Biochar-Enhanced Sulfur: Mechanistic Insights into a Novel and Effective Bactericide
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of the BC
2.3. Preparation of the BC@S and S
2.4. Characterization
2.5. Evaluation of Antibacterial Effect
2.5.1. Culture and Preparation of Bacteria
2.5.2. Antibacterial Experiment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.6.1. Antibacterial Efficiency Analysis
2.6.2. Determination of Sulfur Component Content in the Reaction System
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Dispersion and Surface Morphology Analysis
3.2. Investigation of the Bactericidal Performance of Sulfur Enhanced by Biochar
3.3. Investigation into the Mechanism of Bactericidal Action Augmented by Biochar-Supported Sulfur
3.3.1. Changes in the Surface Properties of BC@S
3.3.2. Changes in Sulfur Composition in the System
3.3.3. Changes in Bacteria and Bactericidal Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abd El-Mageed, T.A.; Rady, M.M.; Taha, R.S.; Abd El Azeam, S.; Simpson, C.R.; Semida, W.M. Effects of integrated use of residual sulfur-enhanced biochar with effective microorganisms on soil properties, plant growth and short-term productivity of Capsicum annuum under salt stress. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 261, 108930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anikina, I.; Kamarova, A.; Issayeva, K.; Issakhanova, S.; Mustafayeva, N.; Insebayeva, M.; Mukhamedzhanova, A.; Khan, S.M.; Ahmad, Z.; Lho, L.H.; et al. Plant protection from virus: A review of different approaches. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1163270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttimer, C.; McAuliffe, O.; Ross, R.P.; Hill, C.; O’Mahony, J.; Coffey, A. Bacteriophages and Bacterial Plant Diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Abrahamian, P.; Carvalho, R.; Choudhary, M.; Paret, M.L.; Vallad, G.E.; Jones, J.B. Future of Bacterial Disease Management in Crop. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2022, 60, 259–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.R.; Singh, D.; Singh, R. Biological control of postharvest diseases of fruits and vegetables by microbial antagonists: A review. Biol. Control 2009, 50, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabri, M.; El Handi, K.; El Tousy, A.; De Stradis, A.; Elbeaino, T. Synergistic antibacterial activity of Lactococcus lactis and Xylella phage MATE 2 for an effective biocontrol strategy against black rot disease in broccoli. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1468792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincelli, P. Genetic Engineering and Sustainable Crop Disease Management: Opportunities for Case-by-Case Decision-Making. Sustainability 2016, 8, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juroszek, P.; Racca, P.; Link, S.; Farhumand, J.; Kleinhenz, B. Overview on the review articles published during the past 30 years relating to the potential climate change effects on plant pathogens and crop disease risks. Plant Pathol. 2019, 69, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Borgatta, J.; Hudson, B.G.; Tamijani, A.A.; De La Torre-Roche, R.; Zuverza-Mena, N.; Shen, Y.; Elmer, W.; Xing, B.; Mason, S.E.; et al. Advanced material modulation of nutritional and phytohormone status alleviates damage from soybean sudden death syndrome. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, R.; Wilcockson, S.; Koocheki, A.; Leifert, C. Soil management for sustainable crop disease control: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2008, 6, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, Y.F.; Eloi, A.C.L.; de Freitas, H.M.M.; Soares, E.G.O.; Rivillo, D.; Demetrio da Silva, V.; Schrekker, H.S.; Badel, J.L. Imidazolium salts as alternative compounds to control diseases caused by plant pathogenic bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 128, 1236–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Choi, K.S.; Kim, S.; Gwon, Y.; Kim, J. Graphene Oxide-Assisted Promotion of Plant Growth and Stability. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trdá, L.; Janda, M.; Macková, D.; Pospíchalová, R.; Dobrev, P.I.; Burketová, L.; Matušinsky, P. Dual Mode of the Saponin Aescin in Plant Protection: Antifungal Agent and Plant Defense Elicitor. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 01448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, R.M. Elemental sulphur as an induced antifungal substance in plant defence. J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 1947–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.J.; Paria, S. Use of sulfur nanoparticles as a green pesticide on Fusarium solani and Venturia inaequalis phytopathogens. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 10471–10478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, H.; Kawano, G.; Nagasawa, H.; Sakuda, S. Isolation of Elemental Sulfur as a Self-Growth-Inhibiting Substance Produced by Legionella pneumophila. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 4809–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy Choudhury, S.; Ghosh, M.; Mandal, A.; Chakravorty, D.; Pal, M.; Pradhan, S.; Goswami, A. Surface-modified sulfur nanoparticles: An effective antifungal agent against Aspergillus niger and Fusarium oxysporum. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 90, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.-J.; Pamer, E.G. A spoonful of sugar could be the medicine. Nature 2017, 546, 479–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Shalabayev, Z.; Baláž, M.; Daneu, N.; Dutková, E.; Bujňáková, Z.; Kaňuchová, M.; Danková, Z.; Balážová, Ĺ.; Urakaev, F.; Tkáčiková, Ĺ.; et al. Sulfur-Mediated Mechanochemical Synthesis of Spherical and Needle-Like Copper Sulfide Nanocrystals with Antibacterial Activity. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 12897–12909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dop, R.A.; Neill, D.R.; Hasell, T. Sulfur-Polymer Nanoparticles: Preparation and Antibacterial Activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 20822–20832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Sun, Y.; Sun, Z.; Yang, M.; Gui, R. Zero-dimensional sulfur nanomaterials: Synthesis, modifications and applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 438, 213913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libenson, L.; Hadley, F.P.; McIlroy, A.P.; Wetzel, V.M.; Mellon, R.R. Antibacterial effect of elemental sulfur. J. Infect. Dis. 1953, 93, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Ingle, A.P.; Paralikar, P. Sulfur and sulfur nanoparticles as potential antimicrobials: From traditional medicine to nanomedicine. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2016, 14, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, S.; Pangeni, R.; Park, J.W.; Rhim, J.-W. Preparation of sulfur nanoparticles and their antibacterial activity and cytotoxic effect. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. Biol. Appl. 2018, 92, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardhi, D.M.; Karaman, D.S.; Timonen, J.; Wu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Satija, S.; Mehta, M.; Charbe, N.; McCarron, P.A.; Tambuwala, M.M.; et al. Anti-bacterial activity of inorganic nanomaterials and their antimicrobial peptide conjugates against resistant and non-resistant pathogens. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 586, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.Z.; Wu, Z.Y.; Liu, L.; Cui, W.; Du, D.L.; Xue, Y.L. NIR light responsive MoS2 nanomaterials for rapid sterilization: Optimum photothermal effect via sulfur vacancy modulation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Lee, K.T.; Nazar, L.F. A highly ordered nanostructured carbon–sulphur cathode for lithium–sulphur batteries. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D.; Sarswat, A.; Ok, Y.S.; Pittman, C.U. Organic and inorganic contaminants removal from water with biochar, a renewable, low cost and sustainable adsorbent—A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 160, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiluweit, M.; Nico, P.S.; Johnson, M.G.; Kleber, M. Dynamic Molecular Structure of Plant Biomass-Derived Black Carbon (Biochar). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.W.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Z.H.; Sui, Y.L.; Zhang, X.P.; Wu, L. Cassia seed-derived N-P double-doped porous carbon as an efficient sulfur host material for high-performance Li-S batteries. Adv. Powder Technol. 2024, 35, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.X.; Wang, B.M.; Sui, D.P.; Wang, C.T.; Hua, Y.J. Electrochemical coverage of reduced graphene oxide layers on sulfur supported by biochar for enhancing performance of Li-S battery. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 395, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajib, S.K. Preparation and Characterization of Activated Biochar for Lithium-Sulfur Battery Application. Master’s Thesis, Auburn University, AL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.Q.; Li, Q.W.; Hou, J.B.; Zhao, H.Z. Porous 3D graphene-based biochar materials with high areal sulfur loading for lithium-sulfur batteries. Sustain. Energ. Fuels 2018, 2, 2197–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, S.; Banik, C.; Laird, D.A. Estimating the organic oxygen content of biochar. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Chen, Z.M.; Chen, B.L. H/C atomic ratio as a smart linkage between pyrolytic temperatures, aromatic clusters and sorption properties of biochars derived from diverse precursory materials. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Jia, L.T.; Zhu, Y.; Hou, B.; Li, D.B.; Sun, Y.H. Novel preparation of nitrogen-doped graphene in various forms with aqueous ammonia under mild conditions. Rsc. Adv. 2012, 2, 11249–11252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.-F.; Peng, Y.; Wei, J.; Peng, J.; Lin, X.-Y.; Tang, M.