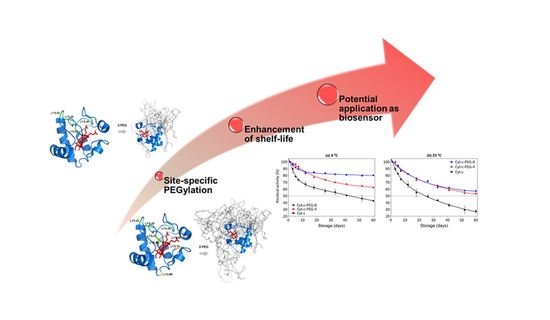
Lysine-PEGylated Cytochrome C with Enhanced Shelf-Life Stability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cyt-c PEGylation Reaction
2.3. In Silico Studies: Molecular Visualization of Cyt-c PEGylation
2.4. Purification of PEGylated Conjugates
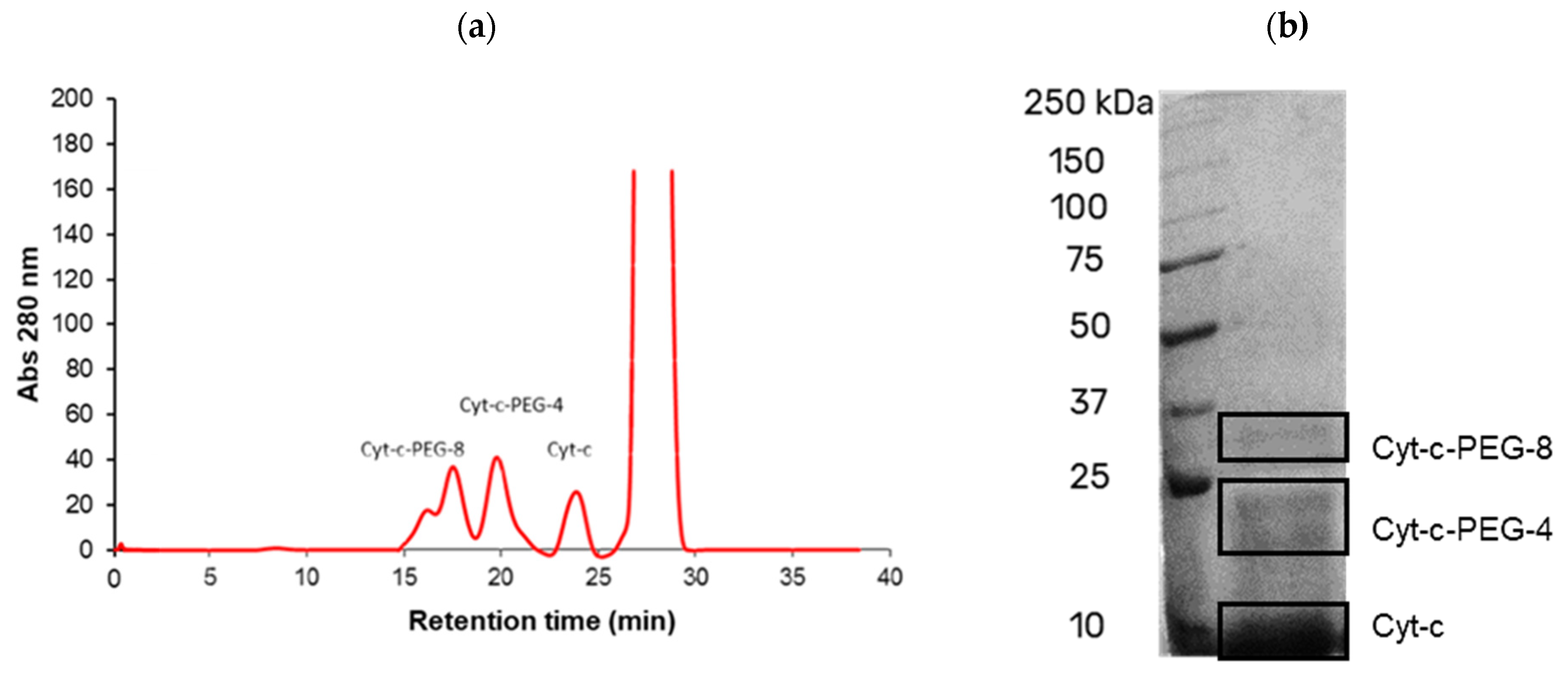
2.5. Determination of PEGylation Degree of Cyt-c Conjugates by SEC
2.6. Gel Electrophoresis
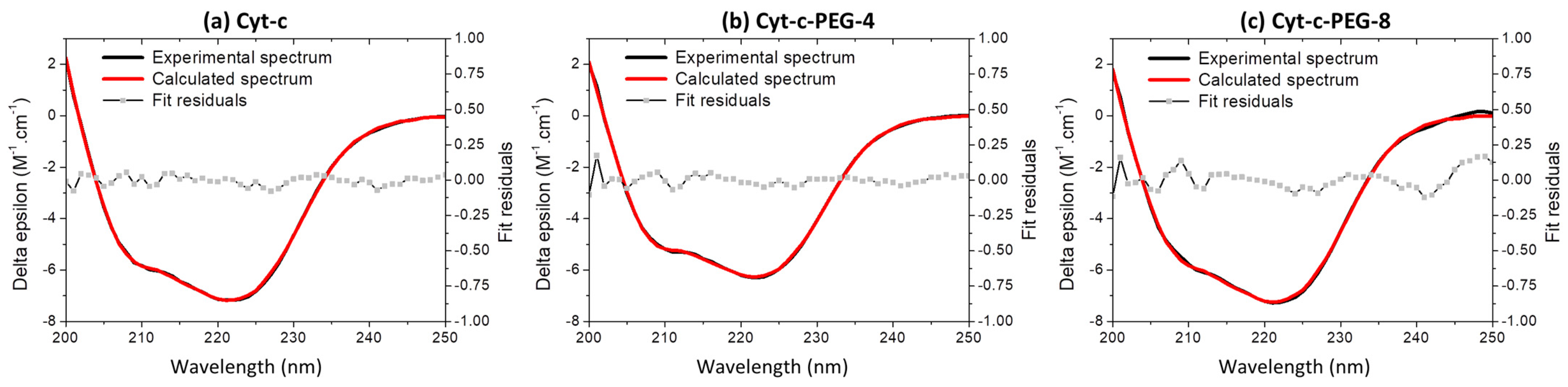
2.7. Circular Dichroism (CD) Spectroscopy
2.8. Determination of Cyt-c Long-Term Stability
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Cyt-c PEGylation
3.2. Formatting of Mathematical Components
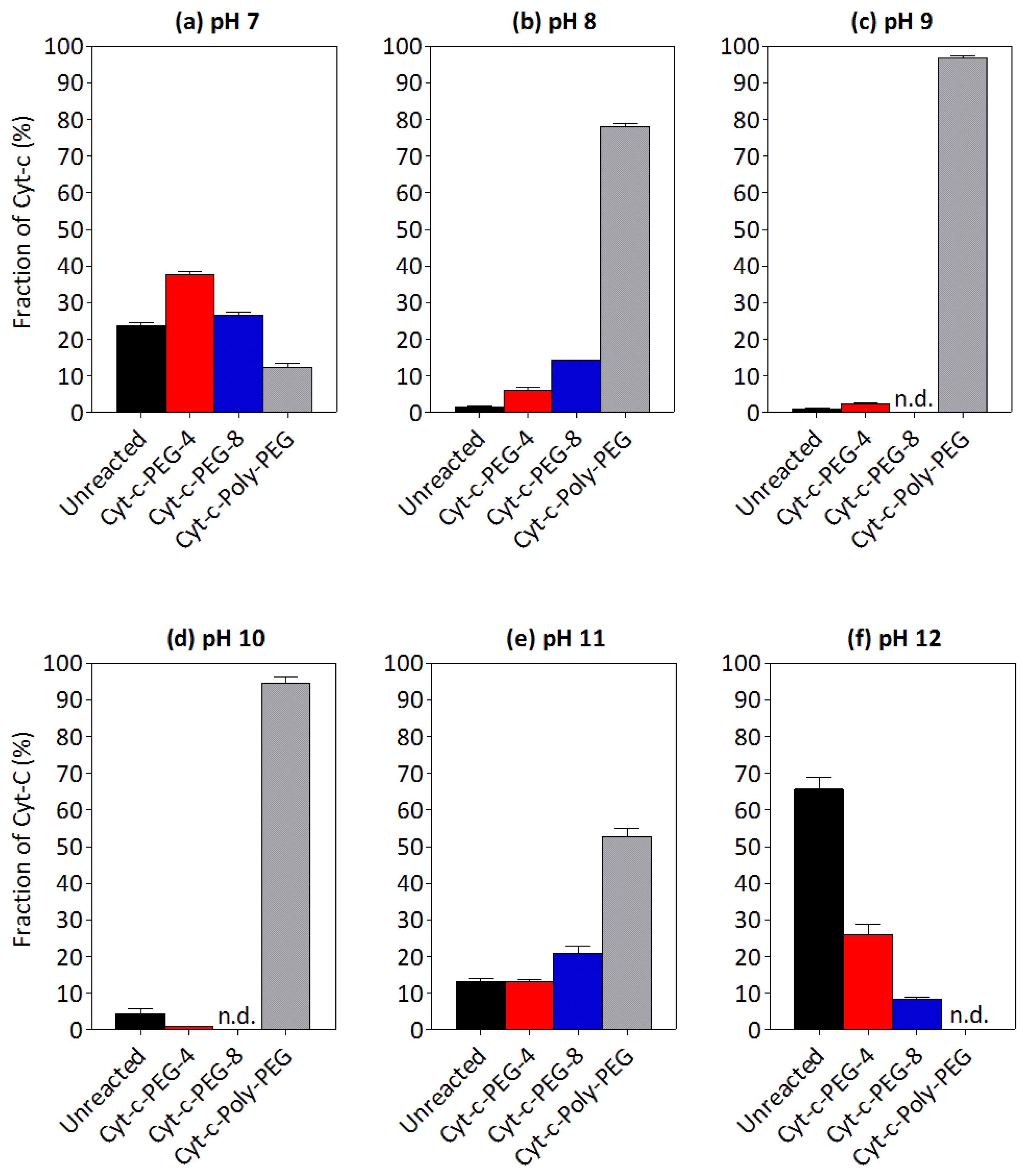
3.3. Effect of pH on the PEGylation of Cyt-c
3.4. Effect of mPEG Derivative Concentration on the Cyt-c PEGylation Reaction
3.5. Effect of Reaction Time on the PEGylation of Cyt-c
3.6. Effect of PEGylation on the Cyt-c Structure
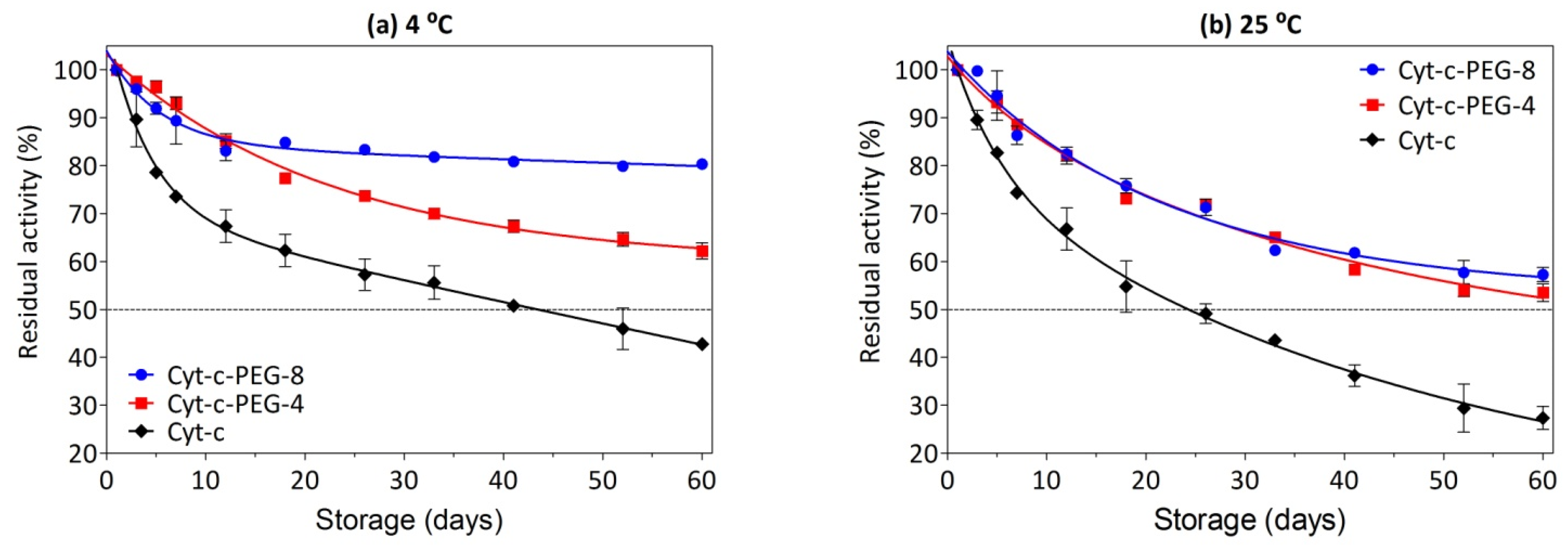
3.7. Effect of PEGylation on Long-Term Stability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vazquez-Duhalt, R. Cytochrome c as a biocatalyst. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 1999, 7, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago-Rodríguez, L.; Méndez, J.; Flores-Fernandez, G.M.; Pagán, M.; Rodríguez-Martínez, J.A.; Cabrera, C.R.; Griebenow, K. Enhanced stability of a nanostructured cytochrome c biosensor by PEGylation. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2011, 663, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Arellano, H.; Buenrostro-Gonzalez, E.; Vazquez-Duhalt, R. Biocatalytic transformation of petroporphyrins by chemical modified cytochrome c. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2004, 85, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Luo, Z.; Liu, J.; Ding, X.; Li, J.; Cai, K. Cytochrome c end-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles as redox-responsive drug delivery vehicles for liver tumor-targeted triplex therapy in vitro and in vivo. J. Control. Release 2014, 192, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Cruz, M.; Figueroa, C.M.; González-Robles, T.; Delgado, Y.; Molina, A.; Méndez, J.; Morales, M.; Griebenow, K. Activation