Encapsulation of Anti-Tuberculosis Drugs within Mesoporous Silica and Intracellular Antibacterial Activities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
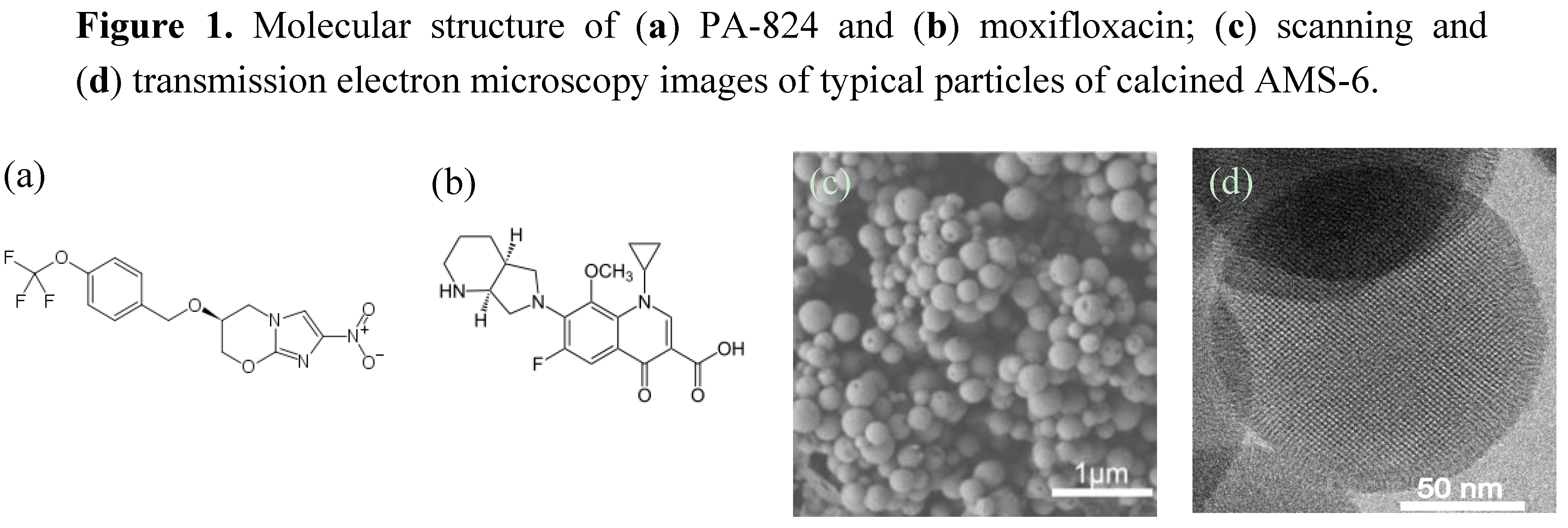
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Loading and Dissolution Studies
| Samples | Surface area (m2/g) | Pore width (Å) | Total pore volume (cm3/g) | Loading amount (wt%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMS-6 | 894 | 54.9 | 1.07 | - |
| AMS-6-PA824 | 513 | 52.0 | 0.55 | 28.0 |
