Copper-Guanosine Nanorods (Cu-Guo NRs) as a Laccase Mimicking Nanozyme for Colorimetric Detection of Rutin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Reagents and Apparatus
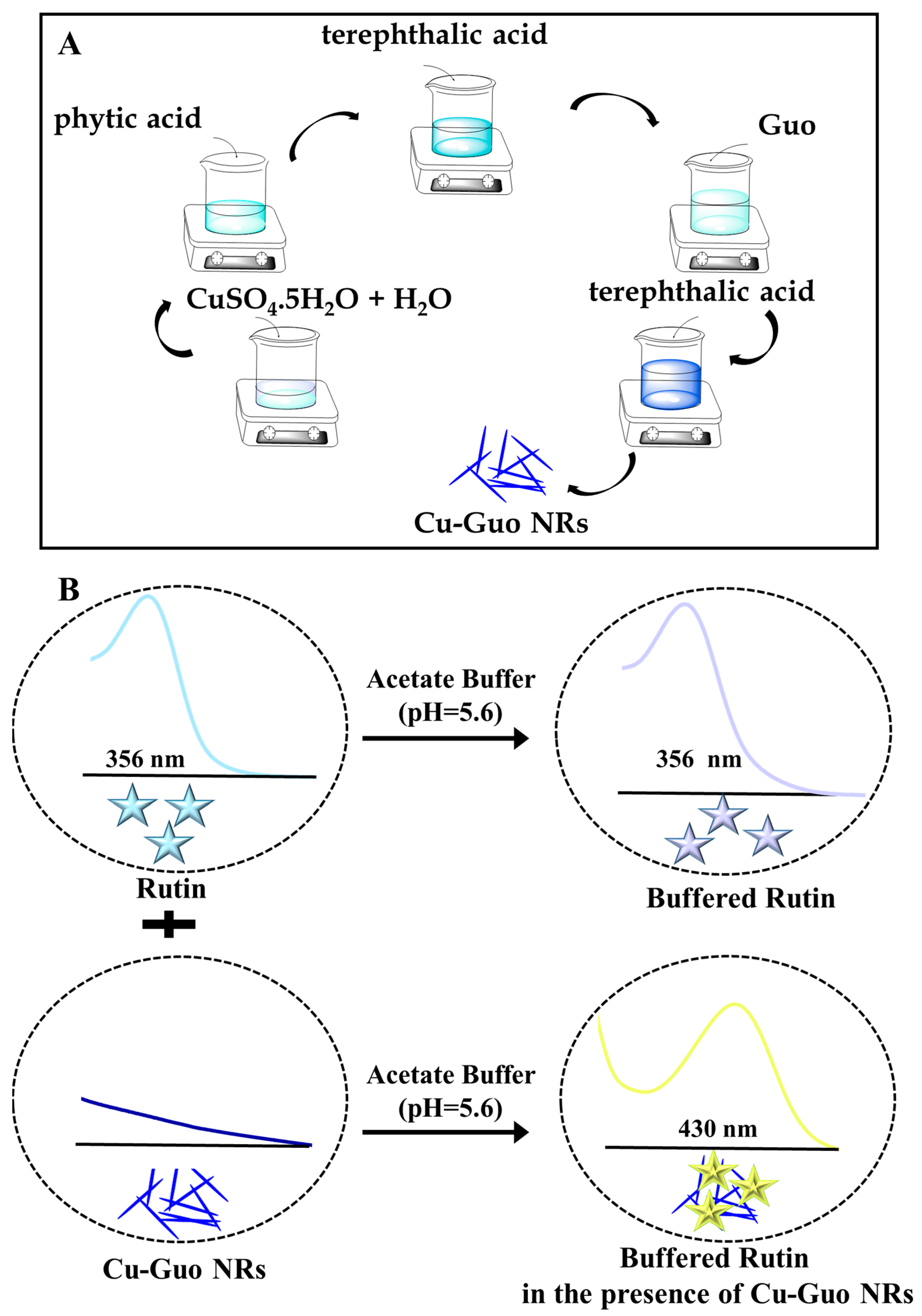
2.2. Preparation of Cu-Guo NRs Nanozymes
2.3. General Procedure for Colorimetric Detection of Rtn
2.4. Preparation of Real Samples
3. Results
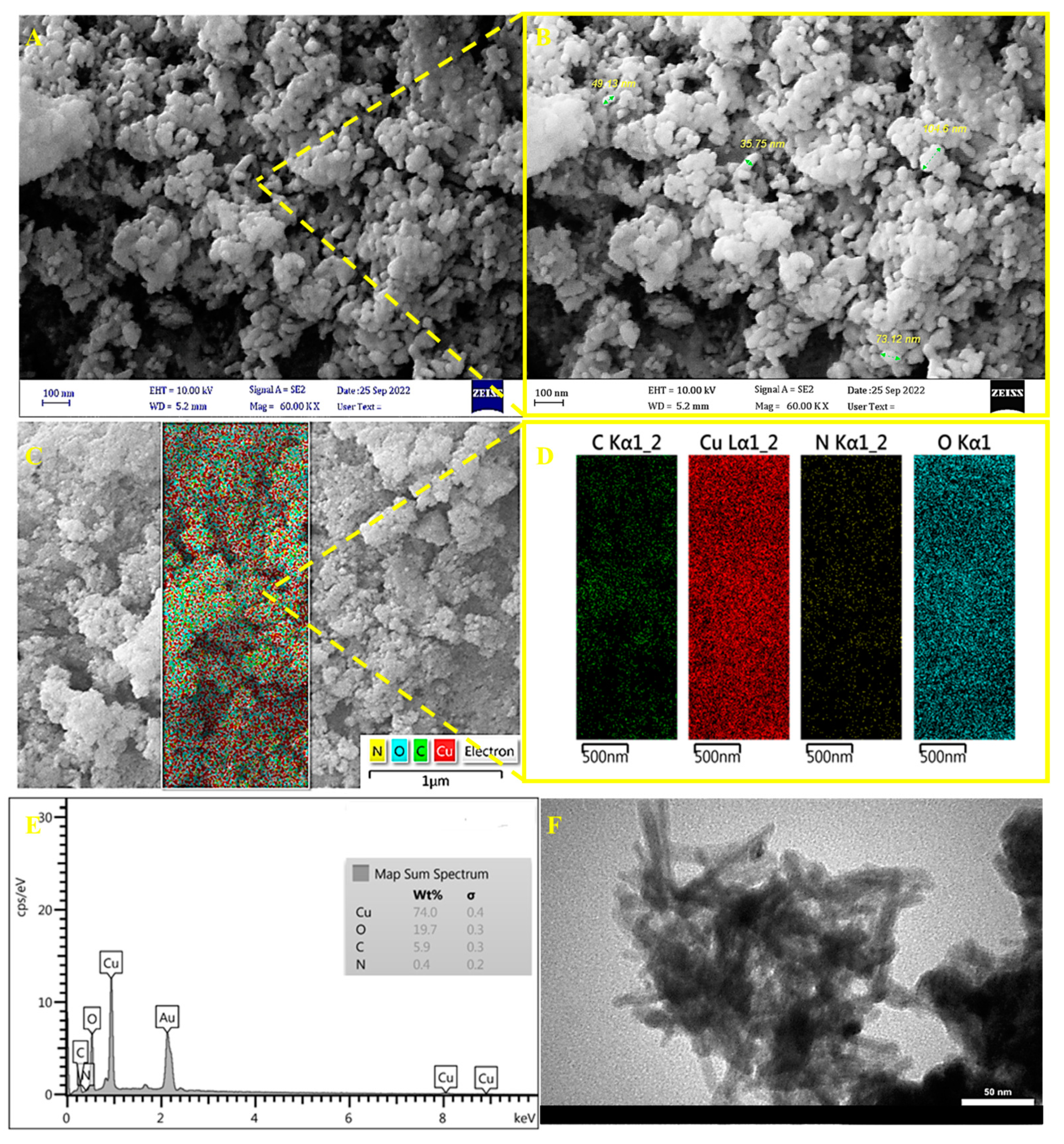
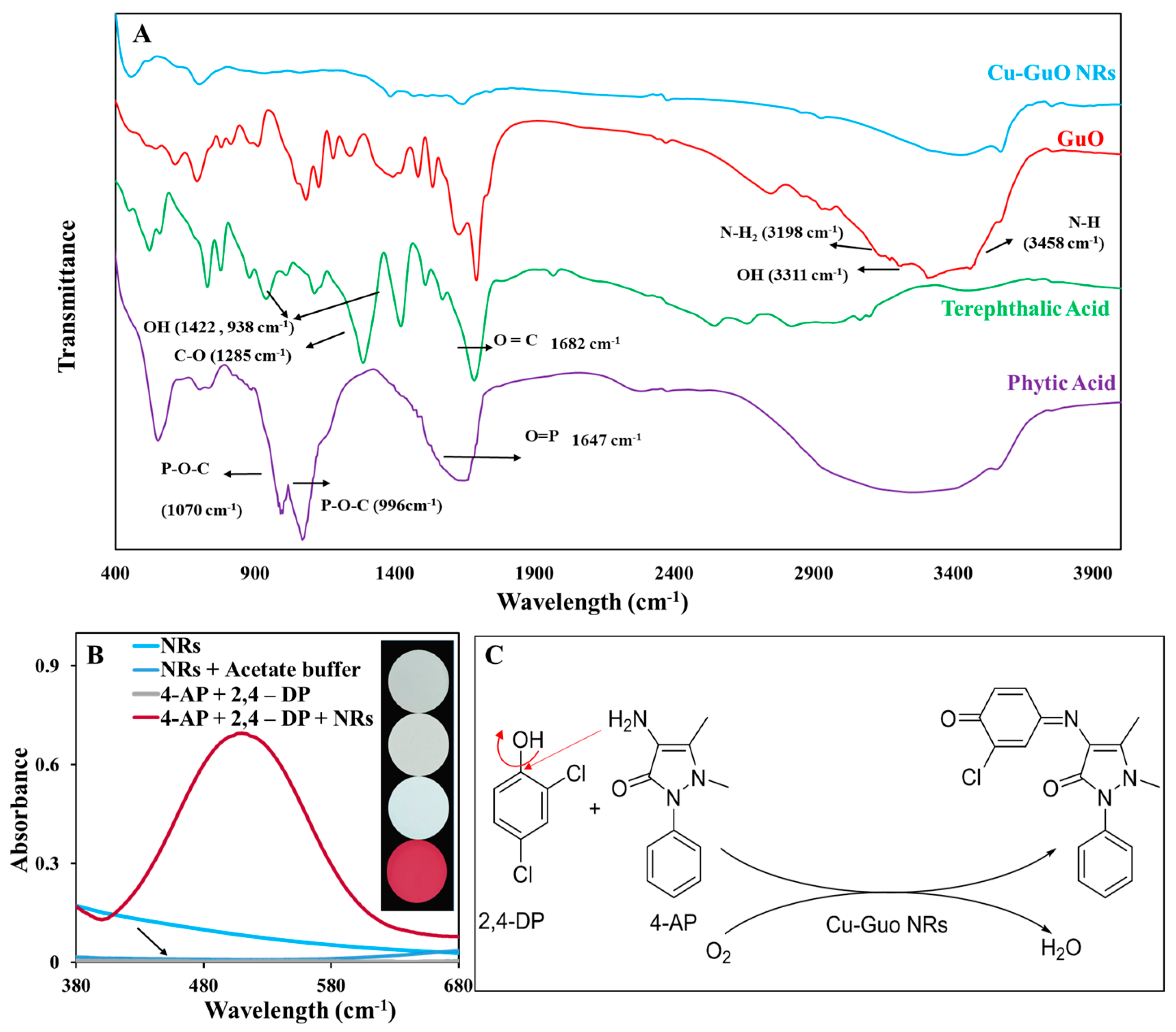
3.1. Morphology and Characterization of Cu-Guo NRs
3.2. Evaluation of the Laccase-like Catalytic Activity of Cu-Guo NRs
3.3. Principle of the Nanozyme Activity of Cu-Guo NRs in Rtn Detection
3.4. Optimization of the Measurement Conditions
3.5. Rtn Detection
3.6. Selectivity and Anti-Interference Study
3.7. Real Sample Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gholivand, M.B.; Mohammadi-Behzad, L.; Hosseinkhani, H. Application of a Cu–chitosan/multiwalled carbon nanotube film-modified electrode for the sensitive determination of rutin. Anal. Biochem. 2016, 493, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganeshpurkar, A.; Saluja, A.K. The Pharmacological Potential of Rutin. Saudi Pharm. J. 2017, 25, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinska, D.; Szawara-Nowak, D.; Zielinski, H. Determination of the antioxidant activity of rutin and its contribution to the antioxidant capacity of diversified buckwheat origin material by updated analytical strategies. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2010, 60, 315. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.-S.; Gong, J.; Liu, F.-T.; Mohammed, U. Naturally occurring polyphenolic antioxidants modulate IgE-mediated mast cell activation. Immunology 2000, 100, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihme, N.; Kiesewetter, H.; Jung, F.; Hoffmann, K.H.; Birk, A.; Müller, A.; Grützner, K.I. Leg oedema protection from a buckwheat herb tea in patients with chronic venous insufficiency: A single-centre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1996, 50, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschner, E.E.; Ruperto, J.; Wong, G.; Newmark, H.L. Quercetin and rutin as inhibitors of azoxymethanol-induced colonic neoplasia. Carcinogenesis 1991, 12, 1193–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panasiak, W.; Wleklik, M.; Oraczewska, A.; Luczak, M. Influence of flavonoids on combined experimental infections with EMC virus and Staphylococcus aureus in mice. Acta Microbiol. Pol. 1989, 38, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.F. Sensitive Fluorometric Method for the Determination of Rutin in Combined Tablet Dosage Form. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 75, 614–618. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.