Synergistic Removal of Cr(VI) Utilizing Oxalated-Modified Zero-Valent Iron: Enhanced Electron Selectivity and Dynamic Fe(II) Regeneration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Preparation of Oxalated nFe0
2.3. Batch Experiments of Cr(VI) Removal
2.4. Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
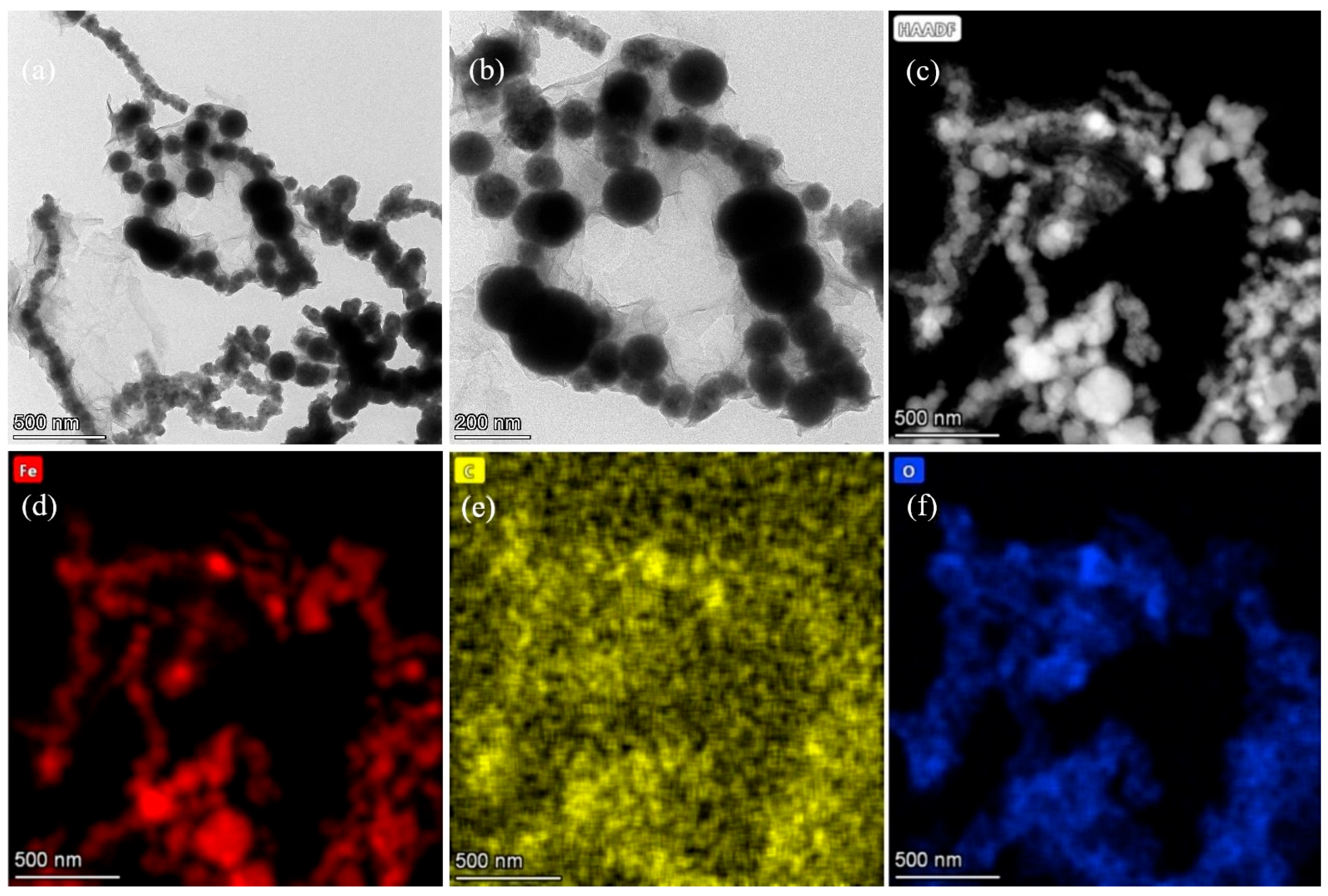
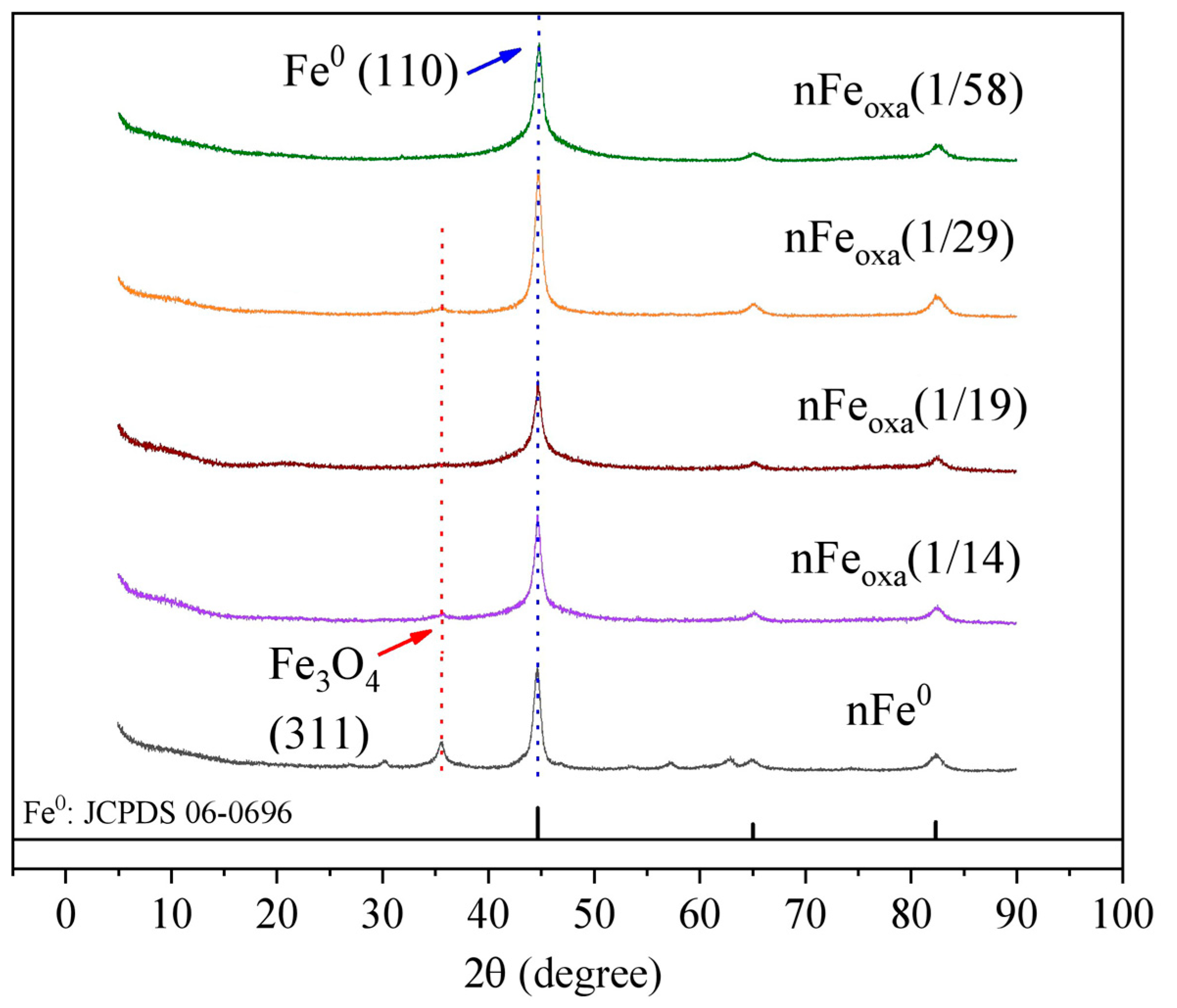
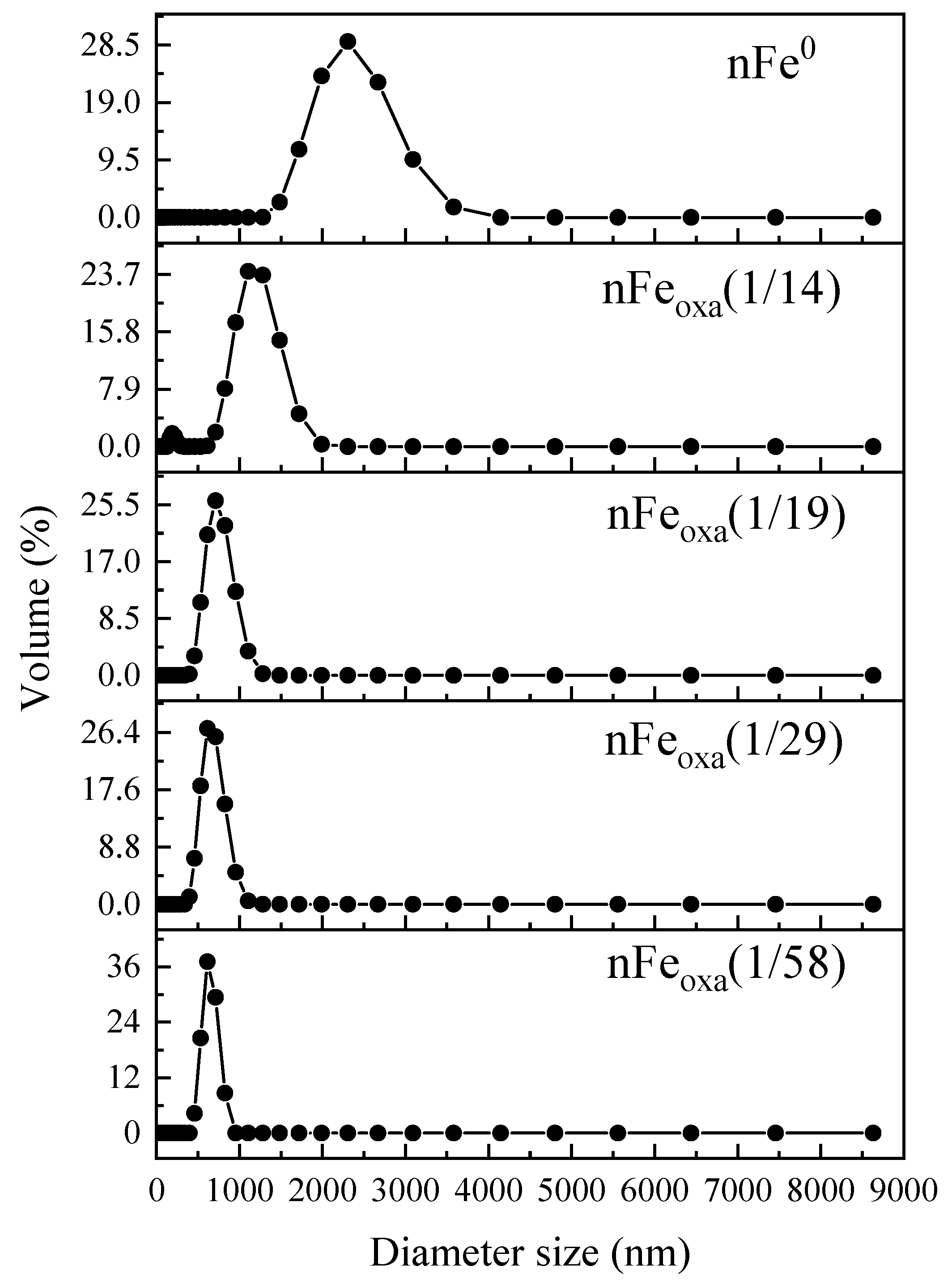
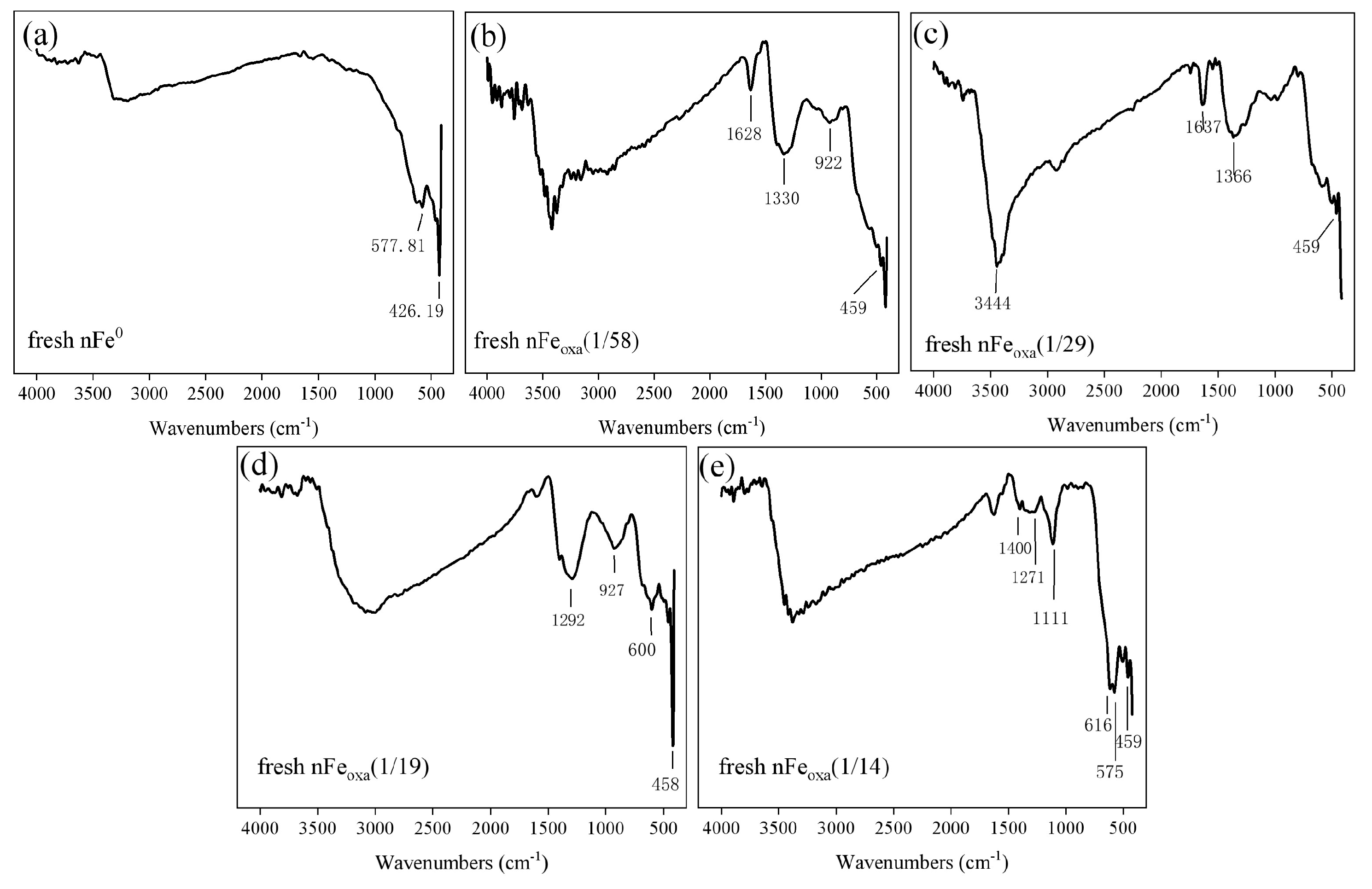
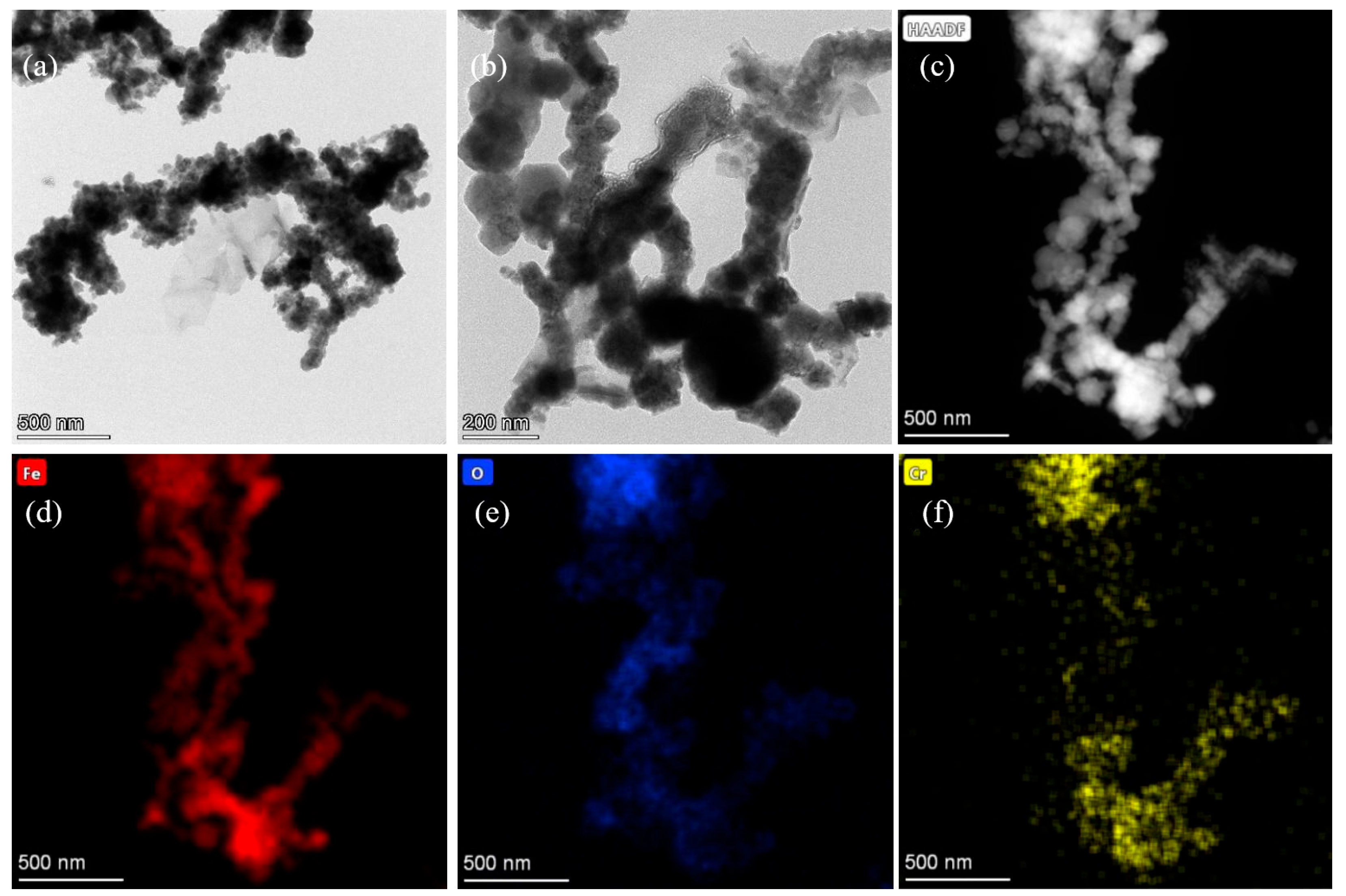
3.1. Characterization of nFeoxa
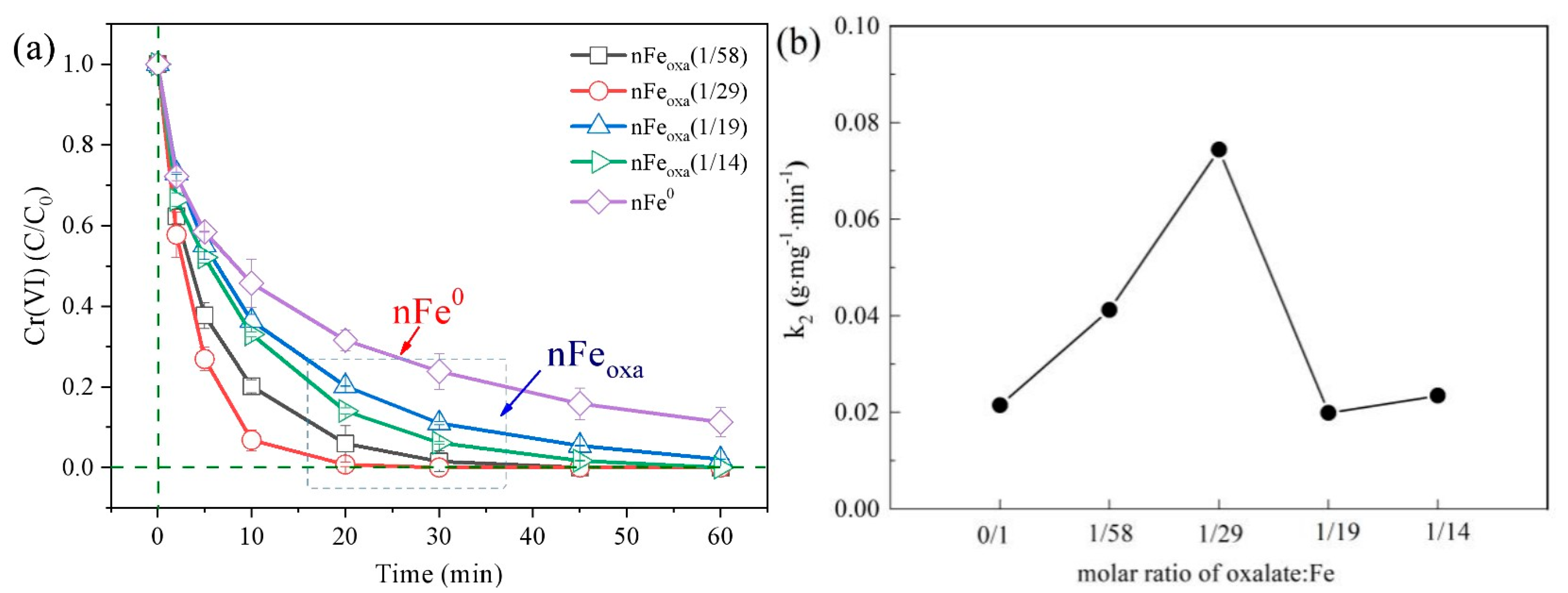
3.2. Effect of Different S/Fe Molar Ratios
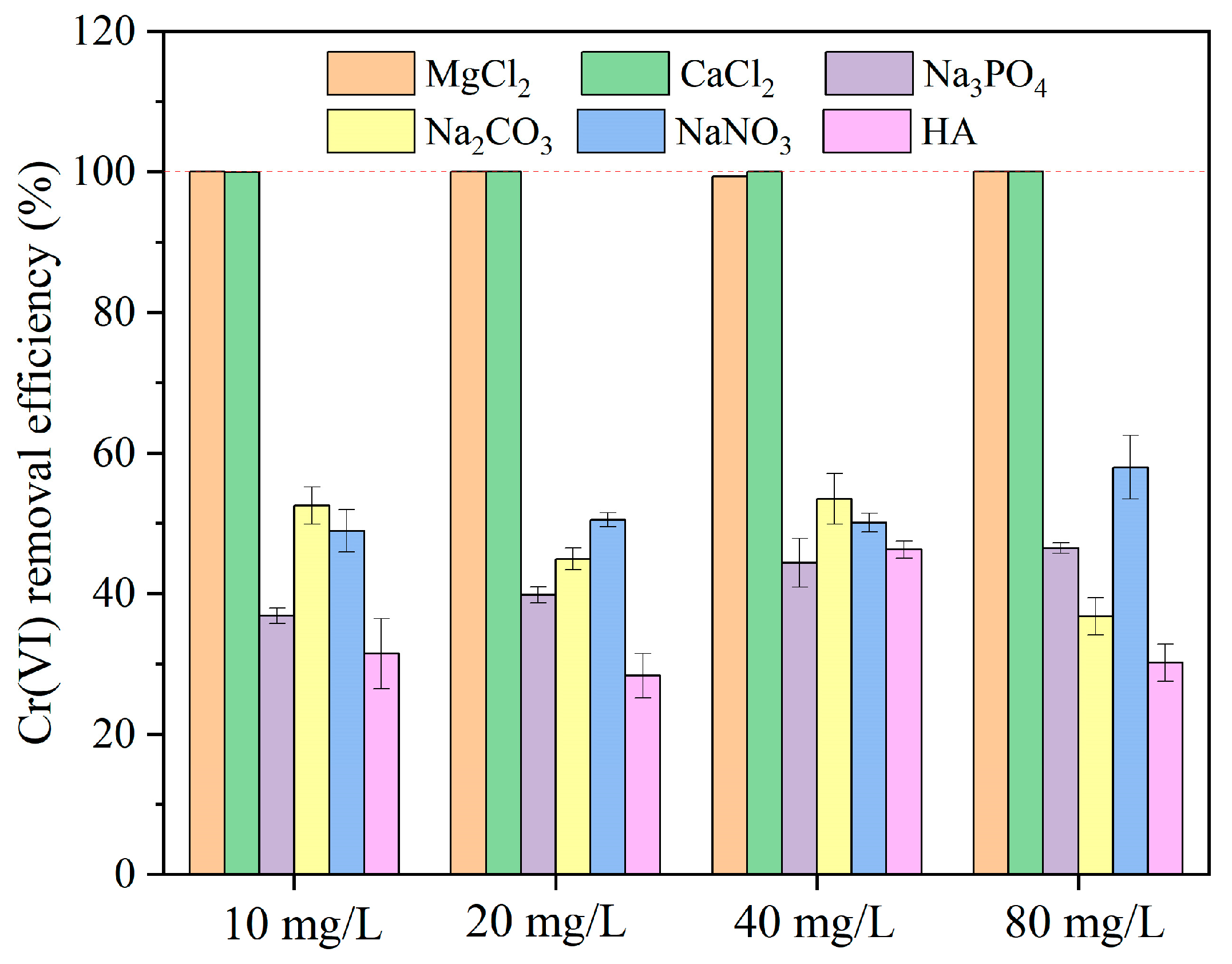
3.3. Effect of Co-Existing Ions and Humic Acid
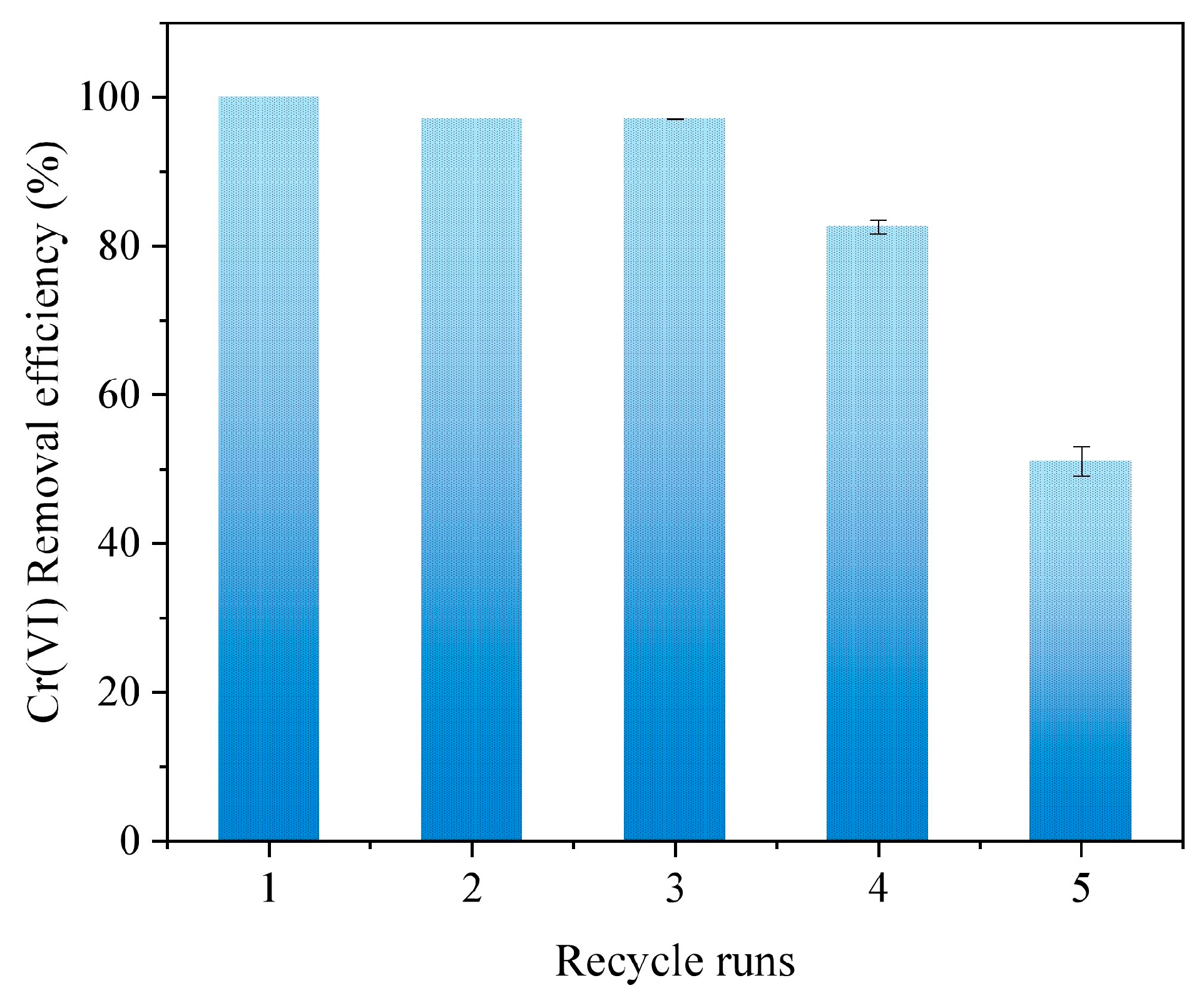
3.4. Reusability
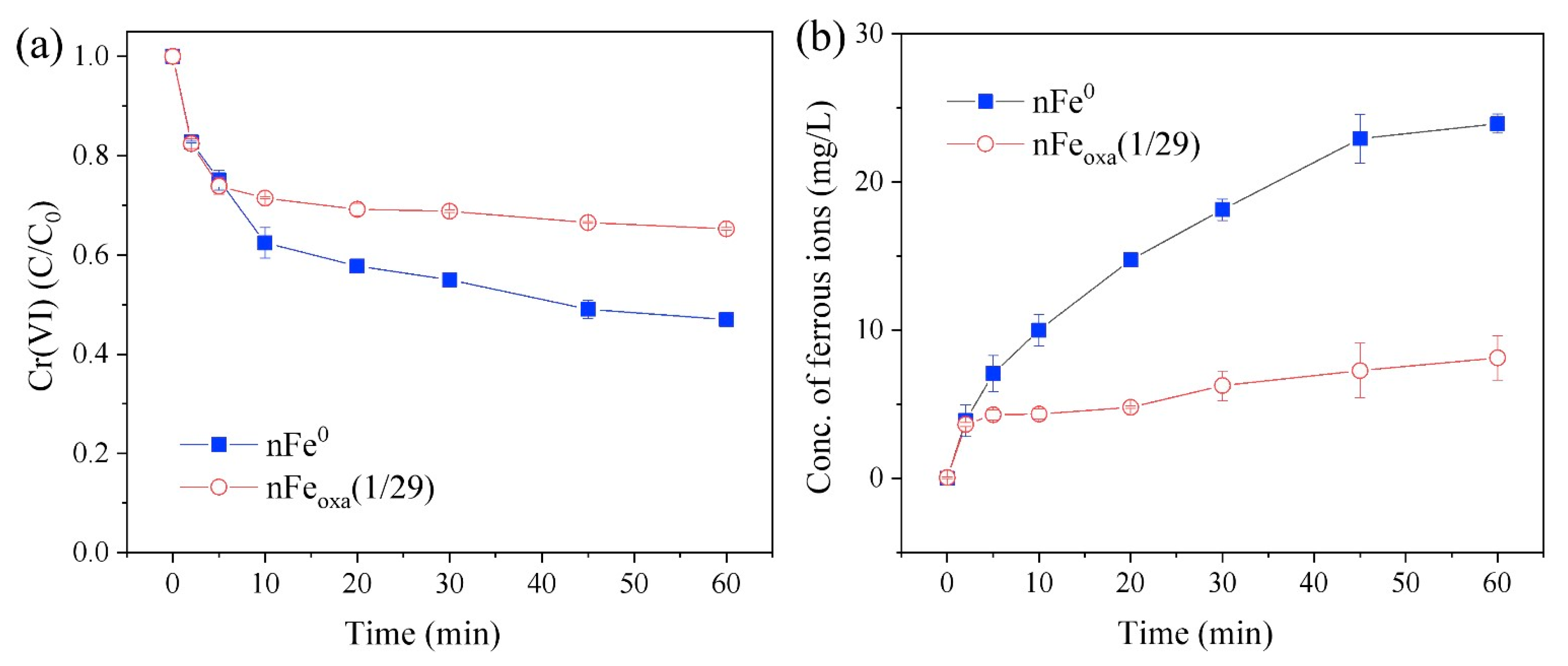
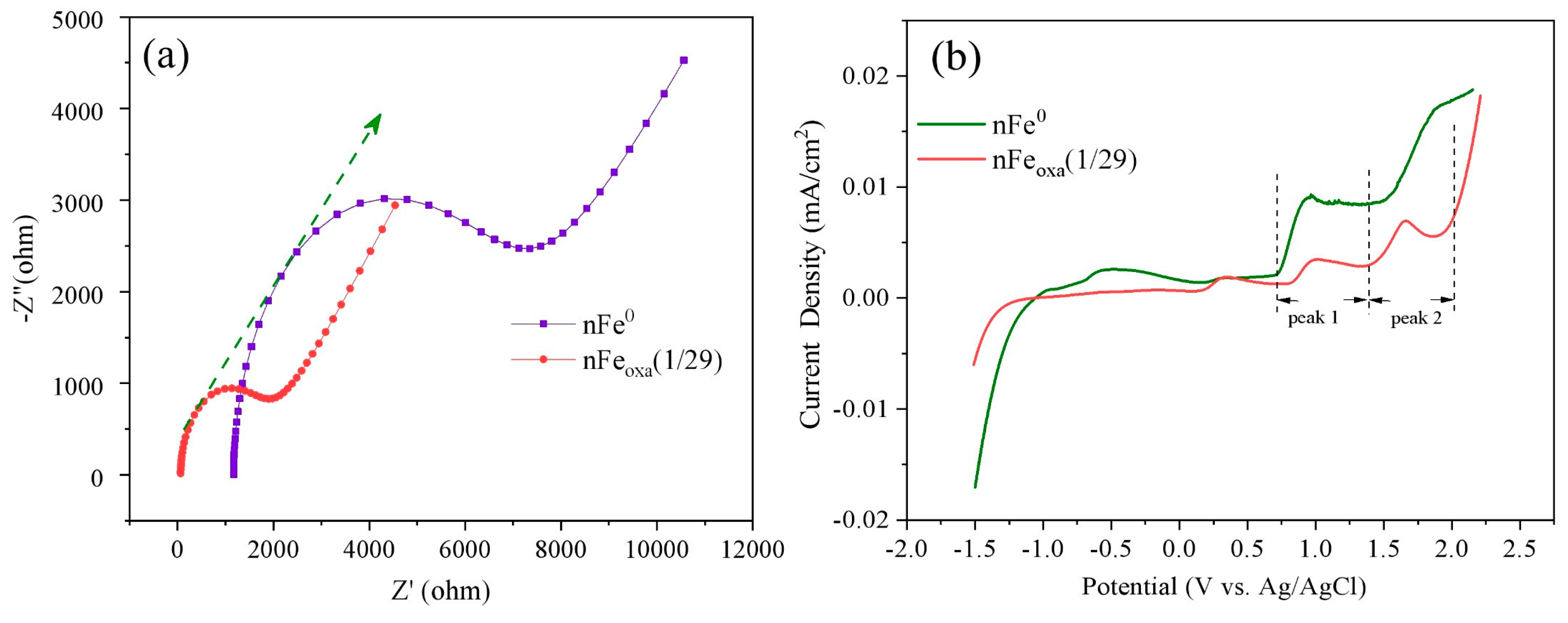
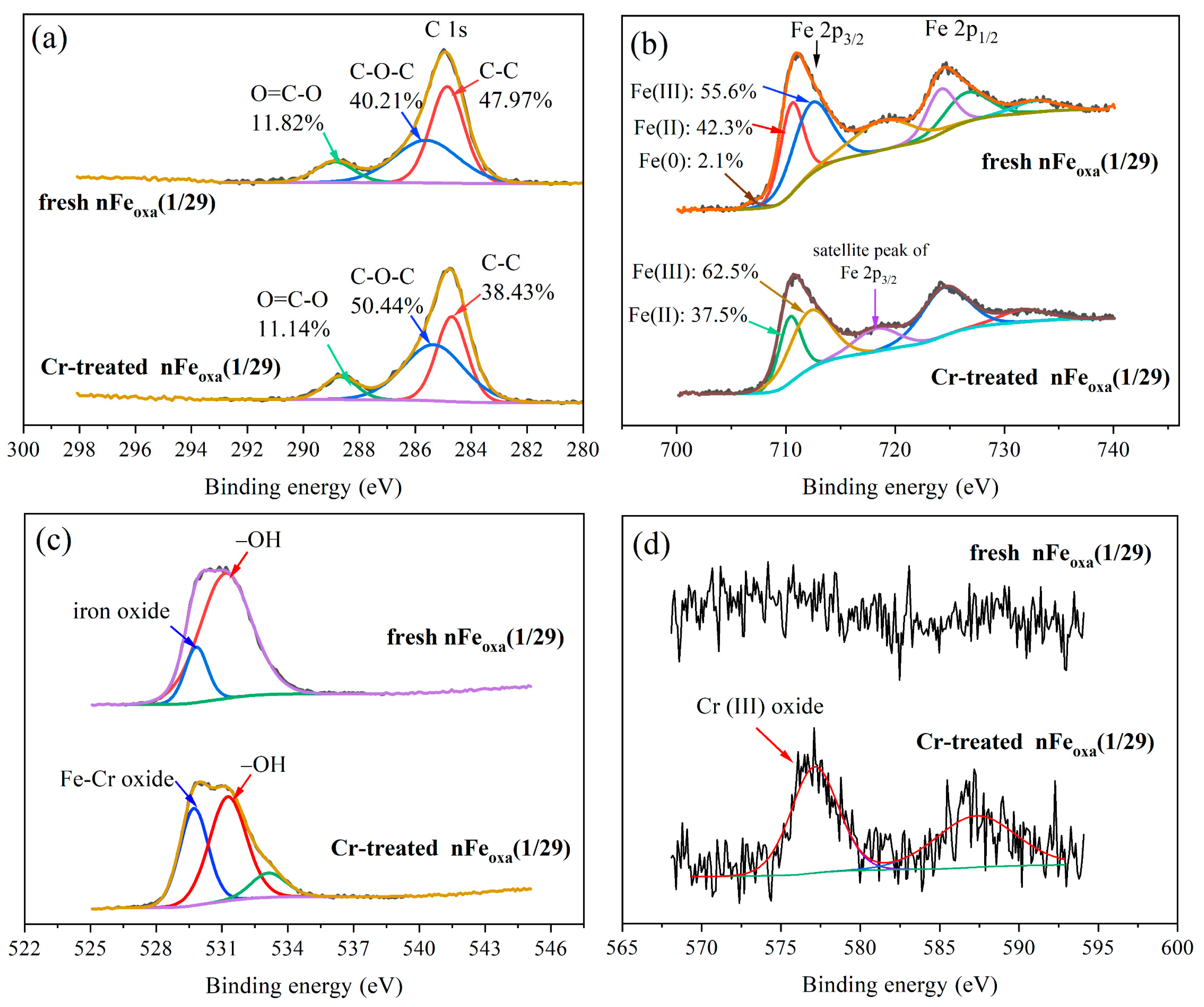
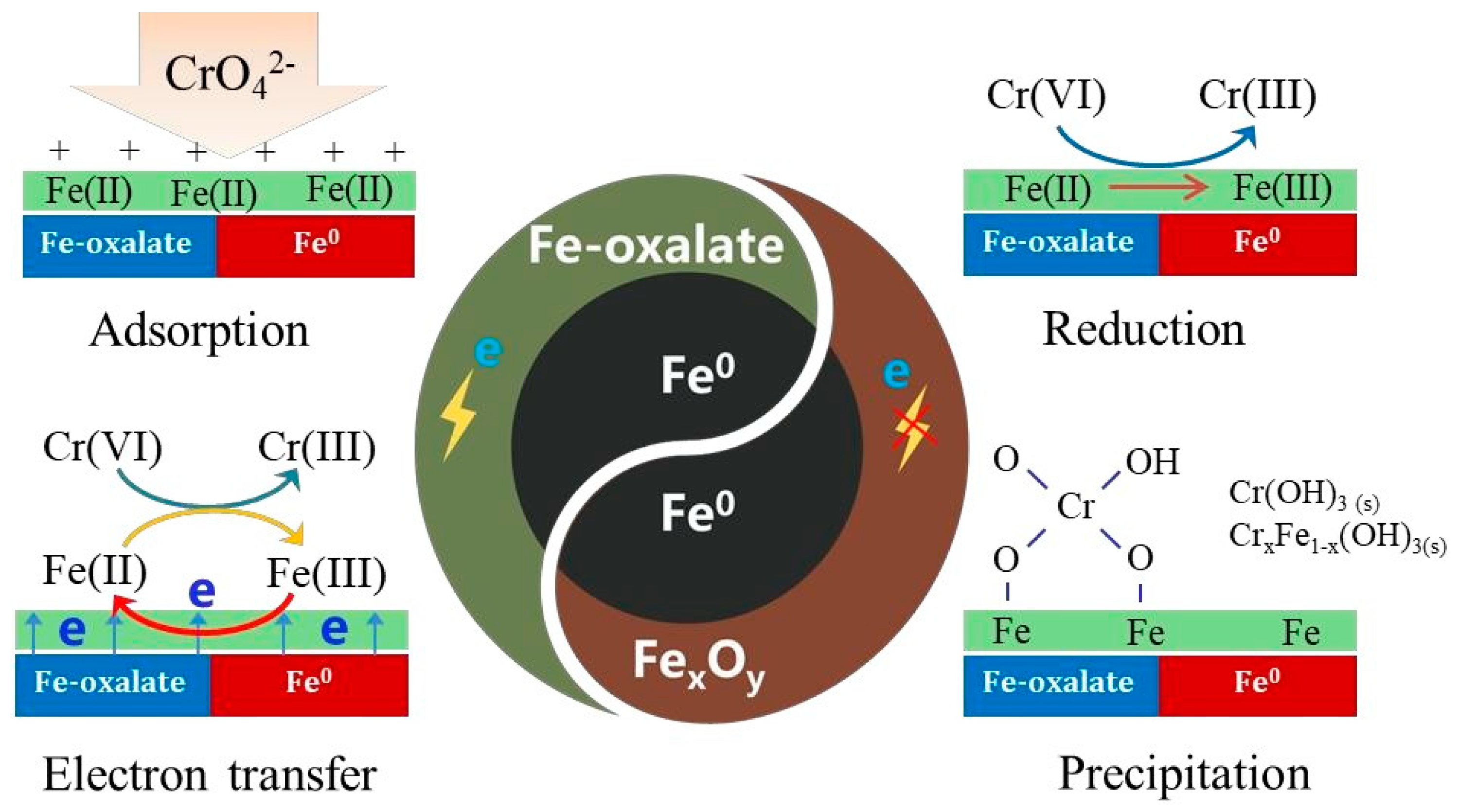
3.5. Mechanism of Cr(VI) Sequestration by nFeoxa
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gan, R.; Ye, Y.; Zhan, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Wan, J.; Pei, X.; Li, Q.; et al. One-step strategy for efficient Cr(VI) removal via phytate modified zero-valent iron: Accelerated electron transfer and enhanced coordination effect. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 466, 133636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; You, Y.; Fan, Z.; Sheng, G.; Ma, J.; Huang, Y.; Xu, H. Controllable integration of nano zero-valent iron into MOFs with different structures for the purification of hexavalent chromium-contaminated water: Combined insights of scavenging performance and potential mechanism investigations. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 935, 173395. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, J.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X.; Yu, H.; Lin, Y.; Huang, K.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, C. Light-triggered oxidative activity of chromate at neutral pH: A colorimetric system for accurate and on-site detection of Cr(VI) in natural water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 440, 129812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Huang, Y.; Liu, H. Fabrication of Chitin microspheres supported sulfidated nano zerovalent iron and their performance in Cr (VI) removal. Chemosphere 2023, 338, 139609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Wang, R.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, T.; Yu, Y.; Lan, J.; Du, Y. Changes of MRGs and ARGs in Acinetobacter sp. SL-1 used for treatment of Cr(VI)-contaminated wastewater with waste molasses as carbon source. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 919, 170770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, M.; Wang, D.; Du, F.; Xu, N.; Sun, W.; Han, Z. Cr(VI) removal during cotransport of nano-iron-particles combined with iron sulfides in groundwater: Effects of D. vulgaris and S. putrefaciens. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 472, 134583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Jia, F.; Ai, Z.; Zhang, L. Iron oxide shell mediated environmental remediation properties of nano zero-valent iron. Environ. Sci.-Nano 2017, 4, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Yang, K.; Lin, D. A versatile nanocomposite Fe0@SiO2@CaO2 for reductive, oxidative, and coagulation removal of organic and inorganic contaminants from water. Biochem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Wang, X.; Khan, A.; Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T.; Wang, X. Environmental remediation and application of nanoscale zero valent iron and its composites for the removal of heavy metal ions: A review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 7290–7304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.; Huang, X.; Li, M.; Zhang, W. Mapping the reactions in a single zero-valent iron nanoparticle. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 14293–14300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yuan, S.; Kong, J.; Chen, C.; Yu, C.; Huang, L.; Sun, H.; Peng, X.; Hu, Y. Tea saponin co-ball milled commercial micro zero-valent iron for boosting Cr(VI) removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 473, 134668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, K.; Kang, S.-K.; Ahn, S.; Woo, M.; Yang, S. Fe(0) nanoparticles for nitrate reduction: Stability, reactivity, and transformation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 5514–5519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, N.; Li, Y.; Zhang, F. Catalytic dechlorination of polychlorinated biphenyls in subcritical water by Ni/Fe nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Hu, Z.; Peng, Z.; Zeng, G.; Chen, G.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, M.; Wan, J.; Wang, X.; Qin, X. Cadmium immobilization in river sediment using stabilized nanoscale zero-valent iron with enhanced transport by polysaccharide coating. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 210, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Li, Z.; Yi, Y.; Tsang, E.; Fang, Z. Increasing the electron selectivity of nanoscale zero-valent iron in environmental remediation: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, K.; Feng, X. Selective removal of Cr(VI) by tannic acid and polyethyleneimine modified zero-valent iron particles with air stability. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 458, 132018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, X.; Wang, W.; Ling, L.; Zhang, W. Heavy metal-nZVI reactions: The core-shell structure and applications for heavy metal treatment. Acta Chim. Sin. 2017, 75, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Xu, Y.; Dai, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, G. Application of sequential extraction analysis to Pb(Ⅱ) recovery by zerovalent iron-based particles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 351, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Wang, B.; He, F.; Bradley, M.; Tratnyet, P. Mechanochemically Sulfidated Microscale Zero Valent Iron: Pathways, Kinetics, Mechanism, and Efficiency of Trichloroethylene Dechlorination. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12653–12662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Liang, L.; Pan, B.; Zhang, W.; Guan, X. Advances in sulfidation of zerovalent iron for Water decontamination. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 13533–13544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; He, X.; Lei, L.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, L.; Wu, G. Development of ionic liquid filled chitosan capsules to remove Cr(VI) from acidic solution: Adsorption properties and mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Huang, K.; Luo, W.; Tao, X.; Dang, Z.; Yin, H.; Guo, C.; Lu, G. Debromination of 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-47) by synthetic Pd/Fe0 and Cu/Fe0 in different protic solvents. Chemosphere 2018, 212, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, K.; Song, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Mao, X.; Wang, D. Understanding the electrode reaction process of dechlorination of 2,4-dichlorophenol over Ni/Fe nanoparticles: Effect of pH and 2,4-dichlorophenol concentration. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 84, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ni, R.; Yuan, T.; Gao, Y.; Kong, W.; Zhang, P.; Yue, Q.; Gao, B. Effects of green synthesis, magnetization, and regeneration on ciprofloxacin removal by bimetallic nZVI/Cu composites and insights of degradation mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 382, 121008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Huang, D.; Zeng, G.; Wan, J.; Zhang, C.; Xu, R.; Cheng, M.; Deng, R. Nanoscale zero-valent