Preparation of Cellulose-Grafted Acrylic Acid Stabilized Jujube Branch Biochar-Supported Nano Zero-Valent Iron Composite for Cr(VI) Removal from Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Chemicals and Equipment
2.2. Sample Synthesis
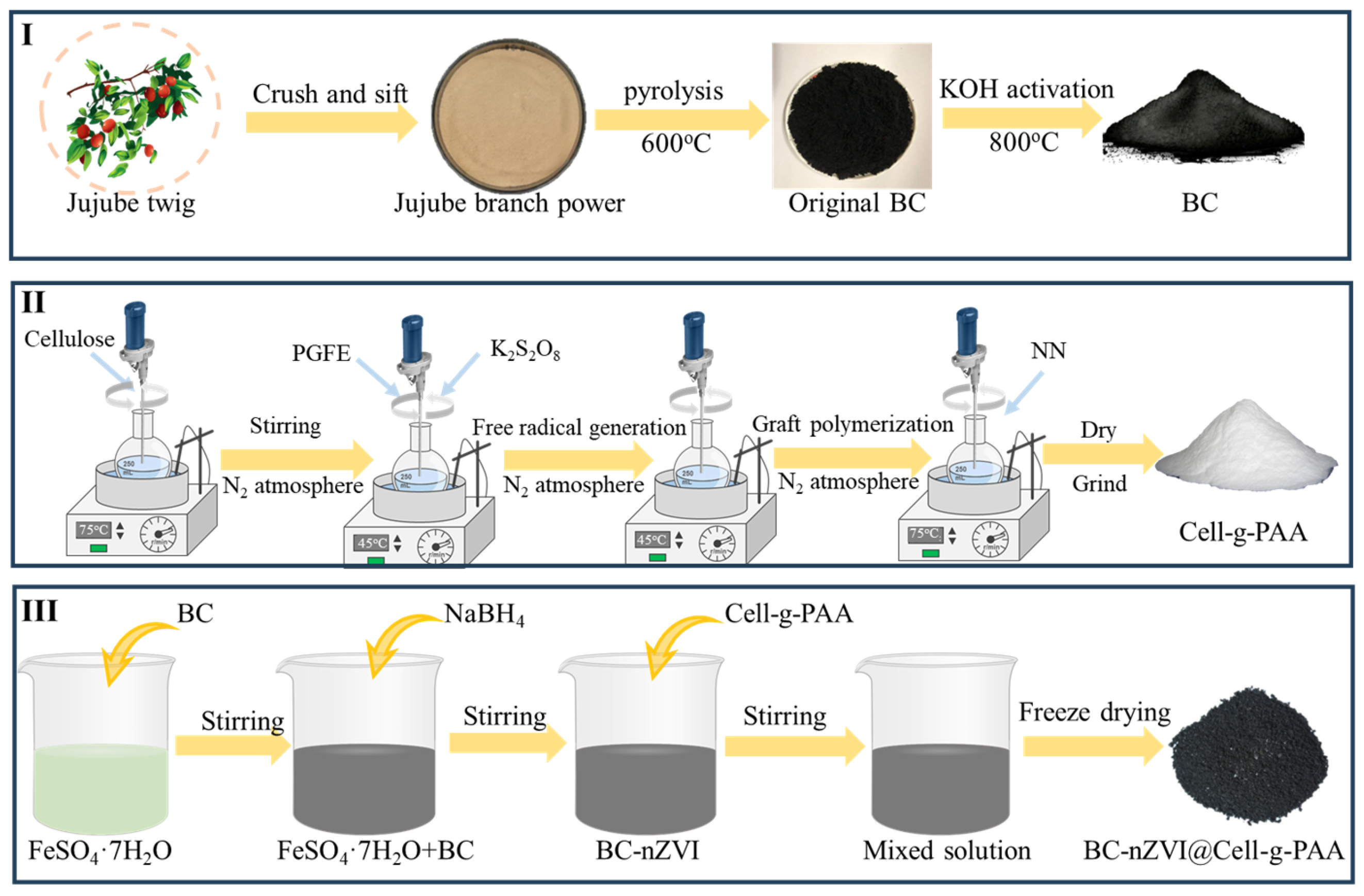
