Abstract
Instead of molecularly imprinting a whole protein molecule, imprinting protein epitopes is gaining popularity due to cost and solubility issues. Belonging to the matrix metalloproteinase protein family, MMP-1 is an interstitial collagenase that degrades collagen and may be involved in cell migration, cell proliferation, the pro-inflammatory effect, and cancer progression. Hence, it can serve as a disease protein biomarker and thus be useful in early diagnosis. Herein, epitopes of MMP-1 were identified by screening its crystal structure. To identify possible epitopes for imprinting, MMP-1 was cleaved in silico with trypsin, pepsin at pH = 1.3, and pepsin at pH > 2.0 using Peptide Cutter, generating peptide fragments containing 8 to 12 amino acids. Five criteria were applied to select the peptides most suitable as potential epitopes for MMP-1. The triphenylamine rhodanine-3-acetic acid (TPARA) functional monomer was synthesized to form a stable pre-polymerization complex with a selected template epitope. The complexed functional monomer was then copolymerized with 3,4-ethoxylenedioxythiophene (EDOT) using potentiodynamic electropolymerization onto indium–tin–oxide (ITO) electrodes. The composition of the molecularly imprinted poly(TPARA-co-EDOT) (MIP) was optimized by maximizing the film’s electrical conductivity. Cyclic voltammetry was used to determine MMP-1 concentration in the presence of the Fe(CN)63−/Fe(CN)64− redox probe actuating the “gate effect.” A calibration curve was constructed and used to determine the usable concentration range and the limit of detection as ca. 0.001 to 10.0 pg/mL and 0.2 fg/mL MMP-1, respectively. Finally, the MMP-1 concentration in the A549 human lung (carcinoma) culture medium was measured, and this determination accuracy was confirmed using an ELISA assay.
1. Introduction
Unlike the natural recognizing units of sensors, artificial ones, including molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs), are used as such units in sensors for determining biomolecular compounds. The development of conductive MIPs has recently improved electrochemical sensing performance [1]. Several monomers have been employed, including pyrrole, phenylenediamine, aniline [2,3], aminothiophenol, aminophenyl boronic acid, aminophenol, thiophene, etc., as well as their copolymers and composites [4]. Instead of imprinting a whole protein molecule [5], protein epitope imprinting is gaining popularity [6], owing to both cost and solubility issues [7,8]. The protein crystal structure and analysis of antibody binding sites, aided by the Protein Data Bank, can be used to identify possible epitopes. Epitopes can be generated by digesting protein in silico with different enzymes using Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST) software [7,9]. The resulting epitopes can then be categorized according to several criteria, including their location in the protein molecule (exposed or hidden), aggregation properties, and length, optimally between 8 and 12 amino acids. Epitopes satisfying all these criteria are likely to be highly compatible with imprinting.
Matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) is an interstitial collagenase that degrades collagen types I, II, and III; its overexpression is implicated in the invasive growth of tumor cells [10]. The biological effects of MMP-1 include migration of keratinocytes, re-epithelialization, cell migration, platelet aggregation, increasing the bioavailability of insulin-like growth factors-1 (IGF-1), cell proliferation, pro-inflammatory effect, and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) activation in cancer progression [11]. In pulmonary epithelial cells and skin fibroblasts, environmental factors, e.g., tobacco smoking, increase the expression levels of MMP-1 [12]. A typical MMP consists of several domains, including predomain, propeptide, catalytic, and hemopexin [11]. The propeptide domain, usually composed of ~80 amino acids (AAs), also contains a highly conserved sequence, PRCGVPDV. The catalytic domain consists of ~170 AAs containing conserved three histidine sequences required for zinc chelation. A typical MMP contains a linking peptide, known as a hinge region, of variable length and a hemopexin domain of ~200 AAs [11].
Several assay systems have been developed to diagnose and treat (MMP-expression)-associated diseases [13], including bioassays, zymography assays, immunoassays, fluorimetric assays, radioisotopic-phage-displayed assays, multiple-enzyme/multiple-reagent assays, and activity-based profiling assays. Electrochemical biosensors’ advantages include their low cost and high sensitivity for small molecules [14,15,16], as well as nucleic acids [17,18,19], peptides [3,20,21], and proteins [22,23]. For example, an electrochemical sensor has been fabricated for determining MMP-2 based on the hydrolytic cleavage of specific substrate peptides (PLGVRs). A specially designed ferrocenecetic-acid (Fc)-modified peptide ligand served as the recognition unit of this chemosensor. This peptide was hydrolytically cleaved and then removed from the electrode surface. That decreased the differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) peak current, resulting in a sensor signal that varied linearly with the protein concentration of 1 to 200 ng/mL, with a limit of detection of 0.3 ng/mL [23]. Our previous work demonstrated the optimized molar ratio of functional monomers to templates with the linear dynamic concentration range of 50–500 nM [24].
In the present study, MMP-1 was first screened with BLAST to search for epitope candidates. Using the available crystal structure of MMP-1, these epitope candidates were located in the MMP-1 molecule. The exposed, stable, non-aggregating peptide epitopes selected were next molecularly imprinted in conductive polymers and simultaneously deposited on indium–tin–oxide (ITO) electrodes. The MIP composition was optimized by maximizing the poly(TPARA-co-EDOT) film’s electrical conductivity. Subsequently, the electrode surface morphology was characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Cyclic voltammetry (CV) was then used to determine MMP-1 in the presence of the Fe(CN)63−/Fe(CN)64− redox probe, actuating the “gate effect” [25]. Finally, MMP-1, produced by A549 human lung (carcinoma), was collected in the culture media and then determined with MIP film-coated electrodes.