iron coated with rhamnolipid as an effective stabilizer for immobilization of Cd and Pb in river sediments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 341, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, A.; Sheng, D.; Sun, K.; Si, Y.; Azeem, M.; Abbas, A.; Bilal, M. Remediation of heavy metals polluted environment using fe-based nanoparticles: Mechanisms, influencing factors, and environmental implications. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, A.; Zhang, W. The influence of polyelectrolyte modification on nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI): Aggregation, sedimentation, and reactivity with Ni(Ⅱ) in water. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 303, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Bae, S.; Han, S.; Chang, Y.; Lee, W. Reductive dechlorination of trichloroethylene by polyvinylpyrrolidone stabilized nanoscale zerovalent iron particles with Ni. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 340, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, M.; Pan, B.; Zhang, W.; Shi, Z.; Guan, X. Enhanced reactivity and electron selectivity of sulfidated zerovalent iron toward chromate under aerobic conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimkova, S.; Cernik, M.; Lacinova, L.; Filip, J.; Jancik, D.; Zboril, R. Zero-valent iron nanoparticles in treatment of acid mine water from in situ uranium leaching. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.-J.; Chan, A.; Ali, S.; Saha, A.; Haushalter, K.J.; Lam Macrina, W.; Parker, J.; Brenner, M.; Mahon, S.; Patel, H.; et al. Hydrogen Sulfide Mechanisms of Toxicity and Development of an Antidote. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Avellan, A.; Li, H.; Clark, E.; Henkelman, G.; Kaegi, R.; Lowry, G. Iron and sulfur precursors affect crystalline structure, speciation, and reactivity of sulfidized nanoscale zerovalent Iron. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 13294–13303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Ding, H.; Tan, Y.; Yang, D.; Pan, Y.; Liao, W.; He, F. Dramatically Enhanced Phenol Degradation upon FeS Oxygenation by Low-molecular-weight Organic Acids. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 459, 132260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Feng, Q.; Li, Z.; Jin, T.; Zhang, Y.; Southam, G. Inhibition of iron oxidation in Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans by low-molecular-weight organic acids: Evaluation of performance and elucidation of mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 927, 171919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakora, F.; Phillips, D. Root exudates as mediators of mineral acquisition in low-nutrient environments. Plant Soil 2002, 245, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wang, G. Activation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil by low molecular weight organic acids. Mod. Gard. 2018, 6, 39–41. [Google Scholar]
