REASSURED Multiplex Diagnostics: A Critical Review and Forecast
Abstract
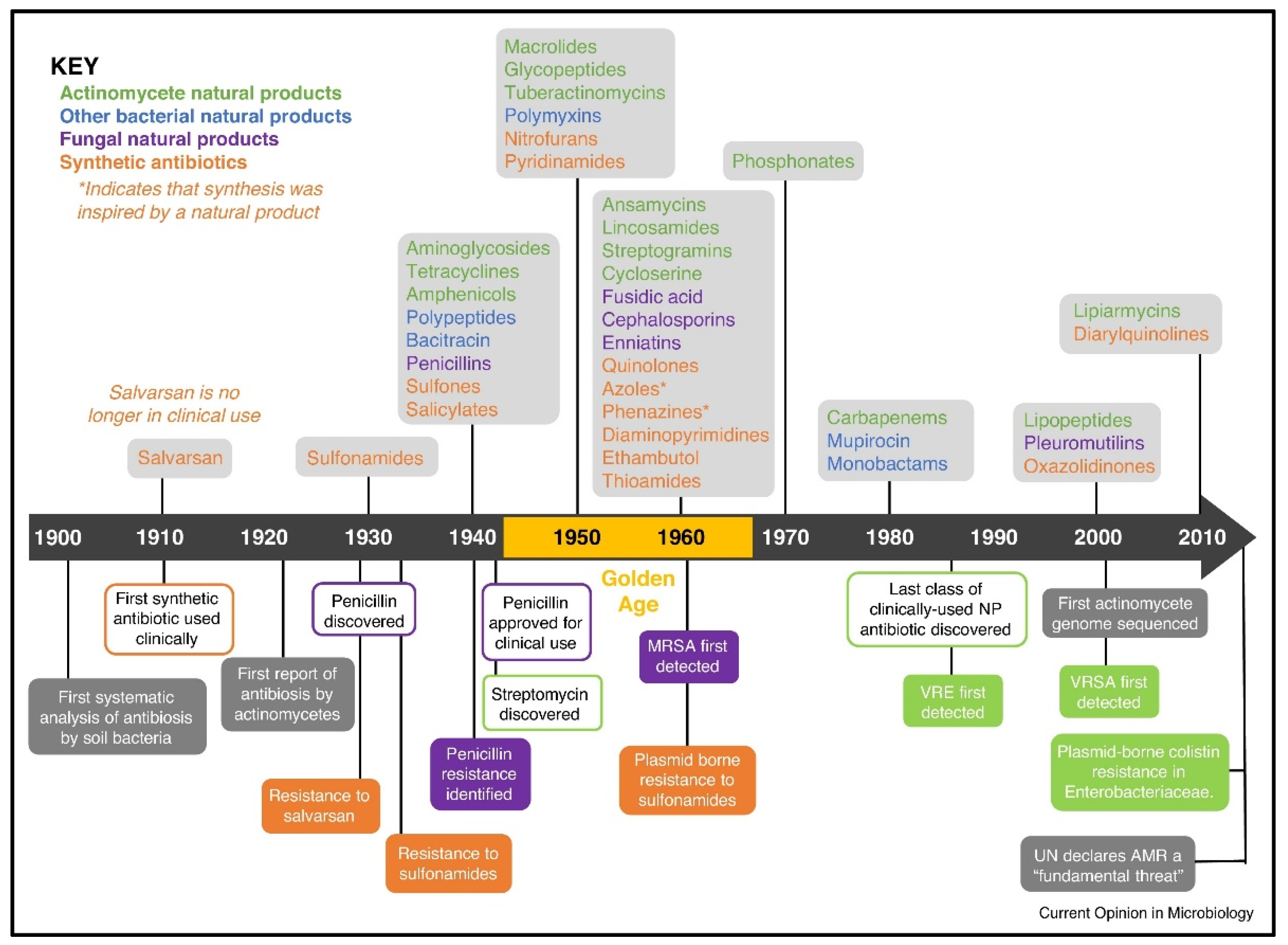
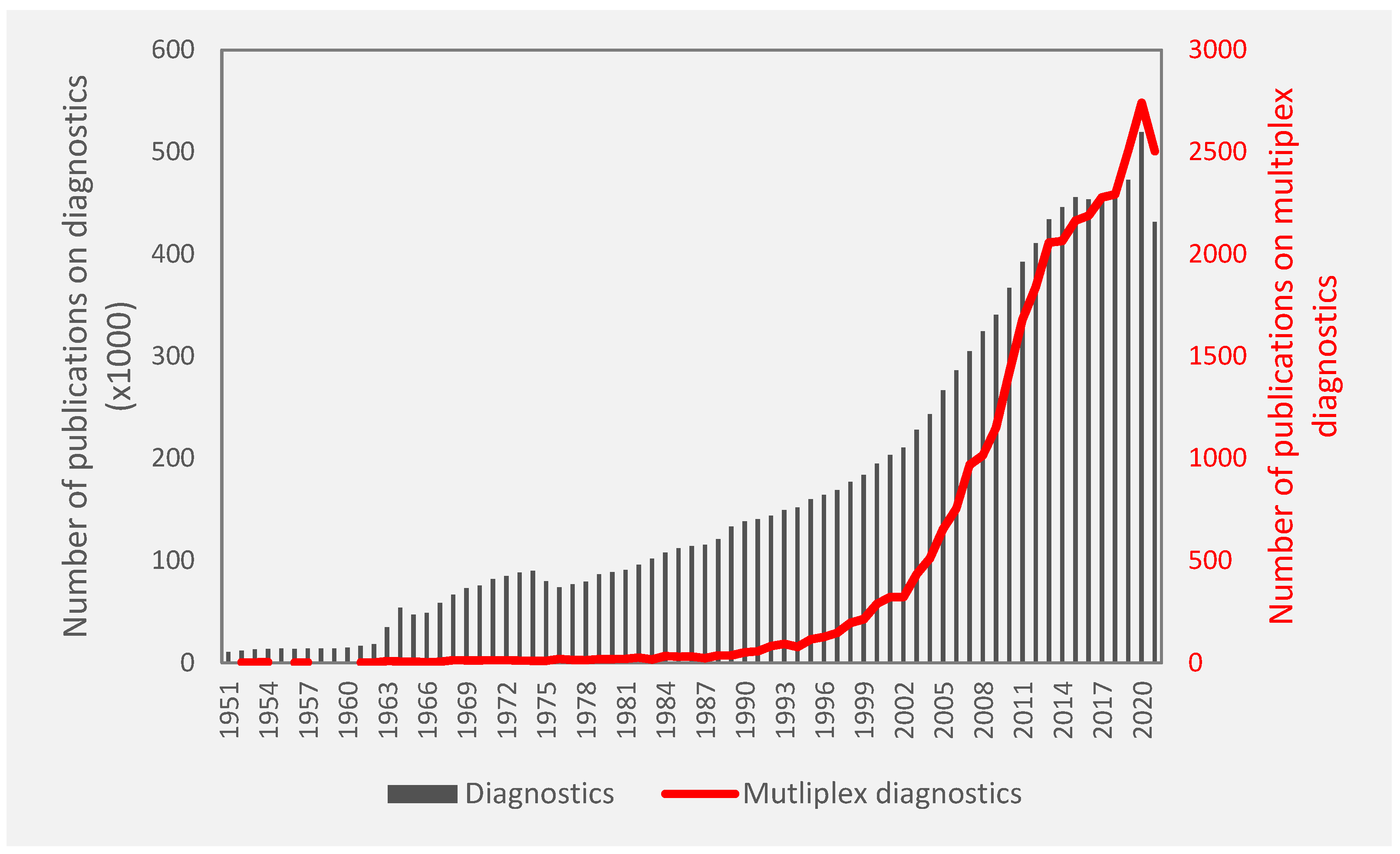
1. Introduction
1.1. Multiplexed Diagnostics
1.2. REASSURED Diagnostics
2. Clinically Available Multiplexed Diagnostics
2.1. Proteins and Peptides
2.2. Nucleic Acids
2.3. Small Molecules, Lipids, and Other Biomarkers
3. Multiplexed Diagnostics in Research or Academia
3.1. Proteins and Peptides
3.2. Nucleic Acids
4. Next Generation Multiplex Diagnostics
5. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patrinos, G.P.; Ansorge, W.; Danielson, P.B. (Eds.) Molecular Diagnostics, 3rd ed.; Elsevier/Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mayeux, R. Biomarkers: Potential uses and limitations. Neurotherapeutics 2004, 1, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimse, S.B.; Sonawane, M.D.; Song, K.-S.; Kim, T. Biomarker detection technologies and future directions. Analyst 2016, 141, 740–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, P.D.; Song, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhang, S.; Sesso, H.D.; Mora, S.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Rexrode, K.E.; Moorthy, M.V.; Li, C.; et al. Lipid biomarkers and long-term risk of cancer in the Women’s Health Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 1397–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Lewin Group, Inc. The Value of Diagnostics Innovation, Adoption and Diffusion into Health Care. July 2005. Available online: https://www.lewin.com/content/dam/Lewin/Resources/Site_Sections/Publications/ValueofDiagnostics.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2022).
- Mugambi, M.L.; Peter, T.; Martins, S.F.; Giachetti, C. How to implement new diagnostic products in low-resource settings: An end-to-end framework. BMJ Glob. Health 2018, 3, e000914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roundtable on Translating Genomic-Based Research for Health and Board on Health Sciences Policy; Institute of Medicine. Genome-Based Diagnostics: Demonstrating Clinical Utility in Oncology: Workshop Summary. Washington (DC). National Academies Press (US). 27 December 2013. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK195902/ (accessed on 10 February 2022).
- Kettler, H.; White, K.; Hawkes, S. Mapping the Landscape of Diagnostics for Sexually Transmitted Infections: Key Findings and Recommendations. World Health Organization. 2004. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/68990 (accessed on 10 February 2022).
