Fabrication of Novel Printable Electrically Conductive Adhesives (ECAs) with Excellent Conductivity and Stability Enhanced by the Addition of Polyaniline Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
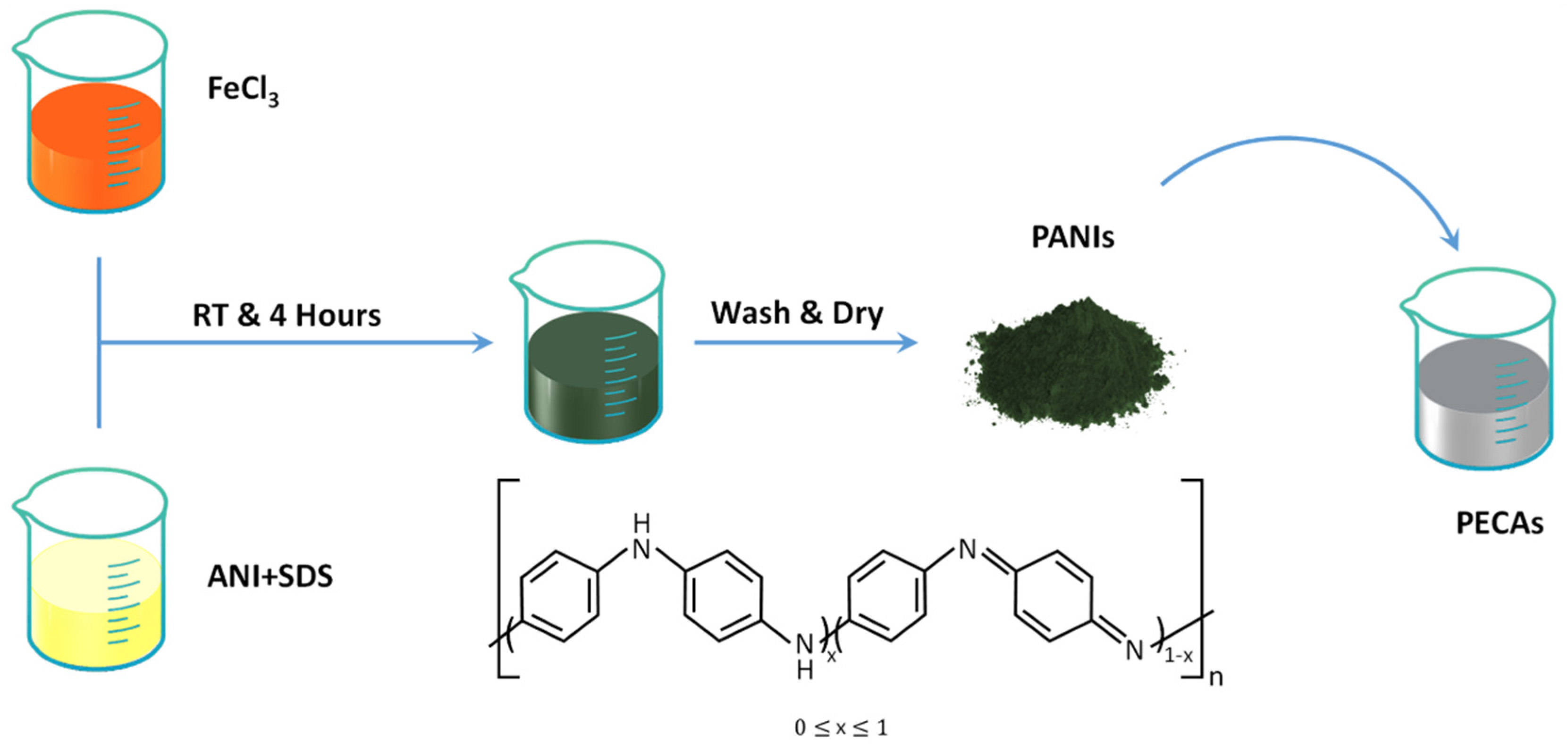
2.2. Synthesis of PANIs Nanoparticles
2.3. Preparation of ECAs
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Experimental Results and Discussion
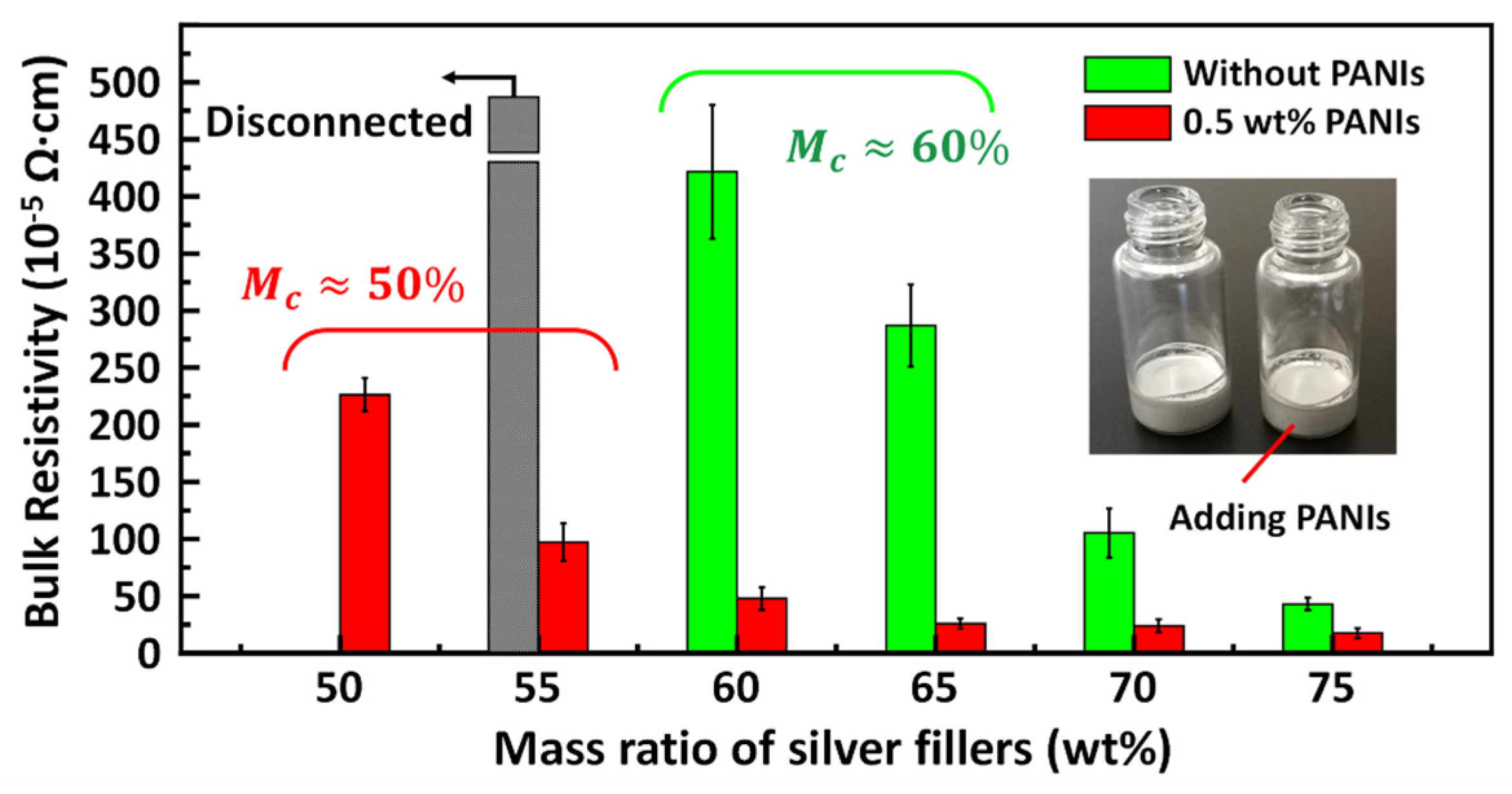
3.2. Electrical Properties of PECAs
3.3. Mechanical Property and Reliability
3.4. Applications
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lekawa-Raus, A.; Haladyj, P.; Koziol, K. Carbon nanotube fiber-silver hybrid electrical conductors. Mater. Lett. 2014, 133, 186–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Lin, W.; Li, Z.; Zhang, R.; Wen, H.; Gao, B.; Chen, G.; Gao, P.; Yuen, M.M.F.; Wong, C.P. Water-based isotropically conductive adhesives: Towards green and low-cost flexible electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 4582–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y.; Liao, Y.C. Adhesive Stretchable Printed Conductive Thin film patterns on PDMS surface with an atmospheric plasma treatment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 11868–11874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suriati, G.; Mariatti, M.; Azizan, A. Effects of filler shape and size on the properties of silver filled epoxy composite for electronic applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2011, 22, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Yang, J. React-on-Demand (RoD) fabrication of highly conductive metal-polymer hybrid structure for flexible electronics via one-step direct writing or printing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1704671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande, S.; Singh, B.; Mathur, R.; Dhami, T.; Saini, P.; Dhawan, S. Improved electromagnetic interference shielding properties of MWCNT-PMMA composites using layered structures. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Le, T.; Wu, Z.; Yao, Y.; Li, L.; Tentzeris, M.; Moon, K.S.; Wong, C.P. Rational design of a printable, highly conductive silicone-based electrically conductive adhesive for stretchable radio-frequency antennas. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, M.; Yang, C.; Sun, H.; Gao, Z.; Yuen, M.M.F.; Yang, S. Highly conductive die attach adhesive from percolation control and its applications in light-emitting device thermal management. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 014101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, R.; Moon, K.S.; Liu, Y.; Hansen, K.; Le, T.; Wong, C.P. Highly conductive, flexible, polyurethane-based adhesives for flexible and printed electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 1459–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, Q.; Long, X.; Li, T.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, K.; E, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Yao, Y. In situ generation of photosensitive silver halide for improving the conductivity of electrically conductive adhesives. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface 2017, 9, 29047–29054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wan, C.; Fu, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, X.; Li, M. Study on the effects of adipic acid on properties of dicyandiamide-cured electrically conductive adhesive and the interaction mechanism. J. Electron. Mater. 2014, 43, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Xie, Y.T.; Yuen, M.M.F.; Xu, B.; Gao, B.; Xiong, X.M.; Wong, C.P. Silver Surface iodination for enhancing the conductivity of conductive composites. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 2580–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, Q.; Cheng, L.; Li, T.; Lu, H.; Tang, L.; Zhang, K.; E, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; et al. Conductivity enhancement of polymer composites using high-temperature short-time treated silver fillers. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2017, 100, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuhisa, N.; Inoue, D.; Zalar, P.; Jin, H.; Matsuba, Y.; Itoh, A.; Yokota, T.; Hashizume, D.; Someya, T. Printable elastic conductors by in situ formation of silver nanoparticles from silver flakes. Nat. Mater. 2017, 16, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patole, A.; Lubineau, G. Carbon nanotubes with silver nanoparticle decoration and conductive polymer coating for improving the electrical conductivity of polycarbonate composites. Carbon 2015, 81, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.; Cho, H.W.; Kim, T.; Kim, D.; Sung, B.J.; Lim, S.; Kim, H. Effects of silica particles on the electrical percolation threshold and thermomechanical properties of epoxy/silver nanocomposites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 043104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoli, B.M.; Gumfekar, S.; Hu, A.; Zhou, Y.N.; Zhao, B. Thiocarboxylate functionalization of silver nanoparticles: Effect of chain length on the electrical conductivity of nanoparticles and their polymer composites. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 20048–20056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Chen, X.Y.; Xiao, F. The sintering behavior of electrically conductive adhesives filled with surface modified silver nanowires. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2011, 25, 1465–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermant, M.C.; van der Schoot, P.; Klumperman, B.; Koning, C.E. Probing the cooperative nature of the conductive components in polystyrene/poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly(styrene sulfonate)-single-walled carbon nanotube composites. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 2242–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.H.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.Q.; Xiao, H.M.; Du, S.S.; Zhang, J.Y.; Hu, N.; Fu, S.Y. Significantly enhanced electrical conductivity of silver nanowire/polyurethane composites via graphene oxide as novel dispersant. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 132, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Cui, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chiang, S.W.; Lin, W.; Duan, H.; Li, J.; Kang, F.; Wong, C.P. Fractal dendrite-based electrically conductive composites for laser-scribed flexible circuits. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Han, S.I.; Jung, D.; Hwang, H.J.; Lim, C.; Bae, S.; Park, O.K.; Tschabrunn, C.M.; Lee, M.; Bae, S.Y.; et al. Highly conductive, stretchable and biocompatible Ag-Au core-sheath nanowire composite for wearable and implantable bioelectronics. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuhisa, N.; Kaltenbrunner, M.; Yokota, T.; Jinno, H.; Kuribara, K.; Sekitani, T.; Someya, T. Printable elastic conductors with a high conductivity for electronic textile applications. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, P.; Trinidad, J.; Chen, L.; Lee, B.; Chen, A.; Persic, J.; Lyn, R.; Leonenko, Z.; Zhao, B. PEDOT:PSS nano-gels for highly electrically conductive silver/epoxy composite adhesives. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lu, J.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Wang, F. From amorphous to crystalline: Practical way to improve electrical conductivity of water-borne conducting polyaniline. Polymer 2011, 52, 3059–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Zhou, N.; Gong, K.; Liu, H.; Liu, Q.; Sun, D.; Wang, Q.; Shao, Q.; Liu, H.; Qiu, B.; et al. Intracellular polymer substances induced conductive polyaniline for improved methane production from anaerobic wastewater treatment. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 5912–5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Bi, H.; Yao, Q.; Ren, D.; Qu, S.; Huang, F.; Chen, L. Three-dimensional tubular graphene/polyaniline composites as high-performance elastic thermoelectrics. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 150, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Huang, G.W.; Xiao, H.M.; Li, Y.Q.; Hu, N.; Fu, S.Y. Largely enhanced electrical conductivity of layer-structured silver nanowire/polyimide composite films by polyaniline. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 156, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuksel, R.; Durucan, C.; Unalan, H.E. Ternary nanocomposite SWNT/WO3/PANI thin film electrodes for supercapacitors. J. Alloys. Compd. 2016, 658, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huangfu, Y.; Ruan, K.; Qiu, H.; Lu, Y.; Liang, C.; Kong, J.; Gu, J. Fabrication and investigation on the PANI/MWCNT/thermally annealed graphene aerogel/epoxy electromagnetic interference shielding nanocomposites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 121, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Guo, J.; Wei, H.; Yan, X.; Ding, D.; Zhang, X.; He, Q.; Tadakamalla, S.; Wang, X.; Ho, T.C.; et al. Transparent anhydride-cured epoxy nanocomposites reinforced with polyaniline stabilized nanosilica. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 8152–8165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Long, J.; Ding, D.; Wang, Q.; Shan, Y.; Umar, A.; Zhang, X.; Weeks, B.L.; Wei, S.; Guo, Z. Significantly enhanced mechanical and electrical properties of epoxy nanocomposites reinforced with low loading of polyaniline nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 21187–21192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; He, Q.; Gu, H.; Wei, S.; Guo, Z. Polyaniline stabilized barium titanate nanoparticles reinforced epoxy nanocomposites with high dielectric permittivity and reduced flammability. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 2886–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Liu, C.; Gao, R. Polyaniline: A novel bridge to reduce the fire hazards of epoxy composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 112, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, T.; Mishra, S.; Shimpi, N.G. Synthesis and sensing applications of polyaniline nanocomposites: A review. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 42196–42222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncel, D.; Demir, H.V. Conjugated polymer nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecher, J.; Mecking, S. Nanoparticles of conjugated polymers. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 6260–6279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Tian, Y.; Mei, Z.; Wu, W.; Tian, Y. Synthesis of polypyrrole nanoparticles and their applications in electrically conductive adhesives for improving conductivity. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 53219–53225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, S.B.; Yslas, E.I.; Rivarola, C.R.; Barbero, C.A. Synthesis of polyaniline (PANI) and functionalized polyaniline (F-PANI) nanoparticles with controlled size by solvent displacement method. Application in fluorescence detection and bacteria killing by photothermal effect. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 125604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.H.; Ting, T.H.; Wang, G.P.; Ho, W.D.; Shih, C.C. Effect of carbon black content on electrical and microwave absorbing properties of polyaniline/carbon black nanocomposites. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2008, 93, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigandi, P.J.; Cogen, J.M.; Pearson, R.A. Electrically conductive multiphase polymer blend carbon-based composites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2014, 54, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruschau, G.R.; Yoshikawa, S.; Newnham, R.E. Resistivities of conductive composites. J. Appl. Phys. 1992, 72, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Tian, Y.; Hao, C.; Wang, S.; Mei, Z.; Wu, W.; Lu, J.; Zheng, Z.; Tian, Y. Fabrication of high performance printed flexible conductors by doping of polyaniline nanomaterials into silver paste. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 1188–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

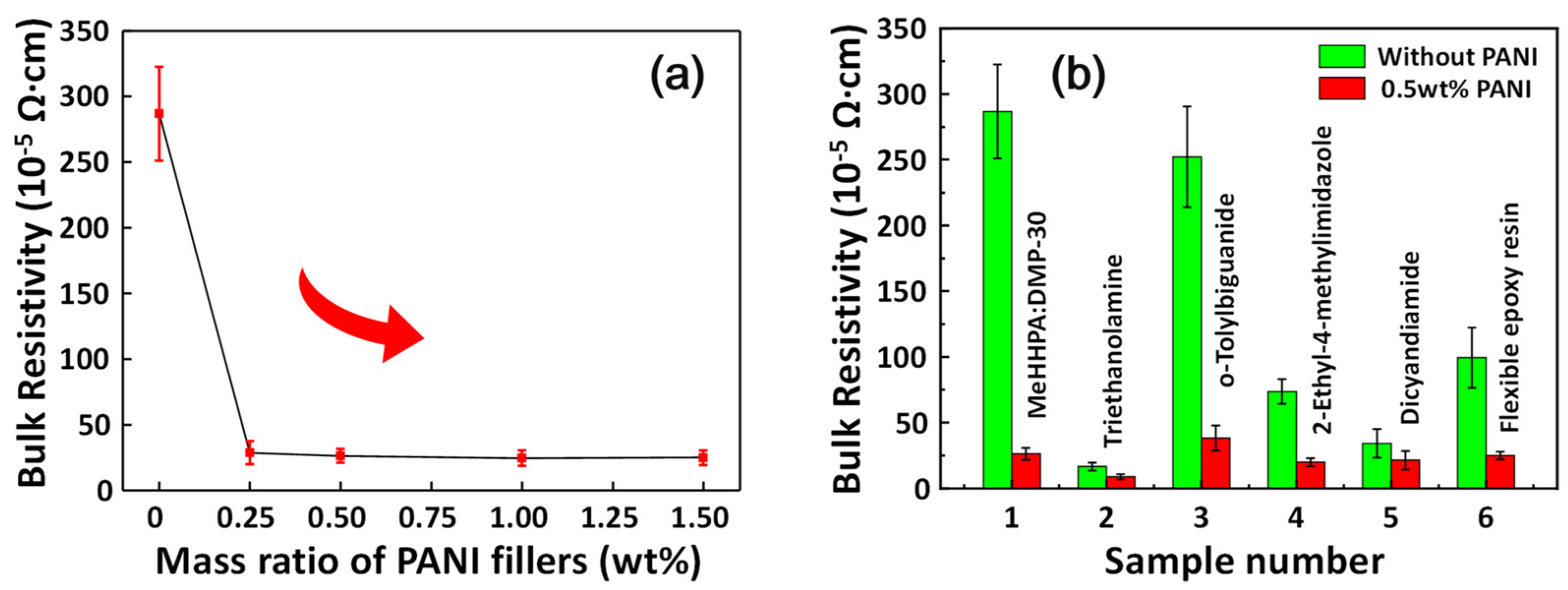

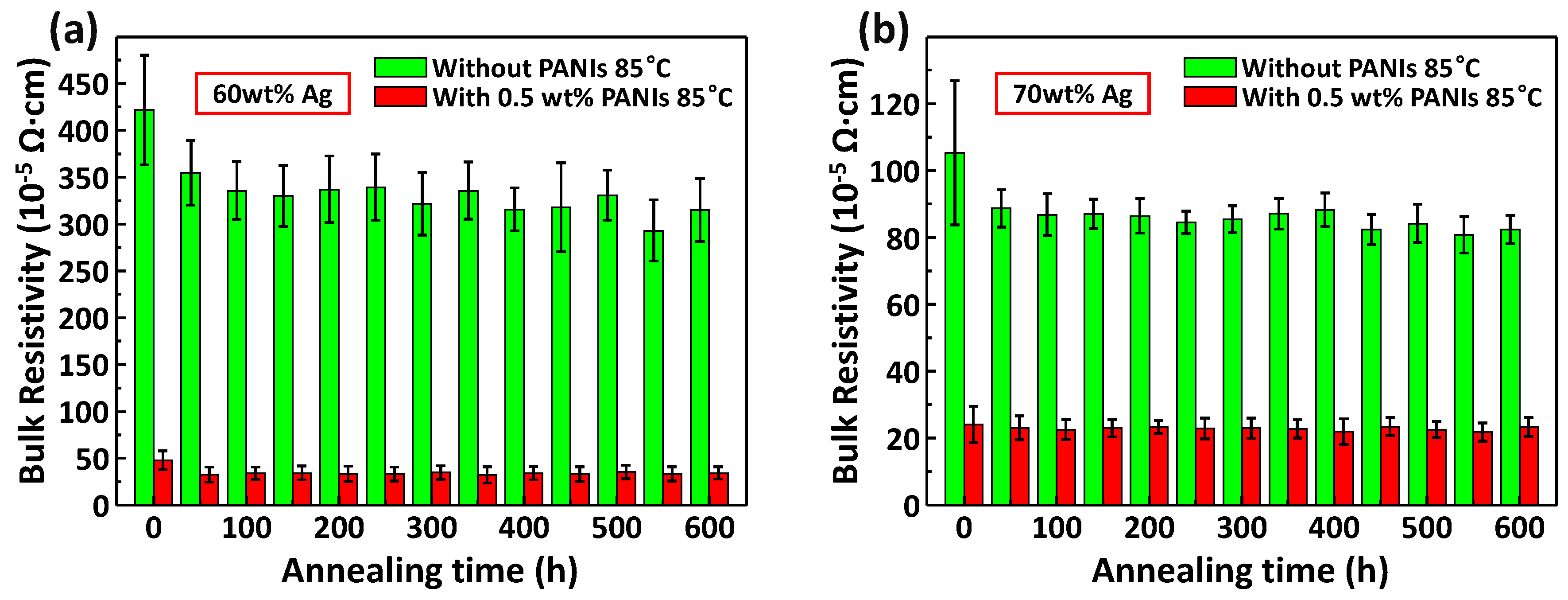
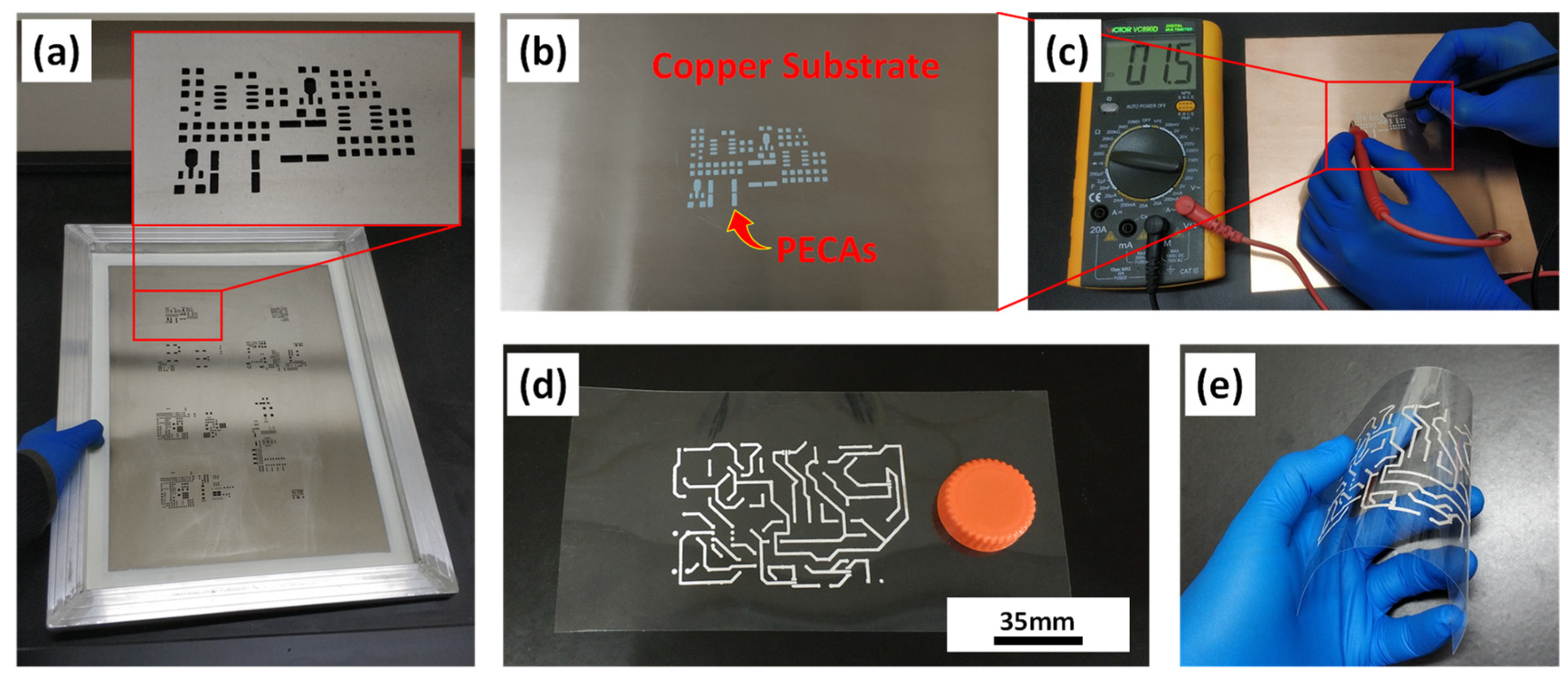
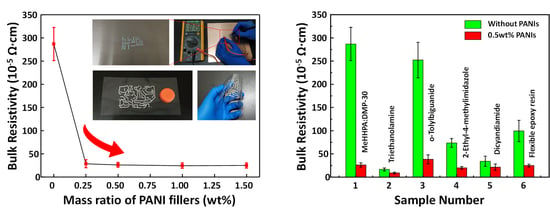
