Asymmetric Mach–Zehnder Interferometric Biosensing for Quantitative and Sensitive Multiplex Detection of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Human Plasma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
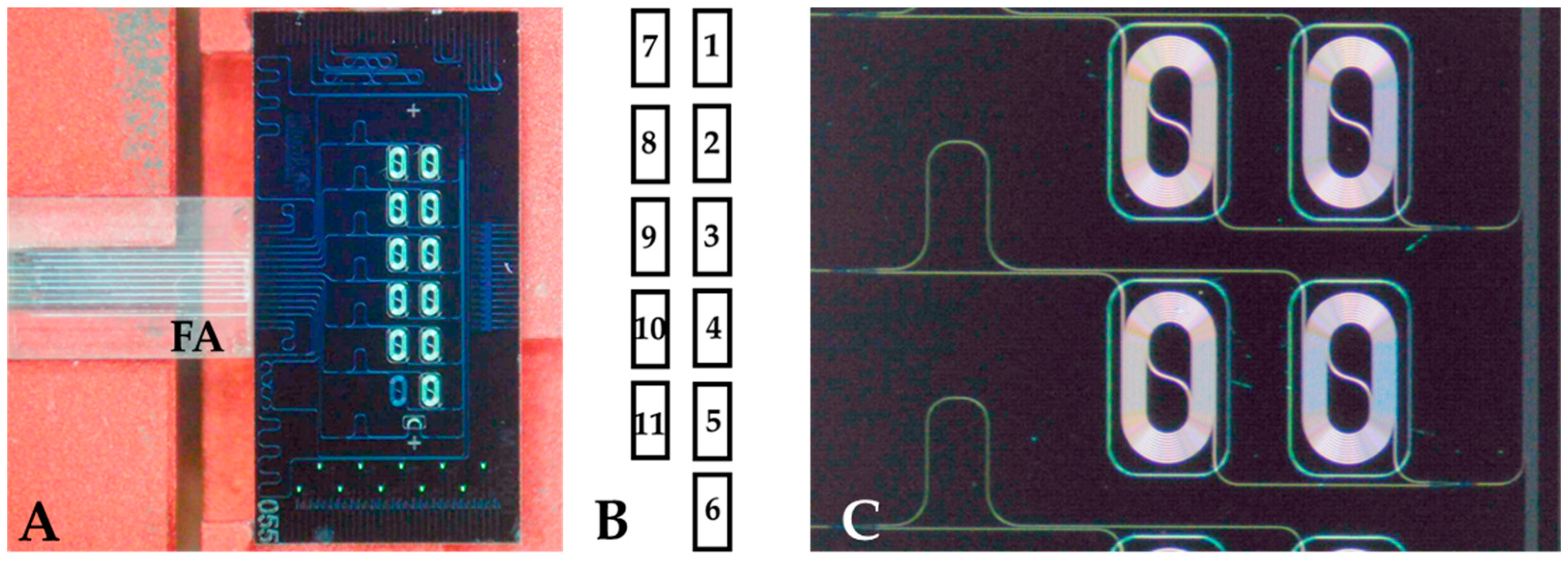
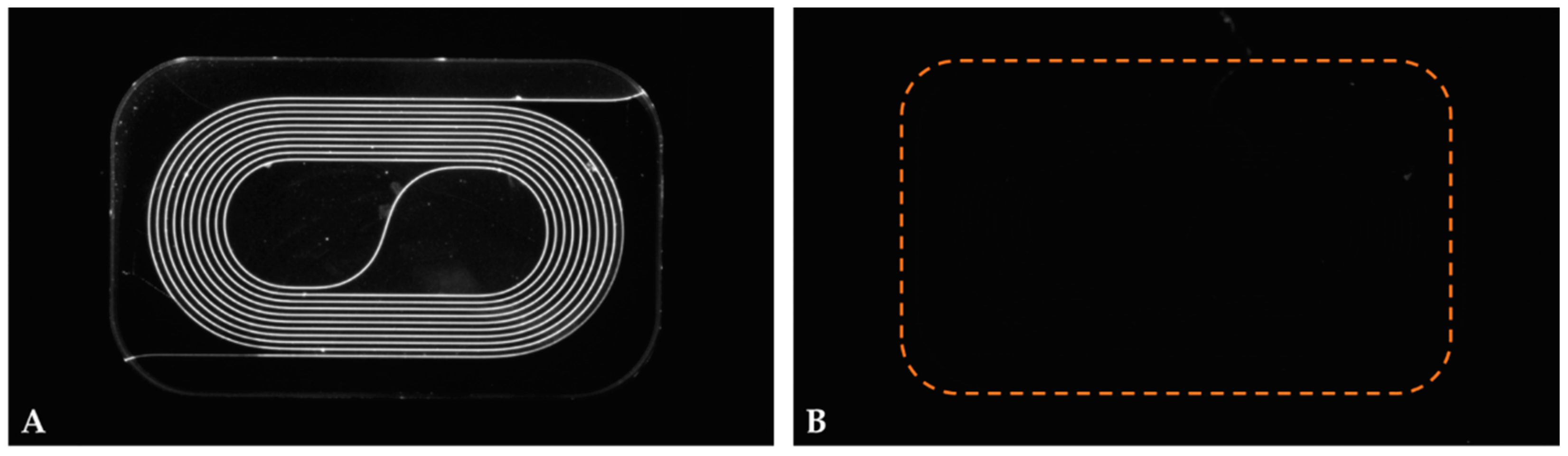
2.2. Chip Design and Operation
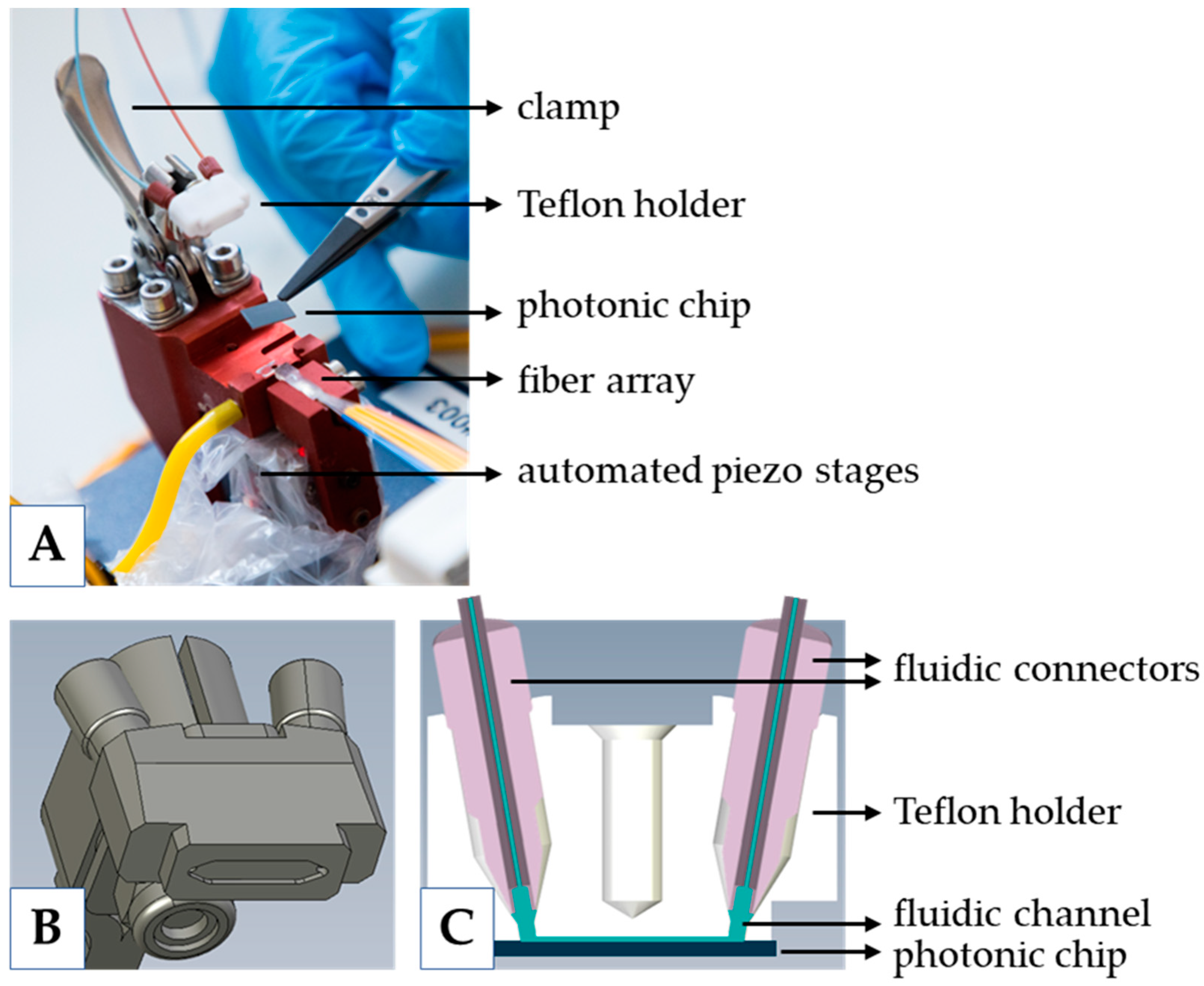
2.3. Measurement Platform
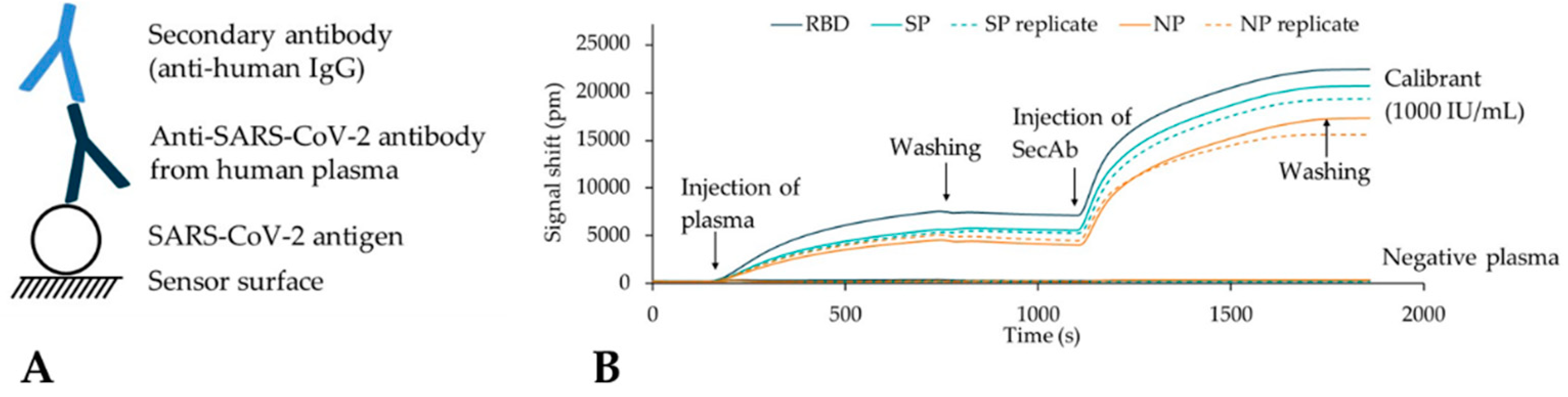
2.4. Chip Functionalization
2.5. Plasma Measurements
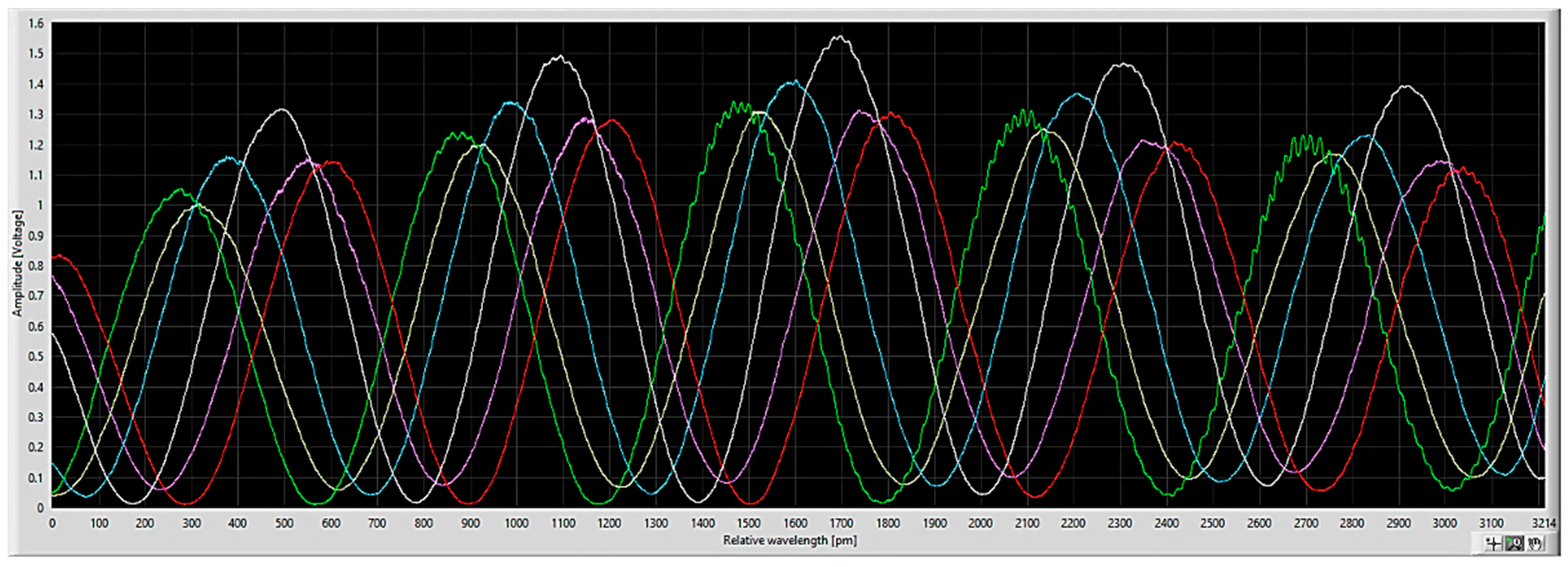
3. Results
3.1. Material-Selective Sensor Modification
