Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Non-Enzymatic Uric Acid Sensor Based on Cobalt Oxide Puffy Balls-like Nanostructure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
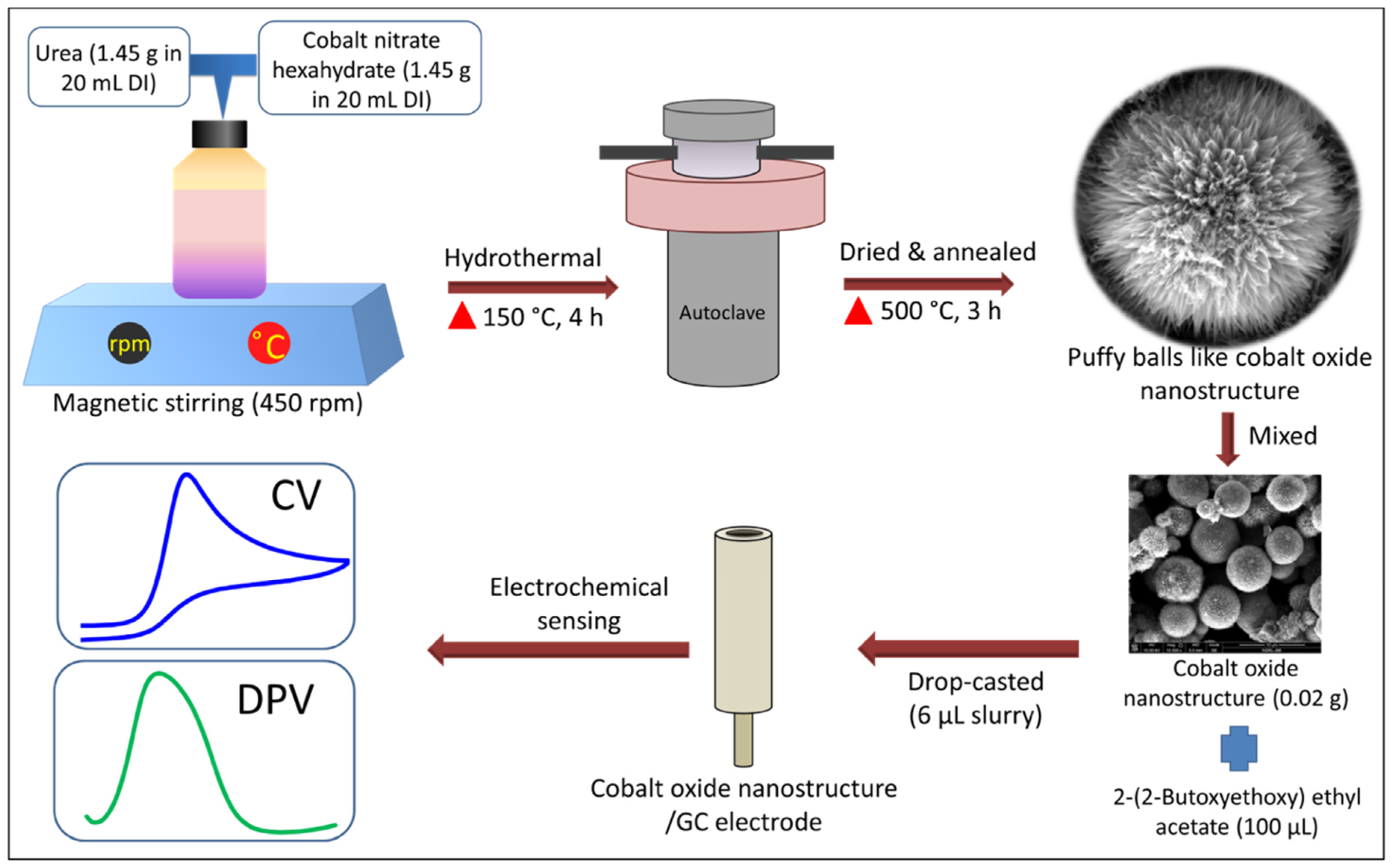
2.2. Synthesis of Puffy Balls-like Cobalt Oxide Nanostructures
2.3. Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical UA Sensor Fabrication
2.4. Material Characterization and Electrochemical Sensing Analysis Equipment
3. Results
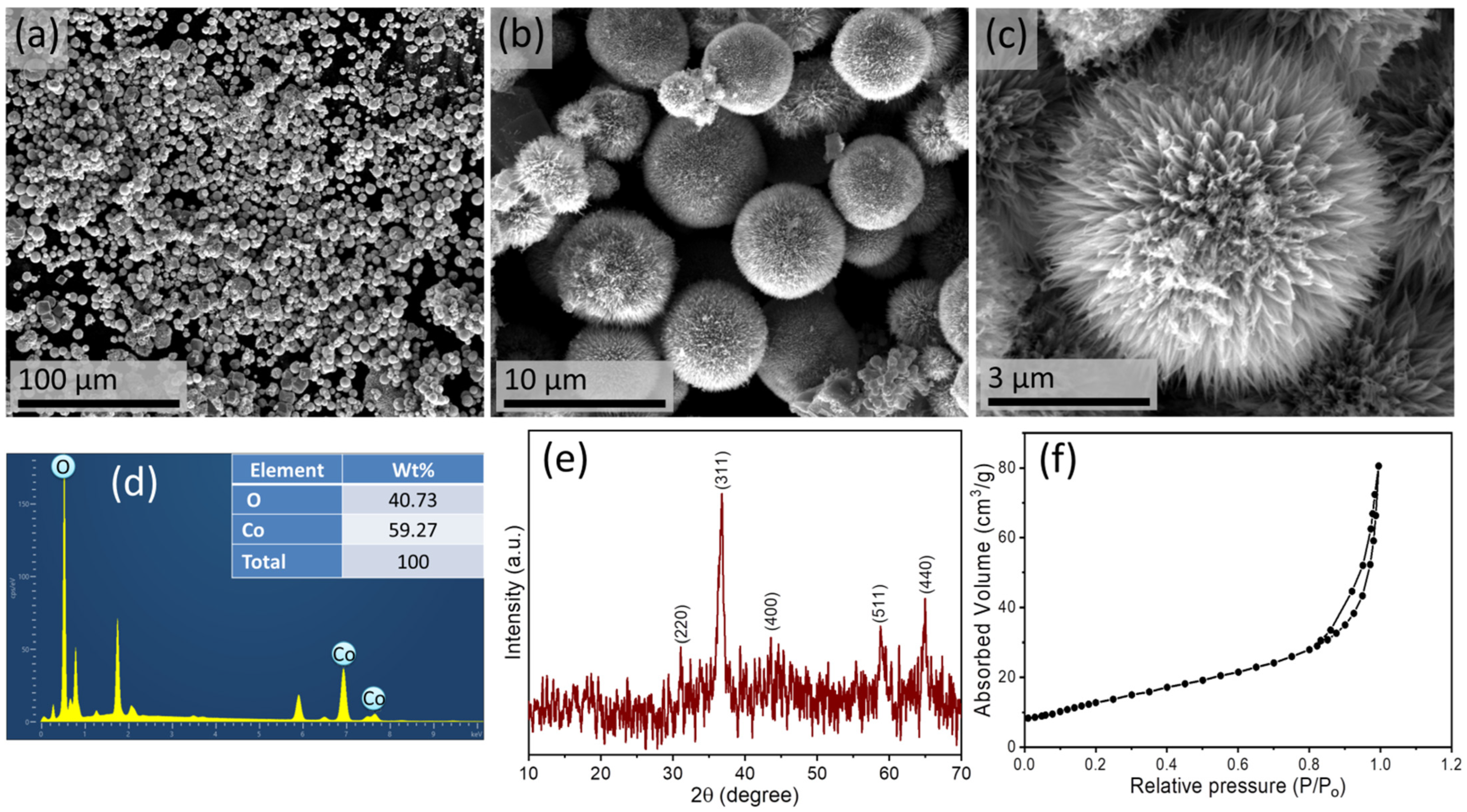
3.1. Analysis of Cobalt Oxide Nanostructure
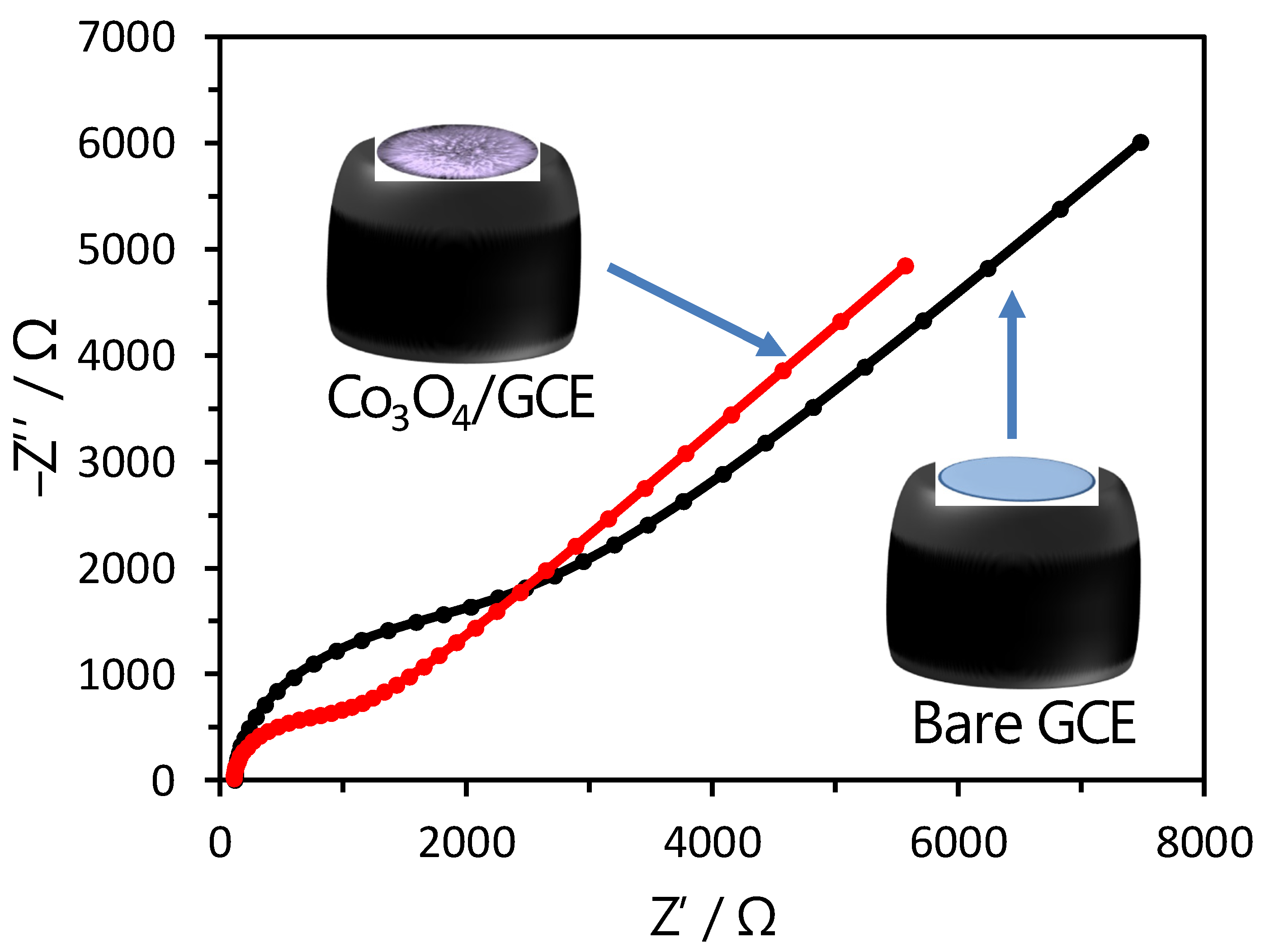
3.2. Electrochemical Sensing Analysis of Cobalt Oxide Puffy Balls/GC Electrodes
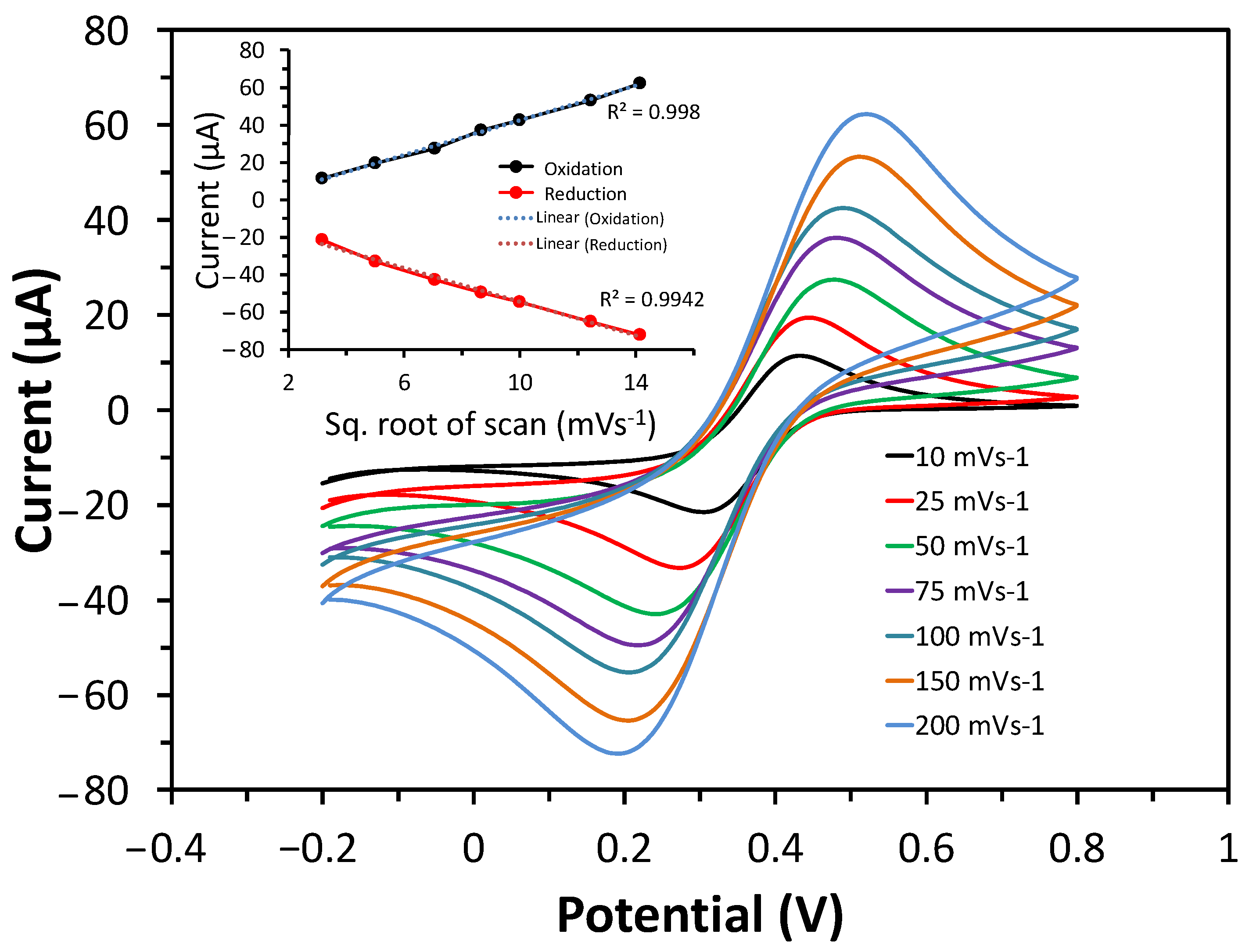
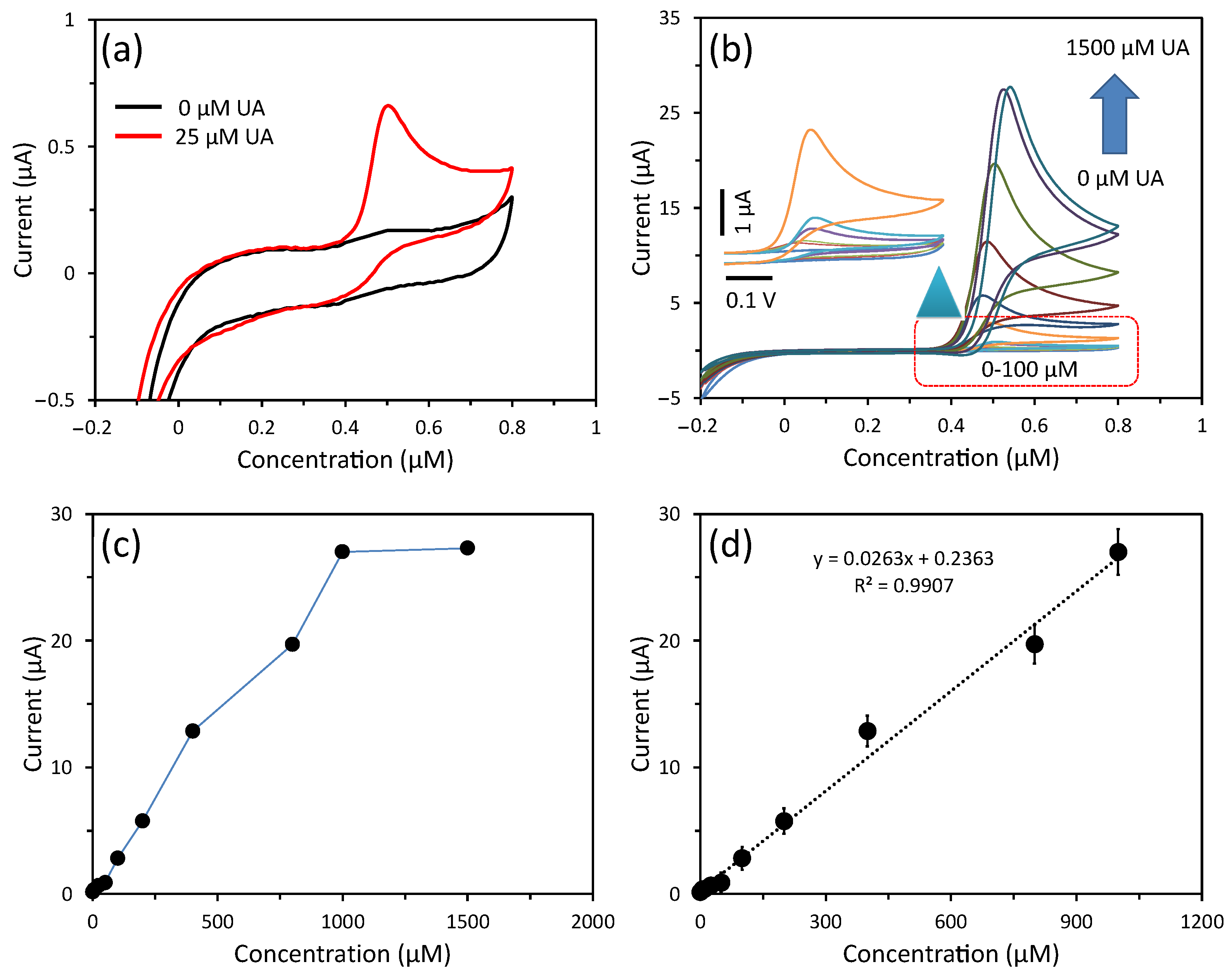
3.3. Detection of UA Using CV
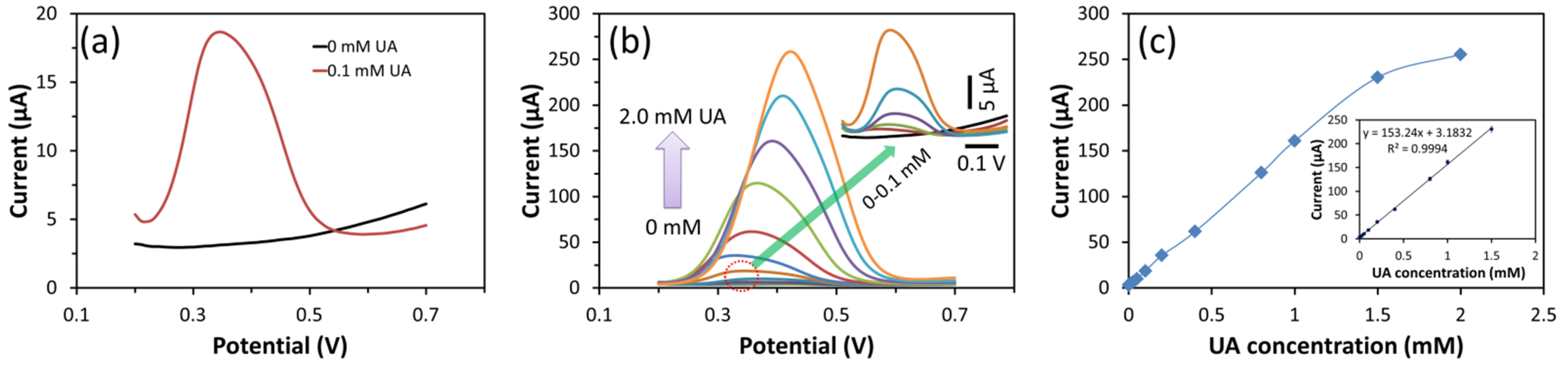
3.4. Detection of UA Using DPV
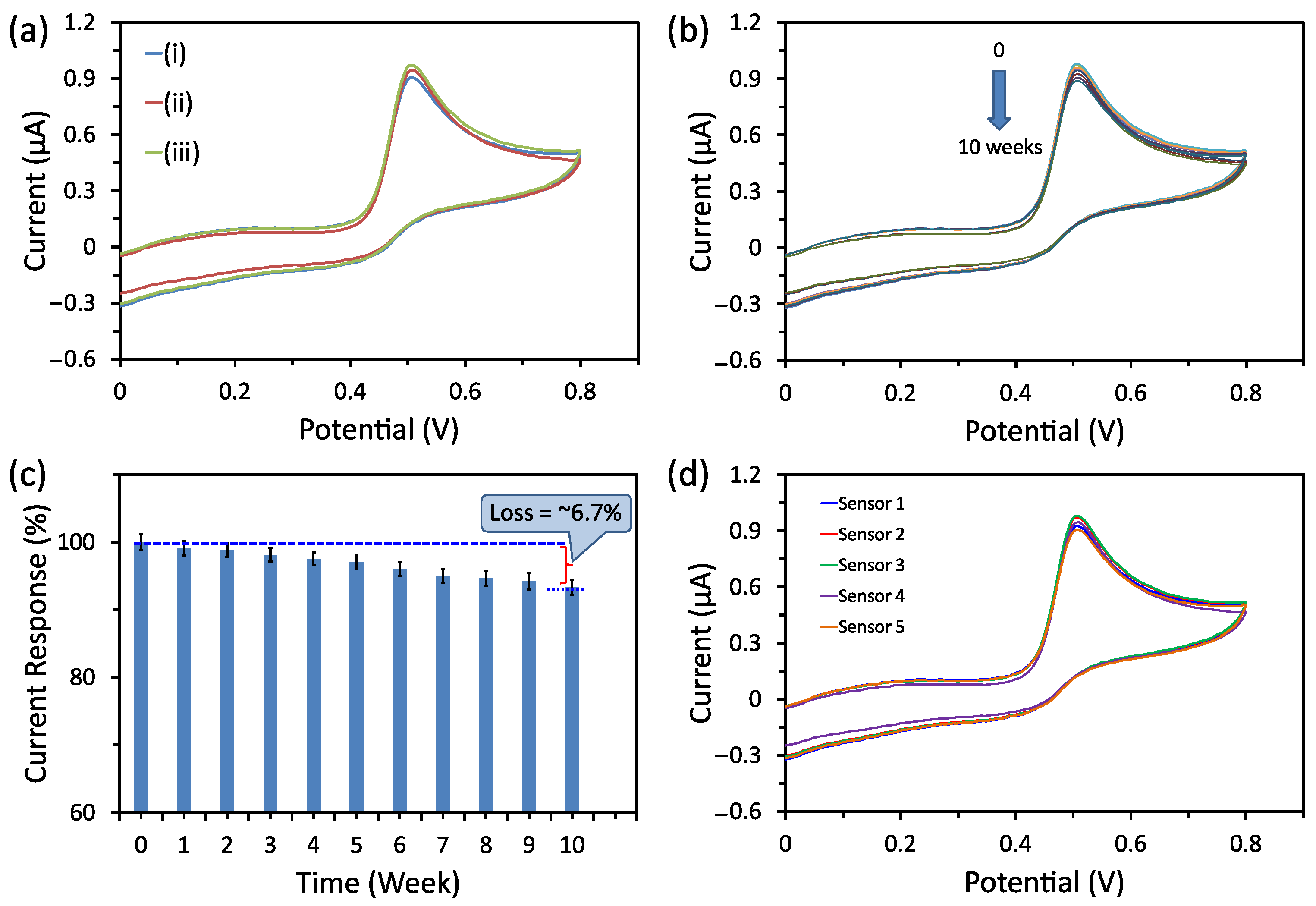
3.5. Selectivity, Stability, and Reproducibility Tests
3.6. UA Detection in Serum Sample
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, X.; Fang, X.; Zhang, C.; Xu, R.; Xu, B. Determination of Serum Uric Acid Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)/Isotope Dilution Mass Spectrometry (ID-MS) as a Candidate Reference Method. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2007, 857, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, K.L.; Kataoka, H.; Lai, J.J. Uric Acid as a Danger Signal in Gout and Its Comorbidities. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2013, 9, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltani, Z.; Rasheed, K.; Kapusta, D.R.; Reisin, E. Potential Role of Uric Acid in Metabolic Syndrome, Hypertension, Kidney Injury, and Cardiovascular Diseases: Is It Time for Reappraisal? Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2013, 15, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderman, M.; Aiyer, K.J.V. Uric Acid: Role in Cardiovascular Disease and Effects of Losartan. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2004, 20, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiba, A.; Vinker, S.; Dinour, D.; Holtzman, E.J.; Shani, M. Uric Acid Levels Within the Normal Range Predict Increased Risk of Hypertension: A Cohort Study. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2015, 9, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, C.; Lanaspa, M.A.; Jensen, T.; Tolan, D.R.; Sanchez-Lozada, L.G.; Johnson, R.J. Uric Acid in Chronic Kidney Disease. Contrib. Nephrol. 2018, 192, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murugan, N.; Chan-Park, M.B.; Sundramoorth, A.K. Electrochemical Detection of Uric Acid on Exfoliated Nanosheets of Graphitic-Like Carbon Nitride (g-C3N4) Based Sensor. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, B3163–B3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Wolfbeis, O.S.; Hahn, Y.-B.; Alshareef, H.N.; Torsi, L.; Salama, K.N. Deposition of Nanomaterials: A Crucial Step in Biosensor Fabrication. Mater. Today Commun. 2018, 17, 289–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Tripathy, N.; Jang, N.K.; Khang, G.; Hahn, Y.-B. Fabrication of Highly Sensitive Uric Acid Biosensor based on Directly Grown ZnO Nanosheets on Electrode Surface. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 206, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, X.; Diao, L.; Li, H.; Tong, Z.; Gu, Z.; Miao, B.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Y.; et al. Highly Sensitive Uric Acid Detection Based on a Graphene Chemoresistor and Magnetic Beads. Biosensors 2021, 11, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Tripathy, N.; Ahn, M.-S.; Hahn, Y.-B. Solution Process Synthesis of High Aspect Ratio ZnO Nanorods on Electrode Surface for Sensitive Electrochemical Detection of Uric Acid. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.H.; Vyas, C.; Grieve, B.; Bartolo, P. Recent Advances in Enzymatic and Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical Glucose Sensing. Sensors 2021, 21, 4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Mahmoudi, T.; Ahn, M.-S.; Hahn, Y.-B. Recent Advances in Nanowires-Based Field-Effect Transistors for Biological Sensor Applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, T.T.; Nine, M.J.; Krebsz, M.; Pasinszki, T.; Coghlan, C.J.; Tran, D.N.H.; Losic, D. Recent Advances in Sensing Applications of Graphene Assemblies and Their Composites. