Technology for Rapid Detection of Cyromazine Residues in Fruits and Vegetables: Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Instrumentations and Equipment
2.3. Preparation of Solutions and Samples
2.3.1. Preparation of Pesticide Standard Solutions
2.3.2. Pretreatment of Test Samples
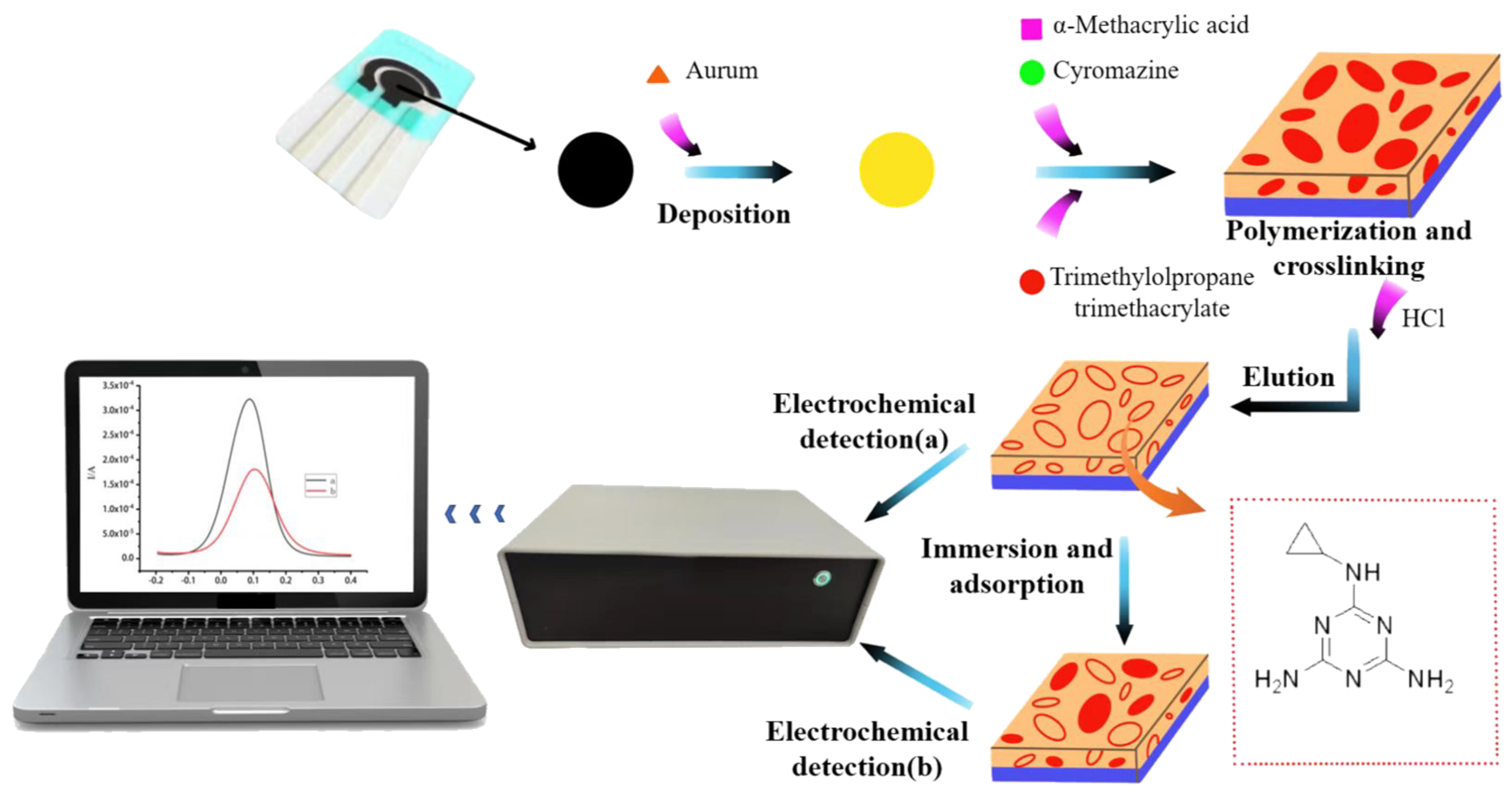
2.4. Preparation of the Modifier
2.5. Preparation of Molecularly Imprinted Sensors
2.6. Electrochemical Characterization and Performance Testing of Sensors
2.6.1. CV and EIS Characterization of Sensors
2.6.2. Scanning Electron Microscope Characterization of Sensors
2.6.3. DPV Performance Testing of Sensors
2.6.4. Repeatability Testing
2.6.5. Interference Test
2.6.6. Actual Sample Recovery Testing
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Analysis of the Results of Electrochemical Characterization
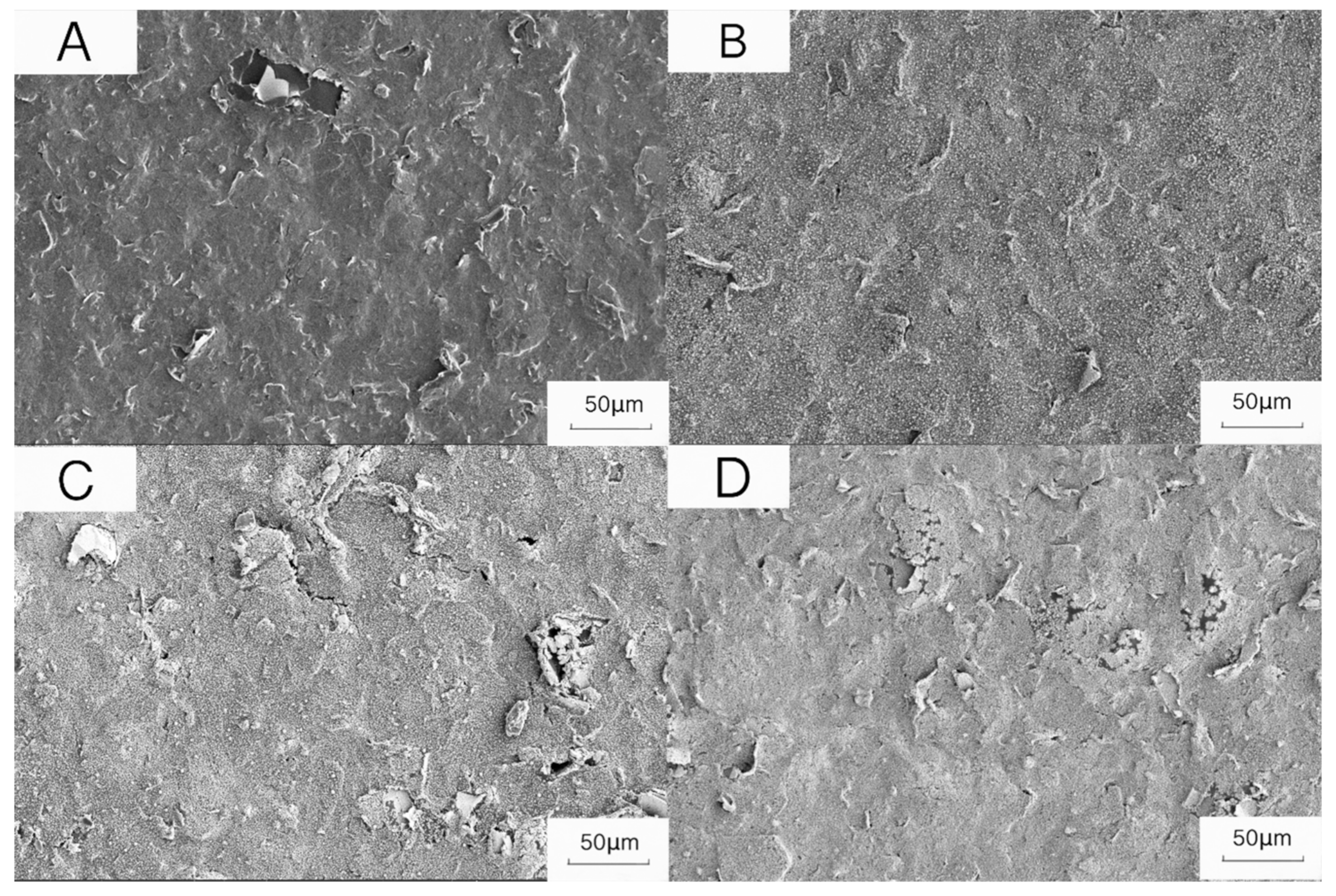
3.2. Characterization Results of the Sensors Using Scanning Electron Microscopy
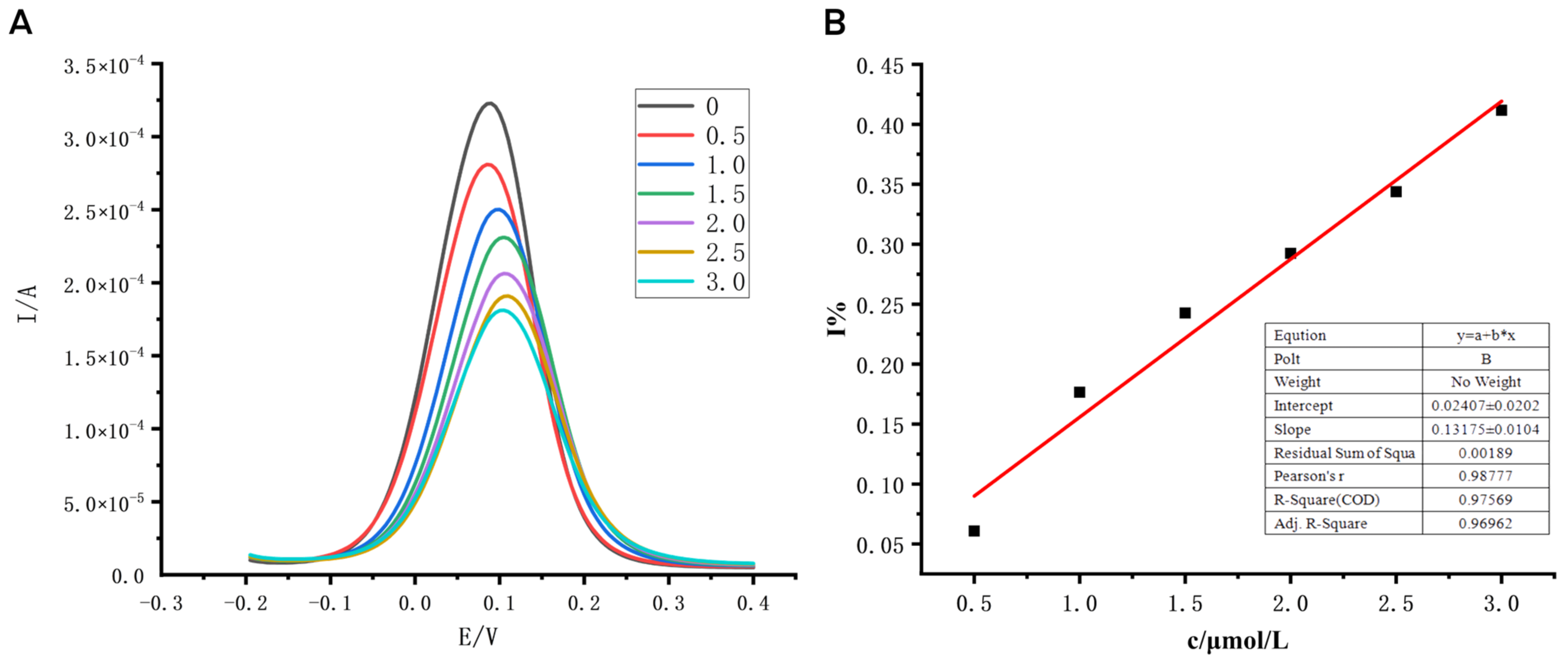
3.3. Performance Test Results of Sensors
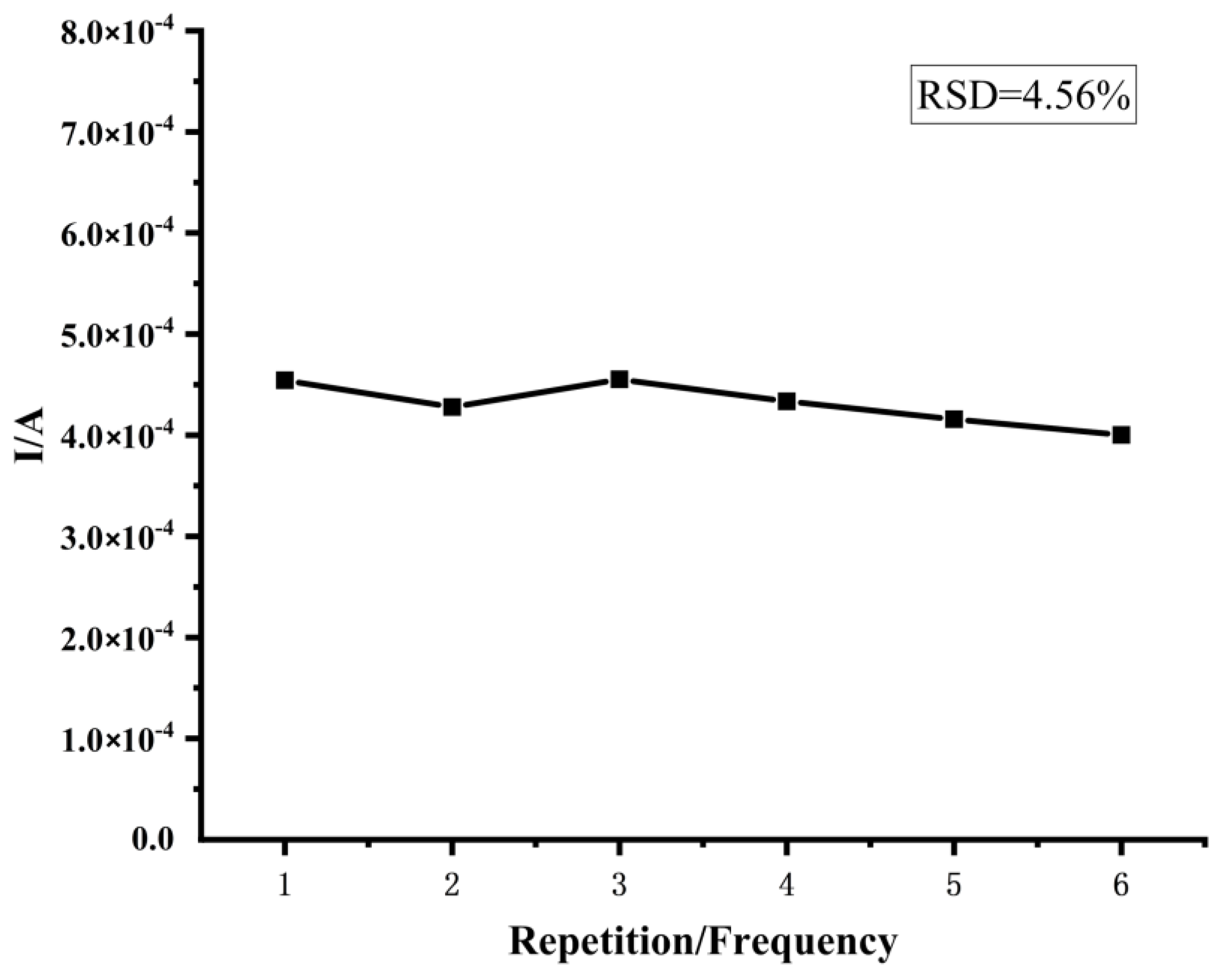
3.4. Results of Repeatability Tests
3.5. Anti-Interference Test Results
3.6. Recovery Analysis of Actual Samples
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, M.; Liang, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Huang, S.H.; Zhang, C.H. Validation and application of a QuEChERS- based method for estimation of the half-lives of cyromazine and acetamiprid in cowpeas and soil by LC-ESI-MS/MS. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 102, 650–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, M.M.; Shad, S.A. Risk assessment of cyromazine and methoxyfenozide resistance suggests higher additive genetic but lower environmental variation supporting quick resistance development in non-target Chrysoperla carnea (Stephens). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, H.B.; Zheng, B.W.; Li, X.Y.; Dang, X.; Zhang, H.B.; Tian, F.X.; Hu, X.J. Sensitive SERS detection of melamine and cyromazine in raw milk using aptamer-based in situ silver nanoparticles synthesis. Results Phys. 2022, 4, 100266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, C.; Lozano, A.; Uclés, S.; Valverde, A.