- Peeling, R.W.; Holmes, K.K.; Mabey, D.; Ronald, A. Rapid tests for sexually transmitted infections (STIs): The way forward. Sex. Transm. Infect. 2006, 82 (Suppl. S5), v1–v6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, A.; Iqbal, N.; Feroz, S.; Ali, A.; Ehsan, M.A.; Khan, S.A.; Rehman, A. Rapid antibody diagnostics for SARS-CoV-2 adaptive immune response. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 4019–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ding, L.; Huang, X.; Xiong, Y. Point-of-care COVID-19 diagnostics powered by lateral flow assay. Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 145, 116452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, C.A.; Garamani, N.; Lee, A.S.; Tung, J.K.; Sahoo, M.K.; Huang, C.; Stevens, B.; Zehnder, J.; Pinsky, B.A. Comparison of the Accula SARS-CoV-2 Test with a Laboratory-Developed Assay for Detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in Clinical Nasopharyngeal Specimens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e01072-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoads, D.D.; Cherian, S.S.; Roman, K.; Stempak, L.M.; Schmotzer, C.L.; Sadri, N. Comparison of Abbott ID Now, DiaSorin Simplexa, and CDC FDA Emergency Use Authorization Methods for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 from Nasopharyngeal and Nasal Swabs from Individuals Diagnosed with COVID-19. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e00760-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinidad, C.V.; Tetlow, A.L.; Bantis, L.E.; Godwin, A.K. Reducing ovarian cancer mortality through early detection: Approaches using circulating biomarkers. Cancer Prev. Res. 2020, 13, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, V.; Aggarwal, A. Early cancer diagnosis: Reaching targets across whole populations amidst setbacks. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 1181–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, W.H.; Ye, W.; Griffin, S.J.; Simmons, R.K.; Davies, M.J.; Khunti, K.; Rutten, G.E.; Sandbaek, A.; Lauritzen, T.; Borch-Johnsen, K.; et al. Early detection and treatment of type 2 diabetes reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality: A simulation of the results of the anglo-danish-dutch study of intensive treatment in people with screen-detected diabetes in primary care (ADDITION-Europe). Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capotosto, L.; Massoni, F.; de Sio, S.; Ricci, S.; Vitarelli, A. Early Diagnosis of Cardiovascular Diseases in Workers: Role of Standard and Advanced Echocardiography. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, e7354691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamcova, M.; Šimko, F. Multiplex biomarker approach to cardiovascular diseases. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2018, 39, 1068–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witte, M.H.; Dellinger, M.T.; Papendieck, C.M.; Boccardo, F. Overlapping biomarkers, pathways, processes and syndromes in lymphatic development, growth and neoplasia. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2012, 29, 707–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Mohan, A.; Guleria, R. Biomarkers in cancer screening, research and detection: Present and future: A review. Biomarkers 2006, 11, 385–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, N.; Dressen, K.; Schroeder, L.; Debald, M.; Schildberg, F.A.; Walgenbach-Bruenagel, G.; Hettwer, K.; Uhlig, S.; Kuhn, W.; Hartmann, G.; et al. Diagnostic relevance of a novel multiplex immunoassay panel in breast cancer. Tumour Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317711381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, D.; Davis, M.M. New approaches to understanding the immune response to vaccination and infection. Vaccine 2015, 33, 5271–5281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, H.A. Cytokine Multiplex Analysis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 511, 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.A.A.; Amini, N.; Yang, L.; Paluh, J.L.; Wang, J. Multiplexed analysis of neural cytokine signaling by a novel neural cell-cell interaction microchip. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 3980–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.W.; Tambyah, P.A.; Hui, D.S.C. Emergence of a novel coronavirus causing respiratory illness from Wuhan, China. J. Infect. 2020, 80, 350–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorramdelazad, H.; Kazemi, M.H.; Najafi, A.; Keykhaee, M.; Emameh, R.Z.; Falak, R. Immunopathological similarities between COVID-19 and influenza: Investigating the consequences of Co-infection. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 152, 104554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadashi, M.; Khaleghnejad, S.; Abedi Elkhichi, P.; Goudarzi, M.; Goudarzi, H.; Taghavi, A.; Vaezjalali, M.; Hajikhani, B. COVID-19 and Influenza Co-infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 681469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, Z.; Islam, M.A.; Aleem, M.A.; Mah-E-Muneer, S.; Ahmmed, M.K.; Ghosh, P.K.; Rahman, M.; Rahman, M.Z.; Sumiya, M.K.; Rahman, M.M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 and influenza virus coinfection among patients with severe acute respiratory infection during the first wave of COVID-19 pandemic in Bangladesh: A hospital-based descriptive study. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e053768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, E.J.; Wahome, E.; Mwangome, M.; Thiong’o, A.N.; Okuku, H.S.; Price, M.A.; Wamuyu, L.; Macharia, M.; McClelland, R.S.; Graham, S.M. Most adults seek urgent healthcare when acquiring HIV-1 and are frequently treated for malaria in coastal Kenya. AIDS 2011, 25, 1219–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Multani, A.; Allard, L.S.; Wangjam, T.; Sica, R.A.; Epstein, D.J.; Rezvani, A.R.; Ho, D.Y. Missed diagnosis and misdiagnosis of infectious diseases in hematopoietic cell transplant recipients: An autopsy study. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 3602–3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin-Reisman, I.; Brauner, A.; Ronin, I.; Balaban, N.Q. Epistasis between antibiotic tolerance, persistence, and resistance mutations. PNAS 2019, 116, 14734–14739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, M.I.; Truman, A.W.; Wilkinson, B. Antibiotics: Past, present and future. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2019, 51, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, J. Tackling Drug-Resistant Infections Globally: Final Report and Recommendations. May 2016. Available online: https://amr-review.org/sites/default/files/160525_Final%20paper_with%20cover.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2022).
