Duplex On-Site Detection of Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio vulnificus by Recombinase Polymerase Amplification and Three-Segment Lateral Flow Strips
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
2.2. Primers and Probes
2.3. RPA-LFS
2.4. Preparation of Spiked Food Samples
2.5. Clinical Samples
2.6. qPCR
3. Results
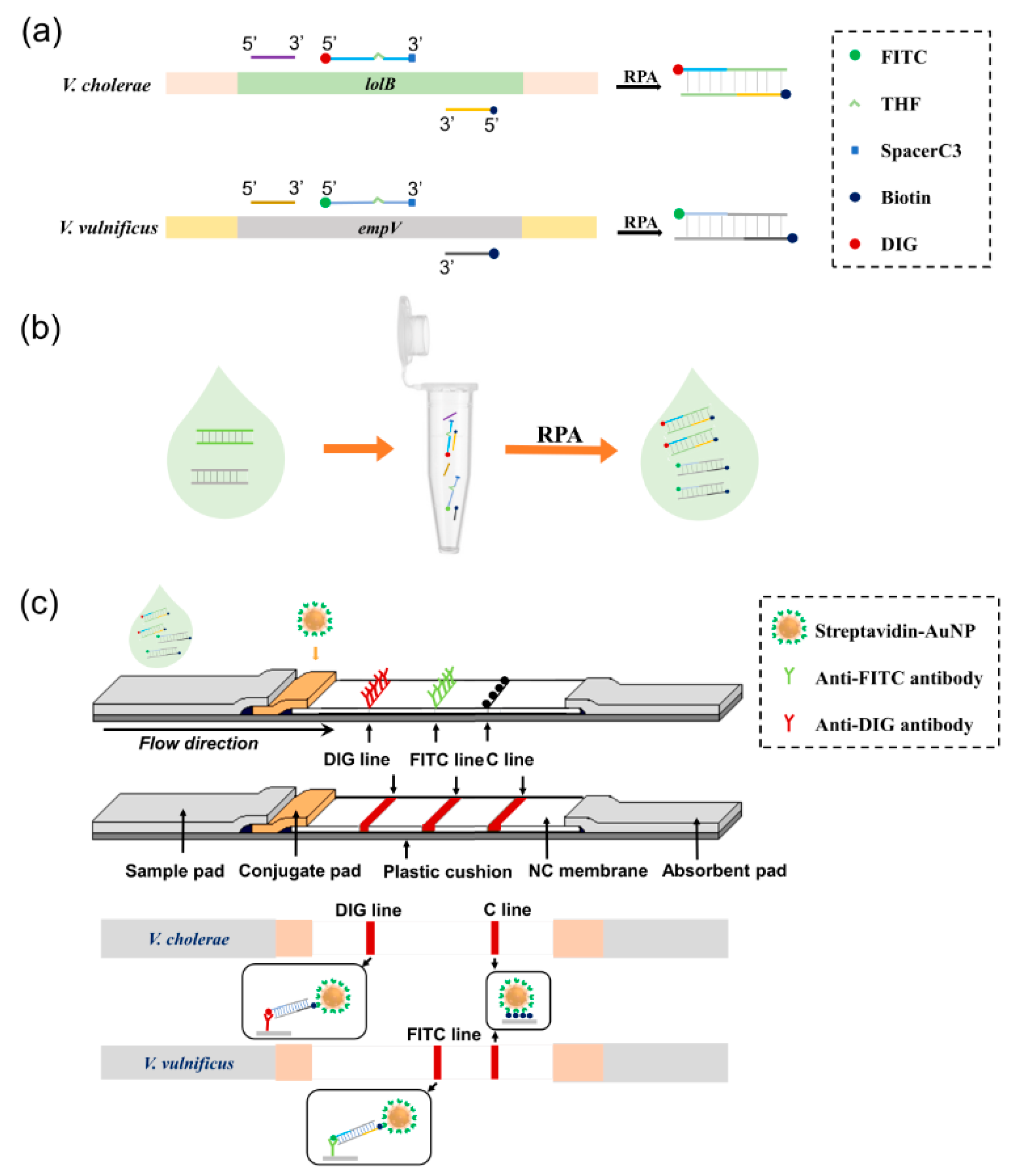
3.1. Principle of the Biosensor
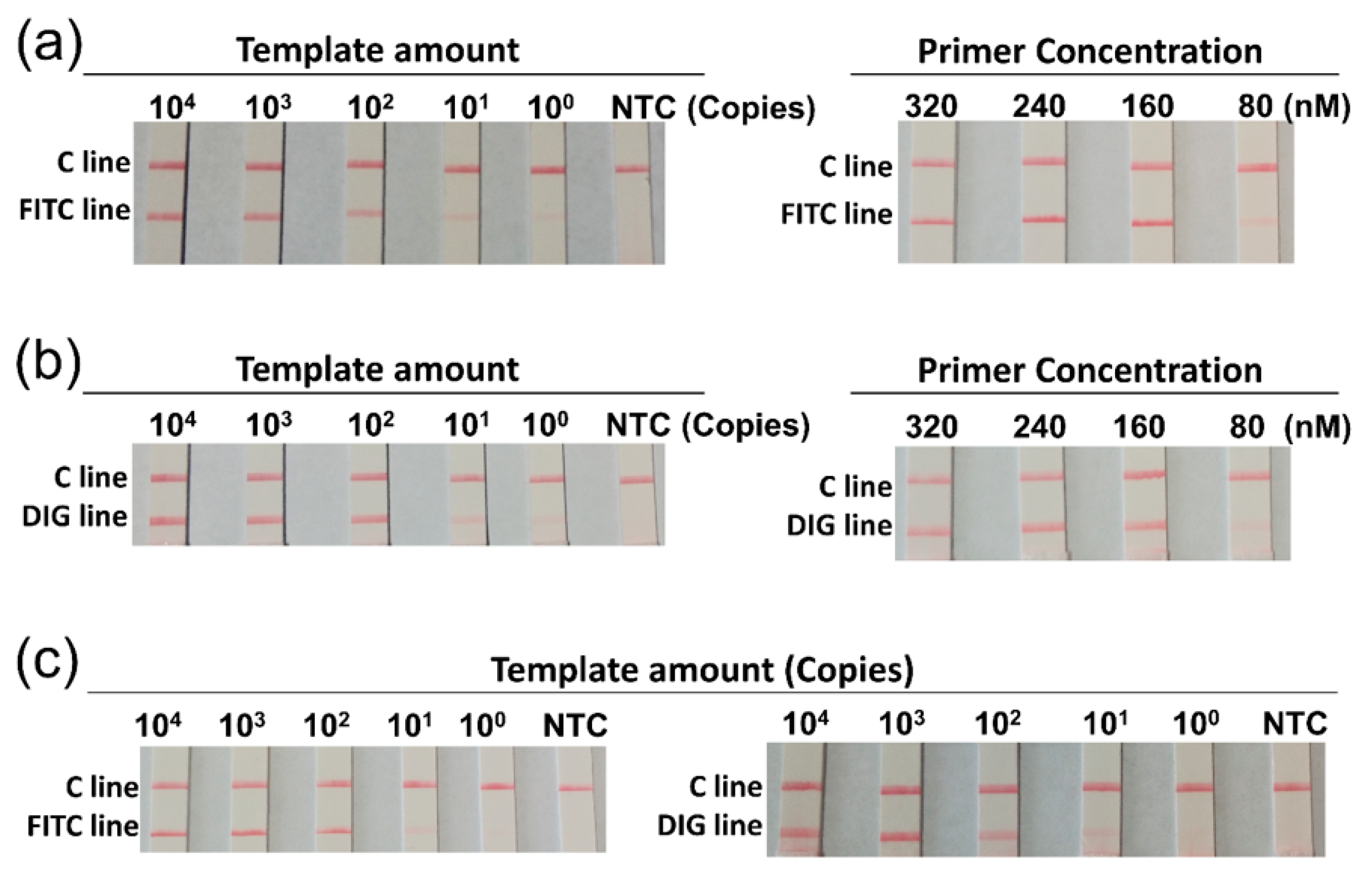
3.2. Optimization of the Duplex RPA Reaction
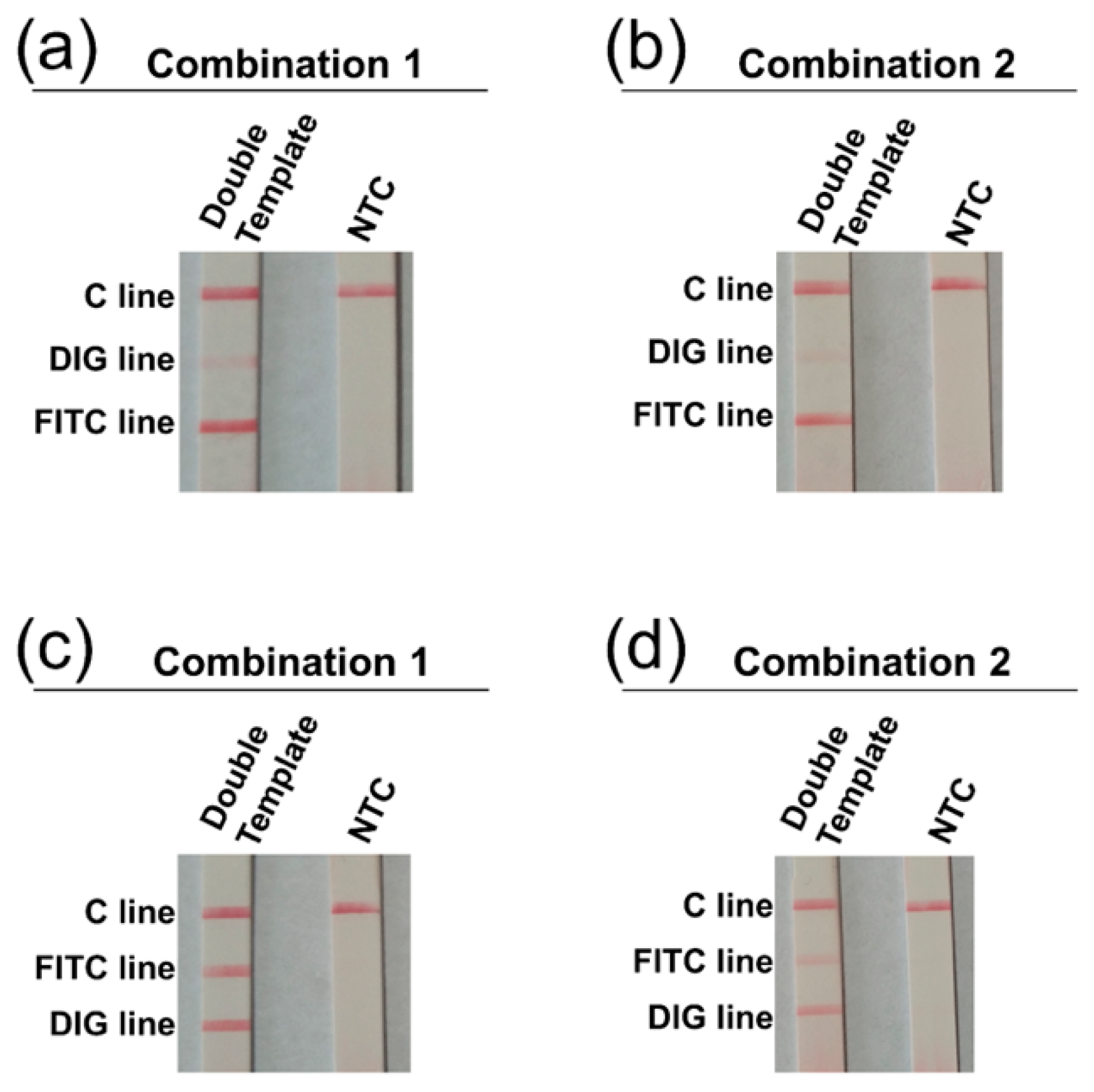
3.3. Determination of Visualization Lines on the 3-Segment Strip
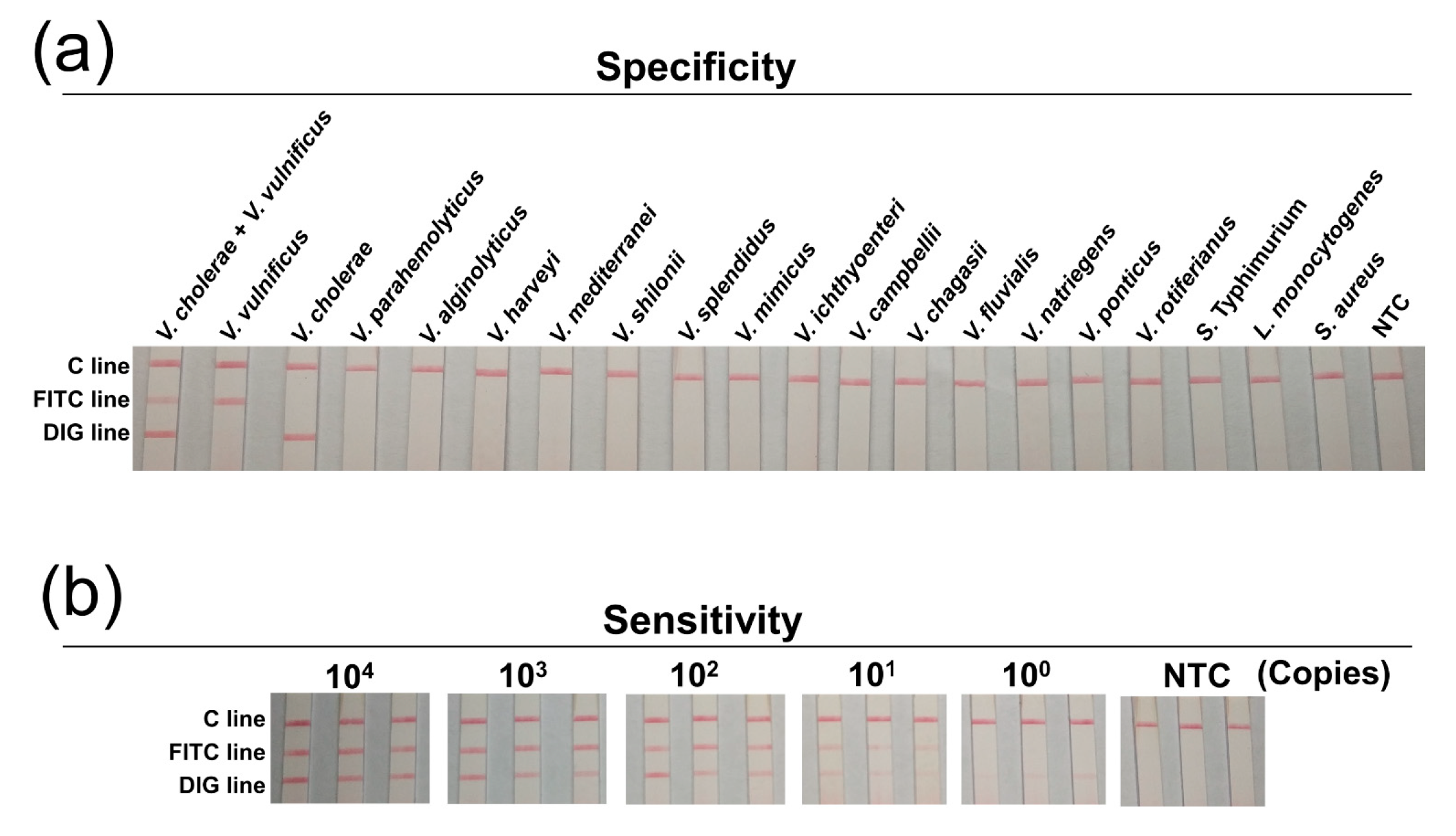
3.4. Specificity and Sensitivity
3.5. Clinical Sample Applications
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Austin, B. Vibrios as causal agents of zoonoses. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, N.A.; MacKinnon, L.; Bishop, R.; Altekruse, S.; Ray, B.; Hammond, R.M.; Thompson, S.; Wilson, S.; Bean, N.H.; Griffin, P.M.; et al. Vibrio parahaemolyticus infections in the United States, 1973–1998. J. Infect Dis. 2000, 181, 1661–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzulli, L.; Colwell, R.R.; Pruzzo, C. Ocean warming and spread of pathogenic vibrios in the aquatic environment. Microbial ecol. 2013, 65, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert-Pillot, A.; Copin, S.; Himber, C.; Gay, M.; Quilici, M.-L. Occurrence of the three major Vibrio species pathogenic for human in seafood products consumed in France using real-time PCR. Int. J. Food Microbio. 2014, 189, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnin-Jusserand, M.; Copin, S.; Le Bris, C.; Brauge, T.; Gay, M.; Brisabois, A.; Grard, T.; Midelet-Bourdin, G. Vibrio species involved in seafood-borne outbreaks (Vibrio cholerae, V. parahaemolyticus and V. vulnificus): Review of microbiological versus recent molecular