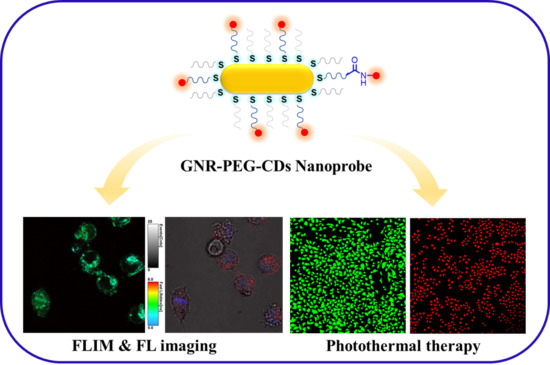
Gold Rod-Polyethylene Glycol-Carbon Dot Nanohybrids as Phototheranostic Probes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Gold Nanorods
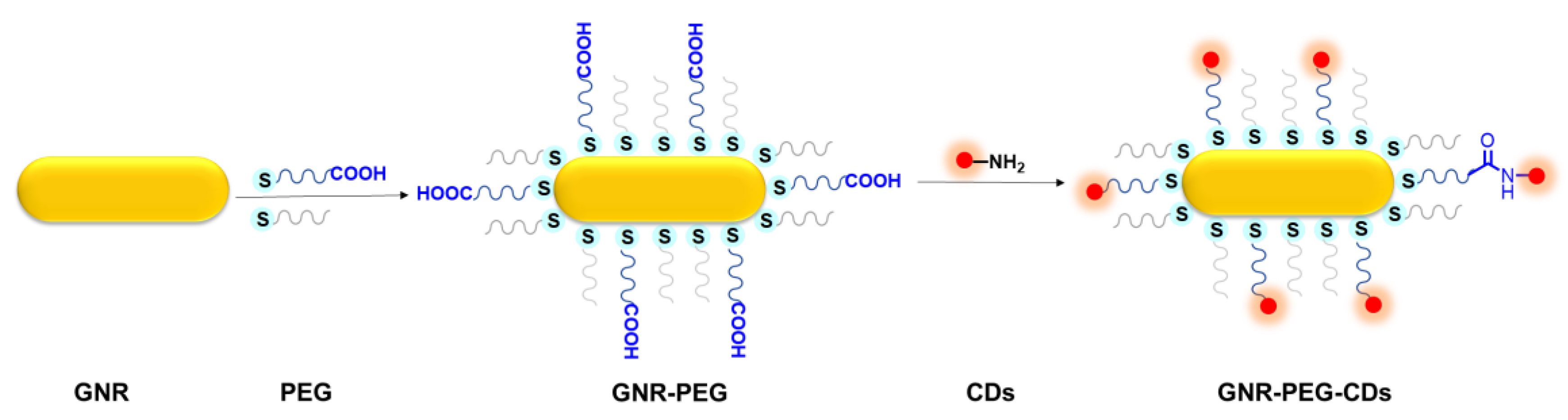
2.3. Preparation of GNR–PEG
2.4. Preparation of GNR–PEG–CDs Nanohybrids
2.5. Measurement of Photothermal Performance
2.6. Cytotoxicity
2.7. Confocal Fluorescence Imaging Measurements
2.8. FLIM Measurements
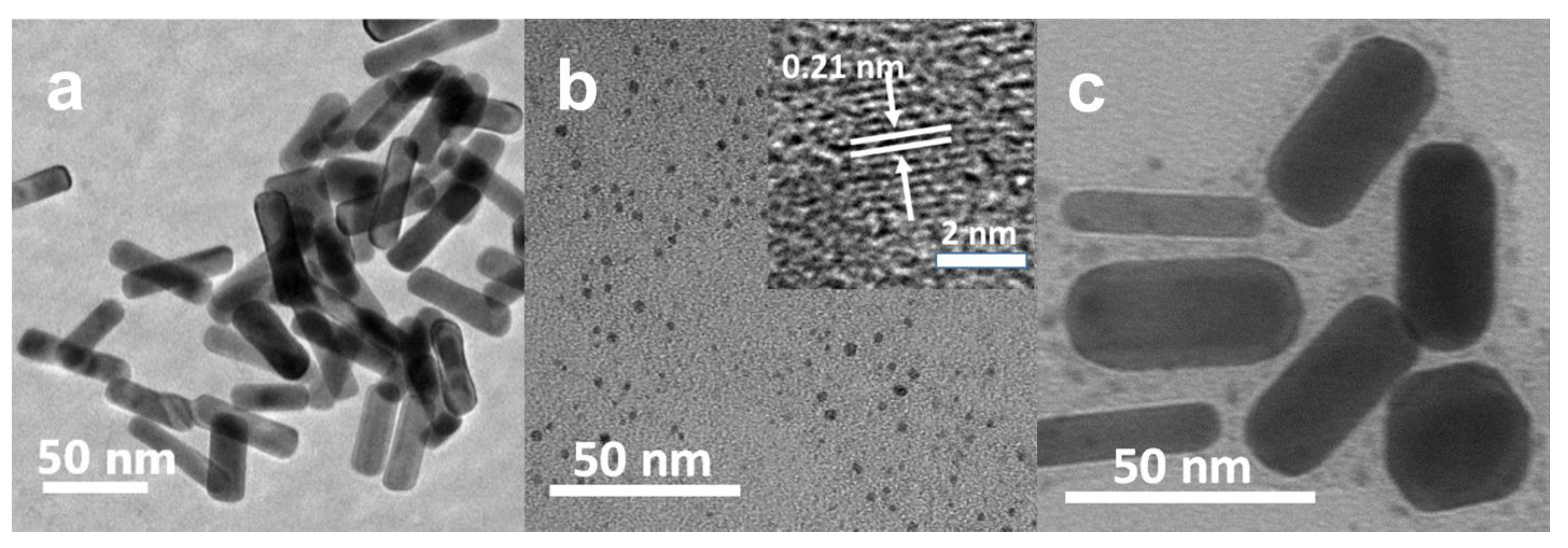
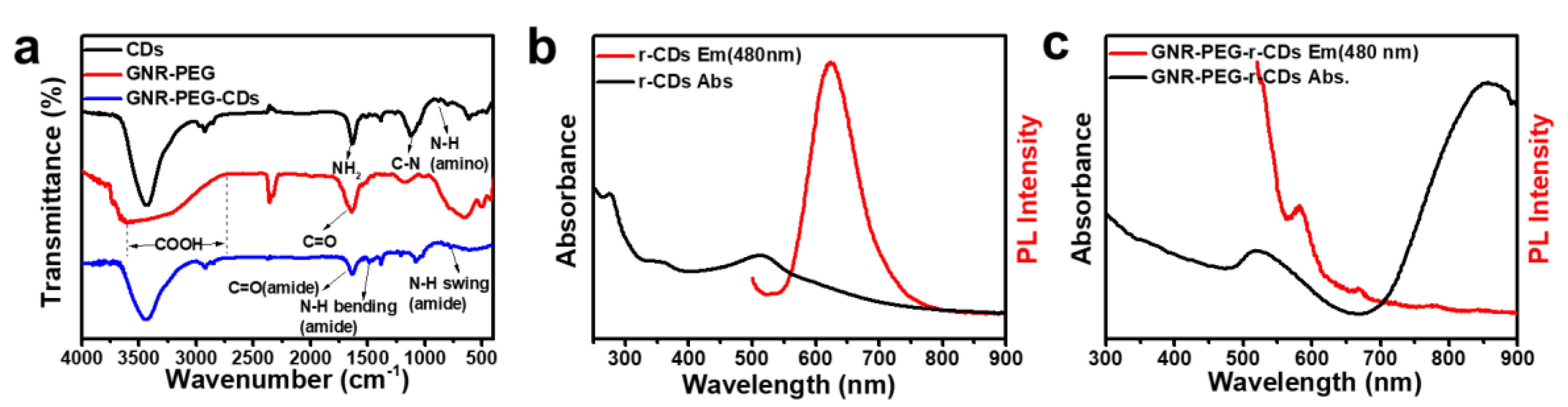
2.9. Sample Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of GNR–PEG-CDs
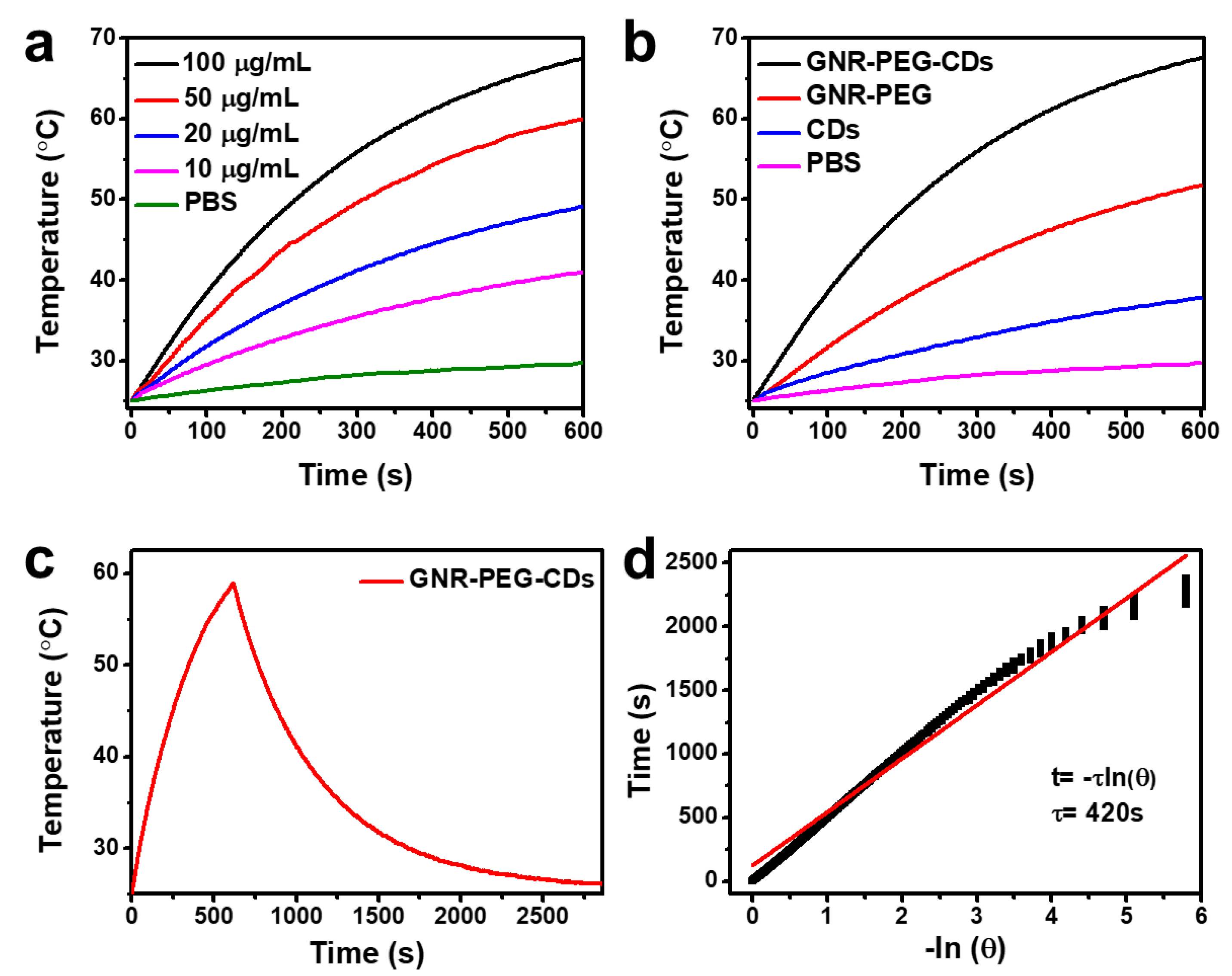
3.2. Temperature Evaluation in Solutions
3.3. In Vitro Dual-Modal Imaging and PTT
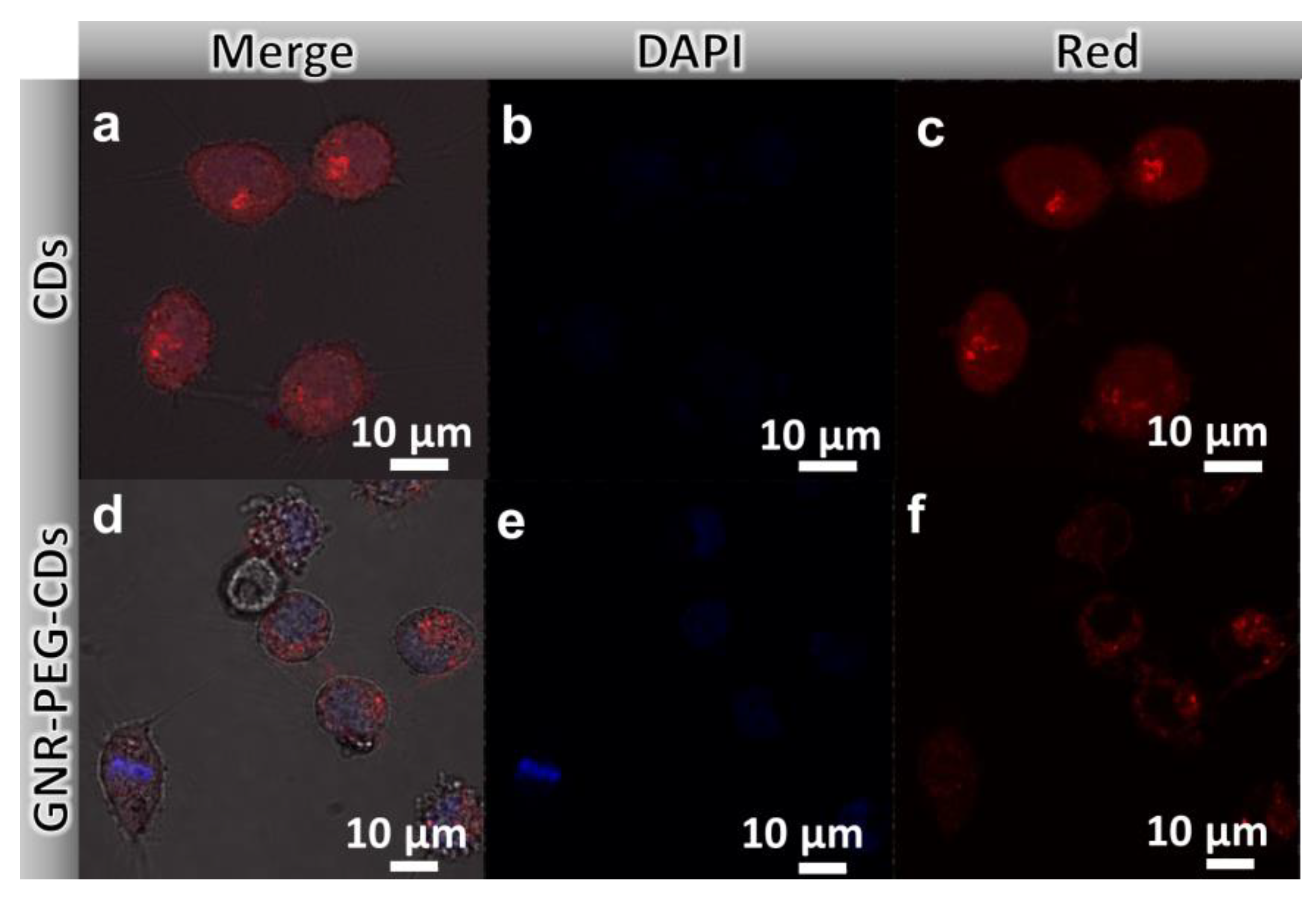
3.3.1. Confocal Laser Scanning Imaging
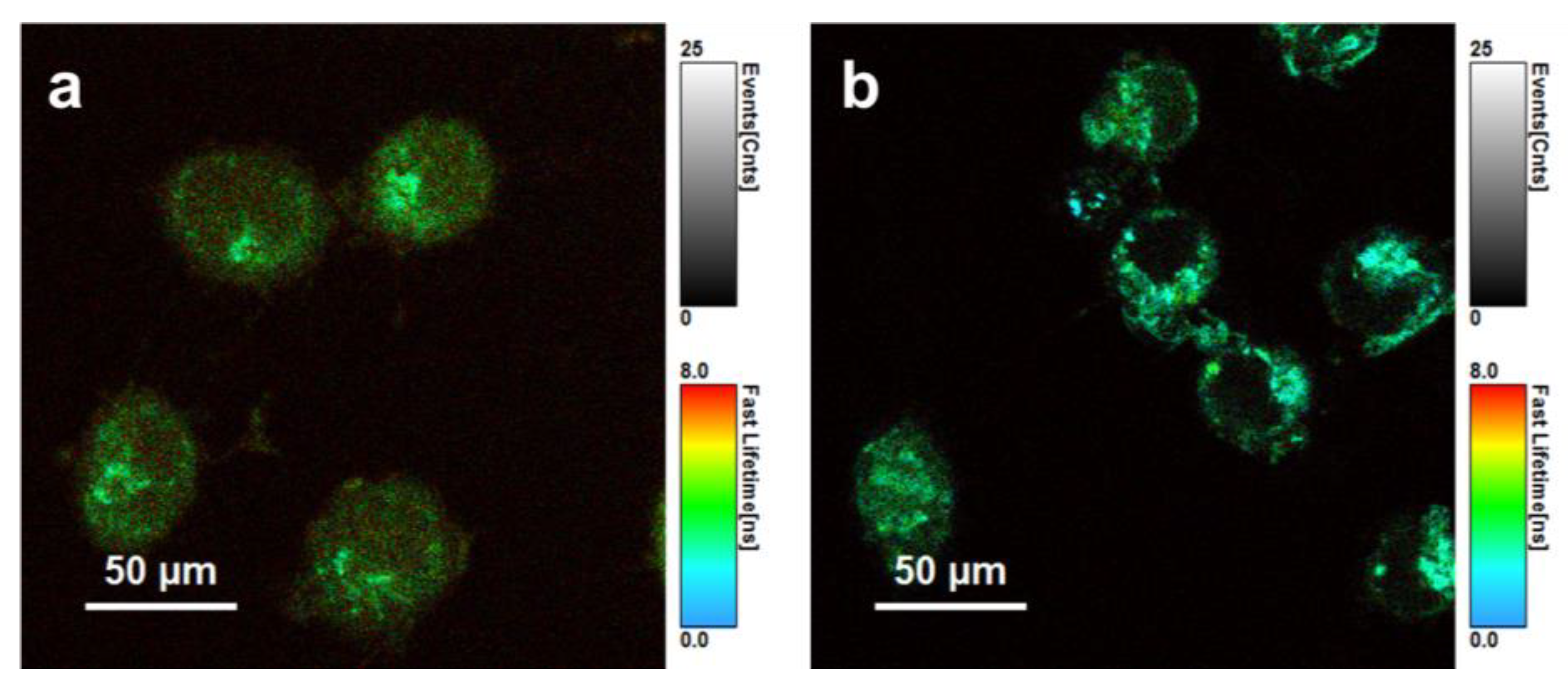
3.3.2. Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging
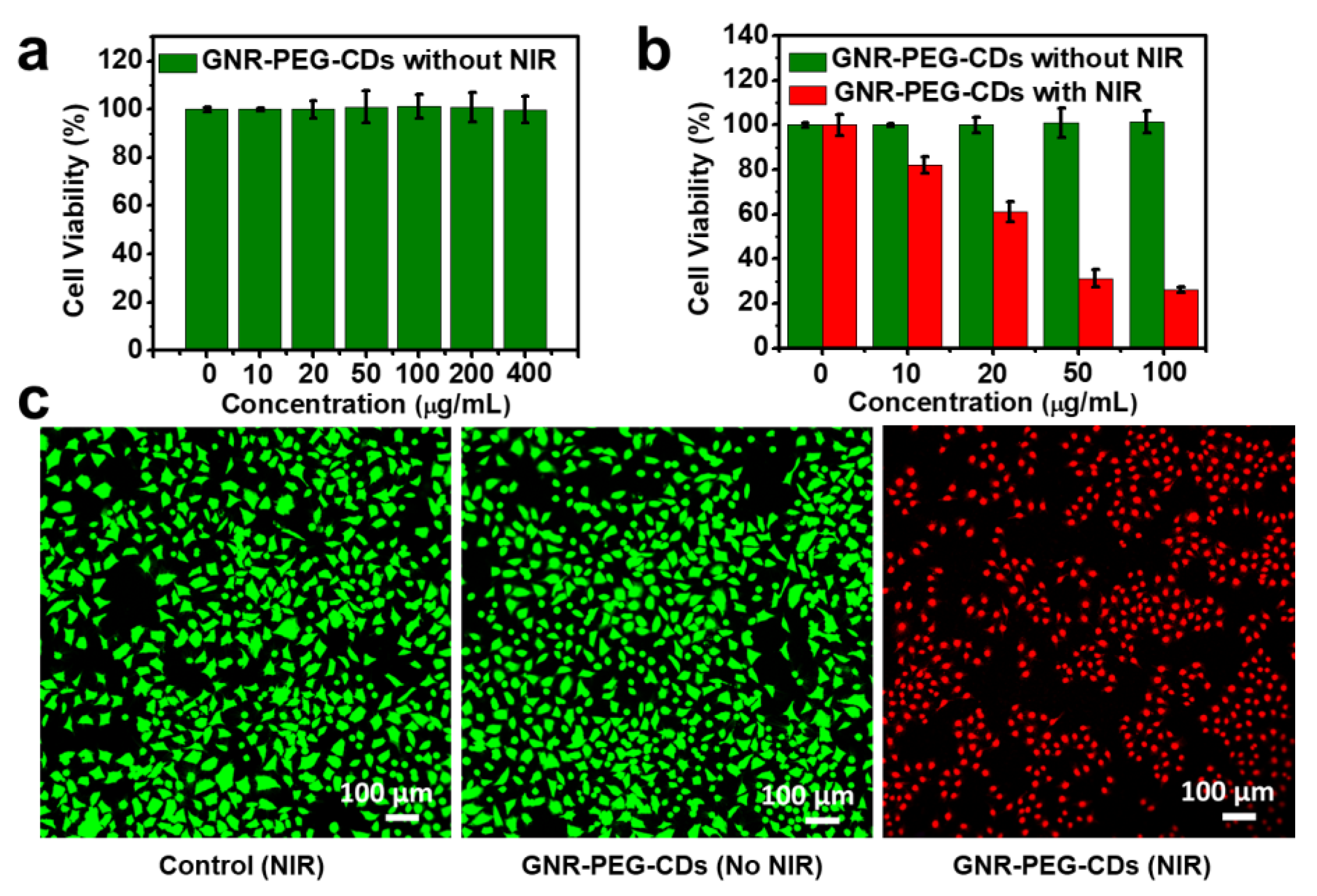
3.3.3. In Vitro Biocompatibility and PTT
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Jemal, A.; Grey, N.; Ferlay, J.; Forman, D. Global cancer transitions according to the human development index (2008–2030): A population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 790–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Huang, J.; Song, S.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Z. Cancer-targeted nanotheranostics: Recent advances and perspectives. Small 2016, 12, 4936–4954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, T.; Ai, X.; An, G.; Yang, P.; Zhao, Y. Charge-convertible carbon dots for imaging-guided drug delivery with enhanced in vivo cancer therapeutic efficiency. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 4410–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Wang, C.; Feng, L.; Yang, K.; Liu, Z. Functional nanomaterials for phototherapies of cancer. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10869–10939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, W.; Zhao, X.; Qian, X.; Pan, F.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Cui, D. Ph-sensitive self-assembling nanoparticles for tumor near-infrared fluorescence imaging and chemo-photodynamic combination therapy. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, H.; Peng, R.; Liu, Z. Carbon nanotubes for biomedical imaging: The recent advances. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1951–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Xu, L.; Ma, W.; Wu, X.; Kuang, H.; Wang, L.; Xu, C. Hierarchical plasmonic nanorods and upconversion core–satellite nanoassemblies for multimodal imaging-guided combination phototherapy. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, N.; Xu, F. NIR-responsive polycationic gatekeeper-cloaked hetero-nanoparticles for multimodal imaging-guided triple-combination therapy of cancer. Small 2017, 13, 1603133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Hao, C.; Sun, M.; Xu, L.; Xu, C.; Kuang, H. Spiky Fe3O4@Au supraparticles for multimodal in vivo imaging. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1800310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, L.; Shen, B.; Cheng, Z. Fluorescent imaging of cancerous tissues for targeted surgery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 76, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, L.V.; Nazeer, S.S.; Jayasree, R.S.; Ajayaghosh, A. Fluorescence imaging assisted photodynamic therapy using photosensitizer-linked gold quantum clusters. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 5825–5832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, W. Fluorescence lifetime imaging—Techniques and applications. J. Microsc. 2012, 247, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Munster, E.; Gadella, T. Fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (flim). In Microscopy Techniques; Rietdorf, J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; Volume 95, pp. 143–175. ISBN 978-3-540-31545-2. [Google Scholar]
- Fixler, D.; Nayhoz, T.; Ray, K. Diffusion reflection and fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy study of fluorophore-conjugated gold nanoparticles or nanorods in solid phantoms. ACS Photonics 2014, 1, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakalova, R.; Ohba, H.; Zhelev, Z.; Ishikawa, M.; Baba, Y. Quantum dots as photosensitizers? Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemeyer, C.M. Nanoparticles, proteins, and nucleic acids: Biotechnology meets materials science. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 4128–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagalkot, V.; Zhang, L.; Levy-Nissenbaum, E.; Jon, S.; Kantoff, P.W.; Langer, R.; Farokhzad, O.C. Quantum dot−aptamer conjugates for synchronous cancer imaging, therapy, and sensing of drug delivery based on bi-fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 3065–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alivisatos, P. The use of nanocrystals in biological detection. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 22, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Cheng, K.; Hou, Y.M.; Fang, Z.; Pan, Z.X.; Wu, W.J.; Hua, J.L.; Zhong, X.H. Efficient CdSe quantum dot-sensitized solar cells prepared by a postsynthesis assembly approach. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 11235–11237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; An, F.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, M.; Li, W.; Hao, X.; Lee, C.S.; Zhang, X. Ultrabright and ultrastable near-infrared dye nanoparticles for in vitro and in vivo bioimaging. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 7803–7809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.Y.; Shen, W.; Gao, Z. Carbon quantum dots and their applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 362–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, S.N.; Baker, G.A. Luminescent carbon nanodots: Emergent nanolights. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6726–6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y. Highly luminescent organosilane-functionalized carbon dots. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Wang, F.; Liu, C. Organic–inorganic hybrid functional carbon dot gel glasses. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1716–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Han, Z.; Yin, Z.; Zhou, C.; Du, F.; Zhou, S.; Chen, P.; Xie, Z. High color rendering index trichromatic white and red leds prepared from silane-functionalized carbon dots. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 9629–9637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Sun, J.; Sun, X.; Song, R.; Xie, Z.; Zhou, S. Precisely controlled up/down-conversion liquid and solid state photoluminescence of carbon dots. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2018, 6, 1800115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chi, C.; Yuan, P.; Su, Y.; Shao, M.; Zhou, N. A hydrothermal route to multicolor luminescent carbon dots from adenosine disodium triphosphate for bioimaging. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 76, 1146–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Pang, H.; Yang, H.B.; Guo, C.; Shao, J.; Chi, Y.; Li, C.M.; Yu, T. Carbon-based dots co-doped with nitrogen and sulfur for high quantum yield and excitation-independent emission. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 7800–7804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Cheng, L.; Cao, Z.; Liu, W. Water-soluble and phosphorus-containing carbon dots with strong green fluorescence for cell labeling. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Jia, Q.; Liu, W.; Guo, L.; Liu, Q.; Lan, M.; Zhang, H.; Meng, X.; Wang, P. Red-emissive carbon dots for fluorescent, photoacoustic, and thermal theranostics in living mice. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4169–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, Y.; Guan, S.; Lu, H.; Meng, X.; Kaassis, A.Y.; Ren, X.; Qu, X.; Sun, C.; Xie, Z.; Zhou, S. Confinement of carbon dots localizing to the ultrathin layered double hydroxides toward simultaneous triple-mode bioimaging and photothermal therapy. Talanta 2018, 184, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Q.; Ge, J.; Liu, W.; Liu, S.; Niu, G.; Guo, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, P. Gold nanorod@silica-carbon dots as multifunctional phototheranostics for fluorescence and photoacoustic imaging-guided synergistic photodynamic/photothermal therapy. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 13067–13077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beack, S.; Kong, W.H.; Jung, H.S.; Do, I.H.; Han, S.; Kim, H.; Kim, K.S.; Yun, S.H.; Hahn, S.K. Photodynamic therapy of melanoma skin cancer using carbon dot–chlorin e6–hyaluronate conjugate. Acta Biomater. 