A Novel Fast Photothermal Therapy Using Hot Spots of Gold Nanorods for Malignant Melanoma Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of PEG-Coated GNRs
2.2. UV-Vis-NIR Absorption Spectroscopy
2.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.4. Cell Culture and Cell Viability
2.5. Cellular Uptake of Gold Nanorods
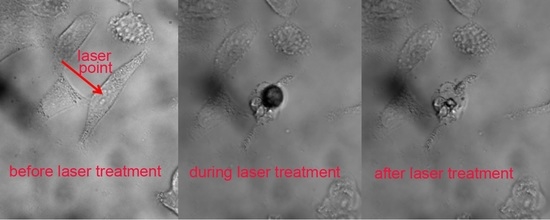
2.6. Photothermal Therapy Experiments
2.7. Numerical Simulations
3. Results and Discussion
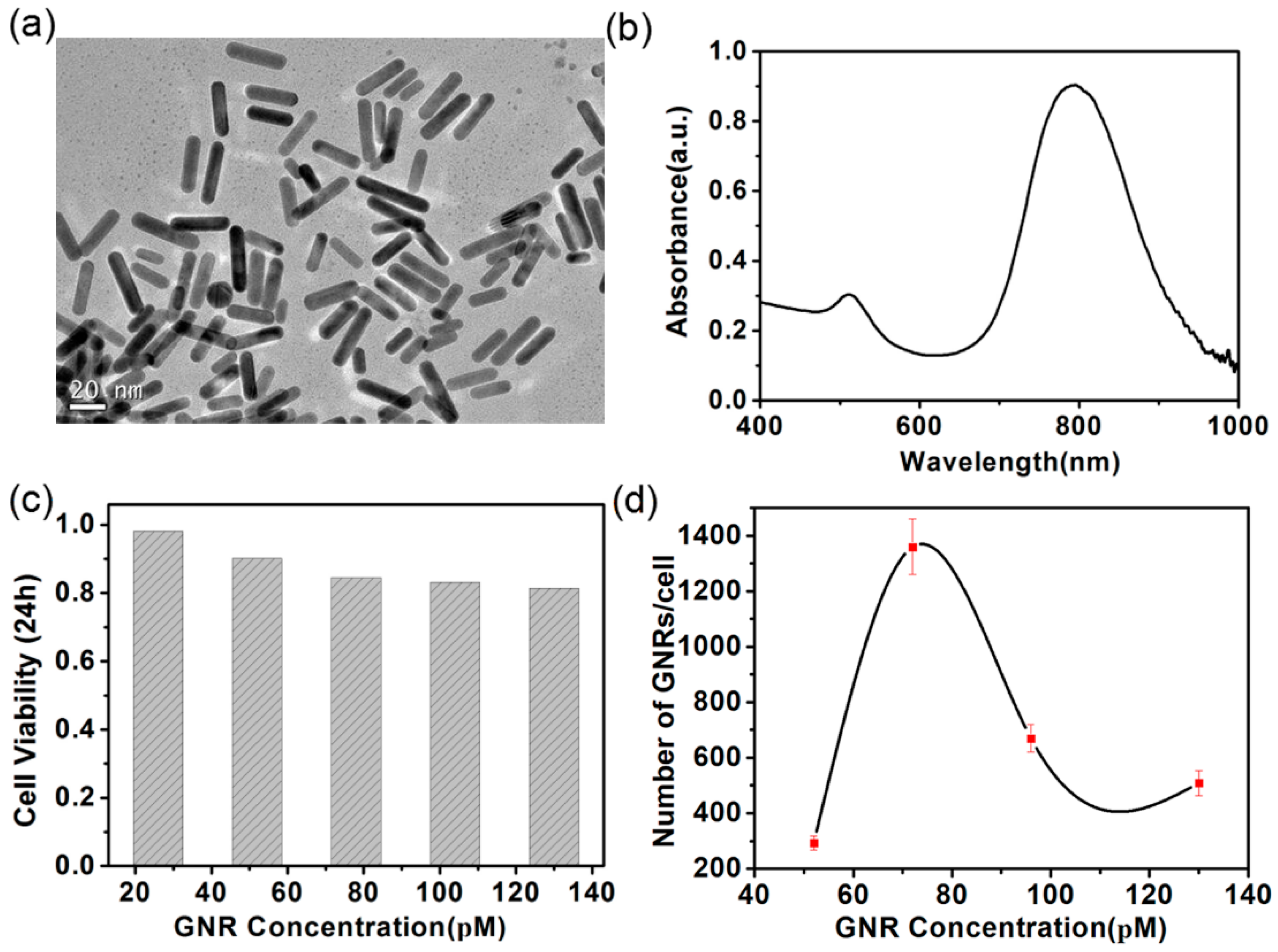
3.1. Characteristic of GNRs
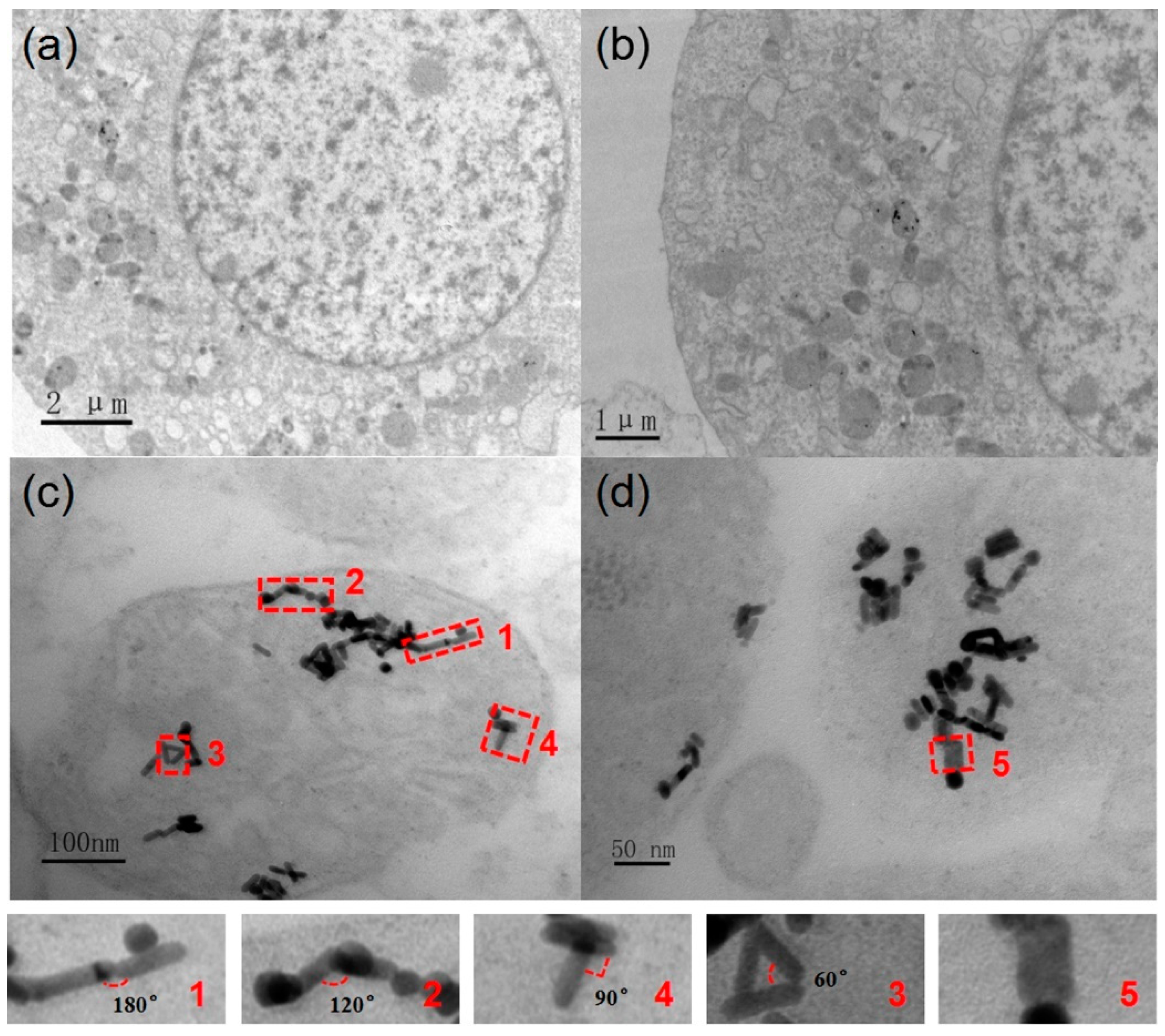
3.2. Interaction between the GNRs and A375 Cells
3.3. The Field Enhancement of GNRs
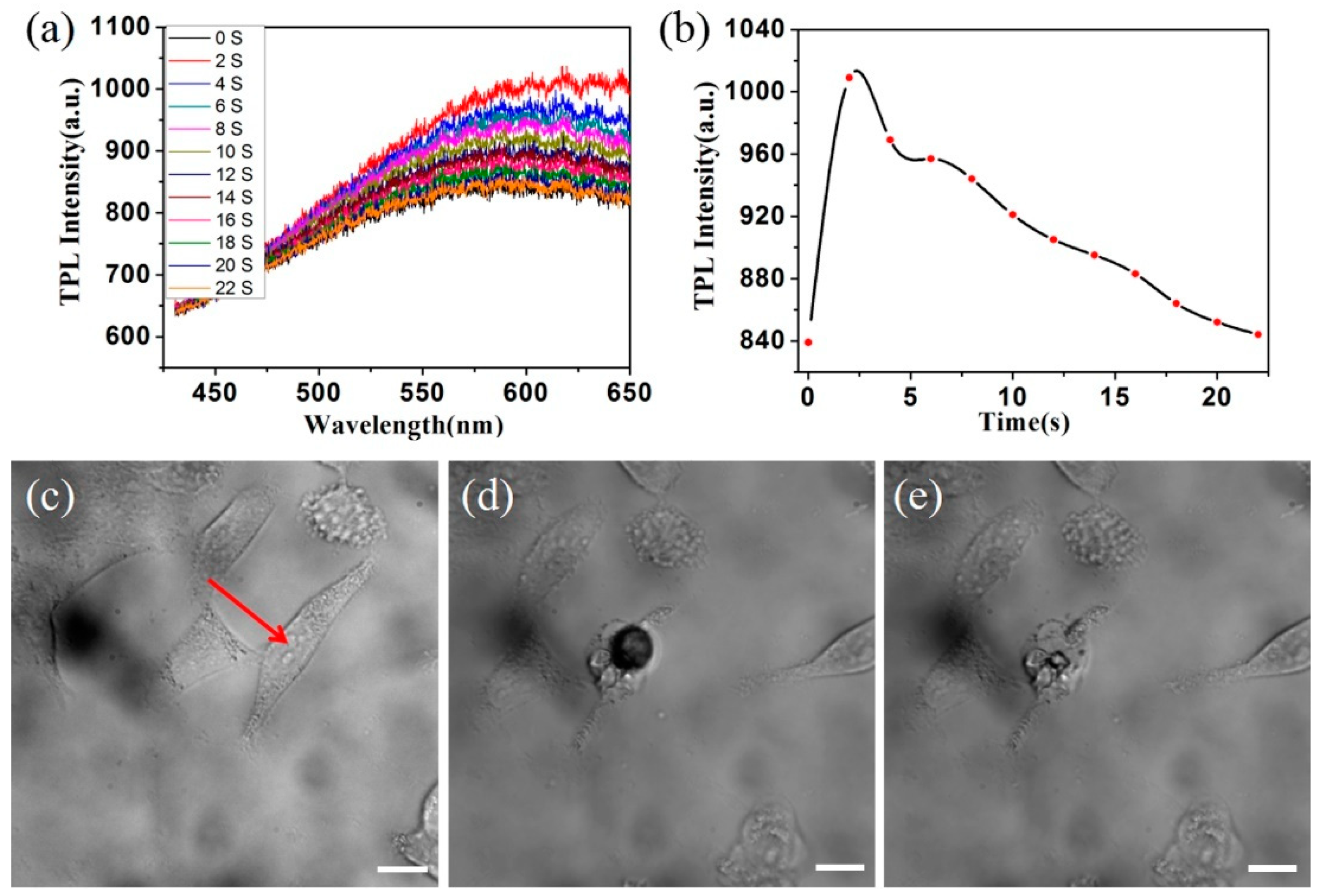
3.4. The Photothermal Therapy of GNRs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kang, B.; Afifi, M.M.; Austin, L.A.; El-Sayed, M.A. The nanoparticle plasmon effect: Observing drug delivery dynamics in single cells via raman/fluorescence imaging spectroscopy. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 7420–7427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durr, N.J.; Larson, T.; Smith, D.K.; Korgel, B.A.; Sokolov, K.; Ben-Yakar, A. Two-photon luminescence imaging of cancer cells using molecularly targeted gold nanorods. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 941–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.C.; Caldarola, M.; Pradhan, B.; Orrit, M. Gold nanorod enhanced fluorescence enables single-molecule electrochemistry of methylene blue. Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 3620–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagallier, A.; Boulais, E.; Boutopoulos, C.; Lachaine, R.; Meunier, M. Multiscale modeling of plasmonic enhanced energy transfer and cavitation around laser-excited nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 3023–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachaine, R.; Boutopoulos, C.; Lajoie, P.Y.; Boulais, É.; Meunier, M. Rational design of plasmonic nanoparticles for enhanced cavitation and cell perforation. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 3187–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, X.L.; Wu, Q.Q.; Zhu, H.H.; Mao, Z.W.; Gao, C.Y. Doxorubicin-conjugated pH-responsive gold nanorods for combined photothermal therapy and chemotherapy of cancer. Acta Biomater. 2018, 3, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.Y.; Wen, T.; Zhao, R.F.; Liu, X.X.; Ji, T.J.; Wang, H.; Shi, X.W.; Shi, J.; Wei, J.Y.; Zhao, Y.L.; et al. Localized electric field of plasmonic nanoplatform enhanced photodynamic tumor therapy. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 11529–11542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huschka, R.; Zuloaga, J.; Knight, M.W.; Brown, L.V.; Nordlander, P.; Halas, N.J. Light-induced release of DNA from gold nanoparticles: Nanoshells and nanorods. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 12247–12255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Liu, J.; Shi, J. Nuclear-targeting gold nanorods for extremely low NIR activated photothermal therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 15952–15961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.H.; El-Sayed, I.H.; Qian, W.; El-Sayed, M.A. Cancer cell imaging and photothermal therapy in the near-Infrared region by using Gold Nanorods. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2115–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.F.; Huff, T.B.; Zweifel, D.A.; He, W.; Low, P.S.; Wei, A.; Cheng, J.X. In vitro and in vivo two-photon luminescence imaging of single gold nanorods. PNAS 2005, 102, 15752–15756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, S.; Ferreira, C.A.; Chen, F.; Ellison, P.A.; Siamof, C.M.; Barnhart, T.E.; Cai, W. Activatable hybrid nanotheranostics for tetramodal imaging and synergistic photothermal/photodynamic therapy. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janani, I.; Lakra, R.; Kiran, M.S.; Korrapati, P.S. Selectivity and sensitivity of molybdenum oxide-polycaprolactone nanofiber composites on skin cancer: Preliminary in-vitro and in-vivo implications. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2018, 49, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Jiang, X.; Li, X.; Hu, Z.; Ji, Y.; Wu, X.; Chen, C. Silica-coated gold nanorods as a light-mediated multifunctional theranostic platform for cancer treatment. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1418–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatua, S.; Paulo, P.M.R.; Yuan, H.F.; Gupta, A.; Zijlstra, P.; Orrit, M. Resonant plasmonic enhancement of single-molecule fluorescence, by individual gold nanorods. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 4440–4449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maltzahn, G.; Centrone, A.; Park, J.H.; Ramanathan, R.; Sailor, M.J.; Hatton, T.A.; Bhatia, S.N. SERS-coded gold nanorods as a multifunctional platform for densely multiplexed near-infrared imaging and photothermal heating. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 3175–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soenen, S.J.; Manshian, B.; Montenegro, J.M.; Amin, F.; Meermann, B.; Thiron, T.; Cornelissen, M.; Vanhaecke, F.; Doak, S.; Parak, W.J.; et al. Cytotoxic effects of gold nanoparticles: A multiparametric Study. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 5767–5783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.D.; Wu, D.; Shen, X.; Chen, J.; Sun, Y.M.; Liu, P.X.; Liang, X.J. Size-dependent radiosensitization of PEG-coated gold nanoparticles for cancer radiation therapy. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6408–6419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkilany, A.M.; Nagaria, P.K.; Hexel, C.R.; Shaw, T.J.; Murphy, C.J.; Wyatt, M.D. Cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of gold nanorods: Molecular origin of cytotoxicity and surface effects. Small 2009, 5, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Talavage, T.; Irudayaraj, J. Gold Nanorod/Fe3O4 Nanoparticle “Nano-Pearl-Necklaces” for Simultaneous Targeting, Dual-Mode Imaging, and Photothermal Ablation of Cancer Cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 2759–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marasini, R.; Pitchaimani, A.; Nguyen, T.D.; Comer, J.; Aryal, S. Influence of Polyethylene Glycol Passivation on the Surface Plasmon Resonance Induced Photothermal Properties of Gold Nanorods. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 13684–13693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhan, X.; Xiong, J.; Peng, S.; Huang, W.; Joshi, R.; Cai, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Yuan, K.; et al. Temperature-dependent cell death patterns induced by functionalized gold nanoparticle photothermal therapy in melanoma cells. Sci Rep. 2018, 8, 8720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.R.K.; Snyder, B.; El-Sayed, M.A. Synthesis and optical roperties of small Au nanorods using a seedless growth technique. Langmuir 2012, 28, 9807–9815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.M.; Xu, L.G.; Bai, R.; Ji, Y.L.; Wu, X.C.; Zhao, Y.L.; Li, Y.F.; Chen, C.Y. Surface chemistry and aspect ratio mediated cellular uptake of Au nanorods. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 7606–7619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.H.; Le, Q.; Lan, S.; Liang, J.X.; Tie, S.L.; Xu, J.L. Modifying the mechanical properties of gold nanorods by copperdoping and triggering their cytotoxicity with ultrasonic wave. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 163, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.B.; Liu, X.S.; Ji, J. More efficient NIR photothermal therapeutic effect from intracellular heating modality than extracellular heating modality: An in vitro study. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 1128–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, K.S. Numerical solution of inital boundary value problems involving Maxwell’s equations in isotropic media. IEEE. Trans. Antenn. Propag. 1966, 14, 302–307. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.; Liou, K.N. Finite-difference time domain method for light scattering by small ice crystals in threedimensional space. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1996, 13, 2072–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, G.G.; Izquierdo, J.G.; Bañares, L.; Tardajos, G.; Rivera, A.; Altantzis, T.; Bals, S.; Rodríguez, O.P.; Martínez, A.G.; Marzaín, L.M.L. Femtosecond laser-controlled tip-to-tip assembly and welding of gold nanorods. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 8282–8288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.; Andrade, G.F.S.; Ahmed, A.; Souza, M.L.; Coombs, N.; Tumarkin, E.; Liu, K.; Gordon, R.; Brolo, A.G.; Kumacheva, E. Probing dynamic generation of hot-spots in self-assembled chains of gold nanorods by surface-enhanced raman scattering. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 7563–7570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.; Ahmed, A.; dos Santos, D.P.; Coombs, N.; Park, J., II; Gordon, R.; Brolo, A.G.; Kumacheva, E. Side-by-side assembly of gold nanorods reduces ensemble-averaged SERS intensity. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 5538–5545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


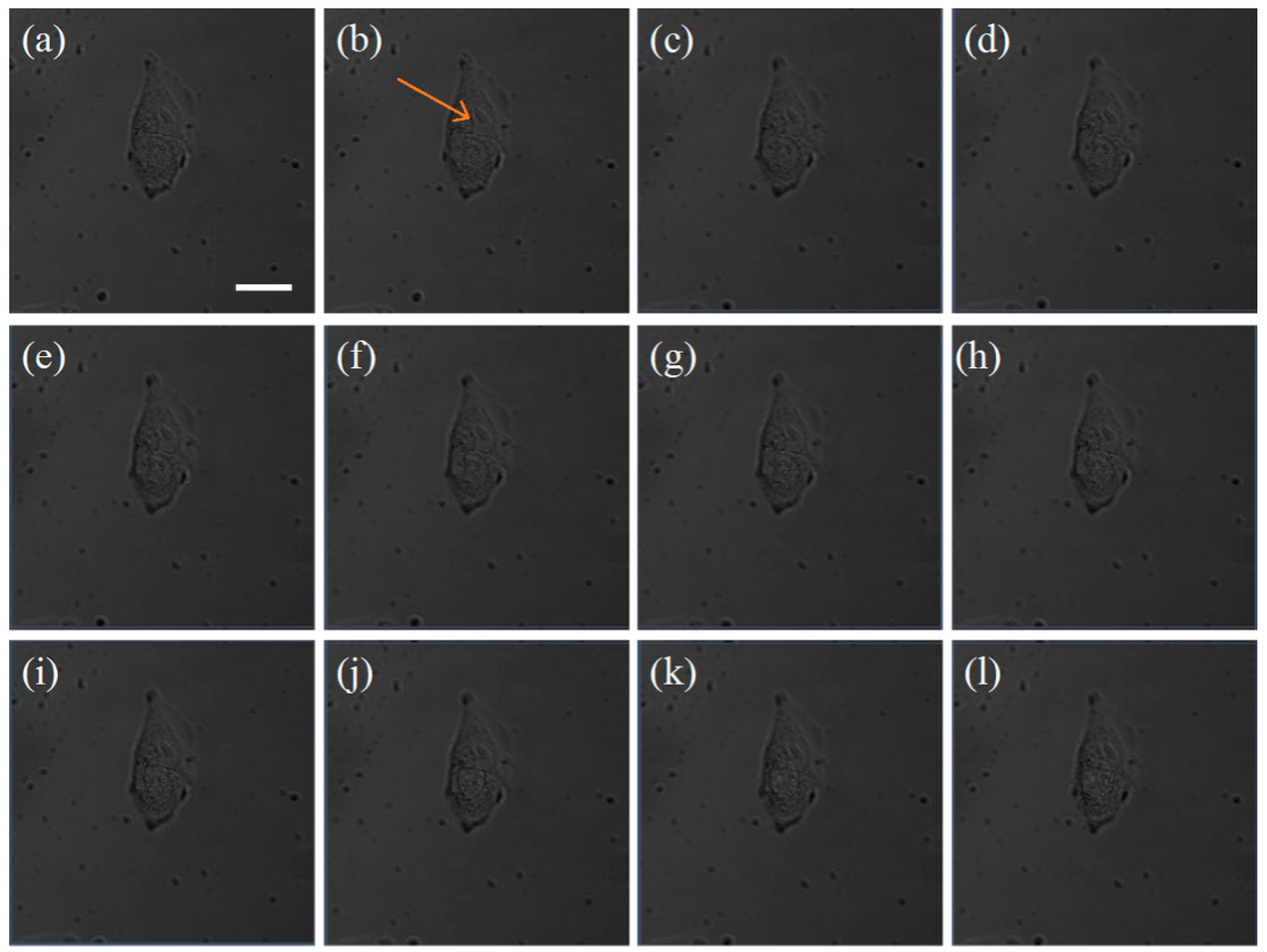
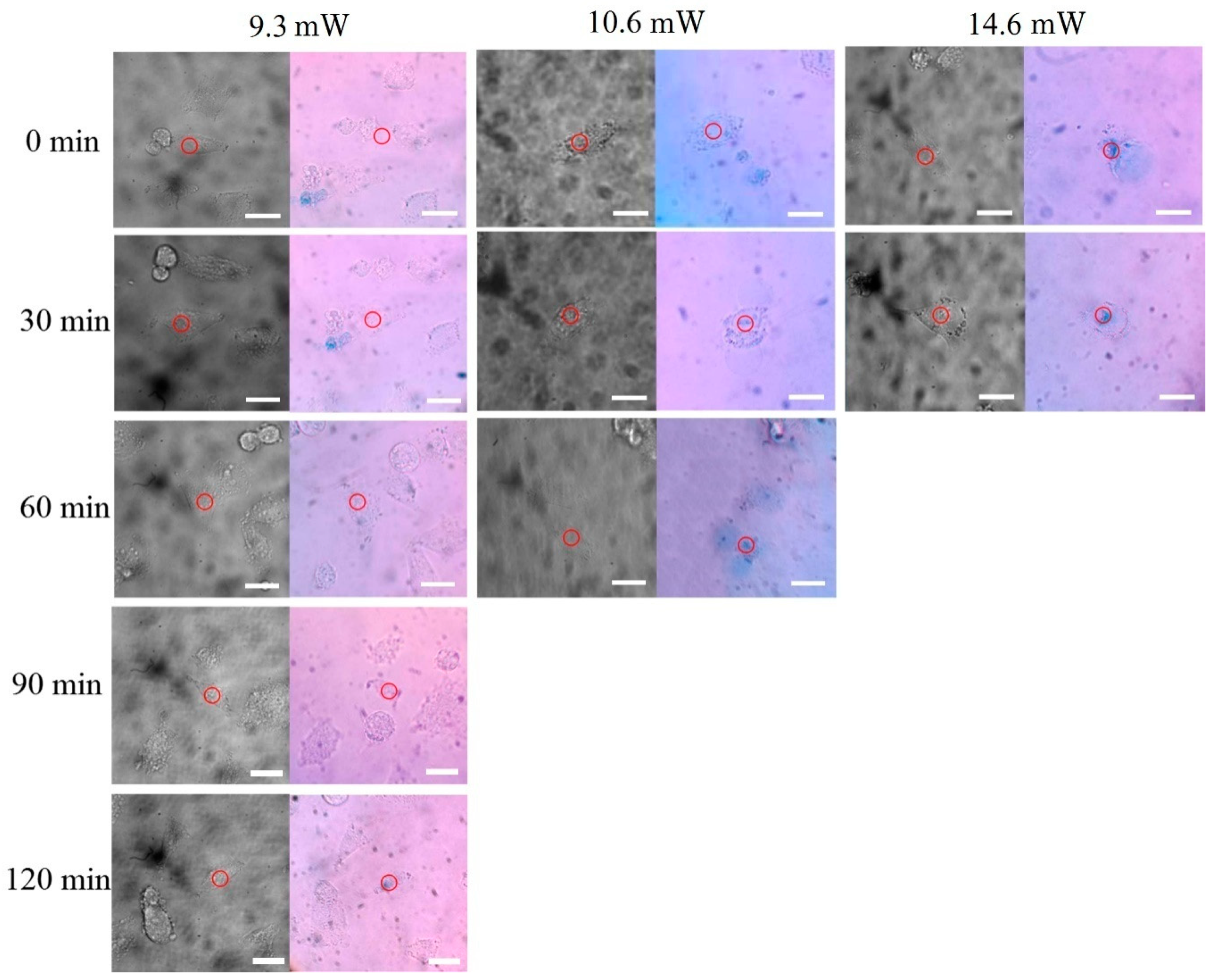
| Power | 14.6 mW | 10.6 mW | 9.3 mW |
| Cell Death Time | after 0 min | after 60 min | after 120 min |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, Y.; Zhang, N.; Liu, X.; Dai, Q.; Liu, H.; Wei, Z.; Tie, S.; Li, Y.; Fan, H.; Lan, S. A Novel Fast Photothermal Therapy Using Hot Spots of Gold Nanorods for Malignant Melanoma Cells. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8110880
Yao Y, Zhang N, Liu X, Dai Q, Liu H, Wei Z, Tie S, Li Y, Fan H, Lan S. A Novel Fast Photothermal Therapy Using Hot Spots of Gold Nanorods for Malignant Melanoma Cells. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(11):880. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8110880
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Yanhua, Nannan Zhang, Xiao Liu, Qiaofeng Dai, Haiying Liu, Zhongchao Wei, Shaolong Tie, Yinyin Li, Haihua Fan, and Sheng Lan. 2018. "A Novel Fast Photothermal Therapy Using Hot Spots of Gold Nanorods for Malignant Melanoma Cells" Nanomaterials 8, no. 11: 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8110880
APA StyleYao, Y., Zhang, N., Liu, X., Dai, Q., Liu, H., Wei, Z., Tie, S., Li, Y., Fan, H., & Lan, S. (2018). A Novel Fast Photothermal Therapy Using Hot Spots of Gold Nanorods for Malignant Melanoma Cells. Nanomaterials, 8(11), 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8110880