Abstract
Developing a water-soluble supramolecular system for the detection and removal of Hg2+ is extremely needed but remains challenging. Herein, we reported the facile construction of a fluorescent supramolecular system (H⊃G) in 100% water through the self-assembly of carboxylatopillar[5]arene sodium salts (H) and diketopyrrolopyrrole-bridged bis(quaternary ammonium) guest (G) by host–guest interaction. With the addition of Hg2+, the fluorescence of H⊃G could be efficiently quenched. Since Hg2+ showed synergistic interactions (coordination and Hg2+- cavity interactions with G and H, respectively), crosslinked networks of H⊃G@Hg2+ were formed. A sensitive response to Hg2+ with excellent selectivity and a low limit of detection (LOD) of 7.17 × 10−7 M was obtained. Significantly, the quenching fluorescence of H⊃G@Hg2+ can be recovered after a simple treatment with Na2S. The reusability of H⊃G for the detection of Hg2+ ions was retained for four cycles, indicating the H⊃G could be efficiently used in a reversible manner. In addition, the H⊃G could efficiently detect Hg2+ concentration in real samples (tap water and lake water). The developed supramolecular system in 100% water provides great potential in the treatment of Hg2+ detection and removal for environmental sustainability.
1. Introduction
Mercury ion (Hg2+), as one of the most toxic heavy metal ions in the environment and aquatically derived food, has become an important worldwide pollution problem. Hg2+ is a neurotoxin and can cause severe adverse effects on human health [1,2,3]. More importantly, as the most stable and toxic form of mercury, methylmercury in aquatic food chains results in serious damage to the heart, brain, kidneys and immune systems. The maximum contaminant level of Hg2+ (10 µg/L) in wastewater discharge was established by World Health Organization (WHO) [4]. Thus far, several functional materials, such as hydrogels, nanoparticles, covalent organic frameworks, porous aromatic frameworks, metal–organic frameworks and others, have shown potential for the possible detection and removal of Hg2+ from wastewater [5,6,7,8,9,10].
Among the various methods for Hg2+ recognition, fluorescent self-assembled materials with advanced architectures and stimuli-responsive properties by the supramolecular host–guest interactions have attracted considerable interest [11,12]. They can sensitively and selectively detect targeted analytes with excellent simplicity and good efficiency [13,14]. Pillar[n]arenes are especially popular supramolecular host molecules for their ability to selectively bind different kinds of guests [15,16]. They have a pillar-like framework and multiple self-assembly driving forces such as hydrophobic/hydrophilic, π⋯π, C-H⋯π, cation⋯π interactions, etc. Thus far, the pillararene-based fluorescent polymer, supramolecular organic framework, gel and supramolecular assembly as Hg2+ sensors have been studied by several groups [17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24]. For instance, Yuan’s group reported pillar[5]arenes bearing phosphine oxide pendents as Hg2+ selective receptors [17]. Wu’s and Yang’s group developed pillar[5]arene and pillar[6]arene-based aggregation-induced emission-active supramolecular system for detection and removal of Hg2+, respectively [18,21]. Lin’s group investigated pillar[5]arene-based polymer and gel as Hg2+ fluorescent sensors [22]. Although considerable research efforts for the development of Hg2+ supramolecular chemosensors have been made, the participation of organic solvents in these cases is needed, which is unfavorable for Hg2+ detection in biological and environmental systems. Moreover, the complicated and tedious synthesis of functional pillararenes is involved. For example, the introduction of Hg2+ recognition sites such as thymine, N or S moiety in pillararene is time-costing and cumbersome. More importantly, strong interference from other metal ions is encountered due to the noncovalent interactions sensing mechanism. Therefore, developing water-soluble pillararene-based supramolecular fluorescent materials with excellent Hg2+ detection performance in pure water is extremely needed but remains challenging. To the best of our knowledge, a fluorescent supramolecular system in pure water for Hg2+ detection and removal has not yet been reported.
Herein, we constructed a supramolecular fluorescent system in pure water, which aims to accomplish the goal of Hg2+ sensing and removal in one pot. Some design intentions are listed as follows. (1) Water-soluble carboxylatopillar[5]arene possessed five carboxylate groups on each rim and good binding ability toward guest molecules [25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36], which was selected as a supramolecular host. It may also have cation⋯π and electrostatic interactions with Hg2+. (2) Given that Hg2+ possesses a high affinity for N and S, cationic thienyl functionalized diketopyrrolopyrrole (DPP) guest with two six-carbon alkyl chains was selected. It would form a fluorescent supramolecular host–guest system with pillar[5]arene host and possess coordination ability with Hg2+. (3) Through synergistic interactions between Hg2+ and host/guest, excellent selectivity and sensitivity would be obtained by fluorescence signal change. By taking these factors into consideration and our research interest in supramolecular fluorescent chemosensors for pollutants [37,38,39,40], water-soluble fluorescent pillar[5]arene supramolecular self-assembly was constructed by carboxylatopillar[5]arene sodium salts (H) and cationic DPP quaternary ammonium (G). The as-prepared supramolecular host–guest system (H⊃G) showed yellow emission with a multi-layered nanostructure. The synergistic interactions between Hg2+ and H⊃G produce crosslinked networks. The intertwined supramolecular complex H⊃G@Hg2+ exhibited strong aggregation-caused quenching (ACQ) fluorescence. This enables convenient detection of Hg2+ and facile monitoring of the removal procedure. Significantly, the quenching fluorescence of H⊃G@Hg2+ can be recovered after treatment with Na2S. As reversible hybrid materials, H⊃G could be efficiently used in the treatment of Hg2+ detection and removal in a reusable manner.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Self-Assembly Behavior of G in Water
A simpler and modified synthetic method of H was developed (Scheme 1). In brief, etherification of OH functionalized pillar[5]arene (P5A1) afforded ethoxycarbonylmethoxy-substituted pillar[5]arene (P5A2). Then, the hydrolysis of P5A2 with NaOH by a one-step reaction generated H in a high yield. However, a three-steps reaction (hydrolysis, acidification and neutralization) from P5A2 to H was needed in the previous synthesis [36]. In addition, the synthesis of G was more straightforward than the reported method [41]. In our case, the N-alkylation and following substitution reaction afforded water-soluble G. On the contrary, tedious protection/deprotection reactions of the amino group and HPLC purification of G were performed [41]. The 1H and 13C NMR spectra of H and G are shown in Figures S1–S4.
