Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Pentachloronitrobenzene by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Combined with Molecularly Imprinted Polymers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instruments and Reagents
2.2. Synthesis of Oil-Soluble Silver Nanoparticles
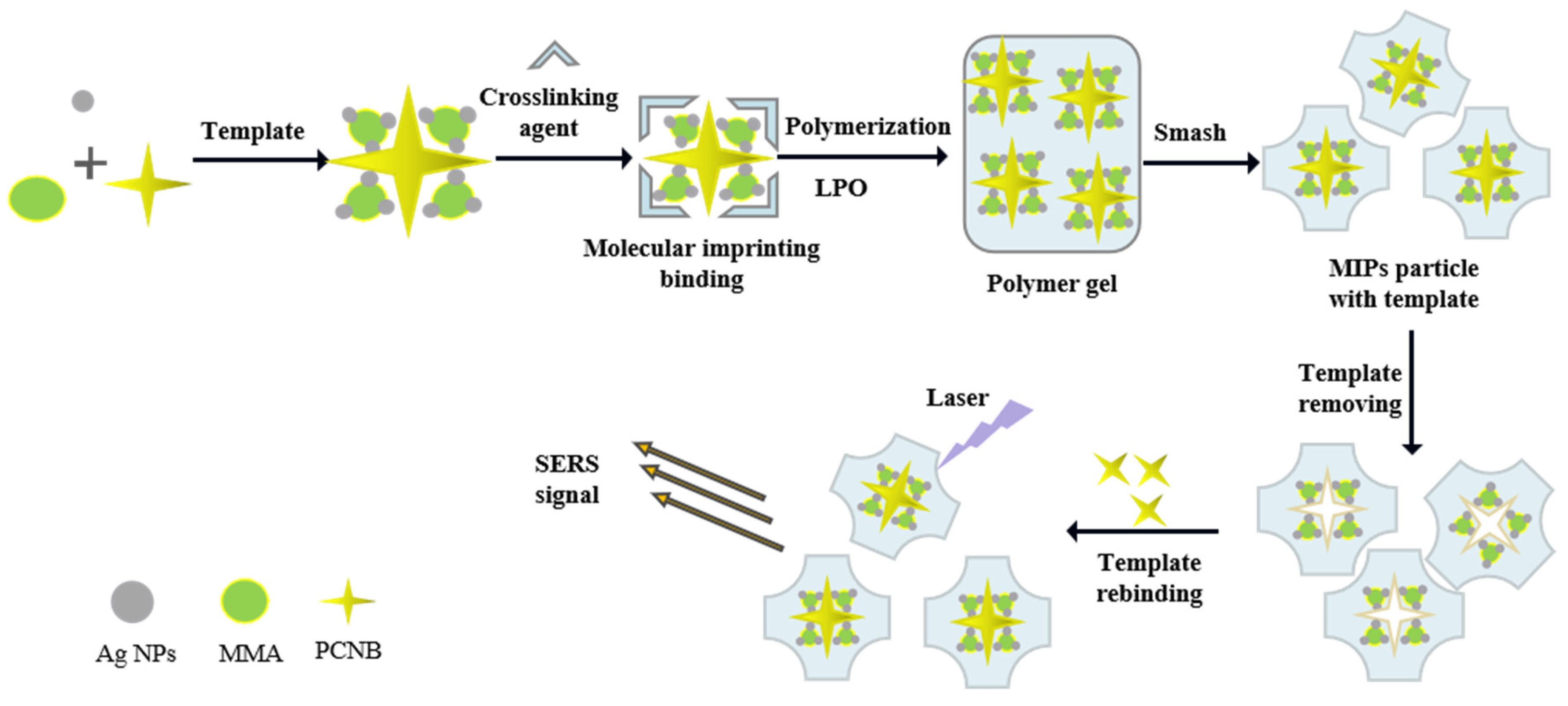
2.3. Preparation of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPS) and Non-Printed Polymers (NIPS) Containing Oil-Soluble Silver Nanoparticles
2.4. Detection of PCNB Using Oil-Soluble Ag NPs-Embedded MIPs as a Substrate
2.5. Application of the Oil-Soluble Ag NPs-Embedded MIPs in Food Samples
2.6. Determination of PCNB in Rice by GC-MS
3. Results and Discussion
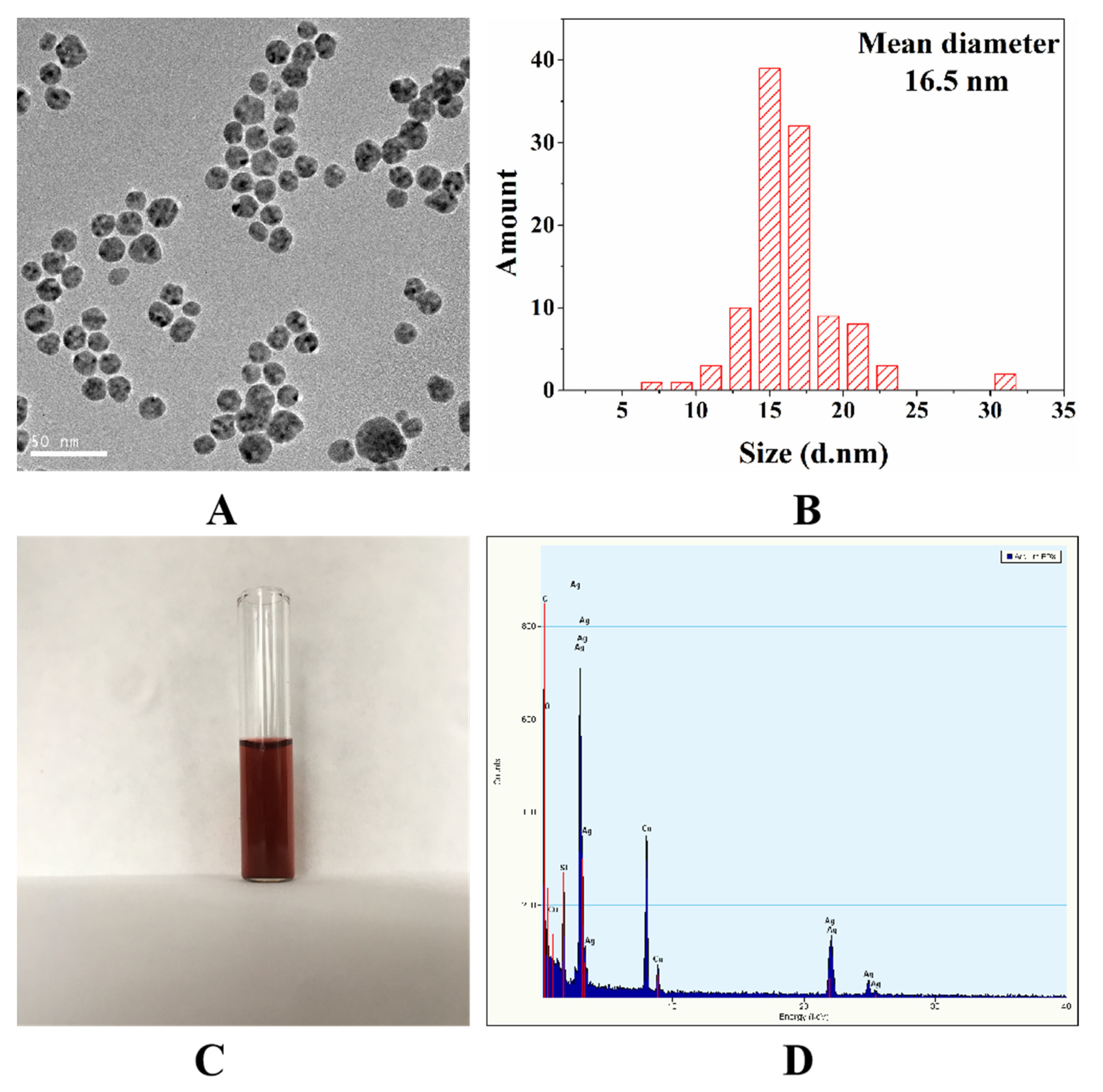
3.1. Characterization of the Oil-Soluble Ag NPs
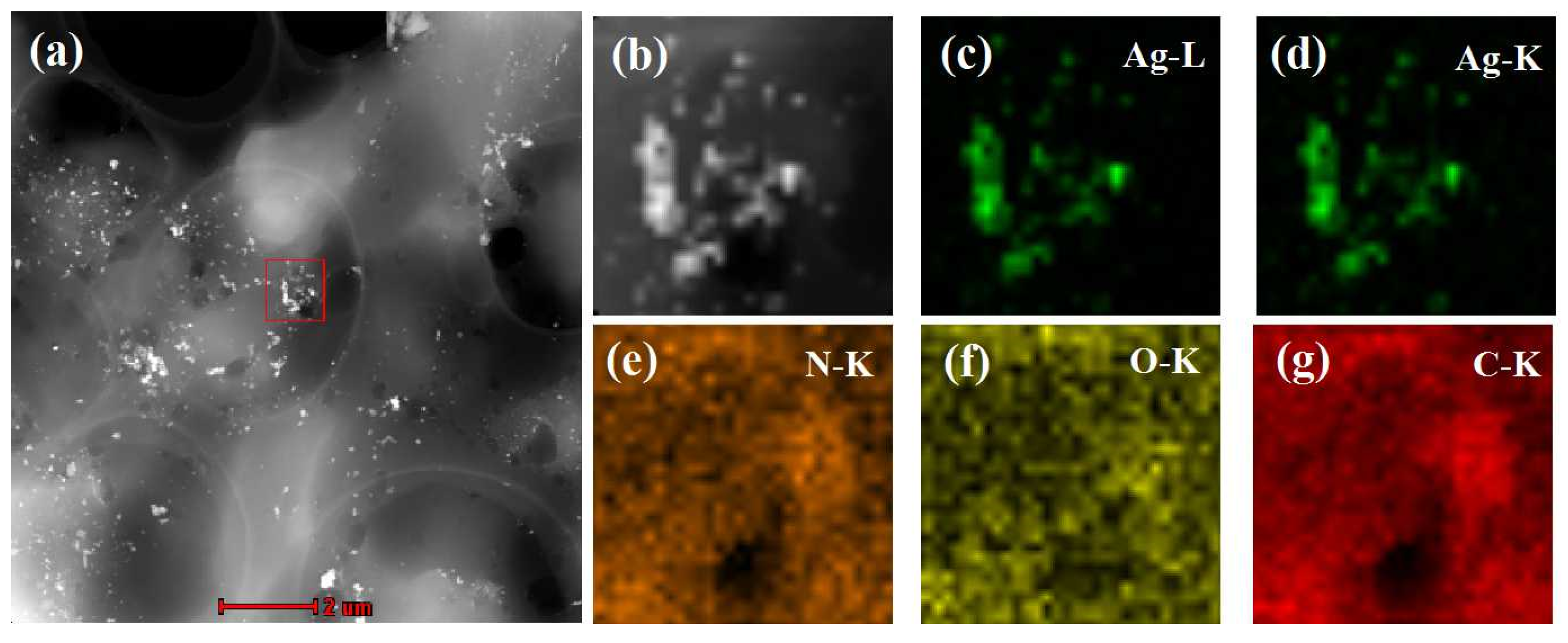
3.2. Characterization of the Oil-Soluble Ag NPs in MIPs
3.3. SERS Selectivity of the Oil-Soluble Ag NPs-Embedded MIPs
3.4. SERS Specificity of the Oil-Soluble Ag NPs-Embedded MIPs
3.5. Detection of PCNB Spiked Using Oil-Soluble Ag NPs-Embedded MIPs as a Substrate
3.6. Detection of PCNB Spiked in a Rice Using the MIPs as a Substrate
3.7. Determination of PCNB in Rice by GC-MS
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arora, P.K.; Bae, H. Toxicity and microbial degradation of nitrobenzene, monochloronitrobenzenes, polynitrobenzenes, and pentachloronitrobenzene. J. Chem. 2014, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Xu, G.; Yu, R.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y. Uptake and accumulation of pentachloronitrobenzene in pak choi and the human health risk. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 42, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, P.K.; Sasikala, C.; Ramana, C.V. Degradation of chlorinated nitroaromatic compounds. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 93, 2265–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, G.F. Handbook of environmental fate and exposure data for organic chemicals, volume 1. Large production and priority pollutants. J. Hazard. Mater. 1991, 26, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.K.; Kim, J.E.; Kwon, G.S. Isolation and identification of a pentachloronitrobenzene (PCNB) degrading bacterium Alcaligenes xylosoxidans PCNB-2 from agricultural soil. J. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 165–168. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.l.; Wang, C.X.; Liu, F.; Ren, X.Y. New Requirements for National Standard for Food Safety (GB 2763—2019) on Spinach and Leaf Vegetables. Biol. Disaster Sci. 2020, 43, 125–130. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.; Zhao, L.; Liu, F. Determination of chlorothalonil residue in cabbage by a modified quechers-based extraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 656–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, A.; Navickiene, S. Mspd procedure for determination of carbofuran, pyrimethanil and tetraconazole residues in banana by GC-MS. Chromatographia 2009, 70, 1265–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balinova, A.; Mladenova, R.; Shtereva, D. Solid-phase extraction on sorbents of different retention mechanisms followed by determination by gas chromatography-mass spectrometric and gas chromatography-electron capture detection of pesticide residues in crops. J. Chromatogr. 2007, 1150, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, L.; Dong, F.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Yao, J.; Zhang, C. Determination of Pentachloronitrobenzene and Its Metabolites in Ginseng by Matrix Solid-Phase Dispersion and GC-MS-MS. Chromatographia 2009, 69, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, W.X.; Shuang, L.; Yue, R.L.; Zhong, B.L. Pesticide Residue Rapid Extraction from Ginseng Tea Using a Modified Luke Method for GC-MS. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peruga, A.; Barreda, M.; Hernández, F. A robust GC-MS-MS method for the determination of chlorothalonil in fruits and vegetables. Food Addit. Contam. 2013, 30, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishida, K.; Furusawa, N. Matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction and high-performance liquid chromatographic determination of residual sulfonamides in chicken. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 937, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, H.S.; Sim, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Park, J.; Chan, L.; Kim, M.K. Simultaneous determination of sodium iron chlorophyllin and sodium copper chlorophyllin in food using high-performance liquid chromatography and ultra-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mecker, L.C.; Tyner, K.M.; Kauffman, J.F.; Arzhantsev, S.; Mans, D.J.; Gryniewicz-Ruzicka, C.M. Selective melamine detection in multiple sample matrices with a portable Raman instrument using surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy-active gold nanoparticles. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 733, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neng, J.; Tan, J.Y.; Jia, K.; Sun, P.L. A Fast and Cost-Effective Detection of Melamine by Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Using a Novel Hydrogen Bonding-Assisted Supramolecular Matrix and Gold-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles. Appl. Sci. 2017, 5, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, X.; Liu, Y. Gold nanoparticles enhanced SERS aptasensor for the simultaneous detection of Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureu. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Kim, K.; Choi, N.; Wang, X.; Lee, J.; Jeon, J.H. Highly sensitive detection of high-risk bacterial pathogens using SERS-based lateral flow assay strips. Sens. Actuators B. Chem. 2018, 270, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Lu, Z.; Tan, X.; Xiao, X.; Wang, P.; Wu, L.; Han, H. ultrasensitive detection of aflatoxin B1 by SERS aptasensor based on exonuclease-assisted recycling amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 97, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.; Glamuzina, B.; Pozniak, I.; Weber, K.; Pinzaru, S.C. Amnesic shellfish poisoning biotoxin detection in seawater using pure or amino-functionalized Ag nanoparticles and SERS. Talanta 2014, 130, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubackova, J.; Fabriciova, G.; Miskovsky, P.; Jancura, D.; Sanchez-Cortes, S. Sensitive surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) detection of organochlorine pesticides by alkyl dithiol-functionalized metal nanoparticles-induced plasmonic hot spots. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.; Guo, X.; Li, X.; Ye, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ying, W.; Yang, H. Template-free synthesis of SERS-active gold nanopopcorn for rapid detection of chlorpyrifos residues. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 241, 1008–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, Q.; Mehedi Hassan, M.; Chen, X.; Ouyang, Q.; Guo, Z.; Zhao, J. A magnetite/PMAA nanospheres-targeting SERS aptasensor for tetracycline sensing using mercapto molecules embedded core/shell nanoparticles for signal amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.C.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, W.C.; Chen, Z.Y.; Du, P.; Zhao, Y.M.; Xu, J. Quantitative and sensitive detection of prohibited fish drugs by surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Chin. Phys. B 2018, 27, 640–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.M.; Emory, S.R. Probing Single Molecules and Single Nanoparticles by Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Science 1997, 275, 1102–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neng, J.; Harpster, M.H.; Zhang, H.; Wilson, W.C.; Johnson, P.A. A versatile SERS-based immunoassay for immunoglobulin detection using antigen-coated gold nanoparticles and malachite green-conjugated protein A/G. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neng, J.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, P.L. Application of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy in fast detection of toxic and harmful substances in food. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 167, 112480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, N.M.; Lindner, W. Chiral recognition applications of molecularly imprinted polymers: A critical review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 389, 377–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, M.; Aboufazeli, F.; Zhad, H.; Sadeghi, O.; Najafi, E. Determination of sulfonamides in chicken meat by magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer coupled to HPLC-UV. Food Anal. Methods 2014, 7, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, T.; Ganjali, M.R.; Zare, M.; Norouzi, P. Selective determination of chloramphenicol at trace level in milk samples by the electrode modified with molecularly imprinted polymer. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 1108–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Lu, X. Rapid detection of Melamine in tap water and milk using conjugated “One-Step” molecularly imprinted polymers-surface enhanced Raman spectroscopic sensor. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, N1272–N1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Sun, X.; Li, Y. Surface enhanced Raman scattering effects of silver colloids with different shapes. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2005, 109, 12544–12548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.B.; Fan, J.; Huang, T.H. PTV-GC-MS/MS determined pesticide residues in vegetables combined with AOC-6000 on-line SPE. In Proceedings of the Chinese Mass Spectrometry Conference (CMSC), Guangdong, China, 9–12 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Yang, S.; Xu, T.; Song, Y.; Zhang, X. Microdroplet-captured tapes for rapid sampling and SERS detection of food contaminants. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 152, 112013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Mei, H.; Dai, X.H.; Yang, X.F.; Yi, S. A multi-residue method for the determination of 124 pesticides in rice by modified QuEChERS extraction and gas chromatography—Tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2012, 138, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Domínguez, G.; Plaza-Bolaos, P.; Romero-González, R.; Garrido-Frenich, A. Analytical approaches for the determination of pesticide residues in nutraceutical products and related matrices by chromatographic techniques coupled to mass spectrometry. Talanta 2014, 118, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, W.X.; Shuang, L. Molecularly imprinted solid—Phase extraction method for the gas chromatographic analysis of organochlorine fungicides in ginseng. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 1393–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hui, J.L.; Jie, S.W.; Chen, C.; Wen, F.S.; Wen, S.Z. Simultaneous determination of 74 pesticide residues in Panax notoginseng by QuEChERS coupled with gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2021, 10, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Method | Linear Range | LOD (mg/kg) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Auto-SPE GC-MS | 0.1–2.0 mg/L | 0.001 | 83.6–96.5 | 5.5–7.1 |
| HPLC | 0.1–50 mg/L | 0.02 | 83.2–94.2 | Less than 5.5 |
| MSPD-GC | 0.005–0.5 μg/mL | 0.002 | 89.4–102.4 | 3.7–7.4 |
| QuEChERS-GC | 0.02–0.3 mg/kg | 0.002 | 86.3–105.4 | Less than 4.15 |
| SERS-MIPs | 0.005–0.15 μg/mL | 0.005 | 94.4–103.3 | 4.6–7.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neng, J.; Liao, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, K. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Pentachloronitrobenzene by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Combined with Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Biosensors 2022, 12, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12020052
Neng J, Liao C, Wang Y, Wang Y, Yang K. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Pentachloronitrobenzene by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Combined with Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Biosensors. 2022; 12(2):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12020052
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeng, Jing, Caiping Liao, Yazhi Wang, Yan Wang, and Kai Yang. 2022. "Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Pentachloronitrobenzene by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Combined with Molecularly Imprinted Polymers" Biosensors 12, no. 2: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12020052
APA StyleNeng, J., Liao, C., Wang, Y., Wang, Y., & Yang, K. (2022). Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Pentachloronitrobenzene by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Combined with Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Biosensors, 12(2), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12020052





