Fabrication and Characterization of a Novel Solid Nano-Dispersion of Emamectin Benzoate with High Dispersibility and Wettability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of SND-EB
2.3. Determination of SND-EB Content
2.4. Morphology Characterization
2.5. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.6. X-Ray Diffraction Analysis
2.7. Particle Size and Zeta Potential Measurements
2.8. Storage Stability Test
2.9. Static Contact Angle
2.10. Dynamic Contact Angle
2.11. Bouncing Behavior
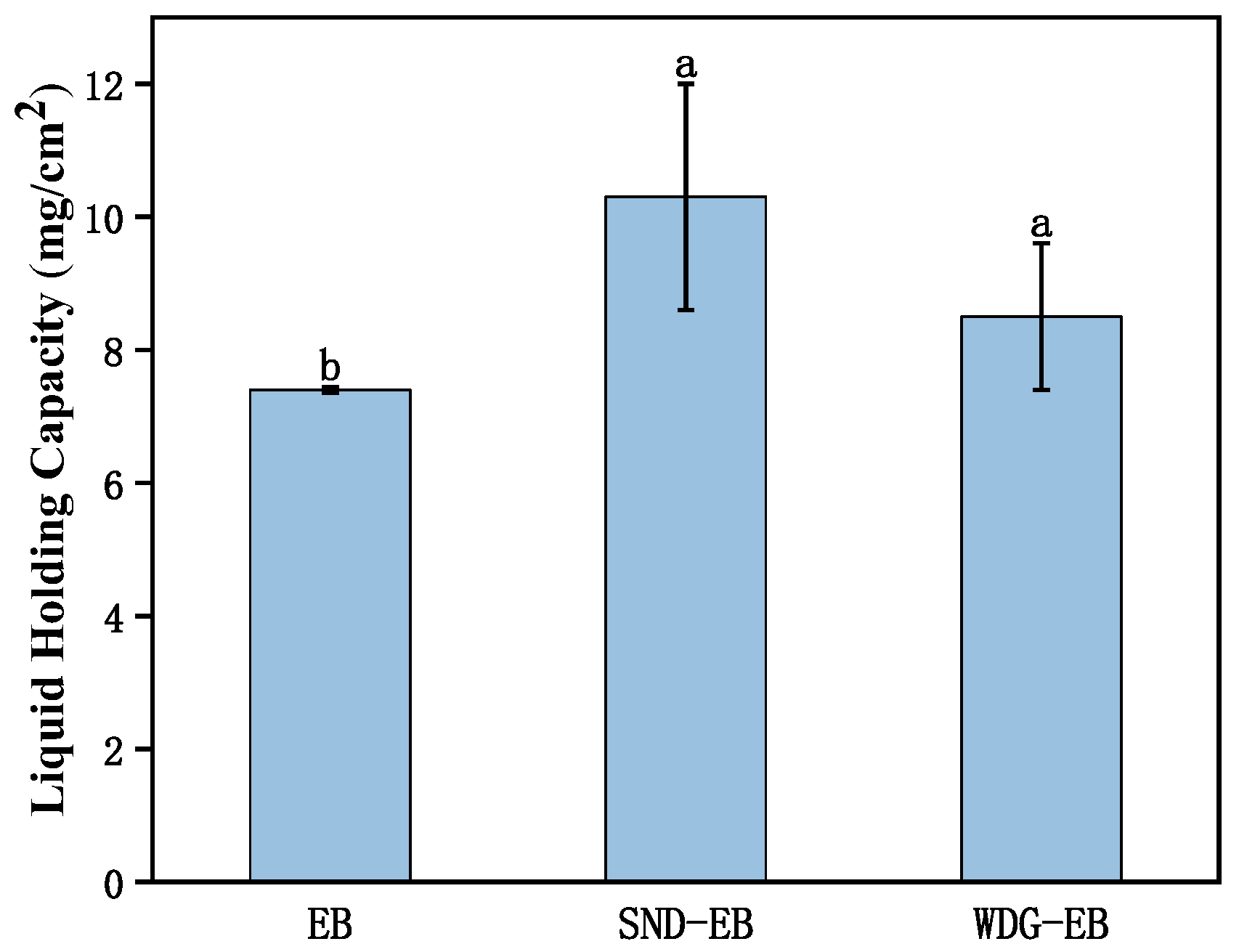
2.12. Leaf Retention
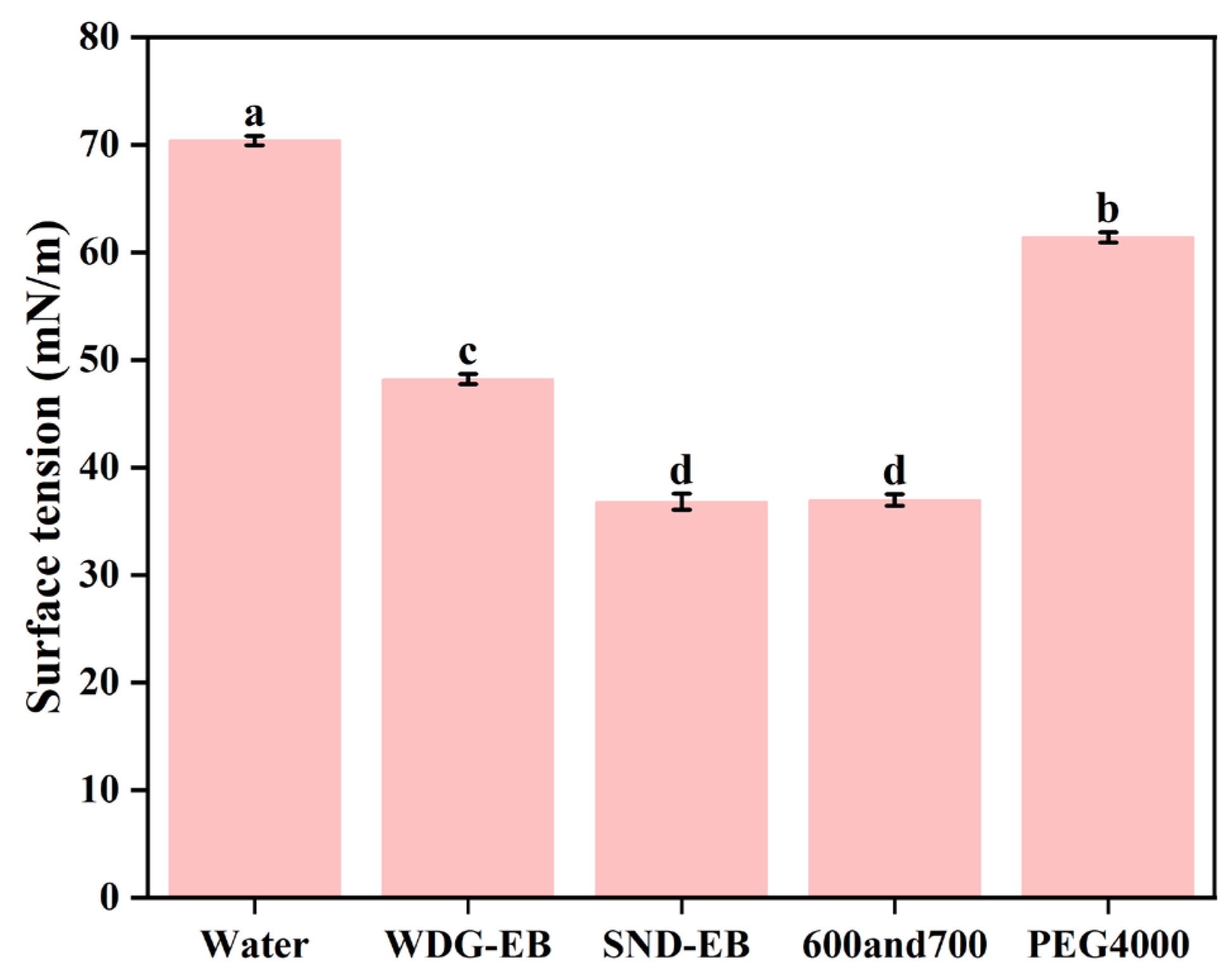
2.13. Measurement of Surface Tension
2.14. Experiment Study of EB Release from SND-EB
2.15. Biological Testing Experiment
2.16. Cell Viability Experiment
3. Results
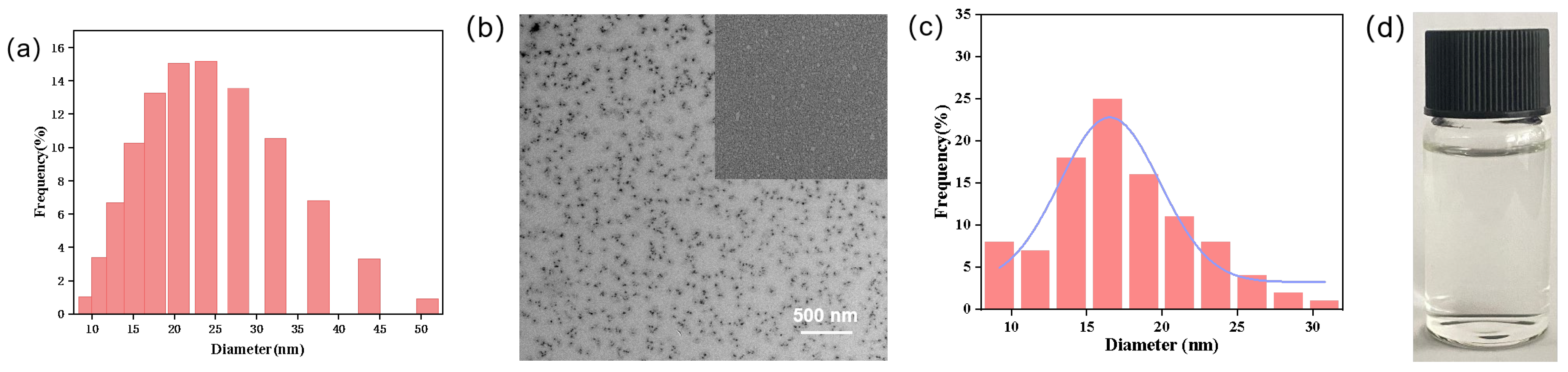
3.1. Particle Size Distribution and Morphology of SND-EB
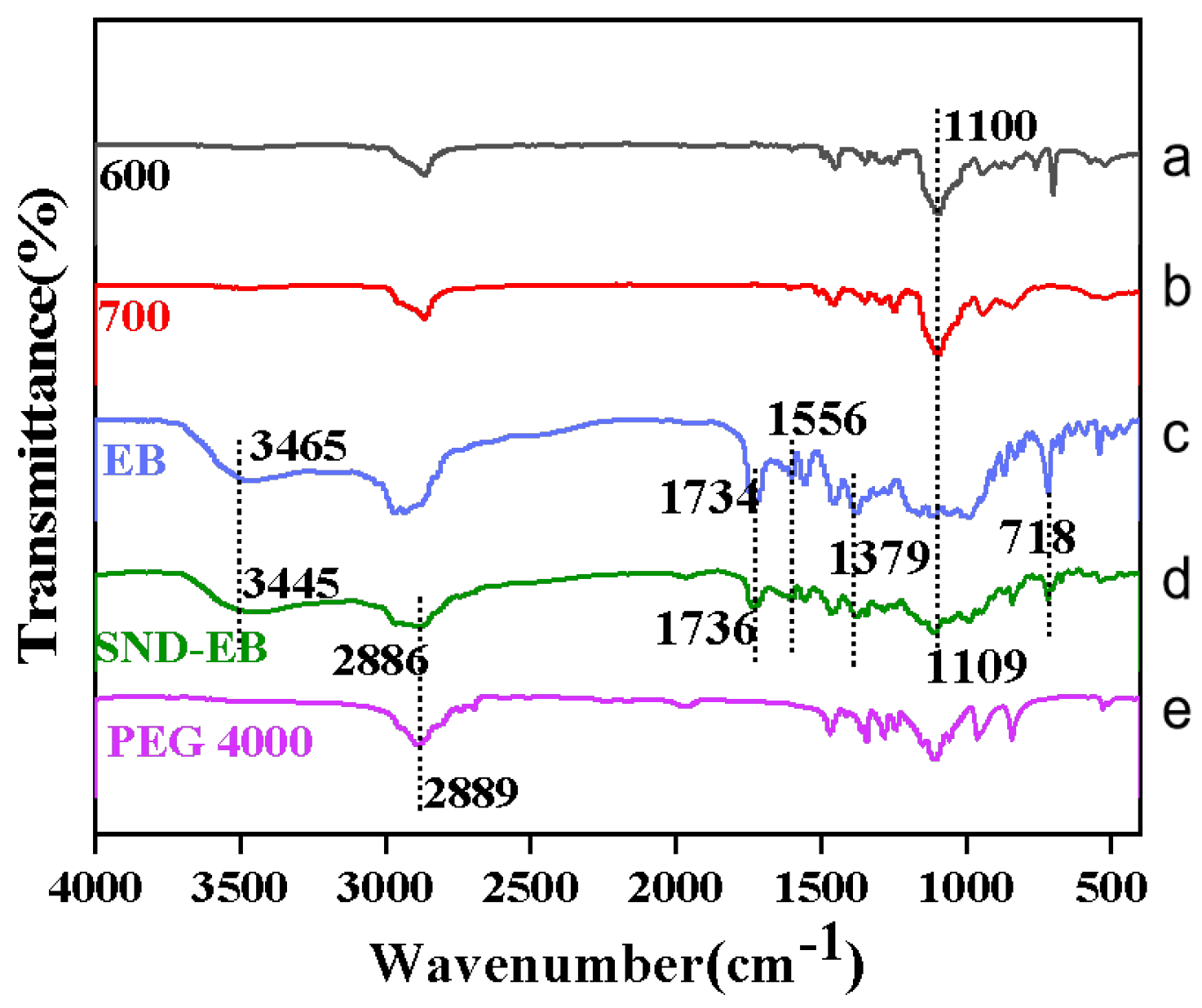
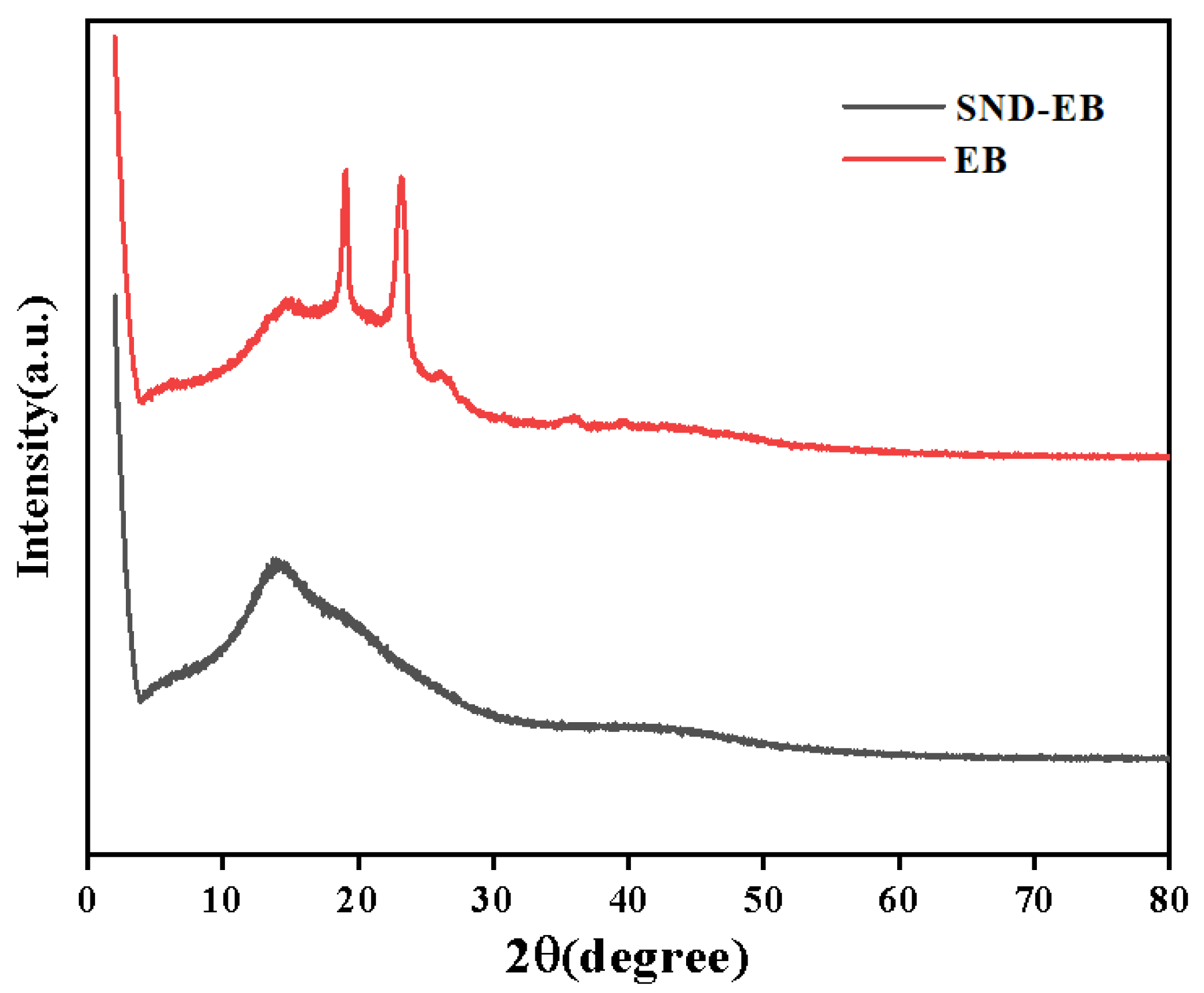
3.2. Structural Characterization of SND-EB
3.3. Stability Analysis
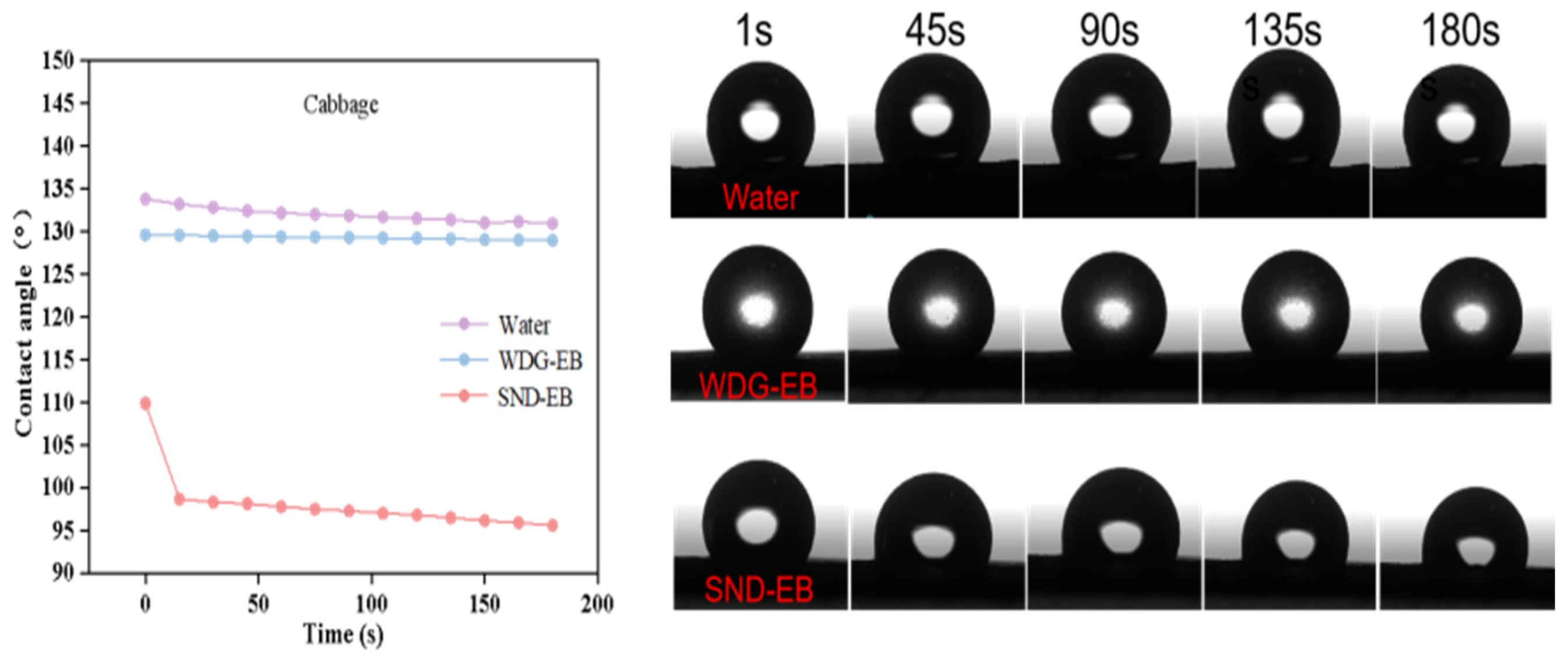
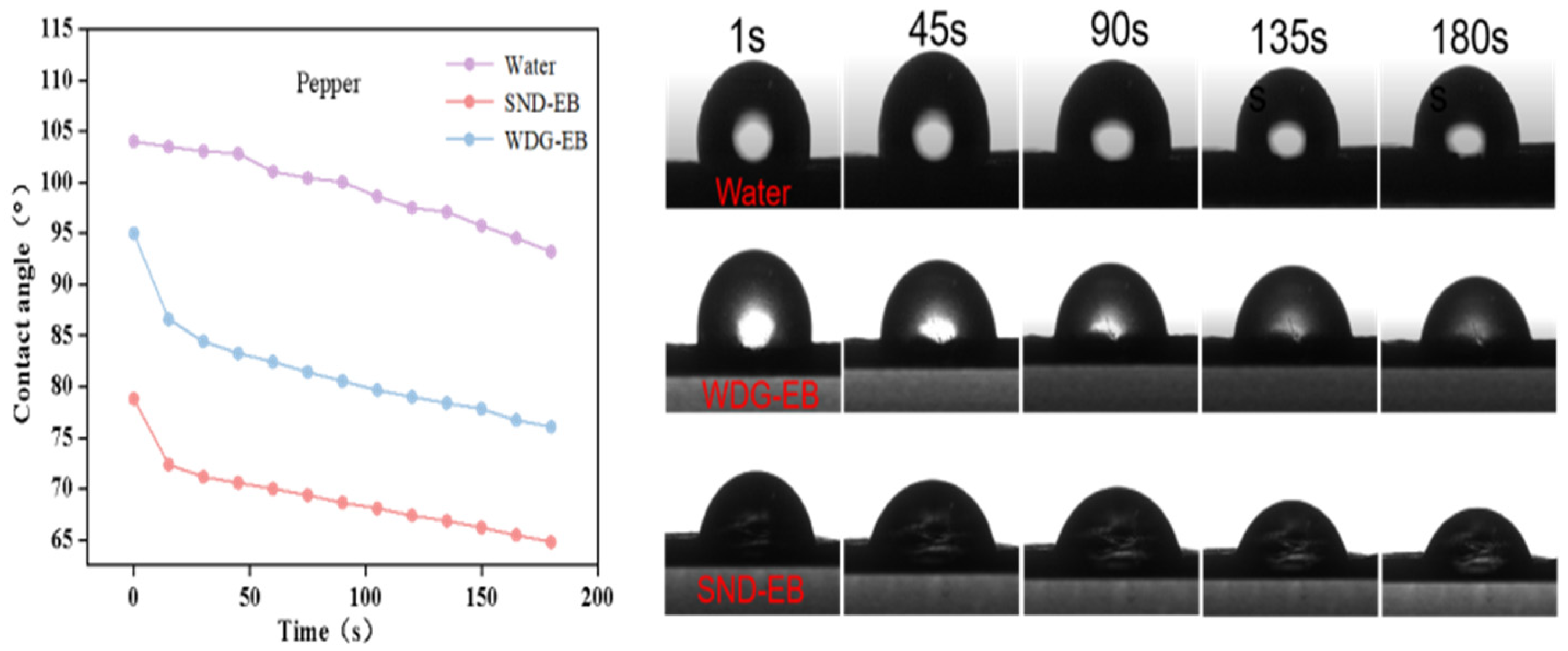
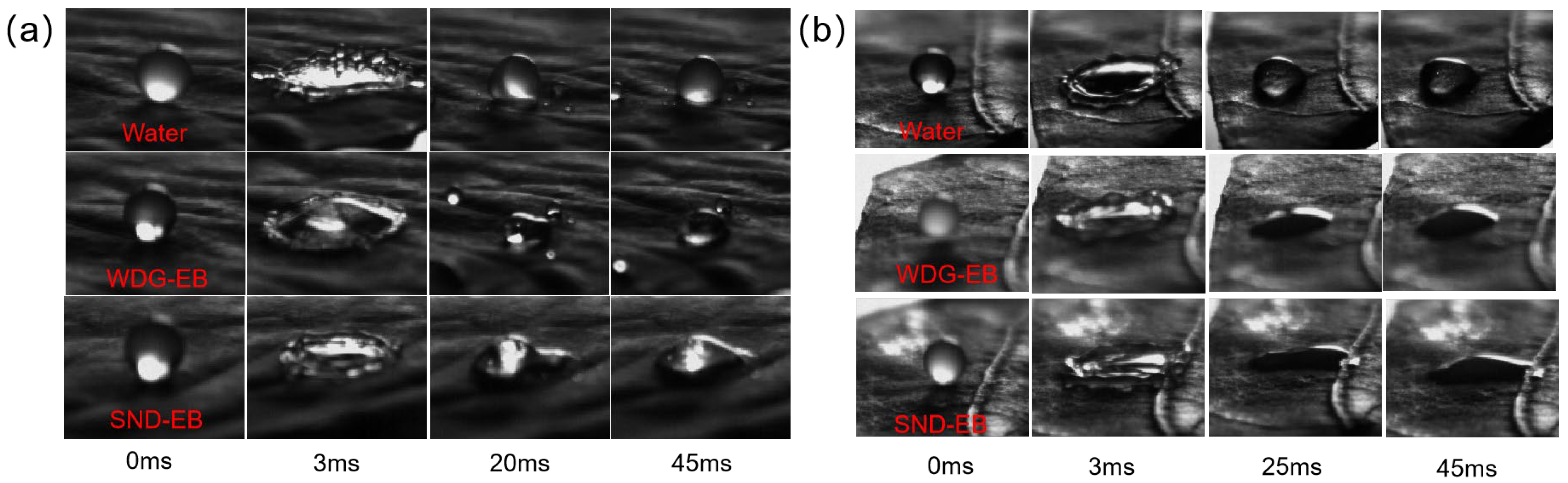
3.4. Wettability, Spreading, and Retention
3.5. Sustained-Release Behavior
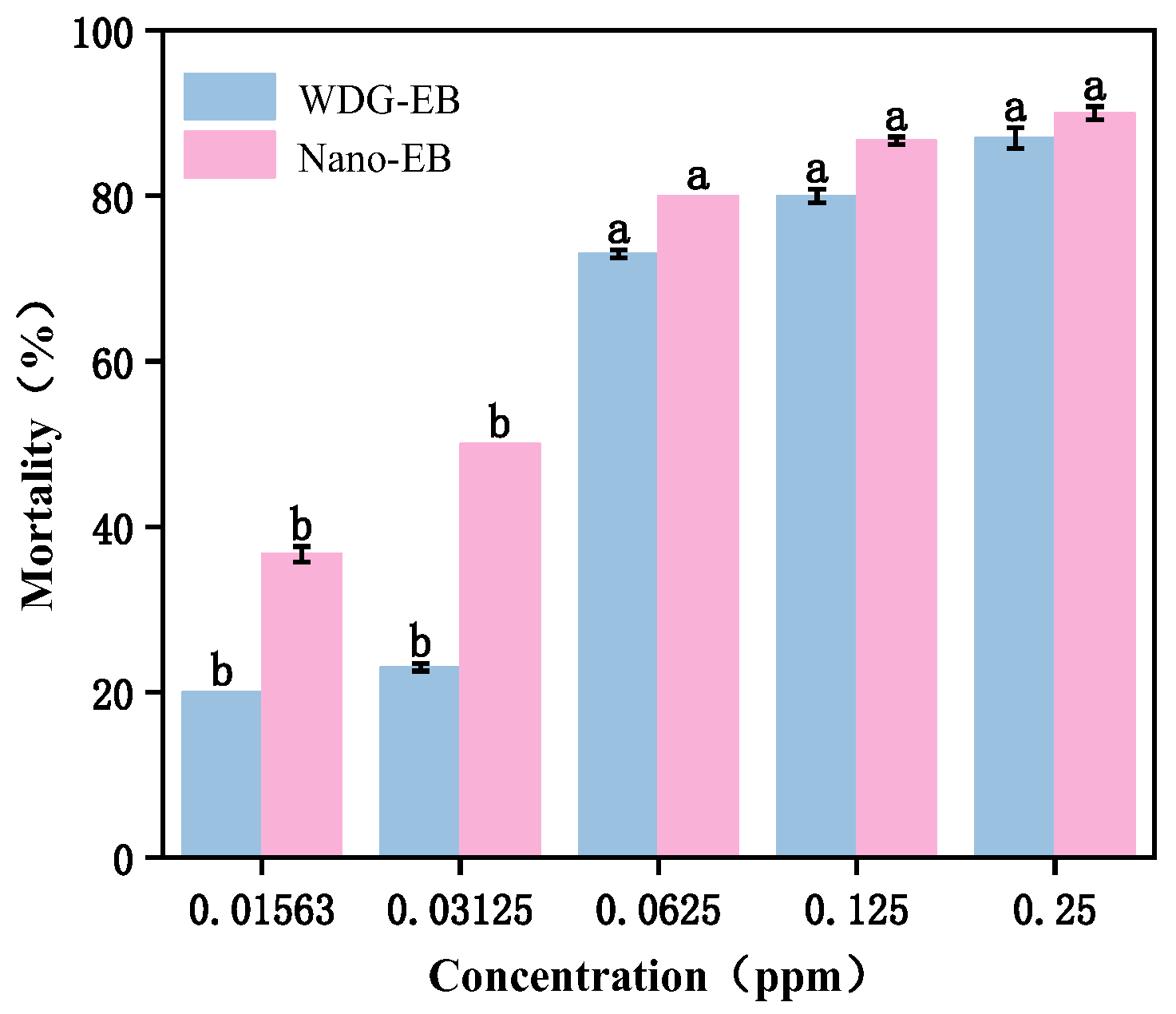
3.6. Insecticidal Activity Against Spodoptera Exigua
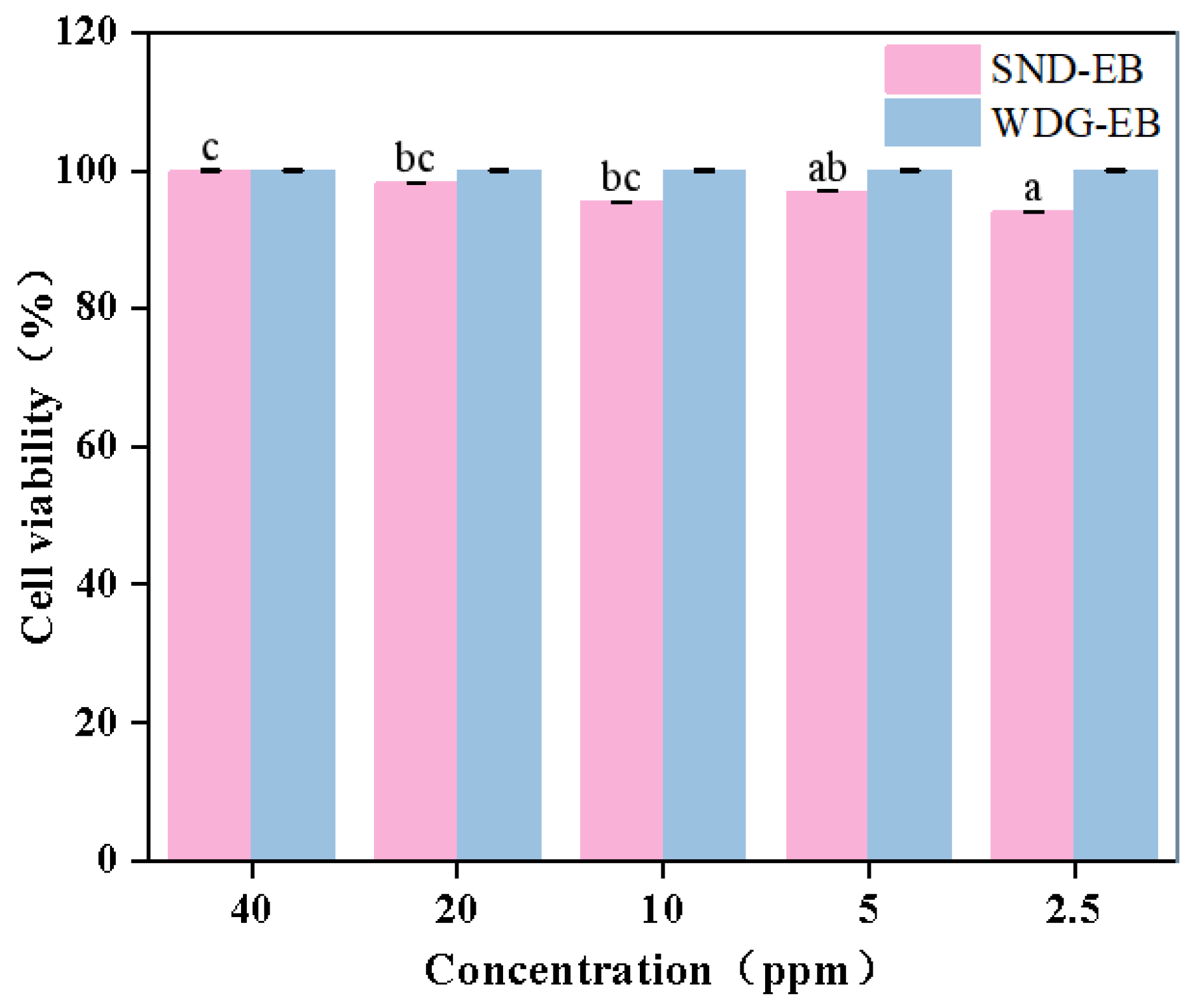
3.7. Cytotoxicity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Li, N.; Sun, C.; Jiang, J.; Wang, A.; Wang, C.; Shen, Y.; Huang, B.; An, C.; Cui, B.; Zhao, X.; et al. Advances in controlled-release pesticide formulations with improved efficacy and targetability. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 12579–12597. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nayara, C.P.A.; Daniel, B.C.; Maísa, D.H.; Anderson, R.M.O. Metabolism studies of chiral pesticides: A critical review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 147, 89–109. [Google Scholar]
