Abstract
The evolution of biosensors and diagnostic devices has been thriving in its ability to provide reliable tools with simplified operation steps. These evolutions have paved the way for further advances in sensing materials, strategies, and device structures. Polymeric composite materials can be formed into nanostructures and networks of different types, including hydrogels, vesicles, dendrimers, molecularly imprinted polymers (MIP), etc. Due to their biocompatibility, flexibility, and low prices, they are promising tools for future lab-on-chip devices as both manufacturing materials and immobilization surfaces. Polymers can also allow the construction of scaffold materials and 3D structures that further elevate the sensing capabilities of traditional 2D biosensors. This review discusses the latest developments in nano-scaled materials and synthesis techniques for polymer structures and their integration into sensing applications by highlighting their various structural advantages in producing highly sensitive tools that rival bench-top instruments. The developments in material design open a new door for decentralized medicine and public protection that allows effective onsite and point-of-care diagnostics.
1. Introduction
Developing new materials and exploiting analytical devices to determine, monitor, control, and quantify specific molecules in the environment and the human body has become necessary in biosensing. Clark and Lyons first introduced biosensors in 1962 when an oxygen electrode was used to selectively detect glucose levels [1]. Since then, numerous studies have focused on improving these tools by developing efficient biosensing devices to detect a variety of other analytes and, more specifically, trace-quantity analytes. Nowadays, biosensors are widely used in biomedicine and health, environmental monitoring, drug development, forensics, and food safety. Despite all the successes in this area, developing more sensitive and selective devices that detect low target concentrations via effective transducing elements and recognition materials is challenging. The selectivity and sensitivity of the biosensing devices can be directly or indirectly affected by the preparation of analyte samples. Some analytes are now detected without the need for preparation procedures. For example, hazardous chemicals and heavy metals such as mercury can be directly traced without sample preparation in contaminated water [1].
Conversely, other samples necessitate intricate multistep preparation procedures to minimize interferences and enrich the target molecules to reach detectable concentrations and enhance analytical performances. Moreover, the presence of interferents and biofouling are two main problematic issues that directly influence the performance of biosensors. Electroactive substances interfere with the results when analytical measurements are made on physiological materials such as blood. For example, interferents such as ascorbate or acetaminophen (paracetamol) can negatively affect the glucose sensors as these substances are oxidized at the electrode surface. Biological fluids such as blood can deposit biomolecules (i.e., proteins) which eventually block the surface area. In this case, the surface biofouling blocks the electron passage through the analyte to the surface and reduces the response signal [2].
Robust automated systems containing advanced materials can significantly enhance analytical performance. The recent development of polymer science has made significant progress in sensitivity and selectivity enhancement, response time shortening, and flexibility increase for the immobilization of biomolecules to biosensor platforms. The earliest polymer structures utilized in biosensing devices were the fluorinated ionomer Nafion [3] and cellulose acetate [4]. After their initial success, a range of other polymers was employed to modify the recognizing surfaces and prevent their biofouling [5]. Polyethylene glycol (PEG) and polyethylene oxide (PEO) are the most commonly used polymer materials [5]. These biocompatible composite polymers are highly soluble in aqueous systems allowing them to mimic the typical conditions found within biological systems. Polymeric structures such as dye-loaded polymersomes can be used successfully to detect illegal drugs (cocaine, methamphetamine, synthetic cannabinoids, etc.) in various bodily fluids, including saliva and urine [6,7].
Along with the advances in polymer science, there has been a clear transition from using their insulating features toward their conductive properties [8]. Many sensor platforms were designed using polymer materials, including planar polymers, vesicular polymers, polymersomes, hydrogel materials, conducting polymers, and molecularly imprinted polymers. However, despite the improvements in polymer materials’ employment in biosensing platforms and their commercialization, the need to improve current systems and their analytical performances is still a subject of interest.
Nanomaterials and nanotechnology have received tremendous interest and have become leaders in analytical chemistry over the last decades. Desirable nanoparticles properties, such as the ability to tailor size, structure, and surface-to-volume ratios, provide excellent possibilities for designing novel sensing systems and enhancing the performance of the current bioanalytical assays. Combining nanomaterials with polymers through physical/chemical crosslinking to polymeric chains leads to nanocomposite polymers with new exclusive properties. The present review encloses a specific overview of these polymeric nanocomposite materials and their impact and integration in biosensing and diagnosis applications. Nanocomposite polymers are a relatively rising material niche with several promising applications. This review takes a broader look at the general sensing abilities of these materials with a significant focus on non-invasive approaches in biomedical applications from our own experiences and the many reports found in the literature. While the combination of polymers and nanomaterials provides many options, the current manuscript mainly focuses on planar and vesicular polymer nanocomposites, hydrogel materials, conducting polymers, and molecularly imprinted polymers in biosensors design.
2. Polymer and Biopolymer Nanocomposites
Polymers have been considered prominent candidates for creating an ideal matrix for entrapment and immobilization of biomolecules in the analytical sciences. Characteristics of most polymers, such as high conductivity, ease of biofunctionalization, flexibility, biocompatibility, highly modifiable chemical functions, etc., make them attractive for biosensor development in different fields from environmental analysis to biomedical applications [9]. Our experience with polymeric and co-polymeric materials also demonstrates the successful application of functional polymers for the immobilization of enzymes [10], micro-organisms [11], antibodies [12], and aptamers [13] in the design of electrochemical biosensors. Historically, polymers have been seen as a practical material choice for electrochemical devices, but recent advances in nanotechnology and the creation of nano-scaled materials has allowed for even further evolution in the biosensor field development due to new intrinsic optical, electrical, and mechanical properties.
Efficient immobilization of bioreceptors (or other components) and optimal signal transduction are crucial for biosensors. Polymers are still key coating matrices for nanomaterials through the fusion of nano-objects and polymers. These combinations have led to the emergence of new nano-scaled hybrid materials or polymer nanocomposites. They have been further employed to construct polymer nanocomposite-based biosensors to obtain highly sensitive and reliable analytical devices by improved catalytical and chemical reactivity, surface specificity, enhanced electrode kinetics, controllable synthesis and morphologies, higher stability, and biocompatibility [14]. As an alternative to synthetic polymers, some features of biopolymers, such as natural origin, biodegradability, recyclability, lower antigenicity, and their suitable interaction with living systems, make them powerful tools for biosensor fabrication [15,16].
Polymeric and biopolymeric nanocomposites refer to a hybrid structure in which a polymer matrix is used as a substrate, and nano-scaled organic or inorganic materials are used as fillers. Typically, the polymers of poly(lactic acid) (PLA), poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO), poly(lactic-co-glycolide) (PLG), poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide) (PNIPAM), and polyurethanes, etc. have been utilized as the matrix phase of polymeric nanocomposites. Biopolymeric nanocomposites, which are also called “Bio-nanocomposites”, “bio-hybrids”, and “green nanocomposites” by the popular terms of recent years, are made up of a nanosized additive in naturally occurring polymers including cellulose, chitin, collagen, silk, keratin, alginate, lignin, starch, polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), etc. [17]. The merging of nanosized filler materials into the polymeric matrix produces interesting and improved mechanical, thermal and optical properties. According to this reinforcement strategy, it can be said that filler materials act as molecular bridges enhancing and controlling dimensional stability, flexibility, strength, toughness, durability, thermal stability and conductivity, optical properties (color and transparency), size, distribution, and shape [15,18,19]. Organic materials (carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and graphene) and inorganic materials (silicates and metal/metal oxides) are the kinds of nanofillers used to prepare nanocomposites made of polymers [18,19]. The characteristics of polymeric nanocomposites are affected by choice of both the filler and matrix. For instance, while the type of polymer matrix significantly determines the hydrophobicity, transparency, strength, toughness, controlled ionizability, crystallinity, functionality, biocompatibility, and biodegradability, the choice of filler considerably affects the structural and functional properties. Hence, unique polymer nanocomposites can be synthesized by various combinations of nanofillers. This diversity provides application-oriented strategies via selection of filler nano-objects for the desired properties of specific fields, including medicine, diagnostics, biomedical applications, food packaging, optoelectronic devices, biosensing, bioimaging, tissue engineering, cosmetics, energy, etc. [17,20].
In parallel to their flexible functionalities and fascinating properties, polymeric nanocomposites have been extensively studied to improve sensor performance and have remarkably allowed the fabrication of many novel biosensors in recent years [21,22,23]. For example, while quantum dots–polymeric nanocomposites exhibit excellent fluorescence properties that can be used in optical biosensors, CNTs–polymeric nanocomposites provide significant enhancement in the mechanical property that can be adapted to an optoelectronic sensing device [20]. The utilization of polymeric nanocomposites provides needs-based designs. It brings additional key performance parameters, including higher sensitivity and selectivity, lower detection limits, good reproducibility, and stability by providing a large and easily adjustable surface area, higher electrical conductivity, and fast electron transfer rate [23].
For polymeric nanocomposites, chemists and material scientists have described various synthesis methods, including ion exchange, template synthesis, sol-gel, in-situ polymerization, hydrothermal route, melt intercalation techniques, etc. [20,24]. The successful design of a polymeric nanocomposite with any required property is a critical step toward the control of interfacial interactions between the nanofiller and the polymer matrix. Understanding the influence of the filler on the size, shape, orientation, dispersion, and compatibility of the polymer matrix is the most important consideration. When creating a new polymer nanocomposite material, an effective formulation is required by considering three main approaches: rationality-based design, functionality-based design, and tailored property-based design. In the design of polymeric nanocomposites, process route, temperature, pressure, and time are the parameters required to be controlled during processing. The nanofiller choice needs to consider the filler shape, size, type, volume, weight, and orientation. In contrast, the matrix preparation needs to consider the kind of polymer, surface nature, and chemistry. Based on the above, the combination of the nanofiller and the polymer matrix must be achieved at a nanoscale level with chemical compatibility and homogenous dispersion.
Polymer nanocomposites are microstructures of hybrid organic–inorganic materials that can be formed into three types; unintercalated (or microcomposite), intercalated (and/or flocculated), or exfoliated (or delaminated). These microstructural forms are controlled by the synthesis method. Of these various synthesis methods, the melt-blending method is eco-friendly because of the lack of solvent usage and is industrially scalable due to its cost effectiveness, however the need for a high temperature that can damage the surface of nanofiller is its main disadvantage. On the other hand, the in-situ polymerization technique provides better exfoliation in comparison to the melt intercalation method. In the case of sol-gel technology, disadvantages such as high temperature, which can cause the degradation and aggregation of polymers, make it uncommon. There are different synthetic methodologies including organic treatment and chemical modifications for the polymer nanocomposites manufacturing process [25]. Click chemistry and ring opening of epoxides and aziridines are very efficient and common chemical concepts in the fabrication of polymer nanocomposites. In particular, click reactions are versatile coupling methods due to advantages that include methodological simplicity, high reaction yield and high reaction rates, moderate reaction conditions, easily removable byproducts etc. CuAAC click reaction, metal-free click reaction, Diels–alder reaction, and Thiol-ene and thiol-yne reactions are the commonly employed click reactions in the fabrication of polymer nanocomposites [26]. Since the concept of this manuscript is mostly applications, the synthetic details are not included in the current paper. Additionally, different surface modification strategies have been developed, something which is also a very critical step in biosensing chemistry and design. Surface modification techniques significantly impact the nanocomposites’ structural and functional properties such as reactivity/chemical reactivity, biocompatibility/bioactivity, hydrophobicity, surface energy, dispersion/stability, and surface roughness. Surface modification can be achieved through different reactions with coupling agents and/or surface adsorption and polymeric molecules’ covalent or non-covalent bonding-based grafting. Along with such functionalization techniques, the reported polymer-nanocomposites-modified electrodes are very promising tools to enhance sensing capabilities in terms of high sensitivity and good selectivity for different types of targets such as drugs, heavy metals, pesticides, pathogens, etc. Polymer nanocomposites still hold a great strength in biosensor design since they provide variable morphologies and architectures on electrode surfaces such as films, vesicles, and dendritic structures [20]. While choosing the nanocomposites-based structural design, the main strategy is to add a nanofiller according to the need to give the final sensor system a targeted feature such as magnetism, fluorescence, electroconductivity, strength etc. The characteristics of a nanofiller considerably affects the properties of the polymer nanocomposites. The incorporation of a nano-scaled structure can add a new feature or improve an existing property. As demonstrated in Figure 1, in order to obtain a nanocomposite structure with magnetic properties, magnetic beads can be added to the composite structure, on the other hand quantum dots can be used as nano-modifier to prepare fluorescent polymeric nanocomposites. For the strength enhancement and hydrolytic stability, silica nanoparticles are a very appropriate choice and for their excellent mechanical stability, CNTs are very attractive nanofillers for the polymer nanocomposites. These unique properties, which are gained by adding nanofillers to polymer nanocomposites, significantly increase the analytical performance of the fabricated sensors. According to this approach, Table 1 represents the common nanofillers and their effect on polymer nanocomposite and advantages for the final properties of the fabricated biosensors. Here, the several forms of polymeric and biopolymeric nanocomposite films, the common nanofillers (Nanoclays, graphene, carbon nanoparticles, and quantum dots) and dendritic/vesicular polymeric nanocomposites from which they are made, and their use in biosensors and point-of-care systems are discussed in detail in light of recent advancements.
