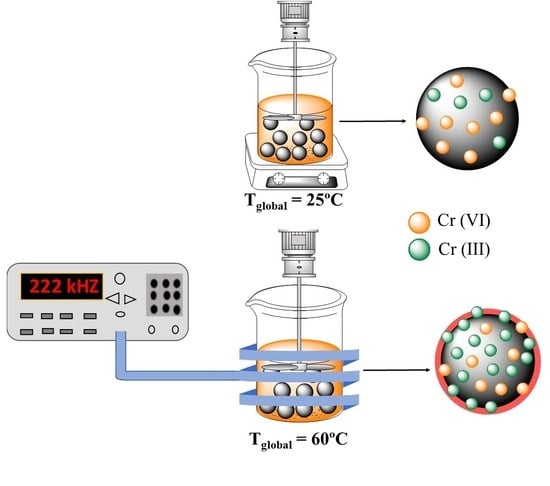
Improvement in Heavy Metal Removal from Wastewater Using an External Magnetic Inductor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Electrochemical Synthesis
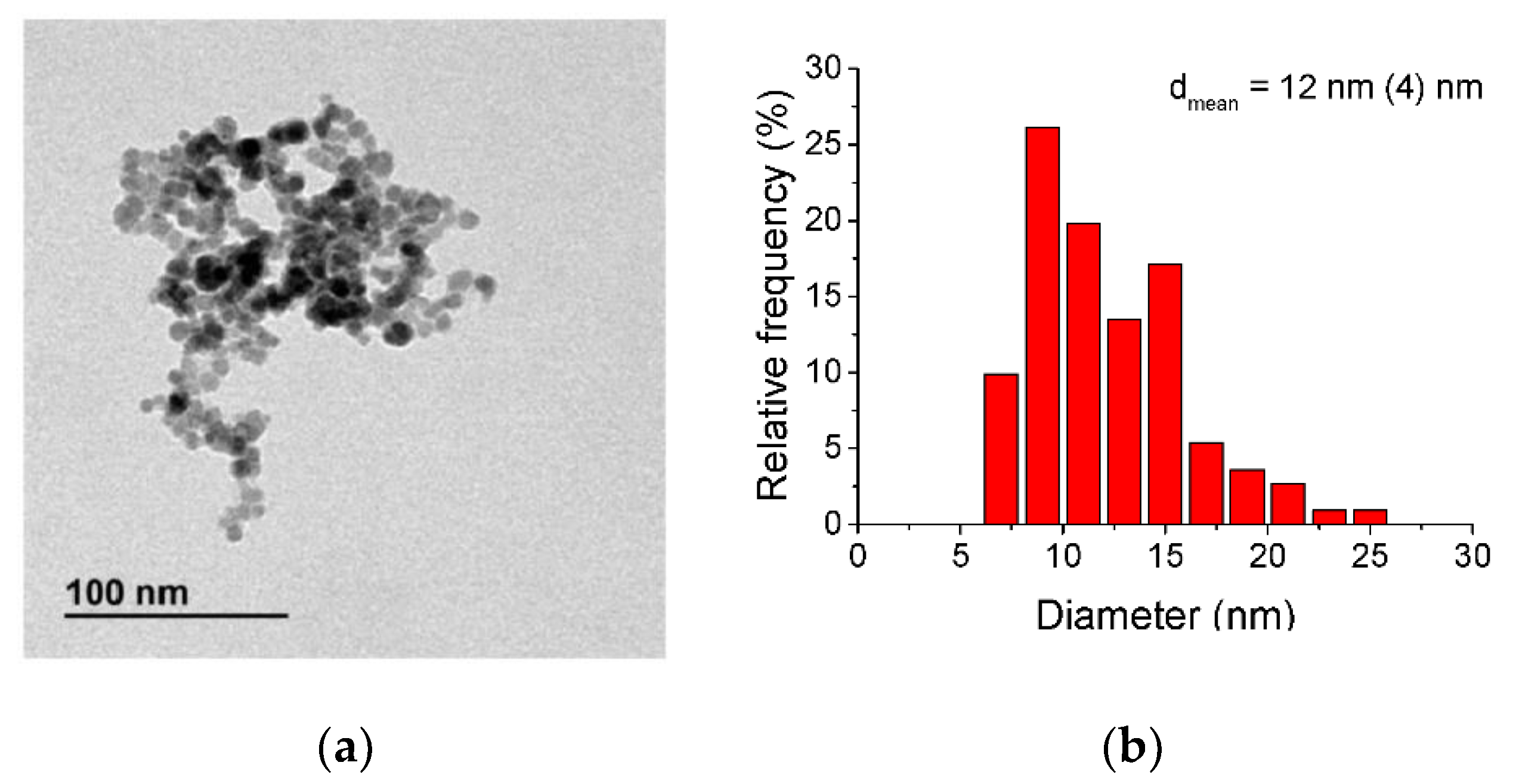
2.2. Material Characterization
2.3. Adsorption Experiments
2.4. Magnetic Inductor Experiments
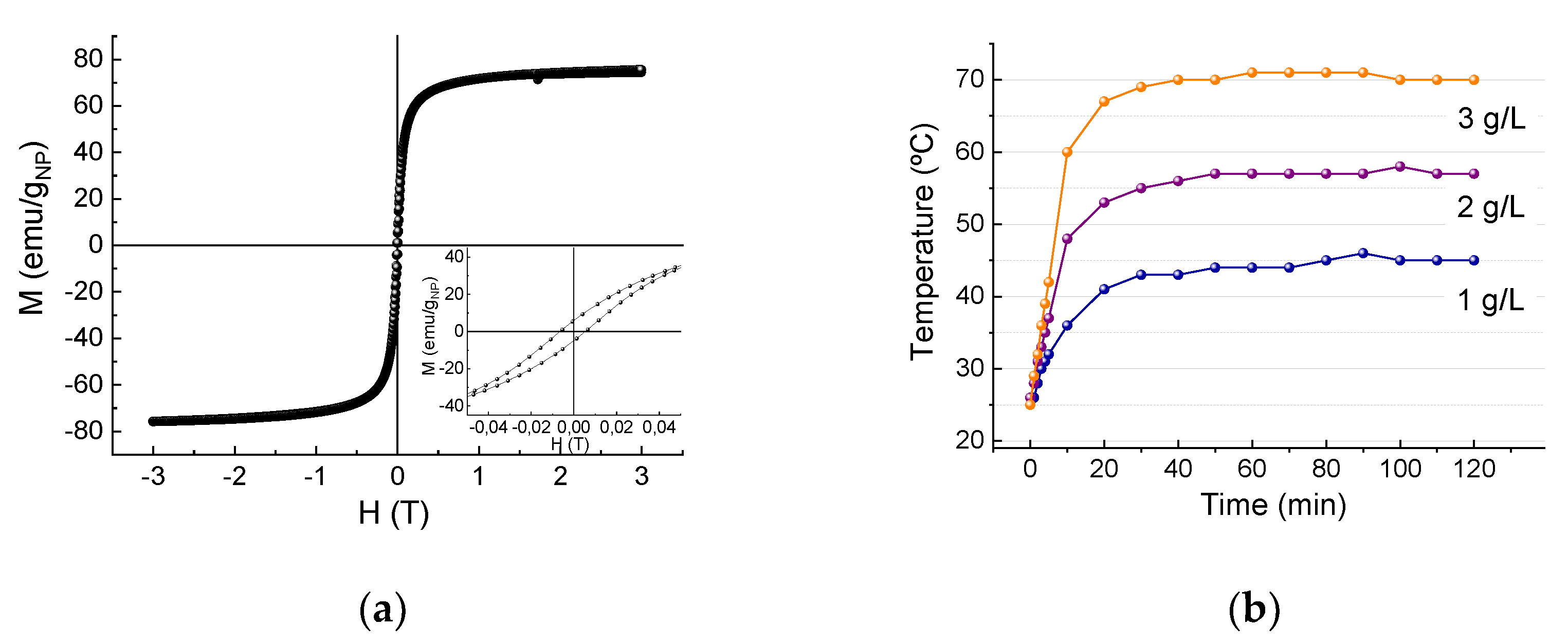
2.4.1. Evaluation of the Maximum Heating Capacity of the Sorbent in Aqueous Media
2.4.2. Adsorption Test with Induction Heating
2.5. Bath Experiments
2.6. Reusability Test
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Concerns on the Adsorption Process
3.1.1. Effect of pH
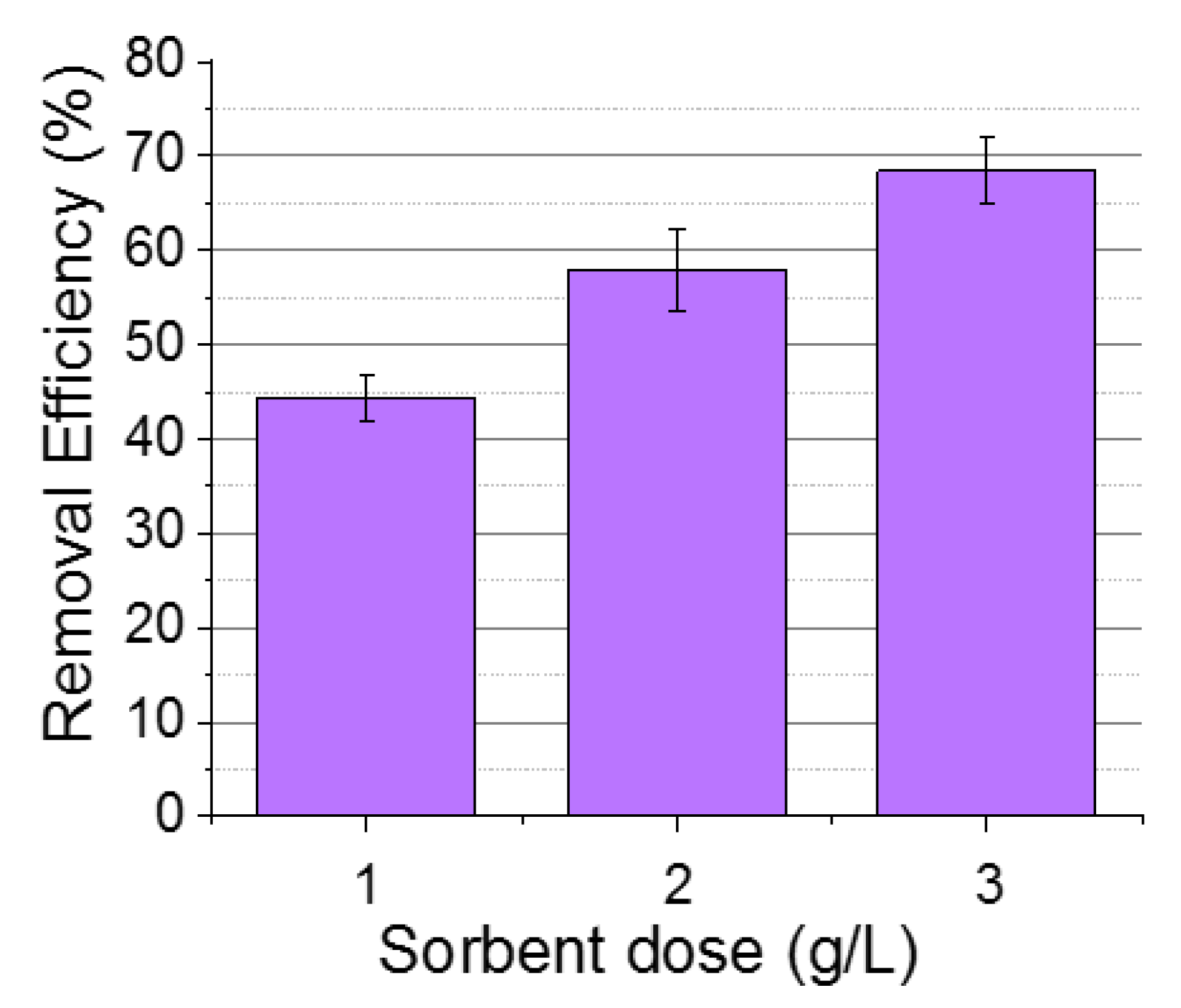
3.1.2. Effect of Sorbate Dose
3.1.3. Kinetic Adsorption Process
3.2. Evaluation of Induction Heating Effect on the Removal of Cr(VI)
3.3. Desorption and Reusability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Persson, L.M.; Breitholtz, M.; Cousins, I.T.; de Wit, C.A.; MacLeod, M.; McLachlan, M.S. Confronting Unknown Planetary Boundary Threats from Chemical Pollution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 12619–12622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gou, X.; Su, Y.; Wang, G. Risk assessment of heavy metals in soils and vegetables around non-ferrous metals mining and smelting sites, Baiyin, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2006, 18, 1124–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duruibe, J.O.; Ogwuegbu, M.O.C.; Egwurugwu, J.N. Heavy metal pollution and human biotoxic effects. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2007, 2, 112–118. [Google Scholar]
- Eichinger, E.; Osborne, J.; Van Cleave, T. Hexavalent chromium elimination: An aerospace industry progress report. Metal Finish. 1997, 95, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I. New generation adsorbents for water treatment. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 5073–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Ma, Q.; Tan, C.; Lim, T.-T.; Huang, L.; Zhang, H. Carbon-Based Sorbents with Three-Dimensional Architectures for Water Remediation. Small 2015, 11, 3319–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.A. Preparation and characterization of chitin/magnetite/multiwalled carbon nanotubes magnetic nanocomposite for toxic hexavalent chromium removal from solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 233, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvani, M.; Asgharinezhad, A.A.; Ebrahimzadeh, H.; Shekari, N. A polyaniline-magnetite nanocomposite as an anion exchange sorbent for solid-phase extraction of chromium(VI) ions. Microchim. Acta 2014, 181, 1887–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, T.A.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Paez-Hernandez, M.E.; Guevara-Lara, A.; Barrado, E.; Hernandez, P. Chromium(VI) Removal from Aqueous Solution by Magnetite Coated by a Polymeric Ionic Liquid-Based Adsorbent. Materials 2017, 10, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zongo, I.; Leclerc, J.-P.; Maïga, H.A.; Wéthé, J.; Lapicque, F. Removal of hexavalent chromium from industrial wastewater by electrocoagulation: A comprehensive comparison of aluminium and iron electrodes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 66, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafiane, A.; Lemordant, D.; Dhahbi, M. Removal of hexavalent chromium by nanofiltration. Desalination 2000, 130, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.-R.; Wang, J.-N.; Li, C.-J. Preparation of hierarchically nanofibrous membrane and its high adaptability in hexavalent chromium removal from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 198–199, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, P.; Samantaray, S.K.; Parida, K. Photocatalytic reduction of hexavalent chromium in aqueous solution over sulphate modified titania. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2005, 170, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Ma, H.; Wang, S.; Shen, M.; Guo, R.; Cao, X.; Zhu, M.; Shi, X. Efficient Catalytic Reduction of Hexavalent Chromium Using Palladium Nanoparticle-Immobilized Electrospun Polymer Nanofibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 3054–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owlad, M.; Aroua, M.K.; Daud, W.A.W.; Baroutian, S. Removal of Hexavalent Chromium-Contaminated Water and Wastewater: A Review. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2009, 200, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Tiwari, P.N. Removal and Recovery of Chromium(VI) from Industrial Waste Water. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1997, 69, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Chen, G.; Lo, I.M.C. Removal and recovery of Cr(VI) from wastewater by maghemite nanoparticles. Water Res. 2005, 39, 4528–4536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeonidis, K.; Kaprara, E.; Samaras, T.; Angelakeris, M.; Pliatsikas, N.; Vourlias, G.; Mitrakas, M.; Andritsos, N. Optimizing magnetic nanoparticles for drinking water technology: The case of Cr(VI). Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 535, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.K.; Naiya, T.K.; Mandal, S.N.; Das, S.K. Adsorption, kinetics and equilibrium studies on removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions using different low-cost adsorbents. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 137, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Lo, I.M.C.; Chen, G. Comparative study of various magnetic nanoparticles for Cr(VI) removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 56, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, L.J.; Muñoz-Bonilla, A.; Mazario, E.; Recio, F.J.; Palomares, F.J.; Herrasti, P. Adsorption of chromium(VI) onto electrochemically obtained magnetite nanoparticles. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 4017–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazarío, E.; Helal, A.S.; Stemper, J.; Mayoral, A.; Decorse, P.; Chevillot-Biraud, A.; Novak, S.; Perruchot, C.; Lion, C.; Losno, R.; et al. Maghemite nanoparticles bearing di(amidoxime) groups for the extraction of uranium from wastewaters. AIP Adv. 2017, 7, 056702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helal, A.S.; Mazario, E.; Mayoral, A.; Decorse, P.; Losno, R.; Lion, C.; Ammar, S.; Hémadi, M. Highly efficient and selective extraction of uranium from aqueous solution using a magnetic device: Succinyl-β-cyclodextrin-APTES@maghemite nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Nano 2018, 5, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zing, Z.; Xu, T.; Su, K.; Pengwei, H.; Minshan, S.; Weidong, S.; Ziyang, L.; Yongsheng, Y. Constructing of the Magnetic Photocatalytic Nanoreactor MS@FCN for Cascade Catalytic Degrading of Tetracycline. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 27250–27258. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; He, Q.; Jiang, C. Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Surface Functionalization Strategies. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2008, 3, 397–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankhurst, Q.A.; Connolly, J.; Jones, S.K.; Dobson, J. Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, R167–R181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tireli, A.A.; Marcos, F.C.F.; Oliveira, L.F.; do Rosário Guimarães, I.; Guerreiro, M.C.; Silva, J.P. Influence of magnetic field on the adsorption of organic compound by clays modified with iron. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 97, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lu, T.; Bai, D.-M.; Lin, D.-Q.; Yao, S.