Impact of the De-Alloying Kinetics and Alloy Microstructure on the Final Morphology of De-Alloyed Meso-Porous Metal Films
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
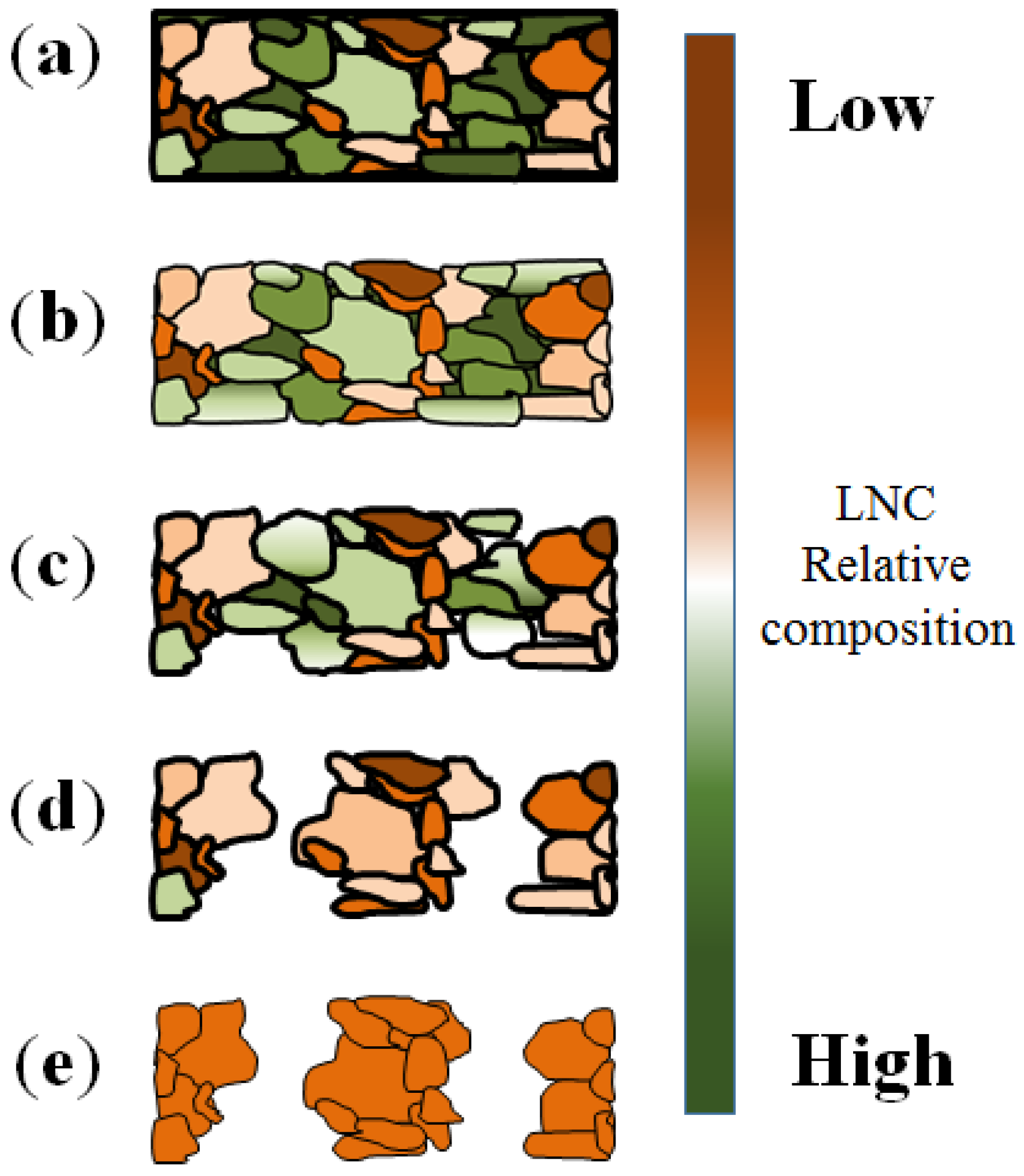
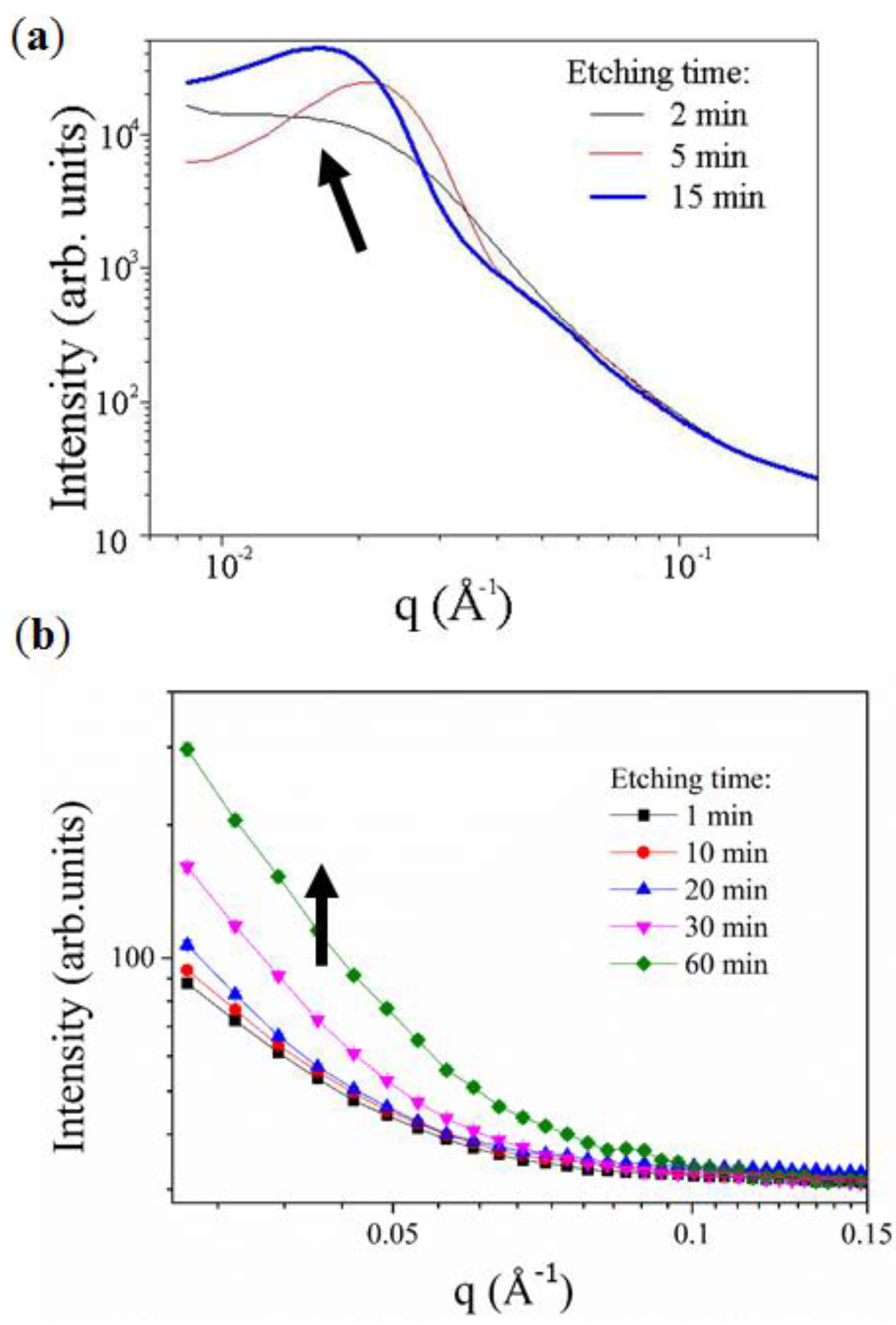
2.1. Kinetics of the De-Alloying Process and Structure-Morphology Relationship
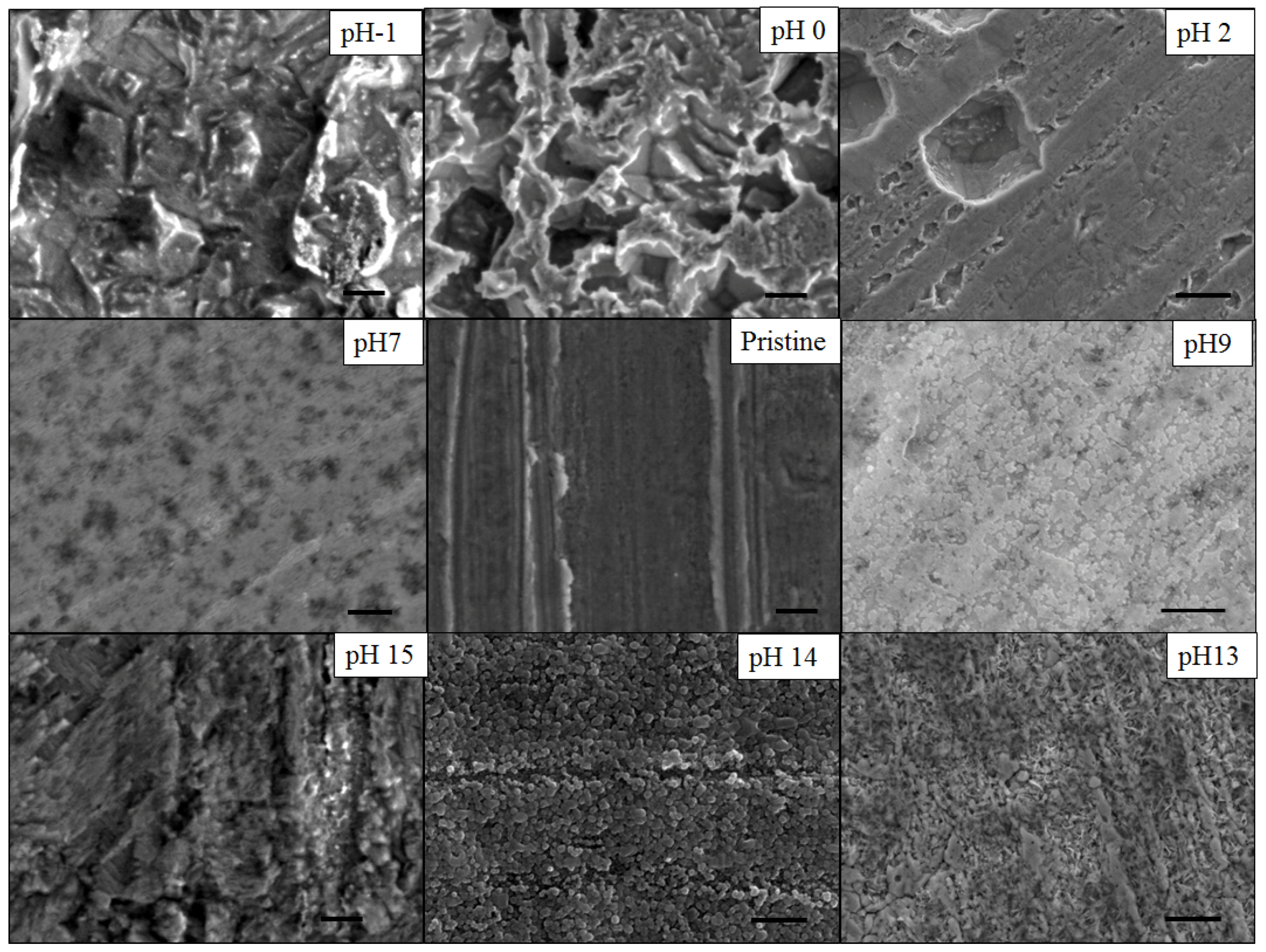

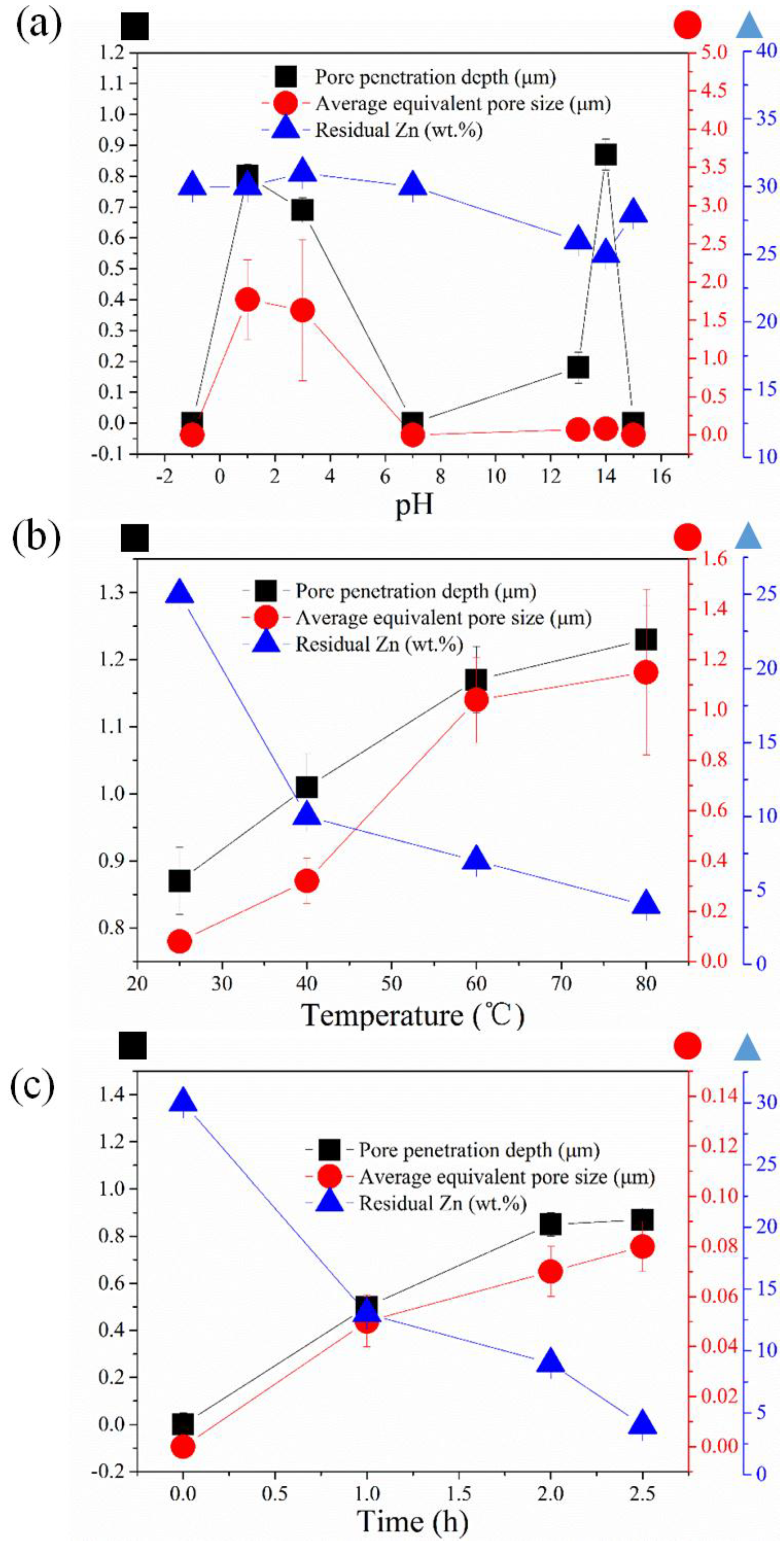
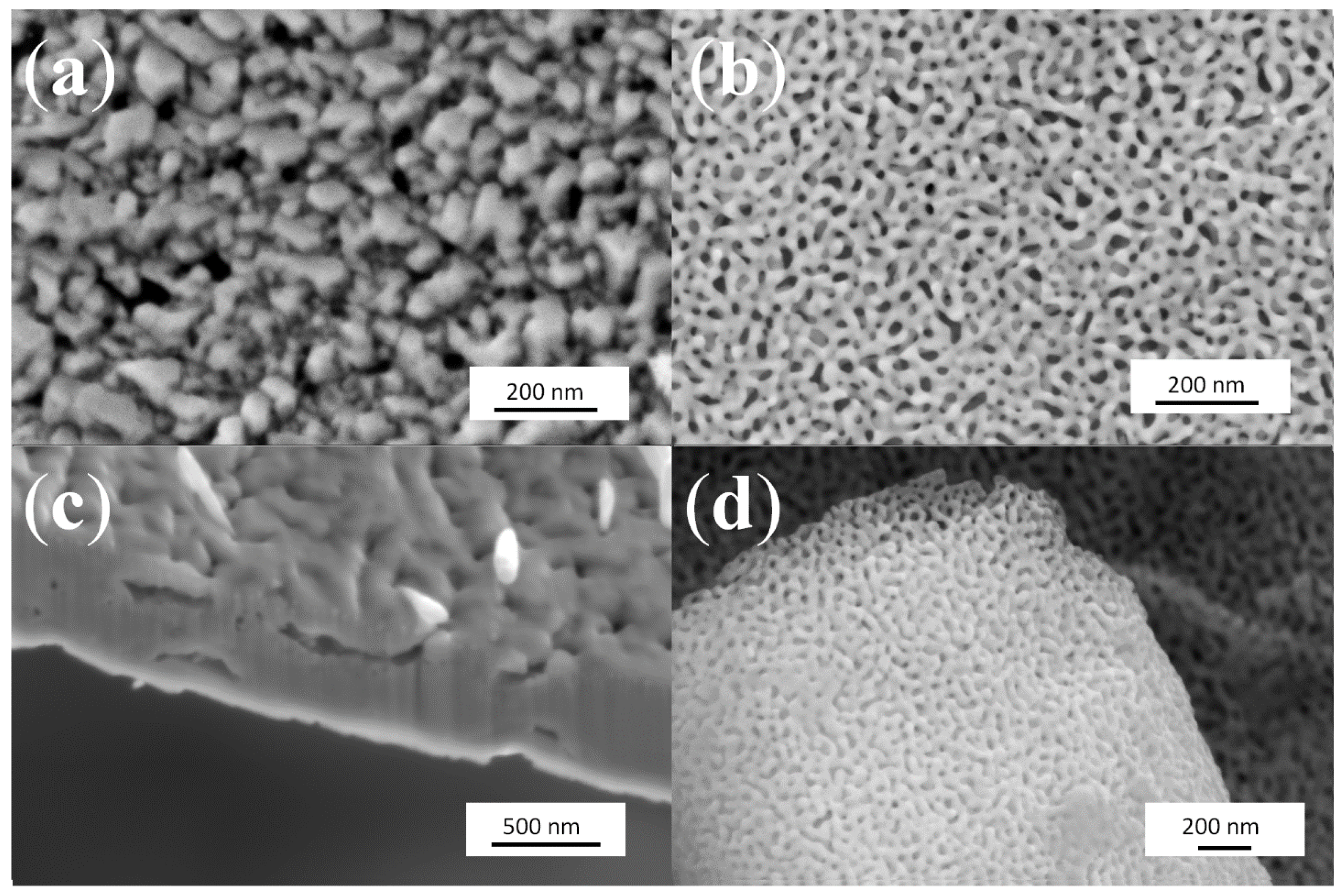
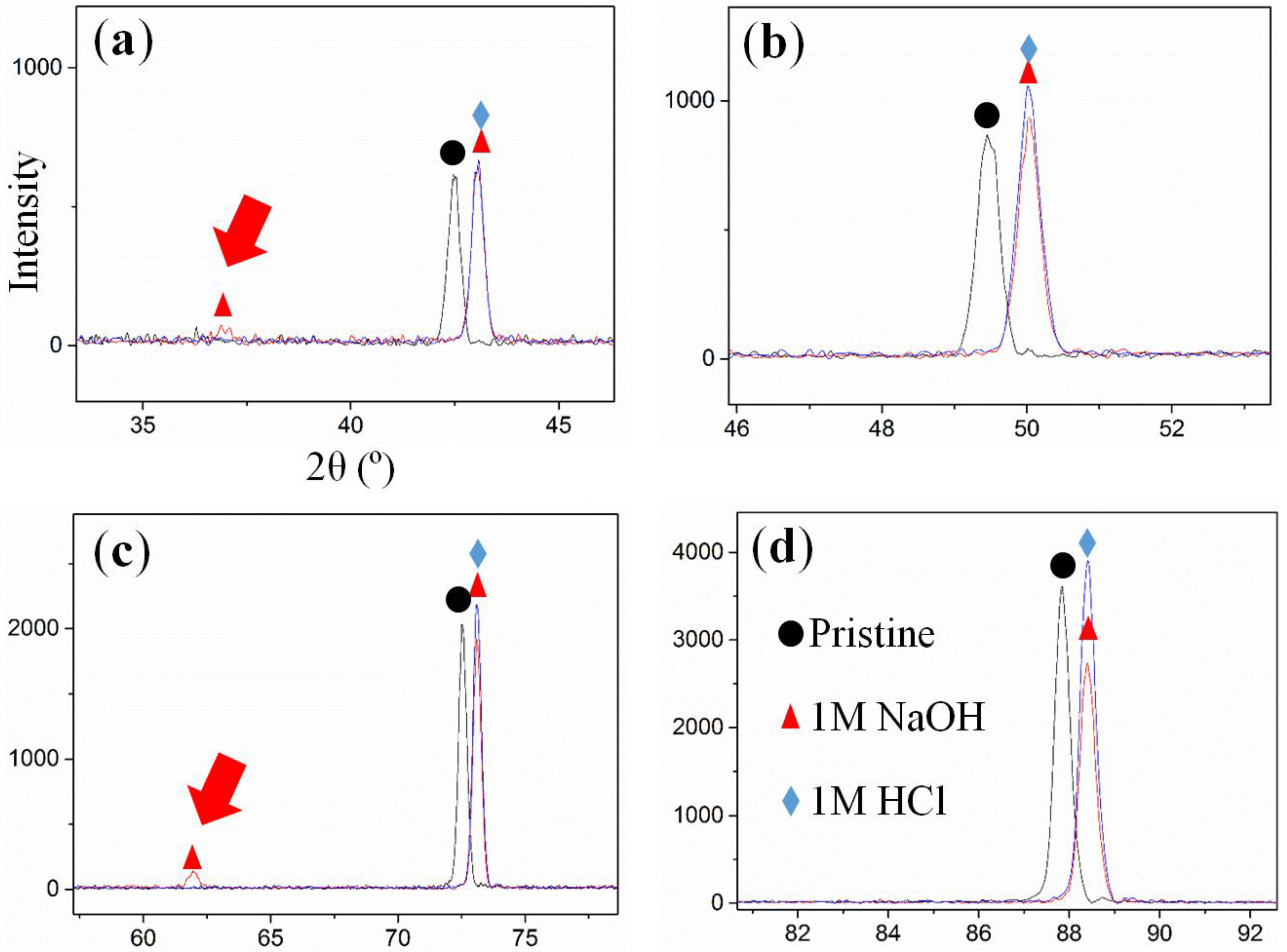
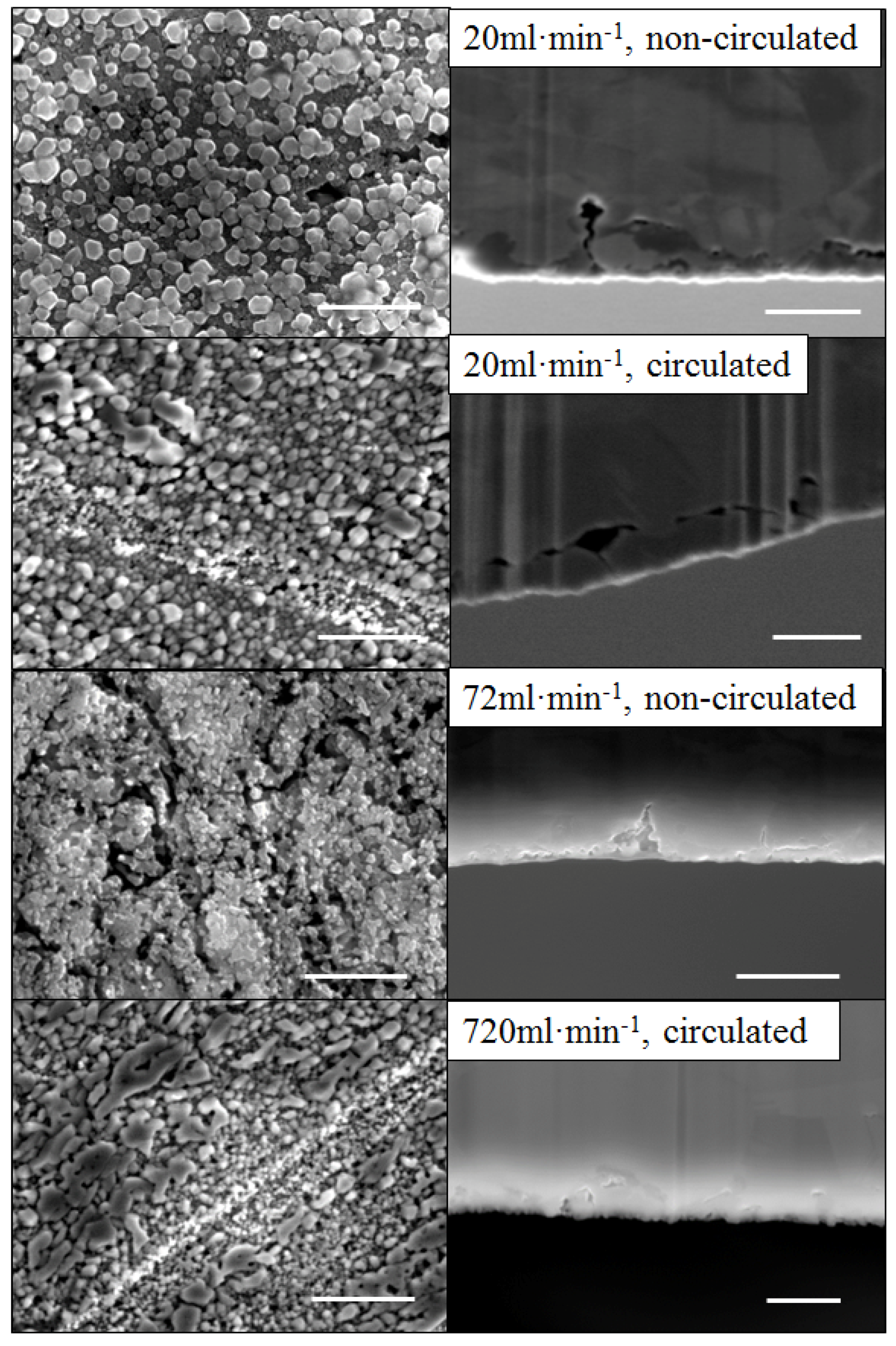
2.2. Maximum Pore Penetration and Material Thickness Change during De-Alloying
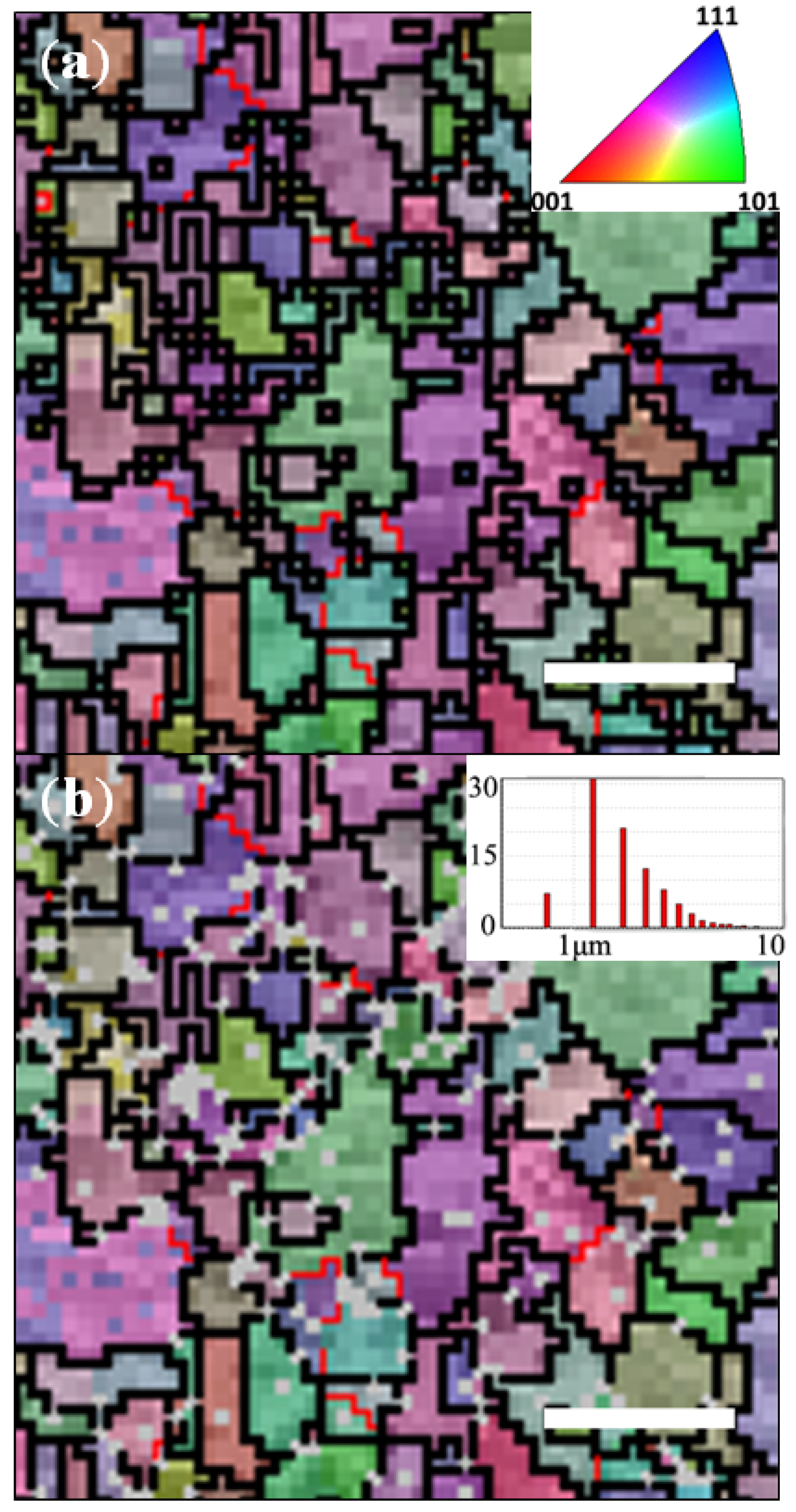
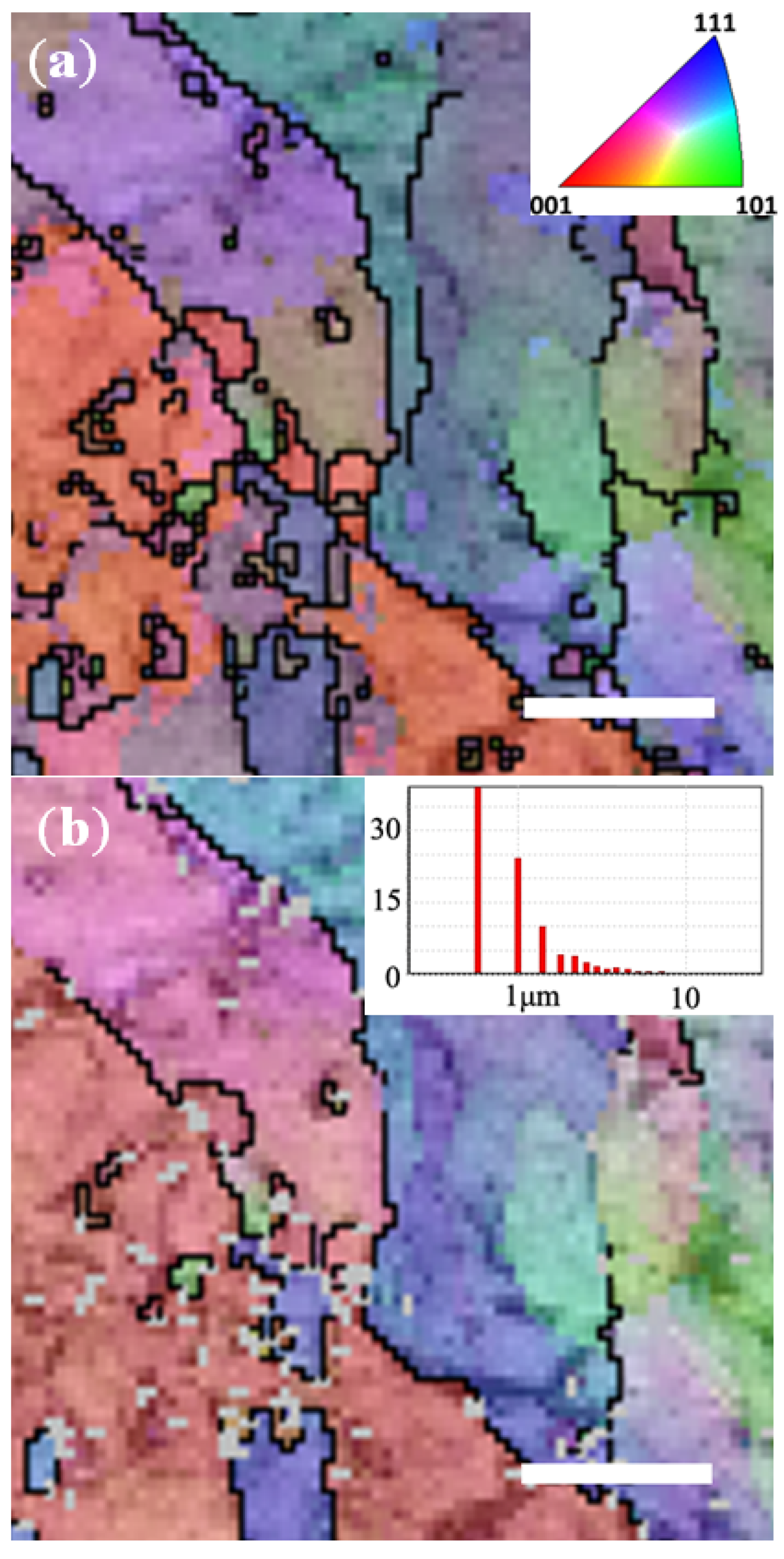
2.3. Preferential De-Alloying Regions Distinguished by Microstructure Analysis
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Pristine Alloy Materials and Chemicals
3.2. Surface Polishing
3.3. Materials Characterization Techniques
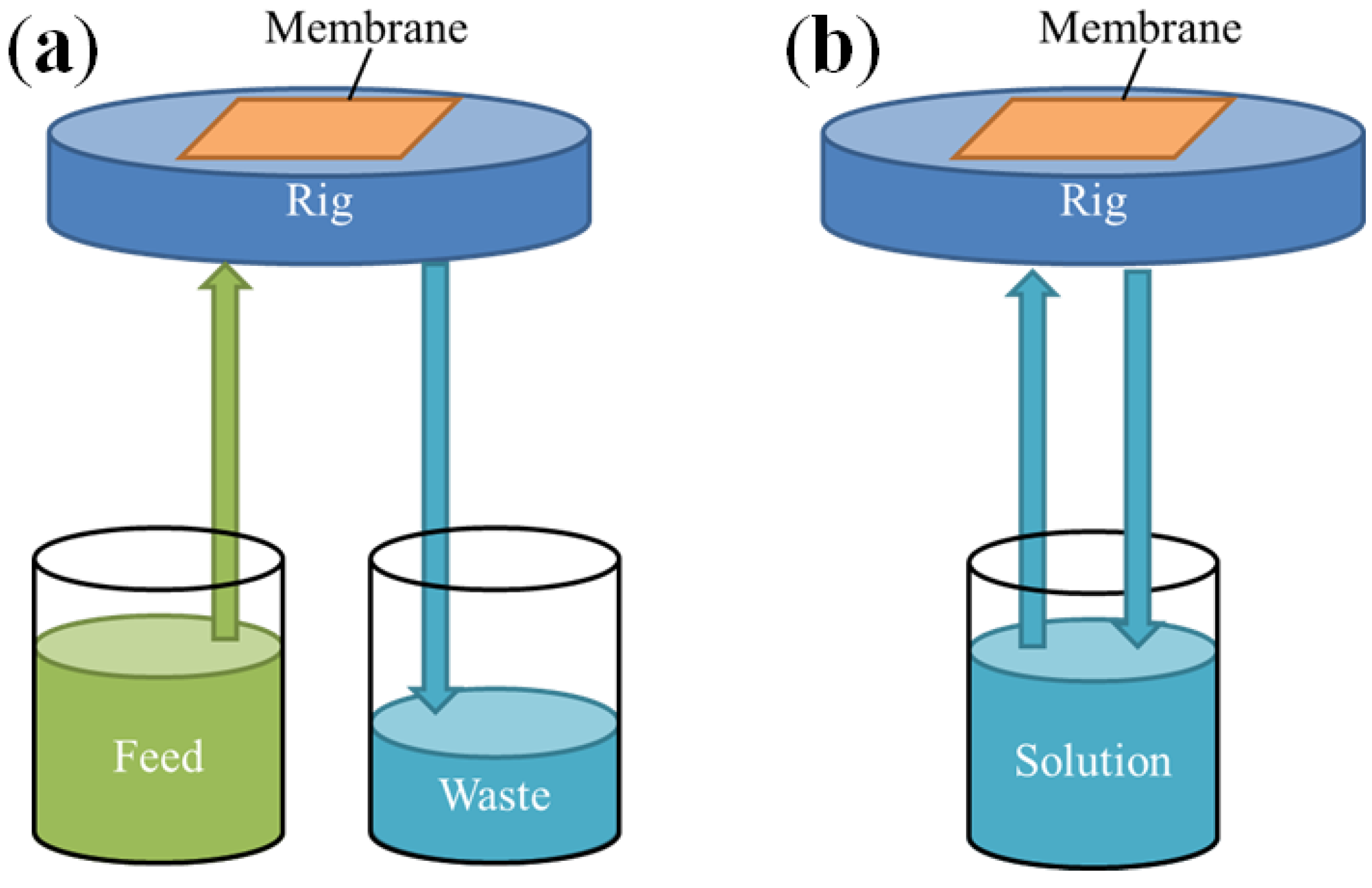
3.4. Chemical De-Alloying Process
3.4.1. Dipping De-Alloying Tests
3.4.2. Cross Flow Solution De-Alloying Tests
3.4.3. In-Position DA for Microscopy Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Authors Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dumée, L.F.; He, L.; Lin, B.; Ailloux, F.-M.; Lemoine, J.-B.; Velleman, L.; She, F.; Duke, M.C.; Orbell, J.D.; Erskine, G.; et al. The fabrication and surface functionalization of porous metal frameworks—A review. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 15185–15206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, D.; Viswanath, R.N.; Weissmüller, J. Surface-stress induced macroscopic bending of nanoporous gold cantilevers. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 793–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biener, J.; Wittstock, A.; Zepeda-Ruiz, L.; Biener, M.; Zielasek, V.; Kramer, D.; Viswanath, R.; Weissmüller, J.; Bäumer, M.; Hamza, A. Surface-chemistry-driven actuation in nanoporous gold. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.