detection methods in seafood products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notomi, T.; Okayama, H.; Masubuchi, H.; Yonekawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Amino, N.; Hase, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, E63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piepenburg, O.; Williams, C.H.; Stemple, D.L.; Armes, N.A. DNA Detection Using Recombination Proteins. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyasekaran, G.; Raj, K.T.; Shakila, R.J.; Thangarani, A.J.; Sukumar, D. Multiplex polymerase chain reaction-based assay for the specific detection of toxin-producing Vibrio cholerae in fish and fishery products. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2011, 90, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapela, M.J.; Fajardo, P.; Garrido, A.; Cabado, A.G.; Ferreira, M.; Lago, J.; Vieites, J.M. Comparison between a TaqMan polymerase chain reaction assay and a culture method for ctx-positive Vibrio cholerae detection. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 4051–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messelhäusser, U.; Colditz, J.; Thärigen, D.; Kleih, W.; Höller, C.; Busch, U. Detection and differentiation of Vibrio spp. in seafood and fish samples with cultural and molecular methods. Int. J. Food. Microbiol. 2010, 142, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker-Austin, C.; Lemm, E.; Hartnell, R.; Lowther, J.; Onley, R.; Amaro, C.; Oliver, J.D.; Lees, D. pilF polymorphism-based real-time PCR to distinguish Vibrio vulnificus strains of human health relevance. Food Microbiol. 2012, 30, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisuk, C.; Chaivisuthangkura, P.; Rukpratanporn, S.; Longyant, S.; Sridulyakul, P.; Sithigorngul, P. Rapid and sensitive detection of Vibrio cholerae by loop-mediated isothermal amplification targeted to the gene of outer membrane protein ompW. Lett. Appl. Microbio. 