Applying Aluminum–Vertically-Aligned Carbon Nanotube Forests Composites for Heat Dissipation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
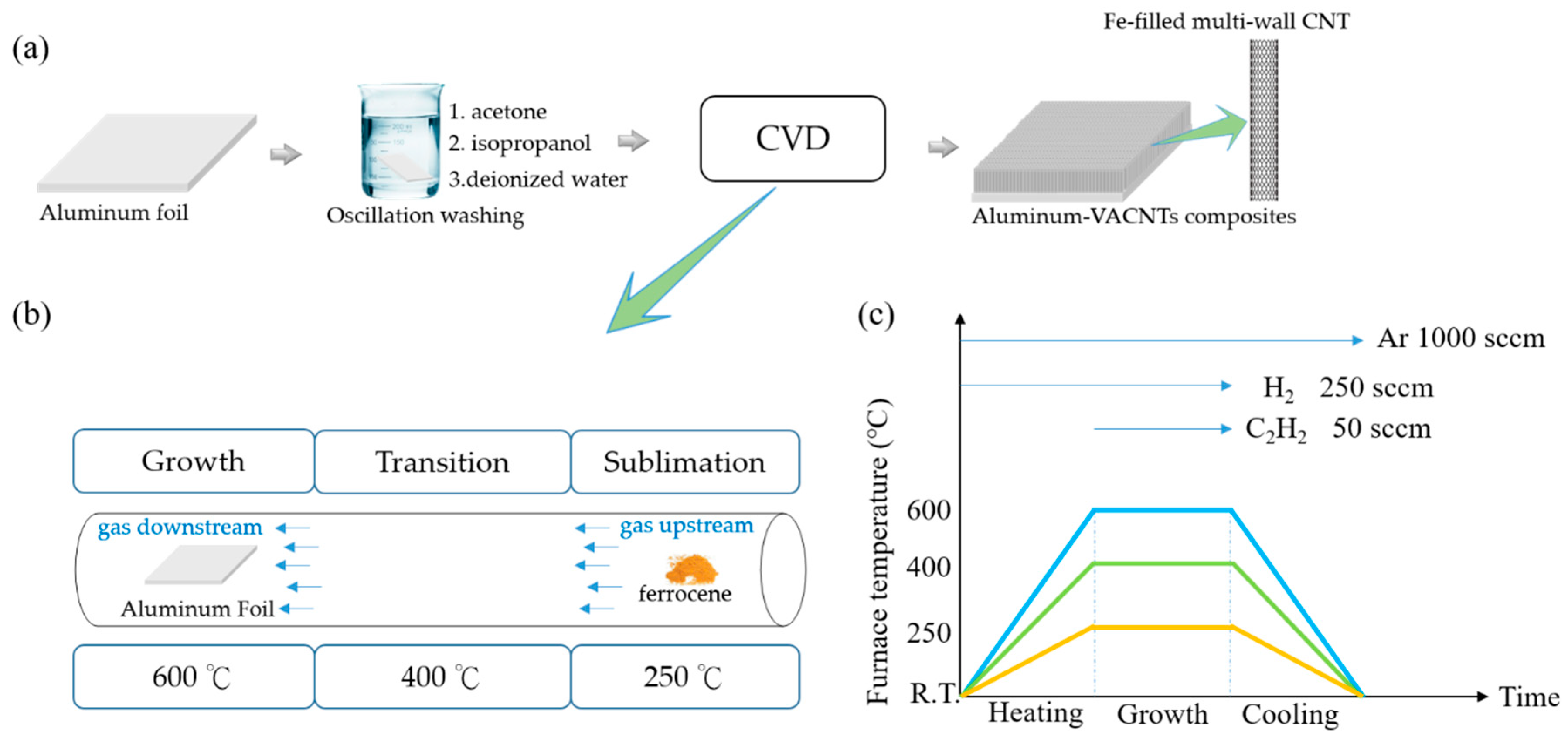
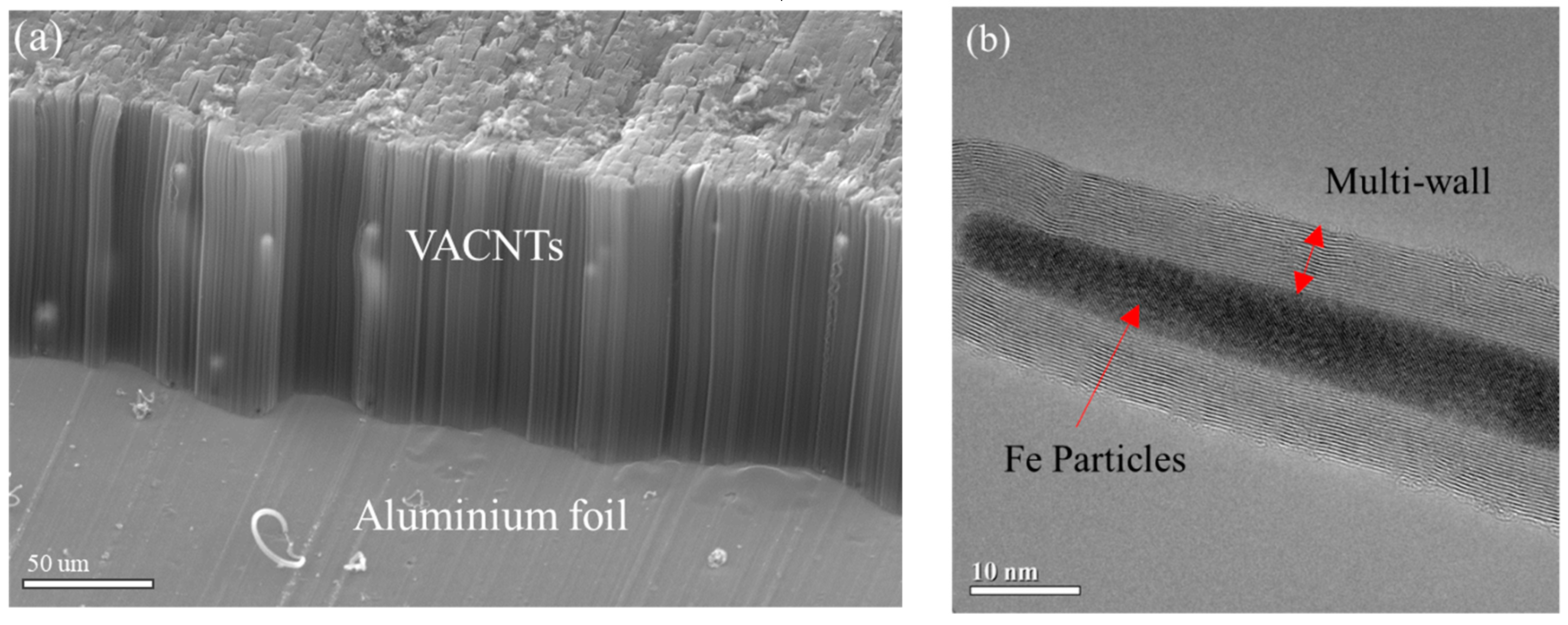
2.1. Aluminum–VACNTs Composites Synthesis
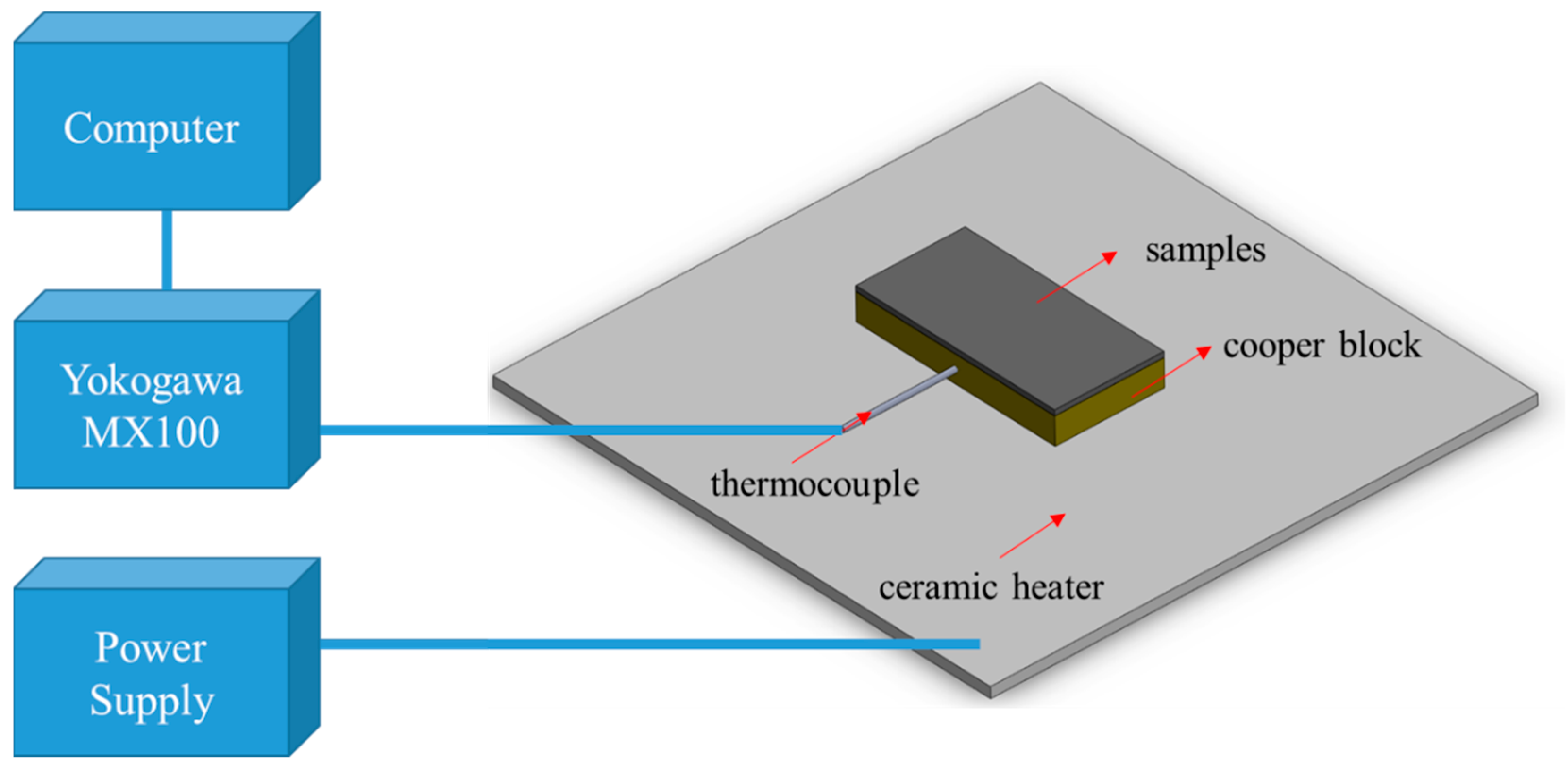
2.2. Heat Dissipation Setup
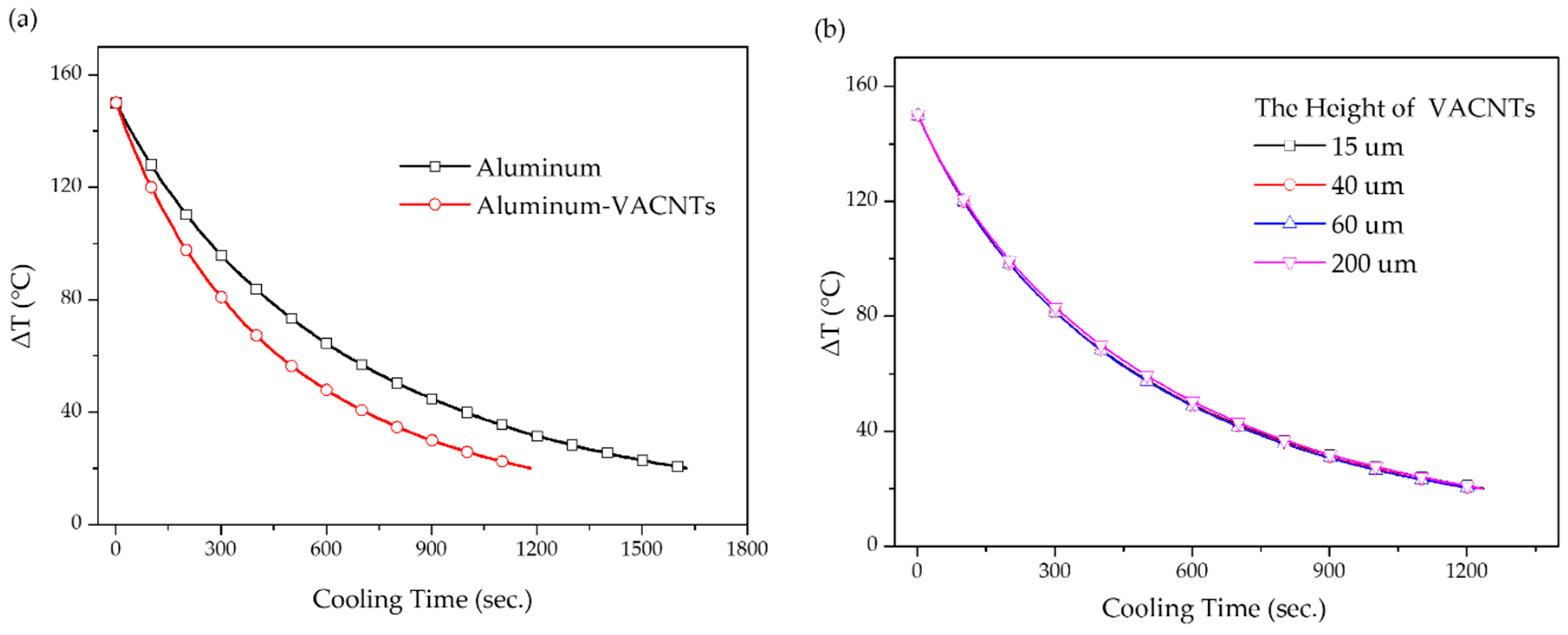
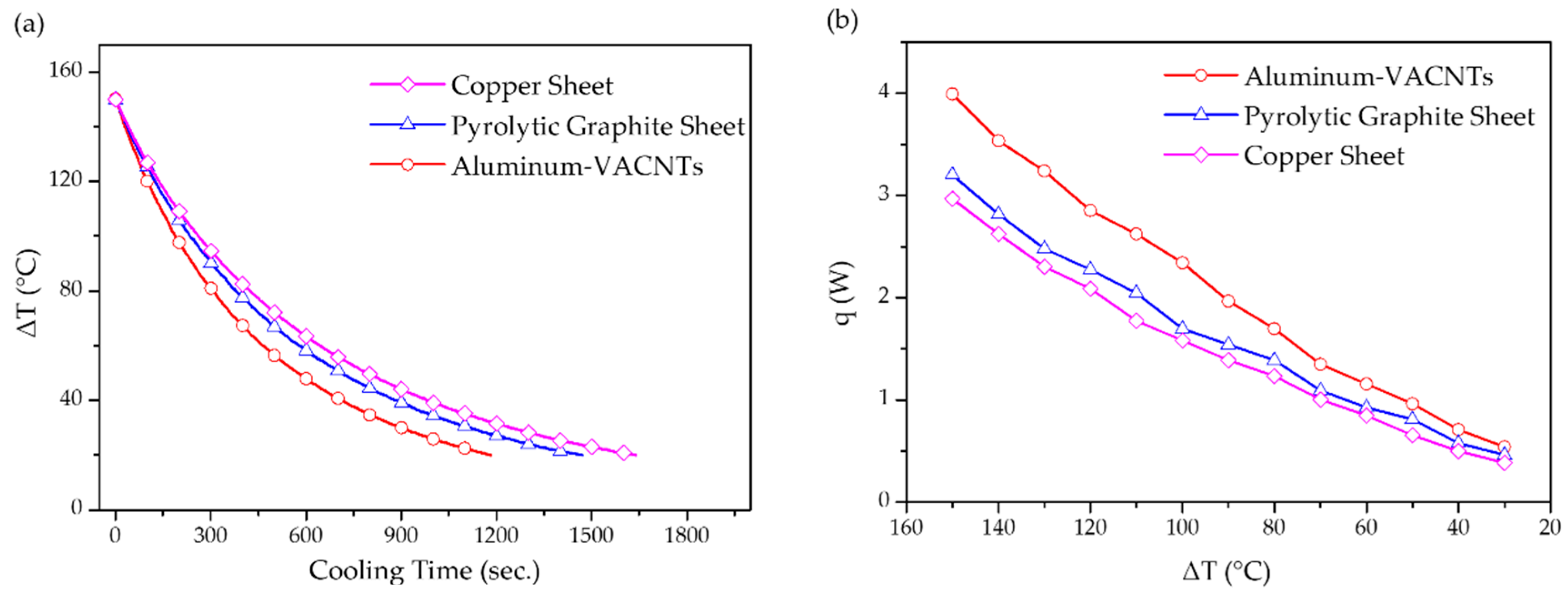
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davis, J.A.; Venkatesan, R.; Kaloyeros, A.; Beylansky, M.; Souri, S.J.; Banerjee, K.; Saraswat, K.C.; Rahman, A.; Reif, R.; Meindl, J.D. Interconnect limits on gigascale integration (GSI) in the 21st century. Proc. IEEE 2001, 89, 305–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meindl, J.D. Interconnect opportunities for gigascale integration. IEEE Micro 2003, 23, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, J.-M.; Im, S.; Jiang, L.; Goodson, K.E. Integrated Microchannel Cooling for Three-Dimensional Electronic Circuit Architectures. J. Heat Transf. 2005, 127, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, B.; Bakir, M.S.; Sekar, D.C.; King, C.R., Jr.; Meindl, J.D. Integrated Microfluidic Cooling and Interconnects for 2D and 3D Chips. IEEE Trans. Adv. Packag. 