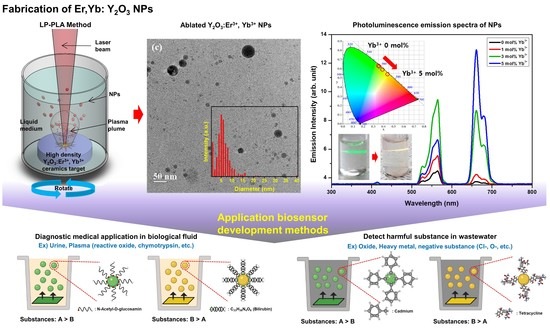
Development of Er3+, Yb3+ Co-Doped Y2O3 NPs According to Yb3+ Concentration by LP–PLA Method: Potential Further Biosensor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Er, Yb:Y2O3 Target Preparation
2.2. Fabrication of Er, Yb:Y2O3 NPs
2.3. Characteristic Analysis of Er, Yb:Y2O3 NPs
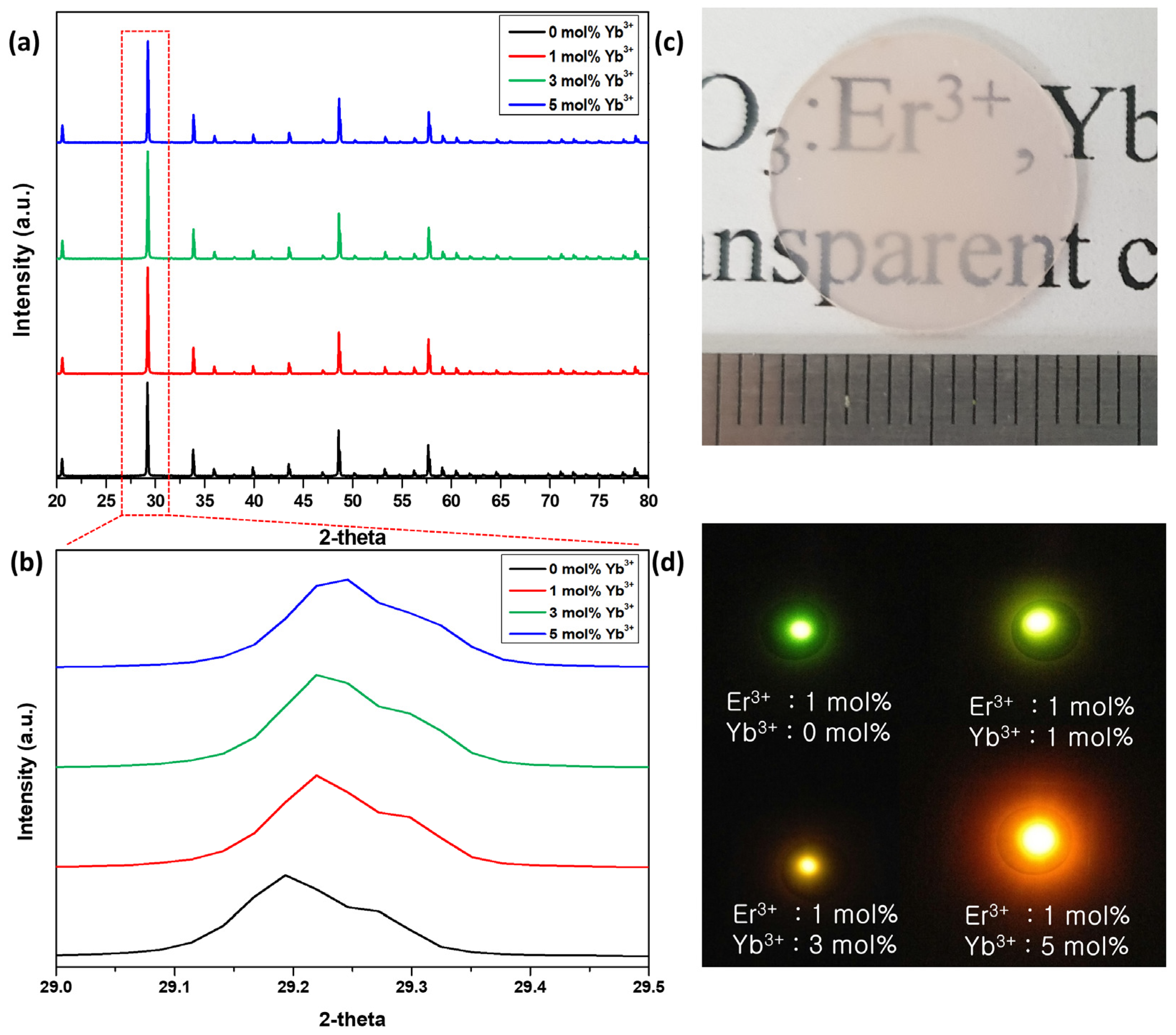
3. Results
3.1. Crystal Structure Analysis and Preparation LP–PLA Targets
3.2. Morphology of NPs by LP–PLA
3.3. Luminescence on Er, Yb:Y2O3 NPs
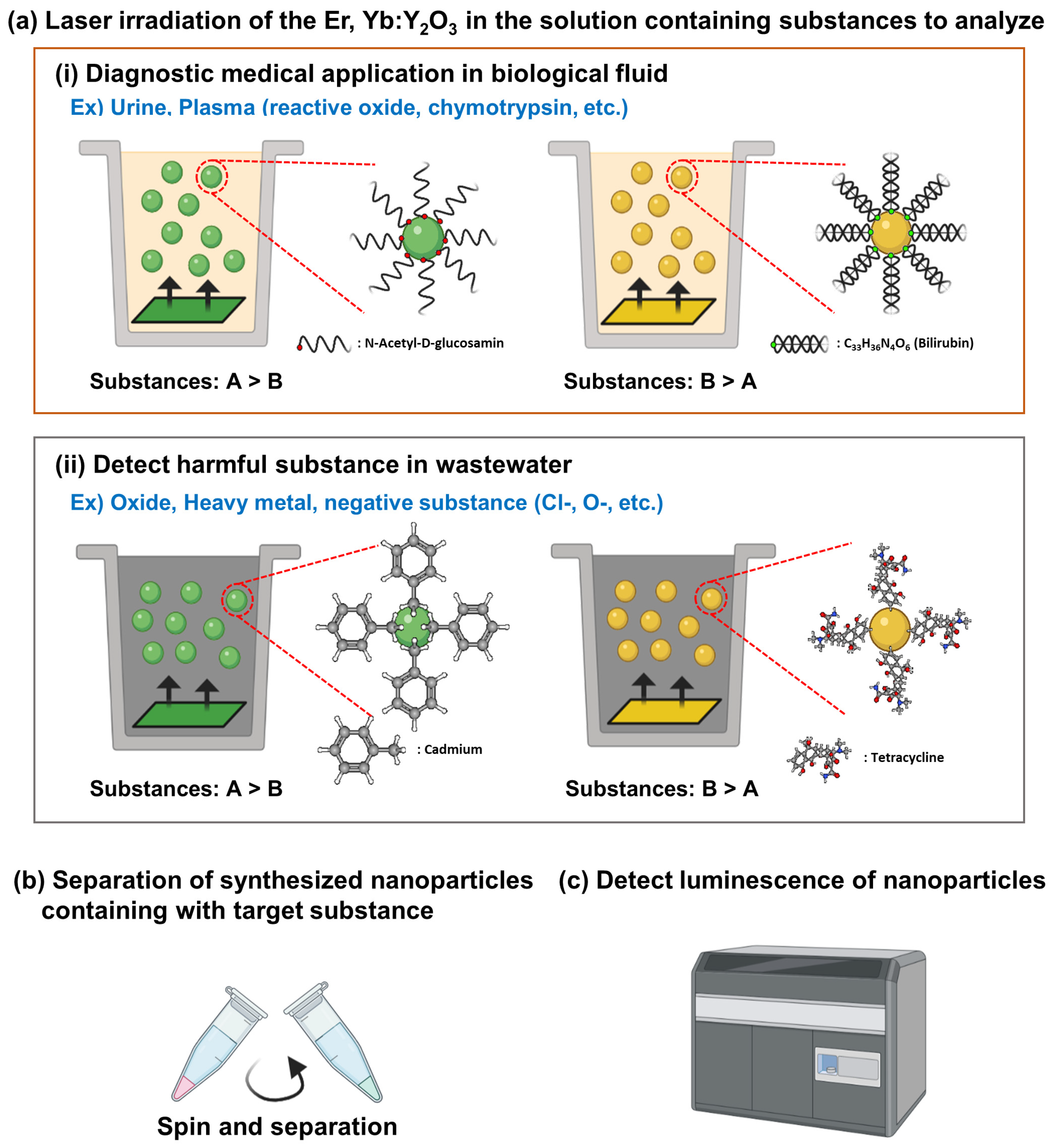
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malekzad, H.; Zangabad, P.S.; Mirshekari, H.; Karimi, M.; Hamblin, M.R. Noble metal nanoparticles in biosensors: Recent studies and applications. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2017, 6, 301–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Selva, M.; Issaabadi, Z.; Luque, R. Waste-to-wealth: Biowaste valorization into valuable bio (nano) materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 4791–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, H.P.; Cesar, C.L.; Barjas-Castro Mde, L. Electrical properties of the red blood cell membrane and immunohematological investigation. Rev. Bras. Hematol. Hemoter. 2011, 33, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirzada, M.; Altintas, Z. Nanomaterials for healthcare biosensing applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajakumar, G.; Mao, L.; Bao, T.; Wen, W.; Wang, S.; Gomathi, T.; Gnanasundaram, N.; Rebezov, M.; Shariati, M.A.; Chung, I.-M.; et al. Yttrium oxide nanoparticle synthesis: An overview of methods of preparation and biomedical applications. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onodera, Y.; Nunokawa, T.; Odawara, O.; Wada, H. Upconversion properties of Y2O3:Er,yb nanoparticles prepared by laser ablation in water. J. Lumin. 2013, 137, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetrone, F.; Boyer, J.-C.; Capobianco, J.A.; Speghini, A.; Bettinelli, M. Significance of yb3+ concentration on the upconversion mechanisms in codoped Y2O3:Er3+, yb3+ nanocrystals. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 96, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, G.; Qin, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Cao, C.; Cui, Y. Upconversion luminescence properties of y2o3:Yb3+, er3+ nanostructures. J. Lumin. 2006, 119–120, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalav, A.; Richards, B.S.; Trupke, T.; Krämer, K.W.; Güdel, H.U. Application of nayf4:Er3+ up-converting phosphors for enhanced near-infrared silicon solar cell response. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 013505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez, N.O.; Quintanilla, M.; Cantelar, E.; Cussó, F.; Ocaña, M. Uniform yf3:Yb,er up-conversion nanophosphors of various morphologies synthesized in polyol media through an ionic liquid. J. Nanopart. Res. 2010, 12, 2553–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auzel, F.; Chen, Y. Photon avalanche luminescence of er3+ ions in liyf4 crystal. J. Lumin. 1995, 65, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Zhou, S.; Jia, T.; Lin, H.; Teng, H. Investigation of up-conversion luminescence properties of re/yb co-doped Y2O3 transparent ceramic (re = er, ho, pr, and tm). Phys. B Condensed. Matter 2011, 406, 3931–3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Ueda, K.-I.; Yagi, H.; Yanagitani, T.; Akiyama, Y.; Kaminskii, A.A. Neodymium doped yttrium aluminum garnet (y3al5o12) nanocrystalline ceramics—a new generation of solid state laser and optical materials. J. Alloys Compd. 2002, 341, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayart, A.; Szczepanski, F.; Blach, J.-F.; Rousseau, J.; Katelnikovas, A.; Saitzek, S. Upconversion luminescence properties and thermal quenching mechanisms in the layered perovskite la1.9er0.1ti2o7 towards an application as optical temperature sensor. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 744, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, A.K.; Rai, V.K. Baznla2o5:Ho3+-yb3+ phosphor for display and security ink application. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2014, 31, 2201–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Wu, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Hao, Z.; Pan, G.-H.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J. Cooperative upconversion luminescence properties of yb3+ and tb3+ heavily codoped silicate garnet obtained by multiple chemical unit cosubstitution. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 2998–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anh, T.; Benalloul, P.; Barthou, C.; Giang, L.t.; Vu, N.; Minh, L. Luminescence, energy transfer, and upconversion mechanisms of y2o3 nanomaterials doped with eu3+, tb3+, tm3+, er3+, and yb3+ ions. J. Nanomater. 2007, 2007, 048247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Rai, V.K. Improved luminescence and temperature sensing performance of Ho3+–Yb3+–Zn2+: Y2O3 phosphor. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 11005–11011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, K.; Mori, K.; Odawara, O.; Wada, H. Preparation of spherical upconversion nanoparticles NaYF4: Yb, Er by laser ablation in liquid and optical properties. J. Laser Appl. 2020, 32, 022062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokatial, L.; Rai, S. Optical properties and up-conversion of pr3+ doped cds nanoparticles in sol–gel glasses. J. Lumin. 2010, 130, 1857–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Chui, P.; Sun, X.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, F.; Sun, K. Hydrothermal synthesis and upconversion luminescent properties of yvo4:Yb3+,er3+ nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 552, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.K.; Mathpal, M.C.; Agarwal, A. Optical properties of sno2 quantum dots synthesized by laser ablation in liquid. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2012, 536, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhu, X.; Peng, J.; Li, F. Core–shell lanthanide upconversion nanophosphors as four-modal probes for tumor angiogenesis imaging. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 11290–11300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, M.; Cao, T.; Sun, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, Q.; Li, F. A cyanine-modified nanosystem for in vivo upconversion luminescence bioimaging of methylmercury. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 9869–9876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazio, E.; Gökce, B.; De Giacomo, A.; Meneghetti, M.; Compagnini, G.; Tommasini, M.; Neri, F. Nanoparticles Engineering by Pulsed Laser Ablation in Liquids: Concepts and Applications. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, M.; Cho, W.S.; Choi, M.; Kim, S.J.; Han, B.S.; Kim, S.H.; Jeong, J. The impact of size on tissue distribution and elimination by single intravenous injection of silica nanoparticles. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 189, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wnag, X.; Hu, Y.; Meng, X.; Li, Y.; Zhu, M.; Jin, H. Synthesis of y2o3 phosphor by a hydrolysis and oxidation method. J. Rare Earth 2015, 33, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.C.; Parola, S.; Marty, O.; Mugnier, J. Elaboration, structural characterization and optical properties of the yttrium alkoxide derived y2o3 planar optical waveguides. Opt. Mater. 