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. European Union Proficiency Tests for pesticide residues in fruit and vegetables from 2009 to 2016: Overview of the results and main achievements. Food Control 2017, 82, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, A.K.; Viphavakit, C. A review on all-optical fiber-based VOC sensors: Heading towards the development of promising technology. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 2022, 338, 113455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cennamo, N.; D’Agostino, G.; Perri, C.; Arcadio, F.; Chiaretti, G.; Parisio, E.M.; Vettori, C.; Marzo, F.D.; Cennamo, R.; Porto, G.; et al. Proof of concept for a quick and highly sensitive on-site detection of SARS-CoV-2 by plasmonic optical fibers and molecularly imprinted polymers. Sensors 2021, 21, 1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousazadeh, M.; Jahangiri-Manesh, A.; Nikkhah, M.; Abbasian, S.; Moshaii, A.; Masroor, M.J.; Norouzi, P. Detection of hexanal gas as a volatile organic compound cancer biomarker using a nanocomposite of gold nanoparticles and selective polymers. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 905, 115962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Okoth, O.K.; Yan, K.; Zhang, J. A highly selective electrochemical sensor for 4-chlorophenol determination based on molecularly imprinted polymer and PDDA-functionalized graphene. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 236, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Huang, J.; Wang, D.; Meng, T.; Yang, X.R. Au and Au-Based nanomaterials: Synthesis and recent progress in electrochemical sensor applications. Talanta 2020, 206, 120210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokonami, S.; Shiigi, H.; Nagaoka, T. Review: Micro- and nanosized molecularly imprinted polymers for high-throughput analytical applications. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 641, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afkhami, A.; Ghaedi, H.; Madrakian, T.; Ahmadi, M.; Mahmood-Kashani, H. Fabrication of a new electrochemical sensor based on a new nano-molecularly imprinted polymer for highly selective and sensitive determination of tramadol in human urine samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 44, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, L.; Wang, S.; Yu, J.; Li, N.; Ge, S.; Yan, M. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Grafted Porous Au-Paper Electrode for a Microfluidic Electro-Analytical Origami Device. Adv. Func. 2013, 23, 3115–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guth, U.; Vonau, W.; Zosel, J. Recent developments in electrochemical sensor application and technology- a review. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2009, 20, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.K.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhou, Z.X.; Nie, Y.L.; Wang, Y.X. Nonenzymatic electrochemical sensor based on CuO-TiO2 for sensitive and selective detection of methyl parathion pesticide in ground water. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 256, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Yang, L. Development of enzymatic electrochemical biosensors for organophosphorus pesticide detection. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2020, 56, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.C.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.P.; Liu, J.X.; Gao, Y.X.; Ma, N. Chemiluminescence sensors based on molecularly imprinted polymers for the determination of organophosphorus in milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 3019–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholivand, M.B.; Torkashvand, M.; Malekzadeh, G. Fabrication of an electrochemical sensor based on computationally designed molecularly imprinted polymers for determination of cyanazine in food samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 713, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, X.; Zhou, H.; Li, C.; Zhu, A.; Xing, Z.; Zhao, Z. Imprinted electrochemical sensor for dopamine recognition and determination based on a carbon nanotube/ polypyrrole film. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 63, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.H.; Lu, Y.L.; Chen, Z.T.; Cheng, C.