-J.; Weissmüller, J. A material with electrically tunable strength and flow stress. Science 2011, 332, 1179–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, R.; Mehta, A. An AC impedance study of the de-alloying of Fe-Ni alloys, and its relevance to chloride SCC of stainless steels. Corros. Sci. 1988, 28, 1183–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, P.; Srivastava, R.; Yu, C.; Strasser, P. In-situ, in-layer de-alloying of Pt-M intermetallics for high performance PEMFC electrode layers: MEA activity and durability studies. ECS Trans. 2007, 11, 933–939. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, R.; Mani, P.; Strasser, P. In situ voltammetric de-alloying of fuel cell catalyst electrode layer: A combined scanning electron microscope/electron probe micro-analysis study. J. Power Sources 2009, 190, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Chen, M. Nanoporous metals for catalytic and optical applications. MRS Bull. 2009, 34, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, C.M. Nanoporous metals: Fabrication strategies and advanced electrochemical applications in catalysis, sensing and energy systems. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7016–7031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittstock, A.; Zielasek, V.; Biener, J.; Friend, C.; Bäumer, M. Nanoporous gold catalysts for selective gas-phase oxidative coupling of methanol at low temperature. Science 2010, 327, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, J.; Fujita, T.; Chen, M.; Erlebacher, J. Oxygen reduction in nanoporous metal–ionic liquid composite electrocatalysts. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 904–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Calmidi, V.; Mahajan, R. Thermophysical properties of high porosity metal foams. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2002, 45, 1017–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Weissmüller, J.R. Hierarchical nested-network nanostructure by dealloying. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 5948–5954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tappan, B.C.; Steiner, S.A.; Luther, E.P. Nanoporous metal foams. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 4544–4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denny, N.R.; Li, F.; Norris, D.J.; Stein, A. In situ high temperature tem analysis of sintering in nanostructured tungsten and tungsten–molybdenum alloy photonic crystals. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 1538–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Kim, S.H.; Song, S.Y.; Do Kim, Y. Transmission electron microscopy studies of sintered Nd-Fe-B magnets prepared by cyclic sintering. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.X. Effect of interface structure on mechanical properties of advanced composite materials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 5115–5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, L.; Dotzauer, D.M.; Hogg, S.R.; Macanás, J.; Lahitte, J.-F.; Bruening, M.L. Catalytic hollow fiber membranes prepared using layer-by-layer adsorption of polyelectrolytes and metal nanoparticles. Cataly. Today 2010, 156, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapovalov, V. Porous metals. MRS Bull. 1994, 19, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumée, L.; Velleman, L.; Sears, K.; Hill, M.; Schutz, J.; Finn, N.; Duke, M.; Gray, S. Control of porosity and pore size of metal reinforced carbon nanotube membranes. Membranes 2010, 1, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumée, L.; Hill, M.R.; Duke, M.; Velleman, L.; Sears, K.; Schütz, J.; Finn, N.; Gray, S. Activation of gold decorated carbon nanotube hybrids for targeted gas adsorption and enhanced catalytic oxidation. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 9374–9378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, R.; Ma, Y.H. Pd–Ag membrane synthesis: The electroless and electro-plating conditions and their effect on the deposits morphology. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 334, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velleman, L.; Losic, D.; Shapter, J.G. The effects of surface functionality positioning on the transport properties of membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 411–412, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velleman, L.; Shapter, J.G.; Losic, D. Gold nanotube membranes functionalised with fluorinated thiols for selective molecular transport. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 328, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, H.; Li, Z.; Sai, H.; Kamperman, M.; Warren, S.C.; Wiesner, U. Block copolymer directed nanoporous metal thin films. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2010, 31, 1960–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, S.C.; Perkins, M.R.; Adams, A.M.; Kamperman, M.; Burns, A.A.; Arora, H.; Herz, E.; Suteewong, T.; Sai, H.; Li, Z.; et al. A silica sol–gel design strategy for nanostructured metallic materials. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; He, C.; Xing, W.; Li, F.; Tong, L.; Chen, Z.; Liao, X.; Steinhart, M. Nanoporous metal membranes with bicontinuous morphology from recyclable block-copolymer templates. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2068–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, S.; Wiesner, U.; Disalvo, F.J. Ordered Porous Mesostructured Materials from Nanoparticle-Block Copolymer Self-Assembly. U.S. Patent 8,569,391 B2, 29 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, F. Layer-by-layer self-assembly construction of highly ordered metal-TiO2 nanotube arrays heterostructures (M/TNTS, M = Au, Ag, Pt) with tunable catalytic activities. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 16487–16498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Sieradzki, K. Mechanisms and morphology evolution in dealloying. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 160, C226–C231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, B. Nanoporous Ag Thin Film via Evaporation and Dealloying Process. Bachelor Thesis, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Chen, Q.; McCue, I.; Snyder, J.; Crozier, P.; Erlebacher, J.; Sieradzki, K. Dealloying of noble-metal alloy nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 