-Y.; Bok, S.-H.; Jeon, S.-M.; Park, Y.B.; Lee, S.-J.; Jeong, T.-S.; Choi, M.-S. Effect of rutin and tannic acid supplements on cholesterol metabolism in rats. Nutr. Res. 2001, 22, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitler, A.D.; Dhillon, P.; Shorter, J. Neurodegenerative disease: Models, mechanisms, and a new hope. Dis. Model. Mech. 2017, 10, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindle, J.V. Ageing, neurodegeneration and Parkinson’s disease. Age Ageing 2010, 39, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahdost-Fard, F.; Roushani, M. Applicability of a nanocomposite consists of quantum dot and silver nanoparticle (AgNP/QD) in the modeling of a BCM-7 aptasensor in early distinguish of autism underlying rutin as a green redox probe. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahdost-Fard, F.; Roushani, M. Designing an ultra-sensitive aptasensor based on an AgNPs/thiol-GQD nanocomposite for TNT detection at femtomolar levels using the electrochemical oxidation of Rutin as a redox probe. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Yin, H.; Chen, B.; Xia, G.; Yang, H.; Jia, X. Validated reversed phase-high performance liquid chromatography-diode array detector method for the quantitation of Rutin, a natural immunostimulant for improving survival in aquaculture practice, in toonea sinensis folium. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2012, 8, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memon, A.F.; Solangi, A.R.; Memon, S.Q.; Mallah, A.; Memon, N.; Memon, A.A. Simultaneous Determination of Quercetin, Rutin, Naringin, and Naringenin in Different Fruits by Capillary Zone Electrophoresis. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Chen, L.; Zhong, Y.; Ni, Y. Determination of rutin by chemiluminescence based on a luminol–potassium periodate–ZnSe system. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 4056–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Gao, B.; Chen, P.; Charles, D.; Yu, L. Characterisation of organic and conventional sweet basil leaves using chromatographic and flow-injection mass spectrometric (FIMS) fingerprints combined with principal component analysis. Food Chem. 2014, 154, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, L.; Liu, T.; Ju, P.; Zhu, L.; Ai, S. Sensitive voltammetric determination of rutin in pharmaceuticals, human serum, and traditional Chinese medicines using a glassy carbon electrode coated with graphene nanosheets, chitosan, and a poly(amido amine) dendrimer. Microchim. Acta 2011, 173, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, K.H.G.; Fatibello-Filho, O.; De Mattos, I.L. Square-wave voltammetric determination of rutin in pharmaceutical formulations using a carbon composite electrode modified with copper (II) phosphate immobilized in polyester resin. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 48, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Li, Y.; Tang, H.-W.; Liu, C.-M.; Wu, Q.-S. Determination of Rutin with UV-Vis Spectrophotometric and Laser-Induced Fluorimetric Detections Using a Non-Scanning Spectrometer. Anal. Lett. 2010, 43, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pınar, P.T.; Yardım, Y.; Şentürk, Z. Voltammetric behavior of rutin at a boron-doped diamond electrode. Its electroanalytical determination in a pharmaceutical formulation. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 2013, 11, 1674–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.; Guo, Q.; Yin, Z.; Zhu, X.; Liu, R.; Liu, A.; Huang, S. Polyphenol oxidase/gold nanoparticles/mesoporous carbon-modified electrode as an electrochemical sensing platform for rutin in dark teas. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 2152–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Row, K.H. Determination of Rutin from Ginkgo biloba L. Leaves by Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction with Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Cellulose Polymers and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). Anal. Lett. 2022, 55, 566–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinduja, B.; John, S.A. Sensitive determination of rutin by spectrofluorimetry using carbon dots synthesized from a non-essential amino acid. Spectrochim. Acta Part A: Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 193, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Hu, J.; Zeng, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, H.; Lei, X.; Huang, S.; Guo, L.; Li, L. Electrochemical determination of rutin based on molecularly imprinted poly (ionic liquid) with ionic liquid-graphene as a sensitive element. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 311, 127911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, L.A.; Suchkov, E.A.; Kuznetsov, K.A.; Ryabukha, A.F.; Perfilova, V.N.; Popova, T.A.; Tyurenkov, I.N.; Bychenkova, M.A.; Latypova, G.M.; Kataev, V.A. Quantitative Determination of Rutin in Biological Samples of Rats Upon Administration of Primula veris L. Herbal Dense Extract. Pharm. Chem. J. 2021, 54, 1235–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohani, T.; Ghaderi, A. Electrochemical Behavior and Determination of Rutin at the Copper Nanoparticles-Doped Zeolite A/Graphene Oxide-Modified Electrode. J. Anal. Chem. 2018, 73, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadkish, K.; Shokrollahi, A. Simultaneous determination and extraction of illegal dyes Sudan orange G and Sudan red 7B using ultrasonic assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on deep eutectic solvent followed by derivative UV-VIS spectrophotometry. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Singh, R.; Soares, M.S.; Marques, C.; Zhang, B.; Kumar, S. Convex fiber-tapered seven core fiber-convex fiber (CTC) structure-based biosensor for creatinine detection in aquaculture. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 13898–13914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Singh, R.; Marques, C.; Jha, R.; Zhang, B.; Kumar, S. Taper-in-taper fiber structure-based LSPR sensor for alanine aminotransferase detection. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 43793–43810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Singh, R.; Zhang, B.; Kumar, S. SMF tapered fiber/AuNPs/ZnO based sensor for detection of acetylcholine. In Optics in Health Care and Biomedical Optics XI; Luo, Q., Li, X., Gu, Y., Zhu, D., Eds.; SPIE-International Society of Optical Engineering: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2021; Volume 11900, p. 119003D. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Singh, R.; Kaushik, B.K.; Chen, N.-K.; Yang, Q.S.; Zhang, X. LSPR-Based Cholesterol Biosensor Using Hollow Core Fiber Structure. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 7399–7406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, Q.; Malathi, S.; Marques, C.; Singh, R.; Zhang, B. Plasmon-Based Tapered-in-Tapered Fiber Structure for p-Cresol Detection: From Human Healthcare to Aquaculture Application. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 18493–18500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, N.; Ghasemi, S.; Salimi, A.; Sham, T.-K.; Hallaj, R. CuO nanorods as a laccase mimicking enzyme for highly sensitive colorimetric and electrochemical dual biosensor: Application in living cell epinephrine analysis. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 195, 111228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahdost-Fard, F.; Fahimi-Kashani, N.; Hormozi-Nezhad, M. A ratiometric fluorescence nanoprobe using CdTe QDs for fast detection of carbaryl insecticide in apple. Talanta 2021, 221, 121467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orouji, A.; Abbasi-Moayed, S.; Hormozi-Nezhad, M.R. ThThnated Development of a pH assisted AgNP-based colorimetric sensor Array for simultaneous identification of phosalone and azinphosmethyl pesticides. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 219, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafzadeh, F.; Ghasemi, F.; Hormozi-Nezhad, M.R. Anti-aggregation of gold nanoparticles for metal ion discrimination: A promising strategy to design colorimetric sensor arrays. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 270, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.M.; Solomon, E.I. Electron transfer and reaction mechanism of laccases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 869–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mate, D.M.; Alcalde, M. Laccase engineering: From rational design to directed evolution. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Lin, F.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, B.; Jiang, S.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, J. Multicopper Laccase Mimicking Nanozymes with Nucleotides as Ligands. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 1352–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Liu, J.; Ren, J.; Tang, F.; Meng, X. One-pot synthesis of active copper-containing carbon dots with laccase-like activities. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 19641–19646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Zheng, N.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, L. Laccase-like catalytic activity of Cu-tannic acid nanohybrids and their application for epinephrine detection. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 613, 126105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.D.; Nguyen, P.T.; Le, T.N.; Kim, M.I. DNA-copper hybrid nanoflowers as efficient laccase mimics for colorimetric detection of phenolic compounds in paper microfluidic devices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 182, 113187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Carli, L.; Schnitzler, E.; Ionashiro, M.; Szpoganicz, B.; Rosso, N.D. Equilibrium, thermoanalytical and spectroscopic studies to characterize phytic acid complexes with Mn(II) and Co(II). J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2009, 20, 1515–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, H. Orientation of benzoic acid and terephthalic acid on an alumina surface and their reactivities observed by infrared spectroscopy. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 1991, 4, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohandoss, S.; Atchudan, R.; Edison, T.N.J.I.; Mandal, T.K.; Palanisamy, S.; You, S.; Napoleon, A.A.; Shim, J.-J.; Lee, Y.R. Enhanced solubility of guanosine by inclusion complexes with cyclodextrin derivatives: Preparation, characterization, and evaluation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 224, 115166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Liu, S.; Jiao, K. Electrochemical behavior and determination of rutin on a pyridinium-based ionic liquid modified carbon paste electrode. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 48, 1326–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timbola, A.K.; Souza, C.D.; Soldi, C.; Pizzolatti, M.G.; Spinelli, A. Electro-oxidation of rutin in the presence of p-toluenesulfinic acid. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2007, 37, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Pandey, A.K. Chemistry and Biological Activities of Flavonoids: An Overview. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 162750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarev, S.L.; Knyukshto, V.N. Fluorescence and phosphorescence of rutin. J. Lumin 2013, 142, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.-M.; Wu, H.-Y.; Li, W.-S.; Chen, W.-L.; Lee, Y.-J.; Wu, D.C.; Li, P.; Yeh, A. Kinetic studies of the oxidation of quercetin, rutin and taxifolin in the basic medium by (ethylenediaminetetraacetato) cobalt(III) complex. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2010, 13, 633–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvand, M.; Shabani, A.; Ardaki, M.S. A New Electrochemical Sensing Platform Based on Binary Composite of Graphene Oxide-Chitosan for Sensitive Rutin Determination. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 2332–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Q.; Zhong, M.; Kan, X. Boronic acid based imprinted electrochemical sensor for rutin recognition and detection. Analyst 2016, 141, 5792–5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Material/Probe | Method | LDR (μM) | LOD (μM) | RSD% | pH | Sample | Time | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemically cross-linked Cu-CHIT 1/MWCNT 2 on GCE 3 | Electrochemically | 0.05–100 | 0.01 | 2.43 | 0.04 M Britton–Robinson buffer (pH = 3) | Orange, lemon, lime, apple | 40 s | [1] |
| Carbon composite electrode modified with Cu (II) phosphate immobilized in a polyester resin | Electrochemically | 0.098–2.50 | 0.011 | - | 0.1 M phosphate buffer/ethanol (pH = 6.9) | Pharmaceutical formulations | - | [19] |
| MIP 4 with IL 5-Gr 6 | Electrochemically | 0.029–1.0 | 0.001 | 3.05 | 0.04 M Britton–Robinson buffer (pH = 2.0) | Tablet | 10 min | [25] |
| Boron-doped diamond electrode | Electrochemically | 0.016–0.164 | 0.0028 | 3.5 | 0.1 M Britton–Robinson buffer (pH = 4) | Dietary supplement products | 1 min | [21] |
| Polyphenol oxidase/AuNPs 7/mesoporous carbon-modified electrode | Electrochemically | 1.50–28.00 | 0.51 | 4.6 | 0.1 M phosphate buffered saline (pH = 2) | Dark teas | - | [22] |
| Cu-zeolite A/Gr on GCE | Electrochemically | 0.23–2500 | 0.12 | 1.1–2.1 | oxalate buffer (pH 4.5) | Urine | - | [27] |
| GO-CHIT/GCE | Electrochemically | 0.9–90 | 0.56 | 1.81 | citrate buffer (pH = 4.5) | Fruits | 25 s | [52] |
