Prefab Hollow Glass Microsphere-Based Immunosensor with Liquid Crystal Sensitization for Acute Myocardial Infarction Biomarker Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
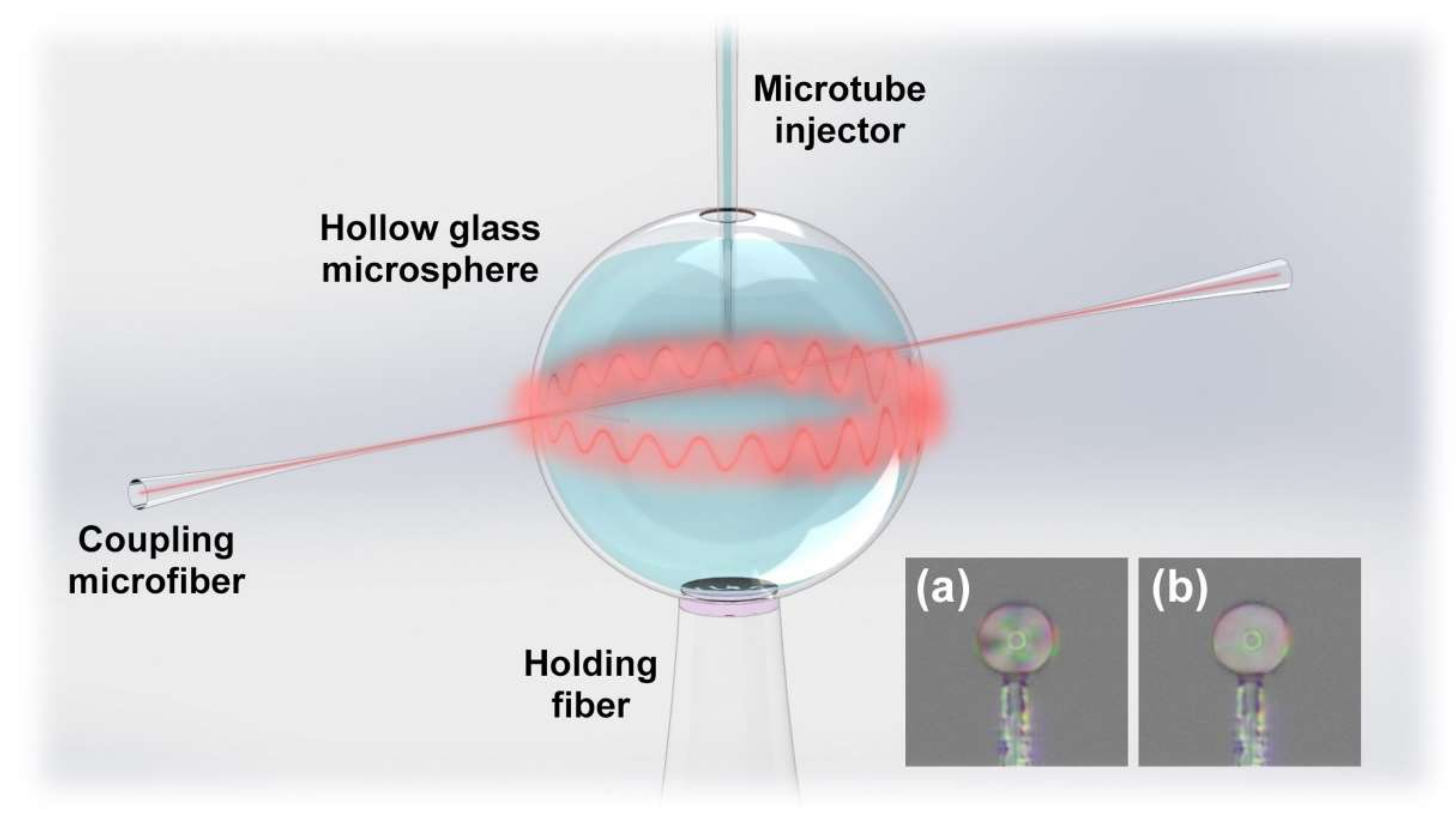
2.2. Fabrication and Principle of the Immunosensor
- Hydroxylation: Inject piranha solution into the HGMS for 30 min and then wash with anhydrous ethanol and deionized water.