2569–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahn, R.W. Materials science: Percolation frustrated. Nature 1997, 389, 121–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Y.; Yu, J.S.; Fujita, T.; Chen, M.W. Nanoporous copper with tunable nanoporosity for SERS applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 1221–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, J.R.; Hodge, A.M.; Biener, J.; Hamza, A.V.; Sieradzki, K. Monolithic nanoporous copper by dealloying Mn–Cu. J. Mater. Res. 2006, 21, 2611–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakamada, M.; Mabuchi, M. Preparation of nanoporous Ni and Ni–Cu by dealloying of rolled Ni–Mn and Ni–Cu–Mn alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2009, 485, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlebacher, J. An atomistic description of dealloying porosity evolution, the critical potential, and rate-limiting behavior. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2004, 151, C614–C626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrish, R.; Dorame, K.; Muscat, A.J. Formation of nanoporous Au by dealloying AuCu thin films in HNO3. Scr. Mater. 2011, 64, 856–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Chien, C.-L.; Searson, P.C. Fabrication of nanoporous nickel by electrochemical dealloying. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 3125–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, W.; Chava, S. Fabrication of metallic nanoporous films by dealloying. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B Microelectron. Nanometer Struct. 2009, 27, 923–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battezzati, L.; Scaglione, F. De-alloying of rapidly solidified amorphous and crystalline alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2011, 509, S8–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Qi, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z. Fabrication and characterization of monolithic nanoporous copper through chemical dealloying of Mg–Cu alloys. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 2120–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, Z.; Qin, F.; Sugawara, Y.; Muto, I.; Hara, N. Fabrication of nanoporous copper by dealloying amorphous binary Ti–Cu alloys in hydrofluoric acid solutions. Intermetallics 2012, 29, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraj, J.; Park, B.J.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, W.T.; Fleury, E. Nanometer-sized porous Ti-based metallic glass. Scr. Mater. 2006, 55, 1063–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Zhao, C.; Wang, X.; Lin, J.; Shao, W.; Zhang, Z.; Bian, X. Formation and characterization of monolithic nanoporous copper by chemical dealloying of Al−Cu alloys. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 6694–6698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Parsons, R.; Jordan, J. Standard Potentials in Aqueous Solution; CRC Press: London, UK, 1985; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Bryk, M.A. Dealloying and Formation of Nanoporosity in Noble-Metal Alloys; University of Toronto: Toronto, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Li, X.G.; Cheng, Y.F. Understand the occurrence of pitting corrosion of pipeline carbon steel under cathodic polarization. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 60, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlebacher, J.; Sieradzki, K.; Karma, A.; Dimitrov, N.; Aziz, M. Evolution of nanoporosity in dealloying. Nature 2001, 410, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renner, F.; Stierle, A.; Dosch, H.; Kolb, D.; Lee, T.L.; Zegenhagen, J. In situ X-ray diffraction study of the initial dealloying and passivation of Cu3Au (111) during anodic dissolution. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, F.; Stierle, A.; Dosch, H.; Kolb, D.; Lee, T.-L.; Zegenhagen, J. Initial corrosion observed on the atomic scale. Nature 2006, 439, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dotzler, C.J.; Ingham, B.; Illy, B.N.; Wallwork, K.; Ryan, M.P.; Toney, M.F. In situ observation of strain development and porosity evolution in nanoporous gold foils. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 3938–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinnappa, R.; Mayanna, S. The dezincification of brass and its inhibition in acidic chloride and sulphate solutions. Corros. Sci. 1987, 27, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad-Allah, A.; Abou-Romia, M.; Badawy, M.; Rehan, H. Passivity of α-brass (Cu:Zn/67:33) and its breakdown in neutral and alkaline solutions containing halide ions. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1991, 21, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimer, A.M.; de Carra, M.A.S.; Rios, E.C.; Pereira, E.C.; Mascaro, L.H. Initial stages of corrosion pits on AISI 1040 steel in sulfide solution analyzed by temporal series micrographs coupled with electrochemical techniques. Corros. Sci. 2013, 76, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Balk, T.J.; Spolenak, R.; Arzt, E. Dealloying of Au–Ag thin films with a composition gradient: Influence on morphology of nanoporous au. Thin Solid Films 2007, 515, 7122–7126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickett, B.; Payer, J. Composition of copper tarnish products formed in moist air with trace levels of pollutant gas: Sulfur dioxide and sulfur dioxide/nitrogen dioxide. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1995, 142, 3713–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, C.; Kritzer, P.; Boukis, N.; Franz, G.; Dinjus, E. The corrosion of tantalum in oxidizing sub- and supercritical aqueous solutions of HCl, H2SO4 and H3PO4. J. Mater. Sci. 1999, 34, 3137–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, X.; Li, S. Synergistic mechanism of boron and arsenic in preventing dezincification of brass. Chin. Sci. Bull. 1997, 42, 1135–1139. [Google Scholar]
- Da Costa, S.L.; Agostinho, S.M.; Nobe, K. Rotating ring-disk electrode studies of Cu-Zn alloy electrodissolution in 1 M HCl effect of benzotriazole. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1993, 140, 3483–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, H.E.; Tatge, E. Standard X-ray diffraction patterns. J. Res. Natl. Bureau Stand. 1951, 46, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard Guide for Electrolytic Polishing of Metallographic Specimens; ASTM E1558-09; American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009; Volume 03.01.