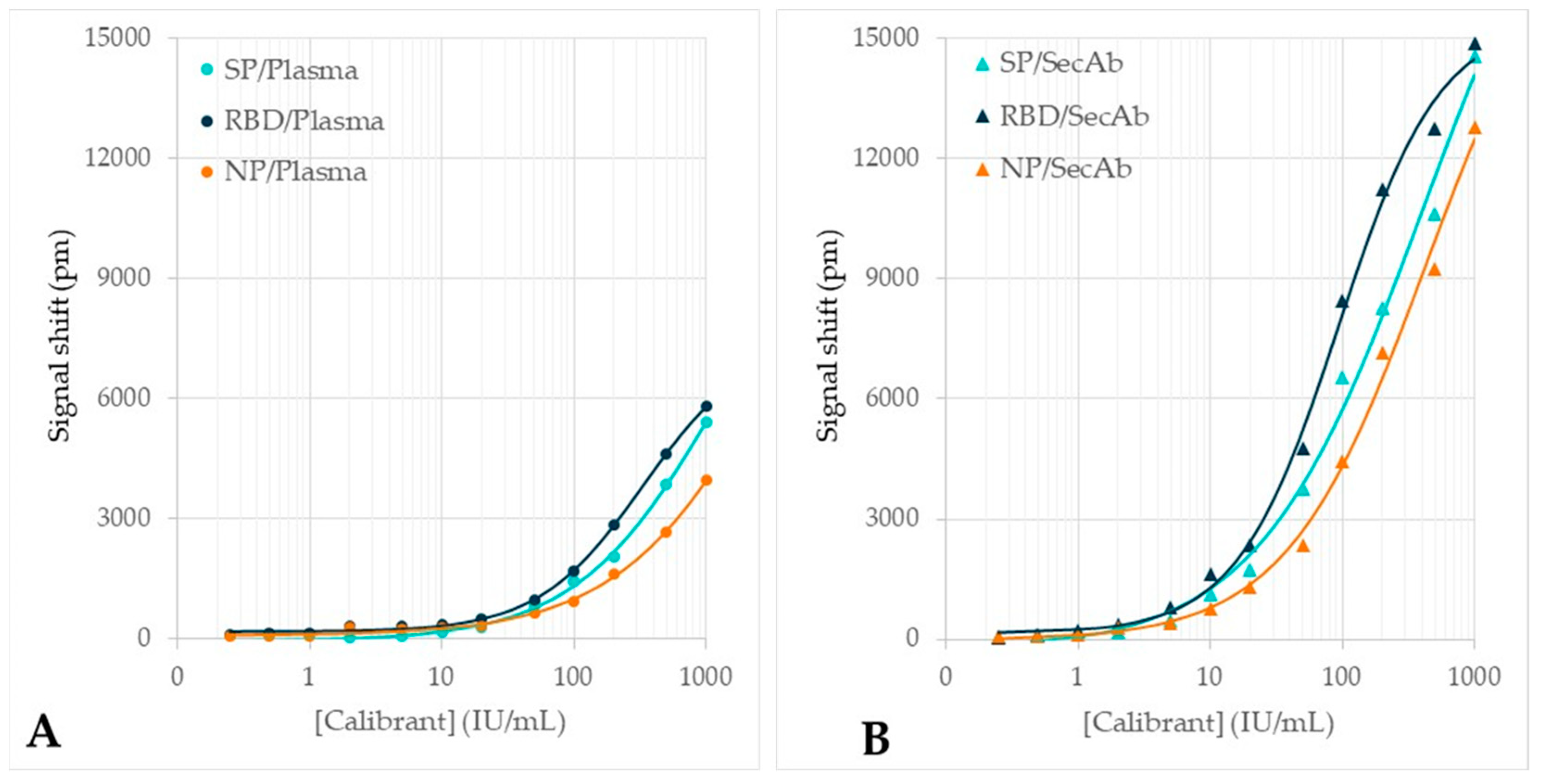
3.2. Testing on Calibrant Dilution Series
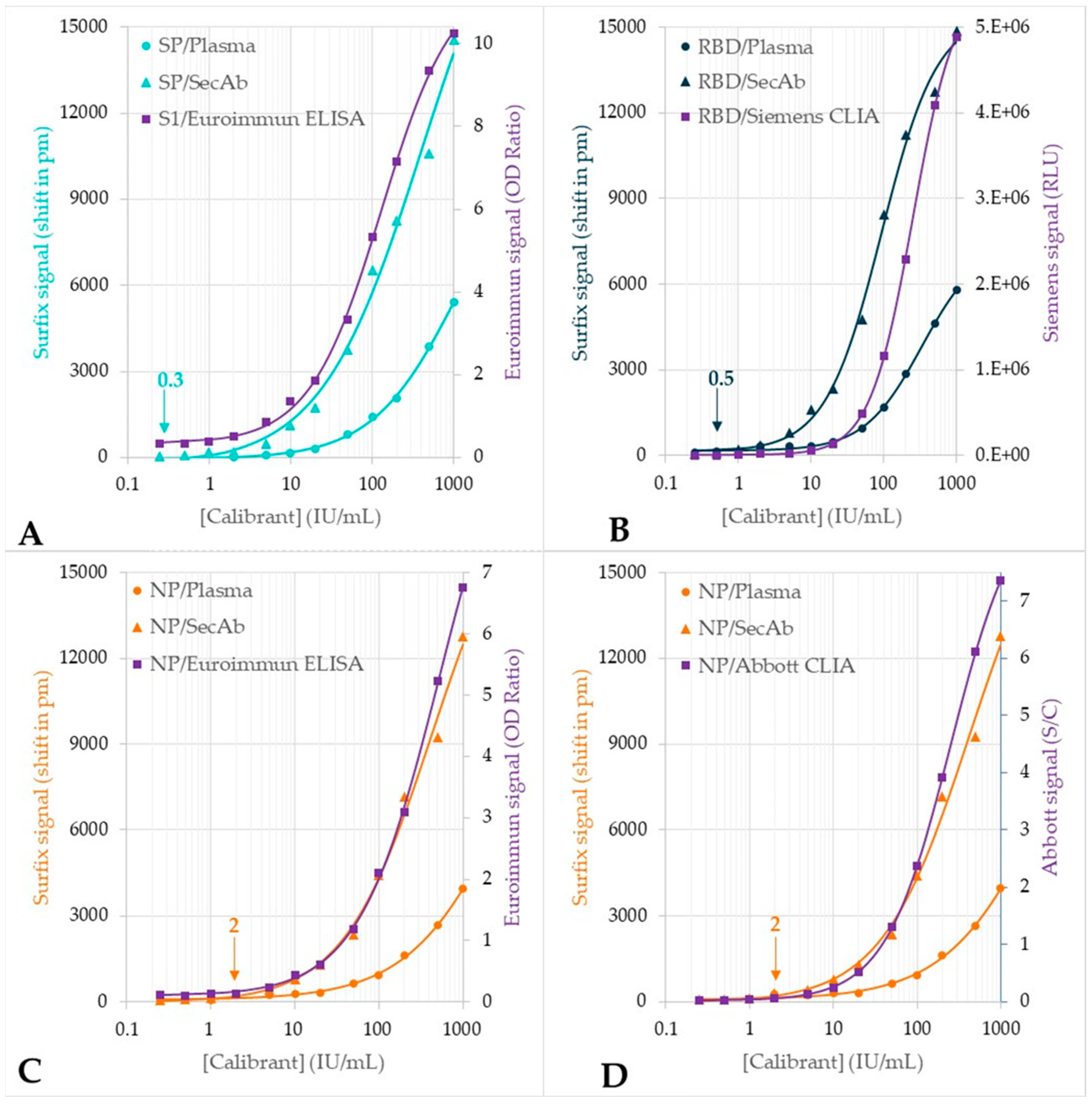
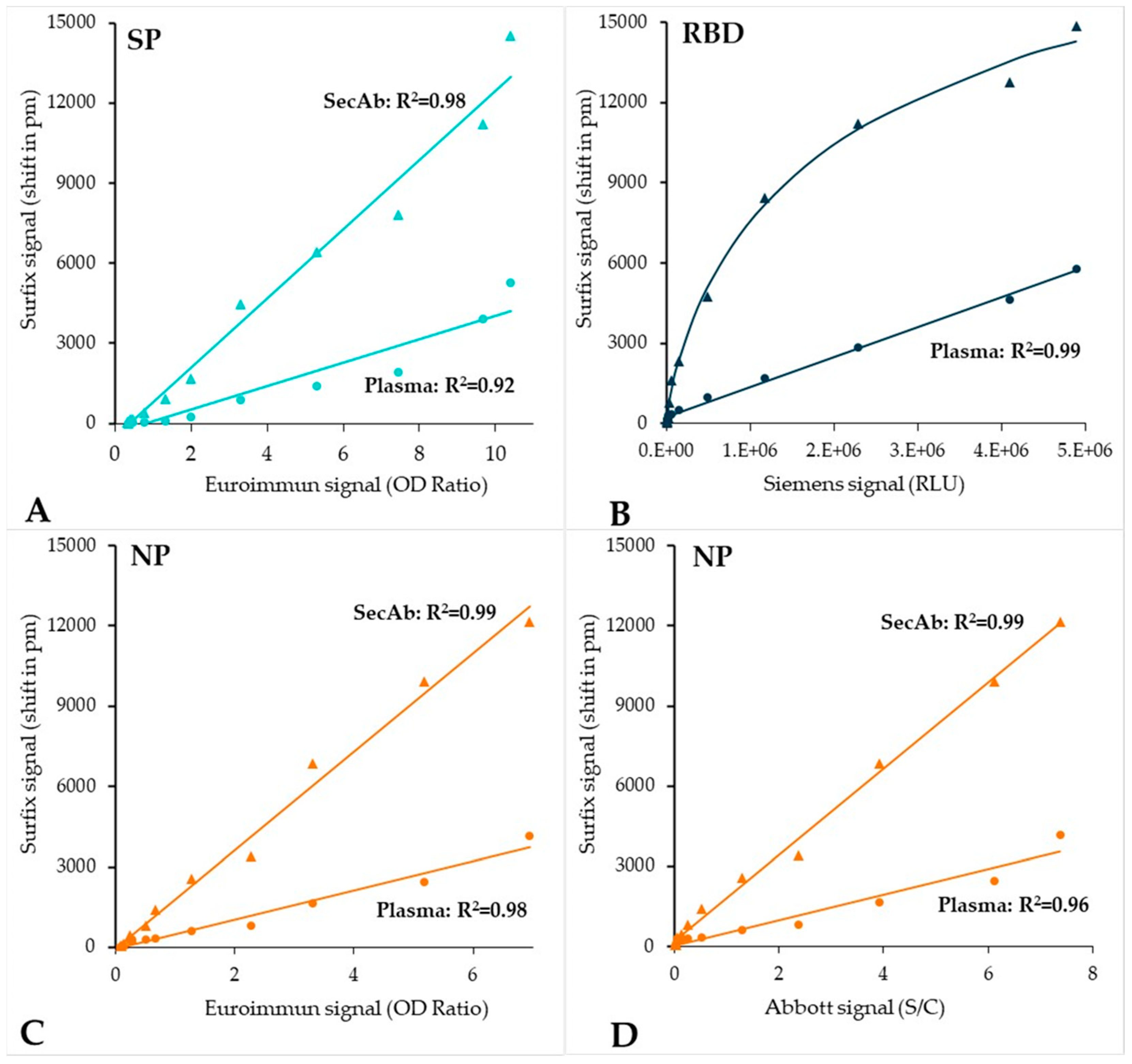
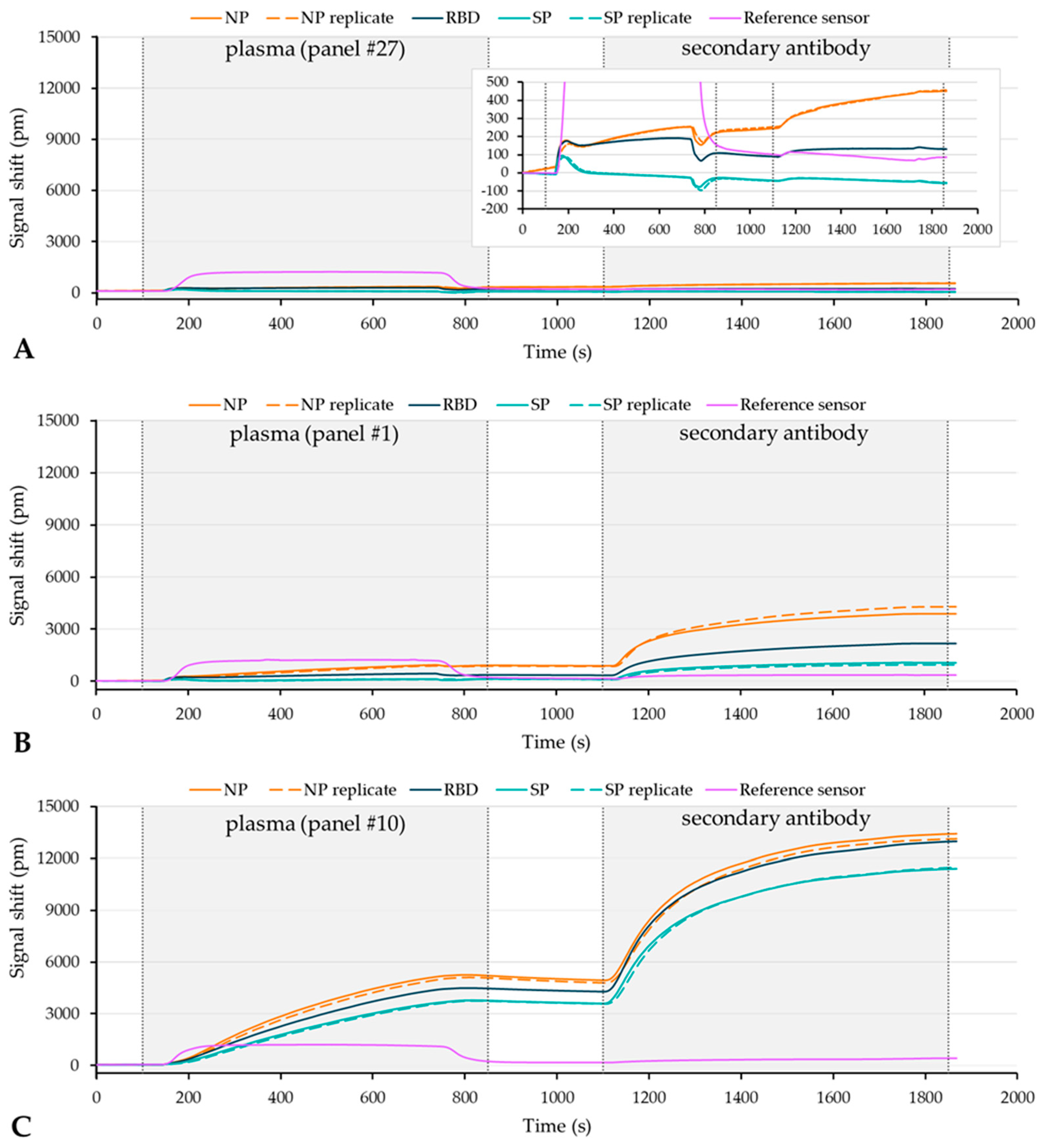
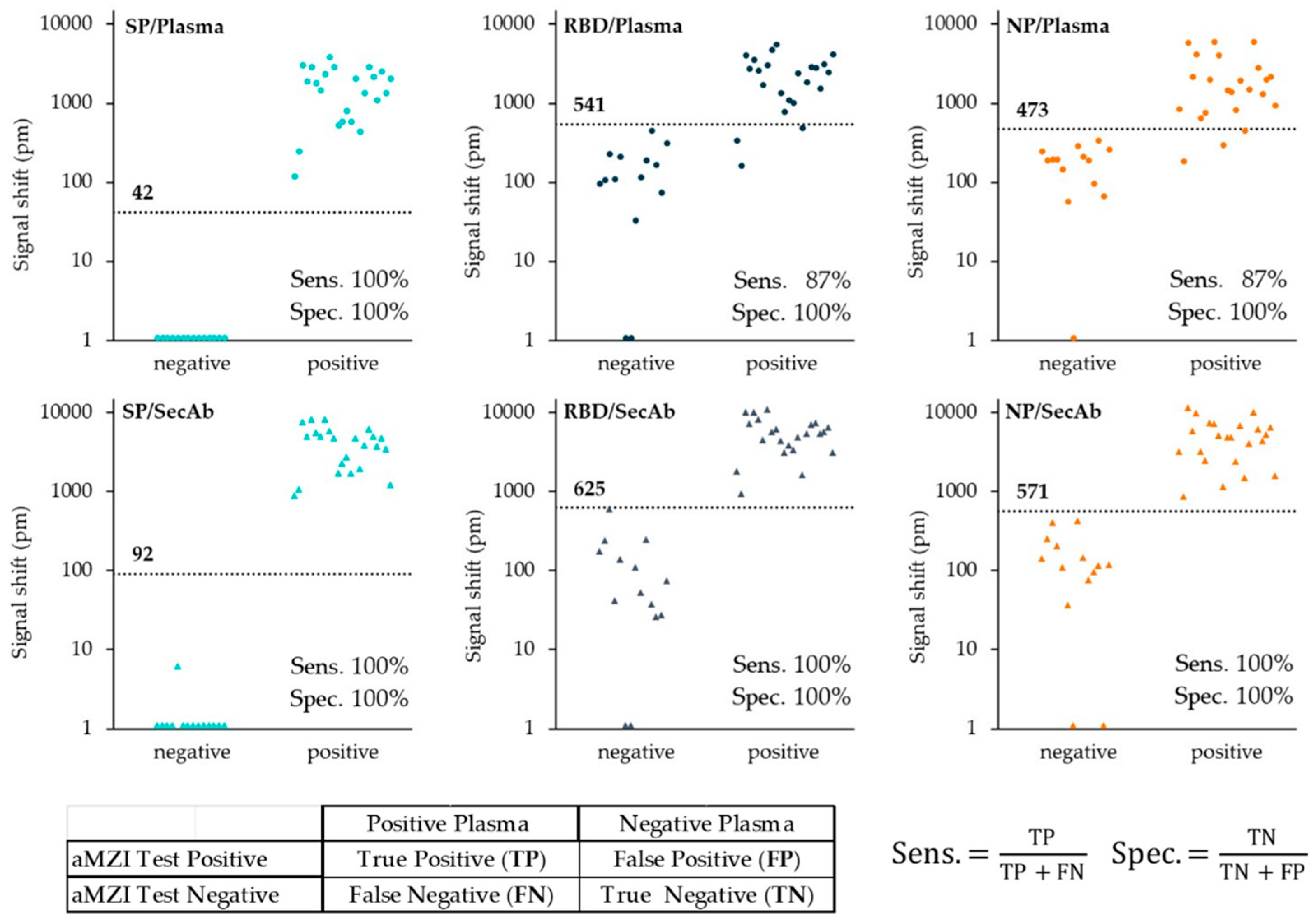
3.3. Testing of the Plasma Verification Panel
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bahadir, E.B.; Sezgintürk, M.K. Applications of Commercial Biosensors in Clinical, Food, Environmental, and Biothreat/Biowarfare Analyses. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 478, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari, S.; Guercetti, J.; Geballa-Koukoula, A.; Tsagkaris, A.S.; Nelis, J.L.D.; Marco, M.P.; Salvador, J.P.; Gerssen, A.; Hajslova, J.; Elliott, C.; et al. Assured Point-of-Need Food Safety Screening: A Critical Assessment of Portable Food Analyzers. Foods 2021, 10, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidt, B.; Siqueira, W.F.; Eersels, K.; Diliën, H.; van Grinsven, B.; Fujiwara, R.T.; Cleij, T.J. Point of Care Diagnostics in Resource-Limited Settings: A Review of the Present and Future of PoC in Its Most Needed Environment. Biosensors 2020, 10, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Deng, Y.; He, N. Point-of-Care Diagnostics for Infectious Diseases: From Methods to Devices. Nano Today 2021, 37, 101092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.Y.; Lan, B.L.; Ramakrishnan, N. Emerging Biosensors to Detect Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): A Review. Biosensors 2021, 11, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Zhou, H.S. Diagnostic Methods and Potential Portable Biosensors for Coronavirus Disease 2019. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 165, 112349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantuoyir, M.M.; Rezaei, N. Serological Tests for COVID-19: Potential Opportunities. Cell Biol. Int. 2021, 45, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamady, A.; Lee, J.J.; Loboda, Z.A. Waning Antibody Responses in COVID-19: What Can We Learn from the Analysis of Other Coronaviruses? Infection 2022, 50, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semmler, G.; Traugott, M.T.; Graninger, M.; Hoepler, W.; Seitz, T.; Kelani, H.; Karolyi, M.; Pawelka, E.; de La Cruz, S.A.; Puchhammer-Stöckl, E.; et al. Assessment of S1-, S2-, and NCP-Specific IgM, IgA, and IgG Antibody Kinetics in Acute SARS-CoV-2 Infection by a Microarray and Twelve Other Immunoassays. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e02890-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinotti, F.; Obolski, U.; Wikramaratna, P.; Giovanetti, M.; Paton, R.; Klenerman, P.; Thompson, C.; Gupta, S.; Lourenço, J. Real-Time Seroprevalence and Exposure Levels of Emerging Pathogens in Infection-Naive Host Populations. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FIND Test Directory. Available online: https://www.finddx.org/covid-19/test-directory/ (accessed on 23 June 2022).
