Simultaneous Imaging of Bio- and Non-Conductive Targets by Combining Frequency and Time Difference Imaging Methods in Electrical Impedance Tomography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Principles of EIT
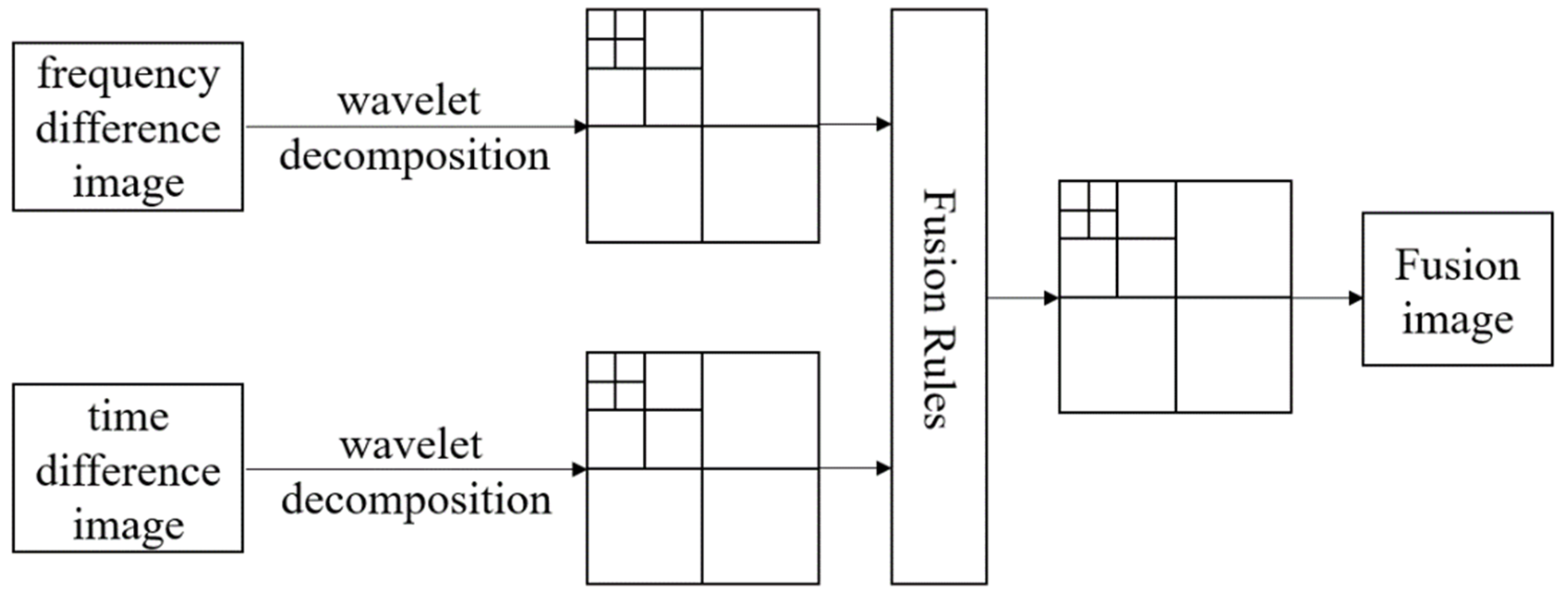
2.2. Wavelet-Based Image Fusion
2.3. Image Quality Evaluation
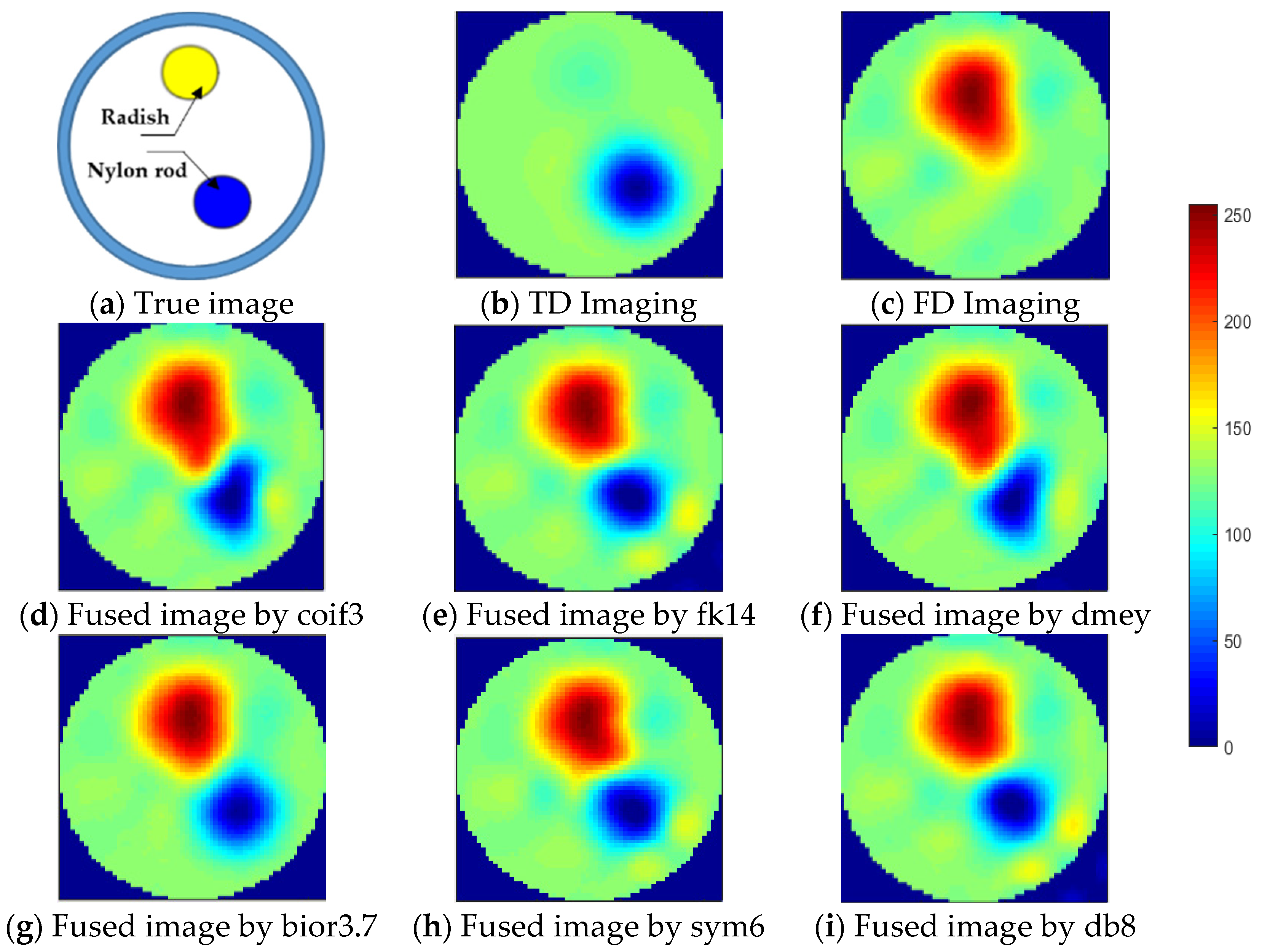
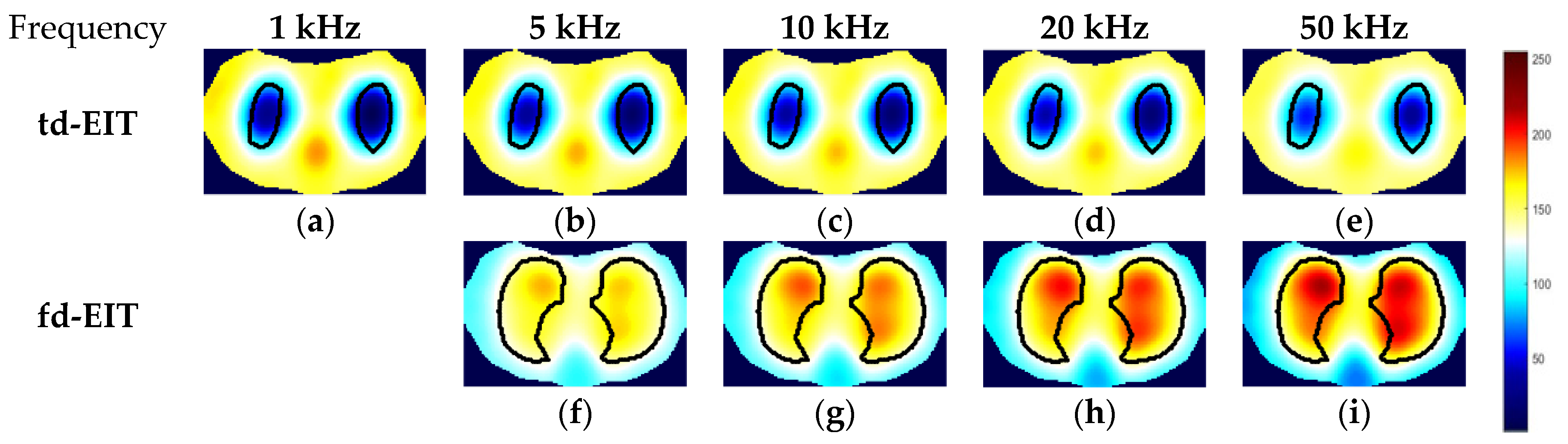
3. Characterization of td- and fd-EIT Imaging by Experiment
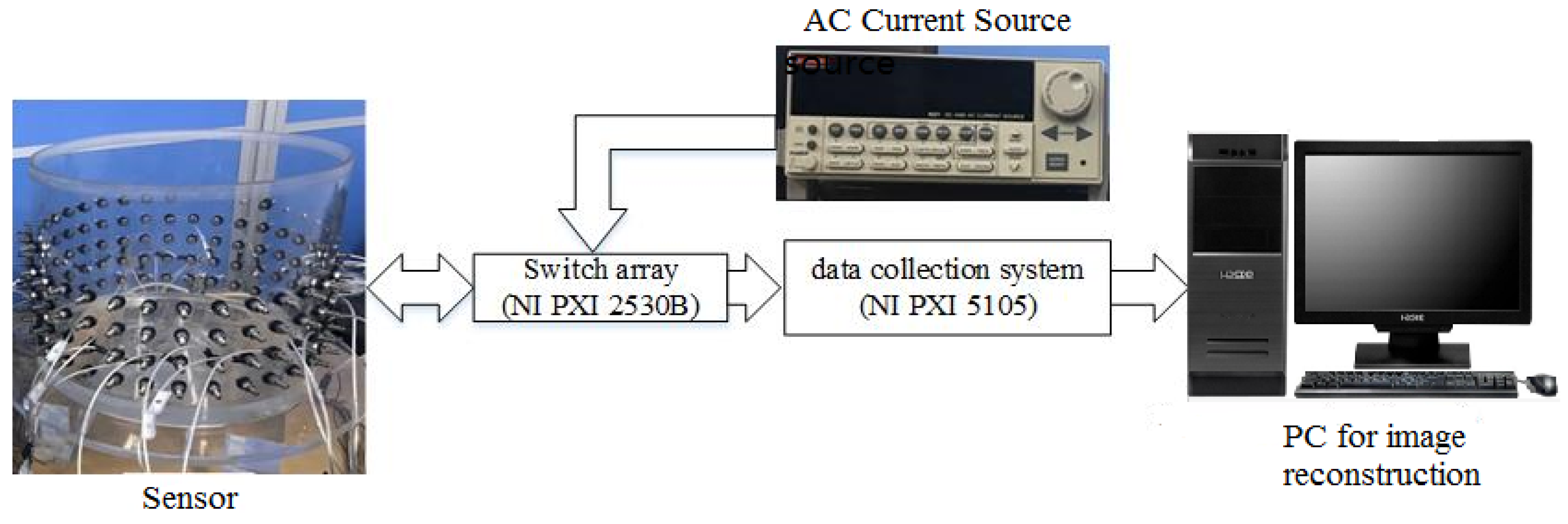
3.1. Experimental Setup
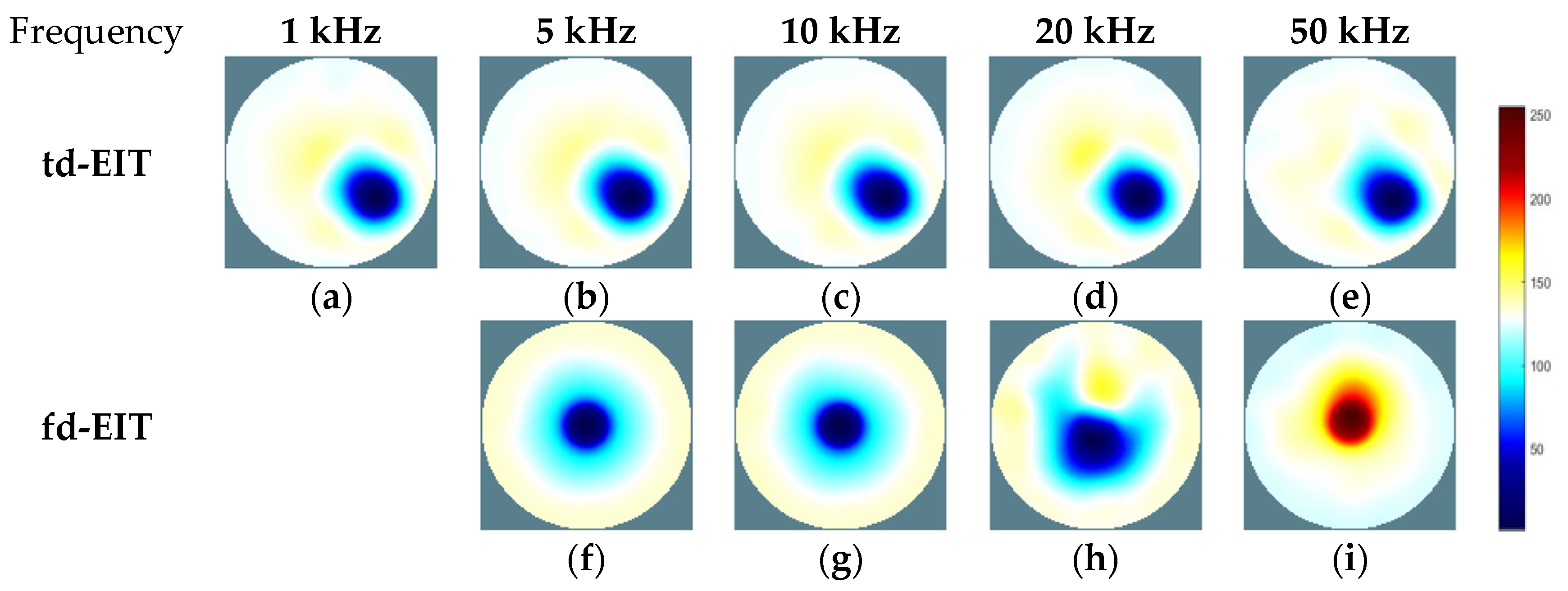
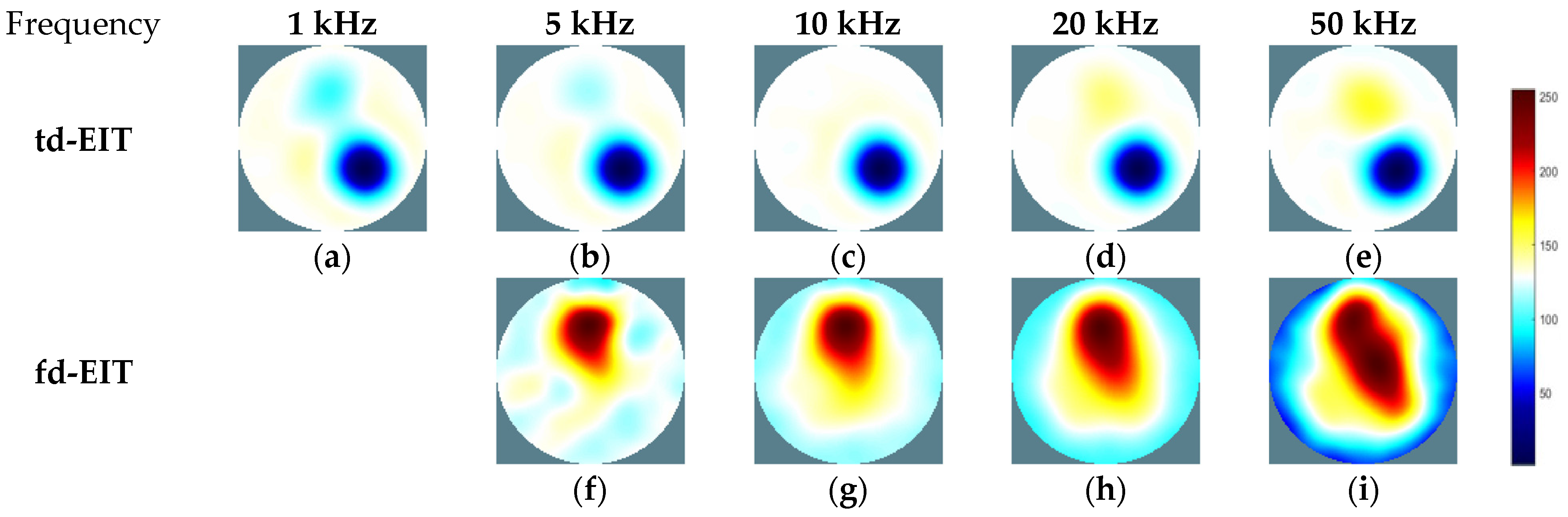
3.2. Experimental Results and Analysis
3.3. Image Fusion with Respect to td- and fd-EIT Imaging
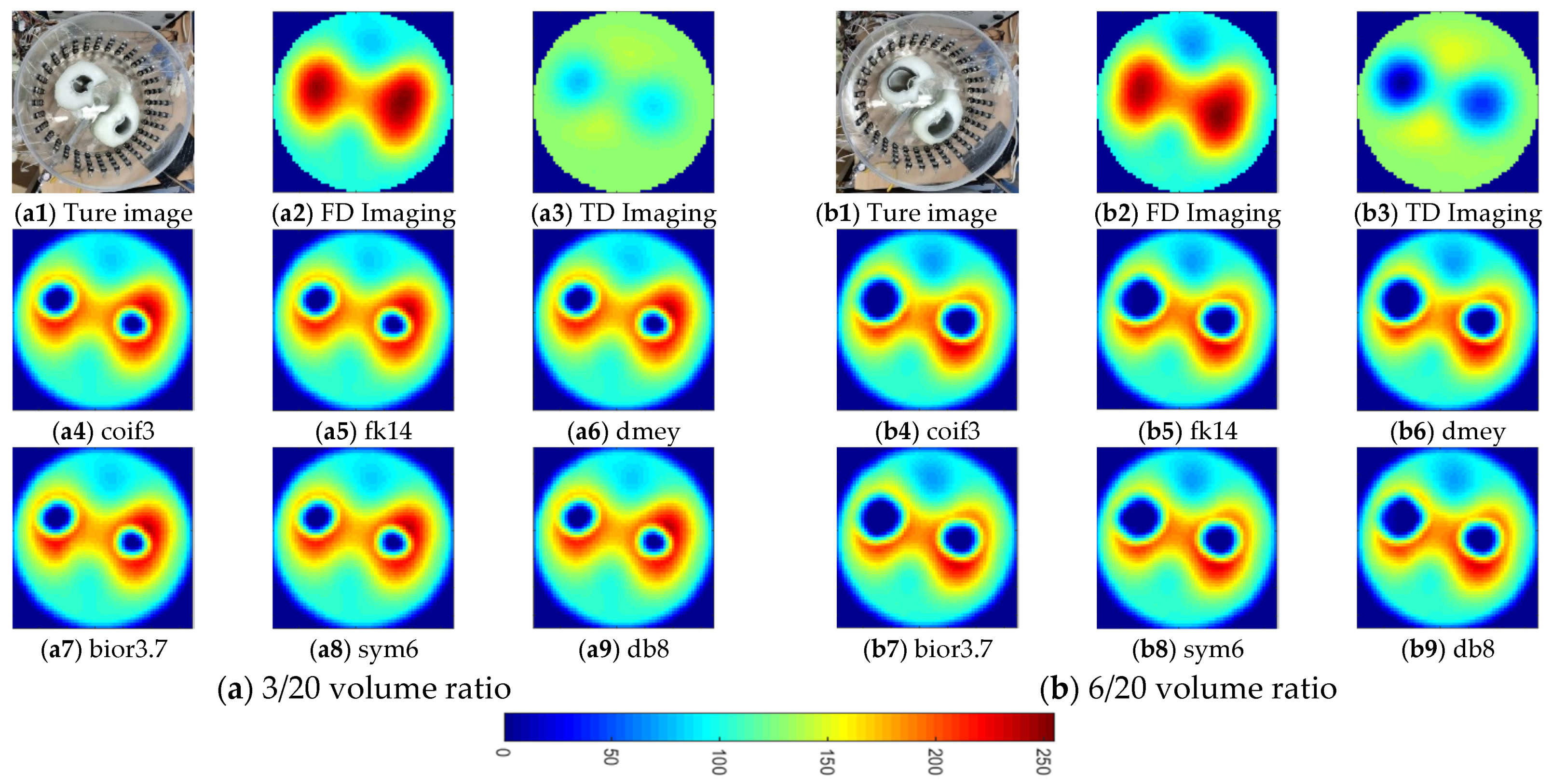
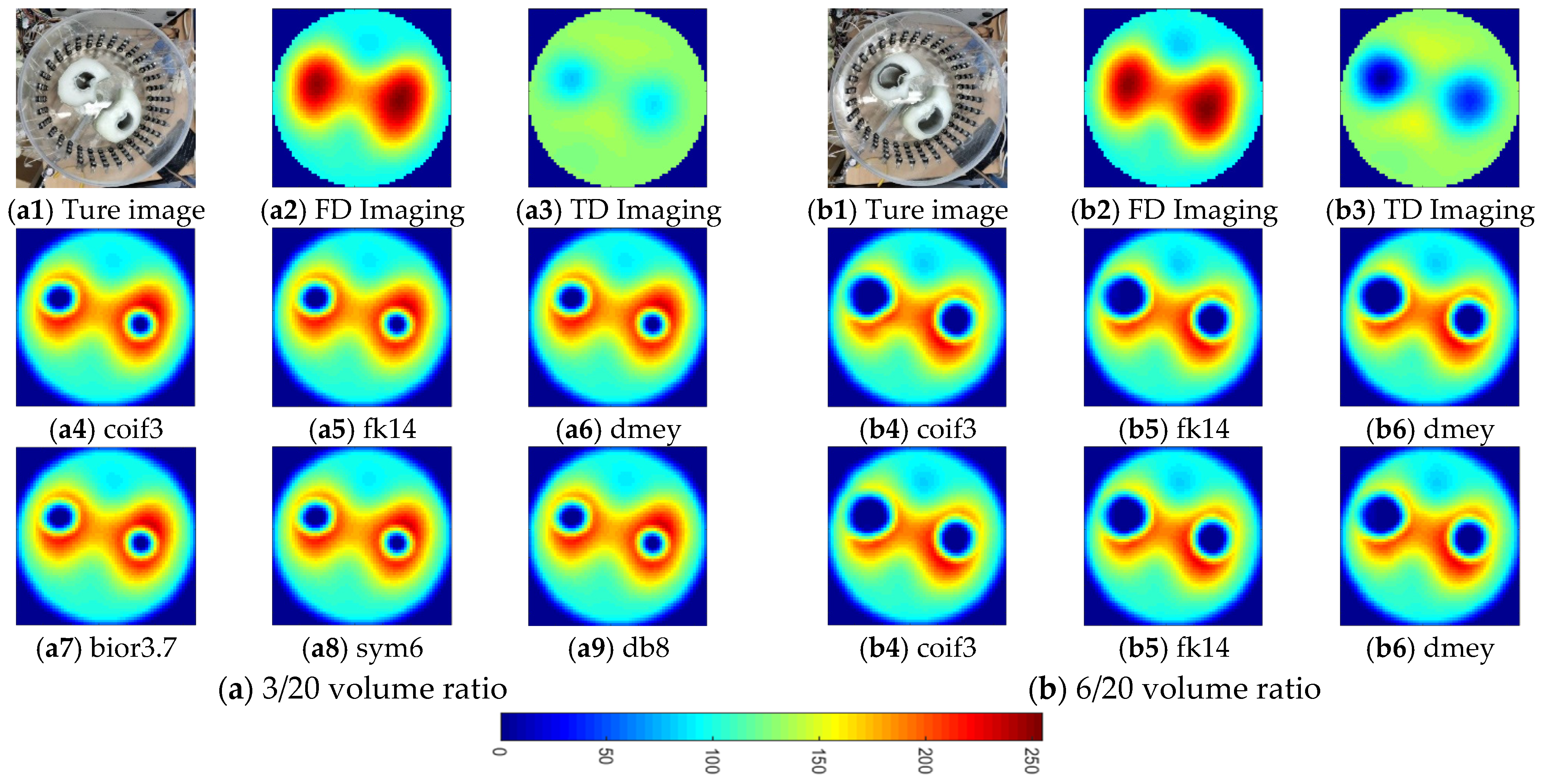
4. Investigation for Improving Lung Ventilation Imaging with Thorax Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, B.H. Electrical impedance tomography (EIT): A review. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2003, 27, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, A.; Arnold, J.H.; Bayford, R.; Borsic, A.; Brown, B.; Dixon, P.; Faes, T.; Frerichs, I.; Gagnon, H.; Garber, Y. GREIT: A unified approach to 2D linear EIT reconstruction of lung images. Physiol. Meas. 2009, 30, S35–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Jia, J. A multi-frequency electrical impedance tomography system for real-time 2D and 3D imaging. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2017, 88, 085110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Woo, E.J.; Seo, J.K. A Fidelity-embedded Regularization Method for Robust Electrical Impedance Tomography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 37, 1970–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Smyl, D.; Du, J. A Parametric Level Set-Based Approach to Difference Imaging in Electrical Impedance Tomography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 38, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Smyl, D.; Du, J. Nonstationary Shape Estimation in Electrical Impedance Tomography Using a Parametric Level Set-Based Extended Kalman Filter Approach. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 1894–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, R.P.; Webster, J.G. An Impedance Camera for Spatially Specific Measurements of the Thorax. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1978, 25, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, A.; Boyle, A. Electrical Impedance Tomography: Tissue Properties to Image Measures. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 64, 2494–2504. [Google Scholar]
- Mellenthin, M.M.; Mueller, J.L.; Camargo, E.D.; Moura, F.D.; Santos, T.; Lima, R.G.; Hamilton, S.J.; Muller, P.A.; Alsaker, M. The ACE1 Electrical Impedance Tomography System for Thoracic Imaging. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2018, 68, 3137–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, D.C.; Brown, B.H. Applied potential tomography. J. Br. Interplanet. Soc. 1989, 42, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.K.; Harrach, B.; Woo, E.J.; Ammari, H. Recent progress on Frequency Difference Electrical Impedance Tomography. ESAIM Proc. 2009, 26, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.K.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.W.; Zribi, H.; Woo, E.J. Frequency-difference electrical impedance tomography (fdEIT): Algorithm development and feasibility study. Physiol. Meas. 2008, 29, 929–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packham, B.; Koo, H.; Romsauerova, A.; Ahn, S.; Mcewan, A.; Jun, S.C.; Holder, D.S. Comparison of frequency difference reconstruction algorithms for the detection of acute stroke using EIT in a realistic head-shaped tank. Physiol. Meas. 2012, 33, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.J.; Milnes, P.; Waterworth, A.R.; Smallwood, R.H.; Brown, B.H. Mk3.5: A modular, multi-frequency successor to the Mk3a EIS/EIT system. Physiol. Meas. 2001, 22, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcewan, A.; Romsauerova, A.; Yerworth, R.; Horesh, L.; Bayford, R.; Holder, D. Design and calibration of a compact multi-frequency EIT system for acute stroke imaging. Physiol. Meas. 2006, 27, S199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, I.O.; Koo, H.; Lee, K.H.; Sang, M.K.; Woo, E.J. Validation of a multi-frequency electrical impedance tomography (mfEIT) system KHU Mark1: Impedance spectroscopy and time-difference imaging. Physiol. Meas. 2008, 29, 295–307. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, T.I.; Wi, H.; Kim, D.Y.; Yoo, P.J.; Woo, E.J. A fully parallel multi-frequency EIT system with flexible electrode configuration: KHU Mark2. Physiol. Meas. 2011, 32, 835–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Guo, R.; Li, M.; Yang, F.; Abubakar, A. Supervised Descent Learning for Thoracic Electrical Impedance Tomography. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 68, 1360–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, S.A.; Czaplik, M.; Orschulik, J.; Hochhausen, N.; Leonhardt, S. Lung Pathologies analyzed with Multi-Frequency Electrical Impedance Tomography: Pilot Animal Study. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2018, 254, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kang, X.; Fang, L.; Hu, J.; Yin, H. Pixel-level image fusion: A survey of the state of the art. Inf. Fusion 2017, 33, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, P.; Woo, E.J. Iterative reconstruction methods using regularization and optimal current patterns in electrical impedance tomography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1991, 10, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polydorides, N.; Lionheart, W. A Matlab toolkit for three-dimensional electrical impedance tomography: A contribution to the Electrical Impedance and Diffuse Optical Reconstruction Software project. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2002, 13, 1871–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionheart, W.R. EIT reconstruction algorithms: Pitfalls, challenges and recent developments. Physiol. Meas. 2004, 25, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peijia, Z.; Jiwu, H. Discrete Wavelet Transform and Data Expansion Reduction in Homomorphic Encrypted Domain. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 2455–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Z.; Jiangbao, Y.; Feng, Z.; Xiangyu, T.; Lifeng, Z. Reconstruction Method of Electrical Capacitance Tomography Based on Wavelet Fusion. In MATEC Web of Conferences, Proceedings of the 2018 6th International Forum on Industrial Design (IFID 2018), Luoyang, China, 18–20 May 2018; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2018; p. 176. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Song, L. An Image Fusion Algorithm for ECT based on Tikhonov Algorithm and Wavelet Transform. Int. J. Signal. Process. Image Process. Pattern Recognit. 2014, 7, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Z. Study on Registration and Fusion Multimodality Medical Image. J. Converg. Inf. Technol. 2013, 8, 163–169. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, W.; Suo, P.; Liu, D.; Sun, S.; Xu, L. Simultaneous Shape and Permittivity Reconstruction in ECT with Sparse Representation: Two-Phase Distribution Imaging. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, T.K.; Nagaraju, J.; Lubineau, G. Electrical impedance spectroscopy (EIS)-based evaluation of biological tissue phantoms to study multifrequency electrical impedance tomography (Mf-EIT) systems. J. Vis. 2016, 19, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wan, N.; Wen, J.; Cheng, G.; Cheng, L. Quantitative detection and evaluation of thrombus formation based on electrical impedance spectroscopy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 141, 111437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, A.; Lionheart, W. Uses and abuses of EIDORS: An extensible software base for EIT. Physiol. Meas. 2006, 27, S25–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, S.; Lau, R.W.; Gabriel, C. The dielectric properties of biological tissue II: Measurements in the frequency range 10 Hz to 20 GHz. Phys. Med. Biol. 1996, 41, 2251–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriel, S.; Lau, R.W.; Gabriel, C. The dielectric properties of biological tissues: III. Parametric models for the dielectric spectrum of tissues. Phys. Med. Biol. 1996, 41, 2271–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Frequency | 1 kHz | 5 kHz | 10 kHz | 20 kHz | 50 kHz | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCR | fd-EIT | \ | 0.8309 | 1.1268 | 1.8621 | 4.0221 |
| td-EIT | 0.7463 | 0.6415 | \ | 1.1047 | 1.0386 | |
| RIE | fd-EIT | \ | 0.3933 | 0.4017 | 0.2950 | 0.4088 |
| td-EIT | 0.0893 | 0.1156 | \ | 0.2160 | 0.2496 | |
