DNA-Modified Liquid Crystal Droplets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
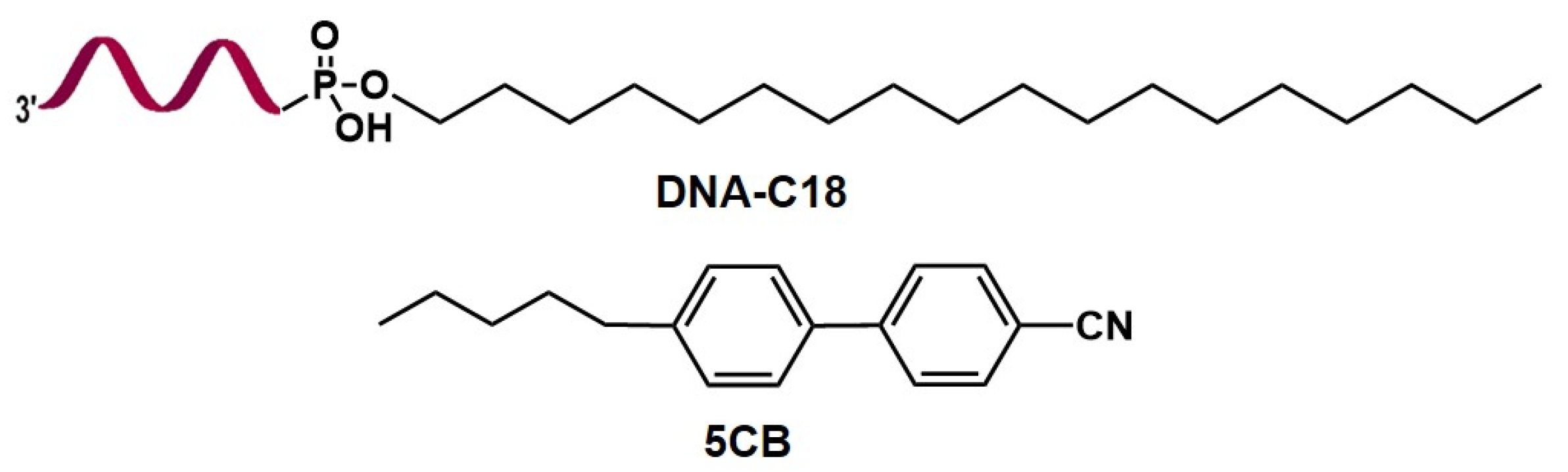
2.2. Synthesis of DNA Amphiphile DNA-C18
2.3. Preparation of DNA-Modified LC Droplets
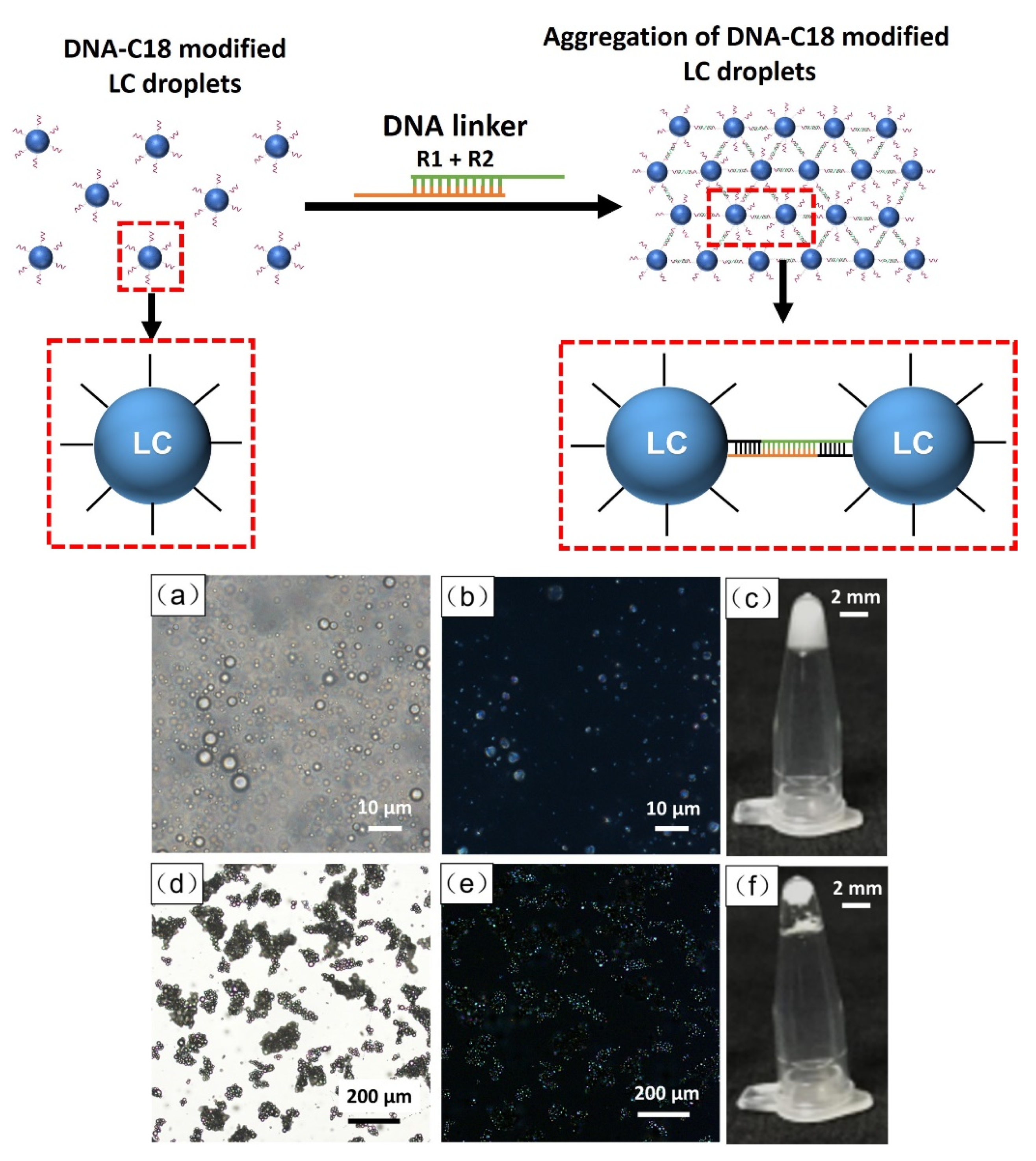
2.4. Aggregation of DNA-Modified LC Droplets
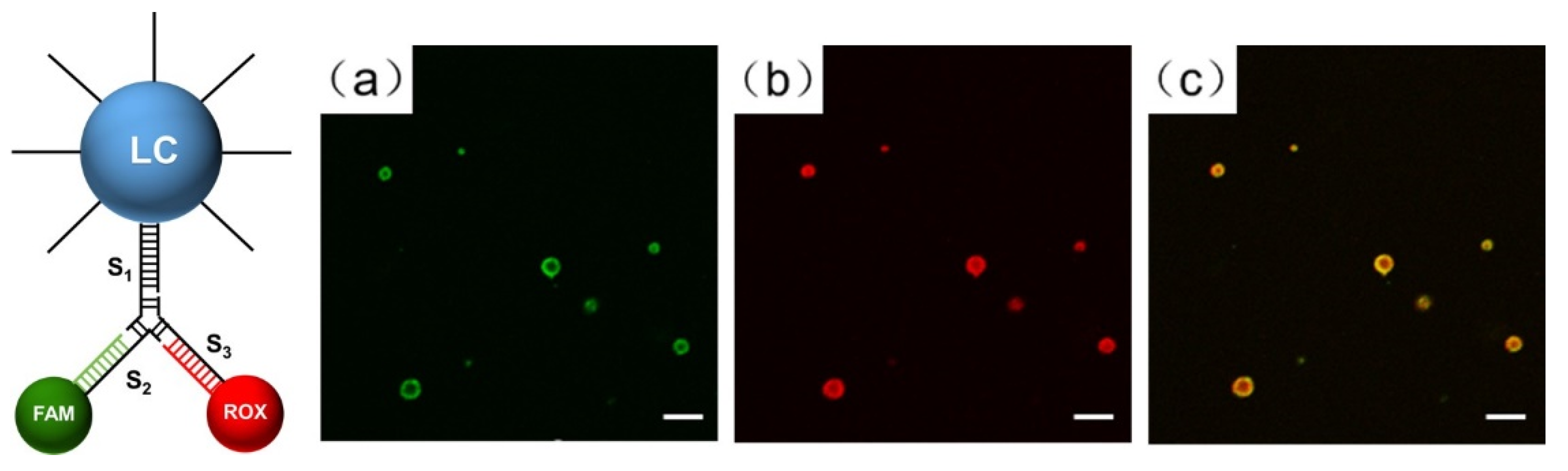
2.5. Fluorescence Experiment
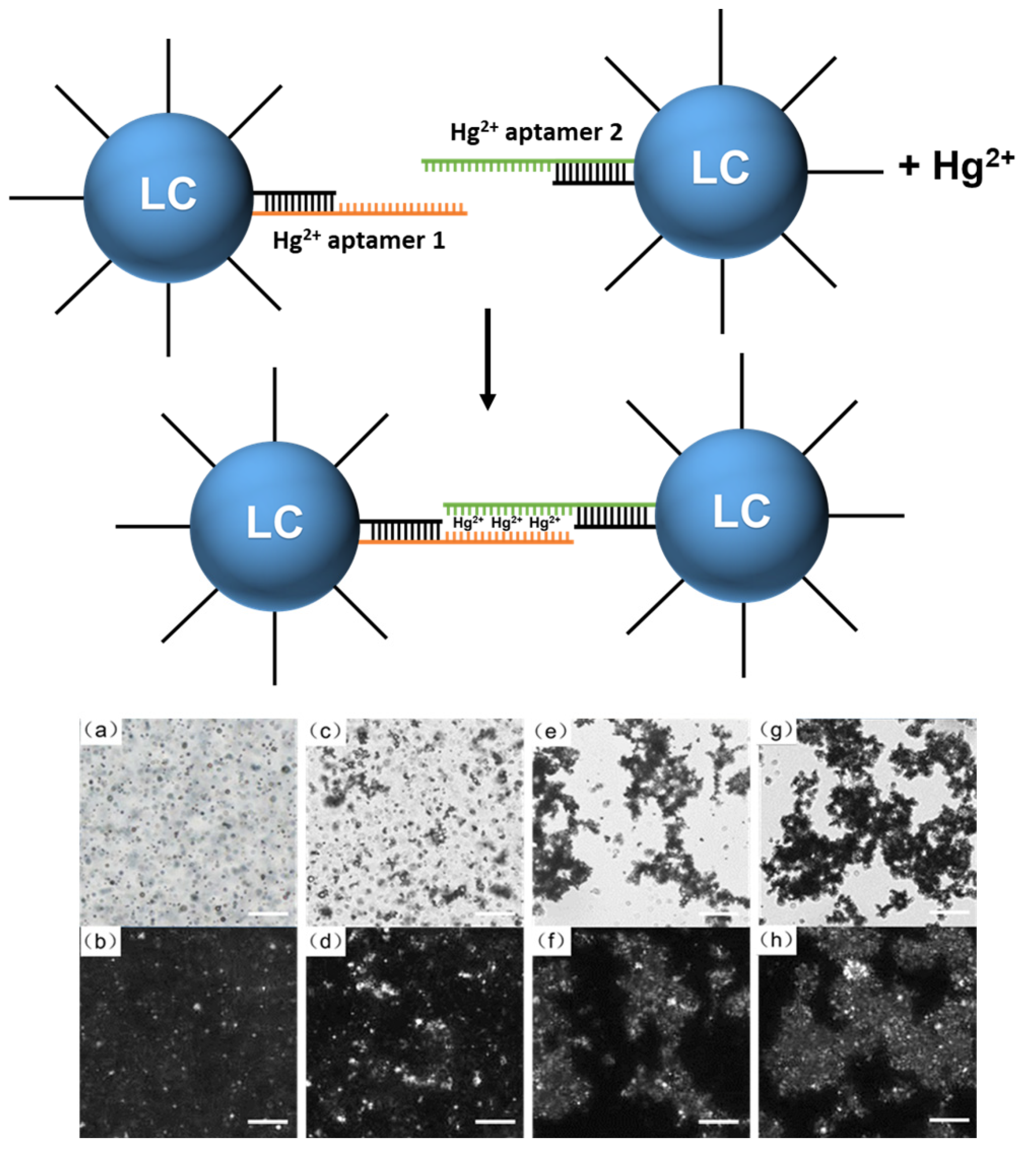
2.6. Hg2+ Responsiveness of DNA-Modified LC Droplets
2.7. Thrombin Responsiveness of DNA-Modified LC Droplets
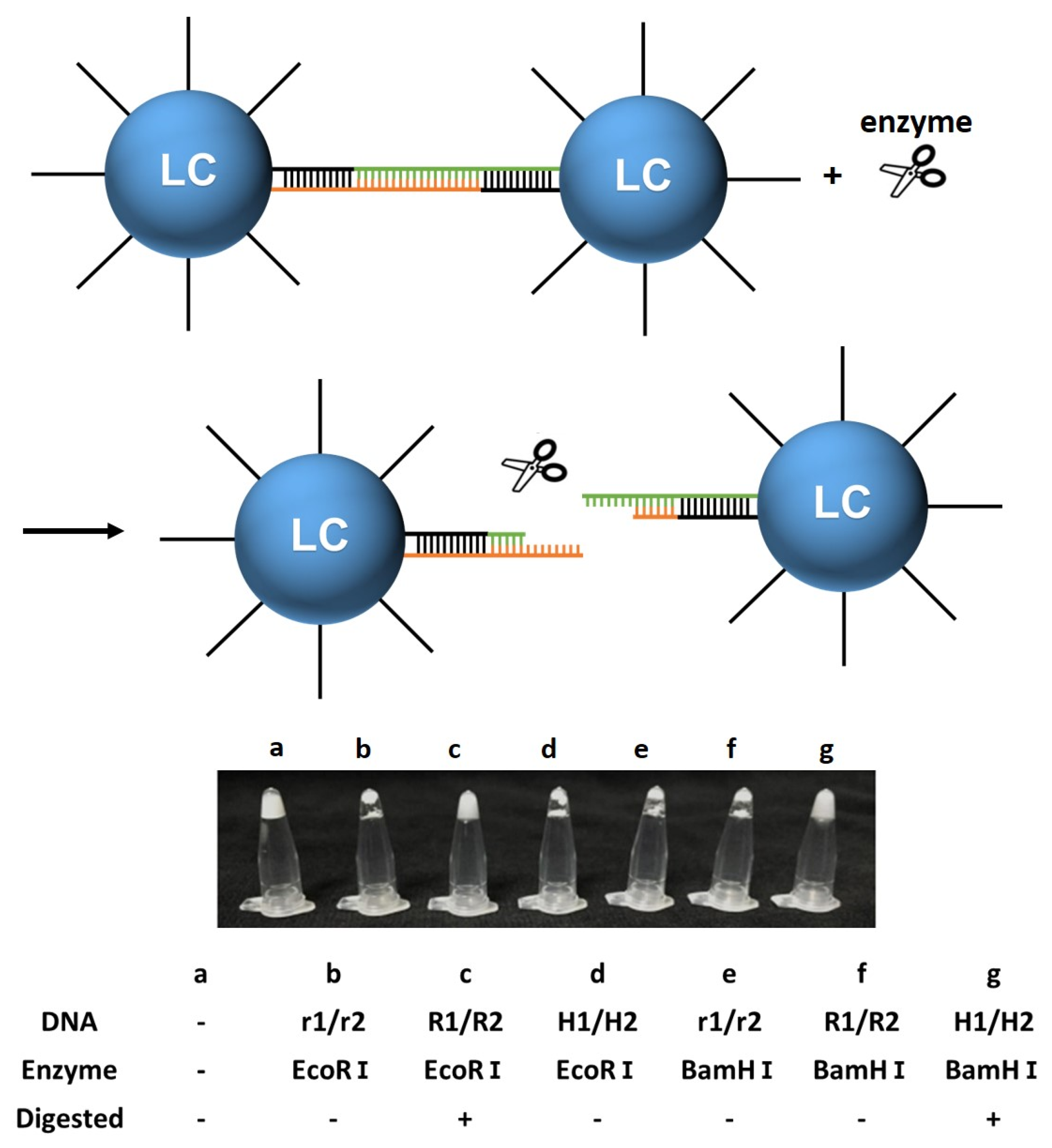
2.8. Enzyme Responsiveness of DNA-Modified LC Droplets
2.9. Preparation of Gold Substrate
2.10. Self-Assembly of 12-Mercaptododecanoic Acid Monolayer
2.11. Formation of Mixed SH-DNA/12-Mercaptododecanoic Acid Monolayer
2.12. DNA Hybridization on Substrate Surface
2.13. Thermal Responsiveness and Repeatability of LC Patterns
2.14. Characterization of LC Optical Signals
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation of DNA-Modified LC Droplets
3.2. The Responsiveness of LC Droplets
3.2.1. Hg2+ Responsiveness
3.2.2. Thrombin Responsiveness
3.2.3. Enzyme Responsiveness
3.3. Printing Patterns with DNA-Modified LC Droplets
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Whitesides, G.M.; Grzybowski, B. Self-assembly at all scales. Science 2002, 295, 2418–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loweth, C.J.; Caldwell, W.B.; Peng, X.; Alivisatos, A.P.; Schultz, P.G. DNA-based assembly of gold nanocrystals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 1808–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Huh, J.; Park, W.; Lee, L.P.; Kwon, Y.J.; Sim, S.J. Gold nanocrystals with DNA-directed morphologies. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Meulen, S.A.J.; Leunissen, M.E. Solid colloids with surface-mobile DNA linkers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 15129–15134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Ducrot, É.; Lee, M.-G.; Yi, G.-R.; Weck, M.; Pine, D.J. Synthetic strategies toward DNA-coated colloids that crystallize. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 10760–10766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Li, Z.; Ma, N. Next-generation DNA-functionalized quantum dots as biological sensors. ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 1705–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, P.H.; Michel, E.; Bauer, C.A.; Vanderet, S.; Hansen, D.; Roberts, B.K.; Calvez, A.; Crews, J.B.; Lau, K.O.; Wood, A.; et al. Selective, controllable, and reversible aggregation of polystyrene latex microspheres via DNA hybridization. Langmuir 2005, 21, 5562–5569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.S.; Wang, Y.; Pine, D.J.; Yi, G.-R. High-density PEO-b-DNA brushes on polymer particles for colloidal superstructures. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 8337–8344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leunissen, M.E.; Dreyfus, R.; Cheong, F.C.; Grier, D.G.; Sha, R.; Seeman, N.C.; Chaikin, P.M. Switchable self-protected attractions in DNA-functionalized colloids. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benkoski, J.J.; Höök, F. Lateral mobility of tethered vesicle−DNA assemblies. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 9773–9779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadorn, M.; Boenzli, E.; Hanczyc, M.M. Specific and reversible DNA-directed self-assembly of modular vesicle-droplet hybrid materials. Langmuir 2016, 32, 3561–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadorn, M.; Boenzli, E.; Sørensen, K.T.; De Lucrezia, D.; Hanczyc, M.M.; Yomo, T. Defined DNA-mediated assemblies of gene-expressing giant unilamellar vesicles. Langmuir 2013, 29, 15309–15319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadorn, M.; Eggenberger Hotz, P. DNA-mediated self-assembly of artificial vesicles. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Städler, B.; Falconnet, D.; Pfeiffer, I.; Höök, F.; Vörös, J. Micropatterning of DNA-tagged vesicles. Langmuir 2004, 20, 11348–11354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, D.; Bargteil, D.; Caciagli, A.; Burelbach, J.; Xing, Z.; Nunes, A.S.; Pinto, D.E.P.; Araújo, N.A.M.; Brujic, J.; Eiser, E. Kinetic control of the coverage of oil droplets by DNA-functionalized colloids. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; McMullen, A.; Pontani, L.-L.; He, X.; Sha, R.; Seeman, N.C.; Brujic, J.; Chaikin, P.M. Sequential self-assembly of DNA functionalized droplets. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadorn, M.; Boenzli, E.; Sørensen, K.T.; Fellermann, H.; Eggenberger Hotz, P.; Hanczyc, M.M. Specific and reversible DNA-directed self-assembly of oil-in-water emulsion droplets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 20320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartner, Z.J.; Bertozzi, C.R. Programmed assembly of 3-dimensional microtissues with defined cellular connectivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Fan, C. Shaping functional materials with DNA frameworks. Trends Chem. 2020, 2, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeman, N.C.; Sleiman, H.F. DNA nanotechnology. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 3, 17068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Pontani, L.-L.; Dreyfus, R.; Chaikin, P.; Brujic, J. Specificity, flexibility and valence of DNA bonds guide emulsion architecture. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 9816–9823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirkin, C.A.; Letsinger, R.L.; Mucic, R.C.; Storhoff, J.J. A DNA-based method for rationally assembling nanoparticles into macroscopic materials. Nature 1996, 382, 607–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caciagli, A.; Zupkauskas, M.; Levin, A.; Knowles, T.P.J.; Mugemana, C.; Bruns, N.; O’Neill, T.; Frith, W.J.; Eiser, E. DNA-coated functional oil droplets. Langmuir 2018, 34, 10073–10080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milam, V.T.; Hiddessen, A.L.; Crocker, J.C.; Graves, D.J.; Hammer, D.A. DNA-driven assembly of bidisperse, micron-sized colloids. Langmuir 2003, 19, 10317–10323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beales, P.A.; Vanderlick, T.K. Specific binding of different vesicle populations by the hybridization of membrane-anchored DNA. J. Phys. Chem. A 2007, 111, 12372–12380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Ding, Y.; Snyder, M.A.; Mittal, J. Effect of nonionic surfactant on association/dissociation transition of DNA-functionalized colloids. Langmuir 2016, 32, 10017–10025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tison, C.K.; Milam, V.T. Reversing DNA-mediated adhesion at a fixed temperature. Langmuir 2007, 23, 9728–9736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelstein, R.L.; Tamanaha, C.R.; Sheehan, P.E.; Miller, M.M.; Baselt, D.R.; Whitman, L.J.; Colton, R.J. The BARC biosensor applied to the detection of biological warfare agents. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2000, 14, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geerts, N.; Jahn, S.; Eiser, E. Direct observation of size fractionation during colloidal crystallization. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2010, 22, 104111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, D.M.; Heller, M.; Esener, S.C.; Schwartz, D.; Tu, G. Selective DNA attachment of micro- and nanoscale particles to substrates. J. Mat. Res. 2002, 17, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Eniola, A.O.; Graves, D.J.; Hammer, D.A. Specific adhesion of micron-sized colloids to surfaces mediated by hybridizing DNA chains. Langmuir 2003, 19, 6905–6911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattaccioli, J.; Baudry, J.; Henry, N.; Brochard-Wyart, F.; Bibette, J. Specific wetting probed with biomimetic emulsion droplets. Soft Matter 2008, 4, 2434–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saez, I.M.; Goodby, J.W. Supermolecular liquid crystals. In Liquid Crystalline Functional Assemblies and Their Supramolecular Structures; Kato, T., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; Volume 128, pp. 1–62. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, T.; Uchida, J.; Ichikawa, T.; Sakamoto, T. Functional liquid crystals towards the next generation of materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 4355–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Han, D.; Yang, J. Applications of microfluidics in liquid crystal-based biosensors. Biosensors 2021, 11, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockwood, N.A.; Gupta, J.K.; Abbott, N.L. Self-assembly of amphiphiles, polymers and proteins at interfaces between thermotropic liquid crystals and aqueous phases. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2008, 63, 255–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, A.M.; Abbott, N.L. Liquid crystalline materials for biological applications. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 746–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Manna, U.; Abbott, N.L.; Lynn, D.M. Covalent immobilization of caged liquid crystal microdroplets on surfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 26892–26903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlton, R.J.; Hunter, J.T.; Miller, D.S.; Abbasi, R.; Mushenheim, P.C.; Tan, L.N.; Abbott, N.L. Chemical and biological sensing using liquid crystals. Liq. Cryst. Rev. 2013, 1, 29–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, T.; Noel, A.; Chen, Y.C.; Liu, T. Applications of liquid crystals in biosensing. Soft Matter 2021, 17, 4675–4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Song, S.; Fan, C.; Wang, S. Optical detection of mercury(II) in aqueous solutions by using conjugated polymers and label-free oligonucleotides. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 1471–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famulok, M.; Mayer, G. Aptamer modules as sensors and detectors. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 1349–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Lan, T.; Lu, Y. Molecular engineering of functional nucleic acid nanomaterials toward in vivo applications. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, e1801158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.; Jo, H.; Oh, S.S. Detection and beyond: Challenges and advances in aptamer-based biosensors. Mater. Adv. 2020, 1, 2663–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wu, C.; Tan, H.; Wu, Y.; Liao, S.; Wu, Z.; Shen, G.; Yu, R. Label-free liquid crystal biosensor based on specific oligonucleotide probes for heavy metal ions. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Li, H.; Zhao, X.; Liao, W.; Zhang, C.X.; Yang, Z. A novel, label-free liquid crystal biosensor for Parkinson’s disease related alpha-synuclein. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 5441–5444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhbakhsh, Z.; Verdian, A.; Rajabzadeh, G. Design of a liquid crystal-based aptasensing platform for ultrasensitive detection of tetracycline. Talanta 2020, 206, 120246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, A.D.; Schwartz, D.K. DNA hybridization-induced reorientation of liquid crystal anchoring at the nematic liquid crystal/aqueous interface. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 8188–8194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, S.L.; Hartono, D.; Yang, K.-L. Self-assembly of cholesterol DNA at liquid crystal/aqueous interface and its application for DNA detection. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 153702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noonan, P.S.; Roberts, R.H.; Schwartz, D.K. Liquid crystal reorientation induced by aptamer conformational changes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 5183–5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noonan, P.S.; Mohan, P.; Goodwin, A.P.; Schwartz, D.K. DNA hybridization-mediated liposome fusion at the aqueous liquid crystal interface. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3206–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, D.; Yang, Z. The assembly of DNA amphiphiles at liquid crystal-aqueous interface. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, I.; Devi, M.; Sharma, D.; Nandi, R.; Pal, S.K. Liquid crystal based detection of Pb(II) ions using spinach RNA as recognition probe. Langmuir 2019, 35, 7816–7823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Yang, Z. Simple and rapid detection of ibuprofen-a typical pharmaceuticals and personal care products horizontal line by a liquid crystal aptasensor. Langmuir 2022, 38, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Fullhart, P.; Mirkin, C.A. Reversible and chemically programmable micelle assembly with DNA block-copolymer amphiphiles. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 1055–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Tian, Y.; Li, F.; Yu, Q.; Tan, S.F.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Z. Investigation of the assembly behavior of an amphiphilic lipopeptide at the liquid crystal-aqueous interface. Langmuir 2019, 35, 2490–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Whitesides, G.M. Features of gold having micrometer to centimeter dimensions can be formed through a combination of stamping with an elastomeric stamp and an alkanethiol ‘‘ink’’ followed by chemical etching. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1993, 63, 2002–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Feng, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, Z.; He, Y.