2004, 27, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuruoka, N.; Sasagawa, T.; Yodo, T.; Yoshimoto, M.; Odawara, O.; Wada, H. Facile preparation of yag: Ce nanoparticles by laser irradiation in water and their optical properties. Springerplus 2016, 5, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Lu, Y.F.; Hong, M.H. Laser ablation of solid substrates in a water-confined environment. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 79, 1396–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Lu, Y.F.; Hong, M.H.; Chen, X.Y. Laser ablation of solid substrates in water and ambient air. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 89, 2400–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svetlichnyi, V.A.; Shabalina, A.V.; Lapin, I.N.; Goncharova, D.A. Metal oxide nanoparticle preparation by pulsed laser ablation of metallic targets in liquid. In Applications of Laser Ablation–Thin Film Deposition, Nanomaterial Synthesis and Surface Modification; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2016; pp. 245–263. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Mamun, S.A.; Ishigaki, T. Influence of Hydrogen Peroxide Addition on Photoluminescence of Y2O3: Eu3+ Nanophosphors Prepared by Laser Ablation in Water. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 97, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, S.J.; Schiffers, W.P.; Gentry, T.P.; Emmony, D.C. A study of the interaction of a laser-generated cavity with a nearby solid boundary. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1999, 32, 1612–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taccogna, F.; Dell’Aglio, M.; Rutigliano, M.; Valenza, G.; De Giacomo, A. On the growth mechanism of nanoparticles in plasma during pulsed laser ablation in liquids. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2017, 26, 045002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Mi, C.-C.; Wang, W.-X.; Liu, C.-H.; Wu, Y.-F.; Xu, Z.-R.; Mao, C.-B.; Xu, S.-K. Immunolabeling and nir-excited fluorescent imaging of hela cells by using nayf4:Yb,er upconversion nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 1580–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetrone, F.; Boyer, J.-C.; Capobianco, J.A.; Speghini, A.; Bettinelli, M. Concentration-dependent near-infrared to visible upconversion in nanocrystalline and bulk y2o3:Er3+. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 2737–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Hou, Y.; Tang, A.; Wu, H.; Teng, F. Upconversion multicolor tuning: Red to green emission from y2o3:Er, yb nanoparticles by calcination. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 233103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Yang, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Jiang, C.; Wang, Y. Fabrication and luminescence properties of er3+ doped yttrium lanthanum oxide transparent ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 7367–7372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasha, K.L.; Yowa, R.M.; Deea, D.M.; Swanlanda, G.-Y.; Grubera, J.B.; Sardara, D.K.; Zhangb, M.; Gorskib, W. Optical characterization of er3+: Y2o3 nanoparticles for biosensor applications. Proc. SPIE 2007, 6449, 64490J. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diego-Rucabado, A.; Candela, M.T.; Aguado, F.; González, J.; Rodríguez, F.; Valiente, R.; Martín-Rodríguez, R.; Cano, I. A comparative study on luminescence properties of y2o3: Pr3+ nanocrystals prepared by different synthesis methods. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agoro, M.A.; Adeniji, A.O.; Adefisoye, M.A.; Okoh, O.O. Heavy metals in wastewater and sewage sludge from selected municipal treatment plants in eastern cape province, south africa. Water 2020, 12, 2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolotsky, A.; Butler, D.; Dong, C.; Gerace, K.; Glavin, N.R.; Muratore, C.; Robinson, J.A.; Ebrahimi, A. Two-dimensional materials in biosensing and healthcare: From in vitro diagnostics to optogenetics and beyond. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 9781–9810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, C.-W.; Park, D.-J. Development of Er3+, Yb3+ Co-Doped Y2O3 NPs According to Yb3+ Concentration by LP–PLA Method: Potential Further Biosensor. Biosensors 2021, 11, 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11050150
Park C-W, Park D-J. Development of Er3+, Yb3+ Co-Doped Y2O3 NPs According to Yb3+ Concentration by LP–PLA Method: Potential Further Biosensor. Biosensors. 2021; 11(5):150. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11050150
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Cheol-Woo, and Dong-Jun Park. 2021. "Development of Er3+, Yb3+ Co-Doped Y2O3 NPs According to Yb3+ Concentration by LP–PLA Method: Potential Further Biosensor" Biosensors 11, no. 5: 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11050150
APA StylePark, C.-W., & Park, D.-J. (2021). Development of Er3+, Yb3+ Co-Doped Y2O3 NPs According to Yb3+ Concentration by LP–PLA Method: Potential Further Biosensor. Biosensors, 11(5), 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11050150