Research Progress in the Synthesis of Carbon Dots and Their Application in Food Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Preparation of CDs
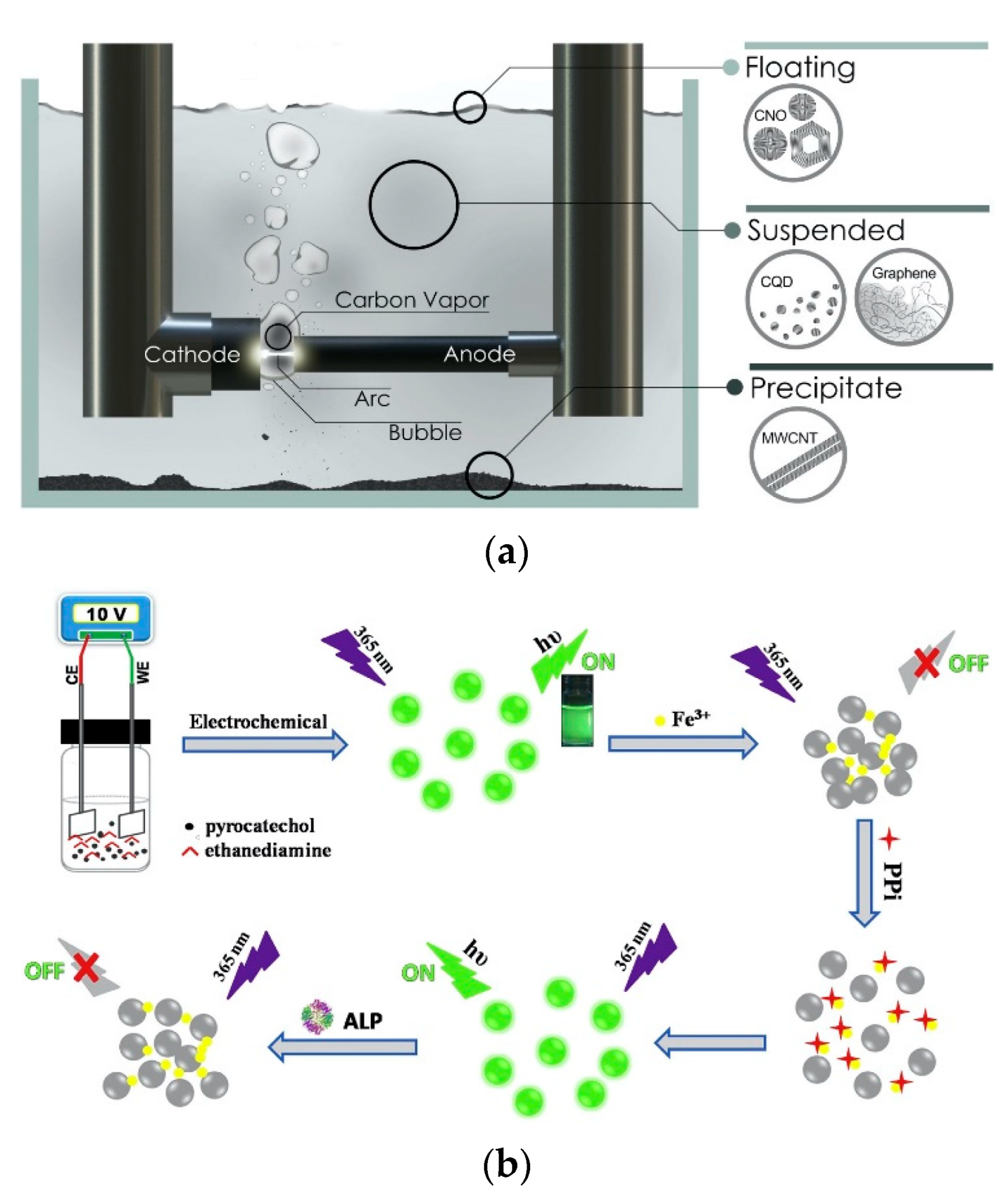
2.1. Top-Down Technique
2.2. Bottom-Up Method
2.3. Fluorescent Properties of CDs
3. Application of CDs in Food Testing
3.1. Nutritional Composition Analysis of Food
3.2. Food Additive Detection
3.3. Detection of Foodborne Pathogens
3.4. Detection of Metal Ions
3.5. Residue Detection of Hazardous Organic Pollutants
3.6. pH Detection
4. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cunha, D.T.; Rosso, V.V.; Pereira, M.B.; Stedefeldt, E. The differences between observed and self-reported food safety practices: A study with food handlers using structural equation modeling. Food Res. Int. 2019, 125, 108637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.Z.; Li, Y.M.; He, W.L. Problems in food safety and food testing and improvement measures. Mod. Food 2020, 12, 170–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.; Lin, Q.Y.; Li, H.; Huang, Z.P.; Kuang, Y.Y.; Chen, H.; Kong, J.L. Rapid detection of malachite green residues in fish using a surface-enhanced Raman scatteringactive glass fiber paper prepared by in situ reduction method. Talanta 2019, 200, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Y.; Miao, S. HPLC determination and MS confirmation of malachite green, gentian violet, and their leuco metabolite residues in channel catfish muscle. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 7109–7114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, A.K.; Blasco, C.; Picó, Y. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry in food safety. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 4018–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.D. (Bio) sensors for measurement of analytes implicated in food safety: A review. Trends Anal. Chem. 2002, 21, 96–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picó, Y.; Font, G.; Ruiz, M.J.; Fernández, M. Control of pesticide residues by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry to ensure food safety. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2006, 25, 917–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Lázaro, D.; Lombard, B.; Smith, H.; Rzezutka, A.; D’Agostino, M.; Helmuth, R.; Schroeter, A.; Malorny, B.; Miko, A.; Guerra, B.; et al. Trends in analytical methodology in food safety and quality: Monitoring microorganisms and genetically modified organisms. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 18, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.W.; Sumathy, K.; Qiao, Q.Q.; Zhou, Z.P. Review on dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs): Advanced techniques and crossmark research trends. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 68, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, D. Efficiency of Wood-Dust of Dalbergia sisoo as Low-Cost Adsorbent for Rhodamine-B Dye Removal. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotr, K.; Jerzy, P.L.; Lukasz, W.; Pawel, S.; Przemyslaw, Z. The Importance of Structural Factors for the Electrochemical Performance of Graphene/Carbon Nanotube/Melamine Powders towards the Catalytic Activity of Oxygen Reduction Reaction. Materials 2021, 14, 2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.Y.; Ray, R.; Gu, Y.L.; Ploehn, H.J.; Gearheart, L.; Raker, K.; Scrivens, W.A. Electrophoretic analysis and purification of fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotube fragments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 