- Nanayakkara, A.K.; Boucher, H.W.; Fowler, V.G., Jr.; Jezek, A.; Outterson, K.; Greenberg, D.E. Antibiotic resistance in the patient with cancer: Escalating challenges and paths forward. A Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 488–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urdea, M.; Penny, L.A.; Olmsted, S.S.; Giovanni, M.Y.; Kaspar, P.; Shepherd, A.; Wilson, P.; Dahl, C.A.; Buchsbaum, S.; Moeller, G.; et al. Requirements for high impact diagnostics in the developing world. Nature 2006, 444, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Roberts, D.; Wood, K.E.; Light, B.; Parrillo, J.E.; Sharma, S.; Suppes, R.; Feinstein, D.; Zanotti, S.; Taiberg, L.; et al. Duration of hypotension before initiation of effective antimicrobial therapy is the critical determinant of survival in human septic shock. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 34, 1589–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westphal, G.A.; Koenig, Á.; Caldeira Filho, M.; Feijó, J.; de Oliveira, L.T.; Nunes, F.; Fujiwara, K.; Martins, S.F.; Gonçalves, A.R.R. Reduced mortality after the implementation of a protocol for the early detection of severe sepsis. J. Crit. Care 2011, 26, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiwanitkit, V.; Err, H. “Syndromic approach” to diagnosis and treatment of critical tropical infections. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 18, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djomand, G.; Gao, H.; Singa, B.; Hornston, S.; Bennett, E.; Odek, J.; McClelland, R.S.; John-Stewart, G.; Bock, N. Genital infections and syndromic diagnosis among HIV-infected women in HIV care programmes in Kenya. Int. J. STD AIDS 2016, 27, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Land, K.J.; Boeras, D.I.; Chen, X.-S.; Ramsay, A.R.; Peeling, R.W. REASSURED diagnostics to inform disease control strategies, strengthen health systems and improve patient outcomes. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudi, T.; Pourhassan-Moghaddam, M.; Shirdel, B.; Baradaran, B.; Morales-Narváez, E.; Golmohammadi, H. On-Site Detection of Carcinoembryonic Antigen in Human Serum. Biosensors 2021, 11, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruppert, C.; Phogat, N.; Laufer, S.; Kohl, M.; Deigner, H.-P. A smartphone readout system for gold nanoparticle-based lateral flow assays: Application to monitoring of digoxigenin. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saisin, L.; Amarit, R.; Somboonkaew, A.; Gajanandana, O.; Himananto, O.; Sutapun, B. Significant Sensitivity Improvement for Camera-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay Readers. Sensors 2018, 18, 4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, L.J. Verigene® gram-positive blood culture nucleic acid test: An in vitro diagnostic assay for identification of gram-positive bacteria associated with bloodstream infections and bacterial resistance markers. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2013, 17, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Jiang, L.; Huang, G.; Pu, H.; Gong, B.; Lin, H.; Ma, S.; Chen, X.; Long, B.; Si, G.; et al. Comparison of different samples for 2019 novel coronavirus detection by nucleic acid amplification tests. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 93, 264–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.V.; Nguyen, V.D.; Nguyen, H.Q.; Chau, T.H.T.; Lee, E.Y.; Seo, T.S. Nucleic acid diagnostics on the total integrated lab-on-a-disc for point-of-care testing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 141, 111466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Nardo, F.; Chiarello, M.; Cavalera, S.; Baggiani, C.; Anfossi, L. Ten years of lateral flow immunoassay technique applications: Trends, challenges and future perspectives. Sensors 2021, 21, 5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, M.; Ziora, Z.M.; Simon, G.P.; Batchelor, W. ASSURED-compliant point-of-care diagnostics for the detection of human viral infections. Rev. Med. Virol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dincer, C.; Bruch, R.; Kling, A.; Dittrich, P.S.; Urban, G.A. Multiplexed Point-of-Care Testing—xPOCT. Trends Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 728–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Huh, H.J.; Park, E.; Chung, D.-R.; Kang, M. Multiplex Molecular Point-of-Care Test for Syndromic Infectious Diseases. BioChip J. 2021, 15, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusling, J.F. Multiplexed Electrochemical Protein Detection and Translation to Personalized Cancer Diagnostics. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 5304–5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, A.C.; Souza, N.C.S.; Figueiredo, W.M.; Costa, A.A.; Inenami, M.; da Silva, R.M.; Levi, J.E.; Pannuti, C.S.; Romano, C.M. Cross reactivity of commercial anti-dengue immunoassays in patients with acute Zika virus infection. J. Med. Virol. 2017, 89, 1477–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Yang, M.; Wu, J.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, X. A self-contained chemiluminescent lateral flow assay for point-of-care testing. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 9132–9137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J. An optimized colorimetric readout method for lateral flow immunoassays. Sensors 2018, 18, 4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesinos, I.; Gruson, D.; Kabamba, B.; Dahma, H.; Van den Wijngaert, S.; Reza, S.; Carbone, V.; Vandenberg, O.; Gulbis, B.; Wolff, F.; et al. Evaluation of two automated and three rapid lateral flow immunoassays for the detection of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 128, 104413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koczula, K.M.; Gallotta, A. Lateral flow assays. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanafiah, K.M.; Arifin, N.; Bustami, Y.; Noordin, R.; Garcia, M.; Anderson, D. Development of multiplexed infectious disease lateral flow assays: Challenges and opportunities. Diagnostics 2017, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souf, S. Recent advances in diagnostic testing for viral infections. Biosci. Horiz. 2016, 9, hzw010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, B.; Cortazar, B.; Tseng, D.; Ozkan, H.; Feng, S.; Wei, Q.; Chan, R.Y.L.; Burbano, J.; Farooqui, Q.; Lewinski, M.; et al. Cellphone-Based Hand-Held Microplate Reader for Point-of-Care Testing of Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 7857–7866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhdanov, A.; Keefe, J.; Franco-Waite, L.; Konnaiyan, K.R.; Pyayt, A. Mobile phone based ELISA (MELISA). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 103, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BinaxNowTM Influenza A&B Card 2. Available online: https://www.globalpointofcare.abbott/en/product-details/binaxnow-influenza-a-and-b-2.html (accessed on 5 January 2022).
- BD VeritorTM Plus System for Flu A + B. Available online: https://bdveritor.bd.com/en-us/main/rapid-antigen-testing/flu-a-b (accessed on 5 January 2022).
- Acucy® Influenza A&B. Available online: https://sekisuidiagnostics.com/products-all/acucy-influenza-ab/ (accessed on 5 January 2022).
- Sofia SARS Antigen FIA. Available online: https://www.quidel.com/immunoassays/rapid-sars-tests/sofia-sars-antigen-fia (accessed on 5 January 2022).