2015, 26, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.; Jing, L.; Hou, Y.; Jiao, M.; Qiao, R.; Jia, Q.; Liu, C.; Fang, F.; Lei, H.; Gao, M. Anchoring group effects of surface ligands on magnetic properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticles: Towards high performance MRI contrast agents. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2694–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.I.; Kim, H.M.; Kim, J.H.; Moon, K.C.; Yoo, B.; Lee, K.T.; Lee, N.; Choi, Y.; Park, W.; Ling, D.; et al. Theranostic probe based on lanthanide-doped nanoparticles for simultaneous in vivo dual-modal imaging and photodynamic therapy. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 5755–5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, S.; Weng, Y.; Li, M.; Liang, R.; Sun, C.; Qu, X.; Zhou, S. An NIR-sensitive layered supramolecular nanovehicle for combined dual-modal imaging and synergistic therapy. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 10367–10374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Rong, P.; Lin, J.; Li, W.; Yan, X.; Zhang, M.G.; Nie, L.; Niu, G.; Lu, J.; Wang, W.; et al. Triphase interface synthesis of plasmonic gold bellflowers as near-infrared light mediated acoustic and thermal theranostics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 8307–8313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickerson, E.B.; Dreaden, E.C.; Huang, X.; El-Sayed, I.H.; Chu, H.; Pushpanketh, S.; McDonald, J.F.; El-Sayed, M.A. Gold nanorod assisted near-infrared plasmonic photothermal therapy (PPTT) of squamous cell carcinoma in mice. Cancer Lett. 2008, 269, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.I.; Sahu, A.; Kim, Y.H.; Tae, G. Photothermal cancer therapy and imaging based on gold nanorods. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 40, 534–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Chen, L.; Huang, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Hu, C.; Han, H. Quantum dots decorated gold nanorod as fluorescent-plasmonic dual-modal contrasts agent for cancer imaging. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Liu, L.; Hu, X.; Zhou, S.; Ankri, R.; Fixler, D.; Xie, Z. Multimodal bioimaging based on gold nanorod and carbon dot nanohybrids as a novel tool for atherosclerosis detection. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 1262–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzberger, J.; Niederer, K.; Pohlit, H.; Seiwert, J.; Worm, M.; Wurm, F.R.; Frey, H. Polymerization of ethylene oxide, propylene oxide, and other alkylene oxides: Synthesis, novel polymer architectures, and bioconjugation. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 2170–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikoobakht, B.; El-Sayed, M.A. Preparation and growth mechanism of gold nanorods (NRs) using seed-mediated growth method. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 1957–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Y.; Wu, A.; Cai, C.; Lin, H. Red, green, and blue luminescence by carbon dots: Full-color emission tuning and multicolor cellular imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 5360–5363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Qian, J.; Jiang, L.; He, S. Fluorescence quenching of quantum dots by gold nanorods and its application to DNA detection. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 063111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Xu, Q.-H. Stable and functionable mesoporous silica-coated gold nanorods as sensitive localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) nanosensors. Langmuir 2009, 25, 9441–9446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Xu, C.; Xu, L.; Sun, C.; Yang, D.; Xu, J.; He, F.; Gai, S.; Yang, P. A novel core–shell structured upconversion nanorod as a multimodal bioimaging and photothermal ablation agent for cancer theranostics. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 2597–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, C. Joseph R. Lakowicz: Principles of fluorescence spectroscopy, 3rd edition. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 390, 1223–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niu, Y.; Ling, G.; Wang, L.; Guan, S.; Xie, Z.; Barnoy, E.A.; Zhou, S.; Fixler, D. Gold Rod-Polyethylene Glycol-Carbon Dot Nanohybrids as Phototheranostic Probes. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8090706
Niu Y, Ling G, Wang L, Guan S, Xie Z, Barnoy EA, Zhou S, Fixler D. Gold Rod-Polyethylene Glycol-Carbon Dot Nanohybrids as Phototheranostic Probes. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(9):706. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8090706
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiu, Yuefang, Guo Ling, Li Wang, Shanyue Guan, Zheng Xie, Eran A. Barnoy, Shuyun Zhou, and Dror Fixler. 2018. "Gold Rod-Polyethylene Glycol-Carbon Dot Nanohybrids as Phototheranostic Probes" Nanomaterials 8, no. 9: 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8090706
APA StyleNiu, Y., Ling, G., Wang, L., Guan, S., Xie, Z., Barnoy, E. A., Zhou, S., & Fixler, D. (2018). Gold Rod-Polyethylene Glycol-Carbon Dot Nanohybrids as Phototheranostic Probes. Nanomaterials, 8(9), 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8090706