Compact Smartphone-Based Laser Speckle Contrast Imaging Endoscope Device for Point-of-Care Blood Flow Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
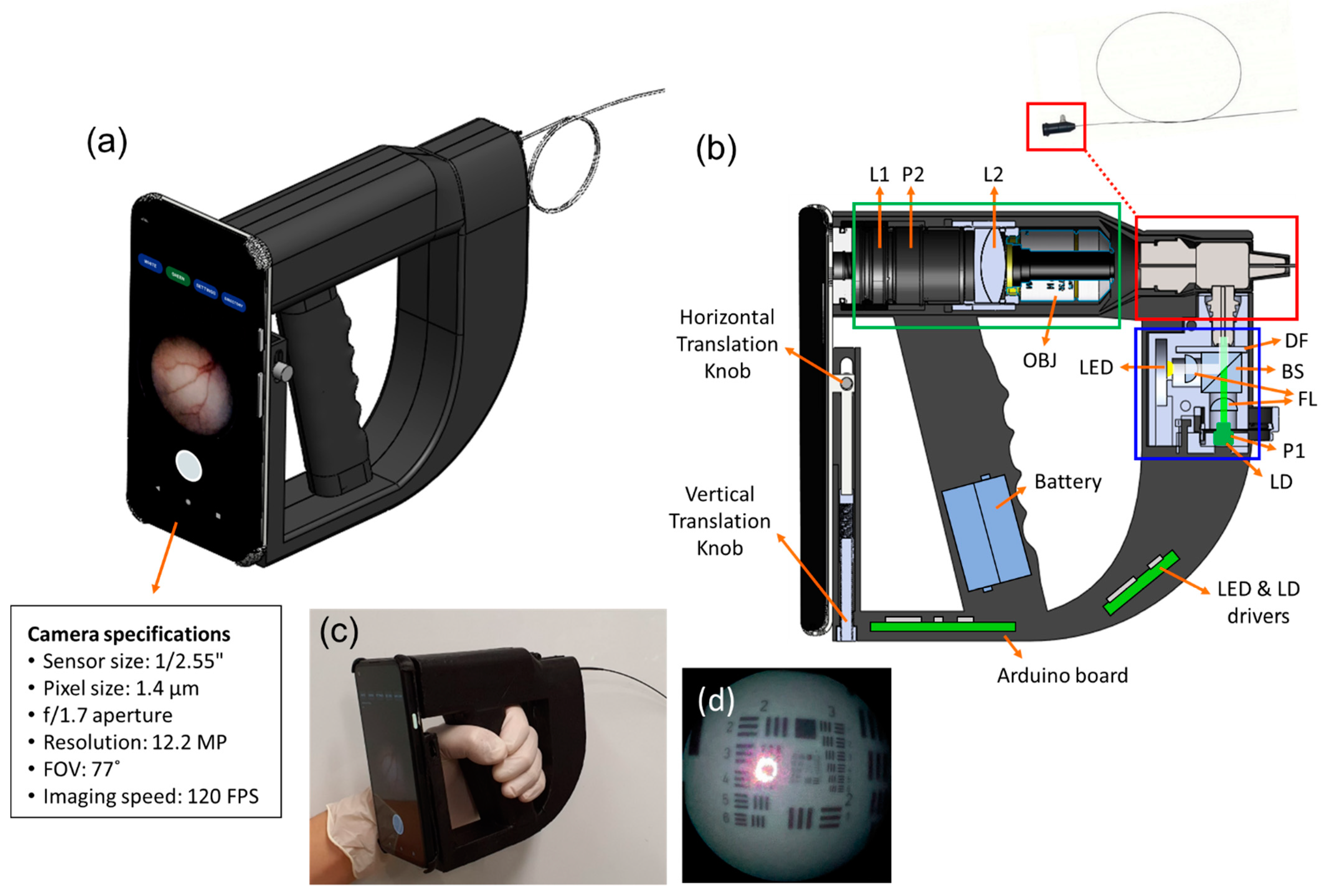
2.1. Implementation of Smartphone-Based Portable LSCI Endoscope Device
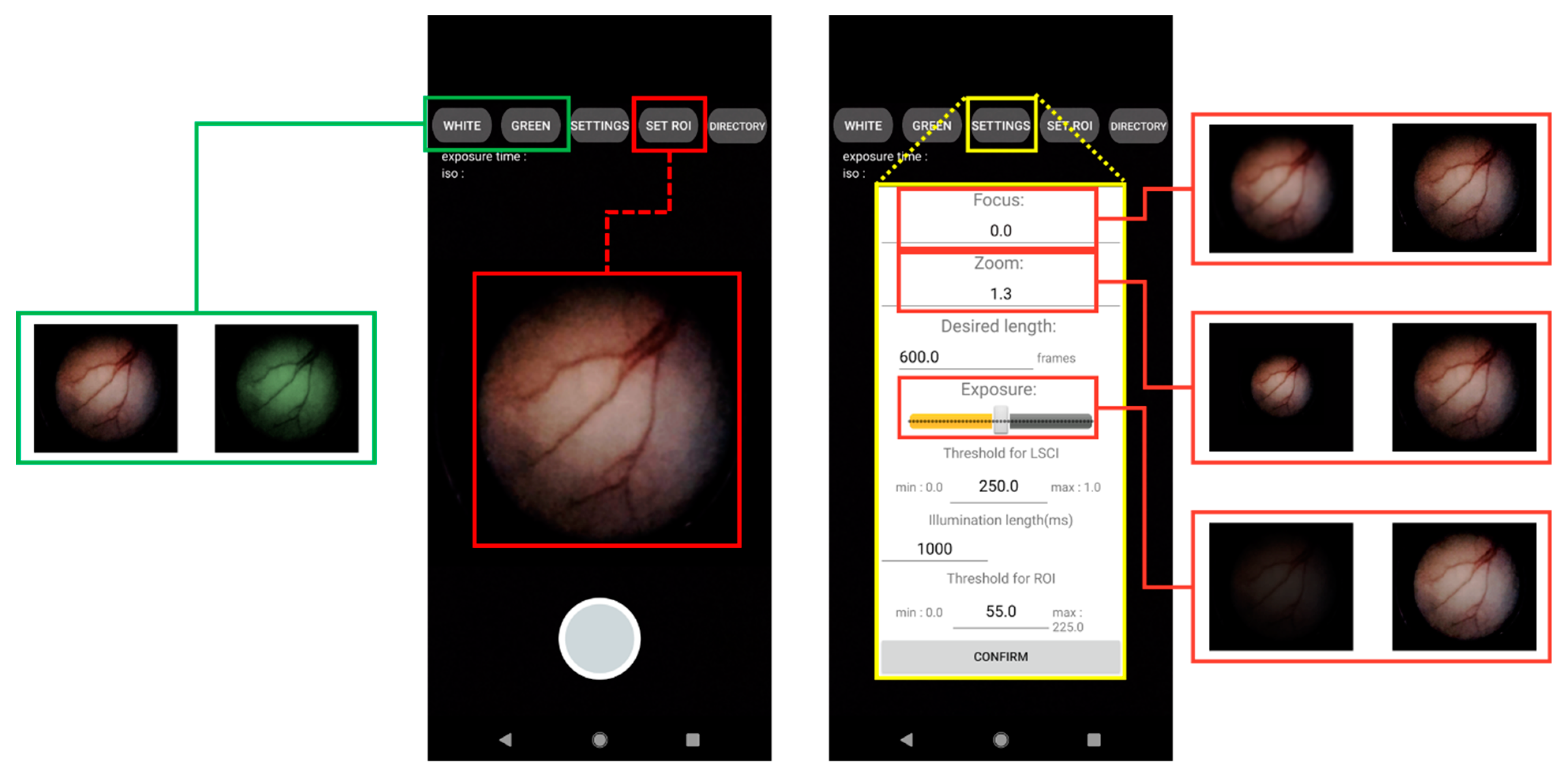
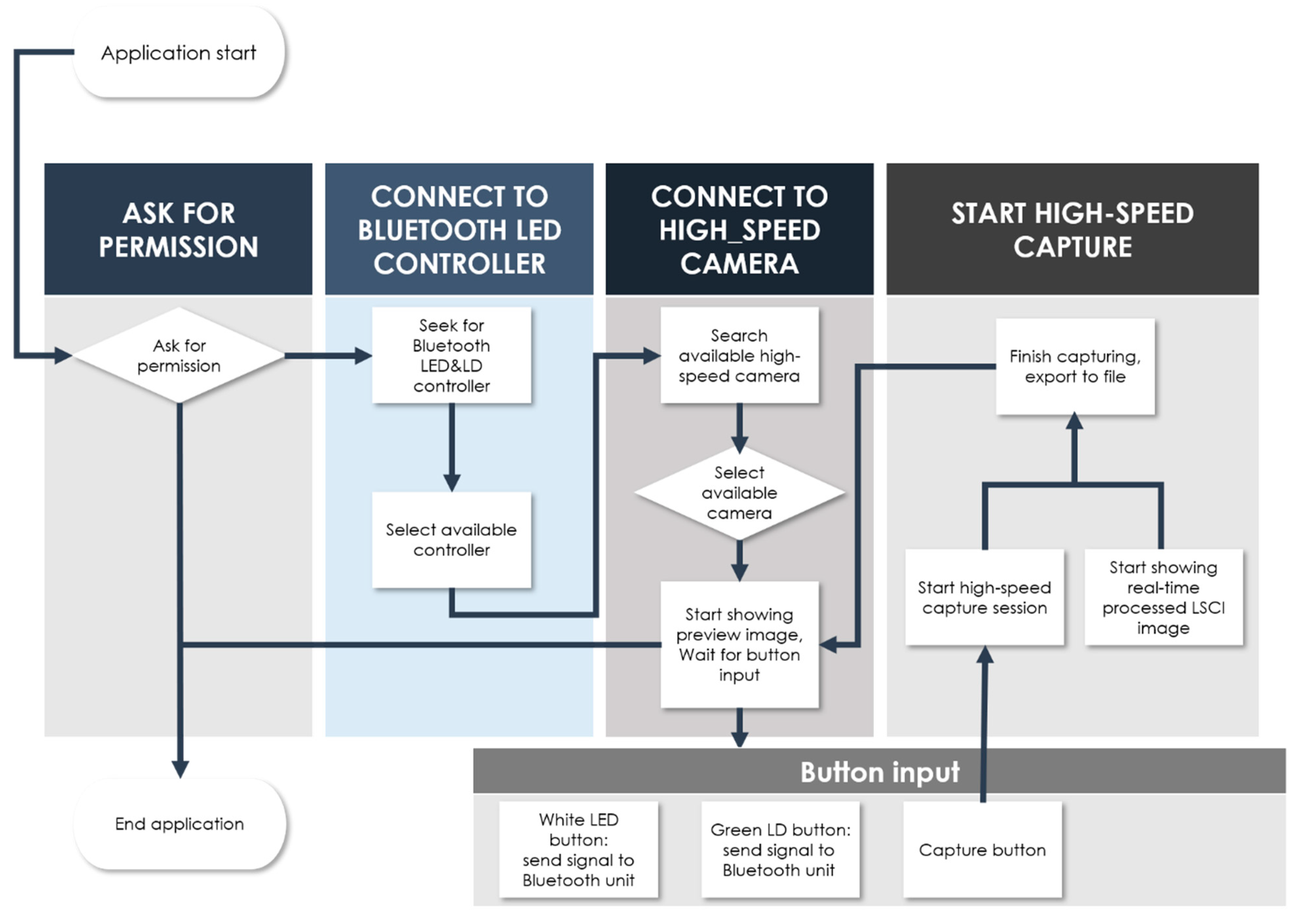
2.2. Development of a User Interface Smartphone App for Real-Time Endoscopy and LSCI
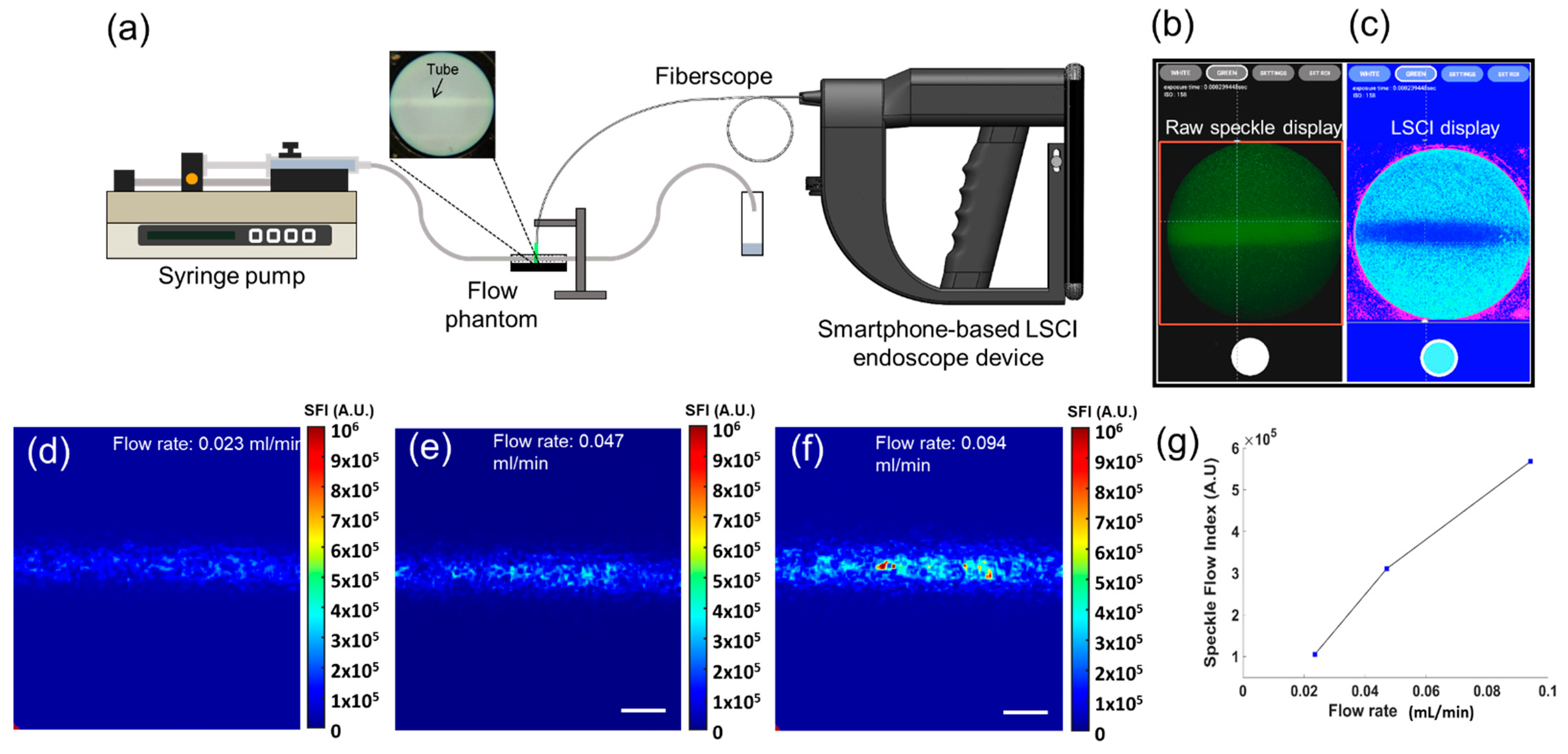
2.3. Procedure of Tissue-Mimicking Flow Phantom Manufacture
2.4. Preparation of Small Animal Model
3. Results
3.1. Tissue-Mimicking Flow Phantom Imaging
3.2. In Vivo Small Animal Imaging
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gulati, S.; Patel, M.; Emmanuel, A.; Haji, A.; Hayee, B.; Neumann, H. The Future of Endoscopy: Advances in Endoscopic Image Innovations. Dig. Endosc. 2020, 32, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, M.; Saito, Y.; Imaoka, H.; Saiko, M.; Yamada, S.; Kondo, H.; Takamaru, H.; Sakamoto, T.; Sese, J.; Kuchiba, A.; et al. Development of a Real-Time Endoscopic Image Diagnosis Support System Using Deep Learning Technology in Colonoscopy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Moura, D.T.H.; Aihara, H.; Thompson, C.C. Robotic-Assisted Surgical Endoscopy: A New Era for Endoluminal Therapies. VideoGIE 2019, 4, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappell, M.S. Therapeutic Endoscopy for Acute Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 7, 214–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.; Blumenfeld, N.R.; Laksanasopin, T.; Sia, S.K. Point-of-Care Diagnostics: Recent Developments in a Connected Age. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 102–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, M.J. Endoscopy in Sharks. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2010, 13, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divers, S.J.; Boone, S.S.; Hoover, J.J.; Boysen, K.A.; Killgore, K.J.; Murphy, C.E.; George, S.G.; Camus, A.C. Field Endoscopy for Identifying Gender, Reproductive Stage and Gonadal Anomalies in Free-Ranging Sturgeon (Scaphirhynchus) from the Lower Mississippi River. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2009, 25, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Lim, C.-H.; Choi, M.-G.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.S.; Cho, Y.K.; Park, J.M.; Cho, Y.S.; Lee, B.I.; Lee, I.S. An Operable, Portable, and Disposable Ultrathin Endoscope for Evaluation of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019, 64, 1901–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H. Comparison of a Novel Bedside Portable Endoscopy Device with Nasogastric Aspiration for Identifying Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding. WJG 2014, 20, 8221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCracken, K.E.; Yoon, J.-Y. Recent Approaches for Optical Smartphone Sensing in Resource-Limited Settings: A Brief Review. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 6591–6601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agu, E.; Pedersen, P.; Strong, D.; Tulu, B.; He, Q.; Wang, L.; Li, Y. The Smartphone as a Medical Device: Assessing Enablers, Benefits and Challenges. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Workshop of Internet-of-Things Networking and Control (IoT-NC), New Orleans, LA, USA, 23–24 June 2013; pp. 