- Federico, M.; Fiona, H.M.T.; Daniele, l.C.; Alexander, M. PEST-CHEMGRIDS, global gridded maps of the top 20 crop-specific pesticide application rates from 2015 to 2025. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 170. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.J.; Gao, S.; Xu, J.Y.; Lu, F.F.; Ma, L.Y.; Su, X.N.; Yang, H. Degrading and phytoextracting atrazine residues in rice (Oryza sativa) and growth media intensified by a phase II mechanism modulator. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 11258–11268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.F.; Liu, J.T.; Zhang, N.; Chen, Z.J.; Yang, H. OsPAL as a key salicylic acid synthetic component is a critical factor involved in mediation of isoproturon degradation in a paddy crop. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121476. [Google Scholar]
- Mostafalou, S.; Abdollahi, M. Pesticides and human chronic diseases: Evidences, mechanisms, and perspectives. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 268, 157–177. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.J.; Lu, Y.C.; Zhang, S.H.; Lu, F.F.; Yang, H. Identification of transcriptome involved in atrazine detoxification and degradation in alfalfa (Medicago sativa) exposed to realistic environmental contamination. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 130, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, R.A.; Iorhemen, O.T.; Tay, J.H. Occurrence, impacts and removal of emerging substances of concern from wastewater. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2016, 5, 161–175. [Google Scholar]
- Parween, T.; Jan, S.; Mahmooduzzafar, S.; Fatma, T.; Siddiqui, Z.H. Selective effect of pesticides on plant—A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 160–179. [Google Scholar]
- Kah, M.; Tufenkji, N.; White, J.C. Nano-enabled strategies to enhance crop nutrition and protection. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Seiber, J.N.; Hotze, M. ACS select on nanotechnology in food and agriculture: A perspective on implications and applications. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 1209–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raliya, R.; Tarafdar, J.C.; Biswas, P. Enhancing the mobilization of native phosphorus in the Mung Bean Rhizosphere using ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by soil fungi. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 3111–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Lombi, E.; Zhao, F.J.; Kopittke, P.M. Nanotechnology: A new opportunity in plant sciences. Trends Plant Sci. 2016, 21, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Cui, H.; Wang, Y.; Sun, C.J.; Cui, B.; Zeng, Z.H. Development strategies and prospects of nano-based smart pesticide formulation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 66, 6504–6512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Chi, D.F.; Yu, J.; Li, H. Dynamics of residues from a novel nano-imidacloprid formulation in soyabean fields. Crop Prot. 2010, 29, 942–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, X.F.; Zhang, G.Y.; Dong, J.F.; Eastoe, J.L. Oil-in-water nanoemulsions for pesticide formulations. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 314, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederiksen, H.K.; Kristensen, H.G.; Pedersen, M. Solid lipid microparticle formulations of the pyrethroid gamma-cyhalothrin—Incompatibility of the lipid and the pyrethroid and biological properties of the formulations. J. Control. Release 2003, 86, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yu, B.; Fang, Y.; Xie, Z.G.; Xiong, Q.Y.; Zhang, D.Y.; Cheng, J.L.; Guo, Q.Z.; Su, Y.H.; Zhao, J.H. Long-lasting, UV shielding, and cellulose-based avermectin nano/micro spheres with dual smart stimuli-microenvironment responsiveness for Plutella xylostella control. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 345, 122553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Nehra, M.; Dilbaghi, N.; Marrazza, G.; Hassan, A.A.; Kim, K.H. Nano-based smart pesticide formulations: Emerging opportunities for agriculture. J. Control. Release 2019, 294, 131–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuruzzaman, M.; Rahman, M.M.; Liu, Y.J.; Naidu, R. Nanoencapsulation, Nano-guard for Pesticides: A new window for safe application. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 1447–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Shen, Y.; Cui, J.X.; Wang, A.Q.; Li, N.J.; Wang, C.; Cui, B.; Sun, C.J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, C.X.; et al. Avermectin loaded carboxymethyl cellulose nanoparticles with stimuli-responsive and controlled release properties. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 152, 112497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Cui, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Li, N.; Wang, C.; Shen, Y.; Liu, P.; Cui, B.; Sun, C.; et al. Preparation and characterization of a novel controlled-release nano-delivery system loaded with pyraclostrobin via high-pressure homogenization. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 2829–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Wang, Y.; Sun, C.; Wang, C.X.; Cui, B.; Sun, C.J.; Zhao, X.; Zeng, Z.H.; Yao, J.W.; Yang, D.S.; et al. Fabrication, characterization, and biological activity of avermectin nano-delivery systems with different particle sizes. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 2. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, A.Q.; Wang, C.X.; Cui, B.; Sun, C.J.; Zhao, X.; Zeng, Z.H.; Shen, Y.; Gao, F.; Liu, G.Q.; et al. Synthesis and characterization of emamectin-benzoate slow-release microspheres with different surfactants. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12761. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, R.; Varghese, S.H.; Nair, B.G.; Maekawa, T.; Yoshida, Y.; Kumar, D.S. Nanoparticulate material delivery to plants. Plant Sci. 2010, 179, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, S.P.; Dugar, R.P. Application of surfactants in solid dispersion technology for improving solubility of poorly water soluble drugs. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2017, 41, 68–77. [Google Scholar]
- Nkansah, P.; Antipas, A.; Lu, Y.; Varma, M.; Rotter, C.; Rago, B.; El-Kattan, A.; Taylor, G.; Rubio, M.; Litchfield, J. Development and evaluation of novel solid nanodispersion system for oral delivery of poorly water-soluble drugs. J. Control. Release 2013, 169, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Shah, S.; Patel, J. Solid dispersion technology as a formulation strategy for the fabrication of modified release dosage forms: A comprehensive review. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 30, 165–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X. Preparation, characterization and bioavailability of oral puerarin nanoparticles by emulsion solvent evaporation method. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 69889–69901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Feng, L.; Pan, Z.Z.; Yu, M.L.; Zeng, Z.H.; Sun, C.J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Cui, H.X. Evaluation of stability and biological activity of solid nanodispersion of lambda-cyhalothrin. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135953. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.B.; Liu, D.X.; Liu, D.K.; Wu, G. Application of solid dispersion technique to improve solubility and sustain release of emamectin benzoate. Molecules 2019, 24, 4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Zhang, D.X.; Hao, L.J.; Zhuang, K.; Liu, F.; Xue, C.B. Epoxy resin gel particles with adjustable stickiness and deformability for pesticide delivery. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 498, 155668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Ding, X.Q.; Gao, F.; Cui, B.; Wang, T.Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, H.Y.; Cui, H.X.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, Z.H.; et al. Thermo-responsive liposome nano-vesicles for co-delivery of emamectin benzoate and nitenpyram with synergistic pest control. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 479, 147548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Yan, W.Y.; Sun, L.; Hou, C.Q.; Wei, N.; Chen, Z.Y.; Feng, J.G. Preparation and characterization of emamectin benzoate nanocapsules based on the dual role of polydopamine. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 4407–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Gao, F.; Chen, L.; Zeng, Z.H.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Cui, H.X.; Cui, B. Size-dependent effect on foliar utilization and biocontrol efficacy of emamectin benzoate delivery systems. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 22558–22570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Guo, N.S.; You, Z.P.; Tan, Y.Q.; Fang, C.Z. Thermal and mechanical properties of PEG 4000 and PUSSPCMs for thermoregulation of asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 412, 134776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Mo, D.M.; Jiang, Y.; Gan, C.F.; Li, W.G.; Wu, A.; Li, X.Y.; Xiao, J.A.; Hu, Q.; Yuan, H.Y.; et al. Fabrication, characterization, and insecticidal activity evaluation of emamectin benzoate–sodium lignosulfonate nanoformulation with pH-responsivity. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 19741–19751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Liao, L.; Xu, H. Study on the influence of thermal characteristics of hyperbranched polyurethane phase change materials for energy storage. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 115, 2228–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Shi, Y.; Yu, Q. Effect of emulsifying process on stability of pesticide nanoemulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 497, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borba, P.A.A.; Pinotti, M.; de Campos, C.E.M.; Pezzini, B.R.; Stulzer, H.K. Sodium alginate as a potential carrier in solid dispersion formulations to enhance dissolution rate and apparent water solubility of BCS II drugs. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 137, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madras, G.; McCoy, B.J. Distribution kinetics of Ostwald ripening at large volume fraction and with coalescence. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 261, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Papierowska, E.; Szporak-Wasilewska, S.; Szewińska, J.; Szatyłowicz, J.; Debaene, G.; Utratna, M. Contact angle measurements and water drop behavior on leaf surface for several deciduous shrub and tree species from a temperate zone. Trees 2018, 32, 1253–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Ma, J.K.; Luo, L.; Yang, L.L.; Cao, X.L.; Tian, D.M.; Li, H.B. Pesticide macroscopic recognition by a naphthol-appended calix [4] arene. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 2976–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Hu, Y.P.; Yin, L.C.; Tang, C.; Yin, C.H. Effects of particle size and surface charge on cellular uptake and biodistribution of polymeric nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3657–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, X.; Guo, Z. Superhydrophobic plant leaves: The variation in surface morphologies and wettability during the vegetation period. Langmuir 2019, 35, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar]