| AMS-6-Moxi | 534 | 52.0 | 0.65 | 40.4 |
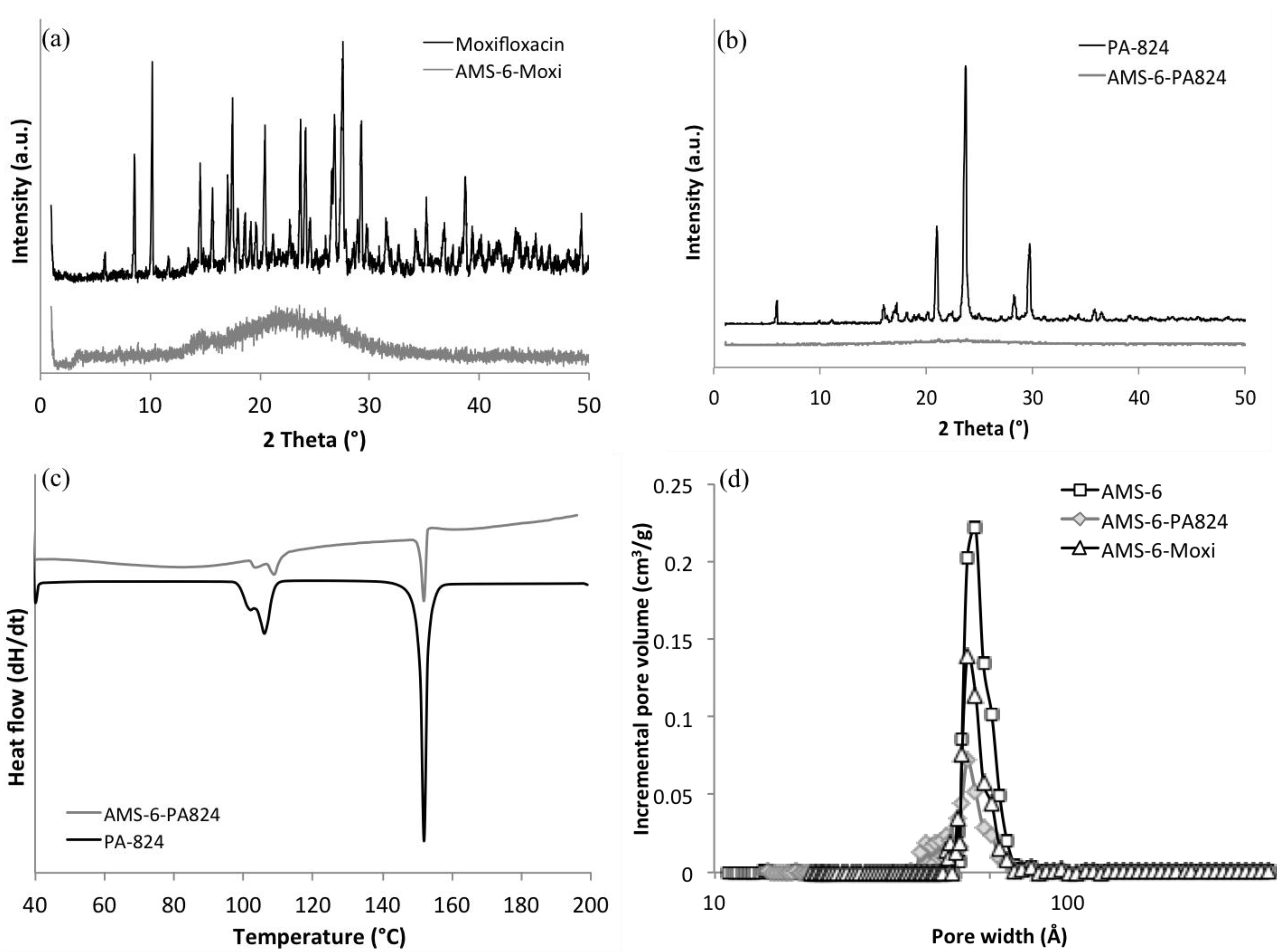

| Sample | Power law: lnF = lnkp + nlnt | Higuchi: F = kHt50%1/2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | kp | R2 | kH | t50% (h) | R2 | |
| PA-824 | 0.83 | 0.22 | 0.92 | 0.31 | 2.45 | 0.86 |
| AMS-6-PA824 | 0.09 | 0.87 | 0.94 | – | – | <0 |
2.2. Intracellular Assay
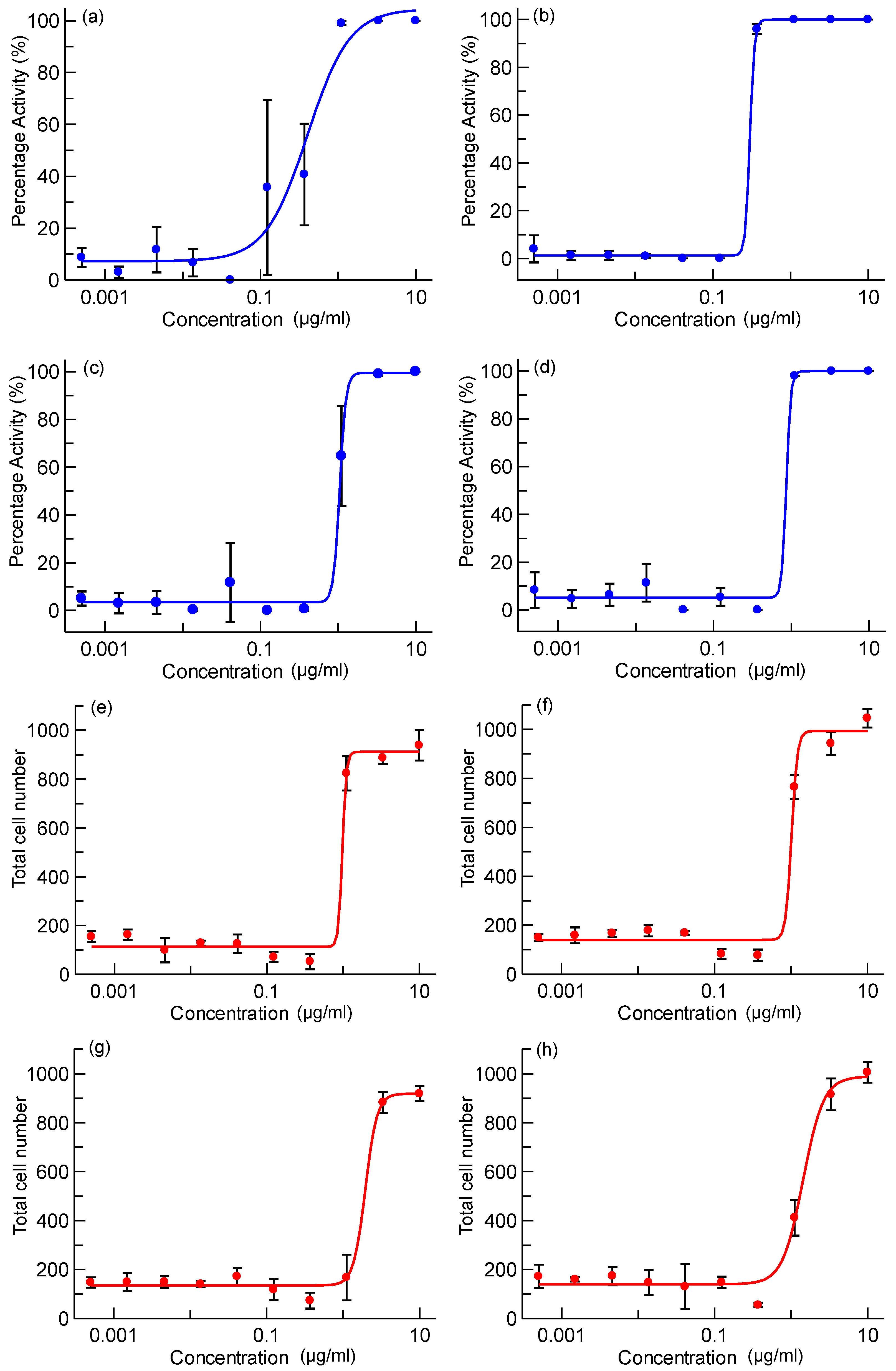

3. Experimental Section
3.1. Synthesis of AMS-6
3.2. Thermogravimetric Analysis
3.3. Nitrogen Sorption Isotherm
3.4. Media for Dissolution Experiments
3.5. Loading of Pharmaceutical Active Ingredients to Mesoporous Silica
3.6. The Release Performance of Drugs in PBS Buffer
3.7. M. tuberculosis Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Supplementary Materials
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Tuberculosis WHO Global Tuberculosis Report 2013. Available online: http://www.who.int/tb/publications/factsheet_global.pdf?ua=1.2013 (accessed on 22 March 2013).