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Yan, Z.P.; Luo, Z.S.; Liu, Q.J. Electrochemical non-enzymatic sensing of glycoside toxins by boronic acid functionalized nano-composites on screen-printed electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 329, 129197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.G.; Chen, X.; Ren, H.L.; Li, X.; Chen, S.Y.; Ye, B.C. A novel electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer-modified C-ZIF67@Ni for highly sensitive and selective determination of carbendazim. Talanta 2022, 237, 122909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.H.; Yang, S.Y.; Zhang, X.; Jia, J.J.; Chen, Q.L.; Lian, Y.Y.; Wang, A.Q.; Zeng, B.; Yang, H.M.; Li, J.L.; et al. Analysis of imidacloprid residues in mango, cowpea and water samples based on portable molecular imprinting sensors. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon, R.; García-Hernández, J.; Palma, P.; Leyva-Morales, J.B.; Zambrano-Soria, M.; Bastidas-Bastidas, P.J.; Godoy, M. Assessment of pesticide residues in vegetables commonly consumed in Chile and Mexico: Potential impacts for public health. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2022, 108, 104420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.L.; Qi, X.M.; Wu, J.T.; Xu, L.J.; Wan, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.W.; Li, Q. Ultrasensitive, label-free voltammetric determination of norfloxacin based on molecularly imprinted polymers and Au nanoparticle-functionalized black phosphorus nanosheet nanocomposite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.L.; Qi, X.M.; Zhang, G.Q.; Wang, S.L.; Li, K.H.; Wu, J.T.; Wan, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q. Low-cost voltammetric sensors for robust determination of toxic Cd(II) and Pb(II) in environment and food based on shuttle-like α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles decorated β-Bi2O3 microspheres. Microche. J. 2022, 179, 107515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.H.; Liu, C.H.; Yin, G.H.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, J.H. Aptamer-molecularly imprinted sensor base on electrogenerated chemiluminescence energy transfer for detection of lincomycin. Biosens. Bioelectro. 