- Silanization (Figure 3b): Inject the mixed solution of 1% (v/v) APTES and 1% (v/v) DMOPA into the hydroxylated HGMS for 30 min, wash with anhydrous ethanol and deionized water, and dry at 110 °C for 30 min.
- Aldehyde modification (Figure 3c): Inject 2% (v/v) GA solution into the silanized HGMS for 30 min, and then wash with anhydrous ethanol and deionized water.
- Antibody incubation and blocking (Figure 3d): 20 μg/mL FITC-cTnI antibody PBS solution was injected into the aldehyde-modified HGMS for 60 min, washed with PBS buffer, and then injected with 80 mM glycine solution for 60 min to block the aldehyde site of the unbound antibody, washed with deionized water.
- LC modification (Figure 3e): Inject 5CB LC after heating to >35 °C into the HGMS for 60 min, and finally clean with deionized water.


3. Results and Discussion
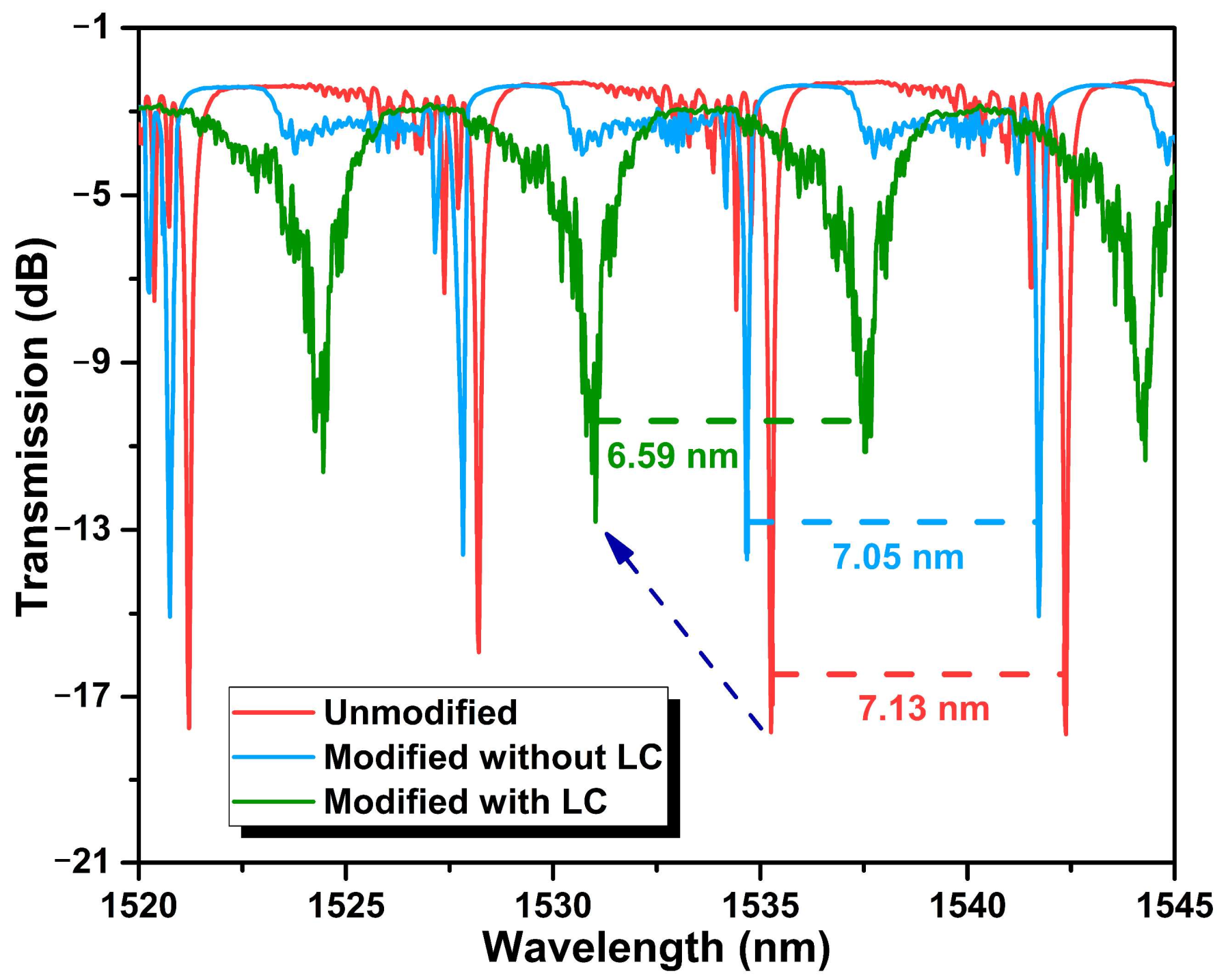
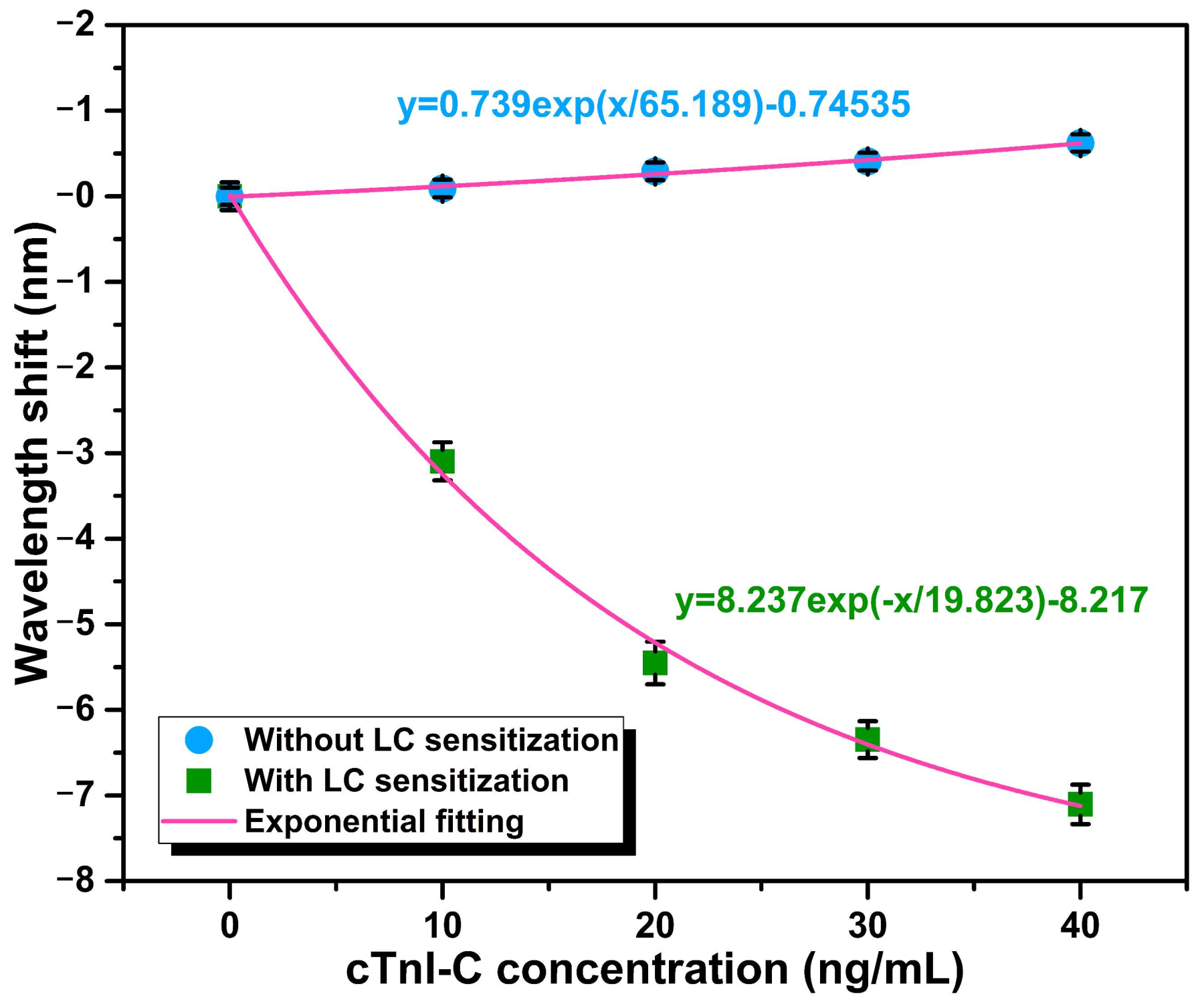
3.1. Static Response to cTnI-C Complex
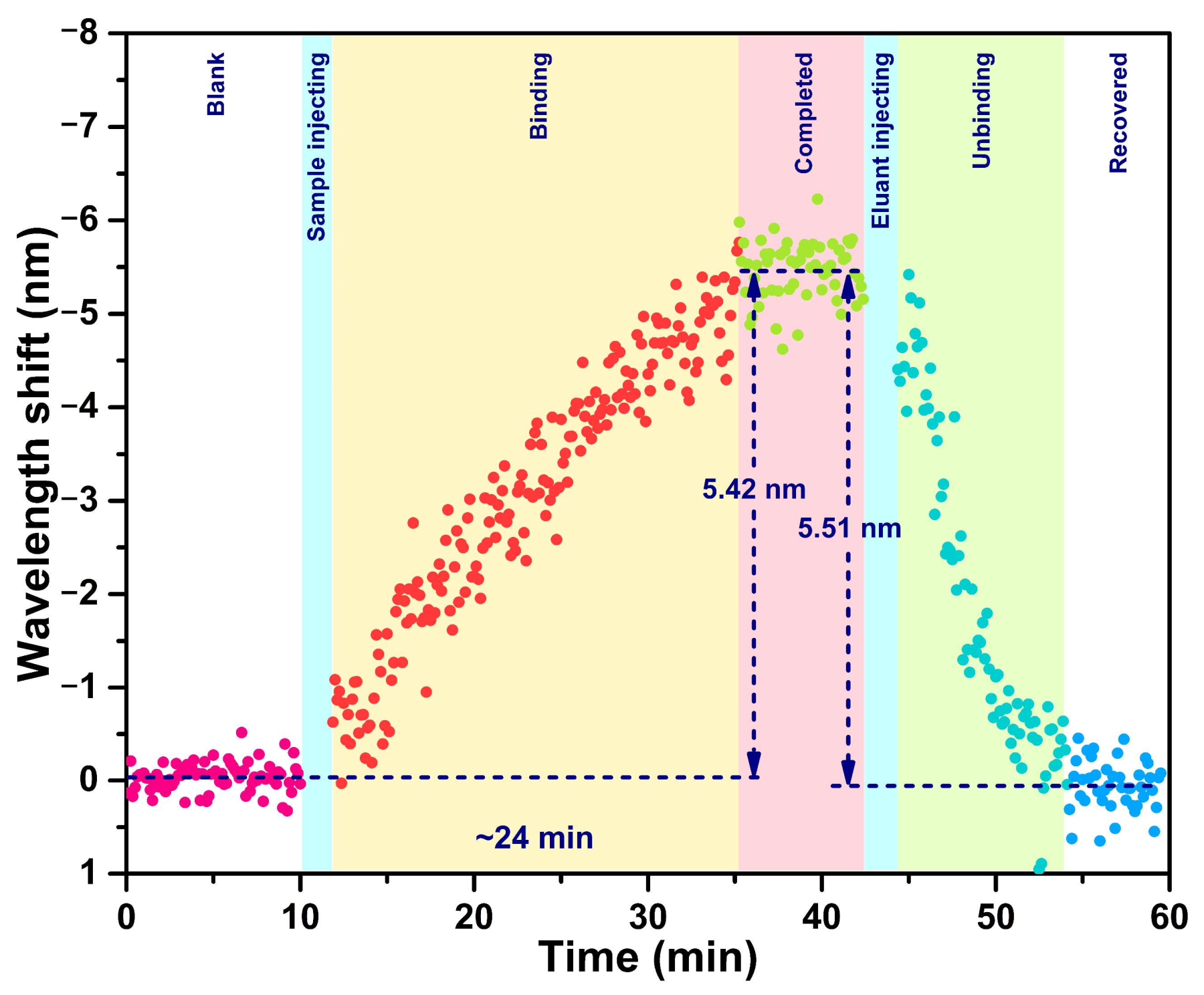
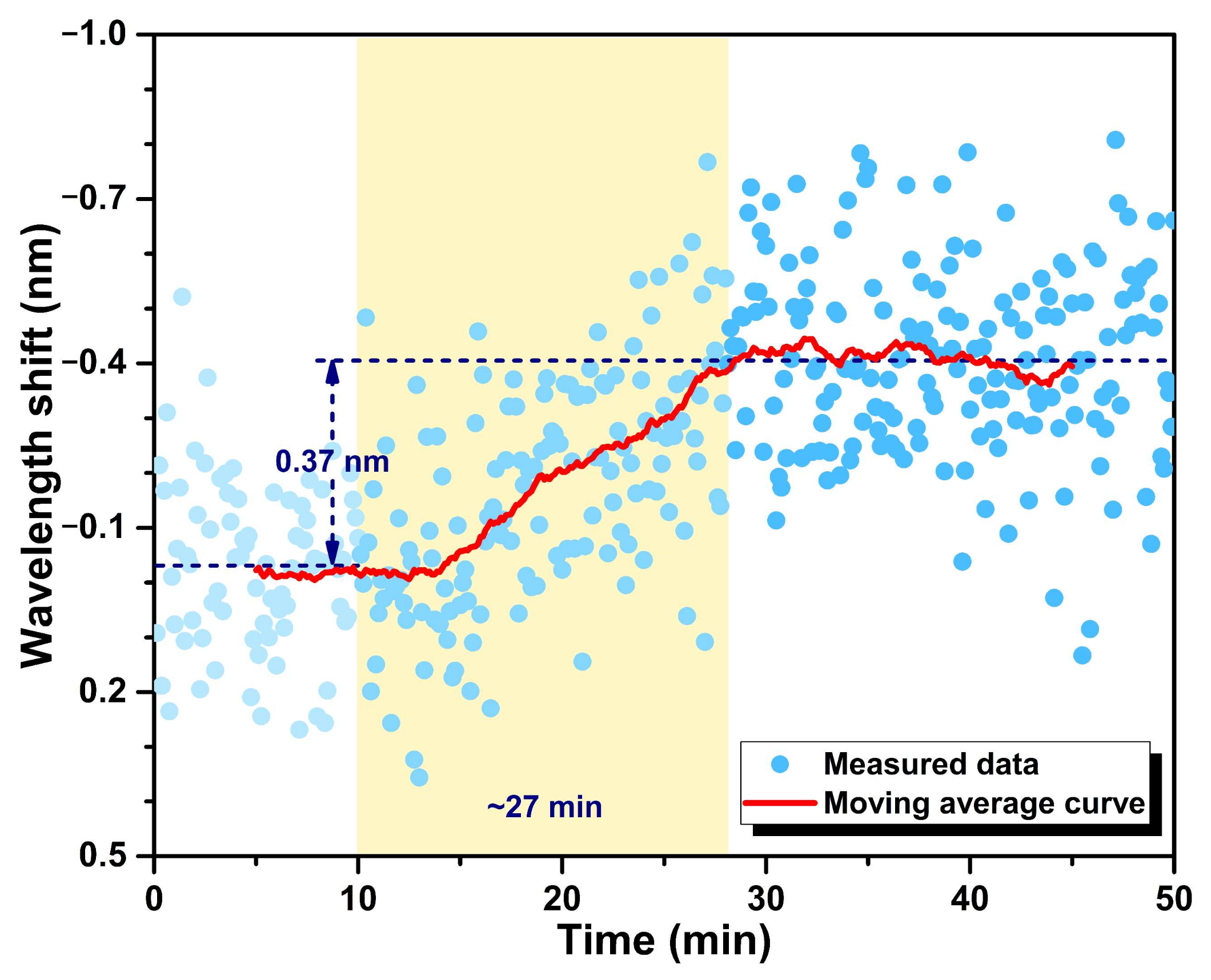
3.2. Dynamic Response to cTnI-C Complex
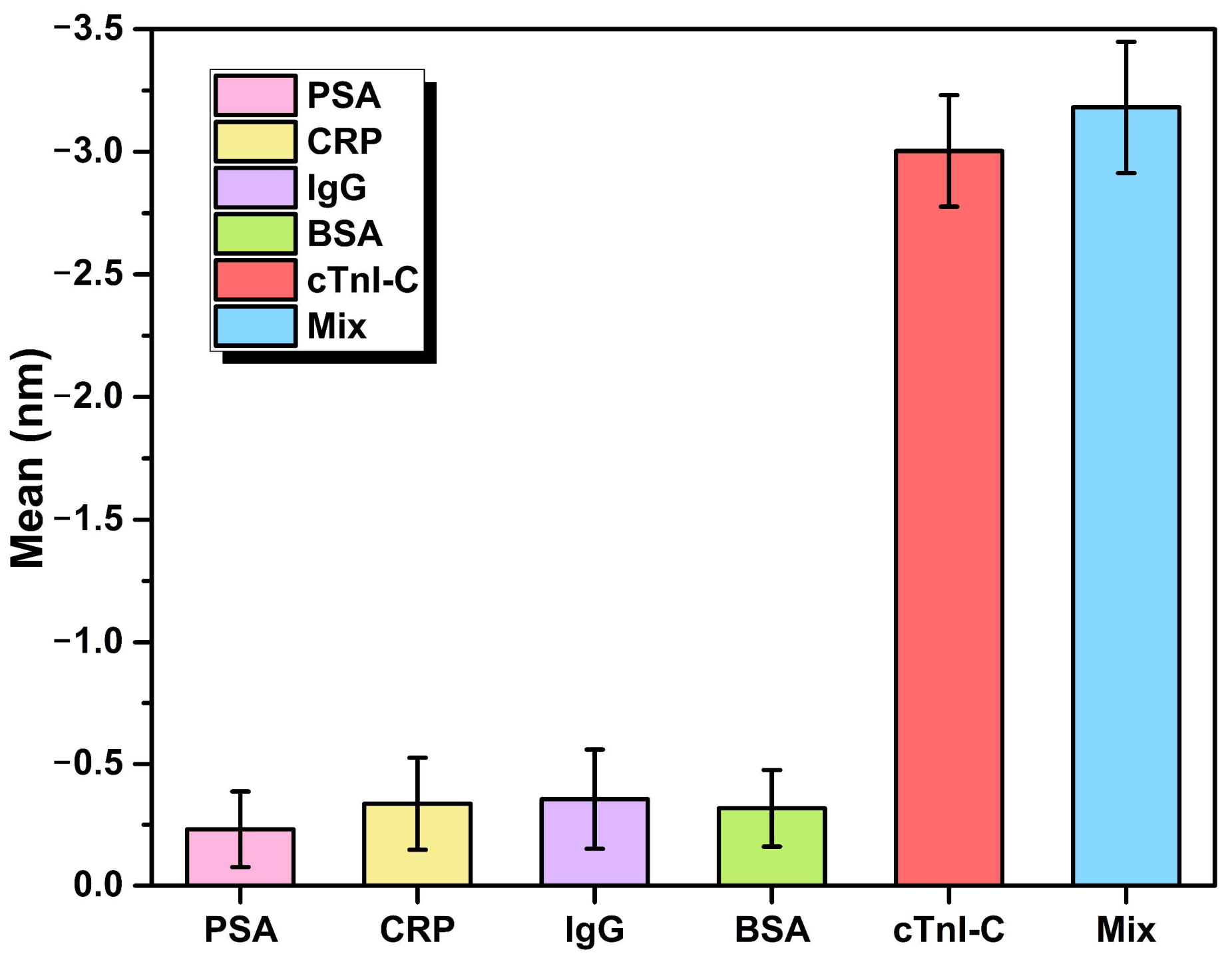
3.3. Stability and Specificity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Calculation of Q Factor
Appendix B. Calculation of LOD
References
- De Lemos, J.A. Increasingly Sensitive Assays for Cardiac Troponins: A Review. JAMA 2013, 309, 2262–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Cassedy, A.; O’Kennedy, R. The role of antibody-based troponin detection in cardiovascular disease: A critical assessment. J. Immunol. Methods 2021, 497, 113108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Jiao, L.; Tang, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Wei, Q. A nanozyme-linked immunosorbent assay for dual-modal colorimetric and ratiometric fluorescent detection of cardiac troponin I. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 288, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, C.; Zhang, D.; Yang, H.; Wang, S.; Chu, M.; Li, P. Chemiluminescence immunoassay for cardiac troponin T by using silver nanoparticles functionalized with hemin/G-quadruplex DNAzyme on a glass chip array. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 3197–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.; Ng, L.L. Biomarkers in acute myocardial infarction. BMC Med. 2010, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aldous, S.J. Cardiac biomarkers in acute myocardial infarction. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 164, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichlin, T.; Hochholzer, W.; Bassetti, S.; Steuer, S.; Stelzig, C.; Hartwiger, S.; Biedert, S.; Schaub, N.; Buerge, C.; Potocki, M.; et al. Early Diagnosis of Myocardial Infarction with Sensitive Cardiac Troponin Assays. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Habets, M.A.W.; Sturkenboom, H.N.; Tio, R.A.; Belfroid, E.; Hoogervorst-Schilp, J.; Siebelink, H.J.; Jansen, C.W.; Smits, P.C. How often and to what extent do admitted COVID-19 patients have signs of cardiac injury? Neth. Heart J. 2021, 29, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque-Ossa, L.C.; García-Ferrera, B.; Reyes-Retana, J.A. Troponin I as a Biomarker for Early Detection of Acute Myocardial Infarction. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2021, 101067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Retana, J.A.; Duque-Ossa, L.C. Acute Myocardial Infarction Biosensor: A Review From Bottom Up. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2021, 46, 100739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabish, T.A.; Hayat, H.; Abbas, A.; Narayan, R.J. Graphene Quantum Dots-Based Electrochemical Biosensing Platform for Early Detection of Acute Myocardial Infarction. Biosensors 2022, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, T.; Yang, M.; Wu, C.; Zhang, W.; Chu, Z.; Jin, W. A handheld testing device for the fast and ultrasensitive recognition of cardiac troponin I via an ion-sensitive field-effect transistor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 193, 113554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, S.; Jayaraj, J.; Prazeres, D.M.F. A Cellulose Paper-Based Fluorescent Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Quantitative Detection of Cardiac Troponin I. Biosensors 2021, 11, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Singh, R.; Chaudhary, S.; Zhang, B.; Kumar, S. 2-D Nanomaterials Assisted LSPR MPM Optical Fiber Sensor Probe for Cardiac Troponin I Detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Li, K.; Wei, Y.; Hao, P.; Chi, M.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y. Ultrasensitive label-free optical microfiber coupler biosensor for detection of cardiac troponin I based on interference turning point effect. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 106, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Liang, L.-L.; Xiao, P.; Sun, L.-P.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Ran, Y.; Jin, L.; Guan, B.