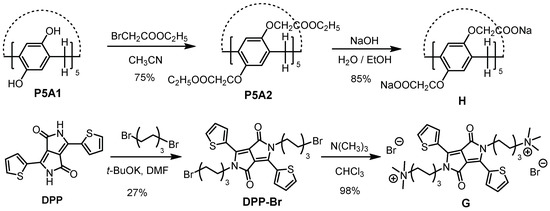
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of host molecule H and guest molecule G.
The aqueous solution of G exhibited a strong shoulder peak at 507/532 nm and a weak band at 350 nm (Figure S5). Its fluorescence showed a shoulder emission at 560 and 600 nm as well as a weak emission at 650 nm (Figure S5). Since G contained a hydrophobic DPP core and two hydrophilic, flexible tails, it tended to form nanoaggregates in water because of the strong π-π stacking among DPP units and the hydrophilic/hydrophobic interaction. 1H NMR spectrum of G proved this assumption, where the chemical shift of hydrogens on thienyl rings of G did not split well and showed broad peaks due to aggregation (Figure S3). The SEM images revealed that G in water formed tight packing with plenty of nanorods form (Figure 2a,b).
2.2. Host–Guest Complexation Studies in Water
The host–guest complexation was investigated between G and H in D2O by 1H NMR titration spectrum. Figure 1a shows the 1H NMR spectra of G in D2O recorded in the absence and in the presence of various amounts of H. Upon addition of H, alkyl protons signals of G displayed a clear upfield shift in sharp contrast with pure G (Δδ = −1.76, −0.33, −0.30, −0.37, −1.62 ppm for protons Hf, He, Hg, Hh, Hd, respectively), indicating the shielding effect of pillar[5]arene cavity and the existence of inclusion complexation. With regard to the 1H NMR spectrum of H, obvious downfield shift (Δδ = 0.14 ppm for protons H2 in phenyl) further confirmed the host–guest inclusion complexation between H and G. Furthermore, 2D NOESY NMR experiments were performed to investigate the relative spatial positions of protons in this host–guest complex (Figure 1b). It exhibited unequivocal correlation peaks between the signals of Hd-Hi on the alkyl chain of the G and H2 on the phenyl of H on viewing the NOESY cross-peaks.
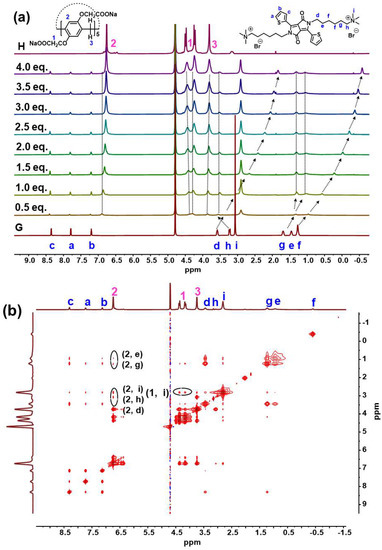
Figure 1.
(a) 1H NMR titration spectra (500 MHz, D2O) of G (8.3 mM) with different equivalents of H. The deuterated water has a chemical shift of 4.79 ppm; (b) NOESY spectrum (500 MHz, D2O) of H⊃G ([H] = 33.2 mM, [G] = 8.3 mM).
SEM was conducted to characterize the morphology of H⊃G. As shown in Figure 2c,d, the scattered H⊃G assemblies with multi-layered nanostructures were observed, which were totally different from that of G. We speculated that the formation of the H⊃G complex was mainly driven by multiple electrostatic interactions, hydrophobic interactions and π-π stacking interactions in aqueous solution. The cooperativity of these noncovalent interactions made G be placed inside the cavity of H successfully.
The complexation between H and G also generated UV-vis and emission spectral changes. Upon addition of H, the redshifted bands from 507 to 512 and 532 to 538 nm with decreased absorption for G were shown, which was ascribed to complexation-induced charge transfer absorption (Figure 3a). Moreover, the absorbance at 350 nm decreased, and the spectrum became broader. As a result, a color change from light pink to pink could be seen, suggesting the formation of a new aggregation state of H⊃G. At the same time, the addition of H led to fluorescence quenching of G to some extent (Figure 3b). For example, the absolute fluorescence quantum yield of G decreased from 39.1% to 3.7% in the absence and presence of 2 equiv. H, respectively. The possible reason can be ascribed to the fact that multi-layered nanostructures gave closer DPP core stacking and resulted in fluorescence quenching of G. At the same time, the zeta potential of −42.43, 2.13 and −40.49 mV for H, G and H⊃G was found, respectively (Figure 3c). Moreover, an obvious Tyndall effect of H⊃G was shown (Figure 3d). All in all, a host–guest system (H⊃G) was constructed successfully by adding H into G aqueous solution, which could induce the change in the aggregation state and fluorescence behavior of G.
