Atmospheric-Pressure Cold Plasma Activating Au/P25 for CO Oxidation: Effect of Working Gas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Catalysts Preparation
2.2. Catalysts Characterization
2.3. Catalytic Activity Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haruta, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Sano, H.; Yamada, N. Novel gold catalysts for the oxidation of carbon monoxide at a temperature far below 0 °C. Chem. Lett. 1987, 16, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruta, M.; Yamada, N.; Kobayashi, T.; Iijima, S. Gold catalysts prepared by coprecipitation for low-temperature oxidation of hydrogen and of carbon monoxide. J. Catal. 1989, 115, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, C.H.; Nørskov, J.K. Green gold catalysis. Science 2010, 327, 278–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saavedra, J.; Doan, H.A.; Pursell, C.J.; Grabow, L.C.; Chandler, B.D. The critical role of water at the gold-titania interface in catalytic CO oxidation. Science 2014, 345, 1599–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Widmann, D.; Behm, R.J. Influence of TiO2 bulk defects on CO adsorption and CO oxidation on Au/TiO2: Electronic metal-support interactions (EMSIs) in supported Au catalysts. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 2339–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, H.H.; Kung, M.C.; Costello, C.K. Supported Au catalysts for low temperature CO oxidation. J. Catal. 2003, 216, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valden, M.; Lai, X.; Goodman, D.W. Onset of catalytic activity of gold clusters on Titania with the appearance of nonmetallic properties. Science 1998, 281, 1647–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widmann, D.; Liu, Y.; Schüth, F.; Behm, R.J. Support effects in the Au-catalyzed CO oxidation-correlation between activity, oxygen storage capacity, and support reducibility. J. Catal. 