2. Materials and Methods
Search for the Most Suitable Epitopes of MMP-1 Protein
MMP-1 has the UniProt id of P03956 (MMP-1_HUMAN) and the PDB id of 1fbl. The crystal structure has been determined for 82% of the protein (the remainder being uncrystallizable). The sequence of MMP-1 is shown in Figure S1 in the Supplementary Materials (https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P03956.fasta, accessed on 14 December 2022). To identify possible epitopes for imprinting, MMP-1 was cleaved in silico with trypsin, pepsin at pH = 1.3, and pepsin at pH > 2.0 using Peptide Cutter (https://web.expasy.org/peptide_cutter/, accessed on 14 December 2022), generating peptide fragments containing 8 to 12 amino acids. Five criteria were applied to select peptides most suitable as potential epitopes for MMP-1.
The first criterion considered was peptide structural stability, represented by the instability index. A protein whose instability index is lower than 40 is predicted to be stable; a value exceeding 40 predicts that the structure is unstable (https://web.expasy.org/protparam/protparam-doc.html, accessed on 14 December 2022).
The second one was aggregation “hot spots.” Aggregating peptides, whose aggregation “hot spots” differed from zero, were considered unsuitable for imprinting.
The third criterion was hydrophobicity, represented by the GRAVY index. Hydrophilic peptides are preferable, as they are more likely to be on the target protein’s surface and provide a uniform environment for chemosensor recognition.
The fourth criterion was selectivity, represented by the E value of the peptide epitope. This criterion distinguishes peptides with the highest possibility of being found only in the MMP-1 protein molecule.
The last criterion involved the cleaved epitopes’ location on the surface of the MMP-1 molecule. All the peptides were sorted according to the above criteria (Table S1 in Supplementary Materials). The most recommended peptide candidates are at the top of this table [25].
3. Results and Discussion
Figure S2 in the Supplementary Materials shows the multi-cyclic potentiodynamic curve for simultaneous formation by electropolymerization and deposition on the electrode of the non-imprinted polymer (NIP) and MIP films of various molar ratios of TPARA-to-EDOT and 0–0.5 μg/mL of the MMP-1 peptide epitopes, vis., AQDDIDGIQAI (peptide A, PA). In Figure S2a, the most pronounced anodic and cathodic peaks, at ~0.75 and ~0.70 V vs. Ag/AgCl, respectively, were obtained in the template absence, apparently corresponding to the TPARA redox behavior. Although no pronounced peak was at other potentials, the current increased with the cycle number, implying that the EDOT and TPARA moieties were simultaneously electropolymerized. Thus, a conductive polymer film was deposited on the ITO surface. The peak current increase in the curve for TPARA:EDOT = 1:4 (Figure S2b) with the template concentration increase was less pronounced than that obtained in the absence of the template (Figure S2a). For TPARA:EDOT = 1:1, the peak currents (Figure S2c) with the template presence were higher than those in its absence. These currents did not increase in consecutive cycles. Presumably, the simultaneous electropolymerization and deposition are dominated by the TPARA, not the EDOT moiety. Notably, the peak currents in Figure S2c are much higher than those in Figures S2a,b. As the TPARA:EDOT molar ratio was increased to 4:1 (Figure S2d), peak currents were similar in shape but higher than those for the equimolar ratio (Figure S2c).
Figure 1a shows the 1st and 20th (last) cycle curves of the multi-cyclic potentiodynamic curve for the MIP film deposition displayed in Figure S2. The peak current increased with the cycle number. However, the higher the 20th cycle peak current, the less PA was doped in the MIP. Figure 1b shows differences in peak currents against the PA concentration for the 20th and 1st electropolymerization cycle at various TPARA-to-EDOT molar ratios. This difference was the highest at the 1:4 molar ratio, implying that TPARA incorporation in the TPARA and EDOT copolymer enhances the electrode process. The peak current difference was much smaller for the TPARA-to-EDOT ratio of 1:1, indicating that TPARA and EDOT hinder each other’s electropolymerization. At intermediate TPARA:EDOT ratios, the peak current difference varied monotonically with the TPARA concentration increase. Remarkably, the lower the peak current difference, the higher the template PA concentration for all TPARA-to-EDOT ratios, inferring that PA incorporation inhibits the electropolymerization of TPARA and EDOT. Our previous work demonstrated the interactions between the peptides of C-reactive protein during electropolymerization [3]. The current intensity of the oxidation peak decreased with the increase in PA concentration, revealing that the latter decreases the electropolymerization/electrodeposition rate of polyaniline, perhaps because of the –NH2 functional group present on the PA side chains [3].
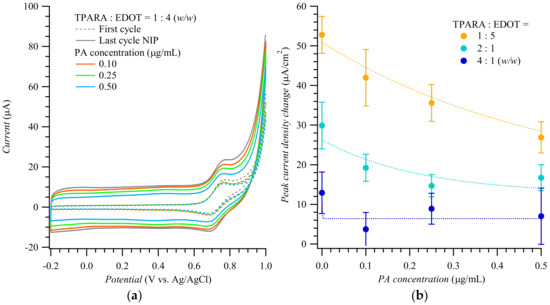
Figure 1.
(a) Potentiodynamic curves of the 1st and 20th cycle during simultaneous electropolymerization and deposition of PA-templated MIP films for different concentrations of the peptide A template. (b) The difference in the peak current of the 20th and 1st polymerization cycle, for different TPARA-to-EDOT ratios, vs. PA template concentration.