2010, 33, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cola, B.A.; Xu, J.; Cheng, C.R.; Xu, X.F.; Fisher, T.S.; Hu, H.P. Photoacoustic characterization of carbon nanotube array thermal interfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 054313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cola, B.A.; Xu, X.; Fisher, T.S. Increased real contact in thermal interfaces: A carbon nanotube/foil material. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 093513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dresselhaus, M.S.; Dresselhaus, G.; Jorio, A. Unusual properties and structure of carbon nanotubes. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2004, 34, 247–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.; Shi, L.; Majumdar, A.; McEuen, P.L. Thermal Transport Measurements of Individual Multiwalled Nanotubes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 215502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pop, E.; Mann, D.; Wang, Q.; Goodson, K.; Dai, H. Thermal Conductance of an Individual Single-Wall Carbon Nanotube above Room Temperature. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balandin, A.A. Thermal properties of graphene and nanostructured carbon materials. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harish, S.; Ishikawa, K.; Einarsson, E.; Aikawa, S.; Chiashi, S.; Shiomi, J.; Maruyama, S. Enhanced thermal conductivity of ethylene glycol with single-walled carbon nanotube inclusions. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 3885–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahil, K.M.F.; Balandin, A.A. Thermal properties of graphene and multilayer graphene: Applications in thermal interface materials. Solid State Commun. 2012, 152, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconnet, A.M.; Panzer, M.A.; Goodson, K.E. Thermal conduction phenomena in carbon nanotubes and related nanostructured materials. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2013, 85, 1295–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Wang, X.; Su, G.; Tang, D.; Zheng, X.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Z.; Norris, P.M.; Bradford, P.D.; Zhu, Y. Remarkably enhanced thermal transport based on a flexible horizontally-aligned carbon nanotube array film. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Zhong, H.; Wang, M.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, Y. Effect of Contact Pressure on the Performance of Carbon Nanotube Arrays Thermal Interface Material. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hone, J.; Llaguno, M.; Nemes, N.; Johnson, A.T.C.; Fischer, J.E.; Walters, D.A.; Casavant, M.; Schmidt, J.; Smalley, R.E. Electrical and Thermal Transport Properties of Magnetically Aligned Single-Wall Carbon Nanotube Films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000, 77, 666–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigg, D.M. Thermal-Conductivity