2010, 276, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delannoy, L.; El, H.N.; Musi, A.; To, N.N.L.; Krafft, J.M.; Louis, C. Preparation of supported gold nanoparticles by a modified incipient wetness impregnation method. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 22471–22478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akita, T.; Lu, P.; Ichikawa, S.; Tanaka, K.; Haruta, M. Analytical TEM study on the dispersion of Au nanoparticles in Au/P25 catalyst prepared under various temperatures. Surf. Interface Anal. 2001, 31, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overbury, S.H.; Schwartz, V.; Mullins, D.R.; Yan, W.; Dai, S. Evaluation of the Au size effect: CO oxidation catalyzed by Au/P25. J. Catal. 2006, 241, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, L.B.; Zhang, J.S.; Zhang, X.L. A review on the recent progress, challenges and perspectives of atmospheric-pressure cold plasma for preparation of supported metal catalysts. Plasma Process. Polym. 2018, 15, 1700234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D.S.; Chang, Z.; Bu, X.H. Perspectives on electron-assisted reduction for preparation of highly dispersed noble metal catalysts. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Neyts, E.C.; Cao, X.; Zhang, X.; Jang, B.W.L.; Liu, C.J. Catalyst Preparation with Plasmas: How Does It Work? ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 2093–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.J.; Qi, B.; Di, L.B.; Zhang, X.L. Partially crystallized Pd nanoparticles decorated TiO2 prepared by atmospheric-pressure cold plasma and its enhanced photocatalytic performance. J. Energy Chem. 2014, 23, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.J.; Zhang, Y.P.; Liu, C.J. Reduction of supported noble-metal ions using glow discharge plasma. Langmuir 2006, 22, 11388–11394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhong, C.J.; Liu, C.J. Highly active and stable Pt-Pd alloy catalysts synthesized by room-temperature electron reduction for oxygen reduction reaction. Adv. Sci. 2017, 4, 1600486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, L.B.; Duan, D.Z.; Park, D.W.; Ahn, W.S.; Lee, B.J.; Zhang, X.L. Cold plasma for synthesizing high performance bimetallic PdCu catalysts: Effect of reduction sequence and Pd/Cu atomic ratios. Top. Catal. 2017, 60, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furusho, H.; Kitano, K.; Hamaguchi, S.; Nagasaki, Y. Preparation of stable water-dispersible PEGylated gold nanoparticles assisted by nonequilibrium atmospheric-pressure plasma jets. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 3526–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Rimmer, R.D.; Gunamgari, J.; Shekhawat, R.S.; Davis, B.J.; Mazumder, M.K.; Lindquist, D.A. Plasma-assisted activation of supported Au and Pd catalysts for CO oxidation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2005, 41, 1373–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Mou, C.Y.; Lee, S.; Li, Y.; Secrest, J.; Jang, B.W.-L. Room temperature O2 plasma treatment of SiO2 supported Au catalysts for selective hydrogenation of acetylene in the presence of large excess of ethylene. J. Catal. 2012, 285, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Liu, C. Synthesis of monodisperse gold nanoparticles in ionic liquid by applying room temperature plasma. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 353–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, X.S.; Zhu, B.; Liu, J.L.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, A.M.; Jang, B.W.-L. Atmospheric-pressure O2 plasma treatment of Au/P25 catalysts for CO oxidation. Catal. Today 2015, 256, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.Y.; Shi, C.; Li, X.S.; Zhang, S.; Liu, J.L.; Zhu, A.M. In-situ plasma regeneration of deactivated Au/P25 nanocatalysts during CO oxidation and effect of N2 content. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 119, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Li, X.S.; Liu, J.L.; Liu, J.B.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, A.M. In-situ regeneration of Au nanocatalysts by atmospheric-pressure air plasma: Significant contribution of water vapor. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 179, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.Q.; Zhu, B.; Li, X.S.; Liu, J.L.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, A.M. Visible-light photocatalytic oxidation of CO over plasmonic Au/P25: Unusual features of oxygen plasma activation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 188, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, L.B.; Zhan, Z.B.; Zhang, X.L.; Qi, B.; Xu, W.J. Atmospheric-Pressure DBD Cold Plasma for Preparation of High Active Au/P25 Catalysts for Low-Temperature CO Oxidation. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2016, 18, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, L.B.; Duan, D.Z.; Zhang, X.L.; Qi, B.; Zhan, Z.B. Effect of TiO2 Crystal Phase and Preparation Method on the Catalytic Performance of Au/TiO2 for CO Oxidation. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2016, 44, 2692–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Xu, W.W.; Duan, D.Z.; Park, D.-W.; Di, L.B. Atmospheric-pressure oxygen cold plasma for synthesizing Au/TiO2 catalysts: Effect of discharge voltage and discharge time. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2018, 46, 2776–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Banfield, J.F. Understanding polymorphic phase transformation behavior during growth of nanocrystalline aggregates: Insights from TiO2. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 3481–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, L.B.; Xu, Z.J.; Zhang, X.L. Atmospheric-pressure cold plasma for synthesizing Ag modified Degussa P25 with visible light activity using dielectric barrier discharge. Catal. Today 2013, 211, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanella, R.; Giorgio, S.; Shin, C.H.; Henry, C.R.; Louisa, C. Characterization and reactivity in CO oxidation of gold nanoparticles supported on TiO2 prepared by deposition-precipitation with NaOH and urea. J. Catal. 2004, 222, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orendorff, C.J.; Sau, T.K.; Murphy, C.J. Shape-dependent plasmon-resonant gold nanoparticles. Small 2006, 2, 636–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haruta, M. Size-and support-dependency in the catalysis of gold. Catal. Today 1997, 36, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delannoy, L.; Weiher, N.; Tsapatsaris, N.; Beesley, A.M.; Nchari, L.; Schroeder, S.L.M.; Louis, C. Reducibility of supported gold (III) precursors: Influence of the metal oxide support and consequences for CO oxidation activity. Top. Catal. 