- Dumee, L.F.; Sears, K.; Schütz, J.A.; Finn, N.; Duke, M.; Mudie, S.; Kirby, N.; Gray, S. Small angle X-ray scattering study of carbon nanotube forests densified into long range patterns by controlled solvent evaporation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 407, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumée, L.; Thornton, A.; Sears, K.; Schütz, J.; Finn, N.; Spoljaric, S.; Shanks, R.; Skourtis, C.; Duke, M.; Gray, S. In situ small angle X-ray scattering investigation of the thermal expansion and related structural information of carbon nanotube composites. Prog. Natl. Sci. Mater. Int. 2012, 22, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, B.; Kong, L.; Hodgson, P.D.; Dumée, L.F. Impact of the De-Alloying Kinetics and Alloy Microstructure on the Final Morphology of De-Alloyed Meso-Porous Metal Films. Nanomaterials 2014, 4, 856-878. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano4040856
Lin B, Kong L, Hodgson PD, Dumée LF. Impact of the De-Alloying Kinetics and Alloy Microstructure on the Final Morphology of De-Alloyed Meso-Porous Metal Films. Nanomaterials. 2014; 4(4):856-878. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano4040856
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Bao, Lingxue Kong, Peter D. Hodgson, and Ludovic F. Dumée. 2014. "Impact of the De-Alloying Kinetics and Alloy Microstructure on the Final Morphology of De-Alloyed Meso-Porous Metal Films" Nanomaterials 4, no. 4: 856-878. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano4040856
APA StyleLin, B., Kong, L., Hodgson, P. D., & Dumée, L. F. (2014). Impact of the De-Alloying Kinetics and Alloy Microstructure on the Final Morphology of De-Alloyed Meso-Porous Metal Films. Nanomaterials, 4(4), 856-878. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano4040856