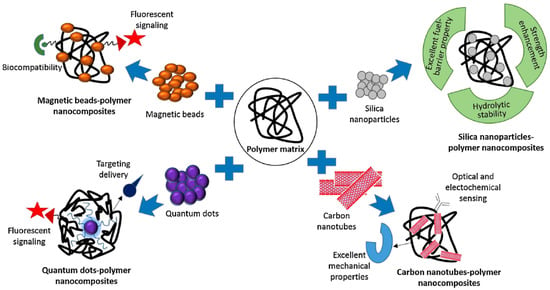
Figure 1.
Effect of nanofiller materials on polymer nanocomposite properties. Reprinted with permission from ref. [20]. ©2018, Elsevier.

Table 1.
The effect of several nanofillers on the improved properties of polymeric nanocomposites and their sensors.
2.1. Nano-Clays
Nanoclay-incorporated polymers or copolymers have been a major focus of scientists working on biosensors. Nanoclays are well known and widely studied 2D nanomaterials in the surface modification of electrodes due to their mechanical and thermal stabilities, inert chemical structure, and unique and varying morphology [33,34]. According to the literature, the first combination of polymer and clay structures was reported by Blumstein in 1965 [35]. After demonstrating the increased thermal stability of polymers with this study, many nanocomposites have been produced to improve mechanical and structural properties. Owing to the remarkable advancements in material science, clay-reinforced polymer composites have been successfully adapted to analytical sciences. For instance, Emre et al. prepared polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) layered silicate nanocomposites and evaluated their combinational use with conducting polymers with the name of poly(4-(2,3-dihydrothieno[3,4-b][1,4]dioxin-5-yl)-7-(2,3-dihydrothieno[3,4-b][1,4]dioxin-7-yl)-2-benzyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazole) (poly(BIPE)) as an immobilization platform for a glucose biosensor. This study demonstrated the prepared nanocomposite as a suitable matrix to protect enzyme molecules and provide proper surface chemistry for biomolecule attachment due to the aromatic groups of the conjugated polymer [36]. Another study regarding clay–polymer nanocomposites showed that a biodegradable polymer polyglycolide (PGA) and natural silicate montmorillonite composites could be applied as a coating material on electrode surfaces. Pyranose oxidase as a model enzyme was immobilized to the composite matrix, and the proposed biosensor was used for glucose detection in beverages without samples pretreatment [37]. Sarkal et al. developed a biopolymer-clay nanocomposite-based pesticide biosensor. The composite film comprising chitosan biopolymer and montmorillonite provided an eco-friendly immobilization matrix for acetylcholinesterase enzyme for organophosphorus pesticide detection with excellent sensing performance [38].
2.2. Graphene
Due to their excellent thermo-mechanical and electrical performance characteristics, graphene or graphene oxide is another widespread additive of polymer nanocomposites used to develop biosensors. Qiu et al. demonstrated the application of chitosan–ferrocene/graphene oxide nanocomposite film as an immobilization platform for a glucose oxidase enzyme. The developed sensor showed a fast response, high stability, good linearity, and sensitivity due to its multi-component structure and the redox mediator ferrocene group [39]. Graphene–polymer composite-based studies were used at the electrochemical sensor level and in the point-of-care test format. A label-free paper-based electrical biosensor chip developed from poly(styrene)-b-poly(acrylic acid) (PS67-b-PAA27) polymer and graphene nanoplatelet composite was recently presented. In this biosensor chip, an anti-cortisol antibody was immobilized over the electrode surface, and a layer-by-layer assembly process was applied for cortisol detection in saliva samples. The graphene nanoplatelet and amphiphilic di-block copolymer composite-based immunosensor exhibited outstanding analytical performance and had great potential for in vitro diagnostics [40].
2.3. Carbon Nanoparticles and Quantum Dots
Among the nanoparticles, multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) and quantum dots (QD) have become prominent in biosensing applications. Another representative study for nanocomposite made from fullerene (C60), MWCNT, polyethyleneimine (PEI), and polymer QDs has been recently reported by Jamei and co-workers. They aimed to show the synergy of each nanocomposite component for the design of an aptasensor to analyze thrombin protein. While the examples above are enzyme- and antibody-based, this study shows that nanocomposites can also be used for aptamer immobilization. The C60/MWCNTs-PEI/PQdot/APT aptasensor exhibited excellent analytical performance in terms of sensitivity, selectivity, repeatability, and stability owing to the successful combination of various materials in the nanocomposite which offers high electrical conductivity, high surface-volume ratio, higher sites for the better attachment of aptamers, and high and stable mechanical and chemical structure [41].
2.4. Dendrimers
Polymer nanocomposites can form film-like surface coating layers as well as dendritic structures. For instance, dendrimers are valuable candidates for electrode covering in terms of their characteristic properties to maximize attachment points and flexible and well-oriented binding sites for biomolecules. When the multi-point binding ability of dendrimers is combined with the power of nanomaterials, dendrimeric nanocomposites have great potential in the fabrication of bioinspired devices and biosensors with high sensitivity and stability. In Luo’s work, the harmonious branched tree-like structure of Poly(amidoamine) (PAMAM)-Au nanocomposite was prepared as a matrix for horseradish peroxidase enzyme immobilization. The proposed mediator-free biosensor was fabricated on a MWCNT-modified glassy carbon electrode. Owing to the three-dimensional network of the hybrid surface material, unique bioelectrocatalytic capabilities were reported [42]. Another dendrimer nanocomposite-based biosensor was developed by Shukla et al. using zirconia-polypropylene imine dendrimer (ZrO2-PPI) nanocomposite to modify screen-printed carbon electrode surfaces by electro-co-deposition. The prepared nano-platform provided a suitable and biocompatible matrix for urease enzyme with its protected activity and high stability [43]. Recently, an interesting application of organic–inorganic composite nanomaterials for point-of-care diagnostics has been reported by Ruiz-Sanchez et al. Their novel approach was to obtain one-dimensional nanochains carrying the unique self-assembling properties of polyamidoamine dendrimers and AuNPs and to investigate their potential use as labels in lateral flow assays (LFA). Their findings confirmed that the prepared gold dendrimer nanocomposites increased the sensitivity by 4-folds compared to traditional AuNP (20 nm)-based sensors. This dendrimer nanocomposite-based approach promises to overcome sensitivity issues, which is the main drawback of LFAs [44].
2.5. Polymer Vesicles
Polymers can be self-assembled into several forms, such as micelles, vesicles, mono- or multi-layers, and nanosized particles. After discussing the micelles-shaped dendrimeric nanocomposite-based biosensor studies, the polymeric vesicles or spherical polymeric nanostructures are evaluated. Polymeric materials allow the obtention of biomimetic vesicles such as polymersomes derived from the self-assembly of various block polymers to produce a nan-sized composite. Because the polymersomes are flexible structures in terms of easy surface functionalization with biomolecules and encapsulation of multiple substances, they represent promising tools for drug delivery, bioimaging, diagnostics, and biosensor applications [45]. Polymersomes greatly impact optical biosensing systems because they allow the encapsulation of different colored dyes or fluorescence molecules and the attachment of antibodies or aptamers on their surface. Recent studies on point-of-care diagnosis, mainly due to the urgent needs associated with the COVID-19 pandemic, have focused on increasing selectivity and sensitivity. For this purpose, our group used dye-loaded polymersomes as labels in the design of paper-based rapid test kits as alternatives to AuNPs in traditional LFAs. Different test designs, including dot-blot assay [46] and lateral flow assay [47] were prepared, and their analytical performance parameters were investigated compared to RT-PCR methods. In the pre-clinical studies, a very high correlation was obtained between the proposed platform and the data from the RT-PCR results, even at low viral loads. This application has presented a novel and valuable scientific approach providing an urgent and cost-effective design strategy for pandemic sensors that can be applied to similar epidemics. Additionally, in the designed polymersome-based dot-blot assay, we reported a reference study that shows a comparison between AuNP-based and dye-loaded polymersome-based spot tests. The proposed diagnostic assay exhibited 10-times better sensitivity than AuNP [46].
As previously mentioned, nano-additives can incorporate into polymeric structures by creating polymer vesicles formed by closing the amphiphilic block copolymeric spherical lamellar structures in the appropriate solvent. For instance, in a similar strategy to develop alternative labels for an immunosensor system, Fe3O4 nanoparticles loaded poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(lactic acid) (PEG-PLA) polymeric vesicles were synthesized to fabricate a sandwich-type electrochemical immunosensor for the detection of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) as a model analyte. In the design strategy, while PEG-PLA polymeric vesicles carried secondary antibodies, the primary antibody was immobilized onto a graphene sheet surface. The prepared immunosensor based on nanoparticle-loaded polymer vesicles exhibited low LOD, high sensitivity, and stability [48].
The basis of such interest in polymer-based nanocomposites is the ability to design various morphologies and compositions with any desired decoration. In the fabrication of polymer and inorganic hybrid nano-objects, increasing the morphological diversity has been the driving force. Starting from this point of view, Fan et al. demonstrated a combined technique for quick preparation of polymer-gold nanocomposites with different morphologies, including sphere, worm, and vesicles. The facile technology they proposed combined the polymerization-induced self-assembly technique with “host-guest” chemistry. For the “host-guest” complexation, β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) and adamantane (Ada) was used. Cyclodextrins are composed of hydrophilic outer parts and a hydrophobic inner cavity, which can form non-covalent inclusion complexes with a guest molecule. This complexation strategy was adapted to achieve AuNP-decorated polymer nanocomposites; AuNP-Polymer sphere nano-flowers, AuNP–polymer sphere nano-patterns, AuNP-Polymer nano-worms, and vesicles. Briefly, β-CD functionalized block copolymer nano-objects were first prepared, and then the structures “host” and “guest” induced quick interactions between β-CD and Ada, which allowed the co-self-assembly of AuNP–polymer composites [49]. Our previous works have adapted the biomimetic property of β-CD units to electrochemical sensor platforms and LFA tests for cocaine detection. With these studies, a poly(p-phenylene) β-cyclodextrin poly(ethylene glycol) (PPP-CD-g-PEG) polymeric structure was specifically synthesized, and the β-CD cavity of the polymer was used as a biorecognition surface due to its ability to form CD–cocaine inclusion complexes [50,51]. It is conceivable that β-CD and inorganic materials (Au, Ag, Si, Fe2O3)-decorated polymer composites may be designed with various morphologies and compositions for biosensor applications in the near future.
In the light of the above reports, it is possible to conclude that coupling polymer nanocomposites with biosensing systems offer significant possibilities for improving sensor performances. Some recently published works on polymer and biopolymer nanocomposites-based biosensors are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Recently developed biosensors based on polymer–biopolymer nanocomposites.
3. Conducting Polymer Nanocomposites
The four valance electrons of some polymers’ constructive carbon atoms are not fully used up in covalent bonds. These polymers are well known as conjugated polymers in which the electron delocalization provides high charge mobility along their carbon backbones. The conjugated polymers can possess semiconducting features or metallic properties depending on the number and kind of atoms within the repeated polymeric units. Conjugated polymers can also be transformed into conducting polymers by doping processes that change the number of π-electrons [74]. Heeger et al. received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for the discovery of the first conducting polymer (polyacetylene). Conducting polymers (CPs) exhibit remarkable features such as high mechanical, electronic, optical, and environmental stability and low operating temperature and are lightweight, offer a simple synthesis, and economical behavior [75]. These outstanding features have led to the fabrication of optical wires, gadgets, and biosensor devices, such as sensor chips for diagnostic and environmental monitoring purposes [76,77].