- Kermekchiev, M.B.; Kirilova, L.I.; Vail, E.E.; Barnes, W.M. Mutants of Taq DNA polymerase resistant to PCR inhibitors allow DNA amplification from whole blood and crude soil samples. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elnifro, E.M.; Ashshi, A.M.; Cooper, R.J.; Klapper, P.E. Multiplex PCR: Optimization and application in diagnostic virology. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henegariu, O.; Heerema, N.A.; Dlouhy, S.R.; Vance, G.H.; Vogt, P.H. Multiplex PCR: Critical parameters and step-by-step protocol. Biotechniques 1997, 23, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daher, R.K.; Stewart, G.; Boissinot, M.; Bergeron, M.G. Recombinase polymerase amplification for diagnostic applications. Clin. Chem. 2016, 62, 947–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notomi, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francois, P.; Tangomo, M.; Hibbs, J.; Bonetti, E.J.; Boehme, C.C.; Notomi, T.; Perkins, M.D.; Schrenzel, J. Robustness of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction for diagnostic applications. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 62, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moonga, L.C.; Hayashida, K.; Kawai, N.; Nakao, R.; Sugimoto, C.; Namangala, B.; Yamagishi, J. Development of a Multiplex Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) Method for Simultaneous Detection of Spotted Fever Group Rickettsiae and Malaria Parasites by Dipstick DNA Chromatography. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Actionable. Accessible. Affordable. SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Rapid PCR Testing. Available online: https://www.mesabiotech.com/ (accessed on 5 January 2022).
- 510(k) Substantial Equivalence Determinatin Decision Summary: Accula Flu A/Flu B Test. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/reviews/K171641.pdf (accessed on 5 January 2022).
- Visby Medical Sexual Health Test. Available online: https://www.visbymedical.com/sexual-health-test/ (accessed on 5 January 2022).
- Visby Medical COVID-19 Test Fast, Accurate, and Actionable PC. Available online: https://www.visbymedical.com/covid-19-test/ (accessed on 5 January 2022).
- Mobile qPCR Thermocyclers. Available online: https://info.biomeme.com/mobile-qpcr-thermocyclers (accessed on 5 January 2022).
- CardioChek PA Analyzer. Available online: https://ptsdiagnostics.com/cardiochek-pa-analyzer/ (accessed on 5 January 2022).
- Curo L7. Available online: https://curofit.com/s/lipidocare-l7-cholesterol-test-kit/ (accessed on 5 January 2022).
- Vashist, S.K.; Luppa, P.B.; Yeo, L.Y.; Ozcan, A.; Luong, J.H.T. Emerging technologies for next-generation point-of-care testing. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 692–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.; Wang, R.; Bever, C.R.S.; Xing, S.; Hammock, B.D.; Pan, T. Smartphone-interfaced lab-on-a-chip devices for field-deployable enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Biomicrofluidics 2014, 8, 064101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Aggarwal, K.; Vinitha, T.U.; Nguyen, T.; Han, J.; Ahn, C.H. A new microchannel capillary flow assay (MCFA) platform with lyophilized chemiluminescence reagents for a smartphone-based POCT detecting malaria. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2020, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, B.; Zhang, C.; Xing, D. A handheld flow genetic analysis system (FGAS): Towards rapid, sensitive, quantitative and multiplex molecular diagnosis at the point-of-care level. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 2597–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rombach, M.; Hin, S.; Specht, M.; Johannsen, B.; Lüddecke, J.; Paust, N.; Zengerle, R.; Roux, L.; Sutcliffe, T.; Peham, J.R.; et al. RespiDisk: A point-of-care platform for fully automated detection of respiratory tract infection pathogens in clinical samples. Analyst 2020, 145, 7040–7047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.Q.; Bui, H.K.; Phan, V.M.; Seo, T.S. An internet of things-based point-of-care device for direct reverse-transcription-loop mediated isothermal amplification to identify SARS-CoV-2. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 195, 113655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, D.J.; Cary, R.B. Lateral flow microarrays: A novel platform for rapid nucleic acid detection based on miniaturized lateral flow chromatography. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-L.; Huang, Y.-J.; Teerapanich, P.; Leïchlé, T.; Chou, C.-F. Multiplexed immunosensing and kinetics monitoring in nanofluidic devices with highly enhanced target capture efficiency. Biomicrofluidics 2016, 10, 034114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Fang, X.; Kong, J. All-in-one microfluidic nucleic acid diagnosis system for multiplex detection of sexually transmitted pathogens directly from genitourinary secretions. Talanta 2021, 221, 121462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortelmans, T.; Kazazis, D.; Padeste, C.; Berger, P.; Li, X.; Ekinci, Y. A nanofluidic device for rapid and multiplexed SARS-CoV-2 serological antibody detection. Res. Square 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, E.-C.; Fu, C.-C.; Hu, L.; Thakur, R.; Feng, J.; Lee, L.P. Self-powered integrated microfluidic point-of-care low-cost enabling (SIMPLE) chip. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1501645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuypers, J.; Jerome, K.R. Applications of Digital PCR for Clinical Microbiology. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 1621–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Liu, C.; Tong, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, K. Principles of digital PCR and its applications in current obstetrical and gynecological diseases. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 7209–7222. [Google Scholar]
- Badran, S.; Chen, M.; Coia, J.E. Multiplex Droplet Digital Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay for Rapid Molecular Detection of Pathogens in Patients With Sepsis: Protocol for an Assay Development Study. JMIR Res. Protoc. 2021, 10, e33746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouters, Y.; Dalloyaux, D.; Christenhusz, A.; Roelofs, H.M.; Wertheim, H.F.; Bleeker-Rovers, C.P.; Te Morsche, R.H.; Wanten, G.J. Droplet digital polymerase chain reaction for rapid broad-spectrum detection of bloodstream infections. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 13, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Jiang, Y.; Cao, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, N.; Shi, D. Droplet digital PCR as an emerging tool in detecting pathogens nucleic acids in infectious diseases. Clin. Chim. Acta 2021, 517, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheit, T.; Landi, S.; Gemignani, F.; Snijders, P.J.; Vaccarella, S.; Franceschi, S.; Canzian, F.; Tommasino, M. Development of a sensitive and specific assay combining multiplex PCR and DNA microarray primer extension to detect high-risk mucosal human papillomavirus types. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 2025–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tian, M.; Tian, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, H.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Xue, F.; Jin, N. Microarray Multiplex Assay for the Simultaneous Detection and Discrimination of Influenza A and Influenza B Viruses. Indian J. Microbiol. 2014, 54, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Selck, D.A.; Karymov, M.A.; Sun, B.; Ismagilov, R.F. Increased Robustness of Single-Molecule Counting with Microfluidics, Digital Isothermal Amplification, and a Mobile Phone versus Real-Time Kinetic Measurements. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 11129–11136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, F.; Sun, B.; Kreutz, J.E.; Davydova, E.K.; Du, W.; Reddy, P.L.; Joseph, L.J.; Ismagilov, R.F. Multiplexed Quantification of Nucleic Acids with Large Dynamic Range Using Multivolume Digital RT-PCR on a Rotational SlipChip Tested with HIV and Hepatitis C Viral Load. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 17705–17712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, R.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Savitha, R.; Renganathan, T.; Pushpavanam, S. Fabrication of laser printed microfluidic paper-based analytical devices (LP-µPADs) for point-of-care applications. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abafogi, A.T.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Mohammed, M.O.; van Noort, D.; Park, S. 3D-Printed Modular Microfluidic Device Enabling Preconcentrating Bacteria and Purifying Bacterial DNA in Blood for Improving the Sensitivity of Molecular Diagnostics. Sensors 2020, 20, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Fanton, A.; Chandrasekaran, S.S.; Charrez, B.; Escajeda, A.M.; Son, S.; Mcintosh, R.; Bhuiya, A.; de León Derby, M.D.; Switz, N.A.; et al. Rapid, Point-of-Care Molecular Diagnostics with Cas13. 4 April 2021. Available online: https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.12.14.20247874v2 (accessed on 16 December 2021).