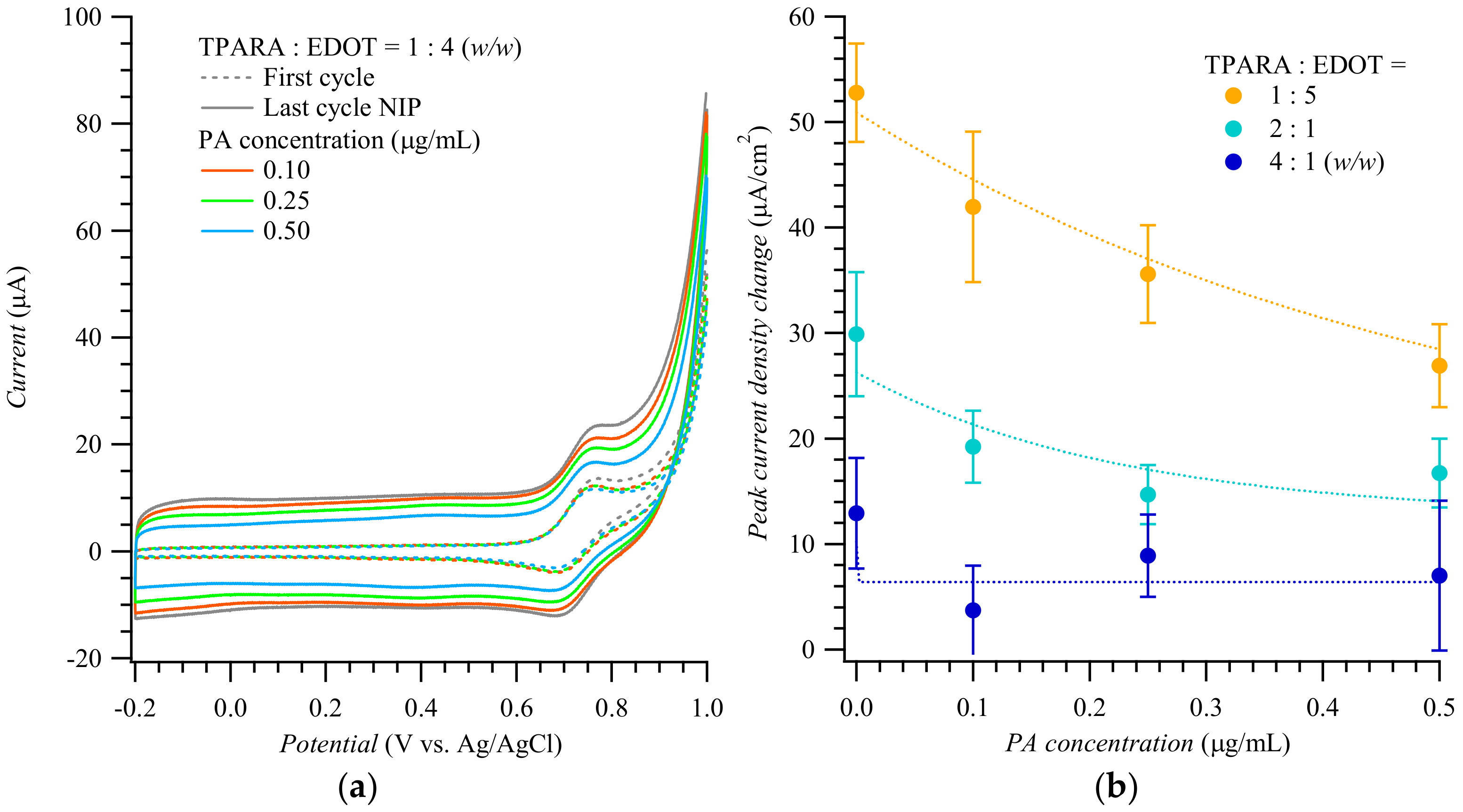
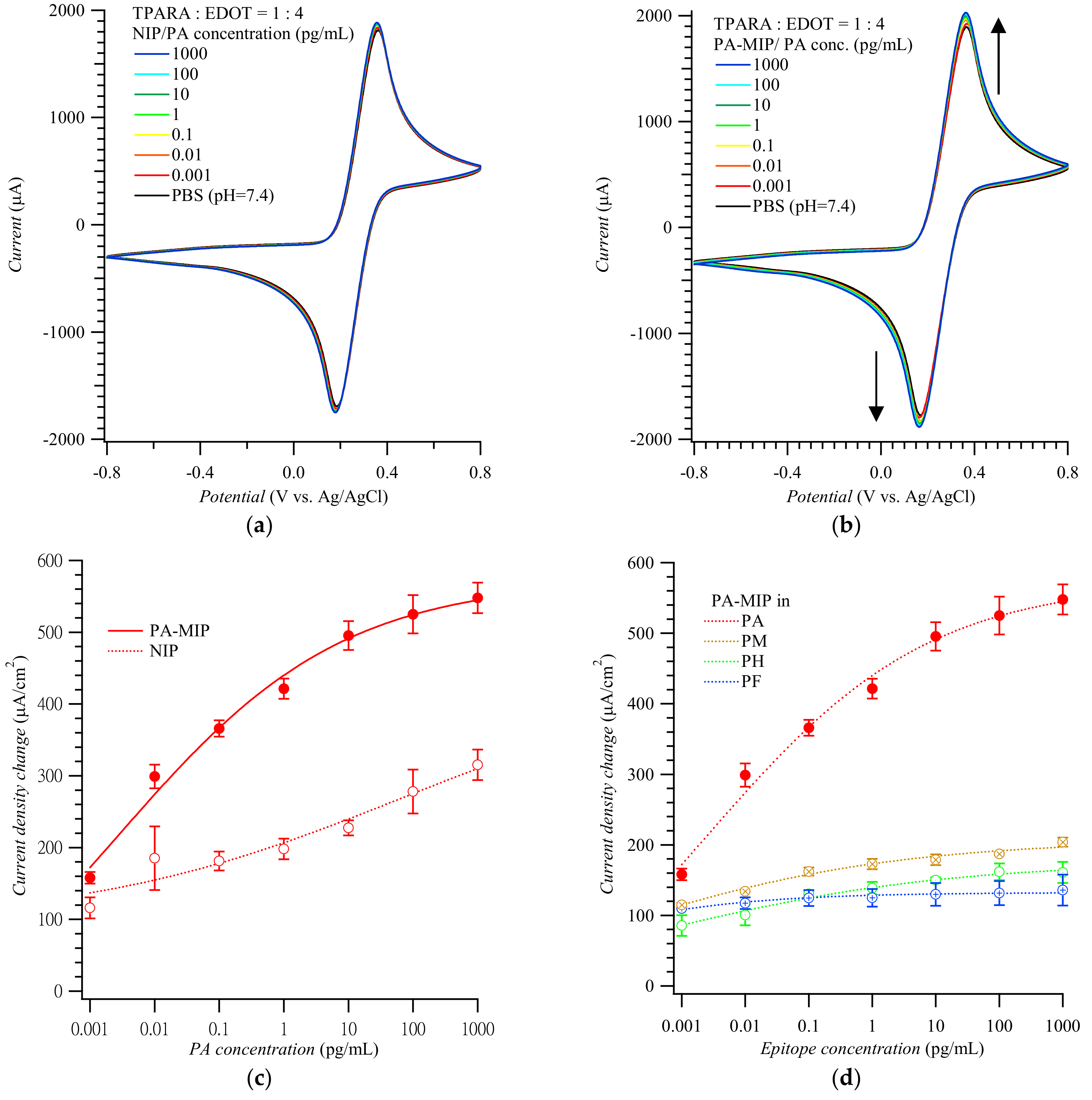
Figure 2 shows CV voltammograms for the Fe(CN)63−/Fe(CN)64− redox probe used to actuate the “gate effect” [17,18,26] at the NIP (Figure 2a) and MIP (Figure 2b) film-coated electrode in the presence of the PA analyte of different concentrations. CV curves in Figure 2a,b display pairs of cathodic and anodic peaks at ~0.20 and ~0.40 V vs. Ag/AgCl, respectively, representing reversible electro-oxidation and electroreduction of the probe. Apparently, the conductive polymer film amplified the peaks of the redox probe to ~2 mA. Expectedly, the peak current change, which accompanied the electrode transfer from the blank PBS solution to that of the (PA analyte)-containing PBS, was higher for the MIP than for the NIP film-coated electrode. The anodic peak current differences in Figure 3a,b were then replotted in Figure 2c as a function of PA concentration. Differences in the anodic peak currents on the MIP film-coated