12736–12737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.P.; Zhou, B.; Lin, Y.; Wang, W.; Fernando, K.A.S.; Pathak, P.; Meziani, M.J.; Harruff, B.A.; Wang, X.; Luo, P.G.J.; et al. Quantum-sized CDs for bright and colorful photoluminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7756–7757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.J.; Li, C.; Ren, Y.J.; Sun, X.B.; Pan, W.; Li, Y.H.; Wang, J.P.; Wang, W.J. CDs: Surface engineering and applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 5772–5788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benzigar, M.R.; Talapaneni, S.N.; Joseph, S.; Ramadass, K.; Singh, G.; Scaranto, J.; Ravon, U.; Al-Bahily, K.; Vinu, A. Recent advances in functionalized micro and mesoporous carbon materials: Synthesis and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 2680–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Tiwari, P.; Mobin, S.M. Sustainable carbon-dots: Recent advances in green CDs for sensing and bioimaging. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2017, 5, 8904–8924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Liang, M.; Xu, L.; Qi, S.; Chen, H.; Chen, X. Solid-phase synthesis of highly fluorescent nitrogendoped carbon dots for sensitive and selective probing ferric ions in living cells. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 9846–9852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.; Behera, B.; Maiti, T.; Mohapatra, S. Simple one-step synthesis of highly luminescent carbon dots from orange juice: Application as excellent bio-imaging agents. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 8835–8837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Lu, F.; Luo, P.; Cao, L.; Mezziani, M.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, M. Carbon dots as nontoxic and high-performance fluorescence imaging agents. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 18110–18114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naik, V.M.; Bhosale, S.V.; Kolekar, G.B. A brief review on the synthesis, characterisation and analytical applications of nitrogen doped CDs. Anal. Methods 2022, 14, 877–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ðorđević, L.; Arcudi, F.; Cacioppo, M.; Prato, M. A multifunctional chemical toolbox to engineer CDs for biomedical and energy applications. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2022, 17, 112–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wareing, T.C.; Gentile, P.; Phan, A.N. Biomass-Based CDs: Current Development and Future Perspectives. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 15471–15501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayab, A.; Murtaza, N.A.; Tooba, J.K. Carbon Quantum Dots for Biomedical Applications: Review and Analysis. Front. Mater. 2021, 8, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magesh, V.; Sundramoorthy, A.K.; Ganapathy, D. Recent Advances on Synthesis and Potential Applications of Carbon Quantum Dots. Front. Mater. 2022, 9, 906838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Wen, Y.M.; Kang, X.H. Halogen-Doped CDs: Synthesis, Application, and Prospects. Molecules 2022, 27, 4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Liu, B.; Liu, Z.M.; Li, J.K. Research progress in the synthesis and biological application of quantum dots. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 20515–20539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, D.S.; Quraishi, M.A.; Verma, C. Carbon nanodots: Recent advances in synthesis and applications. Carbon Lett. 2022, 32, 1603–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Ren, X.; Wang, J.; Sun, M. Synthesis of Homogeneous Carbon Quantum Dots by ULtrafast Dual-Beam Pulsed Laser Ablation for Bioimaging. Mater. Today 2020, 12, 100091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao-Mujica, F.J.; Garcia-Hernández, L.; Camacho-López, S.; Camacho-López, M.; Camacho-López, M.A.; Reyes-Contreras, D.; Pérez-Rodríguez, A.; Peña-Caravaca, J.P.; Páez-Rodríguez, A.; Darias-Gonzalez, J.G.; et al. Carbon Quantum Dots by Submerged Arc Discharge in Water: Synthesis, Characterization, and Mechanism of Formation. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 129, 163301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.J.; Lu, W.J.; Paau, M.C.; Hu, Q.; Wu, X.; Shuang, S.M.; Dong, C.; Choi, M.M.F. Facile synthesis of nitrogen-doped CDs for Fe3+ sensing and cellular imaging. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 861, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.T.; Yang, L.F.; Li, N.B.; Luo, H.Q. An ultrasensitive and selective fluorescence assay for Sudan I and IHI against the influence of Sudan II and IV. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 42, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.T.; Zhang, Y. A Simple and Green Synthesis of Carbon Quantum Dots from Coke for White Light- Emitting Devices. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 33789–33793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iannazzo, D.; Pistone, A.; Ferro, S.; Luca, L.D.; Monforte, A.M.; Romeo, R.; Buemi, M.R.; Pannecouque, C. Graphene Quantum Dots Based Systems as HIV Inhibitors. Bioconjug. Chem. 2018, 29, 3084–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, A.J.; Long, Q.; Wu, Q.Q.; Li, H.T.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Yao, S.Z. Upconversion nanosensor for sensitive fluorescence detection of Sudan I-IV based on inner filter effect. Talanta 2016, 148, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.I.; Wu, W.C.; Periasamy, A.; Chang, H.T. Electrochemical synthesis of photoluminescent carbon nanodots from glycine for highly sensitive detection of hemoglobin. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 2509–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, F.S.; Xu, Y.H.; Liu, M.L.; Sun, J.; Guo, P.R.; Liu, J.Q. Bottom-up electrochemical preparation of solid-state carbon nanodots directly from nitriles/ionic liquids using carbon-free electrodes and the applications in specific ferric ion detection and cell imaging. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 5470–5477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.Y.; Bao, W.J.; Yang, F.; Yan, X.R. Electrochemical Synthesis of FeNx Doped Carbon Quantum Dots for Sensitive Detection of Cu2+ Ion. Green Energy Environ. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, F.S.; Ying, Y.L.; Hua, X.; Niu, Y.S.; Long, Y.T. Electrochemically generated green-fluorescent N-doped carbon quantum dots for facile monitoring alkaline phosphatase activity based on the Fe3+-mediating ON-OFF-ON-OF fluorescent principle. Carbon 2018, 127, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetsuka, H.; Nagoya, A.; Fukusumi, T.; Matsui, T. Molecularly designed, nitrogen functionalized graphene quantum dots for optoelectronic devices. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4632–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.Q.; Pang, H.C.; Yang, B.H.; Guo, C.X.; Shao, J.W.; Chi, Y.W.; Li, C.M.; Yu, T. Carbon-based dots Co-doped with nitrogen and sulfur for high quantum yield and excitation-independent emission. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 7800–7804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marković, Z.; Labudová, M.; Danko, M.; Matijašević, D.; Mičušík, M.; Nádaždy, V.; Kováčová, M.; Kleinová, A.; Špitalský, Z.; Pavlović, V.; et al. Highly Efficient Antioxidant F- and Cl-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots for Bioimaging. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 16327–16338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.D.; Wang, Y.; Shen, X.R.; Su, C.Y.; Yang, J.H.; Piao, M.J.; Jia, F.; Gao, G.H.; Zhang, L.; Lin, Q. One-step synthesis of photoluminescent CDs with excitation-independent emission for selective bioimaging and gene delivery. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 492, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.J.; Lan, M.H.; Zhu, X.Y.; Xue, H.T.; Ng, T.W.; Meng, X.M.; Lee, C.S.; Wang, P.F.; Zhang, W.J. Green synthesis of bifunctional fluorescent CDs from garlic for cellular imaging and free radical scavenging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 17054–17060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.M.; Lin, X.Y.; Wu, L.N.; Zhao, C.F.; Li, S.G.; Liu, A.L.; Lin, X.H.; Lin, L.Q. Nitrogen-doped CDs as a ratiometric fluorescent probe for determination of the activity of acid phosphatase, for inhibitor screening, and for intracellular imaging. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atchudan, R.; Edison, T.N.J.I.; Shanmugam, M.; Perumal, S.; Somanathan, T.; Lee, Y.R. Sustainable synthesis of carbon quantum dots from banana peel waste using hydrothermal process for in vivo bioimaging. Phys. E Low Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2021, 126, 114417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.A.; Mu, Z.; Liu, H.; Huang, J.F.; Li, X.L.; Yang, Y.L. A novel application of fluorine doped CDs combining vortex assisted liquid-liquid microextraction for determination of 4-nitrophenol with spectrofluorimetric method. J. Fluoresc. 2019, 29, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.T.; Liu, Y.L.; Cheng, G.H.; Fan, Z.G.; Yuan, J.Y.; He, S.L.; Zhu, G.F. A novel fluorescent probe based on N, B, F co-doped CDs for highly selective and sensitive determination of sulfathiazole. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Chao, D.Y.; Yu, C.Y.; Zhu, Q.; Zhou, S.H.; Tian, L.; Zhou, L. One-step green solvothermal synthesis of full-color carbon quantum dots based on a doping strategy. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 8939–8946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.Q.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Kong, Y.R.; Xiao, Y.M.; Xu, W. Material and optical properties of fluorescent carbon quantum dots fabricated from lemon juice via hydrothermal reaction. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tungare, K.; Bhori, M.; Racherla, K.S.; Sawant, S. Synthesis, characterization and biocompatibility studies of carbon quantum dots from Phoenix dactylifera. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.E.; Fekry, N.A.; Abdelfattah, A.M. Removal of uranium (VI) from water by the action of microwave-rapid green synthesized carbon quantum dots from starch-water system and supported onto polymeric matrix. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 397, 122770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Xu, Y.; Ding, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, T.Y.; Ding, H.; Chen, Y.H.; Ding, L. Microwave-assisted synthesis of highly luminescent N and S-co-doped CDs as a ratiometric fluorescent probe for levofloxacin. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Gao, T.; Yang, M.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, F.L.; Liu, Y. Microwave-assisted synthesis, Characterization, cell imaging of fluorescent CDs using L-asparagine as precursor. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 3323–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