With growing interest in this subject, many research reports have focused on advancing the properties of CPs and their synthesis approaches. The formation of composite and nanocomposite by the addition of fillers has been widely recommended to enhance the physical and chemical features of CPs. A composite typically consists of two or more constituents in which each component carries its features to the final structural material. Using nanomaterials of different types and shapes as a reinforcing phase in the CPs matrix phase creates a conducting polymer nanocomposite (CPNC). Several methods to produce CPNCs include electrochemical encapsulation, colloidal dispersions, in situ polymerization with nanoparticles, and coating of inorganic polymers [78]. The properties of CPNCs can be tuned by varying the matrix and filler, which results in millions of combinations usable in different applications. Alternative carbon nanomaterial (CNMs) fillers such as single-walled and multi-walled carbon nanotubes, fullerenes, carbon nanofibers, nanospheres, and graphene have been extensively used for CPNCs preparation [21]. The unique features of carbon nanomaterials, such as their environmental stability, surface area, and other properties (physical, chemical, thermal, and electrical), make them unique materials for the twenty-first century. Substantial efforts have been allocated to produce CPNCs with superior fundamental and technological assets through CNM and CP combination [79].
Other than CNMs, metal nanoparticles (silver, gold, platinum, etc.) and their oxide forms have been employed to create CPNCs with advanced features due to their different compositions and dimensions [80,81]. Various techniques such as electrochemical or chemical methods [82], sonochemical methods [83], sol-gel techniques [84], ultrasonic irradiation [85], and photochemical preparation [86] have been actively used to incorporate metals or metal oxide fillers into the preparation of conducting polymer nanocomposites. During preparation, nanocomposites show increased electrical breakdown strength, melting temperature, magnetization, charge capacity, and adopted behaviors such as electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, dielectric, and semiconductivity. These advanced properties make CPNCs great candidates for developing electric-based biosensing platforms.
As an active biosensing platform, CPNCs such as nanocomposites of polypyrrole (PPy) and polyaniline (PANI) conducting polymers have shown high biocompatibility with cells and biological tissues. These features influenced researchers to employ CPNCs in tissue engineering, bio-electrodes, drug delivery, and biosensors to detect biological and synthetic moieties [87]. It has been demonstrated that the electrochemical performance of screen-printed electrodes-based biosensors is highly enhanced following the use of porous carbon, given the latter’s great conductivity and surface area. Moreover, using sulfur and nitrogen to dope carbon enhances its electrocatalytic properties. Taking this advantage, a nanocomposite formed by N and S-doped carbon and the polymer poly3-((2,20:50,2″-terthiophen)-30-yl)-5-aminobenzoic acid (pTTABA) was successfully used for neurotransmitters (NTs) detection. The proposed pTTABA-based amperometric biosensor exhibited a detection range of 0.5 µM to 4.0 mM with a limit of detection (LOD) reaching 112 nM for lactate detection [88]. A similar study proposed a combination of heteroatoms (N and S)-doped porous carbon and 2,2′:5′,5″-terthiophene-3′-p-benzoic acid (TBA) to produce an enhanced electrochemical microfluidic system for NTs determination in human plasma. This biosensor had an NTs detection range of 0.05–130 nM coupled with a highly sensitive LOD of 34–44 pM [89].
In addition to CNM nanocomposites, metal nanocomposites such as Pt and Au with PANI and PPy conducting polymers have been prepared and applied in biosensing applications. An antifouling electrochemical biosensing platform was designed based on embedded AuNPs into the conducting polymer poly(3,4-ethylene dioxythiophene) (PEDOT). The AuNPs functioned as signal enhancers, whereas the PEDOT acted as an antifouling agent over the sensor’s surface [90]. Another electrochemical biosensor comprising 3-mercaptopropionic acid (MPA) capped PtNP-PPy nanocomposite film was developed for C-reactive protein detection. The electrodeposition of Pt nanofibers creates numerous heterogeneous nucleating sites in the polymeric matrix resulting in highly controllable geometrical conformities. This nanocomposite allowed for enhanced orientation and easy access to the interaction between the analytes and biomolecules, leading to the detection of αCRP at a LOD = 4.54 ng/mL [91]. A study examining a PtNPs/PPy-based biosensor for sulfite detection in alcoholic beverages demonstrated satisfactory and fast analytical performances (LOD = 12.4 nM) obtained within 3–5 s [92].
Natural clay is an exciting material for sensor surface modification due to the outstanding features of the material, such as its porosity, ion exchange ability, high stability, and, most importantly, availability and low cost [91,92]. Zheng et al. developed a glucose biosensor using PANI-montmorillonite clay particles–PtNPs nanocomposite for glucose oxidase anchoring via electrodeposition. The biosensor was tested over human serum, providing a broad detection range (10 µM to 1.94 mM) [93]. Erkmen et al. also reported the preparation of a tyrosinase enzyme inhibition-based biosensor for the dual detection of catechol and azinphos-methyl. This platform consisted of a nanocomposite (poly (3,4 ethylene dioxythiophene) and iridium (IV) oxide) and tyrosinase crosslinked through glutaraldehyde. The biosensor could successfully detect catechol and azinphos-methyl samples with a LOD of 17 nM and 2.96 µM, respectively [94]. Several targets can be detected through nanocomposite conducting polymer-based biosensors, including hormones, enzymes, nucleotides, chemicals, organic compounds, microorganisms, neurotransmitters, vitamins, lipids, proteins, etc. Some examples of the pertinent works are summarized in Table 3.

Table 3.
Various nanoparticles/conducting polymer-based nanocomposites and their characterization techniques, target analyte, and detection limit.
4. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanocomposites
Molecular imprinting technology is of great interest in biomimetic molecular recognition. Molecularly imprinted polymers (MIP), in which a target-specific cavity is created using a template, are considered an essential alternative to natural antibodies in bioanalytical devices. Due to their low cost, flexibility, outstanding chemical stability, and high recognition ability, MIPs have been used to fabricate biosensors in numerous studies. These artificial receptors suffer from some drawbacks, including long response time, heterogeneous structure of binding cavity, diffusion rate, etc. The main reason for these limitations is slow binding kinetics arising from the bulky forms of MIPs such as monoliths, thin films, microspheres, etc. The binding efficiency decreases as the recognition sites remain inside the MIP structure. Also, the low surface area of a general MIP results in a limited amount of recognition sites. Low affinity caused by these problems in biosensing systems has been the main focus for transforming the binding event into a successful signal [140]. Hybrid approaches to obtain MIP nanocomposites have great perspectives on enhancing biosensing performance by overcoming the limitations of traditional imprinted polymers. In the hybrid-material strategy, a variety of functional nanomaterials could be used. For their synthesis, the thickness of MIP films is controlled by an inorganic core. Some formation methodologies of such core–shell MIP nanocomposites are controlled through living radical polymerization (CRP, reversible/addition/fragmentation, chain transfer polymerization (RAFT), or atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) [141]. The application of molecular imprinting technology in nanocomposites combines the unique advantages of MIPs, such as affinity, physical and chemical stability, low cost, etc., with optical and/or electrical properties of nano-scaled materials. This synergy makes MIP nanocomposites very feasible tools for biosensor construction. Since the amount of high affinity imprinted sites alone is not enough for the sensitivity of a biosensor, the enlargement of surface area and manipulating interfacial properties by nanomaterials are important approaches in sensing strategies. Additionally, molecular geometry is a crucial factor to improve the binding ability of MIPs. Hence the sensitivity of a biosensor is also directly controlled by the imprinted polymer nanocomposites [142]. To increase detection selectivity and sensitivity, CNTs, AuNP, graphene, QDs and, SiO2, noble metal, Fe3O4 nanoparticles are the common modifiers of MIPs [143,144]. According to the target-oriented sensing strategy, the expected function can be achieved by choosing one of these nano-modifiers to develop different analytical methods, including optical, fluorescence, and electrochemical. For instance, among the nanomaterial-MIP hybrid materials, QDs are typical nanostructures used in fluorescence-based sensing applications due to their photostability and size-dependent fluorescence spectra. Although different nanofluorophores can be used in MIP fluorescence sensors, QDs have received greater attention because they offer narrower emission and broader absorption spectra. According to reports, there are several developed QD–MIP-based sensing methods [143,145]. In addition to fluorescence property, magnetic features can be added to MIPs for the construction of electrochemical biosensors. For example, Fe3O4 nanoparticles has been reported as an appropriate candidate by providing easy and quick fabrication technology to a biosensor system. Thanks to their excellent properties such as stability, catalytic activity, non-toxicity, and high surface area, Fe3O4 nanoparticles have been utilized to improve the sensitivity and selectivity of biosensors. Hence, Fe3O4 nanoparticles provide increased sensitivity while MIP has a unique cavity for the target molecule, and this magnetic MIP nanocomposite creates a precise sensor surface [146]. Another idea for MIP-hybrid-based fabrication strategies has been to utilize graphene for better electron transfer, higher mechanical strength, and increased specific surface area. This approach improves electrochemical assays’ performance due to the graphene nanohybrid-based electrochemical signal amplification [142]. Similarly, to add a particular function to a biosensing surface, SiO2 nanobeads can be used to form nanolayers for enhanced sensing ability [147]; TiO2 nanoparticles to provide high surface area, improved adsorption of the target, and quick electrochemical response [148]; silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) to incorporate optical properties [149]; and MWCNTs to accelerate the electron transfer [140] could be developed.
In a recently published work on a sarcosine sensor for prostate cancer diagnosis, the advantages of MIPs were combined with silica nanoparticles, making the resulting MIP nanocomposite more stable, biocompatible, and highly competitive permeable [150]. Similarly, a MWCNT/imprinted polymer nanocomposite-based potentiometric sensor was designed for lactic acid detection in dairy products. The purpose of the MIP decoration with a nano-object is the enhancement of electrical conductivity between the electrode and MIP surface and to improve the sensitivity with a wide calibration range [151]. In another work, a graphene oxide-based molecularly imprinted nanocomposite was reported for bisphenol A detection via electrochemical measurements. The work reported a combined approach for preparing a 3D network composed of graphene oxide, β-CD, and polyacrylate. The 3D network of these covalently linked components provided a molecular imprint of bisphenol A and presented a selective, rapid, and cost-effective method [152].
AuNPs are promising materials that permit excellent optical and electrical properties in diagnostic science and technology. These properties provide unique added characteristics in the production of MIP–AuNP nanocomposites. AuNPs have been combined with MIPs as nanocomposite films or colloidal particles. They have also been used to form multi-composite structures with other nanoparticles such as CNTi graphene, TiO2, etc. The design of these types of AuNP-based nanohybrid materials has been the main development topic for optical, gravimetric, and electrochemical biosensors. In a recent study, AuNP/MIP nanocomposite thin films were used over the electrode surface to fabricate a chemiresistive sensor to detect hexanal gas, a lung cancer biomarker in exhaled breath. This hybrid sensor layer allowed a successful detection window for hexanal gas with a good selectivity [153]. As previously mentioned, multifunctional hybrid nanocomposites can be designed to obtain multi-hybrid sensors based on AuNP/MIPs combined with CNT, graphene, or TiO2 nanoparticles to add synergic and beneficial effects of these nanoparticles to the designed sensors, including enhanced electron or charge transfer, increased electrocatalytic activity, improved sensor response and sensitivity, good mechanical robustness and chemical stability [154]. Lian et al. have reported a representative work for such an application introducing an imprinted sensor surface based on chitosan–platinum nanoparticles/graphene–AuNPs. With an advantageous combination of self-assembly and electropolymerization techniques, this approach was applied to obtain an erythromycin sensor with improved analytical capabilities [155]. Table 4 reports the MIP-based hybrid sensors decorated with different nanoparticles.

Table 4.
Some nanomaterials combining MIP architectures for biosensor applications.
5. Hydrogel Nanocomposites
The growing trend of using biosensors for rapid diagnosis purposes has led to a greater focus on miniaturized biorecognition two-dimensional (2D) surfaces. However, these planner surfaces have exhibited limited analytical performances due to their narrow dynamic range, instability of the immobilized probes, longer response time, and low LODs [168]. Such constraints on the 2D structural biosensors eventually led to the design of three-dimensional (3D) biosensors. The newly designed biosensors successfully showed higher analytical performance, biocompatibility, enhanced selectivity, sensitivity, and flexibility for implantable devices (Figure 2).
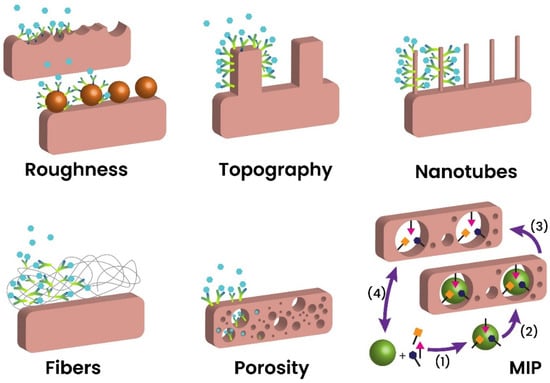
Figure 2.