-O. A label-free cardiac biomarker immunosensor based on phase-shifted microfiber Bragg grating. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Y.; Long, J.; Xu, Z.; Yin, Y.; Hu, D.; Long, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, L.; Liang, H.; Guan, B.-O. Harmonic optical microfiber Bragg grating immunosensor for the accelerative test of cardiac biomarker (cTn-I). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 179, 113081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, R.; Huang, J.; Xu, X.; Yang, L. Immunoassays Using Optical-Fiber Sensor with All-Directional Chemiluminescent Collection. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 6257–6262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apple, F.S.; Fantz, C.R.; Collinson, P.O.; IFCC Committee on Clinical Application of Cardiac Bio-Markers. Implementation of High-Sensitivity and Point-of-Care Cardiac Troponin Assays into Practice: Some Different Thoughts. Clin. Chem. 2020, 67, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Bo, L.; Semenova, Y.; Farrell, G.; Brambilla, G. Optical Microfibre Based Photonic Components and Their Applications in Label-Free Biosensing. Biosensors 2015, 5, 471–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niculescu, A.-G.; Chircov, C.; Bîrcă, A.C.; Grumezescu, A.M. Fabrication and Applications of Microfluidic Devices: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Hu, X.-g.; Hu, S.; Peng, Y. Applications of fiber-optic biochemical sensor in microfluidic chips: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 166, 112447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolotsky, A.; Butler, D.; Dong, C.; Gerace, K.; Glavin, N.R.; Muratore, C.; Robinson, J.A.; Ebrahimi, A. Two-Dimensional Materials in Biosensing and Healthcare: From In Vitro Diagnostics to Optogenetics and Beyond. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 9781–9810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rohaizad, N.; Mayorga-Martinez, C.C.; Fojtů, M.; Latiff, N.M.; Pumera, M. Two-dimensional materials in biomedical, biosensing and sensing applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 619–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Zhou, D.; Su, Y.; Zhou, G.; Yao, L.; Sun, W.; Liu, Y. Correction: A liquid-crystal-based immunosensor for the detection of cardiac troponin I. Analyst 2020, 145, 5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, S.-T. Extended Cauchy equations for the refractive indices of liquid crystals. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 95, 896–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussain, A.; Pina, A.S.; Roque, A.C.A. Bio-recognition and detection using liquid crystals. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 25, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Bian, Q.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; Liang, L. High Sensitivity All Optical Fiber Conductivity-Temperature-Depth (CTD) Sensing Based on an Optical Microfiber Coupler (OMC). J. Lightwave Technol. 2019, 37, 2739–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmer, F.; Arnold, S. Whispering-gallery-mode biosensing: Label-free detection down to single molecules. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Pan, J.; Hu, S. Overview of the coupling methods used in whispering gallery mode resonator systems for sensing. Opt. Laser. Eng. 2020, 127, 105968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandimalla, V.B.; Neeta, N.S.; Karanth, N.G.; Thakur, M.S.; Roshini, K.R.; Rani, B.E.A.; Pasha, A.; Karanth, N.G.K. Regeneration of ethyl parathion antibodies for repeated use in immunosensor: A study on dissociation of antigens from antibodies. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2004, 20, 903–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiavaioli, F.; Gouveia, C.A.J.; Jorge, P.A.S.; Baldini, F. Towards a Uniform Metrological Assessment of Grating-Based Optical Fiber Sensors: From Refractometers to Biosensors. Biosensors 2017, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhuang, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.S.; Lian, J. A Weighted Moving Average-Based Approach for Cleaning Sensor Data. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS ’07), Toronto, ON, Canada, 25–27 June 2007; p. 38. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, P.; Jiang, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, T.; Liu, Y.; Liu, T. Fiber-Laser-Enhanced WGM Microtubule Cavity for Myocardial Infarction Biomarker Detection; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2021; Volume 11901. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, P.; Jiang, J.; Liu, K.; Wang, S.; Wang, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ding, Z.; Liu, T. High-sensitive and disposable myocardial infarction biomarker immunosensor with optofluidic microtubule lasing. Nanophotonics 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, P.; Jiang, J.; Liu, K.; Wang, S.; Jing, J.; Xu, T.; Wang, T.; Liu, Y.; Liu, T. Fiber-integrated WGM optofluidic chip enhanced by microwave photonic analyzer for cardiac biomarker detection with ultra-high resolution. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 208, 114238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niu, P.; Jiang, J.; Liu, K.; Wang, S.; Xu, T.; Wang, Z.; Wang, T.; Zhang, X.; Ding, Z.; Liu, Y.; et al. Prefab Hollow Glass Microsphere-Based Immunosensor with Liquid Crystal Sensitization for Acute Myocardial Infarction Biomarker Detection. Biosensors 2022, 12, 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12070439
Niu P, Jiang J, Liu K, Wang S, Xu T, Wang Z, Wang T, Zhang X, Ding Z, Liu Y, et al. Prefab Hollow Glass Microsphere-Based Immunosensor with Liquid Crystal Sensitization for Acute Myocardial Infarction Biomarker Detection. Biosensors. 2022; 12(7):439. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12070439
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiu, Panpan, Junfeng Jiang, Kun Liu, Shuang Wang, Tianhua Xu, Ziyihui Wang, Tong Wang, Xuezhi Zhang, Zhenyang Ding, Yize Liu, and et al. 2022. "Prefab Hollow Glass Microsphere-Based Immunosensor with Liquid Crystal Sensitization for Acute Myocardial Infarction Biomarker Detection" Biosensors 12, no. 7: 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12070439
APA StyleNiu, P., Jiang, J., Liu, K., Wang, S., Xu, T., Wang, Z., Wang, T., Zhang, X., Ding, Z., Liu, Y., & Liu, T. (2022). Prefab Hollow Glass Microsphere-Based Immunosensor with Liquid Crystal Sensitization for Acute Myocardial Infarction Biomarker Detection. Biosensors, 12(7), 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12070439