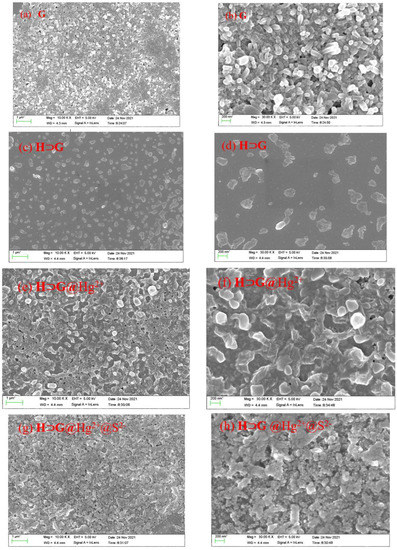
Figure 2.
SEM and enlarged SEM images of the G (a,b), H⊃G (c,d), H⊃G@Hg2+ (e,f) and H⊃G@Hg2+@S2− (g,h). [H] = 2 × 10−5 M, [G] = 10−5 M, [Hg2+] = 2 × 10−5 M, [S2−] = 4 × 10−5 M.
In theory, one G molecule can be complex with two H molecules. Assuming 1:2 inclusion complexation stoichiometry between H and G, the association constants (Ka) could be calculated by using a non-linear least-squares curve-fitting method by use of fluorescence titrations of G with H. The plot of fluorescence change as a function of [H] gave an excellent fit, verifying the validity of the 1:2 inclusion complexation stoichiometry (Figure S6). The Ka value of H⊃G was determined to be 4.8 × 105 M−2, indicating strong complexes were formed.
2.3. Detection of Hg2+ with H⊃G
A series of metal ions including Hg2+, Cu2+, Fe3+, Al3+, Mn2+, Co2+, Sn2+, Cd2+, Ni2+, Au+, Ba2+, Ca2+, Ag+, K+, Fe2+, Mg2+, Pb2+, Na+, Zn2+ and Cr3+ were separately added to H⊃G in 100% water. As shown in Figure 4a, only Hg2+ gave a notable red-shift from 512 to 528 nm and 538 to 561 nm in UV-vis spectra. Meanwhile, the absorption spectrum became broader and extended to 650 nm. As a result, the solution was transformed from pink to purple, which can be observed by naked eyes (Figure 4c). According to a previous study [42], these changes indicated the formation of a typical charge–transfer complex between H⊃G and Hg2+. On the contrary, other metal ions induced absorption intensity change in H⊃G to some extent (Figure S7a), but its maximum absorption peaks at 512 and 538 nm showed no obvious red-shift or blue-shift.
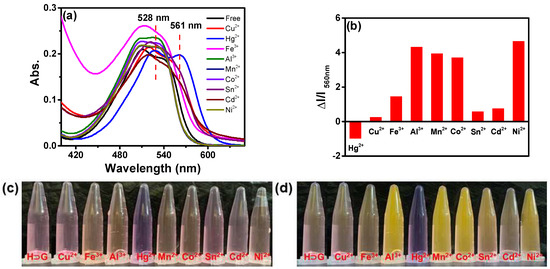
Figure 4.
(a) UV-vis and (b) emission spectra of H⊃G self-assembly in aqueous solution with the addition of 50 equiv. of different metal ions ([G] = 10−5 M, [H] = 2 × 10−5 M, λex = 510 nm). The photos of H⊃G in presence of various metal ions under (c) daylight and (d) 365 nm irradiation.
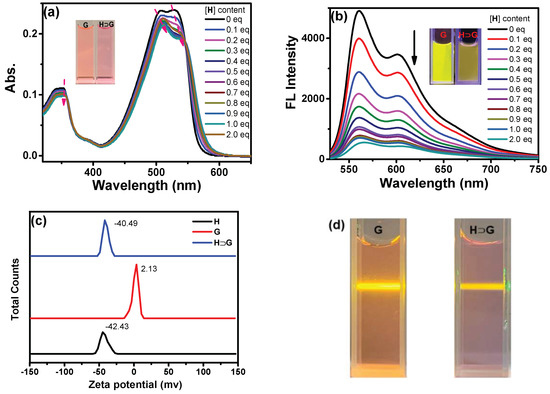
Figure 3.
The (a) UV-vis and (b) emission spectra of G aqueous solution in the presence of increasing amounts of H aqueous solution ([G] = 10−5 M, λex = 510 nm). Insert: Photos of G and H⊃G self-assembly under daylight and 365 nm irradiation; (c) The zeta potential of H (10−5 M), G (10−5 M) and H⊃G aqueous solution; (d) The photographs of Tyndall effect of aqueous solution of G and H⊃G ([H] = 2 × 10−5 M, [G] = 10−5 M).