electrode drastically increased when PA reached 1.0 fg/mL. The MIP film-coated electrode selectivity was also examined (Figure 2d). The CV anodic peak current differences for other MMP-1 epitopes, including PA, PH, PM, and PF, varied from 100 to 200 μA/cm2; i.e., they were even lower than those for the PA template on the NIP film-coated electrode.
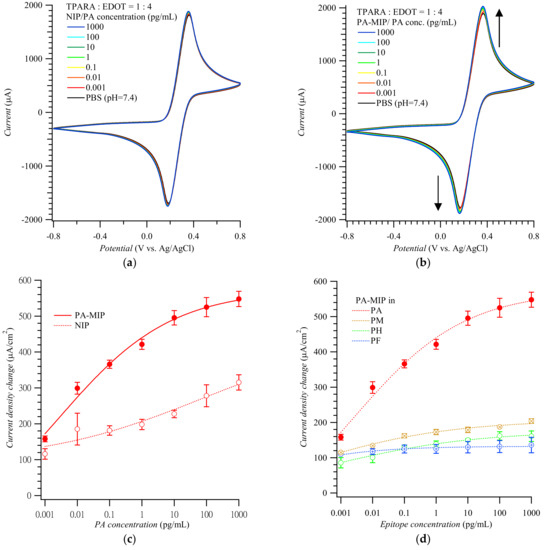
Figure 2.
Cyclic voltammograms for target epitopes at different concentrations using (a) the NIP- and (b) PA-templated poly(TPARA-co-EDOT) film-coated electrodes; vertical arrows indicate current changes in consecutive cycles. (c) Calibration plots for the PA analyte epitope from (a,b). (d) Interfering effect of other epitopes from MMP-1 at various concentrations. Peak current changes were measured at anodic peak potentials of 0.24 to 0.29 V vs. Ag/AgCl in 125 mM KCl, 5 mM K4Fe(CN)6, and 5 mM K3Fe(CN)6. Peptides PA, PH, PM, and PF are AQDDIDGIQAI, HGYPKDIYSS, MIAHDFPGIGHK, and FKGNKYWAVQGQNV, respectively.