- Gootenberg, J.S.; Abudayyeh, O.O.; Kellner, M.J.; Joung, J.; Collins, J.J.; Zhang, F. Multiplexed and portable nucleic acid detection platform with Cas13, Cas12a, and Csm6. Science 2018, 360, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, J.; Langelier, C.; Kuchta, A.; Batson, J.; Teyssier, N.; Lyden, A.; Caldera, S.; McGeever, A.; Dimitrov, B.; King, R.; et al. FLASH: A next-generation CRISPR diagnostic for multiplexed detection of antimicrobial resistance sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, B.C.; Steimberg, N.; Mazzoleni, G. Point-of-Care Pathogen Detection with CRISPR-based Programmable Nucleic Acid Binding Proteins. ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 1566–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, C.M.; Myhrvold, C.; Thakku, S.G.; Freije, C.A.; Metsky, H.C.; Yang, D.K.; Ye, S.H.; Boehm, C.K.; Kosoko-Thoroddsen, T.S.F.; Kehe, J.; et al. Massively multiplexed nucleic acid detection with Cas13. Nature 2020, 582, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Razavi Bazaz, S.; Morshedi Rad, D.; Shimoni, O.; Jin, D.; Rawlinson, W.; Ebrahimi Warkiani, M. A Portable RT-LAMP/CRISPR Machine for Rapid COVID-19 Screening. Biosensors 2021, 11, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; de Dieu Habimana, J.; Mukama, O.; Li, Z.; Odiwuor, N.; Jing, H.; Nie, C.; Hu, M.; Lin, Z.; Wei, H.; et al. Rational Programming of Cas12a for Early-Stage Detection of COVID-19 by Lateral Flow Assay and Portable Real-Time Fluorescence Readout Facilities. Biosensors 2021, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, Z.S.; Joung, H.A.; Goncharov, A.; Liang, J.; Nugroho, K.; Di Carlo, D.; Garner, O.B.; Ozcan, A. Deep learning-enabled point-of-care sensing using multiplexed paper-based sensors. NPJ Digit. Med. 2020, 3, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, B.; Lin, H.; Yang, C.; Guo, J.; Cui, B.; Pan, W.; Feng, J.; Luo, T.; Chu, F.; et al. Multiplexed analysis of small extracellular vesicle-derived mRNAs by droplet digital PCR and machine learning improves breast cancer diagnosis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 194, 113615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miglietta, L.; Moniri, A.; Pennisi, I.; Malpartida-Cardenas, K.; Abbas, H.; Hill-Cawthorne, K.; Bolt, F.; Jauneikaite, E.; Davies, F.; Holmes, A.; et al. Coupling Machine Learning and High Throughput Multiplex Digital PCR Enables Accurate Detection of Carbapenem-Resistant Genes in Clinical Isolates. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 775299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellington, A.A.; Kullo, I.J.; Bailey, K.R.; Klee, G.G. Antibody-Based Protein Multiplex Platforms: Technical and Operational Challenges. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Medicine (US) Forum on Microbial Threats and Global Infectious Disease Surveillance and Detection. In Assessing the Challenges—Finding Solutions, Workshop Summary; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK52875/ (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- World’s Most Portable Molecular Diagnostics System Unveiled at AACC. 28 July 2015. Available online: https://www.tbonline.info/posts/2015/7/28/worlds-most-portable-molecular-diagnostics-system-/ (accessed on 6 January 2022).
- Cepheid Targets Development of a Point of Care HIV Viral Load Test From a Few Drops of Blood. 8 September 2016. Available online: https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/cepheid-targets-development-of-a-point-of-care-hiv-viral-load-test-from-a-few-drops-of-blood-300324397.html (accessed on 6 January 2022).
- Advocates Urge Cepheid to Reinstate Plans to Commercialize GeneXpert Omni. 14 October 2021. Available online: https://www.tbonline.info/posts/2021/10/14/advocates-urge-cepheid-reinstate-plans-commerciali/ (accessed on 6 January 2022).
- Branigan, D, Time for $5 Coalition Urges Cepheid to Reinstate Plans to Launch GeneXpert Omni. 14 October 2021. Available online: https://www.tbonline.info/media/uploads/documents/time_for_$5_coalition_open_letter_to_cepheid_14oct2021.pdf (accessed on 6 January 2022).
