A Label and Probe-Free Zika Virus Immunosensor Prussian Blue@carbon Nanotube-Based for Amperometric Detection of the NS2B Protein
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. ZIKV Isolates Culture and Serum Samples
2.3. Apparatus
2.4. SPE Manufacture
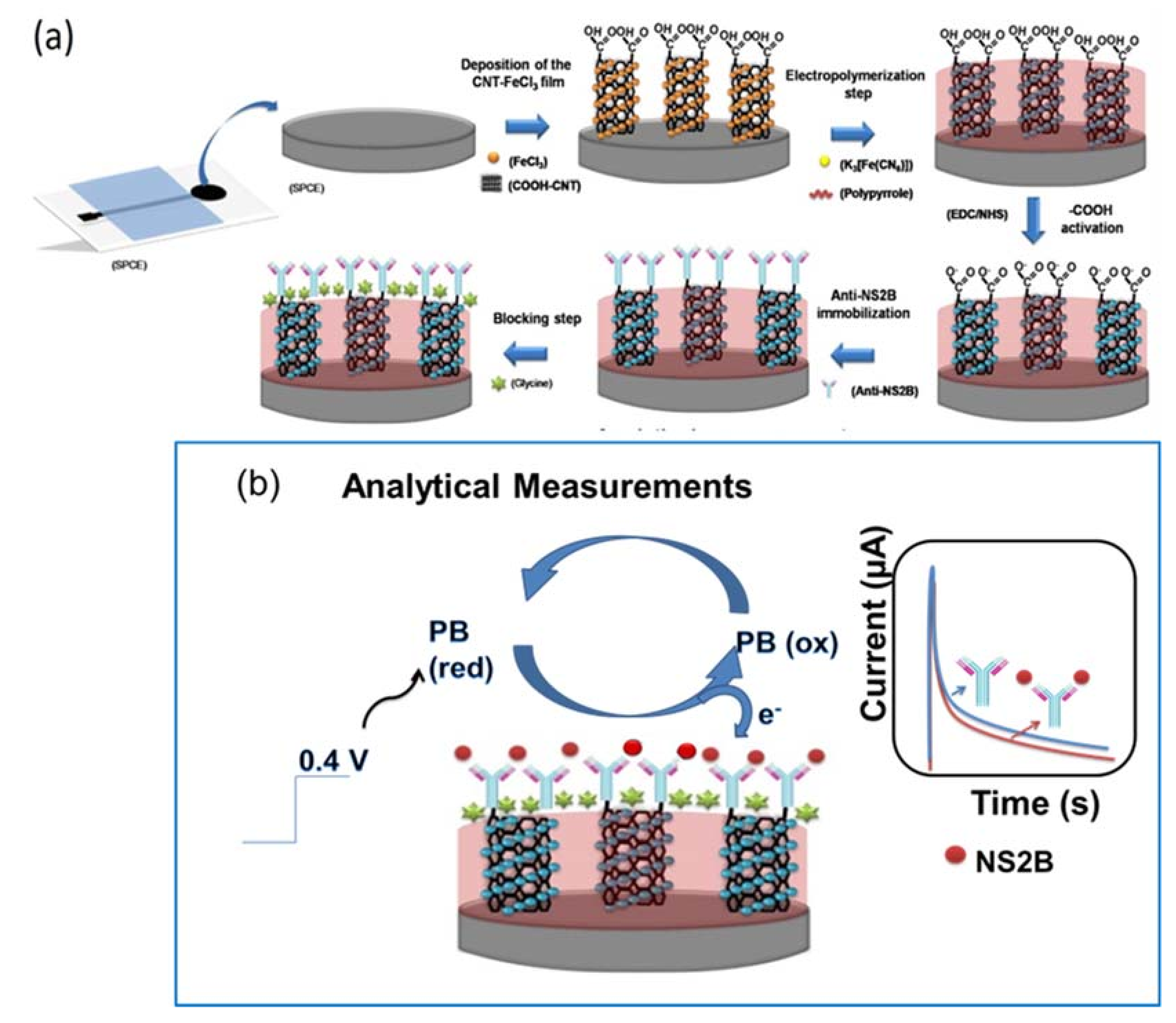
2.5. Preparation of the PB@CNT-PPy Nanocomposite
2.6. Anti-NS2B Immobilization
2.7. Analytical Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of PB@CNT-PPy Nanocomposite
3.2. Chemical Characterization of the PB@CNT-PPy Nanocomposite Film
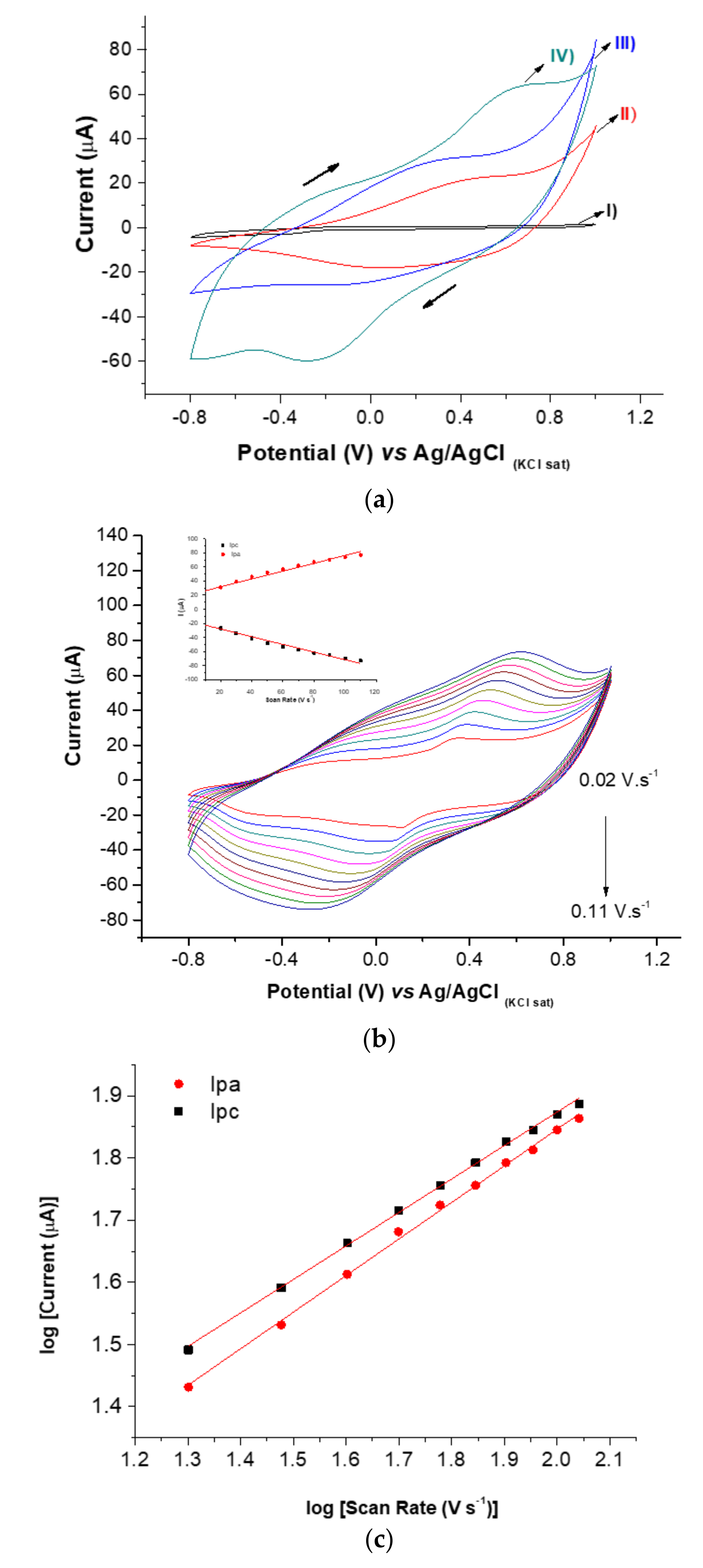
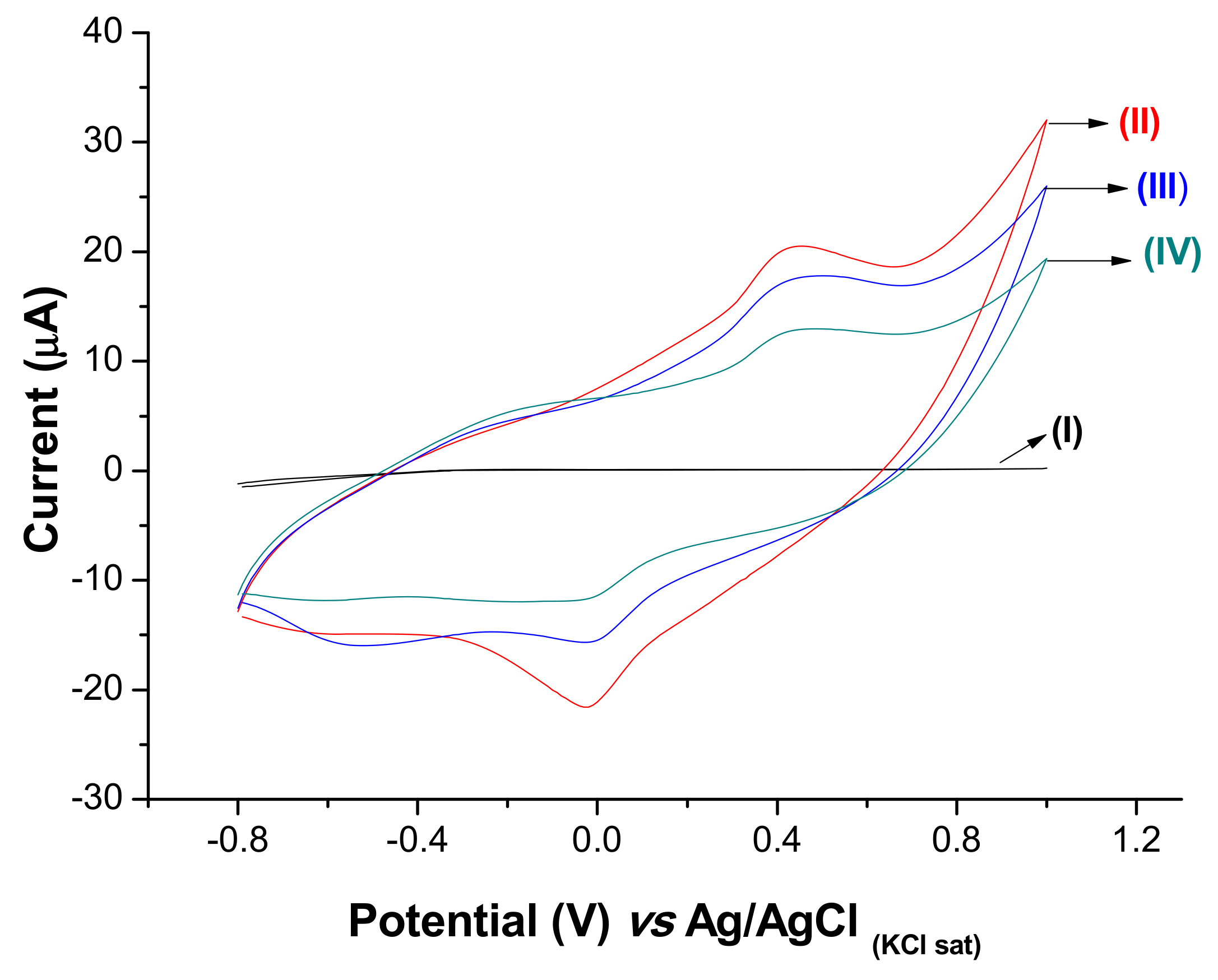
3.3. Electrochemical Characterization of the ZIKV Immunosensor
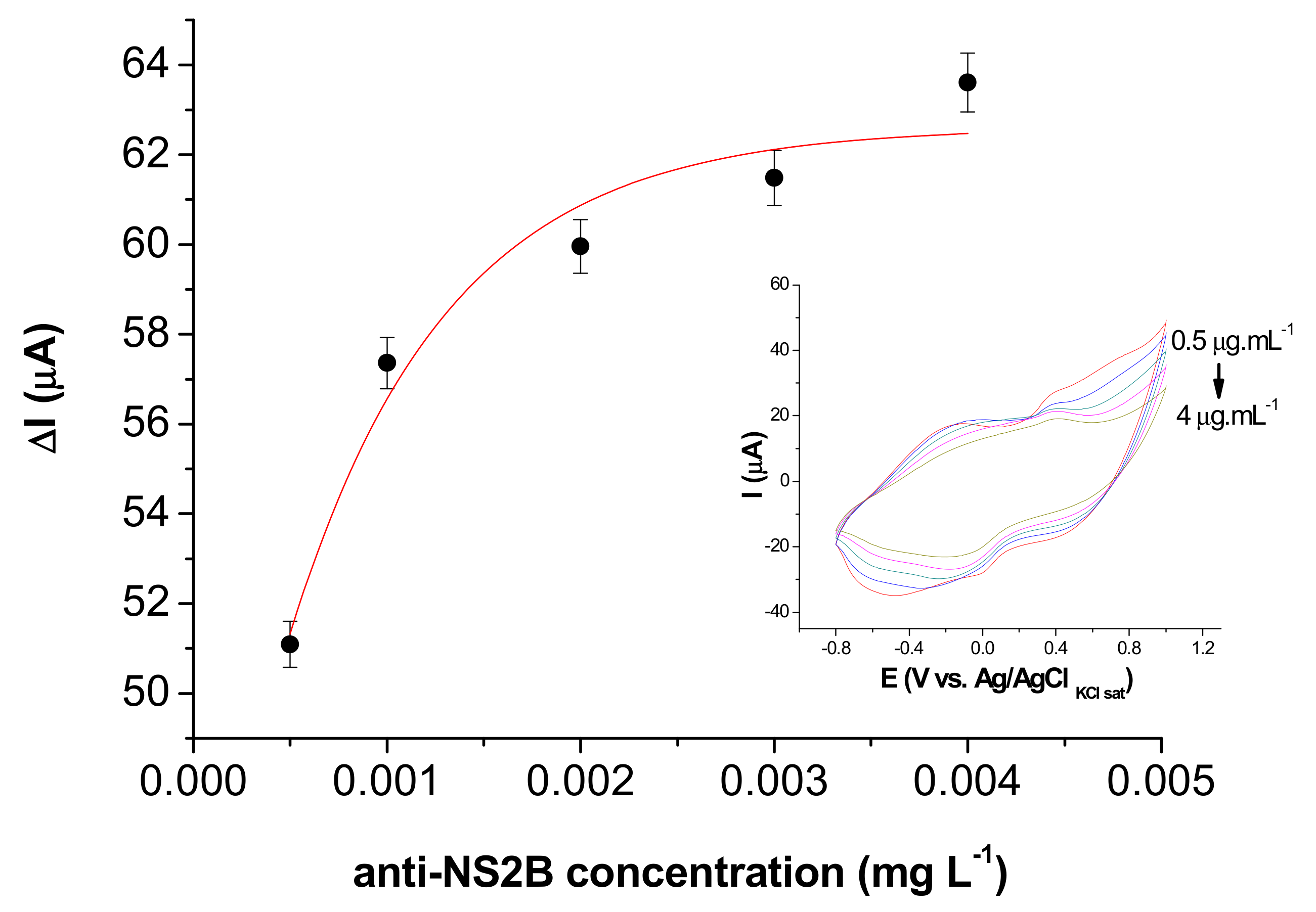
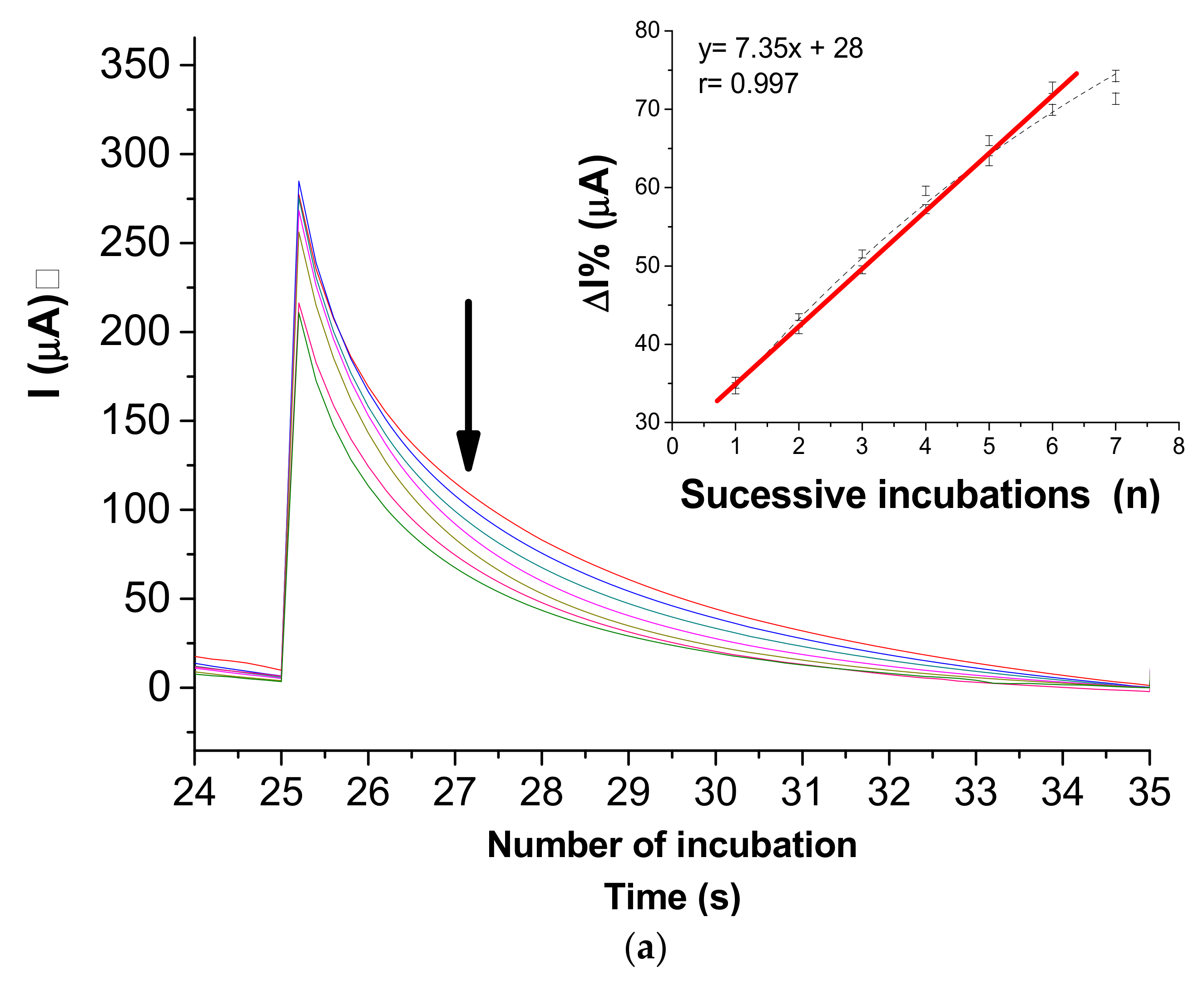
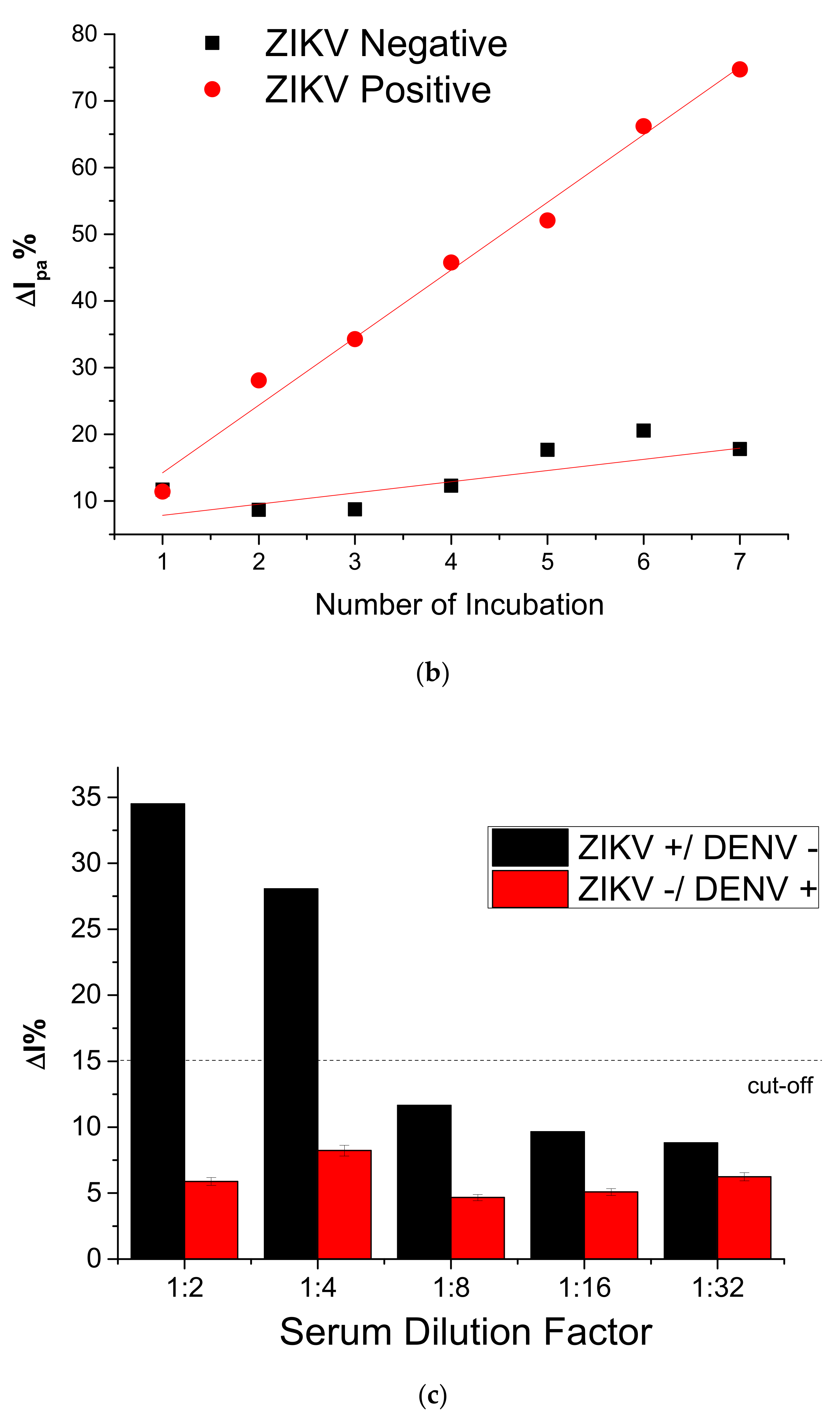
3.4. Immunosensor Response to NS2B Protein
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gulland, A. Zika virus is a global public health emergency, declares WHO. BMJ 2016, 352, i657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, W.K.; de França, G.V.A.; Carmo, E.H.; Duncan, B.B.; de Souza Kuchenbecker, R.; Schmidt, M.I. Infection-related microcephaly after the 2015 and 2016 Zika virus outbreaks in Brazil: A surveillance-based analysis. Lancet 2017, 390, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorbakhsh, F.; Abdolmohammadi, K.; Fatahi, Y.; Dalili, H.; Rasoolinejad, M.; Rezaei, F.; Salehi-Vaziri, M.; Shafiei-Jandaghi, N.Z.; Gooshki, E.S.; Zaim, M.; et