-M.; Fan, Q.-H.; Liu, D. Amphiphilic DNA-dendron hybrid: A new building block for functional assemblies. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 7187–7190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Bukusoglu, E.; Abbott, N.L. A practical guide to the preparation of liquid crystal-templated microparticles. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, J.K.; Abbott, N.L. Principles for manipulation of the lateral organization of aqueous-soluble surface-active molecules at the liquid crystal−aqueous interface. Langmuir 2009, 25, 2026–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, I.-H.; Miller, D.S.; Bertics, P.J.; Murphy, C.J.; Pablo, J.J.d.; Abbott, N.L. Endotoxin-induced structural transformations in liquid crystalline droplets. Science 2011, 332, 1297–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McUmber, A.C.; Noonan, P.S.; Schwartz, D.K. Surfactant–DNA interactions at the liquid crystal-aqueous interface. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 4335–4342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, E.M.; Lippard, S.J. Tools and tactics for the optical detection of mercuric ion. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 3443–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoko, M.; Humika, T.; Mitsuru, T.; Hiroshi, Y.; Shuji, O.; Megumi, K.; Yoshiyuki, T.; Yoshinori, K.; Ryuichi, S.; Takashi, F.; et al. MercuryII-mediated formation of thymine−HgII−thymine base pairs in DNA duplexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2172–2173. [Google Scholar]
- Bock, L.C.; Griffin, L.C.; Latham, J.A.; Vermaas, E.H.; Toole, J.J. Selection of single-stranded DNA molecules that bind and inhibit human thrombin. Nature 1992, 355, 564–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasset, D.M.; Kubik, M.F.; Steiner, W. Oligonucleotide inhibitors of human thrombin that bind distinct epitopes. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 272, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Cheng, E.; Yang, Y.; Chen, P.; Zhang, T.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Z.; Liu, D. Self-assembled DNA hydrogels with designable thermal and enzymatic responsiveness. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 1117–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catherine, L.I.; Peter, D.N.; Brooks, J.E. Regulation of the BamHI restriction-modification system by a small intergenic open reading frame, bamHIC, in both Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 1992, 174, 7194–7201. [Google Scholar]
- Albert, J.; Jurgen, A.; Heiner, W.; Gunter, M.; Pingoud, A. Substrate-assisted catalysis in the cleavage of DNA by the EcoRI and EcoRV restriction enzymes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 8499–8503. [Google Scholar]
- Kinsinger, M.I.; Buck, M.E.; Abbott, N.L.; Lynn, D.M. Immobilization of polymer-decorated liquid crystal droplets on chemically tailored surfaces. Langmuir 2010, 26, 10234–10242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-G.; Munir, S.; Park, S.-Y. Cholesteric liquid crystal droplets for biosensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 26407–26417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Savagatrup, S.; Kaplonek, P.; Seeberger, P.H.; Swager, T.M. Janus emulsions for the detection of bacteria. ACS Cent. Sci. 2017, 3, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Liang, X.; Nandi, R.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J.; Dong, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhong, Z.; et al. DNA-Modified Liquid Crystal Droplets. Biosensors 2022, 12, 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12050275
Yang X, Liang X, Nandi R, Tian Y, Zhang Y, Li Y, Zhou J, Dong Y, Liu D, Zhong Z, et al. DNA-Modified Liquid Crystal Droplets. Biosensors. 2022; 12(5):275. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12050275
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xiuxiu, Xiao Liang, Rajib Nandi, Yi Tian, Yiyang Zhang, Yan Li, Jingsheng Zhou, Yuanchen Dong, Dongsheng Liu, Zhengwei Zhong, and et al. 2022. "DNA-Modified Liquid Crystal Droplets" Biosensors 12, no. 5: 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12050275
APA StyleYang, X., Liang, X., Nandi, R., Tian, Y., Zhang, Y., Li, Y., Zhou, J., Dong, Y., Liu, D., Zhong, Z., & Yang, Z. (2022). DNA-Modified Liquid Crystal Droplets. Biosensors, 12(5), 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12050275