2007, 44, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, L.B.; Zhang, X.L.; Xu, Z.J.; Wang, K. Atmospheric-pressure cold plasma for preparation of high performance Pt/TiO2 photocatalyst and its mechanism. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2014, 34, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniells, S.T.; Overweg, A.R.; Makkee, M.; Moulijn, J.A. The mechanism of low-temperature CO oxidation with Au/Fe2O3 catalysts: A combined Mössbauer, FT-IR, and TAP reactor study. J. Catal. 2005, 230, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Gu, X.; Cao, Y.; Yao, X.; Zhang, L.; Tang, C.; Gao, F.; Dong, L. Crystal-plane effects on the catalytic properties of Au/TiO2. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 2768–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.Y.; Zhu, Y.; Tian, L.; Pei, Y.; Qiao, M.H.; Fan, K.N. Influence of Au/TiO2 Catalyst Preparation Parameters on the Selective Hydrogenation of Crotonaldehyde. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 2009, 25, 1853–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, L.B.; Shi, C.; Li, X.S.; Liu, J.L.; Zhu, A.M. Uniformity, structure, and photocatalytic activity of TiO2 films deposited by atmospheric-pressure linear cold plasma. Chem. Vap. Depos. 2012, 18, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

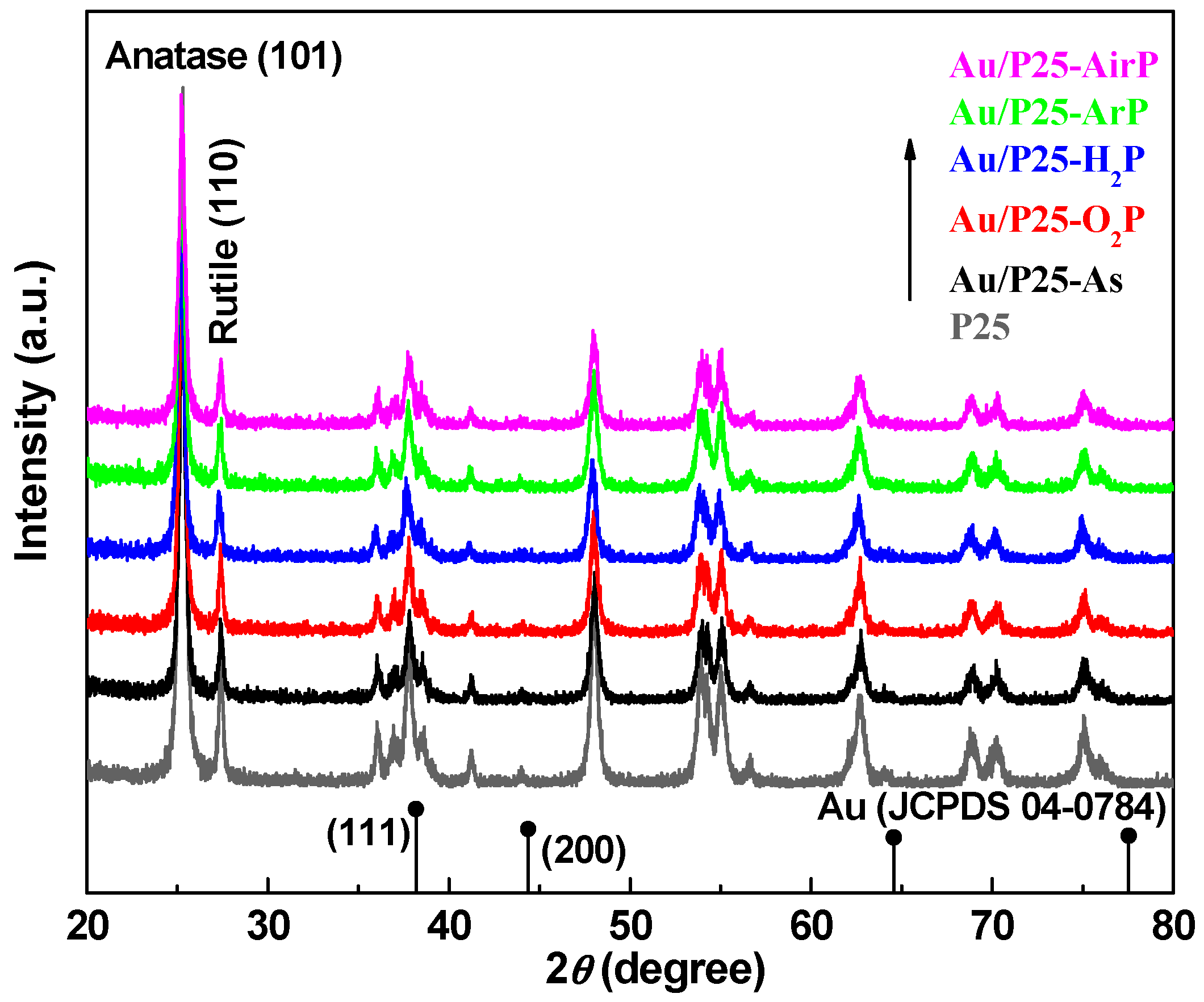
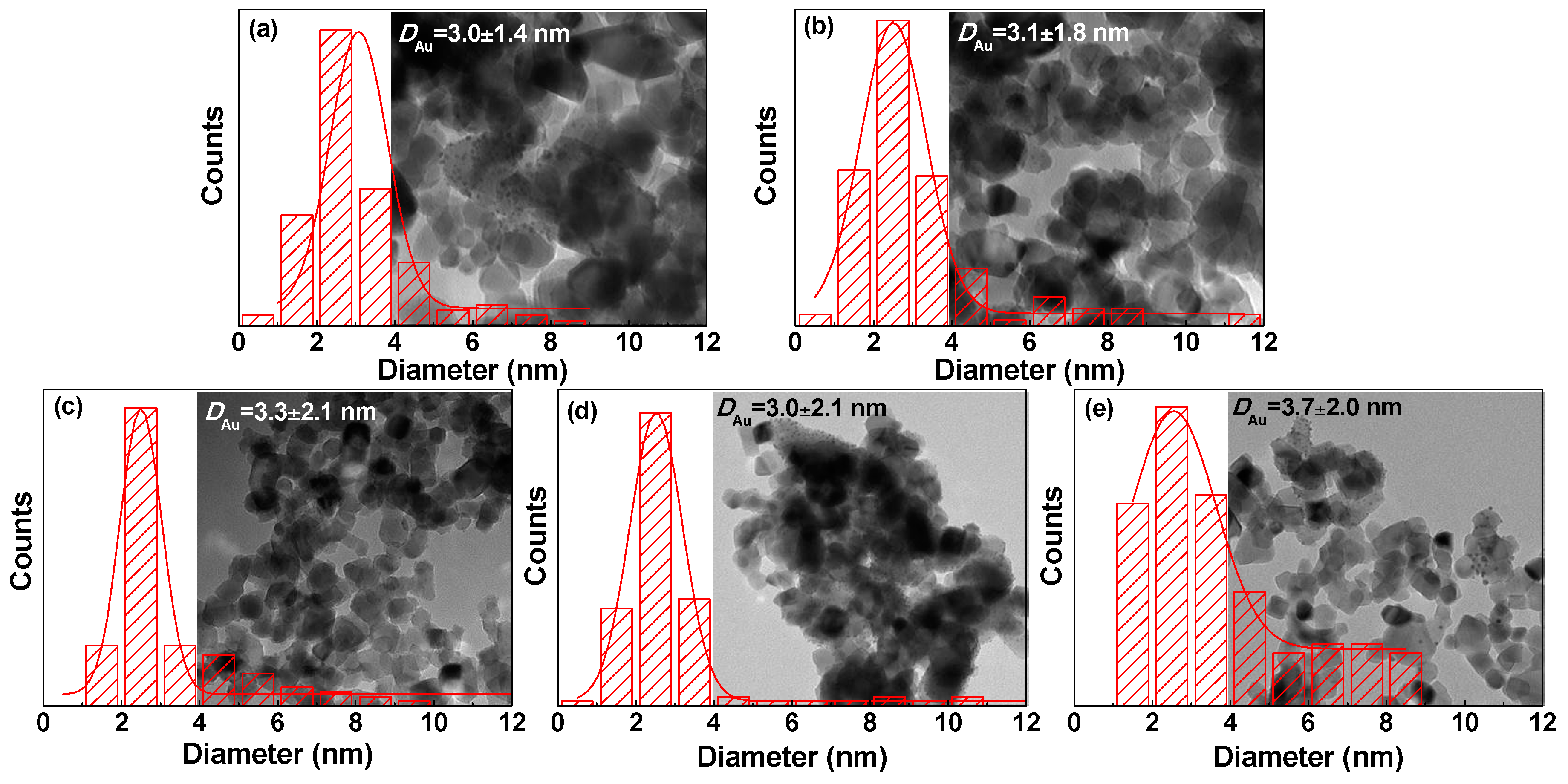
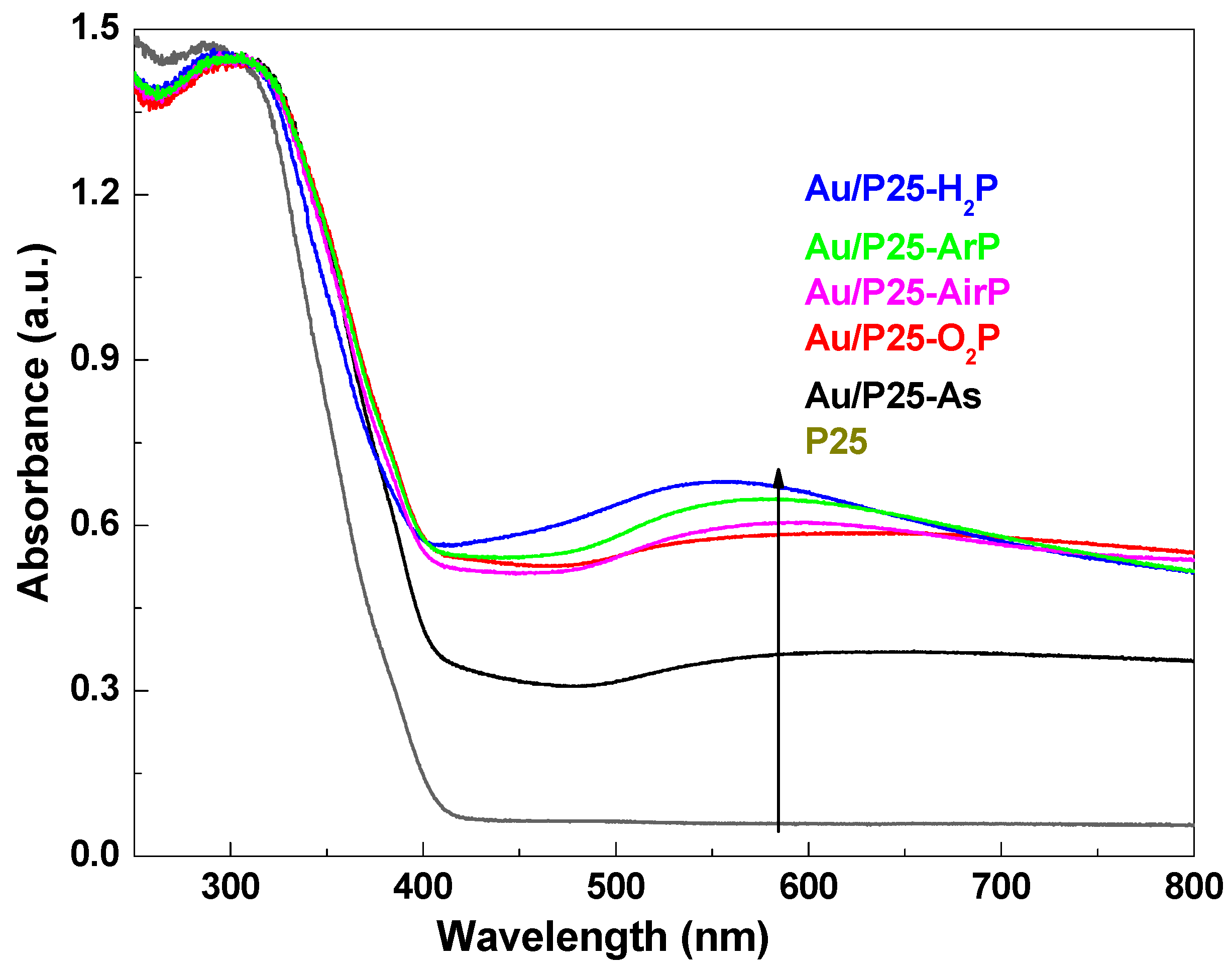

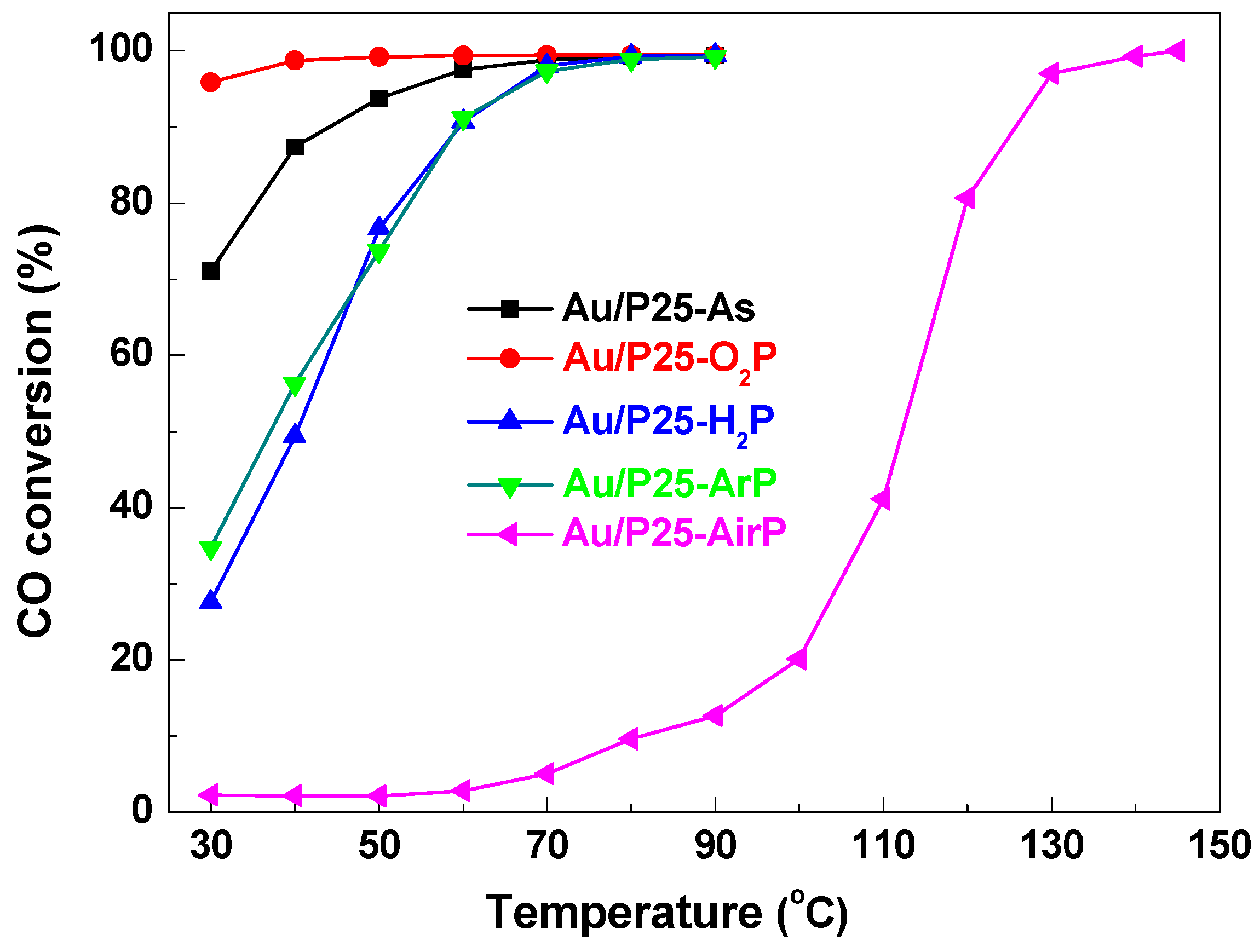
| Samples | 2θ (degree) | Wrutile (%) | Danatase (nm) | Drutile (nm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anatase (101) | Rutile (110) | ||||
| P25 | 25.3 | 27.5 | 17.9 | 21.1 | 31.0 |
| Au/P25-As | 25.2 | 27.4 | 17.3 | 22.3 | 28.4 |