-X.; Cheng, Y.; Men, Z.; Fang, T.; Zhang, J.; et al. Microphysical complexity of black carbon particles restricts their warming potential. One Earth 2024, 7, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yang, P.; Kots, P.A.; Cohen, M.; Chen, Y.; Quinn, C.M.; De Mello, M.D.; Anibal Boscoboinik, J.; Shaw, W.J.; Caratzoulas, S.; et al. Tuning the reactivity of carbon surfaces with oxygen-containing functional groups. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimov, B.A.; Sinegovskaya, L.M.; Gusarova, N.K. Vibrations of the S-S bond in elemental sulfur and organic polysulfides: A structural guide. J. Sulfur. Chem. 2009, 30, 518–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McShan, D.; Yu, H.T. DNA damage in human skin keratinocytes caused by multiwalled carbon nanotubes with carboxylate functionalization. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2014, 30, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursini, C.L.; Cavallo, D.; Fresegna, A.M.; Ciervo, A.; Maiello, R.; Casciardi, S.; Tombolini, F.; Buresti, G.; Iavicoli, S. Study of Cytotoxic and Genotoxic Effects of Hydroxyl-Functionalized Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes on Human Pulmonary Cells. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Si, W.Y.; He, J.J.; Sun, L.; Zhang, C.F.; Wang, N.; Yang, Z.; Li, X.D.; Wang, X.; Deng, W.Q.; et al. Selectively nitrogen-doped carbon materials as superior metal-free catalysts for oxygen reduction. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majid, S.; Ali, A.S.G.; Taieb, S.; Mehran, A.G.; Asim, M.; Shayan, J.; Reza, R.; Meng, X.M.; Jin, Z.; Ge, Q. A review of nitrogen-doped carbon materials for lithium-ion battery anodes. Carbon 2023, 209, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.J.; Umeh, A.; Iyengar, G.A.; Qi, F.J.; Naidu, R. A critical review of different types of biochar-based catalysts and mechanisms in advanced oxidation processes for organic contaminants removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, L.J.; Liu, R.F.; Xu, S.Y.; Mohamed, B.A.; Yang, Z.Q.; Hu, Y.C.; Chen, J.F.; Zhao, S.L.; Wu, Z.B.; Peng, H.Y.; et al. An overview of sulfur-functional groups in biochar from pyrolysis of biomass. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallemans, N.; Howey, D.; Battistel, A.; Saniee, N.F.; Scarpioni, F.; Wouters, B.; La Mantia, F.; Hubin, A.; Widanage, W.D.; Lataire, J. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy beyond linearity and stationarity—A critical review. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 466, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meddings, N.; Heinrich, M.; Overney, F.; Lee, J.S.; Ruiz, V.; Napolitano, E.; Seitz, S.; Hinds, G.; Raccichini, R.; Gabers, M.; et al. Application of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy to commercial Li-ion cells: A review. J. Power Sources 2020, 480, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Guan, L.Q.; Wen, Y.J.; Su, L.Z.; Hu, Z.; Peng, Z.J.; Li, S.K.; Tang, Q.Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, N. Rice husk biochar mediated red phosphorus for photocatalysis and photothermal removal of E. coli. Food Chem. 2023, 410, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

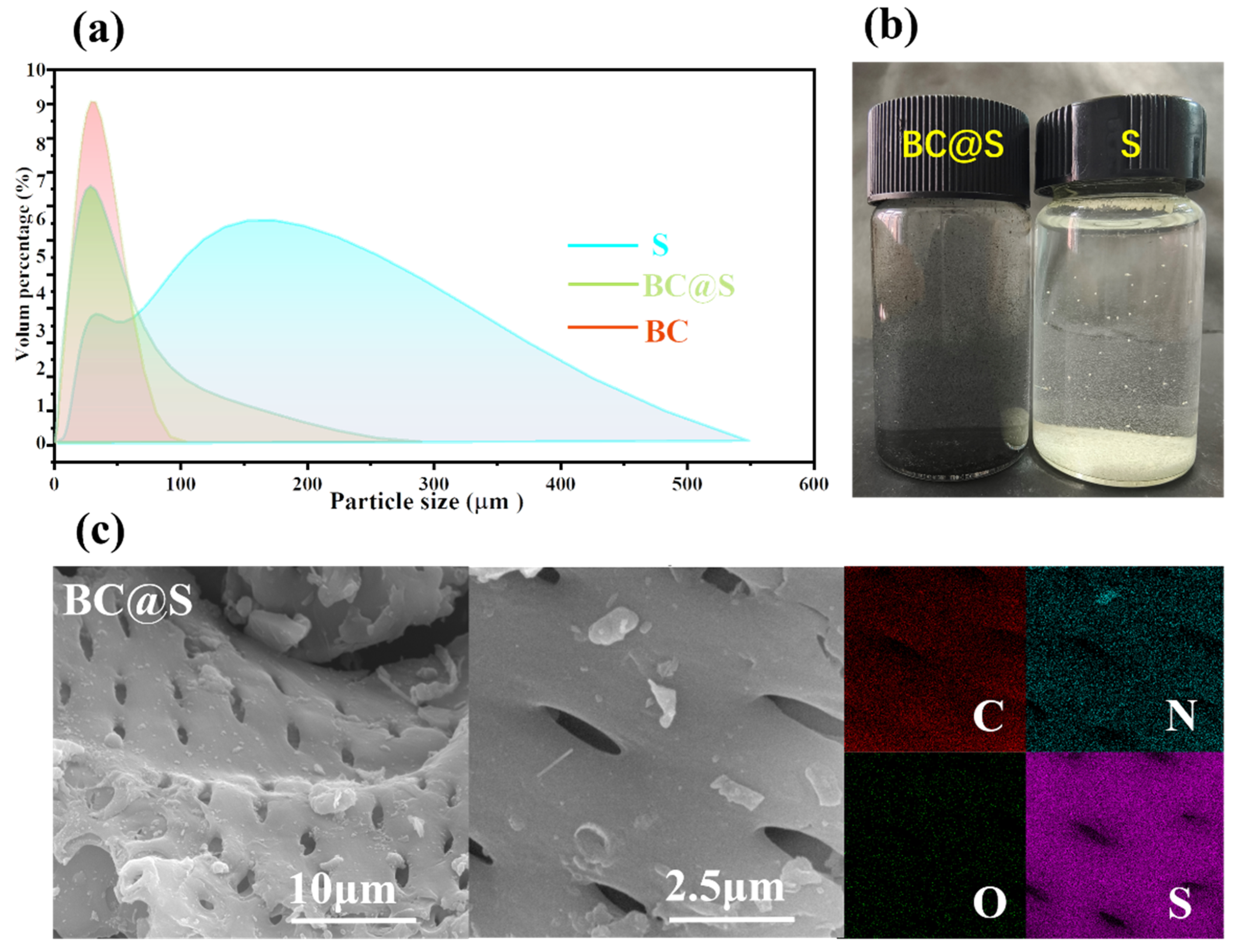
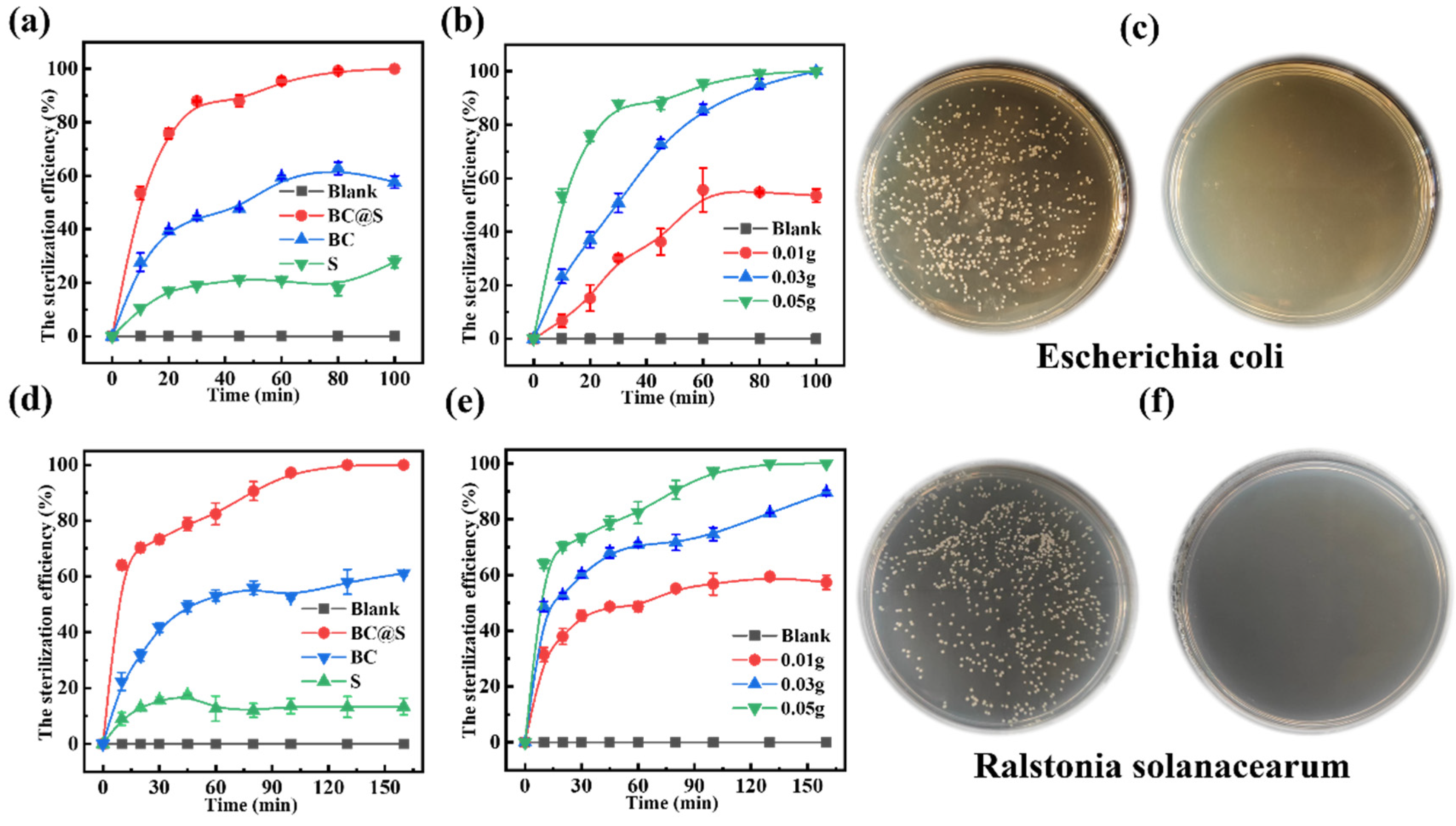

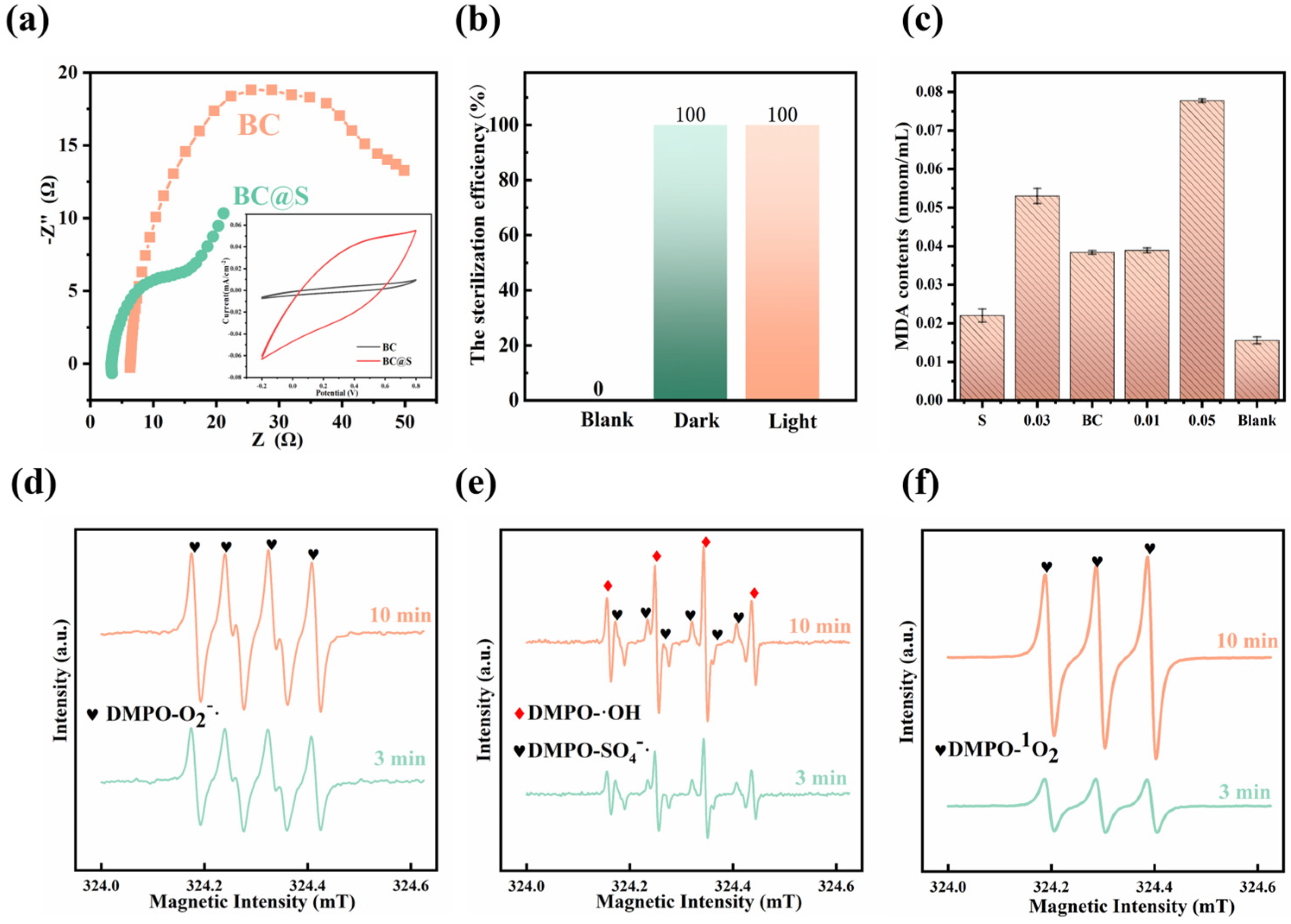
| Elemental Composition (%) | Atomic Ratio (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | C | H | O | S | (O + N)/C | H/C | O/C | |
| BC | 1.17 | 70.81 | 2.43 | 25.02 | 0.57 | 0.37 | 0.03 | 0.35 |
| BC@S | 1.18 | 56.42 | 1.30 | 13.72 | 27.39 | 0.26 | 0.02 | 0.24 |
| S2− | SxOy | SO42− | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before (g·L−1) | 0.0483 ± 0.0032 | 0.3608 ± 0.0173 | 0.1392 ± 0.0355 |
| After (g·L−1) | 0.0464 ± 0.0016 | 0.3762 ± 0.0151 | 0.1444 ± 0.0216 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, Y.; Su, L.; Liu, M.; Zeng, C.; Xiang, B.; Xie, Z.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, N. Biochar-Enhanced Sulfur: Mechanistic Insights into a Novel and Effective Bactericide. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15090697
Peng Y, Su L, Liu M, Zeng C, Xiang B, Xie Z, Hu Z, Zhou N. Biochar-Enhanced Sulfur: Mechanistic Insights into a Novel and Effective Bactericide. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(9):697. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15090697
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Yuanqi, Lezhu Su, Meng Liu, Chen Zeng, Bo Xiang, Zhuoyao Xie, Zijing Hu, and Nan Zhou. 2025. "Biochar-Enhanced Sulfur: Mechanistic Insights into a Novel and Effective Bactericide" Nanomaterials 15, no. 9: 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15090697
APA StylePeng, Y., Su, L., Liu, M., Zeng, C., Xiang, B., Xie, Z., Hu, Z., & Zhou, N. (2025). Biochar-Enhanced Sulfur: Mechanistic Insights into a Novel and Effective Bactericide. Nanomaterials, 15(9), 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15090697