In addition, only Hg2+ could induce the complete fluorescence quenching of H⊃G. The absolute fluorescence quantum yield of H⊃G decreased from 3.7% to 0.02% in the absence and presence of 10 equiv. Hg2+. The addition of other metal ions did not lead to fluorescence quenching of H⊃G. Contrarily, Cu2+, Sn2+, Fe3+, Cd2+ gave less than 2-fold fluorescence enhancement. Al3+, Mn2+, Co2+, Ni2+ could induce 4~5 fold fluorescence enhancement (Figure 4b,d). As shown in Figure S7b, Ca2+, Mg2+, Ba2+ and Pb2+ could induce fluorescence enhancement of H⊃G to a different extent. Fe2+, Ag+, Na+, Au+ and K+ failed to give obvious fluorescence changes in emission spectra. Moreover, the anti-interference experiment indicated the presence of other competing cations did not affect the response of H⊃G towards Hg2+ (Figure S8). Thus, based on UV-vis and emission change in H⊃G in the presence of Hg2+, the visual and highly selective detection of Hg2+ was obtained.
In order to investigate the sensitivity of H⊃G for Hg2+, fluorescence titration experiments were monitored. The fluorescence emission intensity at 560 gradually decreased with an increase in Hg2+ content (Figure 5a). The limit of detection (LOD) of the H⊃G system for Hg2+ was determined to be 7.17 × 10−7 M according to the 3σ/K method (Figure 5b). The detection performance was similar to or superior to reported pillararenes-based supramolecular systems (Table 1).

Figure 5.
(a) Fluorescence spectra of H⊃G self-assembly in the presence of increasing amounts of Hg2+; (b) Plot of fluorescence intensity of H⊃G self-assembly at 565 nm against the concentration of Hg2+ (λex = 510 nm).

Table 1.
The comparison of pillararene-based materials for Hg2+ detection.
2.4. Detection Mechanism of Hg2+ with H⊃G
In order to understand the Hg2+ detection mechanism by use of H⊃G for such a colorimetric and fluorescence phenomenon, the 1H NMR spectra of H⊃G in D2O in the presence of Hg2+ were carried out. As shown in Figure 6, proton signals of thienyl (Ha, Hb and Hc) from G showed a slight upfield shift, but H2, H3 and H1 from H showed an obvious upfield shift in the presence of Hg2+. In addition to this, the splitting peak of H1 disappeared, inferring multiple interactions between H⊃G and Hg2+ were involved. The 1H NMR titration spectra suggested that synergistic interactions between Hg2+ and host/guest occurred. As we know, the previous work revealed that metal ions could efficiently perturb the microenvironment of host–guest systems [47,48].
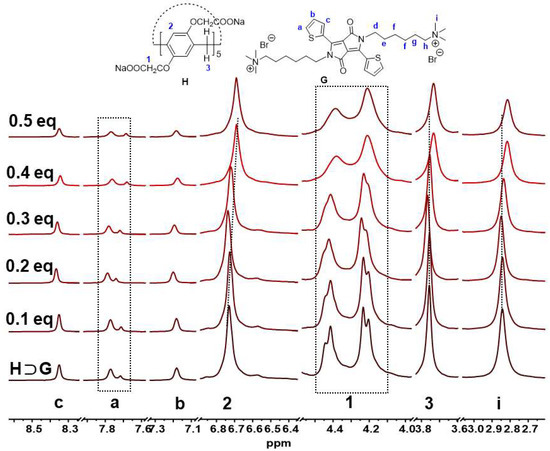
Figure 6.
Partial 1H NMR titration spectra (500 MHz, D2O) of H⊃G ([G] = 4 mM, [H] = 8 mM) with different equivalents of Hg2+.
At the same time, the control complexation experiment between Hg2+ and H or G alone was investigated through 1H NMR, UV-vis and emission spectra. As shown in Figure S9, for free H, the methylene protons at both rims (H1) were split into two sets of peaks (4.40 and 4.15 ppm) in a 1:1 integration. However, upon the addition of Hg2+, the peak H1 was merged into a singlet at 4.20 ppm. Meanwhile, the proton signals from the phenyl moieties (H2) shifted upfield, and proton signals from the methylene bridge (H3) changed from a singlet to a broad peak. The distinct changes indicated an interaction between Hg2+ and H was present. As shown in Figure S10, 1H NMR spectra of G showed obvious changes upon the addition of Hg2+. The thienyl and N-CH2 protons signals of G displayed a down-field shift in sharp contrast with pure G (Δδ = 0.03, 0.04, 0.03, 0.07 ppm for protons Hc, Ha, Hb, Hd, respectively), indicating the coordination of Hg2+ with S and N atoms of G occurred. The 1H NMR results were in accordance with a previous study where thienyl DPP could bind to Hg2+ with S and N atoms [49]. The presence of Hg2+ led to a broad absorption band and an up-shifted baseline of H (Figure S11), indicating Hg2+ can be bound inside the electron-rich cavity of H to form an inclusion complex. On the other hand, Hg2+ also induced an obvious change in UV-vis spectra of G (Figure S12). As a control, other metal ions failed to take effect on G and H simultaneously (Figures S13 and S14). As shown in Figure S15, H⊃G was stable and had excellent detection performance for Hg2+ at pH < 8. Upon increase in pH value, H⊃G was easy to disassemble due to the hydrolysis of G under alkaline conditions. Therefore, under acidic and neutral conditions, the H⊃G complex had a good recognition effect on Hg2+.
Figure S16 shows the Stern–Volmer plot of H⊃G quenched by Hg2+. At a low concentration of Hg2+, the quenching efficiency of H⊃G was more efficient, and I0/I vs. the concentration of the quencher gave a linear plot, indicating a static quenching between H⊃G and Hg2+ was involved.