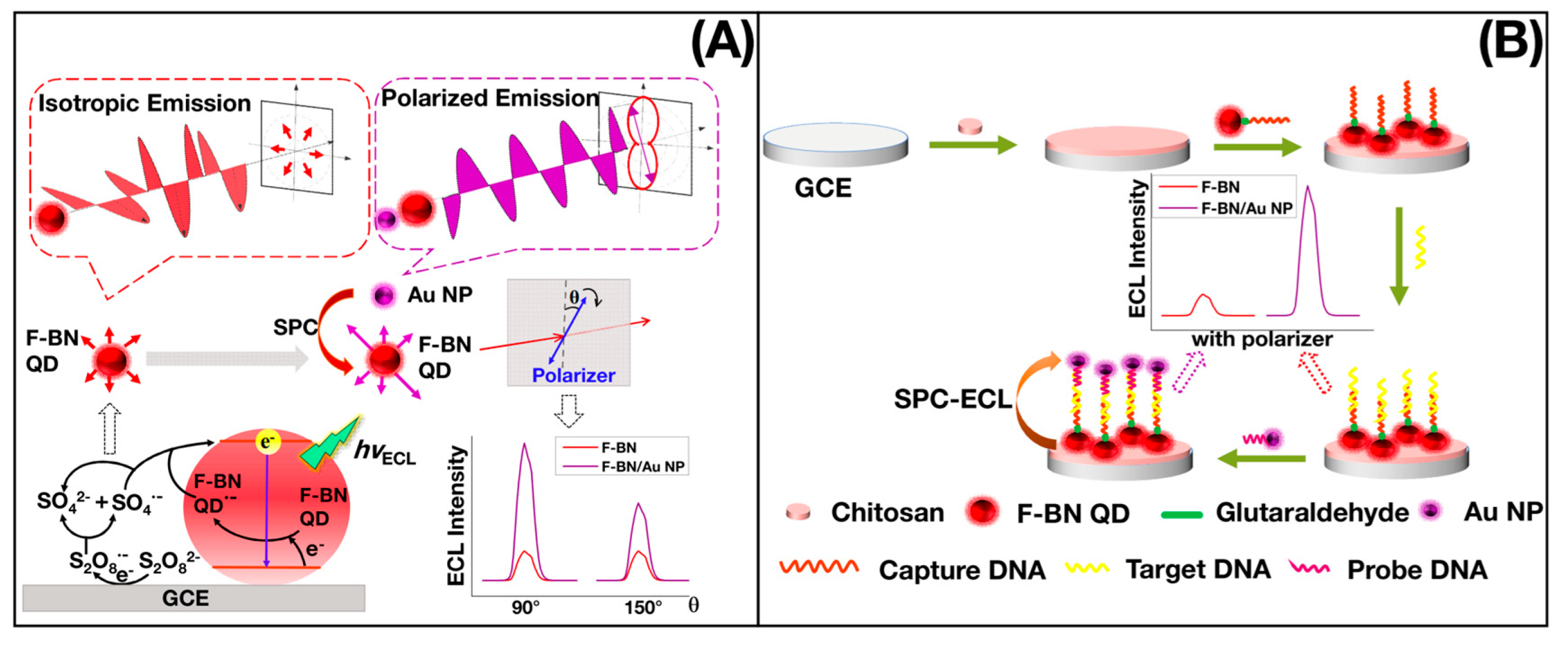
- Liang, Z.H.; Zhan, Q.; Nie, Y.X.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Q. Polarized-electrochemiluminescence biosensor based on surface plasmon coupling strategy and fluorine-doped BN quantum dots. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 9223–9229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.T.; He, X.D.; Liu, Y.; Yu, H.; Kang, Z.H.; Lee, S.T. Synthesis of fluorescent carbon nanoparticles directly from artive carbon via a one-step ultrasonic treatment. Mater. Res. Bull. 2011, 46, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.T.; He, X.D.; Liu, Y.; Huang, H.; Lian, S.Y.; Lee, T.S.; Kang, Z.H. One-step ultrasonic synthesis of water-solublecarbon nano particles with excellent photoluminescent properties. Carbon 2011, 49, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.W.; Zhang, L.X.; Huang, L.S.; Zheng, G.; Zhang, P.; Jin, Y.; Jiao, Z.F.; Sun, X.S. Study on the fluorescence properties of CDs prepared via combustion process. J. Lumin. 2019, 206, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.G.; Xing, M.; Wu, Q.L. A universal facile synthesis of nitrogen and sulfur co-doped CDs from cellulose- based biowaste for fluorescent detection of Fe3+ ions and intracellular bioimaging. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 99, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Qu, D.; Yang, D.X.; Nie, B.; Zhao, Y.K.; Fan, H.; Sun, Z.C. Synthesis of CDs with multiple color emission by controlled graphitization and surface functionalization. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.Z.; Liu, T.; Paau, M.C.; Wang, M.N.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.Z.; Wu, C.F.; Du, J.; Xiao, D.; Choi, M.M.F. One pot selective synthesis of water and organic soluble CDs with green fluorescence emission. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 11667–11675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yu, H.J.; Bian, T.; Zhao, Y.F.; Zhou, C.; Shang, L.; Liu, Y.H.; Wu, L.Z.; Tung, C.H.; Zhang, T.R. Highly luminescent nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots as effective fluorrescent probes for mercuric and iodide ions. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 1922–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Fu, Z.; Cui, F.L. Synthesis of CDs and their application as turn off-on fluorescent sensor for mercury (II) and glutathione. J. Fluoresc. 2020, 30, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Ming, H.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Kang, Z.H. One-step ultrasonic synthesis of fluorescent N-doped CDs from glucose and their visible-light sensitive photocatalytic ability. New J. Chem. 2012, 36, 861–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Xue, W.; Chen, H.; Lin, J.M. Classical Oxidant Induced Chemiluminescence of Fluorescent CDs. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 1051–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Li, R.B.; Lin, L.; Guo, G.S.; Lin, J.M. Determination of L-ascorbic Acid in Human Serum by Chemiluminescence Based on Hydrogen Peroxide sodium Hydrogen Carbonate Cdse/CdS Quantum Dots System. Talanta 2010, 81, 1688–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Z.; Li, J.; Tang, J.L.; Kang, J.; Zhang, Y.H. Study of Influence of Metal ions on CdTe/H2O2 Chemiluminescence. J. Lumin. 