- McGrath, M.; Gey van Pittius, N.C.; van Helden, P.D.; Warren, R.M.; Warner, D.F. Mutation rate and the emergence of drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stover, C.K.; Warrener, P.; VanDevanter, D.R.; Sherman, D.R.; Arain, T.M.; Langhorne, M.H.; Anderson, S.W.; Towell, J.A.; Yuan, Y.; McMurray, D.N.; et al. A small-molecule nitroimidazopyran drug candidate for the treatment of tuberculosis. Nature 2000, 405, 962–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenaerts, A.J.; Gruppo, V.; Marietta, K.S.; Johnson, C.M.; Driscoll, D.K.; Nicholas, M.; Rose, J.D.; Reynolds, R.C.; Ian, M.; Tompkins, N.M.; et al. Preclinical testing of the nitroimidazopyran PA-824 for activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a series of in vitro and in vivo models preclinical testing of the nitroimidazopyran PA-824 for activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a series. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 2294–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuermberger, E.; Tyagi, S.; Tasneen, R.; Williams, K.N.; Almeida, D.; Rosenthal, I.; Grosset, J.H. Powerful bactericidal and sterilizing activity of a regimen containing PA-824, moxifloxacin, and pyrazinamide in a murine model of tuberculosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 1522–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diacon, A.H.A.; Dawson, R.; von Groote-bidlingmaier, F.; Symons, G.; Venter, A.; Donald, P.R.; van Niekerk, C.; Everitt, D.; Winter, H.; Becker, P.; et al. 14-day bactericidal activity of PA-824, bedaquiline, pyrazinamide, and moxifloxacin combinations: A randomised trial. Lancet 2012, 380, 986–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwers, J.; Brewster, M.E.; Augustijns, P. Supersaturating drug delivery systems: The answer to solubility-limited oral bioavailability? J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 98, 2549–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Manjunatha, U.H.; Goodwin, M.B.; Knox, J.E.; Lipinski, C.A.; Keller, T.H.; Barry, C.E.; Dowd, C.S. Synthesis and antitubercular activity of 7-(R)- and 7-(S)-methyl-2-nitro-6-(S)-(4-(trifluoromethoxy)benzyloxy)-6,7-dihydro-5H-imidazo[2,1-b][1,3]oxazines, analogues of PA-824. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 2256–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, J.A.; Mattson, R.H.; Prevey, M.L.; Scheyer, R.D.; Ouellette, V.L. How often is medication taken as prescribed? A novel assessment technique. JAMA 1989, 261, 3273–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Sklar, G.E.; Oh, V.M.S.; Li, S.C. Factors affecting therapeutic compliance: A review from the patient’s perspective. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2008, 4, 269–286. [Google Scholar]
- Van Hest, R.; Baars, H.; Kik, S.; van Gerven, P.; Trompenaars, M.-C.; Kalisvaart, N.; Keizer, S.; Borgdorff, M.; Mensen, M.; Cobelens, F. Hepatotoxicity of rifampin-pyrazinamide and isoniazid preventive therapy and tuberculosis treatment. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 39, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellaerts, R.; Aerts, C.A.; van Humbeeck, J.; Augustijns, P.; van den Mooter, G.; Martens, J.A. Enhanced release of itraconazole from ordered mesoporous SBA-15 silica materials. Chem. Commun. (Camb) 2007, 13, 1375–1377. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, X.; Zhou, C.; Ballell, L.; Garcia-Bennett, A.E. In vivo enhancement in bioavailability of atazanavir in the presence of proton-pump inhibitors using mesoporous materials. ChemMedChem 2012, 7, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Liong, M.; Zink, J.I.; Tamanoi, F. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a delivery system for hydrophobic anticancer drugs. Small 2007, 3, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, D.L.; Lee, B.-Y.; Xue, M.; Thomas, C.R.; Meng, H.; Ferris, D.; Nel, A.E.; Zink, J.I.; Horwitz, M.A. Targeted intracellular delivery of antituberculosis drugs to Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected macrophages via functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 2535–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, N.; Galiana, I.; Mondragón, L.; Aznar, E.; Climent, E.; Cabedo, N.; Sancenón, F.; Murguía, J.R.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Marcos, M.D.; et al. Enhanced efficacy and broadening of antibacterial action of drugs via the use of capped mesoporous nanoparticles. Chemistry 2013, 19, 11167–11171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regi, M.; Ramila, A.; del Real, R.P.; Perez-Pariente, J. A new property of MCM-41: Drug delivery system. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brohede, U.; Atluri, R.; Garcia-Bennett, A.E.; Strømme, M. Sustained release from mesoporous nanoparticles: Evaluation of structural properties associated with controlled release rate. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2008, 5, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Liong, M.; Li, Z.; Zink, J.I.; Tamanoi, F. Biocompatibility, biodistribution, and drug-delivery efficiency of mesoporous silica nanoparticles for cancer therapy in animals. Small 2010, 6, 1794–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellaerts, R.; Mols, R.; Kayaert, P.; Annaert, P.; van Humbeeck, J.; van den Mooter, G.; Martens, J.A.; Augustijns, P. Ordered mesoporous silica induces pH-independent supersaturation of the basic low solubility compound itraconazole resulting in enhanced transepithelial transport. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 357, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallhov, H.; Kupferschmidt, N.; Gabrielsson, S.; Paulie, S.; Strømme, M.; Garcia-Bennett, A.E.; Scheynius, A. Adjuvant properties of mesoporous silica particles tune the development of effector T cells. Small 2012, 8, 2116–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallhov, H.; Gabrielsson, S.; Strømme, M.; Scheynius, A.; Garcia-Bennett, A.E. Mesoporous silica particles induce size dependent effects on human dendritic cells. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 3576–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chang, J. Mesoporous bioactive glasses: Structure characteristics, drug/growth factor delivery and bone regeneration application. Interface Focus 2012, 2, 292–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupferschmidt, N.; Xia, X.; Labrador, R.H.; Atluri, R.; Ballell, L.; Garcia-Bennett, A.E. In vivo oral toxicological evaluation of mesoporous silica particles. Nanomedicine (Lond) 2012, 8, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Witasp, E.; Kupferschmidt, N.; Bengtsson, L.; Hultenby, K.; Smedman, C.; Paulie, S.; Garcia-Bennett, A.E.; Fadeel, B. Efficient internalization of mesoporous silica particles of different sizes by primary human macrophages without impairment of macrophage clearance of apoptotic or antibody-opsonized target cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 239, 306–319. [Google Scholar]
- Houben, E.N.G.; Nguyen, L.; Pieters, J. Interaction of pathogenic mycobacteria with the host immune system. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2006, 9, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, C.W. Use of Kolmogorov-Johnson-Mehl-Avrami kinetics in recrystallization of metals and crystallization of metallic glasses. Acta Metall. Mater. 1990, 38, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Wakiyama, N.; Usui, F.; Ikeda, M.; Isobe, T.; Senna, M. Stability of amorphous indomethacin compounded with silica. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 226, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siepmann, J.; Peppas, N.A. Higuchi equation: Derivation, applications, use and misuse. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 418, 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- Sinko, P.J.; Singh, Y. Martin’s Physical Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 6th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; Manjunatha, U.; Boshoff, H. PA-824 kills nonreplicating mycobacterium tuberculosis by intracellular NO release. Science 2008, 322, 1392–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, I.; Salvati, A.; Dawson, K.A. Protein-nanoparticle interactions: What does the cell see? Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 546–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z.; Peloquin, C.A.; Singh, R.P.; Derendorf, H.; Tyagi, S.; Ginsberg, A.; Grosset, J.H.; Nuermberger, E.L. PA-824 exhibits time-dependent activity in a murine model of tuberculosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginsberg, A.M.; Laurenzi, M.W.; Rouse, D.J.; Whitney, K.D.; Spigelman, M.K. Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of PA-824 in healthy subjects. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 3720–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Bennett, A.E.; Terasaki, O.; Che, S.; Tatsumi, T. Structural investigations of AMS-n mesoporous materials by transmission electron microscopy. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, X.; Pethe, K.; Kim, R.; Ballell, L.; Barros, D.; Cechetto, J.; Jeon, H.; Kim, K.; Garcia-Bennett, A.E. Encapsulation of Anti-Tuberculosis Drugs within Mesoporous Silica and Intracellular Antibacterial Activities. Nanomaterials 2014, 4, 813-826. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano4030813
Xia X, Pethe K, Kim R, Ballell L, Barros D, Cechetto J, Jeon H, Kim K, Garcia-Bennett AE. Encapsulation of Anti-Tuberculosis Drugs within Mesoporous Silica and Intracellular Antibacterial Activities. Nanomaterials. 2014; 4(3):813-826. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano4030813
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Xin, Kevin Pethe, Ryangyeo Kim, Lluis Ballell, David Barros, Jonathan Cechetto, HeeKyoung Jeon, Kideok Kim, and Alfonso E. Garcia-Bennett. 2014. "Encapsulation of Anti-Tuberculosis Drugs within Mesoporous Silica and Intracellular Antibacterial Activities" Nanomaterials 4, no. 3: 813-826. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano4030813
APA StyleXia, X., Pethe, K., Kim, R., Ballell, L., Barros, D., Cechetto, J., Jeon, H., Kim, K., & Garcia-Bennett, A. E. (2014). Encapsulation of Anti-Tuberculosis Drugs within Mesoporous Silica and Intracellular Antibacterial Activities. Nanomaterials, 4(3), 813-826. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano4030813