| No. | Resin Composition (Mass Ratio) | Curing Process | Resistivity Change (×10−5 Ω·cm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without PANIs | With 0.5 wt% PANIs | |||
| 1 | Epoxy: MeHHPA:DMP-30 = (100:85:0.5) | 150 °C 1 h | 286.8 | 26.1 |
| 2 | Epoxy:Triethanolamine = (100:16) | 120 °C 3 h | 16.7 | 8.8 |
| 3 | Epoxy:o-Tolylbiguanide = (100:14) | 140 °C 2 h | 252.2 | 38.3 |
| 4 | Epoxy:2-Ethyl-4-methylimidazole = (100:3) | 120 °C 1 h | 73.6 | 19.8 |
| 5 | Epoxy: Dicyandiamide = (100:8) | 180 °C 1 h | 34.1 | 21.4 |
| 6 | Self-made modified flexible epoxy resin | RT | 99.4 | 25.0 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, J.; Tian, Y.; Hang, C.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Mei, Z.; Hu, X.; Tian, Y. Fabrication of Novel Printable Electrically Conductive Adhesives (ECAs) with Excellent Conductivity and Stability Enhanced by the Addition of Polyaniline Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9070960
Wen J, Tian Y, Hang C, Zheng Z, Zhang H, Mei Z, Hu X, Tian Y. Fabrication of Novel Printable Electrically Conductive Adhesives (ECAs) with Excellent Conductivity and Stability Enhanced by the Addition of Polyaniline Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(7):960. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9070960
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Jiayue, Yanhong Tian, Chunjin Hang, Zhen Zheng, He Zhang, Zhipeng Mei, Xuanyi Hu, and Yanqing Tian. 2019. "Fabrication of Novel Printable Electrically Conductive Adhesives (ECAs) with Excellent Conductivity and Stability Enhanced by the Addition of Polyaniline Nanoparticles" Nanomaterials 9, no. 7: 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9070960
APA StyleWen, J., Tian, Y., Hang, C., Zheng, Z., Zhang, H., Mei, Z., Hu, X., & Tian, Y. (2019). Fabrication of Novel Printable Electrically Conductive Adhesives (ECAs) with Excellent Conductivity and Stability Enhanced by the Addition of Polyaniline Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials, 9(7), 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9070960