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, Q. Biosensors and Bioelectronics on Smartphone for Portable Biochemical Detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, A.D.; Herrnsdorf, J.; Strain, M.J.; Dawson, M.D. Scalable Visible Light Communications with a Micro-LED Array Projector and High-Speed Smartphone Camera. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 15585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Geng, Z.; Fan, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, H. Point-of-Care Testing Based on Smartphone: The Current State-of-the-Art (2017–2018). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 132, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Fan, Z.; Lv, X.; Su, Y.; Chen, H. Recent Progress in Optical Biosensors Based on Smartphone Platforms. Sensors 2017, 17, 2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivakumar, R.; Lee, N.Y. Recent Progress in Smartphone-Based Techniques for Food Safety and the Detection of Heavy Metal Ions in Environmental Water. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 130096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.K.; Vavilin, A.; You, J.S.; Kim, H.; Ryu, S.Y.; Jang, J.H.; Jung, W. Smartphone-Based Endoscope System for Advanced Point-of-Care Diagnostics: Feasibility Study. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2017, 5, e99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelikoyar, M.M.; Aktas, O.T. Endoscopy in Otolaryngology Utilising Smartphone as the Capturing Device. J. Vis. Commun. Med. 2018, 41, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.H.I.; Sagili, S.R. Smartphone Adaptor Use for Nasal Endoscopy. Eye 2019, 33, 854–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Oh, J.; Choi, S.-H.; Jung, A.; Lee, J.-G.