al. Zika virus infection, basic and clinical aspects: A review article. Iran. J. Public Health 2019, 48, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adibi, J.J.; Marques, E.T.A.; Cartus, A.; Beigi, R.H. Teratogenic effects of the Zika virus and the role of the placenta. Lancet 2016, 387, 1587–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil, P.; Sequeira, P.C.; Freitas, A.D.A.; Zogbi, H.E.; Calvet, G.A.; De Souza, R.V.; Siqueira, A.M.; De Mendonca, M.C.L.; Nogueira, R.M.R.; De Filippis, A.M.B.; et al. Guillain-Barré syndrome associated with Zika virus infection. Lancet 2016, 387, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmi, S.S.; Ali, W.; Bibi, N.; Nouroz, F. A review on Zika virus outbreak, epidemiology, transmission and infection dynamics. J. Biol. Res. 2020, 27, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization Laboratory. Testing for Zika Virus Infection; Interim Guidance; WHO/ZIKV/LAB/16.1; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C.; Wu, J.; Fikrig, E.; Wang, P.; Chen, J.; Eda, S.; Terry, P. Unamplified RNA Sensor for On-Site Screening of Zika Virus Disease in a Limited Resource Setting. ChemElectroChem 2017, 4, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegoke, O.; Morita, M.; Kato, T.; Ito, M.; Suzuki, T.; Park, E.Y. Localized surface plasmon resonance-mediated fluorescence signals in plasmonic nanoparticle-quantum dot hybrids for ultrasensitive Zika virus RNA detection via hairpin hybridization assays. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 94, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansuy, J.M.; Mengelle, C.; Pasquier, C.; Chapuy-Regaud, S.; Delobel, P.; Martin-Blondel, G.; Izopet, J. Zika virus infection and prolonged viremia in whole-blood specimens. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 863–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-H.; Huber, R.G.; Bond, P.J.; Grad, Y.H.; Camerini, D.; Maurer-Stroh, S.; Lipsitch, M. Systematic analysis of protein identity between Zika virus and other arthropod-borne viruses. Bull. World Health Organ. 2017, 95, 517–525I. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felix, A.C.; Souza, N.C.S.; Figueiredo, W.M.; Costa, A.A.; Inenami, M.; da Silva, R.M.G.; Levi, J.E.; Pannuti, C.S.; Romano, C.M. Cross reactivity of commercial anti-dengue immunoassays in patients with acute Zika virus infection. J. Med. Virol. 2017, 89, 1477–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paixão, E.S.; Teixeira, M.G.; Rodrigues, L.C. Zika, chikungunya and dengue: The causes and threats of new and re-emerging arboviral diseases. BMJ Glob. Health 2018, 3, e000530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, N.; Caciula, A.; Price, A.; Thakkar, R.; Ng, J.; Chauhan, L.; Jain, K.; Espinosa, D.; Montoya