- Gong, F.; Wei, H.X.; Li, Q.; Liu, L.; Li, B. Evaluation and Comparison of Serological Methods for COVID-19 Diagnosis. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 682405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmi, Y.; Li, X.; Khan, J.; Ozer, T.; Choi, J.R. Emerging Point-of-Care Biosensors for Rapid Diagnosis of COVID-19: Current Progress, Challenges, and Future Prospects. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 4137–4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Contreras, E.A.; González-González, R.B.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, I.P.; Yee-De León, J.F.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; González-González, E. Microfluidics-Based Biosensing Platforms: Emerging Frontiers in Point-of-Care Testing SARS-CoV-2 and Seroprevalence. Biosensors 2022, 12, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manmana, Y.; Kubo, T.; Otsuka, K. Recent Developments of Point-of-Care (POC) Testing Platform for Biomolecules. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 135, 116160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleghani, N.; Taghipour, F. Diagnosis of COVID-19 for Controlling the Pandemic: A Review of the State-of-the-Art. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 174, 112830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauglitz, G. Critical Assessment of Relevant Methods in the Field of Biosensors with Direct Optical Detection Based on Fibers and Waveguides Using Plasmonic, Resonance, and Interference Effects. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 3317–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, Y.; Anwar, T.B.; Mulchandani, A. Current Status, Advances, Challenges and Perspectives on Biosensors for COVID-19 Diagnosis in Resource-Limited Settings. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2021, 3, 100025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevez, M.C.; Alvarez, M.; Lechuga, L.M. Integrated Optical Devices for Lab-on-a-Chip Biosensing Applications. Laser Photonics Rev. 2011, 6, 463–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Djaileb, A.; Hojjat Jodaylami, M.; Coutu, J.; Ricard, P.; Lamarre, M.; Rochet, L.; Cellier-Goetghebeur, S.; MacAulay, D.; Charron, B.; Lavallée, É.; et al. Cross-Validation of ELISA and a Portable Surface Plasmon Resonance Instrument for IgG Antibody Serology with SARS-CoV-2 Positive Individuals. Analyst 2021, 146, 4905–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schasfoort, R.B.M.; van Weperen, J.; van Amsterdam, M.; Parisot, J.; Hendriks, J.; Koerselman, M.; Karperien, M.; Mentink, A.; Bennink, M.; Krabbe, H.; et al. Presence and Strength of Binding of IgM, IgG and IgA Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 during CoViD-19 Infection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 183, 113165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo-Lozano, O.; Sierra, M.; Soler, M.; Estévez, M.C.; Chiscano-Camón, L.; Ruiz-Sanmartin, A.; Ruiz-Rodriguez, J.C.; Ferrer, R.; González-López, J.J.; Esperalba, J.; et al. Label-Free Plasmonic Biosensor for Rapid, Quantitative, and Highly Sensitive COVID-19 Serology: Implementation and Clinical Validation. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed Nor, S.N.; Rasanang, N.S.; Karman, S.; Zaman, W.S.W.K.; Harun, S.W.; Arof, H. A Review: Surface Plasmon Resonance-Based Biosensor for Early Screening of SARS-CoV2 Infection. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 1228–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.H.; Leirs, K.; Maes, W.; Imbrechts, M.; Callewaert, N.; Lagrou, K.; Geukens, N.; Lammertyn, J.; Spasic, D. Innovative FO-SPR Label-Free Strategy for Detecting Anti-RBD Antibodies in COVID-19 Patient Serum and Whole Blood. ACS Sens. 2022, 7, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzimianski, J.V.; Lorig-Roach, N.; O’Rourke, S.M.; Alexander, D.L.; Kimmey, J.M.; DuBois, R.M. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies by Biolayer Interferometry. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, L.J.; Theel, E.S.; Baumann, N.A.; Bridgeman, A.R.; Blommel, J.H.; Wu, Y.; Karon, B.S. Evaluation of the Genalyte Maverick SARS-CoV-2 Multi-Antigen Serology Panel. J. Clin. Virol. Plus 2021, 1, 100030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikegami, S.; Benirschke, R.C.; Fakhrai-Rad, H.; Motamedi, M.H.; Hockett, R.; David, S.; Lee, H.K.; Kang, J.; Gniadek, T.J. Target Specific Serologic Analysis of COVID-19 Convalescent Plasma. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghari, A.; Wang, C.; Yoo, K.M.; Rostamian, A.; Xu, X.; Shin, J.D.; Dalir, H.; Chen, R.T. Fast, Accurate, Point-of-Care COVID-19 Pandemic Diagnosis Enabled through Advanced Lab-on-Chip Optical Biosensors: Opportunities and Challenges. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2021, 8, 031313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, L.; Buragohain, P.; Borse, V. Strategies for Sensitivity Enhancement of Point-of-Care Devices. Biosens. Bioelectron. X 2022, 10, 100098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzipetrou, M.; Gounaridis, L.; Tsekenis, G.; Dimadi, M.; Vestering-Stenger, R.; Schreuder, E.F.; Trilling, A.; Besselink, G.; Scheres, L.; van der Meer, A.; et al. A Miniature Bio-Photonics Companion Diagnostics Platform for Reliable Cancer Treatment Monitoring in Blood Fluids. Sensors 2021, 21, 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geuzebroek, D.H.; Besselink, G.A.J.; Schreuder, F.; Falke, F.; Leinse, A.; Heideman, R.G. Silicon-Nitride Biophotonic Sensing Platform. In Integrated Optics: Devices, Materials, and Technologies XXIII, Proceedings of the SPIE, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2–7 February 2009; García-Blanco, M., Cheben, P., Eds.; The International Society for Optical Engineering: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2019; p. 10921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoben, W.; Besselink, G.; Roeven, E.; Zuilhof, H.; Schütz-Trilling, A.; van der Meer, A.; Scheres, L.; Leeuwis, H.; Falke, F.; Schreuder, F.; et al. Highly Sensitive Integrated Optical Biosensing Platform Based on an Asymmetric Mach-Zehnder Interferometer and Material-Selective (Bio)Functionalization. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Miniaturized Systems for Chemistry and Life Sciences (MicroTAS 2018), Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 11–15 November 2018; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Chalyan, T.; Potrich, C.; Schreuder, E.; Falke, F.; Pasquardini, L.; Pederzolli, C.; Heideman, R.; Pavesi, L. AFM1 Detection in Milk by Fab’ Functionalized Si3N4 Asymmetric Mach-Zehnder Interferometric Biosensors. Toxins 2019, 11, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chalyan, T.; Guider, R.; Pasquardini, L.; Zanetti, M.; Falke, F.; Schreuder, E.; Heideman, R.G.; Pederzolli, C.; Pavesi, L. Asymmetric Mach-Zehnder Interferometer Based Biosensors for Aflatoxin M1 Detection. Biosensors 2016, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernández-Gavela, A.; Herranz, S.; Chocarro, B.; Falke, F.; Schreuder, E.; Leeuwis, H.; Heideman, R.G.; Lechuga, L.M. Full Integration of Photonic Nanoimmunosensors in Portable Platforms for On-Line Monitoring of Ocean Pollutants. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 297, 126758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, M.J.; Besselink, G.A.J.; Falke, F.; Everhardt, A.S.; Cornelissen, J.J.L.M.; Huskens, J. Highly Sensitive Protein Detection by Asymmetric Mach-Zehnder Interferometry for Biosensing Applications. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 4566–4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wörhoff, K.; Heideman, R.G.; Leinse, A.; Hoekman, M. TriPleX: A Versatile Dielectric Photonic Platform. Adv. Opt. Technol. 2015, 4, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besselink, G.A.J.; Heideman, R.G.; Schreuder, E.; Wevers, L.S.; Falke, F.; Van den Vlekkert, H.H. Performance of Arrayed Microring Resonator Sensors with the TriPleX Platform. J. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 7, 1000209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gajos, K.; Szafraniec, K.; Petrou, P.; Budkowski, A. Surface Density Dependent Orientation and Immunological Recognition of Antibody on Silicon: TOF-SIMS and Surface Analysis of Two Covalent Immobilization Methods. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 518, 146269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozma, P.; Kehl, F.; Ehrentreich-Förster, E.; Stamm, C.; Bier, F.F. Integrated Planar Optical Waveguide Interferometer Biosensors: A Comparative Review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 58, 287–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenberg, J.Y.; Ling, Y.; Kim, S. Non-Specific Adsorption Reduction Methods in Biosensing. Sensors 2019, 19, 2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, S.C.; de Magalhães, M.T.Q.; Homan, E.J. Immunoinformatic Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein and Identification of COVID-19 Vaccine Targets. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 587615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrun, S.N.; Lee, C.Y.P.; Lee, B.; Fong, S.W.; Young, B.E.; Chee, R.S.L.; Yeo, N.K.W.; Torres-Ruesta, A.; Carissimo, G.; Poh, C.M.; et al. Linear B-Cell Epitopes in the Spike and Nucleocapsid Proteins as Markers of SARS-CoV-2 Exposure and Disease Severity. eBioMedicine 2020, 58, 102911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wu, X.; Zhang, X.; Hou, X.; Liang, T.; Wang, D.; Teng, F.; Dai, J.; Duan, H.; Guo, S.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Proteome Microarray for Mapping COVID-19 Antibody Interactions at Amino Acid Resolution. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 2238–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Assay | Mean ± SD (pm) | LOD (IU/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| SP/Direct | −66 ± 21 | 1.4 |
| SP/Indirect | 22 ± 10 | 0.3 |
| RBD/Direct | 201 ± 40 | 9.7 |
| RBD/Indirect | 57 ± 25 | 0.5 |
| NP/Direct | 79 ± 34 | 4.8 |
| NP/Indirect | 111 ± 40 | 2.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Besselink, G.; Schütz-Trilling, A.; Veerbeek, J.; Verbruggen, M.; van der Meer, A.; Schonenberg, R.; Dam, H.; Evers, K.; Lindhout, E.; Garritsen, A.; et al. Asymmetric Mach–Zehnder Interferometric Biosensing for Quantitative and Sensitive Multiplex Detection of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Human Plasma. Biosensors 2022, 12, 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080553
Besselink G, Schütz-Trilling A, Veerbeek J, Verbruggen M, van der Meer A, Schonenberg R, Dam H, Evers K, Lindhout E, Garritsen A, et al. Asymmetric Mach–Zehnder Interferometric Biosensing for Quantitative and Sensitive Multiplex Detection of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Human Plasma. Biosensors. 2022; 12(8):553. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080553
Chicago/Turabian StyleBesselink, Geert, Anke Schütz-Trilling, Janneke Veerbeek, Michelle Verbruggen, Adriaan van der Meer, Rens Schonenberg, Henk Dam, Kevin Evers, Ernst Lindhout, Anja Garritsen, and et al. 2022. "Asymmetric Mach–Zehnder Interferometric Biosensing for Quantitative and Sensitive Multiplex Detection of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Human Plasma" Biosensors 12, no. 8: 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080553
APA StyleBesselink, G., Schütz-Trilling, A., Veerbeek, J., Verbruggen, M., van der Meer, A., Schonenberg, R., Dam, H., Evers, K., Lindhout, E., Garritsen, A., van Amerongen, A., Knoben, W., & Scheres, L. (2022). Asymmetric Mach–Zehnder Interferometric Biosensing for Quantitative and Sensitive Multiplex Detection of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Human Plasma. Biosensors, 12(8), 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080553