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, J.K. A Portable Smartphone-Based Laryngoscope System for High-Speed Vocal Cord Imaging of Patients with Throat Disorders: Instrument Validation Study. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2021, 9, e25816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, Y.; Oh, J.; Hyun, J.; Kim, Y.; Choi, J.; Namgoong, J.; Kim, J.K. Cost-Effective Smartphone-Based Articulable Endoscope Systems for Developing Countries: Instrument Validation Study. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2020, 8, e17057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boas, D.A.; Dunn, A.K. Laser Speckle Contrast Imaging in Biomedical Optics. J. Biomed. Opt. 2010, 15, 011109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briers, D.; Duncan, D.D.; Hirst, E.; Kirkpatrick, S.J.; Larsson, M.; Steenbergen, W.; Stromberg, T.; Thompson, O.B. Laser Speckle Contrast Imaging: Theoretical and Practical Limitations. J. Biomed. Opt 2013, 18, 066018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heeman, W.; Steenbergen, W.; van Dam, G.M.; Boerma, E.C. Clinical Applications of Laser Speckle Contrast Imaging: A Review. J. Biomed. Opt. 2019, 24, 080901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armitage, G.A.; Todd, K.G.; Shuaib, A.; Winship, I.R. Laser Speckle Contrast Imaging of Collateral Blood Flow during Acute Ischemic Stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2010, 30, 1432–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.-Y.; Xia, Q.; Yu, T.-T.; Zhu, J.-T.; Zhu, D. Transmissive-Detected Laser Speckle Contrast Imaging for Blood Flow Monitoring in Thick Tissue: From Monte Carlo Simulation to Experimental Demonstration. Light Sci. Appl. 2021, 10, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, P.; Xu, H.; Li, R.; Huang, G.; Liu, W. Laser Speckle Contrast Imaging Based on a Mobile Phone Camera. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 76730–76737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakovels, D.; Saknite, I.; Krievina, G.; Zaharans, J.; Spigulis, J. Mobile Phone Based Laser Speckle Contrast Imager for Assessment of Skin Blood Flow. In Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Advanced Optical Materials and Devices, Riga, Latvia, 22 October 2014; p. 94210J. [Google Scholar]
- Guven, G.; Hilty, M.P.; Ince, C. Microcirculation: Physiology, Pathophysiology, and Clinical Application. Blood Purif. 2020, 49, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilberman, D.E.; Lipkin, M.E.; Ferrandino, M.N.; Simmons, W.N.; Mancini, J.G.; Raymundo, M.E.; Zhong, P.; Preminger, G.M. The Digital Flexible Ureteroscope: In Vitro Assessment of Optical Characteristics. J. Endourol. 2011, 25, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, D.D.; Kirkpatrick, S.J. Spatio-temporal algorithms for processing laser speckle imaging data. In Proceedings of the SPIE BiOS 2008, San Jose, CA, USA, 28 February 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J. Spatiotemporal Laser Speckle Contrast Analysis for Blood Flow Imaging with Maximized Speckle Contrast. J. Biomed. Opt. 2010, 15, 016003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degoricija, M.; Korac-Prlic, J.; Vilovic, K.; Ivanisevic, T.; Haupt, B.; Palada, V.; Petkovic, M.; Karaman, I.; Terzic, J. The Dynamics of the Inflammatory Response during BBN-Induced Bladder Carcinogenesis in Mice. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos-Nóbrega, C.; Colaço, A.; Lopes, C.; Oliveira, P.A. Review: BBN as an Urothelial Carcinogen. In Vivo 2012, 26, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- White, S.M.; Valdebran, M.; Kelly, K.M.; Choi, B. Simultaneous Blood Flow Measurement and Dermoscopy of Skin Lesions Using Dual-Mode Dermascope. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zlatev, D.V.; Altobelli, E.; Liao, J.C. Advances in Imaging Technologies in the Evaluation of High-Grade Bladder Cancer. Urol. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 42, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S.; Fukuhara, H.; Karashima, T.; Inoue, K. Real-World Experience with 5-Aminolevulinic Acid for the Photodynamic Diagnosis of Bladder Cancer: Diagnostic Accuracy and Safety. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2020, 32, 101999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Lau, L.W.; Cha, J. Dual-Display Laparoscopic Laser Speckle Contrast Imaging for Real-Time Surgical Assistance. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 5962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heeman, W.; Dijkstra, K.; Hoff, C.; Koopal, S.; Pierie, J.-P.; Bouma, H.; Boerma, E.C. Application of Laser Speckle Contrast Imaging in Laparoscopic Surgery. Biomed. Opt. Express 2019, 10, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potapova, E.V.; Seryogina, E.S.; Dremin, V.V.; Stavtsev, D.D.; Kozlov, I.O.; Zherebtsov, E.A.; Mamoshin, A.V.; Ivanov, Y.V.; Dunaev, A.V. Laser Speckle Contrast Imaging of Blood Microcirculation in Pancreatic Tissues during Laparoscopic Interventions. Quantum Electron. 2020, 50, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RFLSI III Laser Speckle Imaging System Flyer V1.0 2021. Available online: https://www.rwdstco.com/product-item/laser-speckle-imaging-system (accessed on 12 May 2022).