- Trokhymchuk, A.; Henderson, D.; Nikolov, A.; Wasan, D.T. A simple calculation of structural and depletion forces for fluids/suspensions confined in a film. Langmuir 2001, 17, 4940–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.C.; Hou, X.J.; Zou, P.Y.; Huang, A.M.; Zhang, M.; Ma, L. Cationic starch modified bentonite-alginate nanocomposites for highly controlled diffusion release of pesticides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 213, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Shi, Y.S.; Xu, X.F.; Zhang, M.; Ma, L. Structure regulation of bentonite-alginate nanocomposites for controlled release of imidacloprid. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 10068–10076. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.Y.; Zhou, C.; Liu, F.; Mu, W. Toxicity of nine insecticides on four natural enemies of Spodoptera exigua. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39060. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, R.X.; Zhao, X.P.; Chen, L.P.; Wu, C.X.; Cang, T.; Wang, Q. Susceptibility of adult Trichogramma nubilale (hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) to selected insecticides with different modes of action. Crop Prot. 2012, 34, 76–82. [Google Scholar]
- Smagghe, G.; Pineda, S.; Carton, B.; Estal, P.D.; Budia, F.; Viñuela, E. Toxicity and kinetics of methoxyfenozide in greenhouse-selected Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Pest Manag. Sci. 2003, 59, 1203–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Jiang, Y.; He, K.Y.; Wang, Y. Eco-friendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles against mosquitoes: Pesticidal impact and indispensable biosafety assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 953, 176006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, A.T. Toxicity of Ulva lactuca and green fabricated silver nanoparticles against mosquito vectors and their impact on the genomic DNA of the dengue vector Aedes aegypti. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 16, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahzad, K.; Manzoor, F. Nanoformulations and their mode of action in insects: A review of biological interactions. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 44, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Bai, X.Y.; Sun, W.; Zhou, X.F.; Dong, Q.Q.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.B.; Bai, W.L.; Zhang, W.P. Deciphering the impact of greenhouse pesticides on hepatic metabolism profile: Toxicity experiments on HepG2 cells using chlorpyrifos and emamectin benzoate. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 275, 116230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



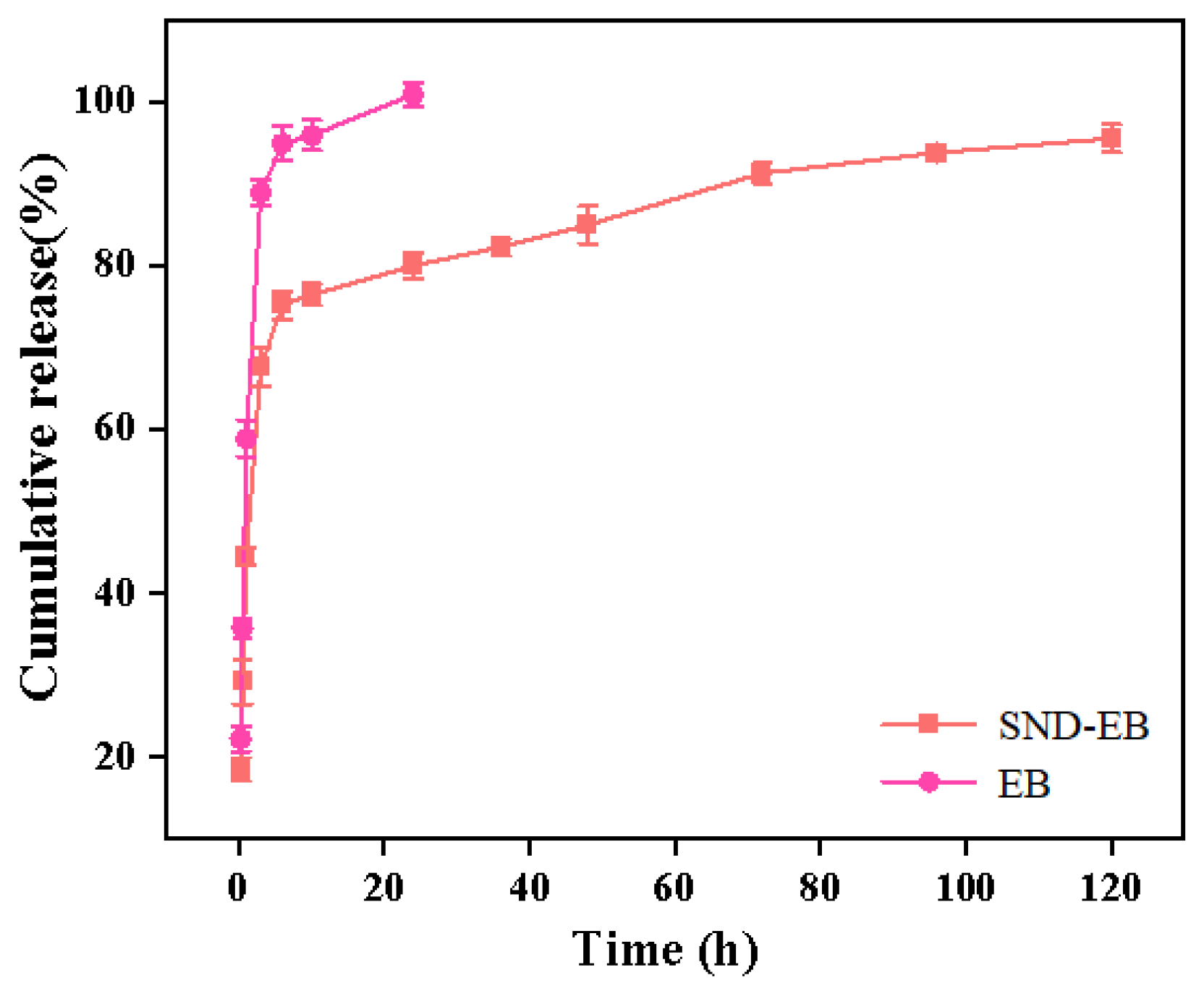
| Sample | Boxlucas1 Equation | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| SND-EB | 0.924 | |
| EB | 0.994 |
| Formulation | Toxicity Regression Equation | LC50 (mg/L) | 95% Confidence Limit | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SND-EB | Y = 2.394 + 1.510X | 0.026 | 0.06–0.047 | 0.938 |
| WDG-EB | Y = 2.417 + 1.851X | 0.049 | 0.026–0.083 | 0.904 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Pan, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhan, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, C.; Cui, H. Fabrication and Characterization of a Novel Solid Nano-Dispersion of Emamectin Benzoate with High Dispersibility and Wettability. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15070495
Li Y, Wang Q, Pan J, Zhao X, Zhan J, Xu X, Zhang M, Wang C, Cui H. Fabrication and Characterization of a Novel Solid Nano-Dispersion of Emamectin Benzoate with High Dispersibility and Wettability. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(7):495. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15070495
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ying, Qing Wang, Junqian Pan, Xiang Zhao, Jinghui Zhan, Xinglong Xu, Meng Zhang, Chunxin Wang, and Haixin Cui. 2025. "Fabrication and Characterization of a Novel Solid Nano-Dispersion of Emamectin Benzoate with High Dispersibility and Wettability" Nanomaterials 15, no. 7: 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15070495
APA StyleLi, Y., Wang, Q., Pan, J., Zhao, X., Zhan, J., Xu, X., Zhang, M., Wang, C., & Cui, H. (2025). Fabrication and Characterization of a Novel Solid Nano-Dispersion of Emamectin Benzoate with High Dispersibility and Wettability. Nanomaterials, 15(7), 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15070495