2010, 50, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surasilp, T.; Longyant, S.; Rukpratanporn, S.; Sridulyakul, P.; Sithigorngul, P.; Chaivisuthangkura, P. Rapid and sensitive detection of Vibrio vulnificus by loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with lateral flow dipstick targeted to rpoS gene. Mol. Cell. Probes. 2011, 25, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Ge, B. Quantitative detection of Vibrio vulnificus in raw oysters by real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 142, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Macdonald, J.; von Stetten, F. Review: A comprehensive summary of a decade development of the recombinase polymerase amplification. Analyst 2018, 144, 31–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobato, I.M.; O’Sullivan, C.K. Recombinase polymerase amplification: Basics, applications and recent advances. Trends Analyst Chem. 2018, 98, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Yu, Y.; Yan, S.; Wang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, W. Real-Time Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay for the Detection of Vibrio cholerae in Seafood. Food Anal Methods 2017, 10, 2657–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Shen, H.; Jiang, G.; Dong, J.; Zhao, P.; Gao, S. A Real-Time Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Method for Rapid Detection of Vibrio vulnificus in Seafood. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 586981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-J.; Lee, H.-J.; Lee, K.-H.; Cho, J.-C. Simultaneous detection of Pathogenic Vibrio species using multiplex real-time PCR. Food Control. 2012, 23, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiergeist, A.; Reischl, U.; Gessner, A. Multicenter quality assessment of 16S ribosomal DNA-sequencing for microbiome analyses reveals high inter-center variability. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2016, 306, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, M.S.; Ahn, T.Y.; Joh, K.; Paik, S.Y.; Kwon, O.S.; Jheong, W.H.; Joung, Y.; Park, D.S. A novel marker for the species-specific detection and quantitation of Vibrio cholerae by targeting an outer membrane lipoprotein lolB gene. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 23, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, H.S.; Parvathi, A.; Karunasagar, I.; Karunasagar, I. A gyrB-based PCR for the detection of Vibrio vulnificus and its application for direct detection of this pathogen in oyster enrichment broths. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 111, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Pollak, N.M.; Macdonald, J. Multiplex Detection of Nucleic Acids Using Recombinase Polymerase Amplification and a Molecular Colorimetric 7-Segment Display. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 11388–11396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture. 2014. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/i3720e/i3720e.pdf (accessed on 12 May 2021).
- Espiñeira, M.; Atanassova, M.; Vieites, J.M.; Santaclara, F.J. Validation of a method for the detection of five species, serogroups, biotypes and virulence factors of Vibrio by multiplex PCR in fish and seafood. Food Microbiol. 2010, 27, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taminiau, B.; Korsak, N.; Lemaire, C.; Delcenserie, V.; Daube, G. Validation of real-time PCR for detection of six major pathogens in seafood products. Food Control. 2014, 44, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Lee, J.