All these results showed that Hg2+ could simultaneously bind G and H by inclusion and coordination interactions, leading to the high selectivity of Hg2+ detection with H⊃G. Namely, as a crosslinking agent, Hg2+ induced H⊃G to perform self-assembly behavior. SEM images confirmed that a denser and crosslinked network was obtained for H⊃G@Hg2+ (Figure 2e–f), which was different from the multi-layered nanostructure of H⊃G. As a result, closer stacking of H⊃G@Hg2+ gave a more pronounced emission quenching effect. The possible Hg2+ detection mechanism was shown in Scheme 2.
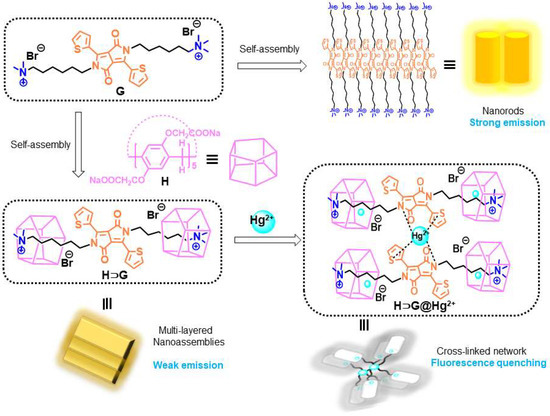
Scheme 2.
Chemical structures and cartoon representations of carboxylatopillar[5]arene sodium salts (H) and diketopyrrolopyrrole-bridged bis(quaternary ammonium) guest (G) and the schematic representations of their self-assembly in absence and presence of Hg2+ in water.
2.5. Reversibility and Application in the Rapid Removal of Hg2+
The reversibility of H⊃G for Hg2+ detection was then evaluated by the addition of Na2S. As shown in Figure 7a, the presence of Na2S aqueous solution could easily recover the fluorescence of H⊃G@Hg2+. In addition, with the alternative addition of Na2S and Hg2+, H⊃G showed reversible fluorescence changes (Figure 7b). There was no significant loss of the sensitivity and responsiveness of H⊃G after at least four times. When the H⊃G-loaded test trip was exposed to Hg2+ aqueous solution, an instant change in emission color from yellow to dark was observed. The following S2− treatment gave a fluorescence “turn on” response (Figure 7c). SEM images indicated that a denser and crosslinked network of H⊃G@Hg2+@S2− was formed (Figure 2g,h).
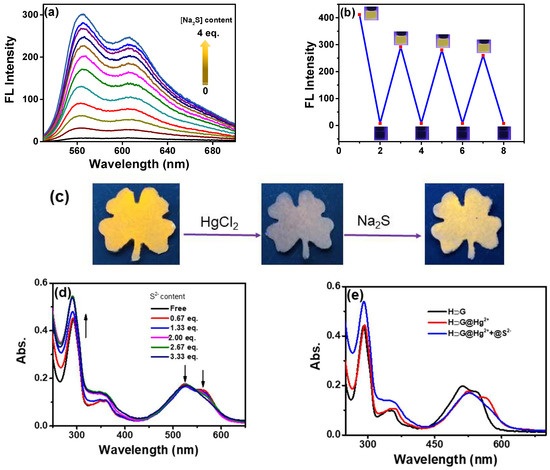
Figure 7.
(a) Emission spectra of H⊃G@Hg2+ self-assembly in the presence of increasing amounts of S2− (from 0 to 4.0 equivalent in aqueous solution); (b) Fluorescent switch of H⊃G self-assembly with alternating addition of Hg2+and S2− (λex = 510 nm, λem = 560 nm, [H] = 2 × 10−5 M, [G] = 10−5 M, [Hg2+] = 5 × 10−5 M, [S2−]=2 × 10−4 M); (c) The photos of H⊃G-loaded filter paper after exposure of Hg2+and subsequent S2− under 365 nm irradiation; (d) UV-vis spectra of H⊃G@Hg2+ in the presence of increasing amounts of S2−; (e) UV-vis spectra of H⊃G, H⊃G@Hg2+, H⊃G@Hg2+@S2−.
The interaction between H⊃G@Hg2+ and S2− was assayed by UV-vis spectral changes. As shown in Figure 7d, the absorption band at 561 nm from G gradually disappeared, and the band at 292 nm from H blue-shifted to 290 nm upon addition of S2−, indicating that multiple interactions were involved between H⊃G@Hg2+ and S2−. As a control, the H, G and H⊃G alone further indicated obvious UV-vis spectral responses to S2− (Figure S13a–c). From these results, it can be seen that the presence of S2− served as both Hg2+ adsorption agent and crosslinker to H⊃G@Hg2+, leading to a denser and more crosslinked network. As shown in Figure 7e, the distinct UV-vis spectra of H⊃G, H⊃G@Hg2+ and H⊃G@Hg2+@S2− were shown.
The performance of H⊃G in the applicable removal of Hg2+ was also investigated. When the aqueous solution of Hg2+ (30 ppm in 10 mL water) was added to the mixture of H⊃G (100 μM) in water, the apparent black precipitate was present immediately. The resulting mixture was stirred or ultrasound for another 12 h to guarantee the complete adsorption of the Hg2+ ion. Then, residual Hg2+ content in the mother liquid after centrifugation was measured by inductively coupled plasma (ICP). The Hg2+ removal efficiency was found to be 80.78% and 76.85% under stirring and ultrasound, respectively, which was slightly lower than the reported pillararene supramolecular system in organic solvents [18,19,20,21,22,23,24]. The possible reason can be ascribed that H⊃G@Hg2+ has higher solubility in water than in organic solvents, leading to higher Hg2+ residual in the mother liquid. Some literature revealed that pillararene could enhance the water dispersibility of insoluble or poorly soluble compounds in water [50,51]. However, in our case, the removal of Hg2+ was performed in pure water without any organic solvents, which was greener and more economical. Therefore, H⊃G maybe have the potential as a versatile absorbent for Hg2+.