| SSIM | fd-EIT | \ | 0.7648 | 0.6764 | 0.4385 | 0.1614 |
| td-EIT | 0.8039 | 0.7071 | \ | 0.8583 | 0.6943 |
| Frequency | 1 kHz | 5 kHz | 10 kHz | 20 kHz | 50 kHz | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCR | fd-EIT | \ | 1.1667 | 1.1667 | 1.4118 | 1.0588 |
| td-EIT | 1.0172 | 1.0221 | 1.0147 | 0.9706 | 1.0049 | |
| RIE | fd-EIT | \ | 0.1407 | 0.1421 | 0.1850 | 0.4487 |
| td-EIT | 0.1017 | 0.0961 | 0.0964 | 0.1157 | 0.0882 | |
| SSIM | fd-EIT | \ | -0.0272 | −0.0272 | −0.0284 | −0.0262 |
| td-EIT | 0.7544 | 0.7549 | 0.7578 | 0.7574 | 0.8169 |
| Frequency | 1 kHz | 5 kHz | 10 kHz | 20 kHz | 50 kHz | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCR | fd-EIT | \ | 1.0129 | 1.3462 | 2.1952 | 4.7882 |
| td-EIT | 1.1007 | 1.1032 | 1.1106 | 1.1253 | 1.1327 | |
| RIE | fd-EIT | \ | 0.3862 | 0.4052 | 0.3079 | 0.4346 |
| td-EIT | 0.0986 | 0.0869 | 0.0844 | 0.1096 | 0.1330 | |
| SSIM | fd-EIT | \ | 0.7832 | 0.7071 | 0.4318 | 0.1339 |
| td-EIT | 0.8939 | 0.8998 | 0.8912 | 0.8930 | 0.8930 |
| Frequency | 1 kHz | 5 kHz | 10 kHz | 20 kHz | 50 kHz | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCR | fd-lung | \ | 0.9063 | 0.9137 | 0.9207 | 0.9470 |
| td-air | 1.2380 | 1.1077 | 1.0575 | 1.0010 | 0.9381 | |
| RIE | fd-EIT | \ | 0.4030 | 0.4032 | 0.4034 | 0.4041 |
| td-EIT | 0.2395 | 0.2354 | 0.2339 | 0.2325 | 0.2308 |
| Frequency | 1 kHz | 5 kHz | 10 kHz | 20 kHz | 50 kHz | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCR | fd-lung | \ | 0.9064 | 0.9145 | 0.9237 | 0.9446 |