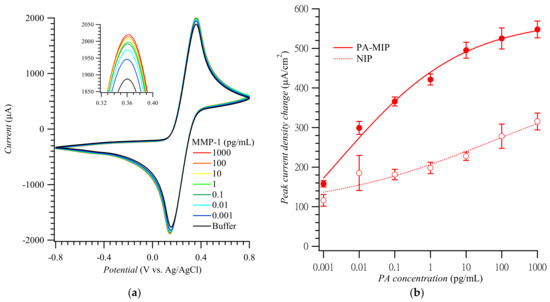
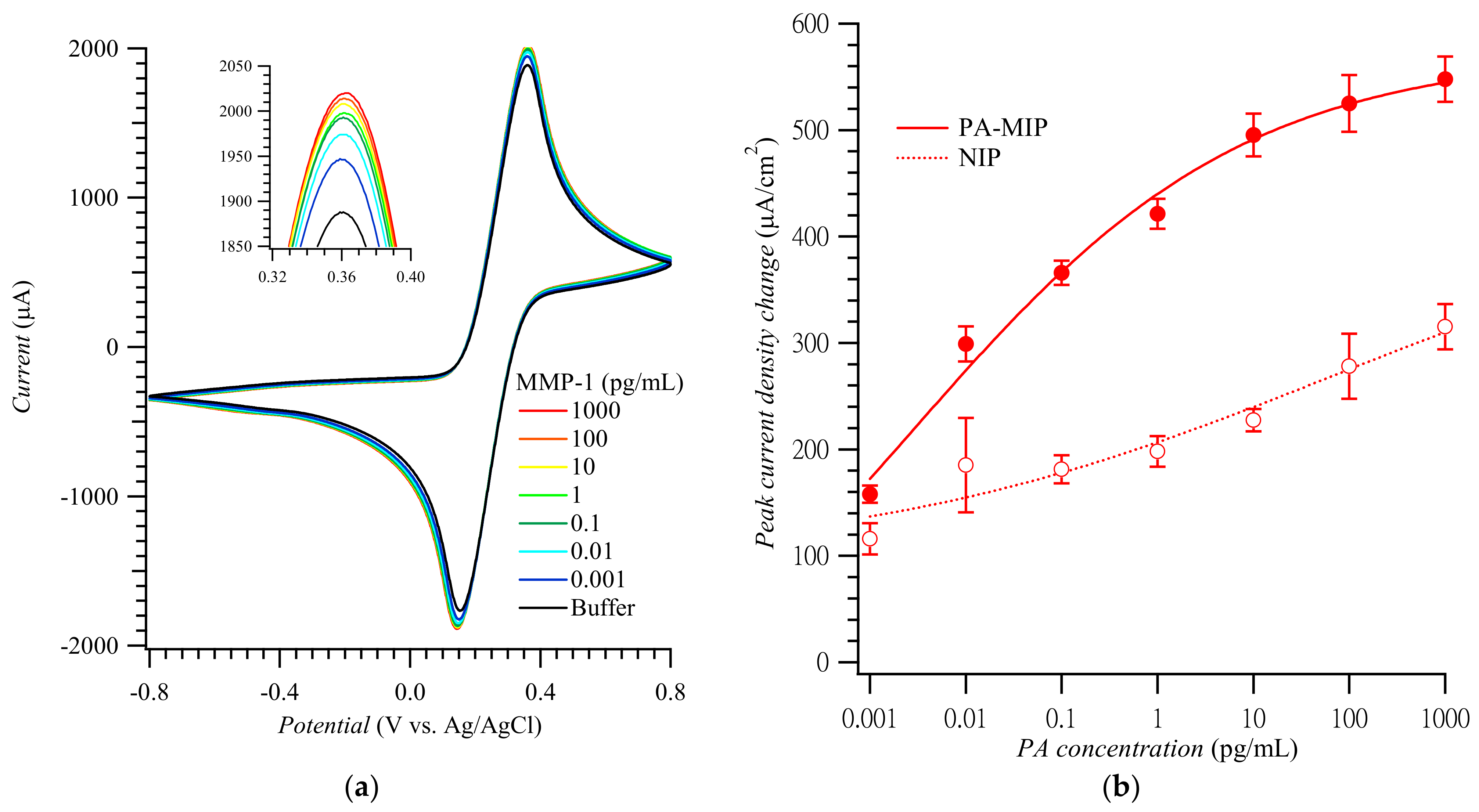
Figure 3.
(a) CV curves and (b) calibration plots of the anodic peak current density change vs. MMP-1 concentration constructed using PA-templated poly(TPARA-co-EDOT) film-coated electrodes in 5 mM K4Fe(CN)6 and 5 mM K3Fe(CN)6 (adapted with permission from Ref. [21]). The anodic peaks were measured in the range of 0.34 to 0.38 V vs. Ag/AgCl.
SEM images of NIP and MIP PA-templated poly(TPARA-co-EDOT) film-coated electrodes are displayed in Figure S3 in the Supplementary Materials. From top to bottom, the graphs show films before and after PA template removal from the film, then after PA analyte binding from its 1.0 pg/mL solution for 30 min. The SEM image of the NIP poly(TPARA-co-EDOT) film-coated electrode before PA template extraction (Figure S3a) shows granular surface deposits with some raised particles. The average granule size of the MIP PA-templated poly(TPARA-co-EDOT) film deposited from 0.5 μg/mL PA (right column in Figure S3) was smaller than that of the NIP film-coated electrode (left column in Figure S3). Results of EDX elemental analyses of the non-templated and PA-templated poly(TPARA-co-EDOT) are summarized in Table 1. The atomic carbon-to-nitrogen-to-oxygen-to-sulfur ratios were ca. 30:1:15:3, indicating that the EDOT-to-TPARA molar ratio was the same as in the stock solution of the 4:1 molar ratio.

Table 1.
Results of EDX elemental analyses of the PA-templated poly(TPARA-co-EDOT).
Figure S4 shows the C 1s deconvoluted XPS spectra; the C 1s envelope could be decomposed into aromatic C, C-S, C=C-O, and C-O-C components corresponding to the binding energies of 284.7, 285.3, 286.1, and 286.9 eV, respectively. The deconvolution results are listed in Table 2. The aromatic C component decreased, and C-S, C=C-O, and C-O-C components increased after NIP film washing, indicating that the TPARA moiety is its primary unreacted component. On the PA analyte-bound NIP film, the aromatic C component recovered to the level characteristic of that before washing, whereas the C-S and C-O-C EDOT components’ content was decreased. However, the C=C-O component content increased after PA analyte binding, arising from PA’s presence. For pAIPs, both the aromatic C and C-S contents decreased. However, the latter decreased more significantly after washing. Furthermore, both C=C-O and C-O-C components’ contents increased. However, the latter increased more significantly after washing, indicating that TPARA is the primary unreacted component in the MIP (as was the case for the NIP). TPARA and EDOT moieties did not completely react and were deposited at the same molar ratio. On the PA analyte-bound MIP film, the aromatic C component almost recovered to the level characteristic of that before washing, whereas the C-S and C=C-O components’ contents slightly increased, and the C-O-C components’ content significantly decreased.