-L. Development of a multiplex real-time recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) assay for rapid quantitative detection of Campylobacter coli and jejuni from eggs and chicken products. Food Control 2017, 73, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersting, S.; Rausch, V.; Bier, F.F.; von Nickisch-Rosenegk, M. Multiplex isothermal solid-phase recombinase polymerase amplification for the specific and fast DNA-based detection of three bacterial pathogens. Microchim. Acta 2014, 181, 1715–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalitha, P.; Siti Suraiya, M.N.; Lim, K.L.; Lee, S.Y.; Nur Haslindawaty, A.R.; Chan, Y.Y.; Ismail, A.; Zainuddin, Z.F.; Ravichandran, M. Analysis of lolB gene sequence and its use in the development of a PCR assay for the detection of Vibrio cholerae. J. Microbiol. Methods 2008, 75, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko Ferrigno, P. Non-antibody protein-based biosensors. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crannell, Z.; Castellanos-Gonzalez, A.; Nair, G.; Mejia, R.; White, A.C.; Richards-Kortum, R. Multiplexed Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay To Detect Intestinal Protozoa. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 1610–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersting, S.; Rausch, V.; Bier, F.F.; von Nickisch-Rosenegk, M. A recombinase polymerase amplification assay for the diagnosis of atypical pneumonia. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 550, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panicker, G.; Bej, A.K. Real-time PCR detection of Vibrio vulnificus in oysters: Comparison of oligonucleotide primers and probes targeting vvhA. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 5702–5709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Species | Strain Type | Designation |
|---|---|---|
| Vibrio cholerae | Reference strain | ATCC 14100 |
| Vibrio vulnificus | Reference strain | ATCC 27562 |