| Au/P25-O2P | 25.3 | 27.4 | 19.1 | 21.0 | 27.9 |
| Au/P25-H2P | 25.2 | 27.4 | 20.1 | 20.1 | 29.1 |
| Au/P25-ArP | 25.3 | 27.4 | 17.2 | 21.5 | 28.0 |
| Au/P25-AirP | 25.2 | 27.4 | 17.4 | 21.6 | 31.0 |
| Samples | DAua | Binding Energy (eV) | Proportion (at%) | Au/Ti Atomic Ratios | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (nm) | Au04f7/2 | Au+4f7/2 | Au0/(Au0+Au+) | [O]s/([O]s+[O]l) | ||
| Au/P25-As | 3.0 ± 1.4 | 83.3 | 84.4 | 56.9 | 27.4 | 0.023 |
| Au/P25-O2P | 3.1 ± 1.8 | 83.3 | 84.4 | 71.4 | 18.9 | 0.019 |
| Au/P25-H2P | 3.3 ± 2.1 | 82.9 | 84.1 | 86.2 | 15.4 | 0.018 |
| Au/P25-ArP | 3.0 ± 2.1 | 83.3 | 84.4 | 81.9 | 17.3 | 0.020 |
| Au/P25-AirP | 3.7 ± 2.0 | 83.3 | 84.5 | 78.3 | 16.5 | 0.018 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Di, L.; Yu, F.; Duan, D.; Zhang, X. Atmospheric-Pressure Cold Plasma Activating Au/P25 for CO Oxidation: Effect of Working Gas. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8090742
Zhang J, Di L, Yu F, Duan D, Zhang X. Atmospheric-Pressure Cold Plasma Activating Au/P25 for CO Oxidation: Effect of Working Gas. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(9):742. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8090742
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jingsen, Lanbo Di, Feng Yu, Dongzhi Duan, and Xiuling Zhang. 2018. "Atmospheric-Pressure Cold Plasma Activating Au/P25 for CO Oxidation: Effect of Working Gas" Nanomaterials 8, no. 9: 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8090742
APA StyleZhang, J., Di, L., Yu, F., Duan, D., & Zhang, X. (2018). Atmospheric-Pressure Cold Plasma Activating Au/P25 for CO Oxidation: Effect of Working Gas. Nanomaterials, 8(9), 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8090742