of Heterophase Polymer Compositions. Adv. Polym. Sci. 1995, 119, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, F.; Zheng, Q.S.; Wang, L.F.; Nan, C.W. Effects of anisotropy, aspect ratio, and nonstraightness of carbon nanotubes on thermal conductivity of carbon nanotube composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 021914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenogin, S.; Xue, L.P.; Ozisik, R.; Keblinski, P.; Cahill, D.G. Role of thermal boundary resistance on the heat flow in carbon-nanotube composites. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 95, 8136–8144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenogina, N.; Shenogin, S.; Xue, L.; Keblinski, P. On the lack of thermal percolation in carbon nanotube composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 133106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Fu, R.L.; Agathopoulos, S.; Zhang, S.D.; Song, X.F.; He, H. Numerical Simulation of Thermal Conductivity of Particle Filled Epoxy Composites. J. Electron. Packag. 2009, 131, 041006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, S.; Yang, M. The effect of heat-transfer passages on the effective thermal conductivity of high filler loading composite materials. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burg, B.R.; Bianco, V.; Schneider, J.; Poulikakos, D. Electrokinetic framework of dielectrophoretic deposition devices. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 124308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burg, B.R.; Schneider, J.; Bianco, V.; Schirmer, N.C.; Poulikakos, D. Selective Parallel Integration of Individual Metallic Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes from Heterogeneous Solutions. Langmuir 2010, 26, 10419–10424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, J.P. Heat Transfer, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1976; pp. 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, C.H.; Huang, H.M. Responses and thermal conductivity measurements of multi-wall carbon nanotube (MWNT)/epoxy composites. J. Anal. Calorim. 2011, 103, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukes, J.R.; Zhong, H.L. Thermal conductivity of individual single-wall carbon nanotubes. J. Heat Trans. Trans. ASME 2007, 129, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Stroscio, M.A.; Dutta, M. Thermal conductivity of carbon nanotubes. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 074316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, L.; Broido, D.A.; Mingo, N. Flexural phonons and thermal transport in graphene. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 115427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.-P.; Ci, L.; Bur, J.A.; Lin, S.-Y.; Ajayan, P.M. Experimental Observation of an Extremely Dark Material Made by a Low-Density Nanotube Array. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, K.; Ishii, J.; Kishida, H.; Hayamizu, Y.; Yasuda, S.; Futaba, D.N.; Yumura, M.; Hata, K. A black body absorber from vertically aligned single-walled carbon nanotubes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6044–6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.-R.; Su, C.-C.; Chang, S.-H. Applying Aluminum–Vertically-Aligned Carbon Nanotube Forests Composites for Heat Dissipation. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 758. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9050758
Li Y-R, Su C-C, Chang S-H. Applying Aluminum–Vertically-Aligned Carbon Nanotube Forests Composites for Heat Dissipation. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(5):758. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9050758
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yan-Rui, Chih-Chung Su, and Shuo-Hung Chang. 2019. "Applying Aluminum–Vertically-Aligned Carbon Nanotube Forests Composites for Heat Dissipation" Nanomaterials 9, no. 5: 758. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9050758
APA StyleLi, Y.-R., Su, C.-C., & Chang, S.-H. (2019). Applying Aluminum–Vertically-Aligned Carbon Nanotube Forests Composites for Heat Dissipation. Nanomaterials, 9(5), 758. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9050758