of caspase-dependent apoptosis by intracellular delivery of cytochrome c-based nanoparticles. J. Nanobiotechnology 2014, 12, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Macone, A.; Masciarelli, S.; Palombarini, F.; Quaglio, D.; Boffi, A.; Trabuco, M.C.; Baiocco, P.; Fazi, F.; Bonamore, A. Ferritin nanovehicle for targeted delivery of cytochrome C to cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Figueroa, C.M.; Suarez, B.N.; Molino, A.; Fernandez, J.C.; Torres, Z.; Griebenow, K. Smart release nano-formulation of cytochrome c and hyaluronic acid induces apoptosis in cancer cells. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 427. [Google Scholar]
- Saxena, M.; Delgado, Y.; Sharma, R.K.; Sharma, S.; de León Guzmán, S.L.P.; Tinoco, A.D.; Griebenow, K. Inducing cell death in vitro in cancer cells by targeted delivery of cytochrome c via a transferrin conjugate. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tothill, I.E. Biosensors developments and potential applications in the agricultural diagnosis sector. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2001, 30, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasut, G.; Veronese, F.M. State of the art in PEGylation: The great versatility achieved after forty years of research. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veronese, F.M. Peptide and protein PEGylation: A review of problems and solutions. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfister, D.; Morbidelli, M. Process for protein PEGylation. J. Control. Release 2014, 180, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, J.H.P.M.; Torres-Obreque, K.M.; Meneguetti, G.P.; Amaro, B.P.; Rangel-Yagui, C.O. Protein PEGylation for the design of biobetters: From reaction to purification processes. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 54, e01009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, H.; Muneyasu, N.Y.; Ohno, K. Conformation and redox reaction of poly(ethylene oxide)-modified horseradish peroxidase in poly(ethylene oxide) oligomers. Chem. Lett. 1997, 26, 381–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, H.; Yamaguchi, N. Redox reaction of poly(ethylene oxide)-modified hemoglobin in poly(ethylene oxide) oligomers at 120 °C. Bioconjugate Chem. 1994, 5, 379–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawahara, N.Y.; Ohkubo, W.; Ohno, H. Effect of cast solvent on the electron transfer reaction for poly(ethylene oxide)-modified myoglobin on the electrode in poly(ethylene oxide) oligomers. Bioconjugate Chem. 1997, 8, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mabrouk, P.A. Effect of PEGylation on the structure and function of horse cytochrome c. Bioconjugate Chem. 1994, 5, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Q.; He, T.; Wang, J.W. PEGylation of cytochrome c at the level of lysine residues mediated by a microbial transglutaminase. Biotechnol. Lett. 2016, 38, 1121–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, D.S.; Mero, A.; Pasut, G. Chemical and enzymatic site specific PEGylation of hGH. Bioconjugate Chem. 2013, 24, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanocs, Succinimidyl PEG NHS, mPEG-NHS(SC). 2017. Available online: http://www.nanocs.net/mPEG-SC-5k-1g.htm (accessed on 30 December 2021).
- Bushnell, G.W.; Louie, G.v.; Brayer, G.D. High-resolution three-dimensional structure of horse heart cytochrome c. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 214, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.H.P.M.; Carretero, G.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Rangel-Yagui, C.O.; Ventura, S.P.M. Multistep purification of cytochrome c PEGylated forms using polymer-based aqueous biphasic systems. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 5800–5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayyab, S.; Qamar, S.; Islam, M. Size exclusion chromatography and size exclusion HPLC of proteins. Biochem. Educ. 1991, 19, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.H.; Jeong, M.S.; Choi, S.Y.; Kang, J.H. Peroxidase activity of cytochrome c. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2004, 25, 1889–1892. [Google Scholar]