Table 2.
Results of XPS elemental analyses of the PA-templated poly(TPARA-co-EDOT) using deconvoluted C 1s bands.
Finally, the CV peaks for NIP and MIP (Figure S5a,b, respectively), with the PA template extracted, film-coated electrodes in 5 mM K4Fe(CN)6 and 5 mM K3Fe(CN)6, 1.0 pg/mL PA, and 1.0 pg/mL MMP-1 in the PBS (pH = 7.4) solution, obeyed the Randles–Ševčik equation of ip = 268600 n3/2 A D1/2 c v1/2 at 25 °C, where ip is the peak current in amperes, n is the number of electrons transferred, A is the electrode surface area in cm2, F is the Faraday constant in C/mol, D is the diffusion coefficient in cm2/s, c is the concentration in mol/cm3, ν is the potential scan rate in V/s, R is the gas constant in J/K mol, and T is the temperature in K. The ac impedance measurements for MIP and NIP film-coated electrodes in 5 mM K4Fe(CN)6 and 5 mM K3Fe(CN)6, 1.0 pg/mL PA, and in the PBS solution (Figure S3c) indicated that the charge transfer resistance (Rct) values were ~30, 28, 22, and 22 Ω, respectively. Moreover, the resistances for MIP film-coated electrodes were lower in the 1.0 pg/mL PA analyte solution than in the plain PBS solution. Figure S5d illustrates the reusability of the MIP film-coated electrodes treated with the same washing procedures as those for the template removal described in the Supplementary Materials. The MMP-1 analyte was then bound from its 1.0 pg/mL solution by the MIP film-coated electrode. The MMP-1 analyte could be determined at least five times without the electrode losing its sensing performance and with a standard deviation of less than 7.3%.
Figure 3a shows CV curves for the MMP-1 of different concentrations. These curves’ anodic peak current densities were replotted to construct the MMP-1 calibration plots for the MIP and NIP film-coated electrodes (Figure 3b) [21]. The imprinting factor, calculated as the ratio of slopes of the calibration plots for the MMP-1 at the MIP to that at the NIP film-coated electrodes in the MMP-1 determination range, was ca. 2.6–3.3. The linear dynamic concentration range and the limit of detection were ca. 0.001 to 10.0 pg/mL and 0.2 fg/mL MMP-1, respectively, which are comparable with other works listed in Table S2.
The calibration plot for the MIP film-coated electrode was then employed for MMP-1 determination in the culture medium of A549 cells. The MMP-1 concentration, determined using the MIP films-coated electrodes, was successfully confirmed using ELISA (Table S2). Imaging of A549 cells (Figure S6 in Supplementary Materials) shows optical, DAPI, anti-(MMP-1)-stained, and merged images from the top left to the bottom right. As expected, there was a pronounced expression of MMP-1 within the cells, as seen in the merged image.
4. Conclusions
Towards the fabrication of a cost-effective MIP-based chemosensor, we adopted a stepwise approach to finding suitable epitopes of a costly MMP-1 protein biomarker. BLAST software was helpful in the search for the most appropriate MMP-1 peptide epitopes. Then, the chosen MMP-1 epitope was successfully imprinted in the poly(TPARA-co-EDOT) film during its simultaneous formation and deposition. For the epitope and whole-MMP-1 protein selective determination, the Fe(CN)63−/Fe(CN)64− redox couple was used as the probe in a “gate effect” transduction applied [25,26]. The imprinting factor was ca. 2.6–3.3. The MMP-1 detectability was at a picogram level; thus, the fabricated chemosensor is suitable for MMP-1 determination in real samples of cancerous tumor human cells, as was demonstrated using A549 cells in tissue culture [21].
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/bios12111018/s1, S1. Experimental methods; Table S1. Peptides and their physico-chemical properties resulting from in silico cleavage of the MMP-1 biomarker; Table S2. The comparison of sensing methods for MMP-1; Table S3. MMP-1 determination in the culture medium of A549 cells using the MIP film-coated electrode chemosensors and the ELISA; Scheme S1. A proposed structural formula of the pA-imprinted poly(TPARA-co-EDOT). Figure S1. FASTA form of matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) biomarker; Figure S2. Potentiodynamic curves for deposition of (a) non-imprinted (NIP) and peptide-imprinted polymer (MIP) films with 0.50 mg/mL PA present during the electropolymerization in a TPARA:EDOT at (b) 1:4 (wt/wt) (c) 1:1, and (d) 4:1 solution on 0.5 × 0.5 cm2 I.T.O. electrodes; Figure S3. S.E.M. images of (a) NIPs, and (b) PA-templated poly(TPARA-co-EDOT) film-coated electrodes (a’) before, (b’) after PA template removal with ethanol, and (a” and b”) after PA analyte binding from the 1 pg/mL PA solution for 30 min; Figure S4. The XPS spectra of non-deconvoluted and deconvoluted C 1s bands for the (a) non-imprinted (NIP) and (b) PA-templated poly(TPARA-co-EDOT) (PA-MIP) films; Figure S5. The CV peaks for (a) the NIP and (b) MIPs in 5 mM K4Fe(CN)6 and 5 mM K3Fe(CN)6, 1.0 pg/mL PA and 1.0 pg/mL MMP-1, in the PBS (pH = 7.4) solution, fitted with the Randles–Ševčik equation. (c) The ac impedance imaginary vs. real component dependence for the MIP and NIP film-coated electrodes in 5 mM K4Fe(CN)6 and 5 mM K3Fe(CN)6, in the 1.0 pg/mL pA, PBS (pH = 7.4) solution and a similar solution without PA. (d) The reusability of the PA-templated (pAIPs) poly(TPARA-co-EDOT) film-coated electrodes. The electrode was used to determine MMP-1 in its 1.0 ng/mL solution, subsequently rinsed, then reused five times; Figure S6. (a) optical, (b) DAPI staining, (c) immunohistochemistry of MMP-1 proteins, and (d) merged images of A549 lung cancer cells at 400X magnification. References [14,16,24,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35] are cited in the supplementary materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.K. and H.-Y.L.; methodology, M.-H.L., C.