Cruz, M.; Balmaseda, A.; et al. Diagnosis of Zika virus infection by peptide array and ELISA. MBio 2018, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiryaev, S.A.; Farhy, C.; Pinto, A.; Huang, C.T.; Simonetti, N.; Ngono, A.E.; Dewing, A.; Shresta, S.; Pinkerton, A.B.; Cieplak, P.; et al. Characterization of the Zika virus two-component NS2B-NS3 protease and structure-assisted identification of allosteric small-molecule antagonists. Antiviral Res. 2017, 143, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Investing to Overcome the Global Impact of Neglected Tropical Diseases; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.U.; Hossain, M.M.; Safavieh, M.; Wong, Y.L.; Rahman, I.A.; Zourob, M.; Tamiya, E. Toward the development of smart and low cost point-of-care biosensors based on screen printed electrodes. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2016, 36, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, M.; Panneer Selvam, A.; Craven, J.E.; Prasad, S. Antibody-Conjugated Gold Nanoparticle-Based Immunosensor for Ultra-Sensitive Detection of Troponin-T. J. Lab. Autom. 2014, 19, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, B.V.M.; Rodríguez, B.A.G.; Sales, G.F.; Sotomayor, M.D.P.T.; Dutra, R.F. An ultrasensitive human cardiac troponin T graphene screen-printed electrode based on electropolymerized-molecularly imprinted conducting polymer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchetto, J.; Fernandes, F.C.B.; Lopes, R.; Bueno, P.R. The capacitive sensing of NS1 Flavivirus biomarker. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, A.M.; Mazon, T. Early diagnosis of Zika infection using a ZnO nanostructures-based rapid electrochemical biosensor. Talanta 2019, 203, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsahi, S.; Lerner, M.B.; Goldstein, J.M.; Lee, J.; Tang, X.; Bagarozzi, D.A.; Pan, D.; Locascio, L.; Walker, A.; Barron, F.; et al. Novel graphene-based biosensor for early detection of Zika virus infection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trindade, E.K.G.; Silva, B.V.M.; Dutra, R.F. A probeless and label-free electrochemical immunosensor for cystatin C detection based on ferrocene functionalized-graphene platform. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trindade, E.K.G.; Dutra, R.F. A label-free and reagentless immunoelectrode for antibodies against hepatitis B core antigen (anti-HBc) detection. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2018, 172, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, F.T.C.; Rodriguez, B.A.G.; Dutra, R.A.F.; Sales, M.G.F. Redox probe-free readings of a Β-amyloid-42 plastic antibody sensory material assembled on copper@carbon nanotubes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 264, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; Lu, L.; Yu, Y. Three-dimensional gold nanoparticles/prussian blue-poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) nanocomposite as novel redox matrix for label-free electrochemical immunoassay of carcinoembryonic antigen. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 239, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanavičius, A.; Ramanavičiene, A.; Malinauskas, A. Electrochemical sensors based on conducting polymer-polypyrrole. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 6025–6037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, R. Polypyrrole Conducting Electroactive Polymers: Synthesis and Stability Studies. J. Chem. 2006, 3, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, F.; Palleschi, G. Sensor and biosensor preparation, optimisation and applications of Prussian Blue modified electrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 21, 389–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itaya, K.; Uchida, I. Nature of Intervalence Charge-Transfer Bands in Prussian Blues. Inorg. Chem. 1986, 25, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanavicius, A.; Rekertaitė, A.I.; Valiūnas, R.; Valiūnienė, A. Single-step procedure for the modification of graphite electrode by composite layer based on polypyrrole, Prussian blue and glucose oxidase. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 240, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Li, T.; Xu, X.; Du, P.; Zeng, J.; Zhu, W.; Yang, B.; Li, C.; Allain, J.