2017, 91, 687–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinali, L.A.F.; de Oliveira, H.L.; Teixeira, L.S.; Borges, W.S.; Borges, K.B. Mesoporous molecularly imprinted polymer core@shell hybrid silica nanoparticles as adsorbent in microextraction by packed sorbent for multiresidue determination of pesticides in apple juice. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wu, J.T.; Liu, Y.; Qi, X.M.; Jin, H.G.; Yang, C.; Liu, J.; Li, G.L.; He, Q.G. Recent advances in black phosphorus-based electrochemical sensors: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1170, 338480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, B.Z.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, Z.P.; Cong, S.; She, Y.X.; Cao, X.L. Synthesis of metal-organic framework @molecularly imprinted polymer adsorbents for solid phase extraction of organophosphorus pesticides from agricultural products. J. Chromatogr. B 2022, 1188, 123081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, S.; Venkatram, R.; Singhal, R.S. Recent advances in the application of molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) in food analysis. Food Control 2022, 139, 109074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.Z.; Ni, B.B.; Zheng, Y.R.; Huang, Y.X.; Li, G.L. A simple and efficient voltammetric sensor for dopamine determination based on ZnO nanorods/electro-reduced graphene oxide composite. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 26, 101375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, S.; Wu, H.Y.; Nie, J.Y.; Ahmad, S.; Muhammad, I.; Zeeshan, M.; Khan, R.; Asim, M. Application, advancement and green aspects of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers in pesticide residue detection. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 804, 150293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunpatee, K.; Kaewdorn, K.; Duangtong, J.; Chaiyo, S.; Chailapakul, O.; Kalcher, K.; Kerr, M.; Samphao, A. A new disposable electrochemical sensor for the individual and simultaneous determination of carbamate pesticides using a nanocomposite modified screen-printed