- Cousins, C.C.; Chou, J.C.; Greenstein, S.H.; Brauner, S.C.; Shen, L.Q.; Turalba, A.V.; Houlihan, P.; Ritch, R.; Wiggs, J.L.; Knepper, P.A.; et al. Resting Nailfold Capillary Blood Flow in Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 103, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-Y.; Yazdani, A.; Li, X.; Douglas, K.A.A.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Karniadakis, G.E. Quantifying Platelet Margination in Diabetic Blood Flow. Biophys. J. 2018, 115, 1371–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Deng, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhong, J.; Li, S.; Peng, L.; Wang, B.; Yang, R.; Zhang, H.; et al. Microvascular Abnormalities in Dry Eye Patients. Microvasc. Res. 2018, 118, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallinowski, F.; Vaupel, P. PH Distributions in Spontaneous and Isotransplanted Rat Tumours. Br. J. Cancer. 1988, 58, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lip, G.Y.; Chin, B.S.; Blann, A.D. Cancer and the Prothrombotic State. Lancet Oncol. 2002, 3, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaupel, P.; Kallinowski, F.; Okunieff, P. Blood Flow, Oxygen and Nutrient Supply, and Metabolic Microenvironment of Human Tumors: A Review. Cancer Res. 1989, 49, 6449–6465. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jain, R.K.; Ward-Hartley, K. Tumor Blood Flow-Characterization, Modifications, and Role in Hyperthermia. IEEE Trans. Son. Ultrason. 1984, 31, 504–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruoslahti, E. Specialization of Tumour Vasculature. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siemann, D.W. The Unique Characteristics of Tumor Vasculature and Preclinical Evidence for Its Selective Disruption by Tumor-Vascular Disrupting Agents. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2011, 37, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Devor, A.; Boas, D.A.; Dunn, A.K. Determination of optimal exposure time for imaging of blood flow changes with laser speckle contrast imaging. Appl. Opt. 2005, 44, 1823–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alex, O. Holcombe, Seeing slow and seeing fast: Two limits on perception. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2009, 13, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burggraaff, O.; Schmidt, N.; Zamorano, J.; Pauly, K.; Pascual, S.; Tapia, C.; Spyrakos, E.; Snik, F. Standardized Spectral and Radiometric Calibration of Consumer Cameras. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 19075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentink, B. Eye-Hand Coordination in Laparoscopy—An Overview of Experiments and Supporting Aids. Minim. Invasive Ther. Allied Technol. 2001, 10, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koesveld, J.J.M.; Tetteroo, G.W.M.; Graaf, E.J.R. Use of Head-Mounted Display in Transanal Endoscopic Microsurgery. Surg. Endosc. 2003, 17, 943–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishioka, J.; Kihara, K.; Higuchi, S.; Nakayama, T.; Takeshita, H.; Yoshida, S.; Nakanishi, Y.; Kijima, T.; Matsuoka, Y.; Numao, N.; et al. New Head-Mounted Display System Applied to Endoscopic Management of Upper Urinary Tract Carcinomas. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2014, 40, 842–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- van Lindert, E.J.; Grotenhuis, J.A.; Beems, T. The Use of a Head-Mounted Display for Visualization in Neuroendoscopy. Comput. Aided Surg. 2004, 9, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Specification | Our Smartphone-Based LSCI System | Commercial LSCI System | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price | 3D-printed case: USD 300 | Total: Less than USD 1850. | More than USD 40,000 |
| LD + LED light sources: USD 200 | |||
| Optical components: USD 1000 | |||
| Pixel 4a smartphone: USD 350 | |||
| Camera bit depth | 8 bits | 12 bits | |
| Wavelength | 532 nm | 785 nm | |
| Display resolution | 400 × 400 pixels | 656 × 494 pixels | |
| Data acquisition speed | 120 FPS | Up to 120 FPS | |
| Dimensions | 70 × 150 × 250 mm3 | 500 × 500 × 300 mm3 (PC not included) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.; Choi, W.J.; Oh, J.; Kim, J.K. Compact Smartphone-Based Laser Speckle Contrast Imaging Endoscope Device for Point-of-Care Blood Flow Monitoring. Biosensors 2022, 12, 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12060398
Kim Y, Choi WJ, Oh J, Kim JK. Compact Smartphone-Based Laser Speckle Contrast Imaging Endoscope Device for Point-of-Care Blood Flow Monitoring. Biosensors. 2022; 12(6):398. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12060398
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Youngkyu, Woo June Choi, Jungmin Oh, and Jun Ki Kim. 2022. "Compact Smartphone-Based Laser Speckle Contrast Imaging Endoscope Device for Point-of-Care Blood Flow Monitoring" Biosensors 12, no. 6: 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12060398
APA StyleKim, Y., Choi, W. J., Oh, J., & Kim, J. K. (2022). Compact Smartphone-Based Laser Speckle Contrast Imaging Endoscope Device for Point-of-Care Blood Flow Monitoring. Biosensors, 12(6), 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12060398