- González-Valdez, J.; Rito-Palomares, M.; Benavides, J. Advances and trends in the design, analysis, and characterization of polymer-protein conjugates for “PEGylaided” bioprocesses. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 2225–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginn, C.; Khalili, H.; Lever, R.; Brocchini, S. PEGylation and its impact on the design of new protein-based medicines. Future Med. Chem. 2014, 6, 1829–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.J.; Bentley, M.D.; Harris, J.M. Chemistry for peptide and protein PEGylation. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.M.; Chess, R.B. Effect of PEGylation on pharmaceuticals. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, T.; Esfandiary, R.; Gandhi, R. The effect of PEGylation on the stability of small therapeutic proteins. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2011, 16, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiser, B.; Dismer, F.; Hubbuch, J. Optimization of random PEGylation reactions by means of high throughput screening. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2014, 111, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.P.; Lin, S.C. Effect of PEGylation on the activity and stability of horseradish peroxidase and L-N-carbamoylase in aqueous phases. Process Biochem. 2015, 50, 1372–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wylie, D.C.; Voloch, M.; Lee, S.; Liu, Y.H.; Cannon-Carlson, S.; Cutler, C.; Pramanik, B. Carboxyalkylated histidine is a pH-dependent product of PEGylation with SC-PEG. Pharm. Res. 2001, 18, 1354–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, J.H.P.M.; Carretero, G.; Ventura, S.P.M.; Converti, A.; Rangel-Yagui, C.O. PEGylation as an efficient tool to enhance cytochrome c thermostability: A kinetic and thermodynamic study. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2019, 7, 4432–4439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micsonai, A.; Wien, F.; Bulyáki, É.; Kun, J.; Moussong, É.; Lee, Y.H.; Goto, Y.; Réfrégiers, M.; Kardos, J. BeStSel: A web server for accurate protein secondary structure prediction and fold recognition from the circular dichroism spectra. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W315–W322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaul, R.; Mattiasson, B. Improving the shelf life of enzymes by storage under anhydrous apolar solvent. Biotechnol. Tech. 1993, 7, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frokjaer, S.; Otzen, D.E. Protein drug stability: A formulation challenge. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myszka, D.G. Improving biosensor analysis. J. Mol. Recognit. 1999, 12, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhao, F.; Xu, Z.; Dong, S. The direct electron transfer of glucose oxidase and glucose biosensor based on carbon nanotubes/chitosan matrix. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 21, 984–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, M.; Mondal, D.; Pereira, M.M.; Freire, M.G.; Venkatesu, P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Long-term protein packaging in cholinium-based ionic liquids: Improved catalytic activity and enhanced stability of cytochrome c against multiple stresses. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 4900–4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, D.K.; Jena, S.; Tulsiyan, K.D.; Dutta, J.; Chakrabarty, S.; Biswal, H.S. Amino-acid-based ionic liquids for the improvement in stability and activity of cytochrome c: A combined experimental and molecular dynamics study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 10100–10109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharmoria, P.; Kumar, A. Unusually high thermal stability and peroxidase activity of cytochrome c in ionic liquid colloidal formulation. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, U.K.; Kumari, M.; Khan, S.H.; Bohidar, H.B.; Patel, R. Mechanism and dynamics of long-term stability of cytochrome c conferred by long-chain imidazolium ionic liquids at low concentration. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 803–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou, A.A.; Efstathiadou, E.; Patila, M.; Polydera, A.C.; Stamatis, H. Deep eutectic solvents as media for peroxidation reactions catalyzed by heme-dependent biocatalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 5145–5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Residue | Theoretical pKa | Location/Secondary Structure |