| MIP/MWCNTs/GCE | Electrochemically | 0.4–10 | 0.11 | 3.01 | buffer (pH = 8.0) | Tablet | 10 min | [53] |
| Mobile phase | HPLC | 1.64–819.0 | 0.16 | - | - | Ginkgo biloba L. Leaves | 40 min | [23] |
| Mobile phase | HPLC | 0.82–40.95 | 0.16 | - | 50 mM buffer KH2PO4 (pH = 4.6) | Blood plasma, cardiomyocytes, and mitochondria of cardiomyocytes | 6–6.5 min | [26] |
| CDs 8 | Spectrofluorimetry | 0.30–9.16 | 0.098 | - | - | Tablet | - | [24] |
| Rutin-Al (III) complex | Spectrophotometry and fluorimetry | 4.09–36.85 and 6.55–39.31 | 0.11 and 0.12 | 1.06 and 1.40 | acetic acid buffer (pH = 4.8) | Tablet | - | [20] |
| Complex with ytterium (III) | Fluorimetry | 0.02–1.96 | 0.0021 | 1.6 | Tris-HCl buffer (pH = 9.5) | Tablet | - | [8] |
| Cu-Guo NRs | Spectrophotometry and visually | 0.77–54.46 | 0.114 | 1.26 | acetate buffer (pH = 5.6) | Blood plasma, urine, tablet, dry propolis extract | 6 min | This Study |
| Sample | Regression Equation | R2 | Added/ Contained (µM) | Found (µM) | Recovery % | RSD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tablet | A = 0.0166 X + 0.0383 | 0.9989 | 0 8.19 16.38 | 3.78 12.33 19.82 | - 104.4 97.9 | 2.41 1.89 2.09 |
| Propolis | A = 0.0156 X + 0.0981 | 0.9991 | 0 8.19 16.38 | 10.29 18.39 25.96 | - 99 95.7 | 2.03 3.26 4.48 |
| Urine (1) | A = 0.0211 X + 0.0014 | 0.9992 | 0 8.19 16.38 | N.D. 8.43 15.95 | - 103 97.4 | - 3.21 2.49 |
| Urine (2) | A = 0.0199 X + 0.002 | 0.999 | 0 8.19 16.38 | N.D. 8.45 15.95 | - 103.2 97.4 | - 2.55 3.93 |
| Plasma | A = 0.0180 X + 0.0042 | 0.9996 | 0 8.19 16.38 | N.D. 8.075 16.72 | - 98.66 102.11 | - 1.92 3.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Davoodi-Rad, K.; Shokrollahi, A.; Shahdost-Fard, F.; Azadkish, K. Copper-Guanosine Nanorods (Cu-Guo NRs) as a Laccase Mimicking Nanozyme for Colorimetric Detection of Rutin. Biosensors 2023, 13, 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030374
Davoodi-Rad K, Shokrollahi A, Shahdost-Fard F, Azadkish K. Copper-Guanosine Nanorods (Cu-Guo NRs) as a Laccase Mimicking Nanozyme for Colorimetric Detection of Rutin. Biosensors. 2023; 13(3):374. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030374
Chicago/Turabian StyleDavoodi-Rad, Kowsar, Ardeshir Shokrollahi, Faezeh Shahdost-Fard, and Kamal Azadkish. 2023. "Copper-Guanosine Nanorods (Cu-Guo NRs) as a Laccase Mimicking Nanozyme for Colorimetric Detection of Rutin" Biosensors 13, no. 3: 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030374
APA StyleDavoodi-Rad, K., Shokrollahi, A., Shahdost-Fard, F., & Azadkish, K. (2023). Copper-Guanosine Nanorods (Cu-Guo NRs) as a Laccase Mimicking Nanozyme for Colorimetric Detection of Rutin. Biosensors, 13(3), 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030374