2008, 128, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Q.; Shu, J.; Chen, J.; Cao, Z.R.; Xiao, A.; Yan, Z.Y. Highly luminescent S,N co-doped carbon quantum dots-sensitized chemiluminescence on luminol-H2O2 system for the determination of ranitidine. Luminescence 2017, 32, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.Y.; Chi, Y.; Dong, Y.Q.; Lin, J.P.; Wang, B.B. Electrochemiluminescence of water-soluble carbon nanocrystals released electrochemically from graphite. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 4564–4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, M.J.; Chowdhury, D.; Nath, B.K. Recent development of modified fluorescent carbon quantum dots-based fluorescence sensors for food quality assessment. Carbon Lett. 2022, 32, 1131–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.L.; Niu, X.Y.; Zhang, H.J.; Xu, L.F.; Zhao, S.G.; Chen, H.L.; Chen, X.G. Switch-on fluorescence sensing of glutathione in food samples based on a graphitic carbon nitride quantum dot (g-CNQD)-Hg2+ chemosensor. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 1747–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.L.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.Y.; Ge, S.G.; Yu, J.H.; Yan, M. Or-off-on fluorescence sensing of glutathione in food samples based on a graphitic carbon nitride (g-CgN4)-Cu2+ strategy. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 3374–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Sheng, L.; Yu, Y.S.; Ma, M.H.; Cai, Z.X.; Huang, X. Rapid and universal detection of ovalbumin based on N, O, P-co-doped CDs-fluorescence resonance energy transfer technology. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 269, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.Q.; Dong, F.; Zhang, J.J.; Zhao, X.; Li, Q.; Guo, Z.Y. Physical and antioxidant properties of edible chitosan ascorbate films. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 2530–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.L.; Zhang, W.G.; Han, Y.; Chen, X.M.; Zhu, L.; Tang, W.Z.; Wang, J.L.; Yue, T.L.; Li, Z.H. N,S co-doped CDs based fluorescent “on-off-on” sensor for determination of ascorbic acid in common fruits. Food Chem. 2018, 258, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.H.; Du, H.Y.; Li, J.R.; Deng, J.; Wang, R.Y.; Chen, Y.L. Sulfur-rich carbon quantum dots based on Alternanthera philoxeroides and thiourea for the detection of tartrazine. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2022, 33, 12808–12818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.Y.; Tang, J.J.; Zhang, M.S.; Yang, X.P. Selective and sensitive detection of tartrazine in beverages by sulfur quantum dots with high fluorescence quantum yield. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 279, 121454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.X.; Sun, J.R.; Yan, F.Y.; Zhang, H.; Ma, R.; Zang, Y.Y.; Guan, S.; Wang, X. Fluorescence Sensing Performance of CDs of Functionalization toward Sunset Yellow. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2021, 39, 2100207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Xue, W.; Chen, H.; Lin, J.M. Peroxynitrousacid-induced chemiluminescence of fluorescent CDs for nitrite sensing. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8245–8251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
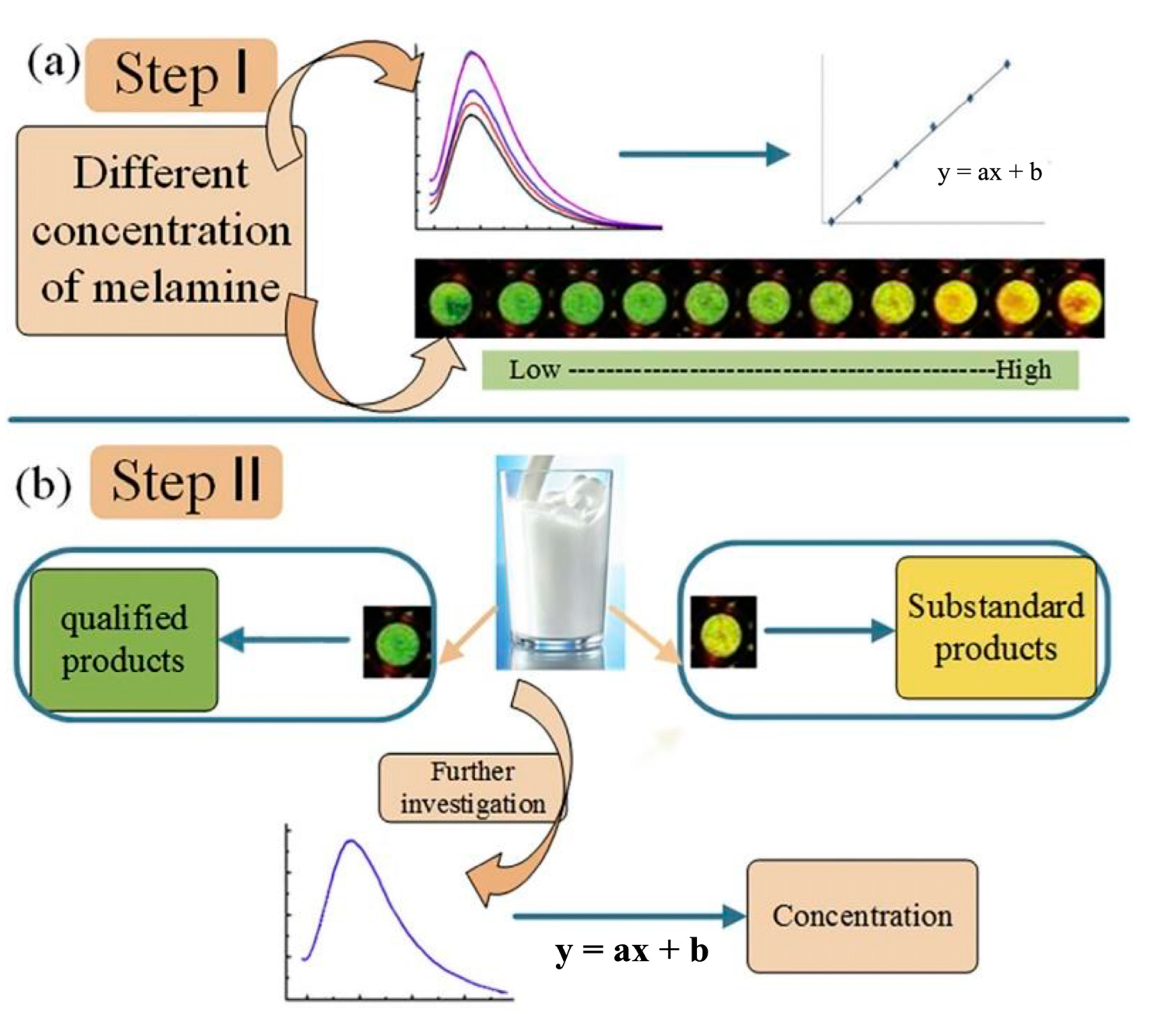