Typical 3D architectures used in biosensors, including roughness enhancement, topographical structures, fiber networks, etc. Molecularly imprinted polymers can be used in four steps: Assembly (1), deposition and polymerization (2), removal (3), and back to the initial step (4). Adapted with permission from Ref. [169]. ©2019, Elsevier B.V.
The 3D polymeric networks in hydrogels can infuse a significant quantity of water and soluble molecules [170]. The weak mechanical strength of hydrogels is a considerable drawback limiting their performance where strength, elasticity, and endurance are highly demanded [171]. Other physicochemical criteria (diffusion, swelling, functional groups) should be closely considered when selecting materials for hydrogel manufacturing. Recent approaches in hydrogel optimization have led to the development of new hydrogel varieties such as nanocomposite hydrogels [172] and double network hydrogels [173]. The nanocomposite hydrogels containing various physically/chemically crosslinked nano-scaled structures among polymeric chains have shown novel properties and behaviors. Nanocomposite hydrogels can be created using different nanomaterials, including carbon-based nanomaterials, polymer NPs, inorganic/ceramic NPs, and metal NPs [174].
Creating nano/micro-sized matrices that benefit the unique properties of both hydrogels and nanomaterials is the main challenge in developing nanocomposite hydrogels. Typically, hydrogels’ flexible and 3D polymeric configuration can host different types of materials as a “guest” [175]. The gelation procedure of the final composite structure happens in any water-based or organic solution resulting in either hydrogel for aqueous media or organogel if made in organic media. Various natural polymers such as chitosan (CS) [176], cellulose [177], alginate [178], collagen [179], and lignin [180], as well as synthetic polymers, including poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) [181], poly (N-isopropyl acrylamide) (PNIPAM) [182], poly(vinyl imidazole) [183], poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) [184], and poly(acrylic acid) (PAA) [185] show the ability to create hydrogels. The “host-guest” interaction between hydrogels and nanomaterials is formed through covalent and non-covalent bonding, such as hydrogen bonding, van der Walls forces, and electrostatic interactions [186]. The application of functionalized nanomaterials can significantly enhance the features of the final nanocomposite hydrogel, namely the mechanical properties and bioactivity [187]. On the contrary, by taking advantage of their chemical structures and forming π-π stacking interactions, non-functionalized nanomaterials (graphene and carbon materials) can also enhance some aspects of hydrogels compared with pure ones [175].
Other than organic-based nanomaterials, inorganic nanomaterials (nanoclays, ceramics, bioactive glass, metallic NPs) are actively utilized to produce nanocomposite hydrogels [174]. The implication of metal NPs and their oxide forms in the hydrogel structure has brought up attractive attributes such as magnetism, electrical and thermal conductivity, and antimicrobial activities. This makes these nanocomposite hydrogels great alternatives as sensors and conductive scaffolds in addition to other applications such as drug delivery [174].
Biosensors containing nanocomposite hydrogels as 3D material supports exhibit distinguishable performance and minimized platform cost. The unique structure of these hybrid hydrogels preserves the biological activity of the probe molecules by reducing steric hindrance and improving probe orientation and stability for enhanced analyte capturing. Introducing conductive materials into hydrogel matrices is a well-known approach for sensor applications due to their functionalities. Amongst conductive materials, graphene and carbon nanomaterials [188,189], nanocrystals [190,191,192], and conducting polymers [186,192,193] are mainly applied as conductive additives to hydrogels. The addition of conducting polymers (PPy and PANI) to the hydrogel matrices usually occurs along with electrochemical polymerization procedures. On the contrary, carbon nanotubes and graphene are generally incorporated into the matrices via various mixing methods.
Depending on the nature of the added conductive components, the charge transfer can be accelerated, and the signal made stronger [190,191,192]. For instance, Wang et al. developed a carbon–PPy hydrogel nanocomposite-based biosensor for acetaminophen detection. The addition of the porous carbon to the matrix enhanced the analytical performance of the sensor in acetaminophen determination at nanomolar levels (LOD = 1.2 nM) [193]. Xu et al. reported the development of a PANI conductive polymer-hydrogel 3D material for xanthine detection. The purine base was detected by measuring the produced hydrogen peroxide [194]. Zhao et al. also reported the development of an animal skin-inspired conductive hydrogel-based biosensor containing polydopamine-AgNPs, PANI, and polyvinyl alcohol for skin sensing and wound-dressing for diabetic patients [195]. Table 2 shows the components of biosensors containing conducting polymers, carbon, and graphene nanocomposite hydrogels. The sensing mechanism of these biosensors strongly depends on the electrochemical charge transfer as the added nanocomposite is beneficial for charge transport.
A limited number of inorganic nano-scaled materials can be used directly in sensing platform formation. Inorganic components have specific characteristics, making them very competitive to reach a defined purpose and function. Therefore, these materials are generally used as primary or secondary components. On the contrary, inorganic nanomaterials can be widely utilized as additives to enhance the analytical performance of sensors. Forming homogeneous dispersions of inorganic materials is hard to achieve, whereas using a strong mixing procedure could denaturalize the hydrogel structure. If inorganic additives are effectively dispersed into hydrogels, the obtained sensor can exhibit steady signal transduction and stable performances. Among the wide range of inorganic materials used to improve performance, nano-scaled silica [196], titanium oxide [197], quantum dots [198], and organosilicates [199] are preferred for the functionalization of hydrogels. For example, Huang et al. reported using a magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles-embedded hydrogel to form a fiber-optic glucose biosensor. The proposed biosensor demonstrated temperature-adjusted glucose-sensing within 50 to 700 mg/dL and an LOD = 8.3 mg/dL [196]. Cui et al. attempted the creation of a TiO2-chitosan and Au nanorods–SiO2 NPs nanocomposite hydrogel embedding acetylcholinesterase for organophosphate pesticides sensing. This biosensor showed a linear range of 18 Nm–13.6 μM and LODs of 5.3 nM and 1.3 nM for dichlorvos (DDVP) and fenthion, respectively [200]. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2) can be used actively as an additive in hydrogel matrices without losing their photocatalytic activity [201]. TiO2 nanocomposite hydrogel can be recycled through heating and separation methods allowing the hybrid gel to be simply remodeled into new hydrogel forms of different shapes and sizes (Figure 3).
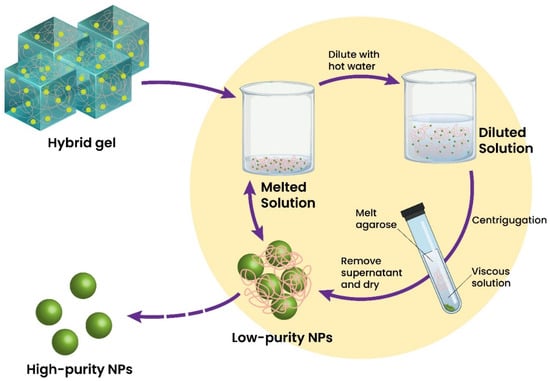
Figure 3.
TiO2/agarose hybrid gel and the recycling and recovery of TiO2 nanoparticles through heating and separation techniques. Adapted with permission from Ref. [201]. ©2017, Royal Society of Chemistry.
Other inorganic nanomaterials such as QDs [202,203,204], noble metal [198,205], and magnetic nanoparticles [206] took part in many research areas. Cadmium Selenide QDs nanocrystals were combined with PEG-based hydrogels and successfully applied for phenol detection [202]. Enzyme encapsulated cadmium telluride QD-based hydrogels with a biocatalysis unit and a fluorescence signaling unit was utilized as a multifunctional material to develop optical biosensors [203]. Magnetic nanoparticles in sensors and biosensors are in high demand due to the limited accessible number of candidate materials. Jia et al. created an aldehyde biosensor based on a responsive photonic hydrogel formed through self-assembled carbon-Fe3O4 NPs and in situ photopolymerized polyacrylamide hydrogels [206]. Table 5 summarizes the notable features of the inorganic nanocomposite hydrogel-based biosensors introduced in this section. Despite organic nanocomposites (polymeric and carbon-based nanocomposites), the mechanism of electrochemical sensing varies depending on the type of inorganic materials. Still, photochemical identification is retained for the hydrogels containing inorganic additives.

Table 5.
Collection of some of the pertinent nanocomposite hydrogel applications for biosensing.
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Biosensors have become a standard analytical tool in various fields, especially healthcare and biomedicine. Despite their several advantages, many challenges such as dynamic range, stability, chemical reactions, etc., obstruct their applications. Consequently, great efforts are focused on developing novel materials and structures to enhance analytical features to reach commercialization.
Polymers and nano-scaled materials have many advantages that can answer and overcome many of the issues faced before. Their combination for the creation of nanocomposite materials provides an exciting opportunity to complement both materials and bypass the disadvantages seen for each material alone.
One of the most critical requirements in polymer nanocomposites synthesis is the creation and then dispersion of the homogenous matrix, which plays an essential key role in the composite’s physical and chemical features. Unfortunately, most applied processes are not feasible economically or cannot deal with poor interfacial adhesion and agglomeration of nanoparticles. Some approaches, such as layer-by-layer assembly and electrospinning, could be applied to create perfectly homogenous polymeric matrices but are not suitable for scaling up or commercialization. The melting process is economically achievable among all the alternative methods, but the final polymeric matrices mostly show poor and non-homogeneous dispersion. Reinforcing the melting process with high shear mixing methods like twin-screw extruding might guarantee adequate dispersion.
Protection and proper orientation of the functional groups in nanocomposites is another challenge that can be overcome by 3D or 4D printing to further enhance the final product’s mechanical properties. It is also important to solve the altered rheological properties resulting from the polymer chain flexibility restriction after nanocomposite integration in the polymer matrices. Hence, selecting nanocomposites with suitable sizes and shapes may provide decent interactions between the polymer and nanomaterials.
Modifying the polymers by changing their morphology, optimum aspect ratio, surface roughness, or introducing functional groups can prevent the possible structural defects related to the synthesis process conditions (temperature, pressure, density, and speed rate). For example, under high temperatures, the chance of having a structure with fewer hollows and porosities is higher. However, these conditions can impose a high cost and waste of materials that must be considered during the design and manufacturing phase. Consequently, developing cost-effective synthesis approaches with commercialization prospects will be interesting.
We have discussed polymer and nano-scaled nanocomposite materials to develop sensing platforms throughout the current review paper. The diversity of these materials show important advances in improving various sensing features such as sensitivity, selectivity, LOD, storage, etc. We hope that these advances will significantly bridge the gap between R&D-based experiments and approved clinical and commercial applications.