- Gotham, D.; McKenna, L.; Deborggraeve, S.; Madoori, S.; Branigan, D. Public investments in the development of GeneXpert molecular diagnostic technology. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buss, B.A.; Baures, T.J.; Yoo, M.; Hanson, K.E.; Alexander, D.P.; Benefield, R.J.; Spivak, E.S. Impact of a multiplex PCR assay for bloodstream infections with and without antimicrobial stewardship intervention at a cancer hospital. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2018, 5, ofy258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.H.; Lin, Y.F.; Tsai, M.H.; Yang, S.; Liao, M.L.; Chao, S.W.; Hwang, C.C. Detection of common diarrhea-causing pathogens in Northern Taiwan by multiplex polymerase chain reaction. Medicine 2018, 97, e11006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, D.; Luu, P.L.; Song, J.Z.; Qu, W.; Risbridger, G.P.; Lawrence, M.G.; Lu, J.; Trau, M.; Korbie, D.; Clark, S.J.; et al. Comprehensive evaluation of targeted multiplex bisulphite PCR sequencing for validation of DNA methylation biomarker panels. Clin. Epigenetics 2020, 12, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olkhov-Mitsel, E.; Zdravic, D.; Kron, K.; van der Kwast, T.; Fleshner, N.; Bapat, B. Novel Multiplex MethyLight Protocol for Detection of DNA Methylation in Patient Tissues and Bodily Fluids. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.Y.; Huang, S.K.; Huynh, K.T.; Salomon, M.P.; Chang, S.C.; Marzese, D.M.; Lanman, R.B.; Talasaz, A.; Hoon, D.S. Multiplex gene profiling of cell-free DNA in patients with metastatic melanoma for monitoring disease. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- “GeneXpert”. Available online: https://www.finddx.org/pricing/genexpert/ (accessed on 8 January 2022).
- Hsiang, E.; Little, K.M.; Haguma, P.; Hanrahan, C.F.; Katamba, A.; Cattamanchi, A.; Davis, J.L.; Vassall, A.; Dowdy, D. Higher cost of implementing Xpert(®) MTB/RIF in Ugandan peripheral settings: Implications for cost-effectiveness. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2016, 20, 1212–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- COVID-19 Testing. Available online: https://info.biomeme.com/covid-19 (accessed on 6 January 2022).