electrode. Microchem. J. 2022, 177, 107318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Guo, X.; Zhang, H. Fluorescence detection of paclobutrazol pesticide residues in apple juice. Int. J. Opt. 2020, 224, 165542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsochatzis, E.D.; Menkissoglu-Spiroudi, U.; Karpouzas, D.G.; Tzimou-Tsitouridou, R. A multi-residue method for pesticide residue analysis in rice grains using matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography–diode array detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 2181–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umapathi, R.; Ghoreishian, S.M.; Sonwal, S.; Rani, G.M.; Huh, Y.S. Portable electrochemical sensing methodologies for on-site detection of pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 435, 214305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi, H.; Sani, P.S.; Orooji, Y.; Majidi, M.R.; Yoon, Y.; Khataee, A. MOF-based sensor platforms for rapid detection of pesticides to maintain food quality and safety. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 165, 113176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Samples | 1 μmol/L Cyromazine Solution | 1 μmol/L Cyromazine Solution + 5 μmol/L Atrazine | 1 μmol/L Cyromazine Solution + 10 μmol/L Atrazine | 1 μmol/L Cyromazine Solution + 20 μmol/L Atrazine | 1 μmol/L Cyromazine Solution + 30 μmol/L Atrazine |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relative suppression | 11.7% | 9.07% | 11.73% | 8.64% | 13.57% |
| Difference between relative suppression and stock solution | 0.00% | 2.63% | 0.03% | 3.06% | 1.87% |
| Samples | 1 μmol/ Cyromazine Solution | 1 μmol/L Cyromazine Solution + 5 μmol/L Metolachlor | 1 μmol/L Cyromazine Solution + 10 μmol/L Metolachlor | 1 μmol/L Cyromazine Solution + 20 μmol/L Metolachlor | 1 μmol/L Cyromazine Solution + 30 μmol/L Metolachlor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relative suppression | 17.40% | 17.20% | 19.07% | 15.36% | 16.27% |
| Difference between relative suppression and stock solution | 0% | 0.20% | 1.67% | 2.04% | 0.93% |
| Samples | Added (μmol/L) | Found (μmol/L) | Recovery (n = 3) | RSD (n = 3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) | 1 | 1 | 99.89% | 4.16% |