| Vibrio parahemolyticus | Reference strain | ATCC 17802 |
| Vibrio alginolyticus | Reference strain | ATCC 17749 |
| Vibrio harveyi | Reference strain | ATCC 43516 |
| Vibrio mediterranei | Reference strain | ATCC 43341 |
| Vibrio shilonii | Reference strain | ATCC BAA-91 |
| Vibrio splendidus | Reference strain | MCCC 1A04096 |
| Vibrio mimicus | Reference strain | MCCC 1A02602 |
| Vibrio ichthyoenteri | Reference strain | MCCC 1A00057 |
| Vibrio campbellii | Reference strain | MCCC 1A02605 |
| Vibrio chagasii | Reference strain | MCCC 1B00386 |
| Vibrio fluvialis | Reference strain | MCCC 1A02761 |
| Vibrio natriegens | Reference strain | MCCC 1D00129 |
| Vibrio ponticus | Reference strain | MCCC 1H00061 |
| Vibrio rotiferianus | Reference strain | MCCC 1B00068 |
| Salmonella Typhimurium | Reference strain | ATCC 14028 |
| Listeria monocytogenes | Reference strain | ATCC 19115 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | Reference strain | ATCC 6538 |
| Method | Target | Primer/Probe Name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Length (bp) | Amplicon Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RPA | V. cholerae | VC-F | ATCTTCAAGCTGTTCAACGGGAATATCTAA | 30 | 218 |
| VC-R | Biotin-ATCAGCGACAATCGTTCAACTTTCAATGGC | 30 | |||
| VC-P1 | DIG-ATCAGGCTTTGTGCATCTTGGTCGCGGTAGA [THF] TTGATCATCATAAGTTTCG-SpC3 | 51 | |||
| VC-P2 | FITC-ATCAGGCTTTGTGCATCTTGGTCGCGGTAGA [THF] TTGATCATCATAAGTTTCG-SpC3 | 51 | |||
| V. vulnificus | VV-F | GAGATGGATTCTTTGTATAACATTGCGT | 28 | 214 | |
| VV-R | Biotin-ACGATGACGTTGGTTGTGTTTCATTATC | 28 | |||
| VV-P1 | FITC-GGTGAAGTTGGCTGGTGGTTATTTTCTGAA [THF] CATGGTTGTTGAGCTC-SpC3 | 47 | |||
| VV-P2 | DIG-GGTGAAGTTGGCTGGTGGTTATTTTCTGAA [THF] CATGGTTGTTGAGCTC-SpC3 | 47 | |||
| qPCR | V. cholerae | VC195F | CCGTTGAGGCGAGTTTGGTGAGA | 23 | 195 |
| VC195R | GTGCGCGGGTCGAAACTTATGAT | 23 | |||
| V. vulnificus | gyr-vv1 | GTCCGCAGTGGAATCCTTCA | 20 | 285 | |