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1702891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasinszki, T.; Krebsz, M.; Tung, T.T.; Losic, D. Carbon Nanomaterial Based Biosensors for Non-Invasive Detection of Cancer and Disease Biomarkers for Clinical Diagnosis. Sensors 2017, 17, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Tian, Q.; Li, X.; Wu, L.; Yu, A.; Lai, G.; Fu, L.; Wei, Q.; Dai, D.; Jiang, N.; et al. A Double-Deck Structure of Reduced Graphene Oxide Modified Porous Ti3C2Tx Electrode towards Ultrasensitive and Simultaneous Detection of Dopamine and Uric Acid. Biosensors 2021, 11, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wu, J.; Qi, X.; Wan, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, L. Molecularly Imprinted Polypyrrole Film-Coated Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):Polystyrene Sulfonate-Functionalized Black Phosphorene for the Selective and Robust Detection of Norfloxacin. Mater. Today Chem. 2022, 26, 101043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Qi, X.; Zhang, G.; Wang, S.; Li, K.; Wu, J.; Wan, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q. Low-cost Voltammetric Sensors for Robust Determination of Toxic Cd(II) and Pb(II) in Environment and Food Based on Shuttle-like α-Fe2O3 Nanoparticles Decorated β-Bi2O3 Microspheres. Microchem. J. 2022, 179, 107515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-C.; Kim, K.-B.; Gurudatt, N.G.; Hussain, K.K.; Choi, C.S.; Park, D.-S.; Shim, Y.-B. Comparison of Enzymatic and Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensors Based on Hierarchical Au-Ni Alloy with Conductive Polymer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 130, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Nagal, V.; Nakate, U.T.; Khan, M.R.; Khosla, A.; Ahmad, R. Engineered CuO Nanofibers with Boosted Nonenzymatic Glucose Sensing Performance. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 067507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnaiah, S.K.; Periakaruppan, P.; Vellaichamy, B. New Electrochemical Sensor Based on a Silver-Doped Iron Oxide Nanocomposite Coupled with Polyaniline and Its Sensing Application for Picomolar Level Detection of Uric Acid in Human Blood and Urine Samples. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 3037–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Du, J.; Wang, H.; Zou, C.E.; Jiang, F.; Yang, P.; Du, Y. A Facile Electrochemical Sensor Based on Reduced Graphene Oxide and Au Nanoplates Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode for Simultaneous Detection of Ascorbic Acid, Dopamine and Uric Acid. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 204, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, B.; Zhong, J.; Yan, B.; Zhang, K.; Zhai, C.; Shiraishi, Y.; Du, Y.; Yang, P. Dopamine and Uric Acid Electrochemical Sensor Based on a Glassy Carbon Electrode Modified with Cubic Pd and Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 497, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.L.D.; Katic, V.; Toledo, K.C.; Bonacin, J.A. Photochemical One-Pot Synthesis of Reduced Graphene Oxide/Prussian Blue Nanocomposite for Simultaneous Electrochemical Detection of Ascorbic Acid, Dopamine, and Uric Acid. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Li, C.; Feng, S.; Chen, S.-M.; Ding, Y.; Chen, C.; Hao, Q.; Yang, T.-H.; Lei, W. A Novel Electrochemical Sensor for Uric Acid Detection Based on PCN/MWCNT. Ionics 2019, 25, 4437–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsierkezos, N.G.; Ritter, U.; Thaha, Y.N.; Downing, C.; Szroeder, P.; Scharff, P. Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Doped with Boron as an Electrode Material for Electrochemical Studies on Dopamine, Uric Acid, and Ascorbic Acid. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, L. PtNi Bimetallic Nanoparticles Loaded MoS2 Nanosheets: Preparation and Electrochemical Sensing Application for the Detection of Dopamine and Uric Acid. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1055, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanvand, Z.; Jalali, F. Simultaneous Determination of lDOPA, L-tyrosine and Uric Acid by Cysteic Acid-Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 98, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkkan, G.; Bas, S.Z.; Atacan, K.; Ozmen, M. An Electrochemical Sensor based on a Co3O4-ERGO Nanocomposite Modified Screen-Printed Electrode for Detection of Uric Acid in Artificial Saliva. Anal. Methods 2022, 14, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Faisal, M.; Alsareii, S.A.; Harraz, F.A. Highly Sensitive and Selective Non-Enzymatic Uric Acid Electrochemical Sensor Based on Novel Polypyrrole-Carbon Black-Co3O4 Nanocomposite. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2022, 5, 920–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagal, V.; Kumar, V.; Khan, M.; Alomar, S.; Tripathy, N.; Singh, K.; Khosla, A.; Ahmad, N.; Hafiz, A.K.; Ahmad, R. A Highly Sensitive Uric Acid Biosensor Based on Vertically Arranged ZnO Nanorods on ZnO Nanoparticles Seeded Electrode. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 18863–18870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvand, M.; Hassannezhad, M. Magnetic Core-Shell Fe3O4@SiO2/MWCNT Nanocomposite Modified Carbon Paste Electrode for Amplified Electrochemical Sensing of Uric Acid. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 36, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Q.; Zhi, N.; Yang, L.; Xu, G.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, S. A Highly Sensitive Uric Acid Electrochemical Biosensor based on a Nano-Cube Cuprous Oxide/Ferrocene/Uricase Modifed Glassy Carbon Electrode. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, K.S.; Ahmad, R.; Mahmoudi, T.; Hahn, Y.-B. High Performance Chemical Sensor with Field-Effect Transistors Array for Selective Detection of Multiple Ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 128064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.S.; Tahira, A.; Chang, F.; Solangi, A.G.; Bhatti, M.A.; Vigolo, B.; Nafady, A.; Ibupoto, Z.H. Highly Heterogeneous Morphology of Cobalt Oxide Nanostructures for the Development of Sensitive and Selective Ascorbic Acid Non-Enzymatic Sensor. Biosensors 2023, 13, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagal, V.; Tuba, T.; Kumar, V.; Alam, S.; Ahmad, A.; Alshammari, M.B.; Hafiz, A.K.; Ahmad, R. A Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical Sensor Composed of Nano-Berry Shaped Cobalt Oxide Nanostructures on a Glassy Carbon Electrode for Uric Acid Detection. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 12333–12341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masrat, S.; Nagal, V.; Khan, M.; Moid, I.; Alam, S.; Bhat, K.S.; Khosla, A.; Ahmad, R. Electrochemical Ultrasensitive Sensing of Uric Acid on Non-Enzymatic Porous Cobalt Oxide Nanosheets-Based Sensor. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagal, V.; Khan, M.; Masrat, S.; Alam, S.; Ahmad, A.; Alshammari, M.B.; Bhat, K.S.; Ahmad, R. Hexagonal Cobalt Oxide Nanosheet-Based Enzymeless Electrochemical Uric Acid Sensor with Improved Sensitivity. New J. Chem. 2023, 47, 4206–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogularasu, S.; Govindasamy, M.; Chen, S.-M.; Akilarasan, M.; Mani, V. 3D graphene Oxide-Cobalt Oxide Polyhedrons for Highly Sensitive Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical Determination of Hydrogen Peroxide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 253, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, S. A Combined Self-Assembly and Calcination Method for Preparation of Nanoparticles-Assembled Cobalt Oxide Nanosheets using Graphene Oxide as Template and their Application for Non-Enzymatic Glucose Biosensing. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 485, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; He, D.; Bie, L.; Jiang, P. Nanoporous Cobalt Oxide Nanowires for Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical Glucose Detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 220, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Madhuri, R.; Sharma, P.K. Probing the Shape Specific Electrochemical Properties of Cobalt Oxide Nanostructures for their Application as Selective and Sensitive Nonenzymatic Glucose Sensors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 6497–6505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.S.; Memon, N.N.; Amin, S.; Chang, F.; Aftab, U.; Abro, M.I.; Chandio, A.; Shah, A.A.; Ibupoto, M.H.; Ansari, M.A.; et al. Facile Non-Enzymatic Lactic Acid Sensor based on Cobalt Oxide Nanostructures. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 1296–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numan, A.; Duraisamy, N.; Omar, F.S.; Mahipal, Y.K.; Ramesh, K.; Ramesh, S. Enhanced Electrochemical Performance of Cobalt Oxide Nanocube Intercalated Reduced Graphene Oxide for Supercapacitor Application. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 34894–34902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.X.; Hu, T.; Chen, S.; Wang, D.; Rao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Dai, F.; Guo, C.; Yang, H.B.; Li, C.M. Single-Atom Cobalt-Based Electrochemical Biomimetic Uric Acid Sensor with Wide Linear Range and Ultralow Detection Limit. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.S.; Tahira, A.; Chang, F.; Memon, N.N.; Nafady, A.; Kasry, A.; Ibupoto, Z.H. Silky Co3O4 Nanostructures for the Selective and Sensitive Enzyme Free Sensing of Uric Acid. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 5156–5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xia, Y.; Wan, X.; Yang, S.; Cai, Z.; Ye, Y.; Li, G. Morphology-Dependent MnO2 Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Nanocomposites for Simultaneous Detection of Trace Dopamine and Uric Acid. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 109, 110615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Modified Electrode | Sensing Method | Detection Range (µM) | Limit of Detection (µM) | Sensitivity (µAcm−2mM−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g-C3N4 NSs/GCE | DPV | 100–1000 | 4.45 | - | [7] |
| Ag-Fe2O3@PANI | DPV | 0.001–0.90 | 0.000102 | 128290 | [21] |
| Au/RGO/GCE | DPV | 8.8–53 | 1.8 | - | [22] |
| Cubic Pd/RGO/GCE | DPV | 4–469.5 | 1.6 | - | [23] |
| RGO/PB 100/GCE | CV | 40–415 | 8.0 | - | [24] |
| PCN/MWCNT/GCE | DPV | 0.2–20 | 0.139 | - | [25] |
| B-MWCNT/GCE | CV | 60–250 | 0.65 | - | [26] |
| PtNi@MoS2 NSs/GCE | DPV | 0.5–600 | 0.1 | - | [27] |
| Cysteic acid/GCE | DPV | 1.0–19 | 0.36 | - | [28] |
| PPy-CB-Co3O4/GCE | CV | 0.75–305 | 0.46 | 0.8786 | [30] |
| Cu2O/ferrocene/uricase/GCE | DPV | 0.1–1000 | 0.0596 | 1.9 | [33] |