-C.L., W.K., J.L.T., C.-Y.L. (Chu-Yun Lin), Z.I., P.B., C.-Y.L. (Chien-Yu Lin), P.S.S., C.-H.Y. and H.-Y.L.; software, Z.I., P.B. and P.S.S.; validation, M.-H.L., C.-C.L. (Chu-Yun Lin), W.K., P.S.S. and H.-Y.L.; formal analysis, M.-H.L., C.-C.L., J.L.T., C.-Y.L. (Chu-Yun Lin), C.-Y.L. (Chu-Yun Lin) and H.-Y.L.; investigation, M.-H.L., C.-C.L., W.K., J.L.T., C.-Y.L. (Chu-Yun Lin), Z.I., P.B., C.-Y.L. (Chien-Yu Lin), P.S.S., C.-H.Y. and H.-Y.L.; resources, C.-H.Y. and H.-Y.L.; data curation, C.-C.L., C.-Y.L. (Chu-Yun Lin), Z.I., P.B. and C.-Y.L. (Chien-Yu Lin); writing—original draft preparation, M.-H.L., C.-C.L., P.S.S., W.K., C.-H.Y. and H.-Y.L.; writing—review and editing, M.-H.L., C.-C.L., W.K., J.L.T., P.S.S., C.-H.Y. and H.-Y.L.; visualization, C.-Y.L. (Chu-Yun Lin) and H.-Y.L.; supervision, W.K., P.S.S., C.-H.Y. and H.-Y.L.; project administration, M.-H.L., W.K., P.S.S. and H.-Y.L.; funding acquisition, M.-H.L., C.-C.L., W.K., P.S.S. and H.-Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
H.Y.L. appreciates the financial support of the Ministry of Science and Technology of R.O.C. under contract nos. MOST 106-2221-E-390-013-MY3, MOST 107-2923-M-390-001-MY3, MOST 108-2923-B-390-001-MY3, MOST 109-2314-B-390-001-MY3 and MOST 110-2221-E-390-003-MY3. W.K. acknowledges Poland’s National Center for Research and Development (NCBR) for financial support through grant no. SensIPF PL-TW/VI/2/2019.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Maziz, A.; Özgür, E.; Bergaud, C.; Uzun, L. Progress in Conducting Polymers for Biointerfacing and Biorecognition Applications. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2021, 3, 100035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-H.; Thomas, J.L.; Su, Z.-L.; Yeh, W.-K.; Monzel, A.S.; Bolognin, S.; Schwamborn, J.C.; Yang, C.-H.; Lin, H.-Y. Epitope imprinting of alpha-synuclein for sensing in Parkinson’s brain organoid culture medium. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 175, 112852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.H.; Liu, K.H.; Thomas, J.L.; Chen, C.Y.; Chen, C.Y.; Yang, C.H.; Lin, H.Y. Doping of MXenes enhances the electrochemical response of peptide-imprinted conductive polymers for the recognition of C-Reactive protein. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 200, 113930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.S.; Pietrzyk-Le, A.; D’Souza, F.; Kutner, W. Electrochemically synthesized polymers in molecular imprinting for chemical sensing. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 3177–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verheyen, E.; Schillemans, J.P.; Wijk, M.V.; Demeniex, M.-A.; Hennink, W.E.; Nostrum, C.F.V. Challenges for the effective molecular imprinting of proteins. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 3008–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-H.; Lin, C.-C.; Thomas, J.L.; Li, J.-A.; Lin, H.-Y. Cellular reprogramming with multigene activation by the delivery of CRISPR/dCas9 ribonucleoproteins via magnetic peptide-imprinted chitosan nanoparticles. Mater. Today Bio 2021, 9, 100091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khumsap, T.; Corpuz, A.; Nguyen, L.T. Epitope-imprinted polymers: Applications in protein recognition and separation. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 11403–11414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquardini, L.; Bossi, A.M. Molecularly imprinted polymers by epitope imprinting: A journey from molecular interactions to the available bioinformatics resources to scout for epitope templates. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 6101–6115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossi, A.M.; Sharma, P.S.; Montana, L.; Zoccatelli, G.; Laub, O.; Levi, R. Fingerprint-Imprinted Polymer: Rational Selection of Peptide Epitope Templates for the Determination of Proteins by Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 4036–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossowski, L. Invasion of connective tissue by human carcinoma cell lines: Requirement for urokinase, urokinase receptor, and interstitial collagenase. Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 6754–6760. [Google Scholar]
- Jabłońska-Trypuć, A.; Matejczyk, M.; Rosochacki, S. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), the main extracellular matrix (E.C.M.) enzymes in collagen degradation, as a target for anticancer drugs. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med.Chem. 2016, 31, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, B.A.; Kolesnikova, N.; Sonett, J.; D’Armiento, J. Extracellular regulated kinase/mitogen activated protein kinase is up-regulated in pulmonary emphysema and mediates matrix metalloproteinase-1 induction by cigarette smoke. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 17690–17696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.-C.; Fang, H.; Xu, W.-F. Advances in assays of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their inhibitors. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med.Chem. 2008, 23, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-H.; O’Hare, D.; Guo, H.-Z.; Yang, C.-H.; Lin, H.-Y. Electrochemical sensing of urinary progesterone with molecularly imprinted poly(aniline-co-metanilic acid)s. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 3782–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-H.; Thomas, J.L.; Liu, W.-C.; Zhang, Z.-X.; Liu, B.-D.; Yang, C.-H.; Lin, H.-Y. A multichannel system integrating molecularly imprinted conductive polymers for ultrasensitive voltammetric determination of four steroid hormones in urine. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-H.; Thomas, J.L.; Su, Z.-L.; Zhang, Z.-X.; Lin, C.-Y.; Huang, Y.-S.; Yang, C.-H.; Lin, H.