- Kantar, C. Heterogeneous processes affecting metal ion transport in the presence of organic ligands: Reactive transport modeling. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2007, 81, 175–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilardi, G.; Parisi, M.; Verdone, N. Simultaneous aggregation and oxidation of nZVI in Rushton equipped agitated vessel: Experimental and modelling. Powder Technol. 2019, 353, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wei, X.; Yin, H.; Zhu, M.; Luo, H.; Dang, Z. Synergistic removal of Cr(VI) by S-nZVI and organic acids: The enhanced electron selectivity and pH-dependent promotion mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Dong, H.; Zeng, Q.; Yang, X.; Zhang, D. Synergistic effects of reduced nontronite and organic ligands on Cr(VI) reduction. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 13732–13741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; He, Y.; Lan, Y.; Mao, J.; Chen, S. Influence of complex reagents on removal of chromium(VI) by zero-valent iron. Chemosphere 2008, 72, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hug, S.-J.; Laubscher, H.; James, B. Iron(III) Catalyzed Photochemical Reduction of Chromium(VI) by Oxalate and Citrate in Aqueous Solutions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadol Hayley, J.; Flynn Elaine, D.; Catalano Jeffrey, G. Oxalate-Promoted Trace Metal Release from Crystalline Iron Oxides under Aerobic Conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, J.; Tang, C.; Duan, G.; Lin, A.; Zhang, T.; Li, S. Enhanced remediation of Cr(VI)-contaminated soil by modified zero-valent iron with oxalic acid on biochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Han, X.; Xia, F.; Yang, Y.; Xu, X.; Deng, S.; Jiang, Y. Enhanced Degradation of 2,4-DNT in Groundwater by Oxalic Acid-Modified Zero-Valent Iron as Persulfate Activator. Res. Environ. Sci. 2022, 35, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Dai, H.; Zhan, P.; Tan, C.; Ning, Z.; Hu, F.; Xu, X.; Peng, X. Rapid reduction of aqueous Cr(VI) by oxalic acid on N-doped lignin charcoal: A significant contribution of structural defects and electronic shuttle effect. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 415, 137883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Adeleye, A.; Keller, A.; Huang, Y.; Dai, C.