In a regeneration treatment, the separated precipitate H⊃G@Hg2+ was dissolved in 10 mL of water, followed by the addition of an excessive amount of Na2S, and a black HgS solid was produced. The absorbent H⊃G was regenerated and recycled after centrifugation (Figure 8).
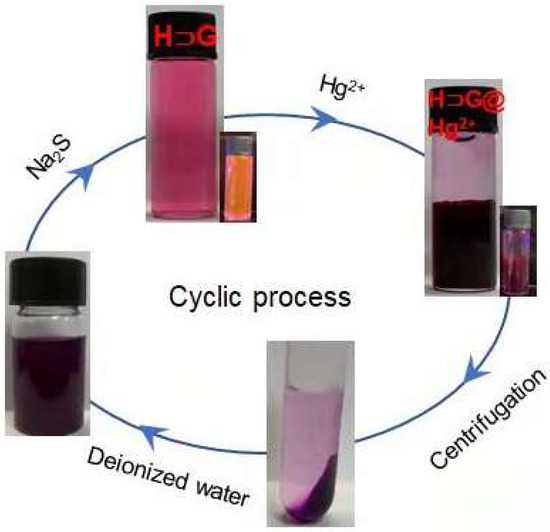
Figure 8.
Representative photos during the process of sensing and removal of Hg2+ and regeneration of absorbent material (H⊃G).
The practical applicability of H⊃G for Hg2+ detection was demonstrated by a real sample analysis in tap water and lake water from the South China University of Technology (SCUT). The aliquots of the tap water and lake water were spiked with known amounts of Hg2+. As shown in Figure S17, the non-spiked lake water and tap water failed to induce fluorescence change in H⊃G. Upon the presence of Hg2+, the emission changes at 560 nm of H⊃G were quenched, which was plotted on the standard calibration curve in Figure 5b, and the recovery of Hg2+ was calculated. As shown in Table 2, up 89.7% recovery was obtained, demonstrating the potential applicability of H⊃G for Hg2+ detection in the real samples.

Table 2.
Detection of mercury ion recovery in lake water and tap water.
3. Conclusions
In summary, a fluorescent supramolecular host–guest system (H⊃G) of water-soluble carboxylatopillar[5]arene sodium salts (H) and a water-soluble DPP derivative (G) was conveniently constructed. Morphological transformation of multi-layered nanostructure was achieved during the addition of H into G aqueous solution, and a fluorescence quenching to some extent was observed. Furthermore, this supramolecular host−guest system (H⊃G) could work as a fluorescent probe to selectively and quantitatively detect Hg2+ ions through the formation of crosslinked network H⊃G@Hg2+. With the addition of the Hg2+ ion, the fluorescence of H⊃G was completely turned off. H⊃G showed a reversible response to Hg2+ with a detection limit of 7.17 × 10−7 M. Our work provided pillararene-based supramolecular fluorescent materials not only for fluorescent detection of Hg2+ with high selectivity but also for efficient removal of Hg2+.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information [36,41] can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/bios12080571/s1, Figure S1: 1H NMR spectrum (500 MHz, D2O) of H; Figure S2: 13C NMR spectrum (125 MHz, D2O) of compound H; Figure S3: 1H NMR spectrum (500 MHz, D2O) of G; Figure S4: 13C NMR spectrum (125 MHz, D2O) of G; Figure S5: Normalized UV-vis, emission spectra of G in aqueous solution (insert: photographs of aqueous solutions of G under daylight and 365 nm light irradiation [G] = 10−5 M); Figure S6: Binding isotherm of the H⊃G complex fitted with a 1:2 binding model according to fluorescence titration experiment ([G] = 10−5 M, λex = 510 nm); Figure S7: (a) The emission spectra of H⊃G in presence of different metal ions. (b) Plot of fluorescence intnsity changes at 560 nm (ΔI/I0) in presence of with the addition of 50.0 equiv. in the presence of 50.0 equiv. of other cations in aqueous solution (Hg2+, Cu2+, Fe3+, Al3+, Mn2+, Co2+, Sn2+, Cd2+, Ni2+); Figure S8: 1H NMR titration spectra (500 MHz, D2O) of H ([H] = 8 mM) with different equivalents of Hg2+; Figure S9: Partial 1H NMR titration spectra (500 MHz, D2O) of G ([G] = 8 mM) upon addition of Hg2+; Figure S10: UV-vis spectra of H upon addition of Hg2+ ([H] = 10−5 M); Figure S11: UV-vis spectra of G upon addition of Hg2+([G] = 10−5 M); Figure S12: UV-vis spectra of (a) G and (b) H upon addition of 5 equiv. of different metal ions ([G] = [H] = 10−5 M); Figure S13: UV-vis spectra of (a) G, (b) H and (c) H⊃G upon addition of various amount of S2− ([G] = [H] = 10−5 M, for H⊃G, [H] = 10−5 M, [G] = 2 × 10−5 M).