| 2 | 2.03 | 101.67% | 1.56% | |
| 3 | 2.70 | 90.14 | 2.61% | |
| Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) | 1 | 0.90 | 94.7% | 4.98% |
| 2 | 2.02 | 101.10% | 1.66% | |
| 3 | 2.72 | 90.64% | 2.52% |
| Samples | Added (μmol/L) | Found (μmol/L) | Recovery (n = 3) | RSD (n = 3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| River water | 1 | 1.08 | 108% | 2.39% |
| 2 | 1.82 | 91.1% | 1.28% | |
| 3 | 2.95 | 98.3% | 3.39% | |
| Water in the paddy field | 1 | 1.16 | 116% | 0.9% |
| 2 | 2.37 | 118% | 2.33% | |
| 3 | 3.43 | 114% | 2.02% | |
| Water in the botanical garden | 1 | 0.925 | 92.5% | 0.87% |
| 2 | 1.91 | 95.6% | 5.79% | |
| 3 | 2.92 | 97.4% | 5.77% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, S.; Wang, A.; Lian, Y.; Jia, J.; Ji, X.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Yang, S.; Liao, J.; Zhou, S. Technology for Rapid Detection of Cyromazine Residues in Fruits and Vegetables: Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensors. Biosensors 2022, 12, 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12060414
Peng S, Wang A, Lian Y, Jia J, Ji X, Yang H, Li J, Yang S, Liao J, Zhou S. Technology for Rapid Detection of Cyromazine Residues in Fruits and Vegetables: Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensors. Biosensors. 2022; 12(6):414. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12060414
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Sihua, Aqiang Wang, Yuyang Lian, Jingjing Jia, Xuncong Ji, Heming Yang, Jinlei Li, Shuyan Yang, Jianjun Liao, and Shihao Zhou. 2022. "Technology for Rapid Detection of Cyromazine Residues in Fruits and Vegetables: Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensors" Biosensors 12, no. 6: 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12060414
APA StylePeng, S., Wang, A., Lian, Y., Jia, J., Ji, X., Yang, H., Li, J., Yang, S., Liao, J., & Zhou, S. (2022). Technology for Rapid Detection of Cyromazine Residues in Fruits and Vegetables: Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensors. Biosensors, 12(6), 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12060414