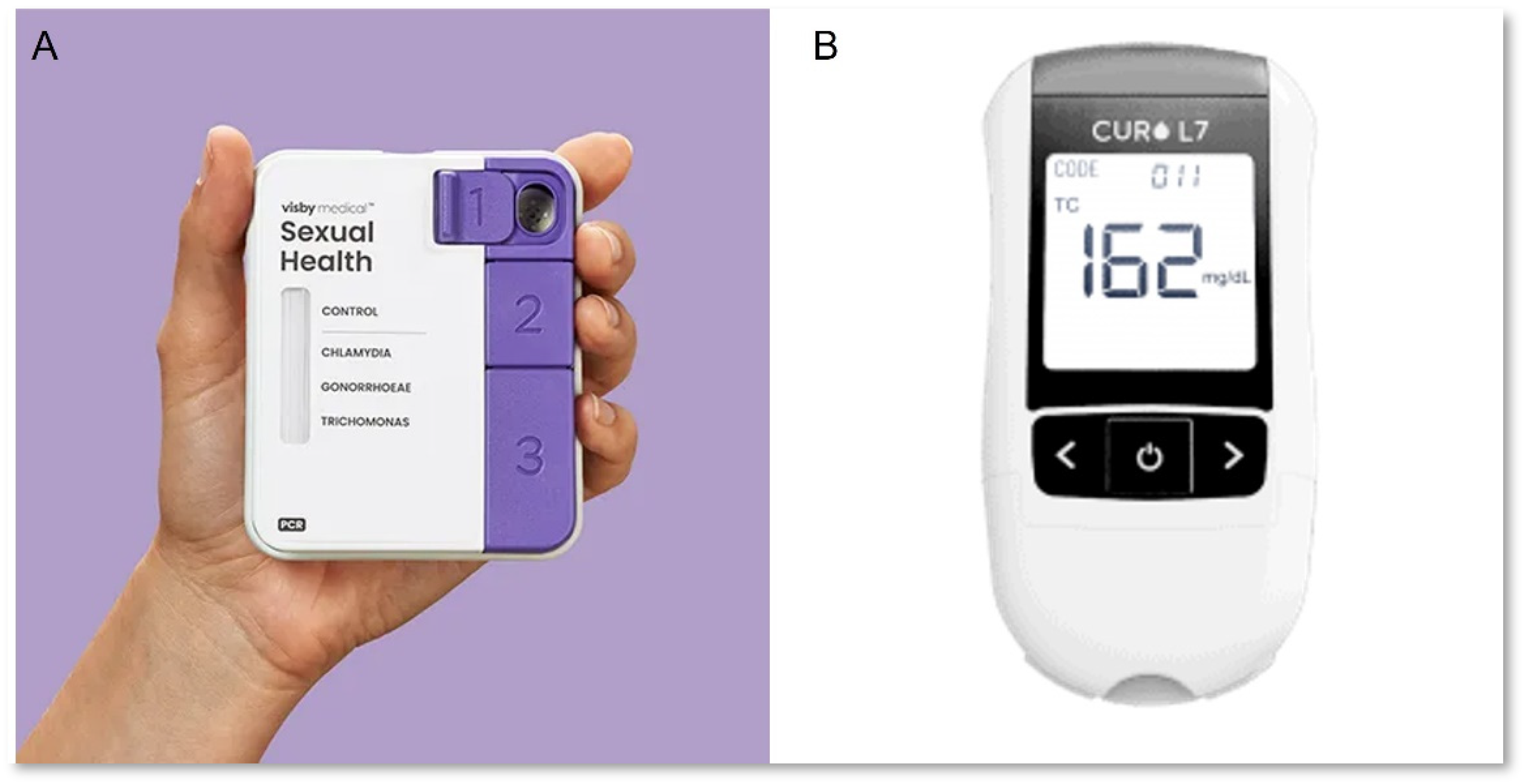
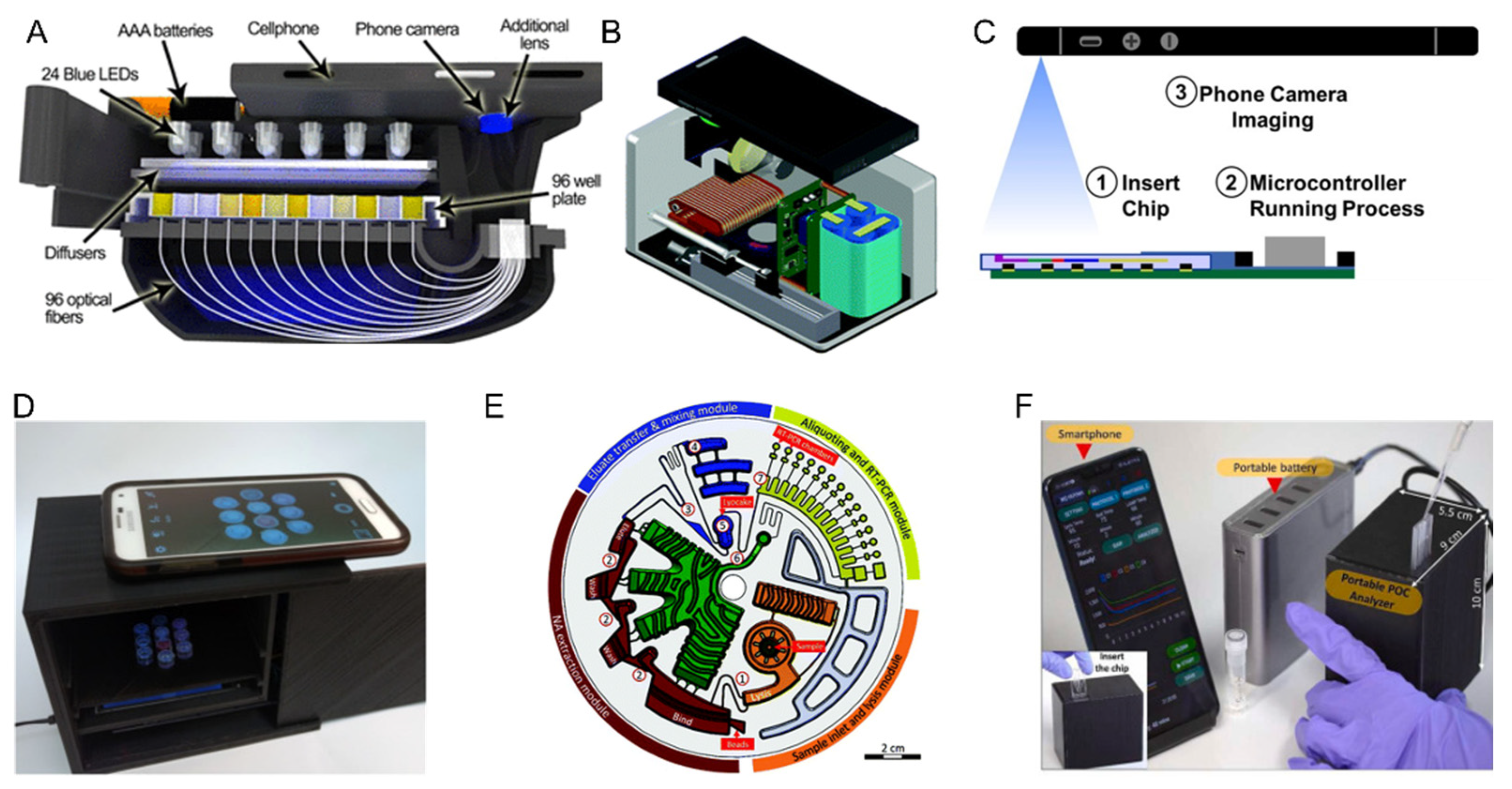
| Test (Multiplex Capacity) | R | E | A | S | S | U | R | E | D | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accula dock Flu A/Flu B Test (2) | 3 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 78% |
| Visby Medical Sexual Health (3) | 3 | 3 | - | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 100% |
| Franklin three9 COVID-19 (27) | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 93% |
| Binax Now Influenza A & B with DIGIVAL (2) | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 81% |
| BD Veritor™ Flu A + B with analyzer (2) | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 89% |
| Sofia® 2 Flu + SARS antigen FIA (3) | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 81% |
| Acucy influenza A and B (2) | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 89% |
| CardioChek PA Analyzer with CHOL + HDL + GLU Panel (3) | 3 | 3 | 3 | - | - | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 100% |
| CuroL7 (6) | 3 | 3 | 3 | - | - | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 100% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Otoo, J.A.; Schlappi, T.S. REASSURED Multiplex Diagnostics: A Critical Review and Forecast. Biosensors 2022, 12, 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12020124
Otoo JA, Schlappi TS. REASSURED Multiplex Diagnostics: A Critical Review and Forecast. Biosensors. 2022; 12(2):124. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12020124
Chicago/Turabian StyleOtoo, Jonas A., and Travis S. Schlappi. 2022. "REASSURED Multiplex Diagnostics: A Critical Review and Forecast" Biosensors 12, no. 2: 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12020124
APA StyleOtoo, J. A., & Schlappi, T. S. (2022). REASSURED Multiplex Diagnostics: A Critical Review and Forecast. Biosensors, 12(2), 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12020124