Author Contributions
X.J.: Investigation, methodology, formal analysis, writing—original draft. L.W.: Conceptualization, Supervision, Validation, Funding acquisition, Writing—review and editing. X.R.: Investigation, Formal analysis. H.T.: Investigation, writing—review and editing. D.C.: Methodology, writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (22071065) and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2022A1515011743). The APC was funded by 2022A1515011743.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
References
- Mahbub, K.R.; Bahar, M.M.; Labbate, M.; Krishnan, K.; Andrews, S.; Naidu, R.; Megharaj, M. Bioremediation of mercury: Not properly exploited in contaminated soils. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 963–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balali-Mood, M.; Naseri, K.; Tahergorabi, Z.; Khazdair, M.R.; Sadeghi, M. Toxic mechanisms of five heavy metals: Mercury, lead, chromium, cadmium, and arsenic. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 643972–643990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Ayensu, W.K.; Ninashvili, N.; Sutton, D. Review: Environmental exposure to mercury and its toxicopathologic implications for public health. Environ. Toxicol. 2003, 18, 149–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.X.; Zheng, F.Y.; Yang, H.; Ni, J.C. Thorough removal of inorganic and organic mercury from aqueous solutions by adsorption on Lemna minor powder. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendrell, M.; Zhai, D.; Er, J.C.; Chang, Y.-T. Combinatorial strategies in fluorescent probe development. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 4391–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Zha, D.; Anslyn, E.V. Recent advances in supramolecular analytical chemistry using optical sensing. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 7840–7892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Shinkai, S. Functionalized magnetic nanoparticles as chemosensors and adsorbents for toxic metal ions in environmental and biological fields. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 4464–4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavase, T.R.; Lin, H.; Shaikh, Q.-U.-A.; Hussain, S.; Li, Z.; Ahmed, I.; Lv, L.; Sun, L.; Shah, S.B.H.; Kalhoro, M.T. Recent advances of conjugated polymer (CP) nanocomposite-based chemical sensors and their applications in food spoilage detection: A comprehensive review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 273, 1113–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Q.-Q.; Wan, H.-J.; Zhang, X.-M. Carbazolic porous framework with tetrahedral core for gas uptake and tandem detection of iodide and mercury. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 21438–21446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; De, S.; Iyer, P.K. Thiazole-containing conjugated polymer as a visual and fluorometric sensor for iodide and mercury. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 2234–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, Y.W. Macrocycle-based porous organic polymers for separation, sensing, and catalysis. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2107401–2107441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, D.; Yang, J.; Yang, Y. Frontispiece: Supramolecular assemblies with aggregation-induced emission properties for sensing and detection. Chem. Eur. J. 2022, 28, 202103185–202103198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, X.-Y.; Song, N.; Yang, Y.-W. A stimuli-responsive pillar[5]arene-based hybrid material with enhanced tunable multicolor luminescence and ion-sensing ability. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2021, 8, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Song, N.; Wang, D.; Tang, B.Z. Supramolecular materials based on AIE luminogens (AIEgens): Construction and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 1144–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogoshi, T.; Yamagishi, T.-A.; Nakamoto, Y. Pillar-shaped macrocyclic hosts pillar[n]arenes: New key players for supramolecular chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 7937–8002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Meier, H. Pillararene-based fluorescent sensors for the tracking of organic compounds. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2019, 30, 1758–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Fang, Y.; Li, Y.; He, L.; Fan, W.; Feng, W.; Yang, Y.; Liao, J.; Liu, N.; Yuan, L. Pillar[5]arenes bearing phosphine oxide pendents as Hg2+ selective receptors. Talanta 2014, 125, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.-B.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.-D.; Liu, L.; Wu, H.-C. Pillararene-based aggregation-induced-emission-active supramolecular system for simultaneous detection and removal of mercury(II) in water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 11889–11894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.G.; Mondal, S.; Ghosh, K. Copillar[5]arene-rhodamine conjugate as a selective sensor for Hg2+ ions. N. J. Chem. 2020, 44, 5921–5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.M.; Dai, D.H.; Wu, J.R.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.W. Recyclable supramolecular assembly-induced emission system for selective detection and efficientremoval of mercury(II). Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 11879–11887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, D.; Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, C.; Wu, J.-R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yang, Y.-W. Supramolecular assembly-induced emission enhancement for efficient mercury(ii) detection and removal. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 4756–4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-M.; Zhu, W.; Huang, X.-J.; Qu, W.-J.; He, J.-X.; Fang, H.; Yao, H.; Wei, T.-B.; Lin, Q. Supramolecular aggregation-induced emission gels based on pillar[5]arene for ultrasensitive detection and separation of multianalytes. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 16597–16606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Fan, Y.Q.; Mao, P.P.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.M.; Yao, H.; Wei, T.B. Pillar[5]arene-based supramolecular organic framework with multi-Guest detection and recyclable separation properties. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-F.; Han, B.-B.; Ma, J.-F.; Liu, X.; Yang, Q.-Y.; Lin, Q.; Yao, H.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Wei, T.-B. Pillar[5]arene-based fluorescent polymer for selective detection and removal of mercury ions. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 47709–47714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.; Ji, X.; Xiang, F.; Chi, X.; Han, C.; He, J.; Abliz, Z.; Chen, W.; Huang, F. A cationic water-soluble pillar[5]arene: Synthesis and host–guest complexation with sodium 1-octanesulfonate. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 12340–12342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogoshi, T.; Hashizume, M.; Yamagishi, T.; Nakamoto, Y. Synthesis, conformational and host-guest properties of water-soluble pillar[5]arene. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 3708–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Qin, S.; Yao, C.; Li, Y.; Cao, D.; Peng, L.; Wang, L. Controllable construction of biocompatible supramolecular micelles and vesicles by water-soluble phosphate pillar[5,6]arenes for selective anti-cancer drug delivery. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 3778–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Wan, Y.; Cai, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Fan, Z.; Conradson, S.D.; Fu, H.; Yuan, L.; Feng, W. Highly efficient and selective pillararene-based organic materials for Hg2+ and CH3Hg+ extraction from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 387, 124087–124096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil-Cruz, L.E.; Liu, P.; Huang, F.; Khashab, N.M. Multifunctional pillar[n]arene-based smart nanomaterials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 31337–31354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Cai, Y.; Feng, W.; Yuan, L. Pillararenes as macrocyclic hosts: A rising star in metal ion separation. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 7883–7898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Dehaen, W. Tailoring pillararene-based receptors for specific metal ion binding: From recognition to supramolecular assembly. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 415, 213313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Jie, K.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, J.; Xia, D.; Huang, F. Nanoparticles with near-infrared emission enhanced by pillararene-based molecular recognition in water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Wang, T.; Jia, K.; Wu, X.; Yao, C.; Shao, W.; Zhang, D.; Hu, X.-Y.; Wang, L. Glucose-responsive supramolecular vesicles based on water-soluble pillar[5]arene and pyridylboronic acid derivatives for controlled insulin delivery. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 6605–6614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbera, L.; Franco, D.; De Plano, L.M.; Gattuso, G.; Guglielmino, S.P.P.; Lentini, G.; Manganaro, N.; Marino, N.; Pappalardo, S.; Parisi, M.F.; et al. A water-soluble pillar[5]arene as a new carrier for an old drug. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 3192–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wei, R.; Yan, G.H.; Sun, J.; Li, C.; Wang, H.; Shi, L.; Capobianco, J.A.; Sun, L. Smart self-assembled nanosystem based on water-soluble pillararene and rare-earth-doped upconversion nanoparticles for pH-Responsive drug delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 4910–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, D.-X.; Sun, Y.-L.; Zheng, Y.B.; Tan, L.-L.; Weiss, P.S.; Yang, Y.-W. Viologen-mediated assembly of and sensing with carboxylatopillar[5]arene-modified gold nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 1570–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Tang, H.; Xu, L.; Wang, L.; Meier, H.; Cao, D. Pillar[5]arene-diketopyrrolopyrrole fluorescent copolymer: A promising recognition and adsorption material for adiponitrile by selective formation of a conjugated polypseudorotaxane. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2017, 38, 1700161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Tang, H.; Li, Z.-H.; Xu, L.; Wang, L.; Cao, D. Bio-inspired AIE pillar[5]arene probe with multiple binding sites to discriminate alkanediamines. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 13114–13117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Wang, L.; Xu, L.; Zhang, G.; Meier, H.; Tang, H.; Cao, D. Fluorescent-cavity host: An efficient probe to study supramolecular recognition mechanisms. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Cheng, J.; Wei, L.; Song, W.; Wang, L.; Tang, H.; Cao, D. Host–guest complexation of monoanionic and dianionic guests with a polycationic pillararene host: Same two-step mechanism but striking difference in rate upon inclusion. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 2021–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qu, Z.; Cao, H.Y.; Sun, H.Y.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, X.Y. pH switchable nanoassembly for imaging a broad range of malignant tumors. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 12446–12452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, G.; Huang, F. Syntheses of a pillar[4]arene[1]quinone and a difunctionalized pillar[5]arene by partial oxidation. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 9876–9878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, T.; Shi, B.; Yao, H.; Zhang, Y. In situ formation of Hg2+-coordinated fluorescent nanoparticles through a supramolecular polymer network used for efficient Hg2+ sensing and separation. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 9172–9176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Ma, J.; Han, B.; Ding, J.; Lin, Q.; Yao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, T. A pillar[5]arene-based multiple-stimuli responsive metal–organic gel was constructed for facile removal of mercury ions. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 5214–5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Liang, G.; Zhong, K.; Lin, Q.; Yao, H.; Wei, T. A novel water soluble pillar[5]arene and phenazine derivative self-assembled pseudorotaxane sensor for the selective detection of Hg2+ and Ag+ with high selectivity and sensitivity. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 10148–10152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Jiang, X.; Ma, X.; Liu, J.; Yao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, T. Novel bispillar[5]arene-based AIEgen and its’ application in mercury(II) detection. Sensor Actuat. B 2018, 272, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, T.-W.; Luo, T.-T.; Wu, J.-Y.; Tsai, C.-C.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chiang, M.-H.; Lu, K.-L. Adaptation of guest molecules: A simple system that amplifies the gentle perturbation of host lattices from nickel(II) to cobalt(II). Inorg. Chim. Acta 2016, 445, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.F.; Lü, B.Z.; Ji, C.D.; Cai, Y.; Yin, M.Z. Supramolecular host-guest system as ratiometric Fe3+ ion sensor based on water-soluble pillar[5]arene. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 36320–36326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, K.; Dong, B.; Shi, H.; Liu, Z.; Liang, B. Thienyl diketopyrrolopyrrole as a robust sensing platform for multiple ions and its application in molecular logic system. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 244, 849–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.M.; Chen, X.; Ding, J.M.; Yu, L.; Ma, D.; Ding, J.D. Improved solubility and bioactivity of camptothecin family antitumor drugs with supramolecular encapsulation by water-soluble pillar[6]arene. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 5283–5288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shangguan, L.; Chen, Q.; Shi, B.; Huang, F. Enhancing the solubility and bioactivity of anticancer drug tamoxifen by water-soluble pillar[6]arene-based host–guest complexation. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 9749–9752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).