Author Contributions
Resources, S.T.; data curation, H.M., F.G., E.G.C.; writing—original draft preparation, H.M., F.G., E.G.C.; writing—review and editing, H.M., S.T.; supervision, S.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Matlou, G.G.; Nkosi, D.; Pillay, K.; Arotiba, O. Electrochemical detection of Hg(II) in water using self-assembled single walled carbon nanotube-poly(m-amino benzene sulfonic acid) on gold electrode. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2016, 10, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gavalas, V.G.; Berrocal, M.J.; Bachas, L.G. Enhancing the blood compatibility of ion-selective electrodes. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 384, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.F.B.; Sherwood, C.S. Biocompatibility of Perfluorosulfonic Acid Polymer Membranes for Biosensor Applications. ACS Symp. Ser. 1994, 556, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maines, A.; Ashworth, D.; Vadgama, P. Diffusion restricting outer membranes for greatly extended linearity measurements with glucose oxidase enzyme electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 1996, 333, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingshott, P.; Griesser, H.J. Surfaces that resist bioadhesion. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 1999, 4, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanizamani, F.; Moulahoum, H.; Timur, S. Noninvasive Optical Sensor for the Detection of Cocaine and Methamphetamine in Saliva Using Rhodamine B-Labeled Polymersomes. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 1146–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulahoum, H.; Ghorbanizamani, F.; Timur, S. Paper-based lateral flow assay using rhodamine B-loaded polymersomes for the colorimetric determination of synthetic cannabinoids in saliva. Mikrochim. Acta 2021, 188, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorbanizamani, F.; Moulahoum, H.; Guler Celik, E.; Timur, S. Ionic liquids enhancement of hydrogels and impact on biosensing applications. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 357, 119075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.M.; Kim, K.H.; Yoon, H.; Kim, H. Chemical Design of Functional Polymer Structures for Biosensors: From Nanoscale to Macroscale. Polymers 2018, 10, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akbulut, H.; Bozokalfa, G.; Asker, D.N.; Demir, B.; Guler, E.; Odaci Demirkol, D.; Timur, S.; Yagci, Y. Polythiophene-g-poly(ethylene glycol) with Lateral Amino Groups as a Novel Matrix for Biosensor Construction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 20612–20622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guler, E.; Soyleyici, H.C.; Demirkol, D.O.; Ak, M.; Timur, S. A novel functional conducting polymer as an immobilization platform. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2014, 40, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz Sengel, T.; Guler, E.; Gumus, Z.P.; Aldemir, E.; Coskunol, H.; Akbulut, H.; Goen Colak, D.; Cianga, I.; Yamada, S.; Timur, S.; et al. An immunoelectrochemical platform for the biosensing of ‘Cocaine use’. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 246, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, T.; Guler, E.; Gumus, Z.P.; Akbulut, H.; Aldemir, E.; Coskunol, H.; Goen Colak, D.; Cianga, I.; Yamada, S.; Timur, S.; et al. Synthesis and application of a novel poly-l-phenylalanine electroactive macromonomer as matrix for the biosensing of ‘Abused Drug’ model. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 7304–7315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzinger, M.; Buzzetti, P.H.M.; Cosnier, S. Polymers and nano-objects, a rational combination for developing health monitoring biosensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 348, 130700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maduraiveeran, G. Bionanomaterial-based electrochemical biosensing platforms for biomedical applications. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 1688–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobi, R.; Ravichandiran, P.; Babu, R.S.; Yoo, D.J. Biopolymer and Synthetic Polymer-Based Nanocomposites in Wound Dressing Applications: A Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, S.; Gohain, M.B.; Yadav, D.; Ingole, P.G. Nanocomposite and bio-nanocomposite polymeric materials/membranes development in energy and medical sector: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 2121–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarz, M.; Tan, B.; Venkatakrishnan, K. Multiplex Photoluminescent Silicon Nanoprobe for Diagnostic Bioimaging and Intracellular Analysis. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1700548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keshavarz, M.; Chowdhury, A.K.M.R.H.; Kassanos, P.; Tan, B.; Venkatakrishnan, K. Self-assembled N-doped Q-dot carbon nanostructures as a SERS-active biosensor with selective therapeutic functionality. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 323, 128703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Sarita; Nehra, M.; Dilbaghi, N.; Tankeshwar, K.; Kim, K.-H. Recent advances and remaining challenges for polymeric nanocomposites in healthcare applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 80, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Kaur, A.; Kaur, H. Review on nanomaterials/conducting polymer based nanocomposites for the development of biosensors and electrochemical sensors. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Mater. 2020, 60, 504–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanaviciene, A.; Plikusiene, I. Polymers in Sensor and Biosensor Design. Polymers 2021, 13, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivastava, S.; Jadon, N.; Jain, R. Next-generation polymer nanocomposite-based electrochemical sensors and biosensors: A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 82, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajik, S.; Beitollahi, H.; Nejad, F.G.; Dourandish, Z.; Khalilzadeh, M.A.; Jang, H.W.; Venditti, R.A.; Varma, R.S.; Shokouhimehr, M. Recent Developments in Polymer Nanocomposite-Based Electrochemical Sensors for Detecting Environmental Pollutants. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 1112–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawaz, J.; Mittal, V. Synthesis of Polymer Nanocomposites: Review of Various Techniques. In Synthesis Techniques for Polymer Nanocomposites; Wiley Online Books: Weinheim, Germany, 2014; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Arslan, M.; Tasdelen, M.A. Polymer Nanocomposites via Click Chemistry Reactions. Polymers 2017, 9, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cele, H.M.; Ojijo, V.; Chen, H.; Kumar, S.; Land, K.; Joubert, T.; de Villiers, M.F.R.; Ray, S.S. Effect of nanoclay on optical properties of PLA/clay composite films. Polym. Test. 2014, 36, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, R.; Shan, S.; Huang, L.; Chen, Z.; Lawson, T.; Lin, M.; Yan, L.; Liu, Y. High-Performance Intraocular Biosensors from Chitosan-Functionalized Nitrogen-Containing Graphene for the Detection of Glucose. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlyapov, V.A.; Kharkova, A.S.; Kurbanaliyeva, S.K.; Kuznetsova, L.S.; Machulin, A.V.; Tarasov, S.E.; Melnikov, P.V.; Ponamoreva, O.N.; Alferov, V.A.; Reshetilov, A.N. Use of biocompatible redox-active polymers based on carbon nanotubes and modified organic matrices for development of a highly sensitive BOD biosensor. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2021, 143, 109706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miodek, A.; Mejri-Omrani, N.; Khoder, R.; Korri-Youssoufi, H. Electrochemical functionalization of polypyrrole through amine oxidation of poly(amidoamine) dendrimers: Application to DNA biosensor. Talanta 2016, 154, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, J.; Crivillers, N.; Ravoo, B.J.; Mas-Torrent, M. Cyclodextrin-based superparamagnetic host vesicles as ultrasensitive nanobiocarriers for electrosensing. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 9884–9889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, M.; Su, W.; Wu, B.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Qiao, B.; Pei, H.; Tu, J.; Chen, D.; et al. Photoelectrochemical Enzyme Biosensor Based on TiO2 Nanorod/TiO2 Quantum Dot/Polydopamine/Glucose Oxidase Composites with Strong Visible-Light Response. Langmuir 2022, 38, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugesan, S.; Scheibel, T. Copolymer/Clay Nanocomposites for Biomedical Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1908101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pavón, E.; Martín-Rodríguez, R.; Perdigón, A.C.; Alba, M.D. New Trends in Nanoclay-Modified Sensors. Inorganics 2021, 9, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumstein, A. Polymerization of adsorbed monolayers. I. Preparation of the clay–polymer complex. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Gen. Pap. 1965, 3, 2653–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emre, F.B.; Kesik, M.; Kanik, F.E.; Akpinar, H.Z.; Aslan-Gurel, E.; Rossi, R.M.; Toppare, L. A benzimidazole-based conducting polymer and a PMMA–clay nanocomposite containing biosensor platform for glucose sensing. Synth. Met. 2015, 207, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unal, B.; Yalcinkaya, E.E.; Gumustas, S.; Sonmez, B.; Ozkan, M.; Balcan, M.; Demirkol, D.O.; Timur, S. Polyglycolide–montmorillonite as a novel nanocomposite platform for biosensing applications. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 9371–9379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, T.; Narayanan, N.; Solanki, P.R. Polymer–Clay Nanocomposite-Based Acetylcholine esterase Biosensor for Organophosphorous Pesticide Detection. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2017, 11, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.-D.; Huang, J.; Liang, R.-P. Nanocomposite film based on graphene oxide for high performance flexible glucose biosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 160, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Misra, S.K.; Wang, Z.; Daza, E.; Schwartz-Duval, A.S.; Kus, J.M.; Pan, D.; Pan, D. Paper-Based Analytical Biosensor Chip Designed from Graphene-Nanoplatelet-Amphiphilic-diblock-co-Polymer Composite for Cortisol Detection in Human Saliva. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 2107–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamei, H.R.; Rezaei, B.; Ensafi, A.A. Ultra-sensitive and selective electrochemical biosensor with aptamer recognition surface based on polymer quantum dots and C60/MWCNTs- polyethylenimine nanocomposites for analysis of thrombin protein. Bioelectrochemistry 2021, 138, 107701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Dong, M.; Lin, F.; Liu, M.; Tang, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, S. Three-dimensional network polyamidoamine dendrimer-Au nanocomposite for the construction of a mediator-free horseradish peroxidase biosensor. Analyst 2011, 136, 4500–4506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.K.; Mishra, A.K.; Mamba, B.B.; Arotiba, O.A. Zirconia-poly(propylene imine) dendrimer nanocomposite based electrochemical urea biosensor. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2014, 66, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Sanchez, A.J.; Parolo, C.; Miller, B.S.; Gray, E.R.; Schlegel, K.; McKendry, R.A. Tuneable plasmonic gold dendrimer nanochains for sensitive disease detection. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 7262–7266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bialas, F.; Reichinger, D.; Becker, C.F.W. Biomimetic and biopolymer-based enzyme encapsulation. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2021, 150, 109864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorbanizamani, F.; Moulahoum, H.; Zihnioglu, F.; Evran, S.; Cicek, C.; Sertoz, R.; Arda, B.; Goksel, T.; Turhan, K.; Timur, S. Quantitative paper-based dot blot assay for spike protein detection using fuchsine dye-loaded polymersomes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 192, 113484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanizamani, F.; Tok, K.; Moulahoum, H.; Harmanci, D.; Hanoglu, S.B.; Durmus, C.; Zihnioglu, F.; Evran, S.; Cicek, C.; Sertoz, R.; et al. Dye-Loaded Polymersome-Based Lateral Flow Assay: Rational Design of a COVID-19 Testing Platform by Repurposing SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Cocktail and Antigens Obtained from Positive Human Samples. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 2988–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Q.; Li, T.; Wang, G.; Li, H.; Qian, Z.; Yang, M. Fe3O4 nanoparticles-loaded PEG-PLA polymeric vesicles as labels for ultrasensitive immunosensors. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 7332–7339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, B.; Liu, Y.; Wan, J.; Crawford, S.; Thang, S.H. Polymerization-Induced Self-Assembly (PISA) and “Host–Guest” Complexation-Directed Polymer/Gold Nanocomposites. ACS Mater. Lett. 2020, 2, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guler, E.; Yilmaz Sengel, T.; Gumus, Z.P.; Arslan, M.; Coskunol, H.; Timur, S.; Yagci, Y. Mobile Phone Sensing of Cocaine in a Lateral Flow Assay Combined with a Biomimetic Material. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 9629–9632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yilmaz Sengel, T.; Guler, E.; Arslan, M.; Gumus, Z.P.; Sanli, S.; Aldemir, E.; Akbulut, H.; Odaci Demirkol, D.; Coskunol, H.; Timur, S.; et al. “Biomimetic-electrochemical-sensory-platform” for biomolecule free cocaine testing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2018, 90, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegoke, O.; Daeid, N.N. Polymeric-coated Fe-doped ceria/gold hybrid nanocomposite as an aptasensor for the catalytic enhanced colorimetric detection of 2,4-dinitrophenol. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 627, 127194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Hu, R.; Fan, G.; Li, G. Graphene oxide/chitosan nanocomposite coated quartz crystal microbalance sensor for detection of amine vapors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 243, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Huang, B.; Chen, L.; Tan, L.; Yao, S. A simple non-enzymatic hydrogen peroxide sensor using gold nanoparticles-graphene-chitosan modified electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 195, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deswal, R.; Narwal, V.; Kumar, P.; Verma, V.; Dang, A.S.; Pundir, C.S. An improved amperometric sarcosine biosensor based on graphene nanoribbon/chitosan nanocomposite for detection of prostate cancer. Sens. Int. 2022, 3, 100174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.P.; Shin, M.; Awasthi, G.P.; Poudel, M.B.; Kim, H.J.; Yu, C. Chitosan polymer matrix-derived nanocomposite (CuS/NSC) for non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 206, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaei, S.; Mozaffari, S.A.; Ebrahimi, F. Polyvinyl alcohol as a crucial omissible polymer to fabricate an impedimetric glucose biosensor based on hierarchical 3D-NPZnO/chitosan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 266, 118105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolat, G.; Abaci, S. Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical Sensing of Malathion Pesticide in Tomato and Apple Samples Based on Gold Nanoparticles-Chitosan-Ionic Liquid Hybrid Nanocomposite. Sensors 2018, 18, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Y.; Feng, B.; Yang, X.; Yang, P.; Ding, Y.; Chen, Y.; Fei, J. Electrochemical biosensing platform based on carboxymethyl cellulose functionalized reduced graphene oxide and hemoglobin hybrid nanocomposite film. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 182, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasconi, M.; Tortolini, C.; Botre, F.; Mazzei, F. Multifunctional au nanoparticle dendrimer-based surface plasmon resonance biosensor and its application for improved insulin detection. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 7335–7342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miodek, A.; Castillo, G.; Hianik, T.; Korri-Youssoufi, H. Electrochemical aptasensor of human cellular prion based on multiwalled carbon nanotubes modified with dendrimers: A platform for connecting redox markers and aptamers. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 7704–7712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, J. Sensitive electrochemical aptamer biosensor for dynamic cell surface N-glycan evaluation featuring multivalent recognition and signal amplification on a dendrimer-graphene electrode interface. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 4278–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, J. Indium tin oxide bipolar electrodes modified with Pt nanoparticles encapsulated inside dendrimers as sensitive electrochemiluminescence platforms. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 906, 115998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apetrei, R.-M.; Camurlu, P. The effect of montmorillonite functionalization on the performance of glucose biosensors based on composite montmorillonite/PAN nanofibers. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 353, 136484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, K.; Ali, M.A.; Singh, C.; Sumana, G.; Malhotra, B.D.; Sharma, A. Highly sensitive porous carbon and metal/carbon conducting nanofiber based enzymatic biosensors for triglyceride detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 246, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Zhang, J.; Fan, Z.; Ding, Y.; Zhou, B.; Yang, R.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, K. Rational Engineering of the DNA Walker Amplification Strategy by Using a Au@Ti3C2@PEI-Ru(dcbpy)3(2+) Nanocomposite Biosensor for Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 RdRp Gene. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 19816–19824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Zhang, K.; Dicko, C.; Bülow, L.; Ye, L. Ag–Polymer Nanocomposites for Capture, Detection, and Destruction of Bacteria. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 1655–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Khan, A.A.P.; Rahman, M.M.; Asiri, A.M.; Alfaifi, S.Y.M.; Taib, L.A. Toward Facile Preparation and Design of Mulberry-Shaped Poly(2-methylaniline)-Ce2(WO4)3@CNT Nanocomposite and Its Application for Electrochemical Cd2+ Ion Detection for Environment Remediation. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 2017, 57, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.A.; Mousavi, S.M.; Bahrani, S.; Gholami, A.; Chiang, W.-H.; Yousefi, K.; Omidifar, N.; Rao, N.V.; Ramakrishna, S.; Babapoor, A.; et al. Bio-enhanced polyrhodanine/graphene Oxide/Fe3O4 nanocomposite with kombucha solvent supernatant as ultra-sensitive biosensor for detection of doxorubicin hydrochloride in biological fluids. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 279, 125743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arotiba, O.; Owino, J.; Songa, E.; Hendricks, N.; Waryo, T.; Jahed, N.; Baker, P.; Iwuoha, E. An Electrochemical DNA Biosensor Developed on a Nanocomposite Platform of Gold and Poly(propyleneimine) Dendrimer. Sensors 2008, 8, 6791–6809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Feng, X.; Shen, J.; Zhu, J.J.; Hou, W. Fabrication of a novel glucose biosensor based on a highly electroactive polystyrene/polyaniline/Au nanocomposite. J. Phys Chem. B 2008, 112, 9237–9242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Zhu, H.; Bazuin, C.G.; Peng, W.; Masson, J.F. Polymer-Templated Gold Nanoparticles on Optical Fibers for Enhanced-Sensitivity Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensors. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Yang, Z.; Wu, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, X. Studies on improved stability and electrochemical activity of titanium carbide MXene-polymer nanocomposites. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 900, 115708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDiarmid, A.G. Synthetic metals: A novel role for organic polymers. Synth. Met. 2001, 125, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatchett, D.W.; Josowicz, M. Composites of intrinsically conducting polymers as sensing nanomaterials. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 746–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, B. Polymer Nanocomposite-Based Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors. In Nanorods Nanocomposites; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghorbani Zamani, F.; Moulahoum, H.; Ak, M.; Odaci Demirkol, D.; Timur, S. Current trends in the development of conducting polymers-based biosensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Umar, M.; Saifi, A.; Kumar, S.; Augustine, S.; Srivastava, S.; Malhotra, B.D. Electrochemical paper based cancer biosensor using iron oxide nanoparticles decorated PEDOT:PSS. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1056, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.X. Syntheses and applications of conducting polymer polyaniline nanofibers. Pure Appl. Chem. 2006, 78, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karousis, N.; Tagmatarchis, N.; Tasis, D. Current progress on the chemical modification of carbon nanotubes. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 5366–5397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suckeveriene, R.Y.; Zelikman, E.; Mechrez, G.; Narkis, M. Literature review: Conducting carbon nanotube/polyaniline nanocomposites. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2011, 17, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Hussain, S.; Singh, S.; Islam, S.S. MWCNT-conducting polymer composite based ammonia gas sensors: A new approach for complete recovery process. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 194, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadrolhosseini, A.R.; Noor, A.S.; Bahrami, A.; Lim, H.N.; Talib, Z.A.; Mahdi, M.A. Application of polypyrrole multi-walled carbon nanotube composite layer for detection of mercury, lead and iron ions using surface plasmon resonance technique. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teh, K.-S.; Lin, L. MEMS sensor material based on polypyrrole–carbon nanotube nanocomposite: Film deposition and characterization. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2005, 15, 2019–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachhav, S.G.; Patil, D.R. Study of Polypyrrole-Coated MWCNT Nanocomposites for Ammonia Sensing at Room Temperature. J. Mater. Sci. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, K.H.; Jeong, S.Y.; Hwang, H.R.; Lee, Y.H. Enhanced Sensitivity of a Gas Sensor Incorporating Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube–Polypyrrole Nanocomposites. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, N.; Kushwaha, C.S.; Shukla, S.K. A review on electrically conducting polymer bionanocomposites for biomedical and other applications. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2019, 69, 709–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, K.K.; Gurudatt, N.G.; Akhtar, M.H.; Seo, K.D.; Park, D.S.; Shim, Y.B. Nano-biosensor for the in vitro lactate detection using bi-functionalized conducting polymer/N, S-doped carbon; the effect of alphaCHC inhibitor on lactate level in cancer cell lines. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 155, 112094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, K.D.; Hossain, M.M.D.; Gurudatt, N.G.; Choi, C.S.; Shiddiky, M.J.A.; Park, D.S.; Shim, Y.B. Microfluidic neurotransmitters sensor in blood plasma with mediator-immobilized conducting polymer/N, S-doped porous carbon composite. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2020, 313, 128017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Wang, G.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Han, Y.; Luo, X. Designed antifouling peptides planted in conducting polymers through controlled partial doping for electrochemical detection of biomarkers in human serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 164, 112317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.K.; Srivastava, A.K.; Kumar, D.; Mulchandani, A.; Rajesh. Protein functionalized Pt nanoparticles-conducting polymer nanocomposite film: Characterization and immunosensor application. Polymer 2014, 55, 4003–4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeloju, S.B.; Hussain, S. Potentiometric sulfite biosensor based on entrapment of sulfite oxidase in a polypyrrole film on a platinum electrode modified with platinum nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 1341–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Liu, M.K.; Yan, Z.P.; Chen, J.F. Highly selective and stable glucose biosensor based on incorporation of platinum nanoparticles into polyaniline-montmorillonite hybrid composites. Microchem. J. 2020, 152, 104266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkmen, C.; Kurbanoglu, S.; Uslu, B. Fabrication of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-iridium oxide nanocomposite based Tyrosinase biosensor for the dual detection of catechol and azinphos methyl. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2020, 316, 128121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattoussi, M.; Matoussi, F.; Raouafi, N. Non-enzymatic amperometric sensor for hydrogen peroxide detection based on a ferrocene-containing cross-linked redox-active polymer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 274, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phetsang, S.; Jakmunee, J.; Mungkornasawakul, P.; Laocharoensuk, R.; Ounnunkad, K. Sensitive amperometric biosensors for detection of glucose and cholesterol using a platinum/reduced graphene oxide/poly(3-aminobenzoic acid) film-modified screen-printed carbon electrode. Bioelectrochemistry 2019, 127, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenoy, G.E.; Marmisolle, W.A.; Azzaroni, O.; Knoll, W. Acetylcholine biosensor based on the electrochemical functionalization of graphene field-effect transistors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 148, 111796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yin, J.; Gao, C.; Qiu, G.; Meng, A.; Li, Q. The construction of electrochemical aptasensor based on coral-like poly-aniline and Au nano-particles for the sensitive detection of prostate specific antigen. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 295, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.J.; Zhang, J.Z.; Liu, Y.J.; Wang, L.L. Novel electrochemical sensing platform based on molybdenum disulfide nanosheets-polyaniline composites and Au nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 194, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, H.; Chen, M.; Ge, H.; Lu, Z.; Liu, X.; Zou, P.; Wang, X.; He, H.; Zeng, X.; Wang, Y. A novel electrochemical sensor based on Au@PANI composites film modified glassy carbon electrode binding molecular imprinting technique for the determination of melamine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Bhardwaj, S.K.; Sharma, A.L.; Kim, K.H.; Deep, A. Development of an advanced electrochemical biosensing platform for E. coli using hybrid metal-organic framework/polyaniline composite. Environ. Res 2019, 171, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xing, X.; Yu, J.; Lian, W.; Li, J.; Cui, M.; Huang, J. A novel label-free electrochemical aptasensor based on graphene-polyaniline composite film for dopamine determination. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 36, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovide, O.; Jahed, N.; Sunday, C.E.; Pokpas, K.; Ajayi, R.F.; Makelane, H.R.; Molapo, K.M.; John, S.V.; Baker, P.G.; Iwuoha, E.I. Electro-oxidation of anthracene on polyanilino-graphene composite electrode. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2014, 205, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Meng, L.; Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Jiao, K. Graphene-based polyaniline arrays for deoxyribonucleic acid electrochemical sensor: Effect of nanostructure on sensitivity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 19050–19056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, N.; Tan, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L. Facile synthesis of NiCo2O4@Polyaniline core-shell nanocomposite for sensitive determination of glucose. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, V.; Singh, K.P.; Yadav, V.L. Polyaniline/MWCNTs/starch modified carbon paste electrode for non-enzymatic detection of cholesterol: Application to real sample (cow milk). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 2173–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phonklam, K.; Wannapob, R.; Sriwimol, W.; Thavarungkul, P.; Phairatana, T. A novel molecularly imprinted polymer PMB/MWCNTs sensor for highly-sensitive cardiac troponin T detection. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2020, 308, 127630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, K.; Babaei, Z. Fabrication and characterization of non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on ternary NiO/CuO/polyaniline nanocomposite. Anal. Biochem. 2016, 498, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohajeri, S.; Dolati, A.; Yazdanbakhsh, K. Synthesis and characterization of a novel non-enzymatic glucose biosensor based on polyaniline/zinc oxide/multi-walled carbon nanotube ternary nanocomposite. J. Electrochem. Sci. Eng. 2019, 9, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Pan, L.; Shi, Y.; Cheng, W.; Shi, Y.; Yu, G. A nanostructured conductive hydrogels-based biosensor platform for human metabolite detection. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 1146–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kailasa, S.; Geeta, B.; Jayarambabu, N.; Reddy, R.K.K.; Sharma, S.; Rao, K.V. Conductive Polyaniline Nanosheets (CPANINS) for a non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Mater. Lett. 2019, 245, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, S.; Yu, J.; Lian, W.; Cui, M.; Xu, W.; Huang, J. Electrochemical immunosensor based on graphene–polyaniline composites and carboxylated graphene oxide for estradiol detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 188, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghamiri, Z.S.; Mohsennia, M.; Rafiee-Pour, H.A. Immobilization of cytochrome c on polyaniline/polypyrrole/carboxylated multi-walled carbon nanotube/glassy carbon electrode: Biosensor fabrication. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2019, 23, 2233–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, P.; Martin, M.; Gonzalez-Mora, J.L. In situ electrodeposition of cholesterol oxidase-modified polydopamine thin film on nanostructured screen printed electrodes for free cholesterol determination. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 837, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phongphut, A.; Sriprachuabwong, C.; Wisitsoraat, A.; Tuantranont, A.; Prichanont, S.; Sritongkham, P. A disposable amperometric biosensor based on inkjet-printed Au/PEDOT-PSS nanocomposite for triglyceride determination. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2013, 178, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albayati, S.A.R.; Kashanian, S.; Nazari, M.; Rezaei, S. Novel fabrication of a laccase biosensor to detect phenolic compounds using a carboxylated multiwalled carbon nanotube on the electropolymerized support. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2019, 42, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thakur, H.; Kaur, N.; Sareen, D.; Prabhakar, N. Electrochemical determination of M. tuberculosis antigen based on Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) and functionalized carbon nanotubes hybrid platform. Talanta 2017, 171, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, I.M.; Robbins, E.M.; Catt, K.A.; Cody, P.A.; Happe, C.L.; Cui, X.T. Enhanced dopamine detection sensitivity by PEDOT/graphene oxide coating on in vivo carbon fiber electrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, K.X.; Xu, J.K.; Duan, X.M.; Lu, L.M.; Hu, D.F.; Zhang, L.; Nie, T.; Brown, K.B. Controllable synthesis of multi-walled carbon nanotubes/poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) core-shell nanofibers with enhanced electrocatalytic activity. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 137, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Turner, A.P.F.; Zhao, M.; Mak, W.C. Processable enzyme-hybrid conductive polymer composites for electrochemical biosensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Deng, H.; Xiong, X.; Li, C.; Li, W. Molecularly imprinted photoelectrochemical sensor for carcinoembryonic antigen based on polymerized ionic liquid hydrogel and hollow gold nanoballs/MoSe2 nanosheets. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1090, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xu, G.; Cui, X.T.; Sheng, G.; Luo, X. Enhanced catalytic and dopamine sensing properties of electrochemically reduced conducting polymer nanocomposite doped with pure graphene oxide. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 58, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, T.; Zhang, K.; Xu, J.; Lu, L.; Bai, L. A facile one-pot strategy for the electrochemical synthesis of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/Zirconia nanocomposite as an effective sensing platform for vitamins B2, B6 and C. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2014, 717–718, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Ren, X.; Yang, M.; Li, X.; He, K.; Rao, A.; Wan, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, S.; Luo, Z. A highly sensitive label-free electrochemical immunosensor based on poly(indole-5-carboxylicacid) with ultra-high redox stability. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 141, 111406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciftci, H.; Tamer, U. Functional gold nanorod particles on conducting polymer poly(3-octylthiophene) as non-enzymatic glucose sensor. React. Funct. Polym. 2012, 72, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thunyakontirakun, W.; Sriwichai, S.; Phanichphant, S.; Janmanee, R. Fabrication of poly(pyrrole-3-carboxylic acid)/graphene oxide composite thin film for glucose biosensor. Mater. Today-Proc. 2019, 17, 2070–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahyar, B.Y.; Kaplan, M.; Ozsoz, M.; Celik, E.; Otles, S. Electrochemical xanthine detection by enzymatic method based on Ag doped ZnO nanoparticles by using polypyrrole. Bioelectrochemistry 2019, 130, 107327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Q.; Han, H.; Feng, F.; Ma, Z. Network nanostructured polypyrrole hydrogel/Au composites as enhanced electrochemical biosensing platform. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Lin, X.Q. Simultaneous determination of dopamine and serotonin on gold nanocluster/overoxidized-polypyrrole composite modified glassy carbon electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 124, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowicka, A.M.; Fau, M.; Rapecki, T.; Donten, M. Polypyrrole-Au Nanoparticles Composite as Suitable Platform for DNA Biosensor with Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Detection. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 140, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyet, N.T.; Thu, V.V.; Lan, H.; Trung, T.; Le, A.T.; Pham, V.H.; Tam, P.D. Simple Label-Free DNA Sensor Based on CeO2 Nanorods Decorated with Ppy Nanoparticles. J. Electron. Mater. 2019, 48, 6231–6239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoder, R.; Korri-Youssoufi, H. E-DNA biosensors of M. tuberculosis based on nanostructured polypyrrole. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 108, 110371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.S.; Xu, J.K.; Lu, L.M.; Wu, L.P.; Zhang, K.X.; Nie, T.; Zhu, X.F.; Wu, Y. Overoxidized polypyrrole/graphene nanocomposite with good electrochemical performance as novel electrode material for the detection of adenine and guanine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 62, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi-Maleh, H.; Tahernejad-Javazmi, F.; Atar, N.; Lutfi, M.; Gupta, V.K.; Ensafi, A.A. A Novel DNA Biosensor Based on a Pencil Graphite Electrode Modified with Polypyrrole/Functionalized Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes for Determination of 6-Mercaptopurine Anticancer Drug. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 3634–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altun, A.; Apetrei, R.M.; Camurlu, P. Reagentless Amperometric Glucose Biosensors: Ferrocene-Tethering and Copolymerization. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 107507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marimuthu, T.; Mohamad, S.; Alias, Y. Needle-like polypyrrole–NiO composite for non-enzymatic detection of glucose. Synth. Met. 2015, 207, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.X.; Liu, K.L.; Xu, Y.; Yuan, M.T.; Gao, T.; Wang, J. Nonenzymatic electrochemical glucose biosensor constructed by NiCo2O4@ Ppy nanowires on nickel foam substrate. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 292, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahnavaz, Z.; Lorestani, F.; Alias, Y.; Woi, P.M. Polypyrrole–ZnFe2O4 magnetic nano-composite with core–shell structure for glucose sensing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 317, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, M.; Aydin, E.B.; Sezginturk, M.K. A highly selective electrochemical immunosensor based on conductive carbon black and star PGMA polymer composite material for IL-8 biomarker detection in human serum and saliva. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 117, 720–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Lin, G.; Zhao, W.; Wu, Q.; Luo, J.; Wei, W.; Liu, X.; Zhu, Y. Necklace-like Molecularly Imprinted Nanohybrids Based on Polymeric Nanoparticles Decorated Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes for Highly Sensitive and Selective Melamine Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 24850–24859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, S.; Benito-Peña, E.; Navarro-Villoslada, F.; Langer, J.; Sanz-Ortiz, M.N.; Reguera, J.; Liz-Marzán, L.M.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C. Multibranched Gold–Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Coated with a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Label-Free Antibiotic Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Analysis. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 7947–7954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Ning, G.; Xu, Z. A molecularly imprinted polymer combined with dual functional Au@Fe3O4 nanocomposites for sensitive detection of kanamycin. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 870, 114216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegoke, O.; Zolotovskaya, S.; Abdolvand, A.; Daeid, N.N. Fabrication of a near-infrared fluorescence-emitting SiO2-AuZnFeSeS quantum dots-molecularly imprinted polymer nanocomposite for the ultrasensitive fluorescence detection of levamisole. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 646, 129013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Liu, A.; Wu, L.; Yu, M.; Wei, W.; Liu, S. Magnetic ferroferric oxide and polydopamine molecularly imprinted polymer nanocomposites based electrochemical impedance sensor for the selective separation and sensitive determination of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT). Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1095, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Niu, H.; Zhang, H. Direct and Highly Selective Drug Optosensing in Real, Undiluted Biological Samples with Quantum-Dot-Labeled Hydrophilic Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Microparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 15741–15749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzali, Z.; Mohadesi, A.; Ali Karimi, M.; Fathirad, F. A highly selective and sensitive electrochemical sensor based on graphene oxide and molecularly imprinted polymer magnetic nanocomposite for patulin determination. Microchem. J. 2022, 177, 107215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quílez-Alburquerque, J.; Descalzo, A.B.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C.; Orellana, G. Luminescent molecularly imprinted polymer nanocomposites for emission intensity and lifetime rapid sensing of tenuazonic acid mycotoxin. Polymer 2021, 230, 124041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Wu, L.; Miao, J.; Wei, W.; Liu, A.; Liu, S. Titanium dioxide and polypyrrole molecularly imprinted polymer nanocomposites based electrochemical sensor for highly selective detection of p-nonylphenol. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1080, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznar-Gadea, E.; Rodríguez-Canto, P.J.; Martínez-Pastor, J.P.; Lopatynskyi, A.; Chegel, V.; Abargues, R. Molecularly Imprinted Silver Nanocomposites for Explosive Taggant Sensing. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 2960–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Puig, S.; Lazo-Fraga, A.R.; Korgel, B.A.; Oza, G.; Dutt, A.; Vallejo-Becerra, V.; Valdés-González, A.C.; Chávez-Ramírez, A.U. Molecularly imprinted polymer-silica nanocomposite based potentiometric sensor for early prostate cancer detection. Mater. Lett. 2022, 309, 131324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, T.; Nayeri, S.; Mirzaee, S. A high performance potentiometric sensor for lactic acid determination based on molecularly imprinted polymer/MWCNTs/PVC nanocomposite film covered carbon rod electrode. Talanta 2019, 192, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Jana, N.R. Selective electrochemical detection of bisphenol A using a molecularly imprinted polymer nanocomposite. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 1536–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousazadeh, M.; Jahangiri-Manesh, A.; Nikkhah, M.; Abbasian, S.; Moshaii, A.; Masroor, M.J.; Norouzi, P. Detection of hexAnal. gas as a volatile organic compound cancer biomarker using a nanocomposite of gold nanoparticles and selective polymers. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 905, 115962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Griffete, N.; Lamouri, A.; Felidj, N.; Chehimi, M.M.; Mangeney, C. Nanocomposites of Gold Nanoparticles@Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: Chemistry, Processing, and Applications in Sensors. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 5464–5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, W.; Liu, S.; Yu, J.; Xing, X.; Li, J.; Cui, M.; Huang, J. Electrochemical sensor based on gold nanoparticles fabricated molecularly imprinted polymer film at chitosan-platinum nanoparticles/graphene-gold nanoparticles double nanocomposites modified electrode for detection of erythromycin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 38, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Jiang, D.; Xu, C.; Ge, Y.; Liu, X.; Wei, Q.; Huang, L.; Ren, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y. Wearable electrochemical biosensor based on molecularly imprinted Ag nanowires for noninvasive monitoring lactate in human sweat. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 320, 128325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, M.; Yang, S.; Tang, W.; Zhang, F.; He, P. Molecularly imprinted polymers-based electrochemical DNA biosensor for the determination of BRCA-1 amplified by SiO2@Ag. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 112, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, L. A novel nanocomposite optosensing sensor based on porous molecularly imprinted polymer and dual emission quantum dots for visual and high selective detection of bovine serum albumin. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 632, 127843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Gálvez, A.; Mayorga-Matinez, C.C.; Parolo, C.; Pons, J.; Merkoçi, A. Magnetic nanoparticle-molecular imprinted polymer: A new impedimetric sensor for tributyltin detection. Electrochem. Commun. 2017, 82, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Jin, M.; Lu, H.; Yao, J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, G.; Shui, L. Molecularly imprinted polymer decorated 3D-framework of functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes for ultrasensitive electrochemical sensing of Norfloxacin in pharmaceutical formulations and rat plasma. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 288, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, S.; Baraneedharan, P.; Balasubrahmanyan, S.; Ramaprabhu, S. Modified graphene based molecular imprinted polymer for electrochemical non-enzymatic cholesterol biosensor. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 86, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Tang, X.; Zhao, L. Molecularly imprinted polymers-based novel optical biosensor for the detection of cancer marker lysozyme. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2022, 334, 113324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motaharian, A.; Hosseini, M.R.M.; Naseri, K. Determination of psychotropic drug chlorpromazine using screen printed carbon electrodes modified with novel MIP-MWCNTs nano-composite prepared by suspension polymerization method. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 288, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, K.; Roushani, M. A nanohybrid probe based on double recognition of an aptamer MIP grafted onto a MWCNTs-Chit nanocomposite for sensing hepatitis C virus core antigen. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 258, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaitong, N.; Chansud, N.; Orachorn, N.; Limbut, W.; Bunkoed, O. A magnetic nanocomposite optosensing probe based on porous graphene, selective polymer and quantum dots for the detection of cefoperazone in milk. Microchem. J. 2021, 171, 106838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roushani, M.; Nezhadali, A.; Jalilian, Z.; Azadbakht, A. Development of novel electrochemical sensor on the base of molecular imprinted polymer decorated on SiC nanoparticles modified glassy carbon electrode for selective determination of loratadine. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 71, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.-j.; Nie, J.; He, B.; Yin, W.; Zheng, J.; Hou, C.-j.; Huo, D.-q.; Yang, M.; Liu, F.-m.; Sun, Q.-q.; et al. Fabrication of S-MoSe2/NSG/Au/MIPs imprinted composites for electrochemical detection of dopamine based on synergistic effect. Microchem. J. 2020, 156, 104845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, A.I.; Reis, N.M. A critical insight into the development pipeline of microfluidic immunoassay devices for the sensitive quantitation of protein biomarkers at the poInt. of care. Analyst 2017, 142, 858–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rebelo, R.; Barbosa, A.I.; Caballero, D.; Kwon, I.K.; Oliveira, J.M.; Kundu, S.C.; Reis, R.L.; Correlo, V.M. 3D biosensors in advanced medical diagnostics of high mortality diseases. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 130, 20–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varaprasad, K.; Raghavendra, G.M.; Jayaramudu, T.; Yallapu, M.M.; Sadiku, R. A mini review on hydrogels classification and recent developments in miscellaneous applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 79, 958–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, M.A.; Su, Y.; Wang, D. Mechanical properties of PNIPAM based hydrogels: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 70, 842–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Hou, K.; Ren, Q.; Chen, G.; Wei, P.; Zhu, M. Nanoparticle-Polymer Synergies in Nanocomposite Hydrogels: From Design to Application. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2018, 39, e1800337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.B.; Wang, X.D.; Shi, X.J.; Yu, K.; Fu, Y.Q. A phenomenological model for dynamic response of double-network hydrogel composite undergoing transient transition. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 151, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahid, F.; Zhao, X.J.; Jia, S.R.; Bai, H.; Zhong, C. Nanocomposite hydrogels as multifunctional systems for biomedical applications: Current state and perspectives. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 200, 108208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Samanta, S.K. Soft-Nanocomposites of Nanoparticles and Nanocarbons with Supramolecular and Polymer Gels and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 11967–12028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahid, F.; Hu, X.H.; Chu, L.Q.; Jia, S.R.; Xie, Y.Y.; Zhong, C. Development of bacterial cellulose/chitosan based semi-interpenetrating hydrogels with improved mechanical and antibacterial properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaeiarani, J.; Bajwa, D.; Shirzadifar, A. A review on cellulose nanocrystals as promising biocompounds for the synthesis of nanocomposite hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 216, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, S.; Sharma, B.; Verma, A.; Chaudhary, J.; Tamulevicius, S.; Thakur, V.K. Recent progress in sodium alginate based sustainable hydrogels for environmental applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 198, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moxon, S.R.; Corbett, N.J.; Fisher, K.; Potjewyd, G.; Domingos, M.; Hooper, N.M. Blended alginate/collagen hydrogels promote neurogenesis and neuronal maturation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 104, 109904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Lu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, H. Lignin-based hydrogels: A review of preparation, properties, and application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 135, 1006–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.C.; Chu, S.; Randolph, M.A.; Bryant, S.J. An in vitro and in vivo comparison of cartilage growth in chondrocyte-laden matrix metalloproteinase-sensitive poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogels with localized transforming growth factor beta3. Acta Biomater. 2019, 93, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Li, H.; Ding, H.; Fan, Z.; Pi, P.; Cheng, J.; Wen, X. Allylated chitosan-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogel based on a functionalized double network for controlled drug release. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 214, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midya, L.; Das, R.; Bhaumik, M.; Sarkar, T.; Maity, A.; Pal, S. Removal of toxic pollutants from aqueous media using poly (vinyl imidazole) crosslinked chitosan synthesised through microwave assisted technique. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 542, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Huang, X.; Zeng, C.; Wang, W.; Ding, C.; Xu, J.; He, Q.; Guo, B. Poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels integrated with cuprous oxide-tannic acid submicroparticles for enhanced mechanical properties and synergetic antibiofouling. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 535, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.L.; Ooi, C.W.; Tan, W.S.; Chan, E.S.; Ho, K.L.; Tey, B.T. Biosensing of hepatitis B antigen with poly(acrylic acid) hydrogel immobilized with antigens and antibodies. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 252, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Mi, H.Y.; Napiwocki, B.N.; Peng, X.F.; Turng, L.S. Mussel-inspired electroactive chitosan/graphene oxide composite hydrogel with rapid self-healing and recovery behavior for tissue engineering. Carbon 2017, 125, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.Y.; Feng, Q.; Xu, J.B.; Xu, X.Y.; Tian, F.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Bian, L.M. Self-Assembled Injectable Nanocomposite Hydrogels Stabilized by Bisphosphonate-Magnesium (Mg2+) Coordination Regulates the Differentiation of Encapsulated Stem Cells via Dual Crosslinking. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1701642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.L.; Cui, M.Z.; Liu, W.F.; Liu, X.G. Highly dispersed conductive polypyrrole hydrogels as sensitive sensor for simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 832, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, M.; Huang, J.; Guo, X.; Wang, L. Near-infrared light-responsive electrochemical protein imprinting biosensor based on a shape memory conducting hydrogel. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 131, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Ali, M.A.; Rai, P.; Ghori, I.; Sharma, A.; Malhotra, B.D.; John, R. Dual-modality microfluidic biosensor based on nanoengineered mesoporous graphene hydrogels. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 760–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Zhao, H.; Du, L.; Gan, X.; Quan, X. A versatile fluorescent biosensor based on target-responsive graphene oxide hydrogel for antibiotic detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 83, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoa, L.T.; Chung, J.S.; Hur, S.H. A highly sensitive enzyme-free glucose sensor based on Co3O4 nanoflowers and 3D graphene oxide hydrogel fabricated via hydrothermal synthesis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 223, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoa, L.T.; Sun, K.G.; Hur, S.H. Highly sensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on Pt nanoparticle decorated graphene oxide hydrogel. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 210, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Wu, L.; Zhang, J.; Dai, W.; Mo, G.; Ye, J. Bifunctional and highly sensitive electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose and hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on NiCo2O4 nanoflowers decorated 3D nitrogen doped holey graphene hydrogel. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 102, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhong, L.; Cui, M.; Liu, W.; Liu, X. Nanomolar Level Acetaminophen Sensor Based on Novel Polypyrrole Hydrogel Derived N-doped Porous Carbon. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.H.; Li, J.J.; Zeng, H.B.; Zhang, X.J.; Cosnier, S.; Marks, R.S.; Shan, D. ATMP-induced three-dimensional conductive polymer hydrogel scaffold for a novel enhanced solid-state electrochemiluminescence biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 143, 111601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Song, S.; Yang, K.; Liu, H.; Yang, Z.; Wang, J.; Yang, B.; Lin, Q. Skin-Inspired Antibacterial Conductive Hydrogels for Epidermal Sensors and Diabetic Foot Wound Dressings. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1901474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, P.P.; Li, M.S.; Zhang, P.F.; Ding, L.Y. Complex of hydrogel with magnetic immobilized GOD for temperature controlling fiber optic glucose sensor. Biochem. Eng. J. 2016, 114, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, N.; Han, K.; Li, M.; Wang, J.; Qian, J. Pure polylysine-based foamy scaffolds and their interaction with MC3T3-E1 cells and osteogenesis. Biomed Mater. 2020, 15, 025004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourreza, N.; Ghomi, M. In situ synthesized and embedded silver nanoclusters into poly vinyl alcohol-borax hydrogel as a novel dual mode “on and off” fluorescence sensor for Fe (III) and thiosulfate. Talanta 2018, 179, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz Zanini, V.I.; Gavilan, M.; Lopez de Mishima, B.A.; Martino, D.M.; Borsarelli, C.D. A highly sensitive and stable glucose biosensor using thymine-based polycations into laponite hydrogel films. Talanta 2016, 150, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.F.; Zhang, T.T.; Lv, Q.Y.; Song, X.; Zhai, X.J.; Wang, G.G. An acetylcholinesterase biosensor based on doping Au nanorod@SiO2 nanoparticles into TiO2-chitosan hydrogel for detection of organophosphate pesticides. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 141, 111452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, N.X.D.; Bae, J.; Kim, I.T.; Park, S.H.; Lee, G.W.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, D.; Son, H.B.; Lee, Y.C.; Hur, J. A recyclable, recoverable, and reformable hydrogel-based smart photocatalyst. Environ. Sci. Nano 2017, 4, 955–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, E.; Son, K.J.; Kim, B.; Koh, W.G. Phenol biosensor based on hydrogel microarrays entrapping tyrosinase and quantum dots. Analyst 2010, 135, 2871–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Wen, D.; Gaponik, N.; Eychmuller, A. Enzyme-encapsulating quantum dot hydrogels and xerogels as biosensors: Multifunctional platforms for both biocatalysis and fluorescent probing. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2013, 52, 976–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liang, K.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Liu, X.; Yin, X.; Chen, D.; Xu, W. Photopolymerized water-soluble maleilated chitosan/methacrylated poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogels as potential tissue engineering scaffolds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Moon, J.Y.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, S.W.; Ahrberg, C.D.; Chung, B.G. Conductive hydrogel/nanowire micropattern-based sensor for neural stem cell differentiation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 258, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Zhang, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, K.; Tan, H.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, J. Responsive Photonic Hydrogel-Based Colorimetric Sensors for Detection of Aldehydes in Aqueous Solution. Langmuir 2018, 34, 3987–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muya, F.N.; Baker, P.G.L.; Iwuoha, E.I. Polysulfone Hydrogel Nanocomposite Alkaline Phosphatase Biosensor for the Detection of Vanadium. Electrocatalysis 2020, 11, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.; Park, J.Y.; Kwon, O.S.; Joo, S.; Lee, C.S.; Bae, J. Incorporation of hydrogel as a sensing medium for recycle of sensing material in chemical sensors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 429, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrosa, V.A.; Yan, J.; Simonian, A.L.; Revzin, A. Micropatterned Nanocomposite Hydrogels for Biosensing Applications. Electroanalysis 2011, 23, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velayudham, J.; Magudeeswaran, V.; Paramasivam, S.S.; Karruppaya, G.; Manickam, P. Hydrogel-aptamer nanocomposite based electrochemical sensor for the detection of progesterone. Mater. Lett. 2021, 305, 130801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.; Mohammadi, S.; Salimi, A. A 3D hydrogel based on chitosan and carbon dots for sensitive fluorescence detection of microRNA-21 in breast cancer cells. Talanta 2021, 224, 121895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Z.; Yu, Z.; Li, M.; Bai, L.; Wang, W.; Chen, H.; Yang, H.; Wei, D.; Yang, L. Corrigendum to “Self-healing and toughness cellulose nanocrystals nanocomposite hydrogels for strain-sensitive wearable flexible sensor” [Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 179 (2021) 324–332]. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 2382–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sagur, H.; Komathi, S.; Khan, M.A.; Gurek, A.G.; Hassan, A. A novel glucose sensor using lutetium phthalocyanine as redox mediator in reduced graphene oxide conducting polymer multifunctional hydrogel. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Zhai, J.; Zhu, C.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Han, Y.; Dong, S. One-pot synthesis of 3-dimensional reduced graphene oxide-based hydrogel as support for microbe immobilization and BOD biosensor preparation. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 63, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liang, B.; Jiang, Q.F.; Li, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, L.Q.; Zhao, Y.M.; Xiong, X.L. Flexible and wearable sensor based on graphene nanocomposite hydrogels. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 075027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Ye, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, T.; Wang, Y.; Li, C. Molecularly Imprinted Photo-electrochemical Sensor for Human Epididymis Protein 4 Based on Polymerized Ionic Liquid Hydrogel and Gold Nanoparticle/ZnCdHgSe Quantum Dots Composite Film. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 12391–12398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Tu, Q.; Long, X.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, H.; Chen, C.; Wang, S.; Min, D. Flexible conductive hydrogel fabricated with polyvinyl alcohol, carboxymethyl chitosan, cellulose nanofibrils, and lignin-based carbon applied as strain and pressure sensor. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 166, 1526–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.L.; Zeng, W.J.; Chai, Y.Q.; Yuan, R.; Zhuo, Y. An Affinity-Enhanced DNA Intercalator with Intense ECL Embedded in DNA Hydrogel for Biosensing Applications. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 11044–11052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xiong, X.R.; Yu, X.Q.; Sun, X.B.; Yang, J.; Zhu, L.; Qin, G.; Dai, Y.H.; Chen, Q. Tough and conductive nanocomposite hydrogels for human motion monitoring. Polym. Test. 2019, 75, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Bazrafshan, A.; Pokutta, A.; Sulejmani, F.; Sun, W.; Combs, J.D.; Clarke, K.C.; Salaita, K. Chameleon-Inspired Strain-Accommodating Smart Skin. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 9918–9926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotanen, C.N.; Tlili, C.; Guiseppi-Elie, A. Amperometric glucose biosensor based on electroconductive hydrogels. Talanta 2013, 103, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Pan, L.; Ma, Z.; Yan, K.; Cheng, W.; Shi, Y.; Yu, G. All Inkjet-Printed Amperometric Multiplexed Biosensors Based on Nanostructured Conductive Hydrogel Electrodes. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 3322–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Gong, Q.; Xia, Z.; Yang, Y.; Chen, C.; Qian, C. Facile preparation of stretchable and self-healable conductive hydrogels based on sodium alginate/polypyrrole nanofibers for use in flexible supercapacitor and strain sensors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 172, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, H.P.; Wang, Y.F.; Fan, X.S.; Liu, T.X. Fast-Recoverable, Self-Healable, and Adhesive Nanocomposite Hydrogel Consisting of Hybrid Nanoparticles for Ultrasensitive Strain and Pressure Sensing. Chem. Mater. 2021, 33, 6146–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, V.; Gupta, T.; Rani, S.; Bandyopadhyay-Ghosh, S.; Ghosh, S.B.; Qiao, L.C.; Liu, G.Z. A hierarchically designed nanocomposite hydrogel with multisensory capabilities towards wearable devices for human-body motion and glucose concentration detection. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 213, 108894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.J.; Guo, J.J.; Yang, C.X. Ratiometric fluorescence sensor for Fe3+ ions detection based on quantum dot-doped hydrogel optical fiber. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 264, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).