| gyr-vv2 | TGGTTCTTACGGTTACGGCC | 20 |
| No. | Food Type | Sample Source | Detection Results for V. cholerae | Detection Results for V. vulnificus | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RPA-LFS | qPCR | RPA-LFS | qPCR | |||
| 1 | Shrimp | Qingdao, China | - | - | - | - |
| 2 | Shrimp | Qingdao, China | - | - | - | - |
| 3 | Shrimp | Qingdao, China | - | - | - | - |
| 4 | Shrimp | Qingdao, China | - | - | - | - |
| 5 | Shrimp | Qingdao, China | + | + | - | - |
| 6 | Shrimp | Qingdao, China | - | - | - | - |
| 7 | Shrimp | Qingdao, China | - | - | + | + |
| 8 | Shrimp | Qingdao, China | + | + | + | + |
| 9 | Shrimp | Qingdao, China | - | - | - | - |
| 10 | Shrimp | Qingdao, China | - | - | - | - |
| 11 | Shrimp | Lianyungang, China | - | - | - | - |
| 12 | Shrimp | Lianyungang, China | - | - | - | - |
| 13 | Shrimp | Lianyungang, China | - | - | - | - |
| 14 | Shrimp | Lianyungang, China | - | - | - | - |
| 15 | Shrimp | Lianyungang, China | - | - | - | - |
| 16 | Shrimp | Lianyungang, China | - | - | + | + |
| 17 | Shrimp | Lianyungang, China | - | - | - | - |
| 18 | Shrimp | Lianyungang, China | + | + | - | - |
| 19 | Shrimp | Lianyungang, China | - | - | - | - |
| 20 | Shrimp | Lianyungang, China | - | - | - | - |
| 21 | Fish | Qingdao, China | - | - | - | - |
| 22 | Fish | Qingdao, China | - | - | - | - |
| 23 | Fish | Qingdao, China | - | - | - | - |
| 24 | Fish | Qingdao, China | - | - | - | - |
| 25 | Fish | Qingdao, China | - | - | - | - |
| 26 | Fish | Yancheng, China | + | + | - | - |
| 27 | Fish | Yancheng, China | + | + | - | - |
| 28 | Fish | Yancheng, China | - | - | - | - |
| 29 | Fish | Yancheng, China | - | - | - | - |
| 30 | Fish | Yancheng, China | - | - | - | - |
| 31 | Shellfish | Qingdao, China | - | - | - | - |
| 32 | Shellfish | Qingdao, China | + | + | - | - |
| 33 | Shellfish | Qingdao, China | - | - | - | - |