| Co3O4 nano berries/GCE | CV | 5–3000 | 2.4 | 206 | [36] |
| Co3O4 porous NSs/GCE | CV | 0–2500 | 10 | 470 | [37] |
| Silky Co3O4 nanomaterial/GCE | CV | 500–3500 | 100 | - | [46] |
| MnO2 NFs/NG/GCE | SDLSV | 10–100 | 0.039 | - | [47] |
| Co3O4 puffy balls/GCE | CV | 0–1000 | 2.4 | 307 | This work |
| Co3O4 puffy balls/GCE | DPV | 0–1500 | 1.6 | 2158 | This work |
| Sample | Added UA (µM) | Found UA (µM) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) (n = 3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human serum (H4522) | 0 | 280 | - | - |
| 50 | 328.7 | 97.4 | 3.1 | |
| 100 | 196.6 | 96.6 | 2.8 | |
| 200 | 391.6 | 95.8 | 3.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nagal, V.; Masrat, S.; Khan, M.; Alam, S.; Ahmad, A.; Alshammari, M.B.; Bhat, K.S.; Novikov, S.M.; Mishra, P.; Khosla, A.; et al. Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Non-Enzymatic Uric Acid Sensor Based on Cobalt Oxide Puffy Balls-like Nanostructure. Biosensors 2023, 13, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030375
Nagal V, Masrat S, Khan M, Alam S, Ahmad A, Alshammari MB, Bhat KS, Novikov SM, Mishra P, Khosla A, et al. Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Non-Enzymatic Uric Acid Sensor Based on Cobalt Oxide Puffy Balls-like Nanostructure. Biosensors. 2023; 13(3):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030375
Chicago/Turabian StyleNagal, Vandana, Sakeena Masrat, Marya Khan, Shamshad Alam, Akil Ahmad, Mohammed B. Alshammari, Kiesar Sideeq Bhat, Sergey M. Novikov, Prabhash Mishra, Ajit Khosla, and et al. 2023. "Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Non-Enzymatic Uric Acid Sensor Based on Cobalt Oxide Puffy Balls-like Nanostructure" Biosensors 13, no. 3: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030375
APA StyleNagal, V., Masrat, S., Khan, M., Alam, S., Ahmad, A., Alshammari, M. B., Bhat, K. S., Novikov, S. M., Mishra, P., Khosla, A., & Ahmad, R. (2023). Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Non-Enzymatic Uric Acid Sensor Based on Cobalt Oxide Puffy Balls-like Nanostructure. Biosensors, 13(3), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030375