| td-air | 4.1290 | 3.3334 | 2.9910 | 2.6587 | 2.2256 | |
| RIE | fd-EIT | \ | 0.4169 | 0.4168 | 0.4169 | 0.4172 |
| td-EIT | 0.2232 | 0.2214 | 0.2208 | 0.2204 | 0.2200 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, X.; Liu, D.; Wei, J.; Bai, X.; Sun, S.; Tian, W. Simultaneous Imaging of Bio- and Non-Conductive Targets by Combining Frequency and Time Difference Imaging Methods in Electrical Impedance Tomography. Biosensors 2021, 11, 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11060176
Bai X, Liu D, Wei J, Bai X, Sun S, Tian W. Simultaneous Imaging of Bio- and Non-Conductive Targets by Combining Frequency and Time Difference Imaging Methods in Electrical Impedance Tomography. Biosensors. 2021; 11(6):176. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11060176
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Xue, Dun Liu, Jinzhao Wei, Xu Bai, Shijie Sun, and Wenbin Tian. 2021. "Simultaneous Imaging of Bio- and Non-Conductive Targets by Combining Frequency and Time Difference Imaging Methods in Electrical Impedance Tomography" Biosensors 11, no. 6: 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11060176
APA StyleBai, X., Liu, D., Wei, J., Bai, X., Sun, S., & Tian, W. (2021). Simultaneous Imaging of Bio- and Non-Conductive Targets by Combining Frequency and Time Difference Imaging Methods in Electrical Impedance Tomography. Biosensors, 11(6), 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11060176