|---|---|---|
| N terminal | 11.8 | N terminal moiety |
| Lys5 | >12.0 | alpha-helix |
| Lys7 | 10.9 | alpha-helix |
| Lys8 | 9.7 | alpha-helix |
| Lys13 | 10.8 | alpha-helix |
| Lys22 | 9.9 | Ω loop |
| Lys25 | 11.2 | Ω loop |
| Lys27 | 10.9 | Ω loop |
| Lys39 | 10.3 | Ω loop |
| Lys53 | 10.7 | alpha-helix |
| Lys55 | 10.4 | alpha-helix transition |
| Lys60 | 10.4 | alpha-helix transition |
| Lys72 | 8.6 | alpha-helix |
| Lys73 | 11.0 | alpha-helix |
| Lys79 | 10.4 | Ω loop |
| Lys86 | 10.3 | Ω loop |
| Lys87 | 10.7 | alpha-helix transition |
| Lys88 | 10.4 | alpha-helix |
| Lys99 | >12.0 | alpha-helix |
| Lys100 | 10.7 | alpha-helix |
| Cyt-c Form | Alpha | Beta | Random |
|---|---|---|---|
| Native | 41 | 22 | 37 |
| Cyt-c-PEG-4 | 41 | 19 | 40 |
| Cyt-c-PEG-8 | 38 | 26 | 36 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santos, J.H.P.M.; Feitosa, V.A.; Meneguetti, G.P.; Carretero, G.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Ventura, S.P.M.; Rangel-Yagui, C.O. Lysine-PEGylated Cytochrome C with Enhanced Shelf-Life Stability. Biosensors 2022, 12, 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12020094
Santos JHPM, Feitosa VA, Meneguetti GP, Carretero G, Coutinho JAP, Ventura SPM, Rangel-Yagui CO. Lysine-PEGylated Cytochrome C with Enhanced Shelf-Life Stability. Biosensors. 2022; 12(2):94. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12020094
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantos, João H. P. M., Valker A. Feitosa, Giovanna P. Meneguetti, Gustavo Carretero, João A. P. Coutinho, Sónia P. M. Ventura, and Carlota O. Rangel-Yagui. 2022. "Lysine-PEGylated Cytochrome C with Enhanced Shelf-Life Stability" Biosensors 12, no. 2: 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12020094
APA StyleSantos, J. H. P. M., Feitosa, V. A., Meneguetti, G. P., Carretero, G., Coutinho, J. A. P., Ventura, S. P. M., & Rangel-Yagui, C. O. (2022). Lysine-PEGylated Cytochrome C with Enhanced Shelf-Life Stability. Biosensors, 12(2), 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12020094