-Y. Doping of transition metal dichalcogenides in molecularly imprinted conductive polymers for the ultrasensitive determination of 17β-estradiol in eel serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 150, 111901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-H.; Thomas, J.L.; Chen, J.-Z.; Jan, J.-S.; Lin, H.-Y. Activation of tumor suppressor p53 gene expression by magnetic thymine-imprinted chitosan nanoparticles. Chem. Comm. 2016, 52, 2137–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Pan, M.; Hu, J.; Wang, F.; Liu, X. Electrochemical Biosensor for MicroRNA Detection Based on Cascade Hybridization Chain Reaction. ChemElectroChem 2018, 5, 1380–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Aamri, M.; Yammouri, G.; Mohammadi, H.; Amine, A.; Korri-Youssoufi, H. Electrochemical biosensors for detection of microRNA as a cancer biomarker: Pros and cons. Biosensors 2020, 10, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-H.; Thomas, J.L.; Liao, C.-L.; Jurcevic, S.; Crnogorac-Jurcevic, T.; Lin, H.-Y. Polymers imprinted with three REG1B peptides for electrochemical determination of Regenerating Protein 1B, a urinary biomarker for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 1773–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-H.; Lin, C.-C.; Kutner, W.; Thomas, J.L.; Lin, C.-Y.; Iskierko, Z.; Ku, Y.-S.; Lin, C.-Y.; Borowicz, P.; Sharma, P.; et al. Peptide-imprinted conductive polymer on continuous monolayer molybdenum disulfide transferred electrodes for electrochemical sensing of Matrix Metalloproteinase-1 in lung cancer culture medium. Biosens. Bioelectron. X 2022, 100258, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-H.; Thomas, J.L.; Chang, Y.-C.; Tsai, Y.-S.; Liu, B.-D.; Lin, H.-Y. Electrochemical sensing of nuclear matrix protein 22 in urine with molecularly imprinted poly (ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol) coated zinc oxide nanorod arrays for clinical studies of bladder cancer diagnosis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 79, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Ye, H.; Yu, L.; Chi, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, G. Tailor-made peptide sensor for detection of matrix metalloproteinase 2 in blood serum. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 5371–5374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartold, K.; Iskierko, Z.; Borowicz, P.; Noworyta, K.; Lin, C.-Y.; Kalecki, J.; Sharma, P.S.; Lin, H.-Y.; Kutner, W. Molecularly imprinted polymer-based extended-gate field-effect transistor (EG-FET) chemosensor for selective determination of matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) protein. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 208, 114203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lach, P.; Cieplak, M.; Majewska, M.; Noworyta, K.R.; Sharma, P.S.; Kutner, W. “Gate Effect” in p-Synephrine Electrochemical Sensing with a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer and Redox Probes. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 7546–7553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.S.; Garcia-Cruz, A.; Cieplak, M.; Noworyta, K.R.; Kutner, W. Gate effect’ in molecularly imprinted polymers: The current state of understanding. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2019, 16, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-H.; Huang, L.-R.; Chih, Y.-K.; Lin, W.-C.; Liu, F.-J.; Wang, T.-L. Molecular assembled self-doped polyaniline copolymer ultra-thin films. Polymer 2007, 48, 3237–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behl, M.; Hattemer, E.; Brehmer, M.; Zentel, R. Tailored Semiconducting Polymers: Living Radical Polymerization and NLO-Functionalization of Triphenylamines. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2002, 203, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-H.; Chen, H.-L.; Chuang, Y.-Y.; Wu, C.-G.; Chen, C.-P.; Liao, S.-H.; Wang, T.-L. Characteristics of triphenylamine-based dyes with multiple acceptors in application of dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Power Sources 2009, 188, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Tsai, T.-C.; Thomas, J.L.; Lee, M.-H.; Liu, B.-D.; Lin, H.-Y. Urinalysis with molecularly imprinted poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol) potentiostat sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2611–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-Y.; O'Hare, D.; Chao, I.J.; Wei, H.-W.; Liang, Y.-F.; Liu, B.-D.; Lee, M.-H.; Lin, H.-Y. Integrated potentiostat for electrochemical sensing of urinary 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid with molecularly imprinted poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Jian, M.; Li, X.; Wei, J.; Meng, X.; Wang, Z. Biosensors and bioassays for determination of matrix metalloproteinases: State of the art and recent advances. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 3261–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarzewicz, A.; Romanowicz, L.; Sveklo, I.; Gorodkiewicz, E. The development of a matrix metalloproteinase-1 biosensor based on the surface plasmon resonance imaging technique. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 6428–6435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, Y.-C.; Huang, W.-T.; Chiang, P.-H.; Tang, M.-C.; Lin, C.-S. Aqueous zymography screening of matrix metalloproteinase activity and inhibition based on colorimetric gold nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 32, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krismastuti, F.S.H.; Pace, S.; Voelcker, N.H. Porous Silicon Resonant Microcavity Biosensor for Matrix Metalloproteinase Detection. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3639–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).