-Assisted Target Recycling Amplification with L-ssDNA Probe Free in Buffer
2.4. Exonuclease III Digestion of dsDNA with 3′ 4-nt Overhang dsDNA or Blunt-Ended dsDNA
3. Results and Discussion
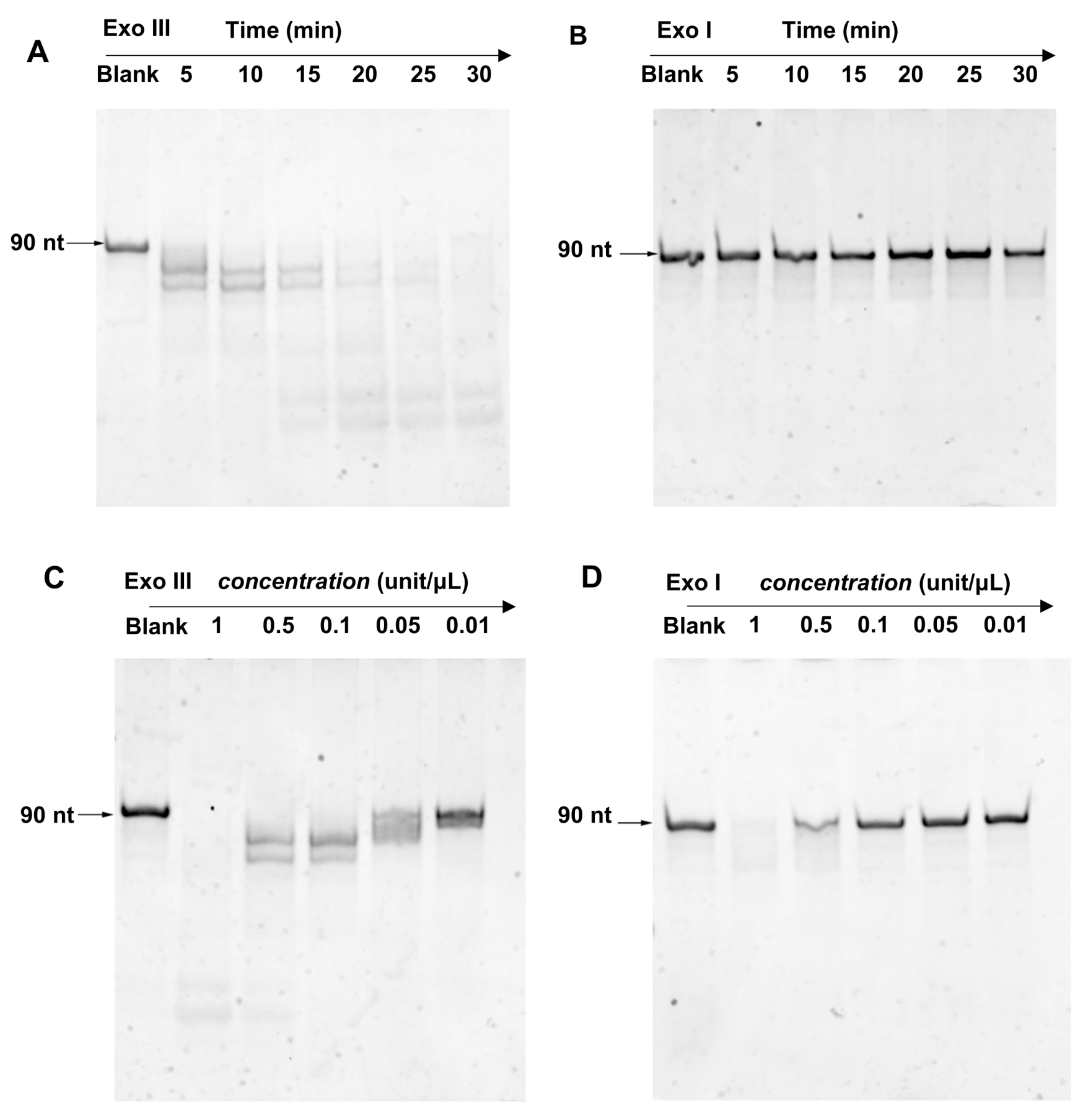
3.1. Exo III ssDNA Cleavage Property
3.2. Comparison of Exo III and Exo I ssDNA Cleavage Property
3.3. Exo III ssDNA Substrate in Target Recycling Assays
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Richardson, C.C.; Lehman, I.R.; Kornberg, A.A. A Deoxyribonucleic acid phosphatase-exonuclease from Escherichia coli. II. Characterization of the exonuclease activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1964, 239, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linxweiler, W.; Hörz, W. Sequence specificity of exonuclease III from E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982, 10, 4845–4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, R.; Liu, X.; Willner, I. Amplified multiplexed analysis of DNA by the exonuclease III-catalyzed regeneration of the target DNA in the presence of functionalized semiconductor quantum dots. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 4456–4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayers, J.R.; Schmidt, W.; Eckstein, F. 5′–3′ Exonucleases in phos-phorothioate-based oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988, 16, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.-H.; Wu, R. New rapid methods for DNA sequencing based on exonuclease III digestion followed by repair synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982, 10, 2065–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, B. Endonuclease II of Escherichia coli is exonuclease III. J. Biol. Chem. 1976, 251, 1896–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Q.; Wang, C.; Liu, P.; Zhang, G.; Song, L.; Fu, Y. Functionalized europium-porphyrin coordination polymer: Rational design of high performance electrochemiluminescence emitter for mucin 1 sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 191, 113422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; Qin, L.; Wang, M.; Wang, P. Signal-on electrochemical detection of DNA methylation based on the target-induced conformational change of a DNA probe and exonuclease III-assisted target recycling. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 149, 111847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xie, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Yin, H.; Yang, Z.; Ai, S. Rapid detection of Dam methyltransferase activity based on the exonuclease III-assisted isothermal amplification cycle. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 2771–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.J.; Cui, L.; Huang, J.; Yan, L.; Lin, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, W.Y.; Kang, H. Linear molecular beacons for highly sensitive bioanalysis based on cyclic Exo III enzymatic amplification. Biosens Bioelectron. 2011, 27, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, X.; Zhu, D.; Yao, G.; Su, S.; Chao, J.; Liu, H.; Zuo, X.; Wang, L.; Shi, J.; Wang, L.; et al. An Exonuclease III-Powered, On-Particle Stochastic DNA Walker. Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 1881–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Xuan, M.; Huo, S.; Fan, J.; Chakraborty, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Herrmann, A.; Zheng, L. Four-Dimensional Deoxyribonucleic Acid–Gold Nanoparticle Assemblies. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 17250–17255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Ding, L.; Song, W.; Yang, M.; Ju, H. Liberation of Protein-Specific Glycosylation Information for Glycan Analysis by Exonuclease III-Aided Recycling Hybridization. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 2923–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Qi, P.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, D. Sensitive quantitative detection of bacterial DNA based on lysozyme signal probe and Exo III-aided cycling amplification reaction. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 231, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Qu, X.; Li, S.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, S.; Huang, J. Exonuclease III-powered DNA Walking Machine for Label-free and Ultrasensitive Electrochemical Sensing of Antibiotic. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 297, 126771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Cao, A.; Zhang, L.F.; Zhang, C.Y. Rapid and label-free monitoring of exonuclease III-assisted target recycling amplification. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 10845–10851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Sismour, A.M.; Benner, S.A. Nucleoside alpha-thiotriphosphates, polymerases and the exonuclease III analysis of oligonucleotides containing phosphorothioate linkages. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 3118–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Hou, T.; Lu, T.; Li, F. Autonomous exonuclease III-assisted isothermal cycling signal amplification: A facile and highly sensitive fluorescence DNA glycosylase activity assay. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 9626–9631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, C.; Yan, Y.; Xiang, H.; Zhu, D.; Cheng, W.; Ju, H.; Ding, S. A new mode for highly sensitive and specific detection of DNA based on exonuclease III-assisted target recycling amplification and mismatched catalytic hairpin assembly. Chem Commun. 2015, 51, 4220–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, Y.; Yuan, H.; Guo, Z.; Li, X.-Q.; Yang, Z.; Zong, C. Exonuclease III Can Efficiently Cleave Linear Single-Stranded DNA: Reshaping Its Experimental Applications in Biosensors. Biosensors 2023, 13, 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13060581
Shen Y, Yuan H, Guo Z, Li X-Q, Yang Z, Zong C. Exonuclease III Can Efficiently Cleave Linear Single-Stranded DNA: Reshaping Its Experimental Applications in Biosensors. Biosensors. 2023; 13(6):581. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13060581
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Yi, Haoyu Yuan, Zixuan Guo, Xiu-Qing Li, Zhiqing Yang, and Chengli Zong. 2023. "Exonuclease III Can Efficiently Cleave Linear Single-Stranded DNA: Reshaping Its Experimental Applications in Biosensors" Biosensors 13, no. 6: 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13060581
APA StyleShen, Y., Yuan, H., Guo, Z., Li, X.-Q., Yang, Z., & Zong, C. (2023). Exonuclease III Can Efficiently Cleave Linear Single-Stranded DNA: Reshaping Its Experimental Applications in Biosensors. Biosensors, 13(6), 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13060581