- Hu, X.T.; Shi, J.Y.; Shi, Y.Q.; Zou, X.B.; Arslan, M.; Zhang, W.; Huang, X.W.; Li, Z.H.; Xu, Y.W. Use of a smartphone for visual detection of melamine in milk based on Au @ Carbon quantum dots nanocomposites. Food Chem. 2019, 272, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.X.; Guo, Y.Z.; Liang, S.; Huo, S.Y.; Chu, T.T.; Ma, J.L.; Chen, X.H.; Zhou, J.H.; Sun, R.C. Preparation of sulfur-doped carbon quantum dots from lignin as a sensor to detect Sudan I in an acidic environment. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 10788–10796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, C.; Luglig, A.; Ossiprandi, M.C.; Turroni, F.; Milani, C.; Duranti, S.; Mancabelli, L.; Mangifesta, M.; Alessandri, G.; Sinderen, D.V.; et al. Next generation sequencing-based multigene panel for high throughput detection of food-borne pathogens. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 256, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyachuba, D.G. Foodborne illness: Is it on the rise? Nutr. Rev. 2010, 68, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, C.I.; Chang, H.T.; Lin, C.H.; Shen, Y.W.; Unnikrishnan, B.; Li, Y.J.; Huang, C.C. One step synthesis of biofunctional carbon quantum dots for bacterial labeling. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 68, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Choudhary, M.; Singh, H. CDs and graphene oxide based FRET immunosensor for sensitive detection of Helicobacter pylori. Anal. Biochem. 2022, 654, 114801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, Y. Rapid and sensitive detection of Salmonella typhimurium using aptamer-conjugated CDs as fluorescence probe. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 1701–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Singh, S.; Bhardwaj, S.K.; Kaur, G.; Khatri, M.; Deep, A.; Bhardwaj, N. Development of carbon quantum dot-based lateral flow immunoassay for sensitive detection of aflatoxin M1 in milk. Food Chem. 2022, 393, 133374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.B.; Zhao, W.L.; Luo, L.J.; Liu, X.H.; Bi, X.Y.; Li, J.M.; Jiang, P.A.; You, T.Y. Electrochemiluminescence of Carbon-based Quantum Dots: Synthesis, Mechanism and Application in Heavy Metal Ions Detection. Electroanalysis 2021, 34, 608–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Han, L.; Gao, X.; He, W.; Chu, R.R.; Ma, Y.F. Application of Carbon Quantum dot Fluorescent Materials in Metal Ions Detection. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 245, 03080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, M.; Junaid, H.M.; Tabassum, S.; Kanwal, F.; Abid, K.; Fatima, Z.; Shah, A.T. Metal Ion Detection by CDs—A Review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2020, 52, 756–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.H.; Jia, H.S.; Li, N.; Li, X.Y.; Yu, Z.Y.; Wang, J.; Song, Y.T. High-fluorescent CDs (CDs) originated from China grass carp scales (CGCS) for effective detection of Hg(I) ions. Microchem. J. 2019, 145, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.F.; Hao, D.; Wei, L.F.; Zhang, A.Y.; Sun, C.Y.; Wang, R. One-step preparation of red-emitting CDs for visual and quantitative detection of copper ions. Luminescence 2020, 36, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Z.X.; Wang, W.H.; Zhan, X.Z.; Du, X.J.; Zhang, Q.M.; Zhang, R.; Li, K.; Li, J.H.; Xu, W.P. One-pot synthesis of dual CDs using only an N and S co-existed dopant for fluorescence detection of Ag+. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 208, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.T.; Wang, J.L.; Zhan, X.Q.; Wu, Y.G. CDs-based Fluorescent Aptasensor for Detection of Dimethoate Pesticide. Chinese J. Anal. Chem. 2020, 48, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, D.D.; Li, H.X.; Yan, X.; Lin, Y.H.; Lu, G. Biosensors based on fluorescence carbon nanomaterials for detection of pesticides. Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 134, 116126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Teng, X.M.; Wang, Y.S.; Si, S.X.; Ju, J.; Pan, W.; Wang, J.P.; Sun, X.B.; Wang, W.J. CDs based fluorescence methods for the detections of pesticides and veterinary drugs: Response mechanism, selectivity improvement and application. Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 144, 116430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.W.; Zou, X.M.; Song, S.H.; Chen, G.H. Quantum dots applied to methodology on detection of pesticide and veterinary drug residues. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 1307–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Song, Y.; Zhu, C.Z.; Li, H.X.; Du, D.; Su, X.G.; Lin, Y.H. MnO2 Nanosheet-CDs Sensing Platform for Sensitive Detection of Organophosphorus Pesticides. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 2618–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.W.; Tang, J.Q.; Liu, H.L. Rapid determination of lambda-cyhalothrin using a fluorescent probe based on ionic liquid-sensitized CDs coated with molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 5309–5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.Z.; Zhao, S.J.; Wu, S.L.; Huang, L.; Xu, T.; Xing, X.J.; Lan, M.H.; Song, X.Z. A CDs based fluorescent probe for turn-on sensing of ampicillin. Dye. Pigm. 2020, 172, 107846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Ma, Y.; Gu, M.Y.; Huo, X.Y.; Ma, S.N.; Lu, Y.N.; Ning, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tian, B.; Feng, Z.B. CDs derived from the maillard reaction for pH sensors and Cr (VI) detection. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.X.; Jin, H.; Gao, C.L.; Gui, R.J.; Wang, Z.H. Ratiometric, visual, dual-signal fluorescent sensing and imaging of pH/ copper ions in real samples based on CDs fluorescein isothiocyanate composites. Talanta 2017, 162, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, K.; Huang, R.M.; Yu, J.G.; Jiang, X.Y. Temperature, pH, and Cr(VI) ions sensing with green synthetic CDs. Desalin. Water Treat. 2021, 204, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.B.; Wei, W.; Fu, Z.D.; Gao, W.L.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zhao, Q.; Deng, F.M.; Lu, X.Y. Review on carbon dots in food safety applications. Talanta 2019, 194, 809–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gao, X.; Feng, Y.; Wang, H.; Lei, C.; Yan, Y.; Liu, S. Research Progress in the Synthesis of Carbon Dots and Their Application in Food Analysis. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12121158
Yu Y, Zhang L, Gao X, Feng Y, Wang H, Lei C, Yan Y, Liu S. Research Progress in the Synthesis of Carbon Dots and Their Application in Food Analysis. Biosensors. 2022; 12(12):1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12121158
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Yuan, Lili Zhang, Xin Gao, Yuanmiao Feng, Hongyuan Wang, Caihong Lei, Yanhong Yan, and Shuiping Liu. 2022. "Research Progress in the Synthesis of Carbon Dots and Their Application in Food Analysis" Biosensors 12, no. 12: 1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12121158
APA StyleYu, Y., Zhang, L., Gao, X., Feng, Y., Wang, H., Lei, C., Yan, Y., & Liu, S. (2022). Research Progress in the Synthesis of Carbon Dots and Their Application in Food Analysis. Biosensors, 12(12), 1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12121158