| 34 | Shellfish | Qingdao, China | + | + | - | - |
| 35 | Shellfish | Qingdao, China | - | - | - | - |
| 36 | Shellfish | Lianyungang, China | - | - | + | + |
| 37 | Shellfish | Lianyungang, China | - | - | - | - |
| 38 | Shellfish | Lianyungang, China | - | - | - | - |
| 39 | Shellfish | Lianyungang, China | - | - | - | - |
| 40 | Shellfish | Lianyungang, China | - | - | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, P.; Liao, L.; Ma, C.; Zhang, X.; Yu, J.; Yi, L.; Liu, X.; Shen, H.; Gao, S.; Lu, Q. Duplex On-Site Detection of Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio vulnificus by Recombinase Polymerase Amplification and Three-Segment Lateral Flow Strips. Biosensors 2021, 11, 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11050151
Wang P, Liao L, Ma C, Zhang X, Yu J, Yi L, Liu X, Shen H, Gao S, Lu Q. Duplex On-Site Detection of Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio vulnificus by Recombinase Polymerase Amplification and Three-Segment Lateral Flow Strips. Biosensors. 2021; 11(5):151. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11050151
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Pei, Lei Liao, Chao Ma, Xue Zhang, Junwei Yu, Longyu Yi, Xin Liu, Hui Shen, Song Gao, and Qunwei Lu. 2021. "Duplex On-Site Detection of Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio vulnificus by Recombinase Polymerase Amplification and Three-Segment Lateral Flow Strips" Biosensors 11, no. 5: 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11050151
APA StyleWang, P., Liao, L., Ma, C., Zhang, X., Yu, J., Yi, L., Liu, X., Shen, H., Gao, S., & Lu, Q. (2021). Duplex On-Site Detection of Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio vulnificus by Recombinase Polymerase Amplification and Three-Segment Lateral Flow Strips. Biosensors, 11(5), 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11050151