-J. Self-immobilization of a magnetic biosorbent and magnetic induction heated dye adsorption processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 972–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, N.S.; Sohaili, J.; Muda, K.; Sillanpää, M. Magnetic Field Application and its Potential in Water and Wastewater Treatment Systems. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2014, 43, 206–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aigbe, U.O.; Das, R.; Ho, W.H.; Srinivasu, V.; Maity, A. A novel method for removal of Cr(VI) using polypyrrole magnetic nanocomposite in the presence of unsteady magnetic fields. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 194, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, I.; Lopez, C.; Menendez, N.; Casillas, N.; Herrasti, P. Design, Construction and Evaluation of a 3D Printed Electrochemical Flow Cell for the Synthesis of Magnetite Nanoparticles. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, H688–H697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo-Cubero, A.; Gago, R.; Palomares, F.J.; Mücklich, A.; Vinnichenko, M.; Vázquez, L. Nanopatterning dynamics on Si(100) during oblique 40-keV Ar+erosion with metal codeposition: Morphological and compositional correlation. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 86, 085436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamiya, H.; Jeyadevan, B. Hyperthermic effects of dissipative structures of magnetic nanoparticles in large alternating magnetic fields. Sci. Rep. 2011, 1, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabb, C.P.; Carmean, R.N.; Sumerlin, B.S. Probing the surface-localized hyperthermia of gold nanoparticles in a microwave field using polymeric thermometers. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 5662–5669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosensweig, R.E. Heating magnetic fluid with alternating magnetic field. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2002, 252, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebodos, R.L.; Vikesland, P.J. Effects of Oxidation on the Magnetization of Nanoparticulate Magnetite. Langmuir 2010, 26, 16745–16753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotaś, J.; Stasicka, Z. Chromium occurrence in the environment and methods of its speciation. Environ. Pollut. 2000, 107, 263–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owalude, S.O.; Tella, A.C. Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions by adsorption on modified groundnut hull. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2016, 5, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, C.-C.; Ibe, A.H.; Rivera, K.K.P.; Arazo, R.O.; de Luna, M.D.G. Hexavalent chromium removal from aqueous solution by adsorbents synthesized from groundwater treatment residuals. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2017, 27, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, Y.C.; Srivastava, V. Comparative Studies of Removal of Cr(VI) and Ni(II) from Aqueous Solutions by Magnetic Nanoparticles. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2011, 56, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrey, J.; Mehdaoui, B.; Respaud, M. Simple models for dynamic hysteresis loop calculations of magnetic single-domain nanoparticles: Application to magnetic hyperthermia optimization. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 83921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Corato, R.; Espinosa, A.; Lartigue, L.; Tharaud, M.; Chat, S.; Pellegrino, T.; Ménager, C.; Gazeau, F.; Wilhelm, C. Magnetic hyperthermia efficiency in the cellular environment for different nanoparticle designs. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 6400–6411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffete, N.; Fresnais, J.; Espinosa, A.; Taverna, D.; Wilhelm, C.; Ménager, C. Thermal Polymerization on the Surface of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Mediated by Magnetic Hyperthermia: Implications for Multishell Grafting and Environmental Applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, S.; Friese, C.; Lammel, C.; Mazac, K.; Kirschning, A. Inductive Heating for Organic Synthesis by Using Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles Inside Microreactors. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 8950–8953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yu, M.; Qiu, T. Adsorption thermodynamics and kinetics of Cr(VI) on KIP210 resin. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedinger, A.; Guardia, P.; Curcio, A.; Garcia, M.A.; Cingolani, R.; Manna, L.; Pellegrino, T. Subnanometer Local Temperature Probing and Remotely Controlled Drug Release Based on Azo-Functionalized Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2399–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, J.T.; Moros, M.; del Pino, P.; Rivera, S.; Grazú, V.; de la Fuente, J.M. DNA as a Molecular Local Thermal Probe for the Analysis of Magnetic Hyperthermia. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 11526–11529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Cai, Q.; Xu, W.; Yang, M.; Cai, Y.; Dionysiou, D.D.; O’Shea, K.E. Cr(VI) Adsorption and Reduction by Humic Acid Coated on Magnetite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 8078–8085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendelewicz, T.; Liu, P.; Doyle, C.S.; Brown, G.E. Spectroscopic study of the reaction of aqueous Cr(VI) with Fe3O4 (111) surfaces. Surf. Sci. 2000, 469, 144–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesinger, M.C.; Payne, B.P.; Grosvenor, A.P.; Lau, L.W.M.; Gerson, A.R.; Smart, R.S.C. Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Cr, Mn, Fe, Co and Ni. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 2717–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronniemi, M.; Sainio, J.; Lahtinen, J. Chemical state quantification of iron and chromium oxides using XPS: The effect of the background subtraction method. Surf. Sci. 2005, 578, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thermo Scientific XPS. Available online: https://xpssimplified.com/elements/iron.php (accessed on 22 July 2019).

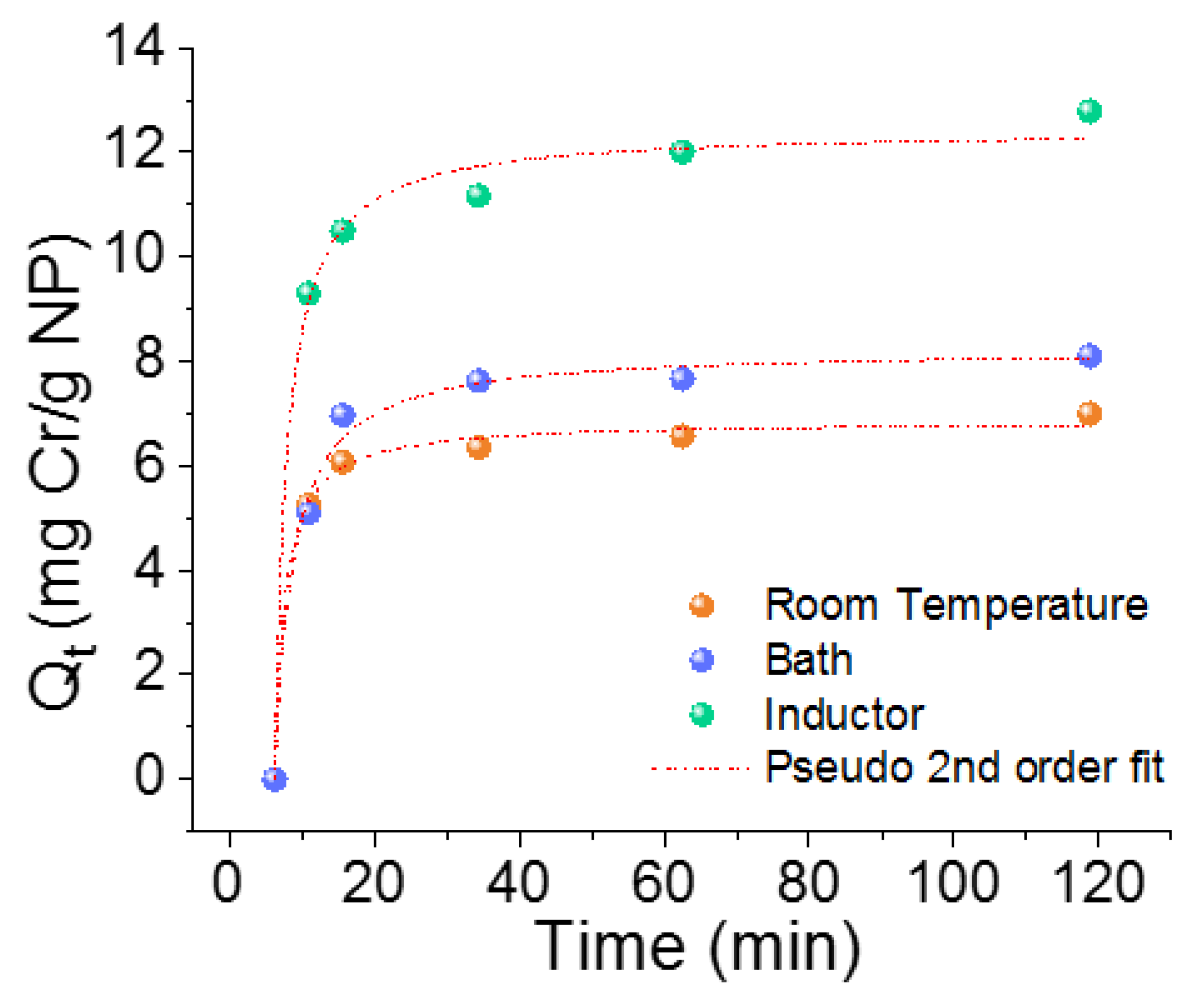
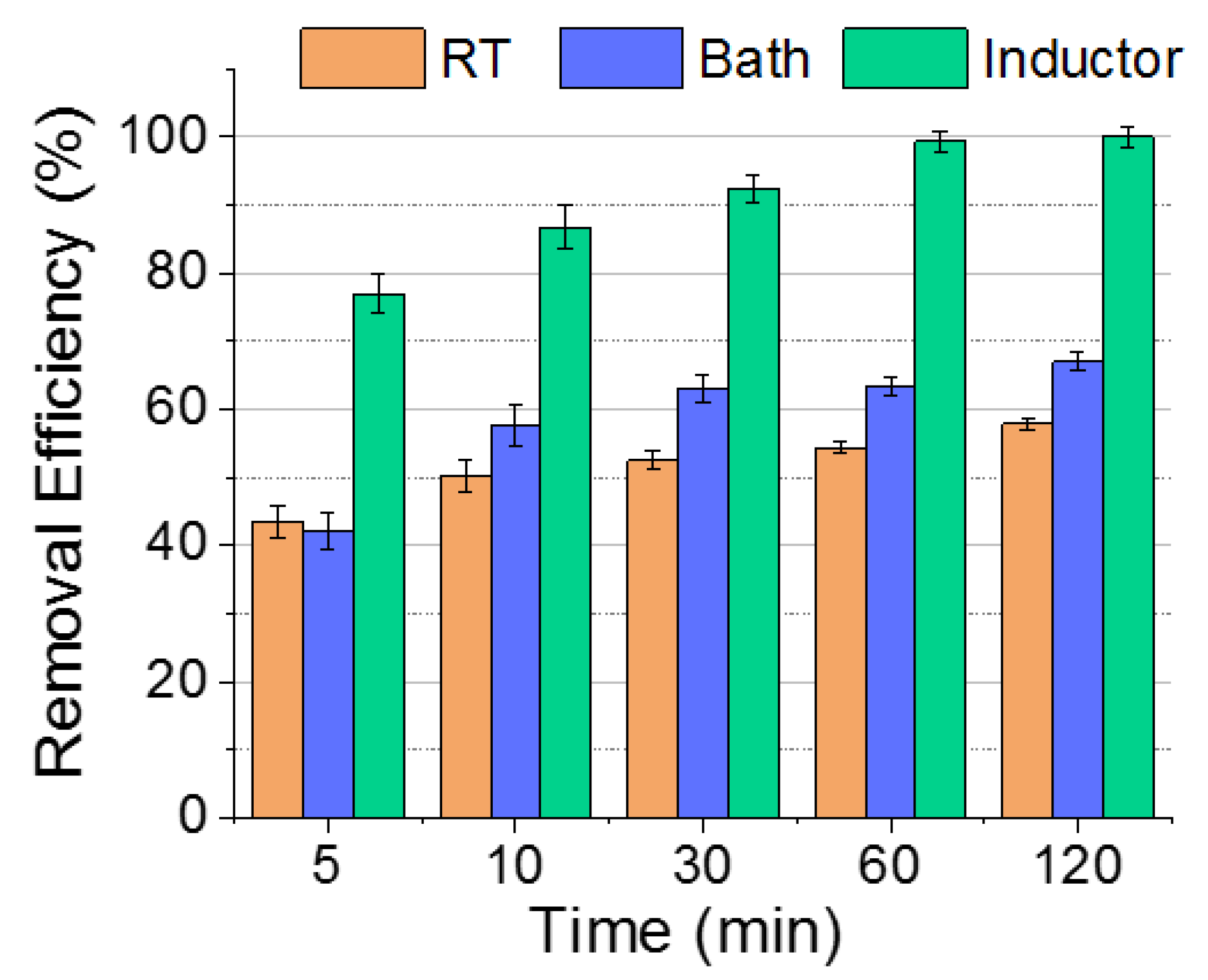
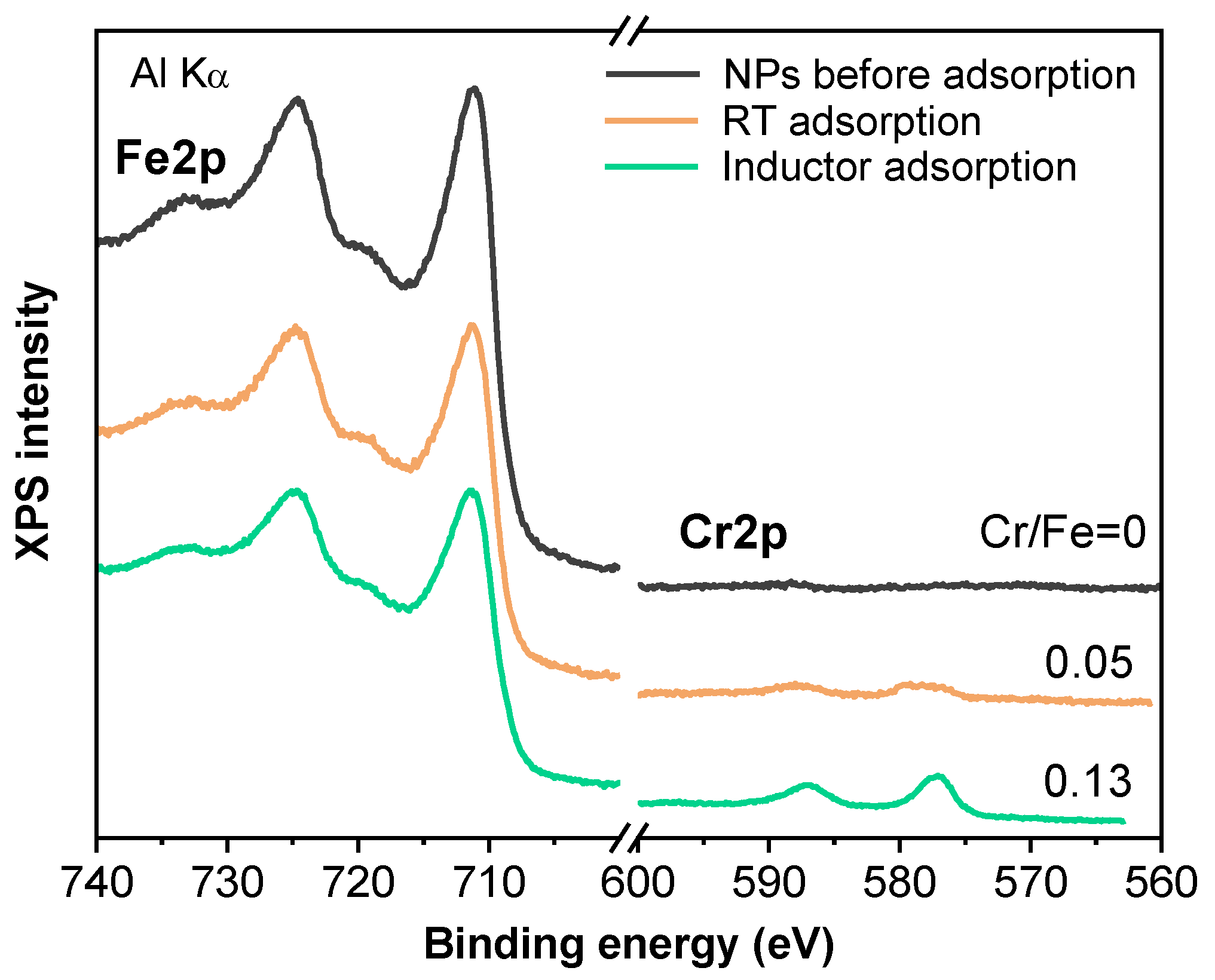
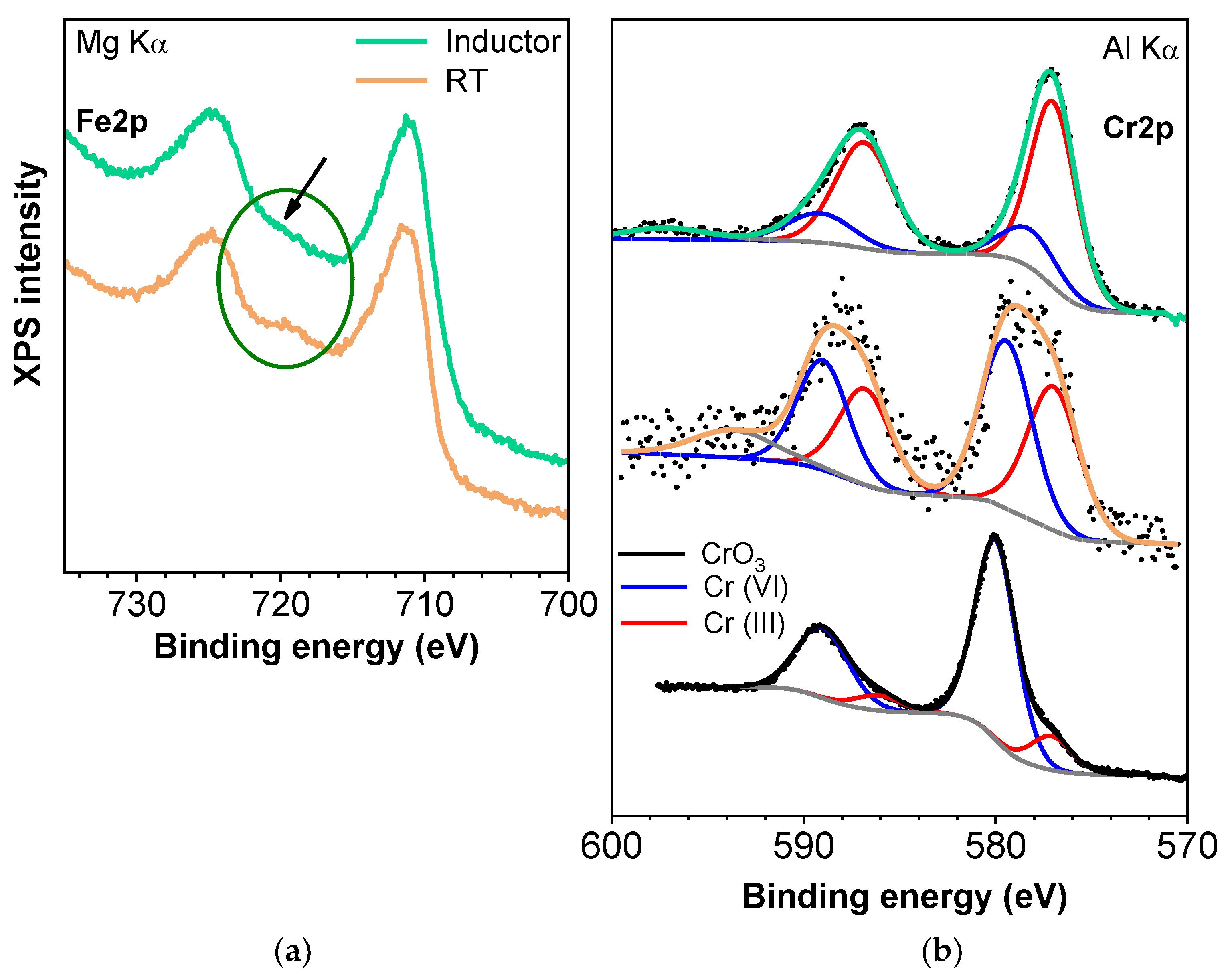

| Constant | Units | NPs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RT | Bath | Inductor | ||
| qe | mg/g | 6.6(1) | 7.8(1) | 11.9(4) |
| k1 | min−1 | 0.30(4) | 0.21(1) | 0.28(5) |
| R2 | 0.991 | 0.997 | 0.982 | |
| qe | mg/g | 6.9(1) | 8.2(2) | 12.4(3) |
| k2 | g/mg | 0.10(2) | 0.046(9) | 0.045(9) |
| R2 | 0.996 | 0.991 | 0.993 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rivera, F.L.; Palomares, F.J.; Herrasti, P.; Mazario, E. Improvement in Heavy Metal Removal from Wastewater Using an External Magnetic Inductor. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9111508
Rivera FL, Palomares FJ, Herrasti P, Mazario E. Improvement in Heavy Metal Removal from Wastewater Using an External Magnetic Inductor. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(11):1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9111508
Chicago/Turabian StyleRivera, Fernanda Lyzeth, Francisco Javier Palomares, Pilar Herrasti, and Eva Mazario. 2019. "Improvement in Heavy Metal Removal from Wastewater Using an External Magnetic Inductor" Nanomaterials 9, no. 11: 1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9111508
APA StyleRivera, F. L., Palomares, F. J., Herrasti, P., & Mazario, E. (2019). Improvement in Heavy Metal Removal from Wastewater Using an External Magnetic Inductor. Nanomaterials, 9(11), 1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9111508