A Novel Magnetic Actuation Scheme to Disaggregate Nanoparticles and Enhance Passage across the Blood–Brain Barrier
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
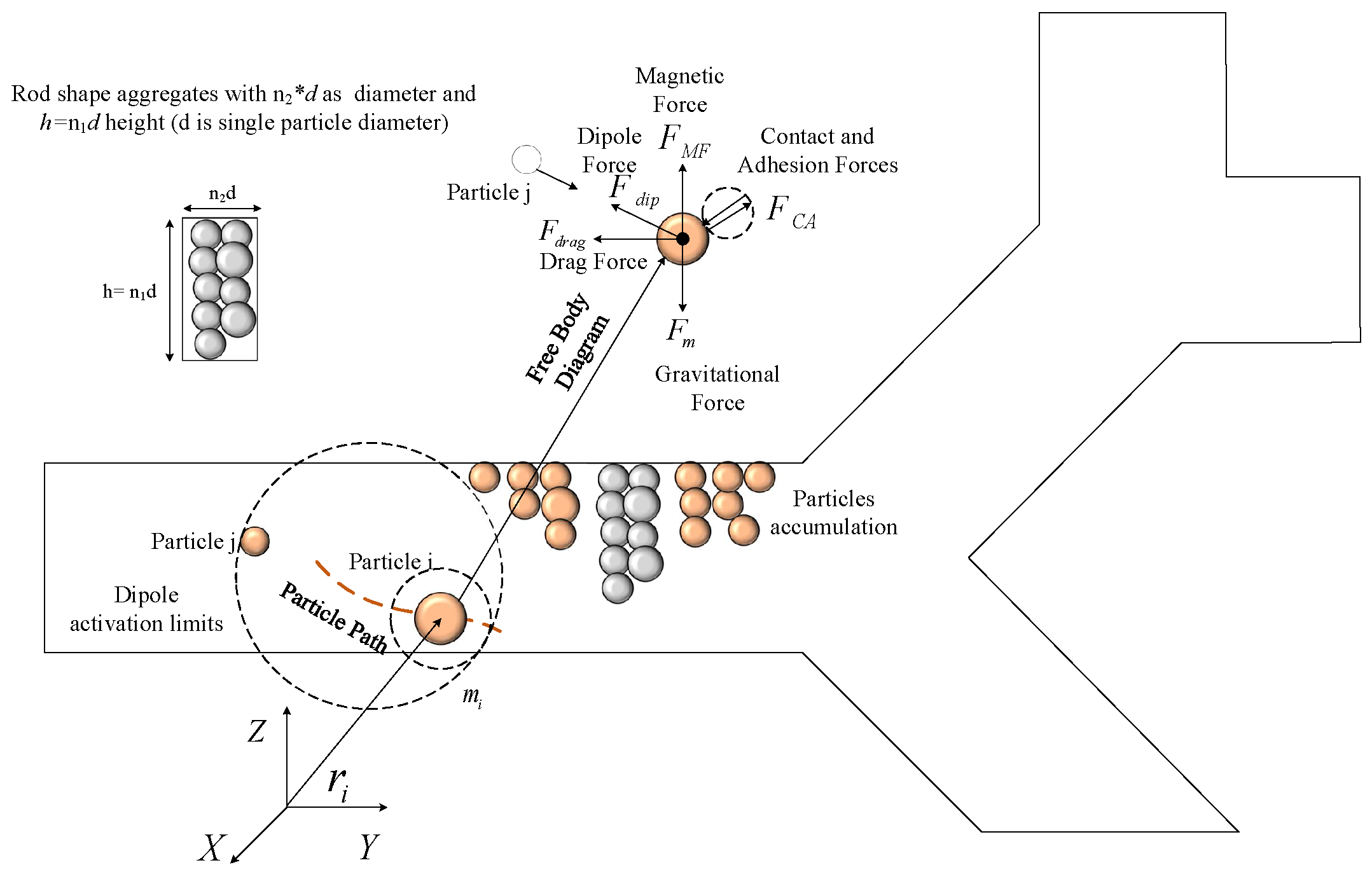
2.1. Governing Dynamic Forces in MDD
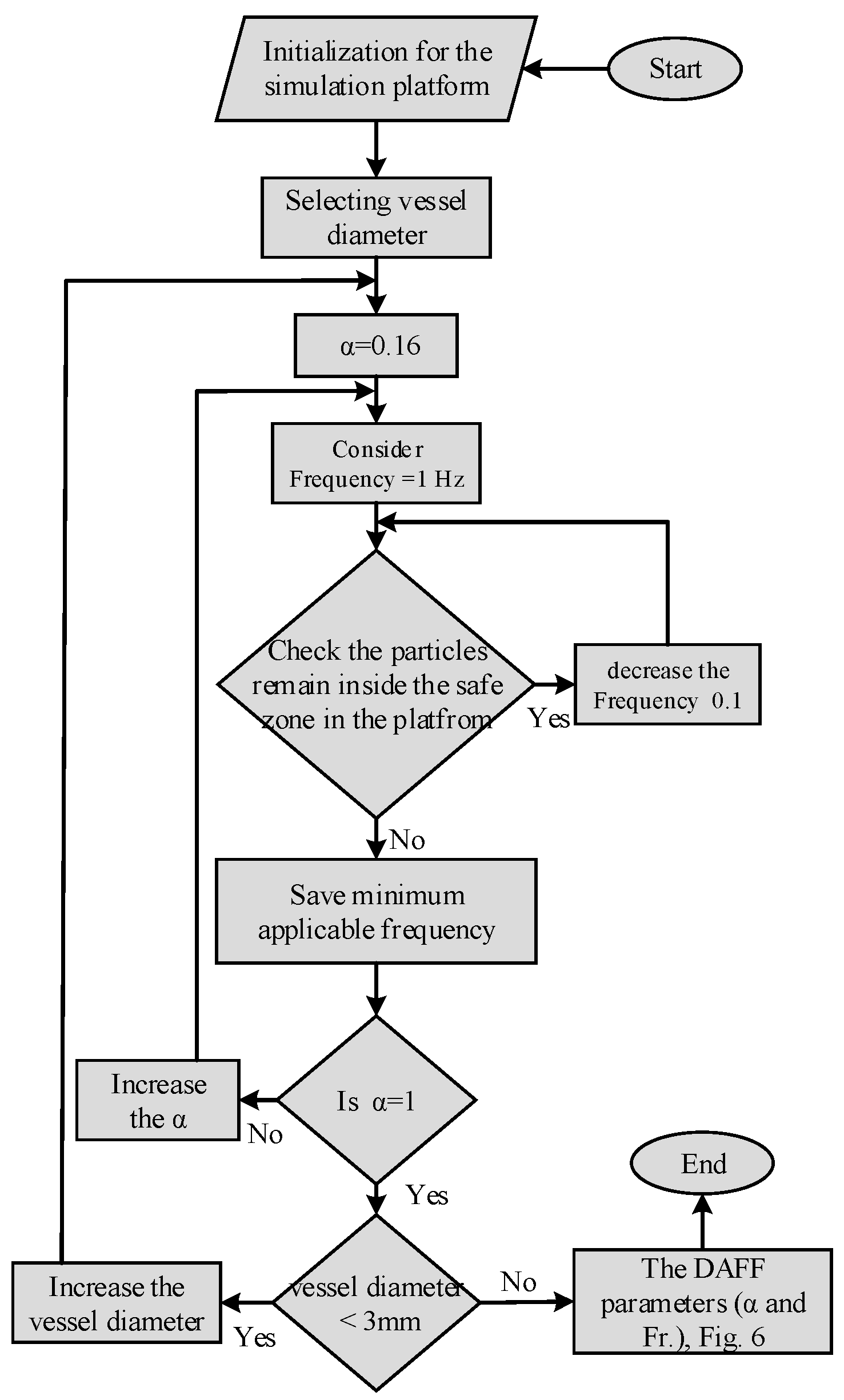
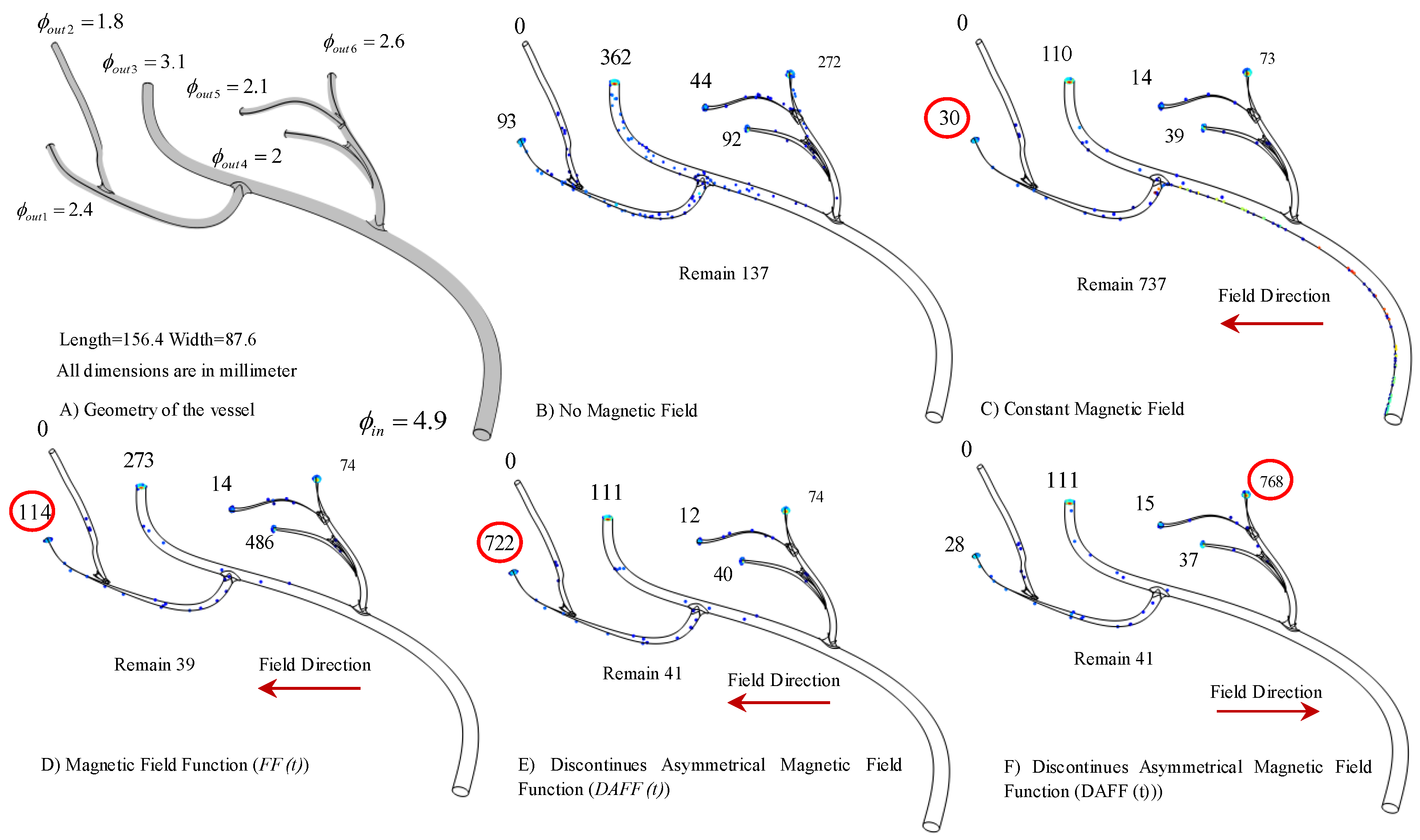
2.2. Simulation Platform for Steering Aggregated MNPs in Bifurcations
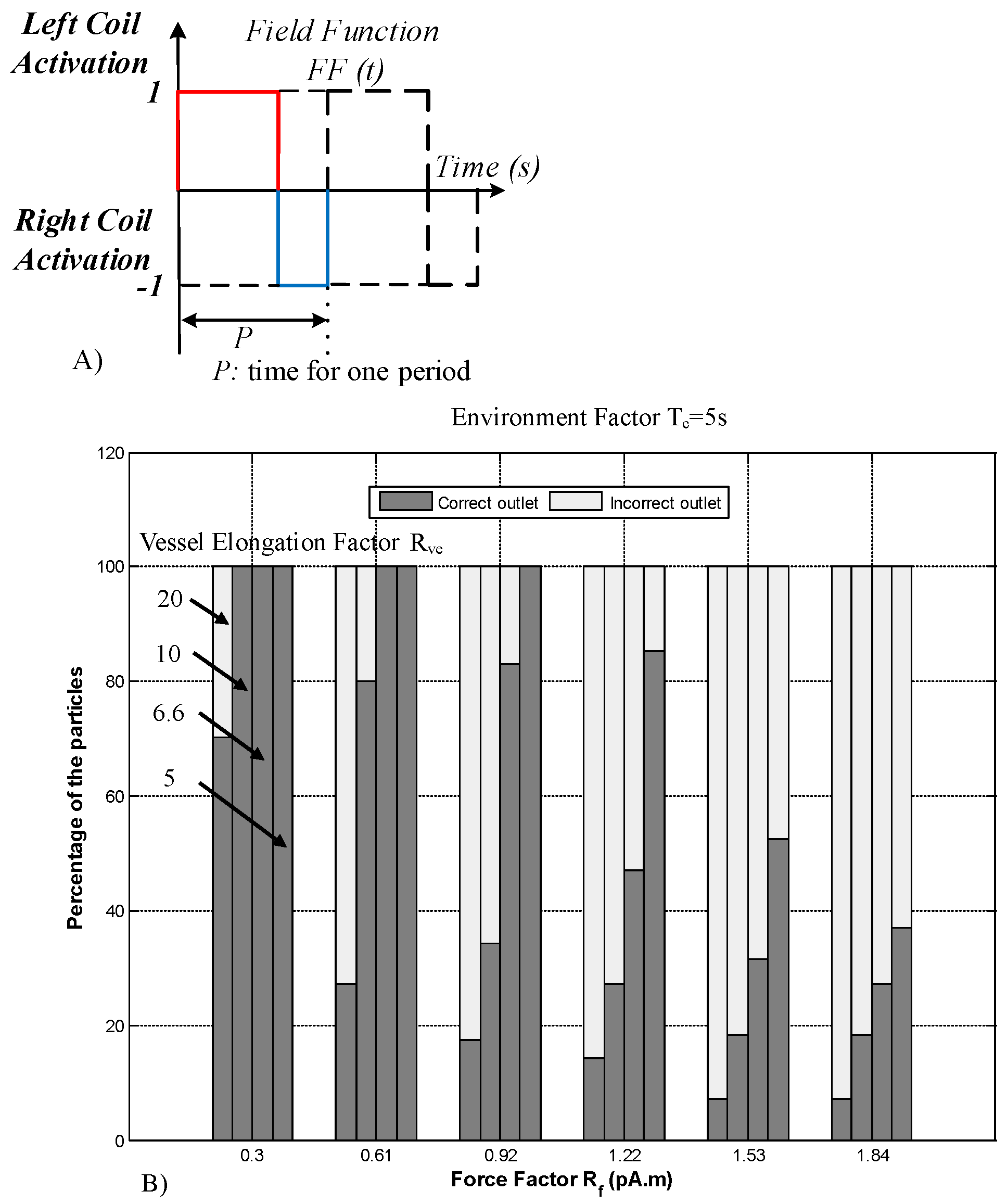
2.2.1. The Influential Parameters in Targeting Performance
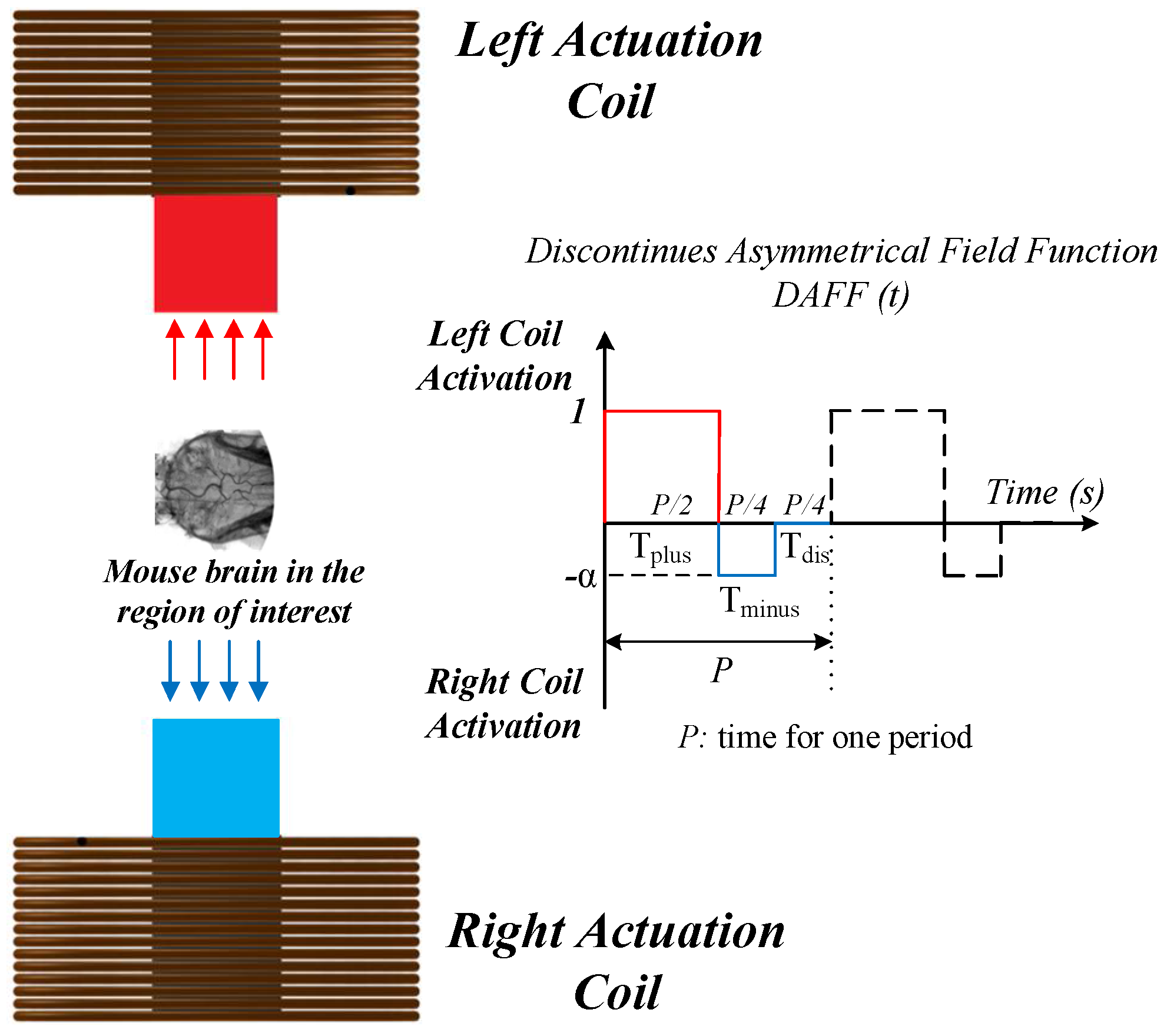
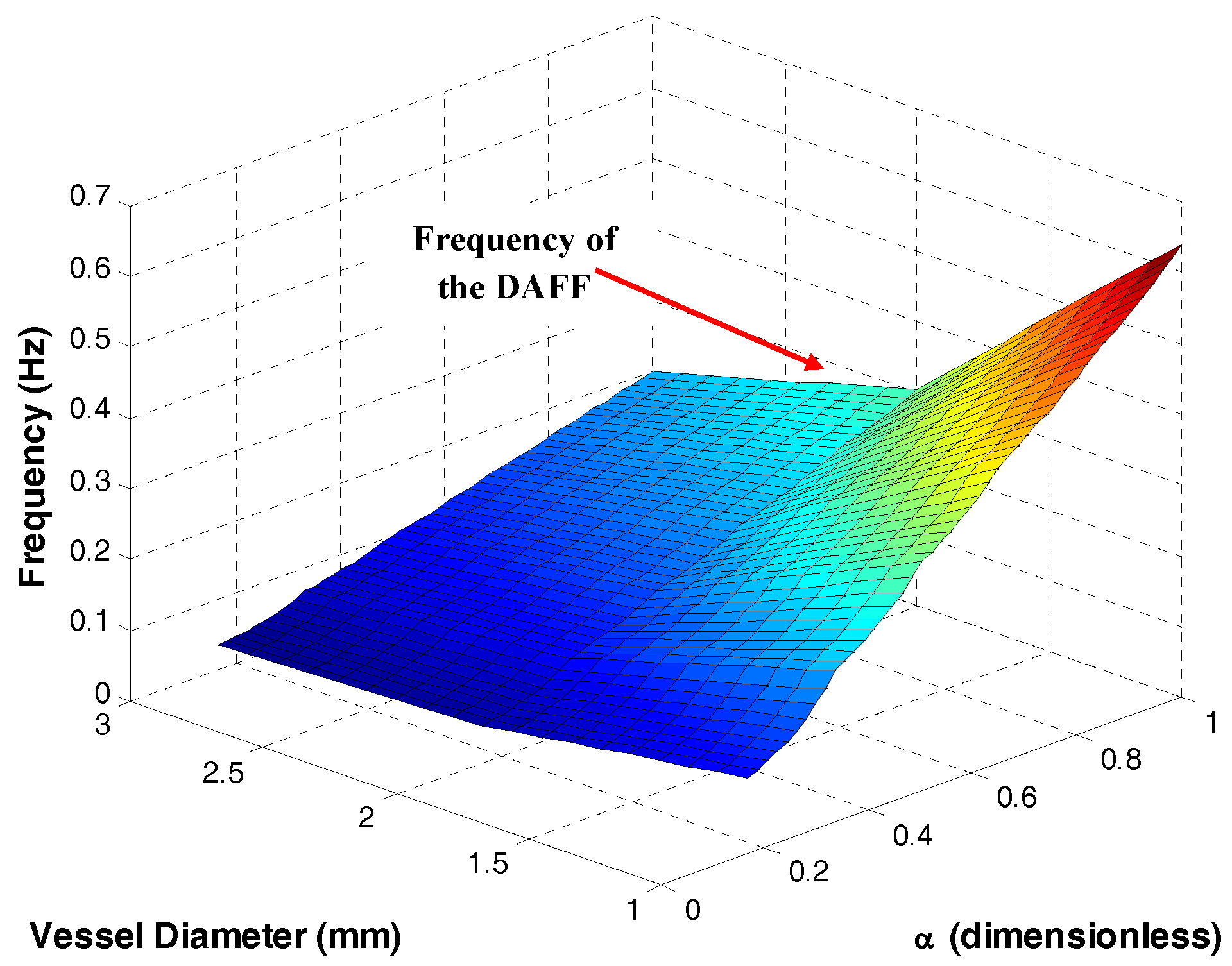
2.2.2. The DAFF Design
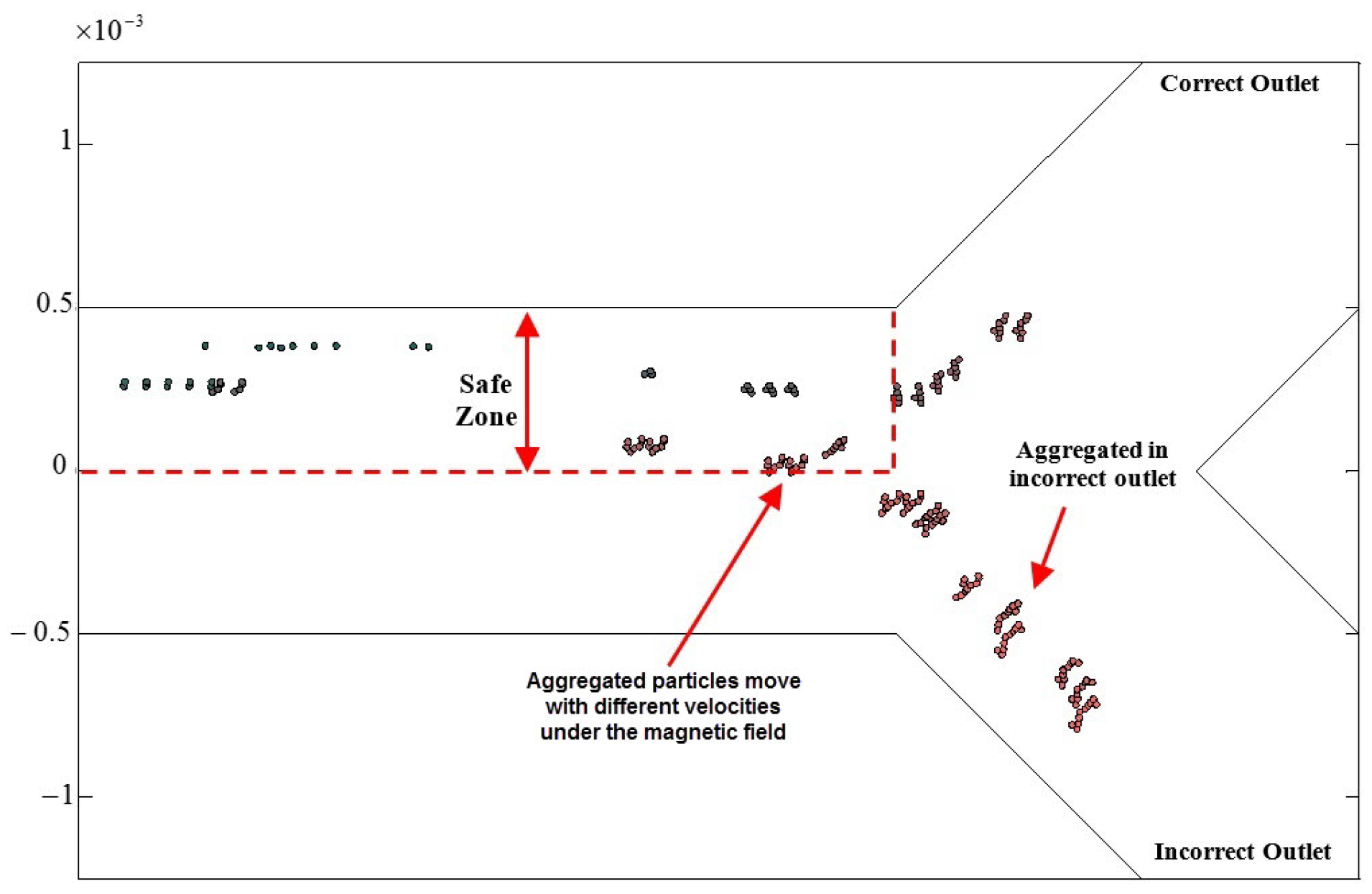
2.3. In Vitro Study of Guidance of MNPs in a Y-Shaped Channel
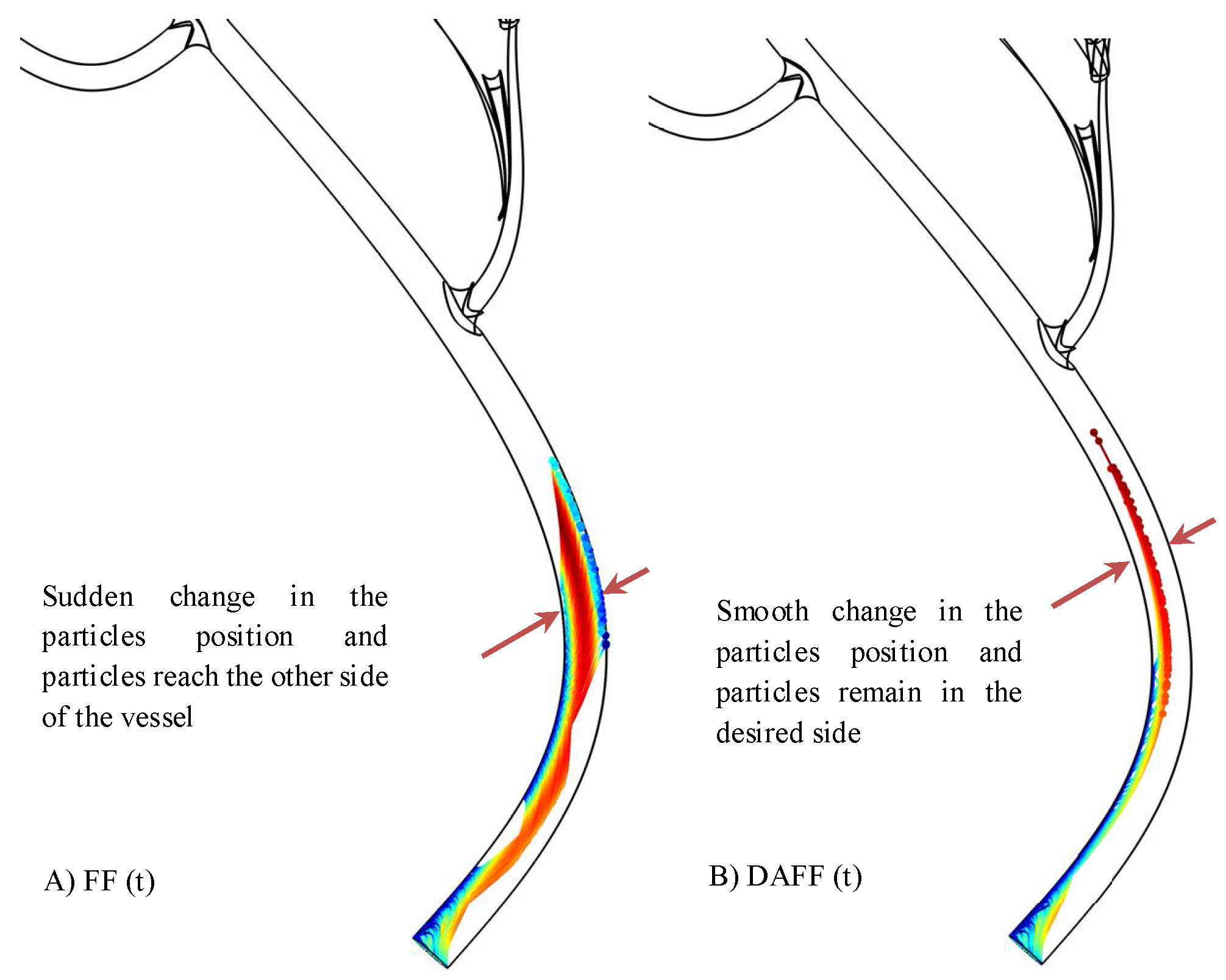
2.4. Realistic Model Simulation
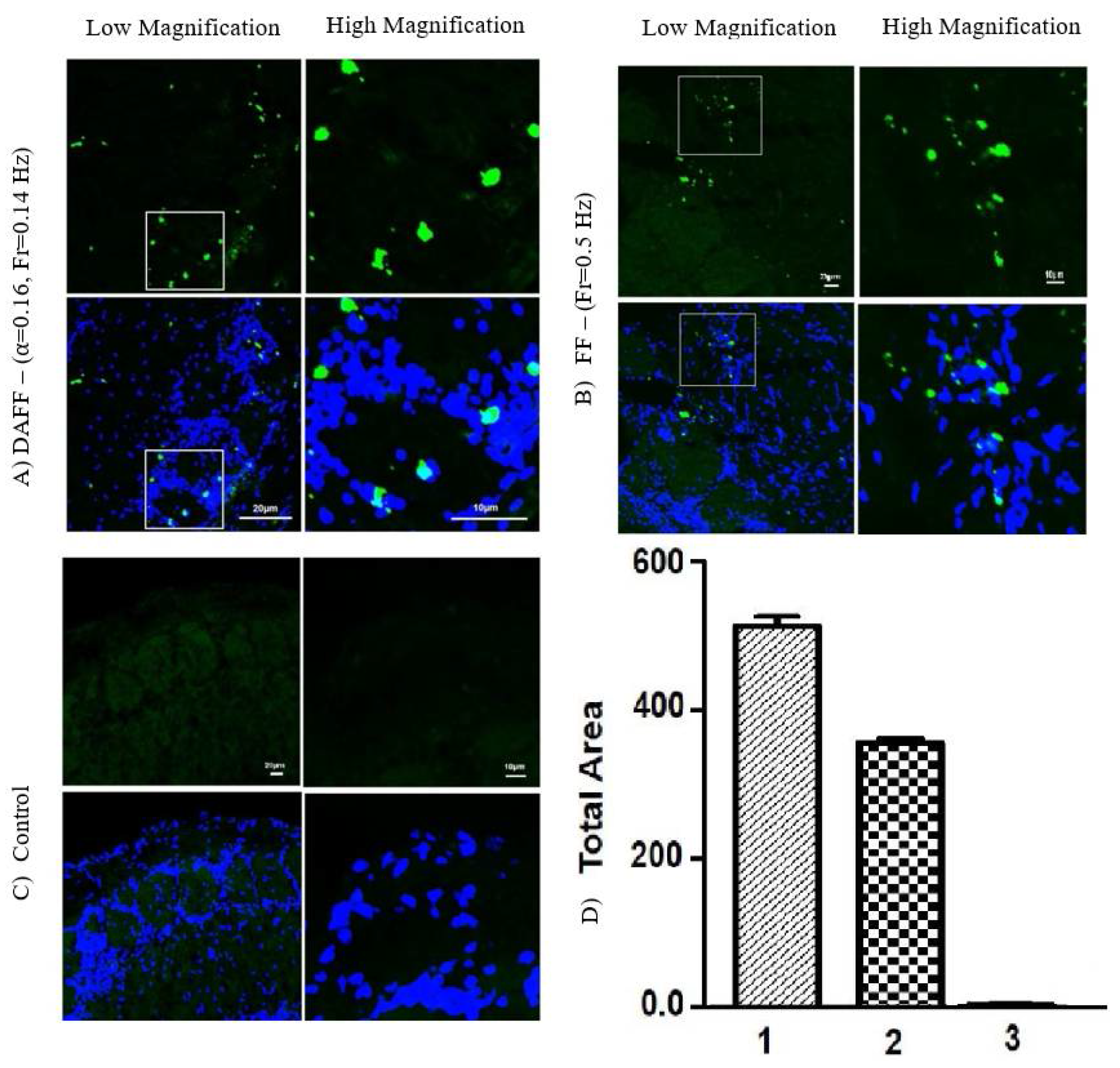
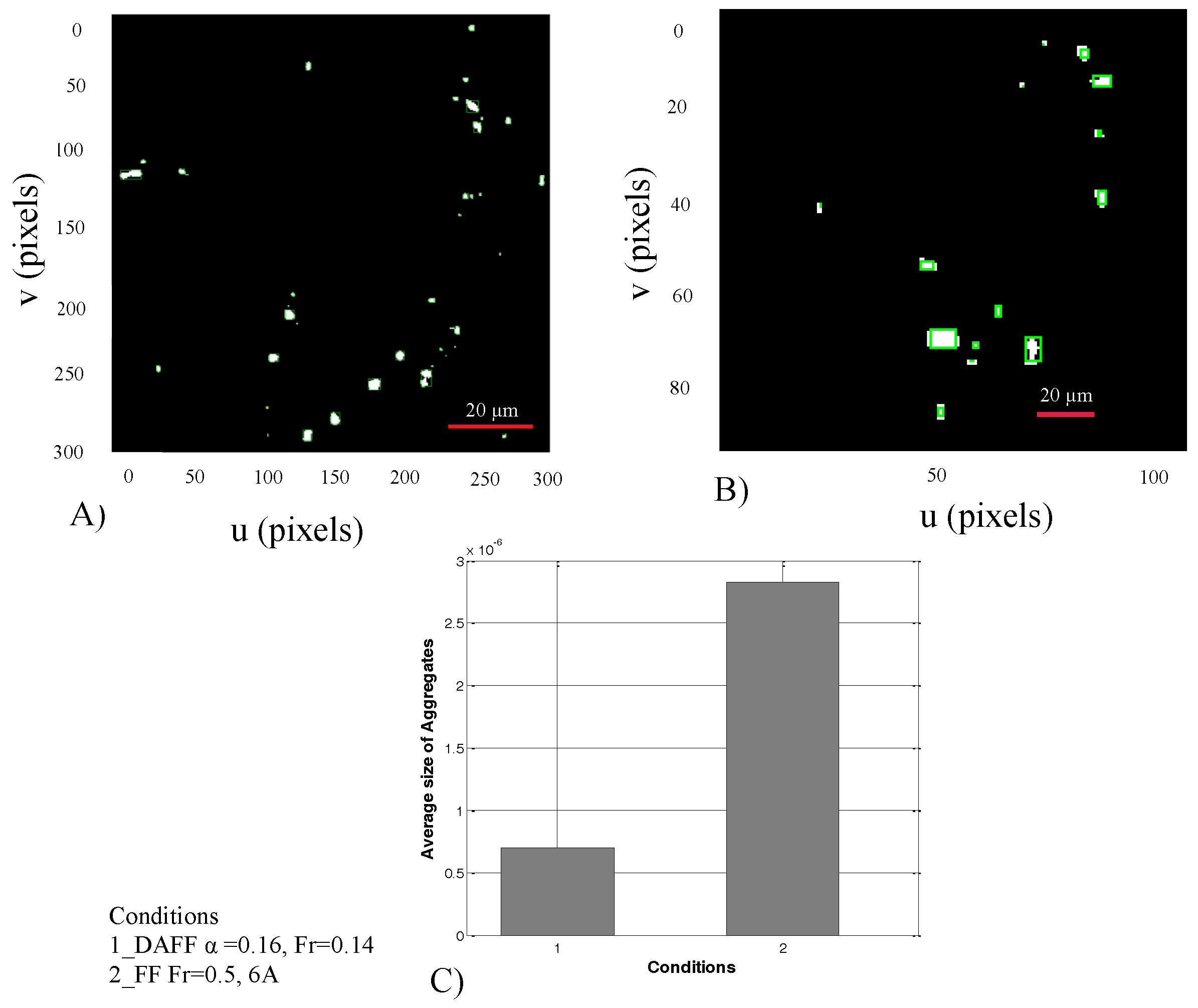
2.5. Passage of the BBB
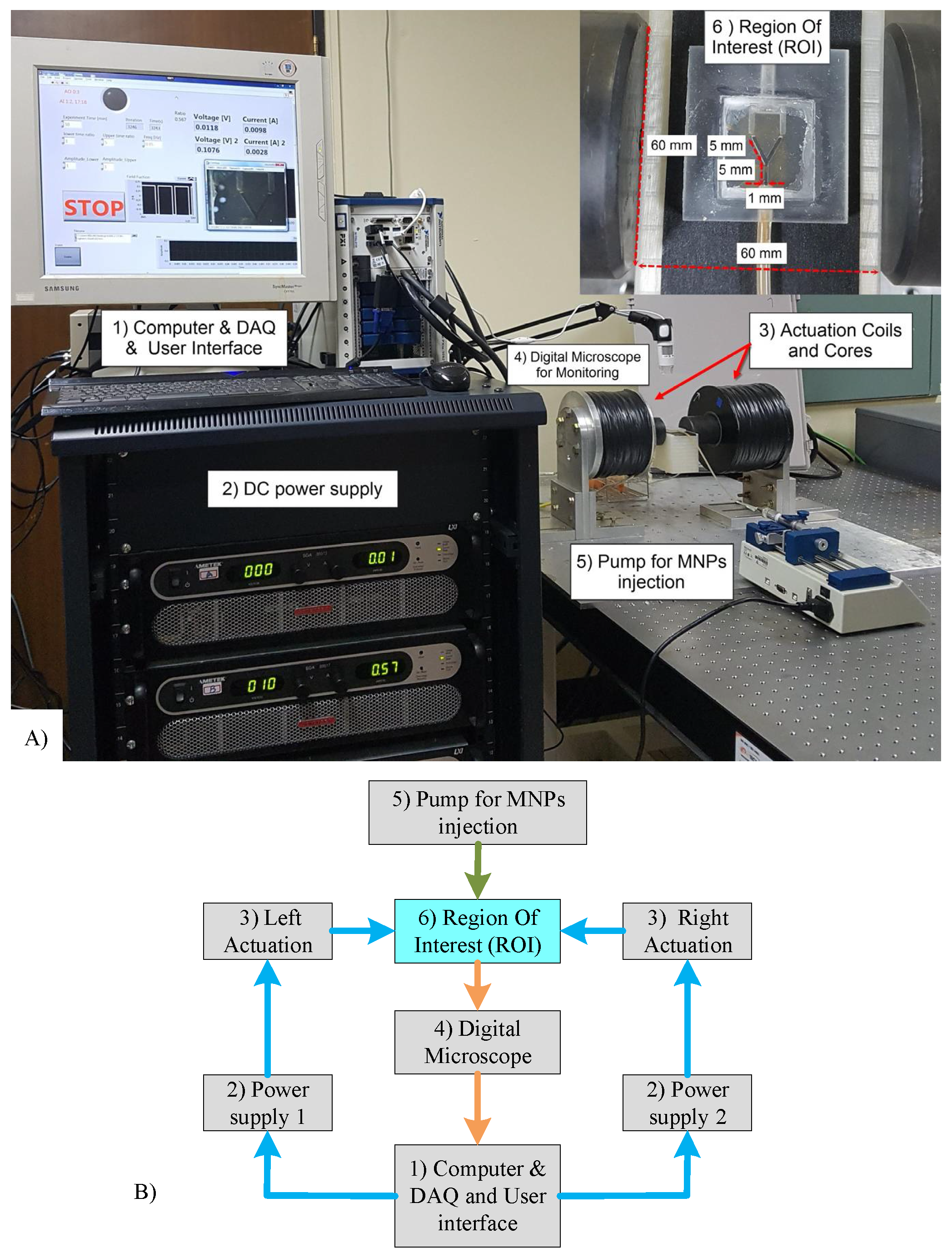
3. Experimental Section
3.1. System Setup
3.2. In Vitro Study
3.3. In Vivo Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoshiar, A.; RaeisiFard, H. A simulation algorithm for path planning of biological nanoparticles displacement on a rough path. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 17, 5578–5581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshiar, A.K.; Raeisifard, H. A study of the nonlinear primary resonances of a micro-system under electrostatic and piezoelectric excitations. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2015, 229, 1904–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeisifard, H.; Bahrami, M.N.; Yousefi-Koma, A.; Fard, H.R. Static characterization and pull-in voltage of a micro-switch under both electrostatic and piezoelectric excitations. Eur. J. Mech-A/Solids 2014, 44, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korayem, M.; Omidi, E. Robust controlled manipulation of nanoparticles using atomic force microscope. Micro Nano Lett. 2012, 7, 927–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korayem, M.; Zakeri, M. Sensitivity analysis of nanoparticles pushing critical conditions in 2-D controlled nanomanipulation based on AFM. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2009, 41, 714–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekawy, M.; Saito, A.; Shimizu, H.; Tominaga, T. Targeting of apoptotic cells using functionalized Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 874–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Meng, Y.; Li, C.; Qian, M.; Huang, R. Receptor-mediated drug delivery systems targeting to glioma. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilnawaz, F.; Sahoo, S.K. Therapeutic approaches of magnetic nanoparticles for the central nervous system. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 1256–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merino, S.; Martín, C.; Kostarelos, K.; Prato, M.; Vázquez, E. Nanocomposite hydrogels: 3D polymer–nanoparticle synergies for on-demand drug delivery. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 4686–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shityakov, S.; Roewer, N.; Broscheit, J.A.; Förster, C. In silico models for nanotoxicity evaluation and prediction at the blood-brain barrier level: A mini-review. Comput. Toxicol. 2017, 2, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béduneau, A.; Saulnier, P.; Benoit, J.P. Active targeting of brain tumors using nanocarriers. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 4947–4967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arruebo, M.; Fernández-Pacheco, R.; Ibarra, M.R.; Santamaría, J. Magnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nano Today 2007, 2, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankhurst, Q.A.; Thanh, N.T.K.; Jones, S.K.; Dobson, J. Progress in applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 224001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosbach, K.; Schröder, U. Preparation and application of magnetic polymers for targeting of drugs. FEBS Lett. 1979, 102, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenjereš, S.; Righolt, B. Simulations of magnetic capturing of drug carriers in the brain vascular system. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2012, 35, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunnoo, T.; Puangmali, T. Capture efficiency of biocompatible magnetic nanoparticles in arterial flow: A computer simulation for magnetic drug targeting. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larimi, M.; Ramiar, A.; Ranjbar, A. Numerical simulation of magnetic nanoparticles targeting in a bifurcation vessel. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 362, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chertok, B.; David, A.E.; Yang, V.C. Brain tumor targeting of magnetic nanoparticles for potential drug delivery: Effect of administration route and magnetic field topography. J. Control. Release 2011, 155, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tehrani, M.D.; Yoon, J. Statistical investigation of efficiency of the nanomagnetic particle steering in blood vessels. In Proceedings of the 7th IEEE International Conference on Nano/Molecular Medicine and Engineering, Phuket, Thailand, 10–13 November 2013; pp. 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Mathieu, J.B.; Martel, S. Steering of aggregating magnetic microparticles using propulsion gradients coils in an MRI Scanner. Magn. Reson. Med. 2010, 63, 1336–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, S.D.; Lee, J.; Ramachandran, S.; Eliceiri, B.P.; Shubayev, V.I.; Lal, R.; Jin, S. Magnetic targeting of nanoparticles across the intact blood–brain barrier. J. Control. Release 2012, 164, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Wang, J.T.W.; Mei, K.C.; Al-Jamal, W.T.; Al-Jamal, K.T. Real-time monitoring of magnetic drug targeting using fibered confocal fluorescence microscopy. J. Control. Release 2016, 244, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaswamy, B.; Kulkarni, S.D.; Villar, P.S.; Smith, R.S.; Eberly, C.; Araneda, R.C.; Depireux, D.A.; Shapiro, B. Movement of magnetic nanoparticles in brain tissue: Mechanisms and impact on normal neuronal function. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2015, 11, 1821–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tehrani, M.D.; Yoon, J.H.; Kim, M.O.; Yoon, J. A novel scheme for nanoparticle steering in blood vessels using a functionalized magnetic field. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soheilian, R.; Choi, Y.S.; David, A.E.; Abdi, H.; Maloney, C.E.; Erb, R.M. Toward accumulation of magnetic nanoparticles into tissues of small porosity. Langmuir 2015, 31, 8267–8274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, K.A.; Shin, M.C.; Yu, F.; Yang, M.; David, A.E.; Yang, V.C.; Rosania, G.R. Pulsed magnetic field improves the transport of iron oxide nanoparticles through cell barriers. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 2161–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, F.U.; Hoshiar, A.K.; Do, T.D.; Noh, Y.; Shah, S.A.; Khan, M.S.; Yoon, J.; Kim, M.O. Osmotin-loaded magnetic nanoparticles with electromagnetic guidance for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 10619–10632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, H.; Maekawa, T. Cluster structures and cluster-cluster aggregations in a two-dimensional ferromagnetic colloidal system. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 2000, 33, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vartholomeos, P.; Mavroidis, C. Simulation platform for self-assembly structures in MRI-guided nanorobotic drug delivery systems. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Anchorage, AK, USA, 3–8 May 2010; pp. 5594–5600. [Google Scholar]
- Vartholomeos, P.; Mavroidis, C. In silico studies of magnetic microparticle aggregations in fluid environments for MRI-guided drug delivery. Biomed. Eng. IEEE Trans. 2012, 59, 3028–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshiar, A.K.; Le, T.A.; Amin, F.U.; Kim, M.O.; Yoon, J. Studies of aggregated nanoparticles steering during magnetic-guided drug delivery in the blood vessels. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 427, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Marshall, J.S.; Liu, G.; Yao, Q. Adhesive particulate flow: The discrete-element method and its application in energy and environmental engineering. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2011, 37, 633–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.A.; Hoshiar, A.K.; Do, T.D.; Yoon, J. A modified functionalized magnetic field for nanoparticle guidance in magnetic drug targeting. In Proceedings of the 2016 13th International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots and Ambient Intelligence (URAI), Xian, China, 19–22 August 2016; pp. 493–496. [Google Scholar]
- Do, T.D.; Amin, F.U.; Noh, Y.; Kim, M.O.; Yoon, J. Guidance of magnetic nanocontainers for treating Alzheimer’s disease using an electromagnetic, targeted drug-delivery actuator. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2016, 12, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, S.; Yoon, J. Nano carriers based targeted drug delivery path planning using hybrid particle swarm optimizer and artificial magnetic fields. In Proceedings of the 2012 12th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems, Gyeonggi-do, Korea, 17–21 October 2012; pp. 1700–1705. [Google Scholar]
- Hoshiar, A.K.; Le, T.A.; Amin, F.U.; Kim, M.O.; Yoon, J. Functionalized Electromagnetic Actuation Method for Aggregated Nanoparticles Steering. In Proceedings of the International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Jeju Island, Korea, 11–15 July 2017; pp. 885–888. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, J.E.; Huh, M.I.; Ryu, B.K.; Do, J.Y.; Jin, S.U.; Moon, M.J.; Jung, J.C.; Chang, Y.; Kim, E.; Chi, S.G.; et al. The effect of static magnetic fields on the aggregation and cytotoxicity of magnetic nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9401–9414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malvindi, M.A.; De Matteis, V.; Galeone, A.; Brunetti, V.; Anyfantis, G.C.; Athanassiou, A.; Cingolani, R.; Pompa, P.P. Toxicity assessment of silica coated iron oxide nanoparticles and biocompatibility improvement by surface engineering. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Particle density | 6450 kg/m |