-P. Characterisation and follow-up study of occult hepatitis B virus infection in anti-HBc-positive qualified blood donors in southern China. Blood Transfus. 2016, 15, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Yu, Z.; Fan, W.; Peng, G.; Qu, M. Effects of functional groups of graphene oxide on the electrochemical performance of lithium-ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 90041–90048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffney, J.S.; Marley, N.A.; Jones, D.E. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy. Charact. Mater. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Li, T.; Han, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Q. Optimizing the polymerization conditions of conductive polypyrrole. J. Photopolym. Sci. Technol. 2016, 29, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.N. Infrared spectra of the Prussian blue analogs. J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 1974, 36, 2465–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, D.; Bastola, P.; Le, L.; Paul, A.M.; Fernandez, E.; Diamond, M.S.; Miao, W.; Bai, F. An ultrasensitive electrogenerated chemiluminescence-based immunoassay for specific detection of Zika virus. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, S.A.; Sobral-Filho, R.G.; Aoki, P.H.B.; Constantino, C.J.L.; Brolo, A.G. Zika Immunoassay Based on Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Nanoprobes. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, B.V.M.; Cordeiro, M.T.; Rodrigues, M.A.B.; Marques, E.T.A.; Dutra, R.F. A Label and Probe-Free Zika Virus Immunosensor Prussian Blue@carbon Nanotube-Based for Amperometric Detection of the NS2B Protein. Biosensors 2021, 11, 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11050157
Silva BVM, Cordeiro MT, Rodrigues MAB, Marques ETA, Dutra RF. A Label and Probe-Free Zika Virus Immunosensor Prussian Blue@carbon Nanotube-Based for Amperometric Detection of the NS2B Protein. Biosensors. 2021; 11(5):157. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11050157
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Bárbara V. M., Marli T. Cordeiro, Marco A. B. Rodrigues, Ernesto T. A. Marques, and Rosa F. Dutra. 2021. "A Label and Probe-Free Zika Virus Immunosensor Prussian Blue@carbon Nanotube-Based for Amperometric Detection of the NS2B Protein" Biosensors 11, no. 5: 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11050157
APA StyleSilva, B. V. M., Cordeiro, M. T., Rodrigues, M. A. B., Marques, E. T. A., & Dutra, R. F. (2021). A Label and Probe-Free Zika Virus Immunosensor Prussian Blue@carbon Nanotube-Based for Amperometric Detection of the NS2B Protein. Biosensors, 11(5), 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11050157