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y. Magnetic sulfide-modified nanoscale zerovalent iron (S-nZVI) for dissolved metal ion removal. Water Res. 2015, 74, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Wang, X.; Cao, S.; Li, M.; Peng, X.; Zhang, L. Oxalate Modification Dramatically Promoted Cr(VI) Removal with Zero-Valent Iron. ACS ES&T Water 2021, 1, 2109–2118. [Google Scholar]
- Flynn, E.; Catalano, J. Competitive and Cooperative Effects during Nickel Adsorption to Iron Oxides in the Presence of Oxalate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 9792–9799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Situm, A.; Rahman, M.; Goldberg, S. Spectral characterization and surface complexation modeling of low molecular weight organics on hematite nanoparticles: Role of electrolytes in the binding mechanism. Environ. Sci. Nano 2016, 3, 910–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhou, T.; Wu, X.; Mao, J. Distinguishing homogeneous-heterogeneous degradation of norfioxacin in a photochemical Fenton-like system (Fe3O4/UV/oxalate) and the interfacial reaction mechanism. Water Res. 2017, 119, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kar, A.; Acharya, A.; Mundlapati, V.; Pradhan, G.; Biswal, H.; Dash, A. Ligand substitution and electron transfer reactions of trans-(diaqua)(salen)manganese(iii) with oxalate: An experimental and computational study. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 58867–58879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Cai, Q.; Xu, W.; Yang, M.; Cai, Y.; Dionysiou, D.; O’Shea, K. Cr(VI) Adsorption and Reduction by Humic Acid Coated on Magnetite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 8078–8085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Jiang, G. Efficient Removal of Cr(VI) from Aqueous Solution with Fe@Fe2O3 Core−Shell Nanowires. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 6955–6960. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.; Huang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, Z. Reductive removal of selenate by zero-valent iron: The roles of aqueous Fe2+ and corrosion products, and selenate removal mechanisms. Water Res. 2014, 67, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Huang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, Z. Promotion effect of Mn2+ and Co2+ on selenate reduction by zero-valent iron. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 244, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Hana, K. Reactivity of Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron in Unbuffered Systems: Effect of pH and Fe(II) Dissolution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10536–10543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.; Zhu, B. Effects of anions on the kinetics and reactivity of nanoscale Pd/Fe in trichlorobenzene dechlorination. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Shea, P.; Yang, J.; Kim, J. Halide salts accelerate degradation of high explosives by zerovalent iron. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 147, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Wu, J.; Li, P.; Wang, X.; Zhu, N.; Wu, P.; Yang, B. Experimental study of zero-valent iron induced nitrobenzene reduction in groundwater: The effects of pH, iron dosage, oxygen and common dissolved anions. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 184, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Hua, B.; Bao, Z.; Yang, J.; Liu, C.; Deng, B. Uranium(VI) Removal by Nanoscale Zerovalent Iron in Anoxic Batch Systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7783–7789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, S.; Tian, H.; Huang, C.; Wang, P.; Zeng, Q.; Peng, H.; Liu, S.; Li, A. Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by amino-modified biochar supported nano zero-valent iron. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2020, 40, 3931–3938. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, X.; Hu, Y.; Tang, J.; Sheng, T.; Jiang, G.; Xu, X. Effects of co-existing ions and natural organic matter on removal of chromium (VI) from aqueous solution by nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI)-Fe3O4 nanocomposites. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 218, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, M.; Rao, P.; Lo, I. Effects of hardness and alkalinity on the removal of arsenic(V) from humic acid-deficient and humic acid-rich groundwater by zero-valent iron. Water Res. 2009, 43, 4296–4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanboonchuy, V.; Grisdanurak, N.; Liao, C. Background species effect on aqueous arsenic removal by nano zero-valent iron using fractional factorial design. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 205–206, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, T.; Chang, D.; Chen, D.; Liu, Y.; He, H.; Yuan, P.; Frost, R. Nitrate reduction over nanoscale zero-valent iron prepared by hydrogen reduction of goethite. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 133, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, A.; Jeong, S.; Jang, A.; Choi, H. Reduction of highly concentrated nitrate using nanoscale zero-valent iron: Effects of aggregation and catalyst on reactivity. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 105, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hao, Z.; Zhen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xu, X. Kinetics of nitrate reductive denitrification by nanoscale zero-valent iron. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2010, 88, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Cissoko, N.; Zhu, M.; Xu, X. Effects and mechanism of humic acid on chromium(VI) removal by zero-valent iron (Fe0) nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2011, 36, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Thao, T.; Du, J.; Xu, T.; Cui, Y.; Ling, H.; Kim, S. Novel core-shell sulfidated nano-Fe(0) particles for chromate sequestration: Promoted electron transfer and Fe(II) production. Chemosphere 2021, 284, 131379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
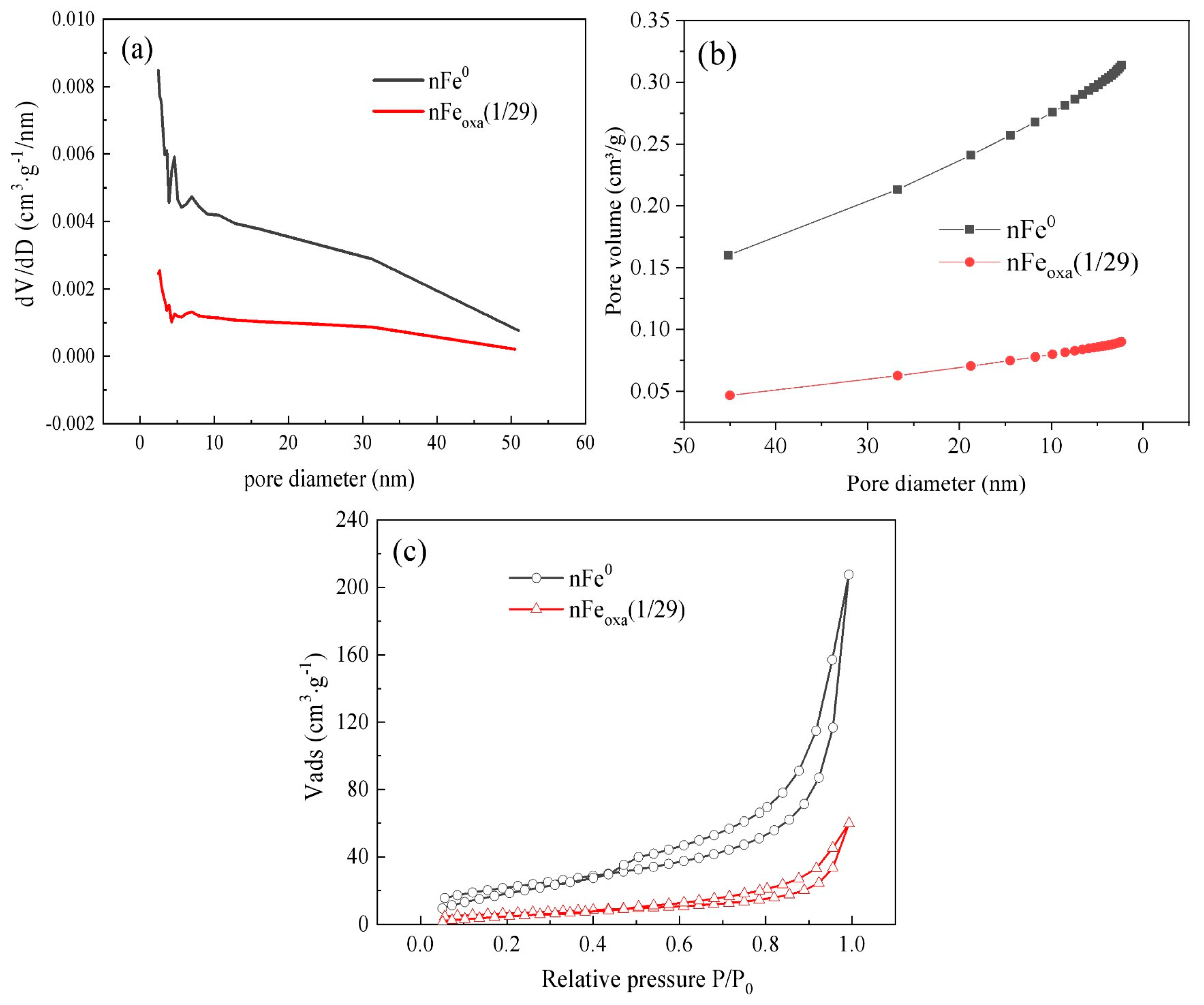
| Materials | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Diameter (nm) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| nFe0 | 80.6138 | 15.9322 | 0.313722 |
| nFeoxa(1/29) | 23.5177 | 15.7567 | 0.090041 |
| Materials | Particle Size D(50) (nm) |
|---|---|
| nFe0 | 2190 |
| nFeoxa(1/14) | 641 |
| nFeoxa(1/19) | 478 |
| nFeoxa(1/29) | 483 |
| nFeoxa(1/58) | 456 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, S.; Du, J.; Ling, H.; Quan, S.; Bao, J.; Yi, C. Synergistic Removal of Cr(VI) Utilizing Oxalated-Modified Zero-Valent Iron: Enhanced Electron Selectivity and Dynamic Fe(II) Regeneration. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15090669
Hou S, Du J, Ling H, Quan S, Bao J, Yi C. Synergistic Removal of Cr(VI) Utilizing Oxalated-Modified Zero-Valent Iron: Enhanced Electron Selectivity and Dynamic Fe(II) Regeneration. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(9):669. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15090669
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Song, Jiangkun Du, Haibo Ling, Sen Quan, Jianguo Bao, and Chuan Yi. 2025. "Synergistic Removal of Cr(VI) Utilizing Oxalated-Modified Zero-Valent Iron: Enhanced Electron Selectivity and Dynamic Fe(II) Regeneration" Nanomaterials 15, no. 9: 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15090669
APA StyleHou, S., Du, J., Ling, H., Quan, S., Bao, J., & Yi, C. (2025). Synergistic Removal of Cr(VI) Utilizing Oxalated-Modified Zero-Valent Iron: Enhanced Electron Selectivity and Dynamic Fe(II) Regeneration. Nanomaterials, 15(9), 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15090669