| Particle diameter | 800 nm |
| Blood density | 1050 kg/m |
| Blood viscosity | 0.004 Pa·s |
| Air relative permeability | 1 (dimensionless) |
| Blood relative permeability | 1 (dimensionless) |
| Blood temperature | 293.15 K |
| Symbol | Quantity | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Vessel length | 10 mm | |
| Normal exit time | 5 s | |
| Vessel elongation | (dimensionless) | |
| Force Factor | pA·m |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoshiar, A.K.; Le, T.-A.; Amin, F.U.; Kim, M.O.; Yoon, J. A Novel Magnetic Actuation Scheme to Disaggregate Nanoparticles and Enhance Passage across the Blood–Brain Barrier. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8010003
Hoshiar AK, Le T-A, Amin FU, Kim MO, Yoon J. A Novel Magnetic Actuation Scheme to Disaggregate Nanoparticles and Enhance Passage across the Blood–Brain Barrier. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoshiar, Ali Kafash, Tuan-Anh Le, Faiz Ul Amin, Myeong Ok Kim, and Jungwon Yoon. 2018. "A Novel Magnetic Actuation Scheme to Disaggregate Nanoparticles and Enhance Passage across the Blood–Brain Barrier" Nanomaterials 8, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8010003
APA StyleHoshiar, A. K., Le, T.-A., Amin, F. U., Kim, M. O., & Yoon, J. (2018). A Novel Magnetic Actuation Scheme to Disaggregate Nanoparticles and Enhance Passage across the Blood–Brain Barrier. Nanomaterials, 8(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8010003