2.2.1. Preparation of BC and BC-nZVI
2.2.2. Synthesis of BC-nZVI@Cell-g-PAA Composites
2.3. Characterization Methods
2.4. Cr(VI) Removal Experiments
2.5. Isotherm and Adsorption Kinetics
3. Results and Discussion
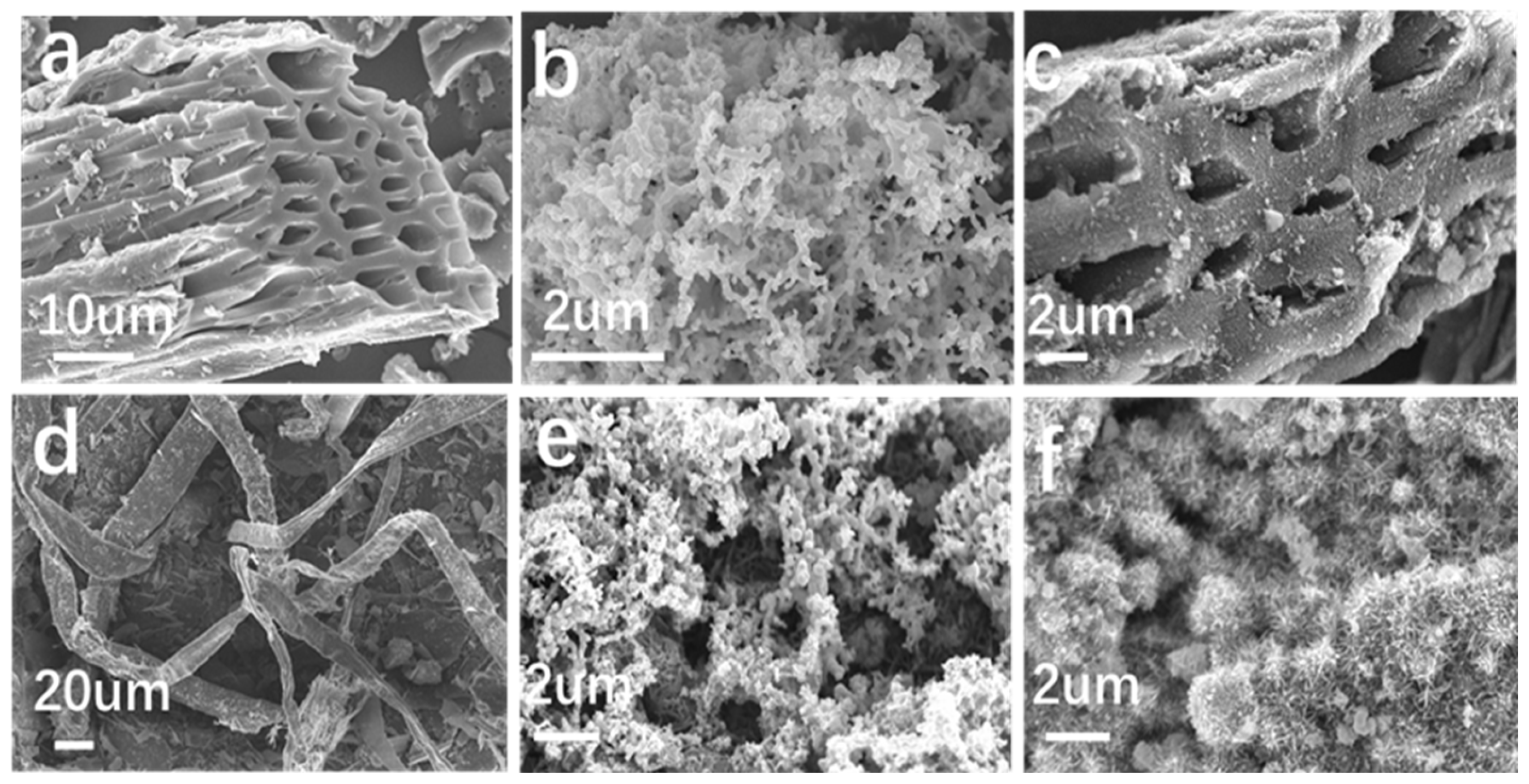
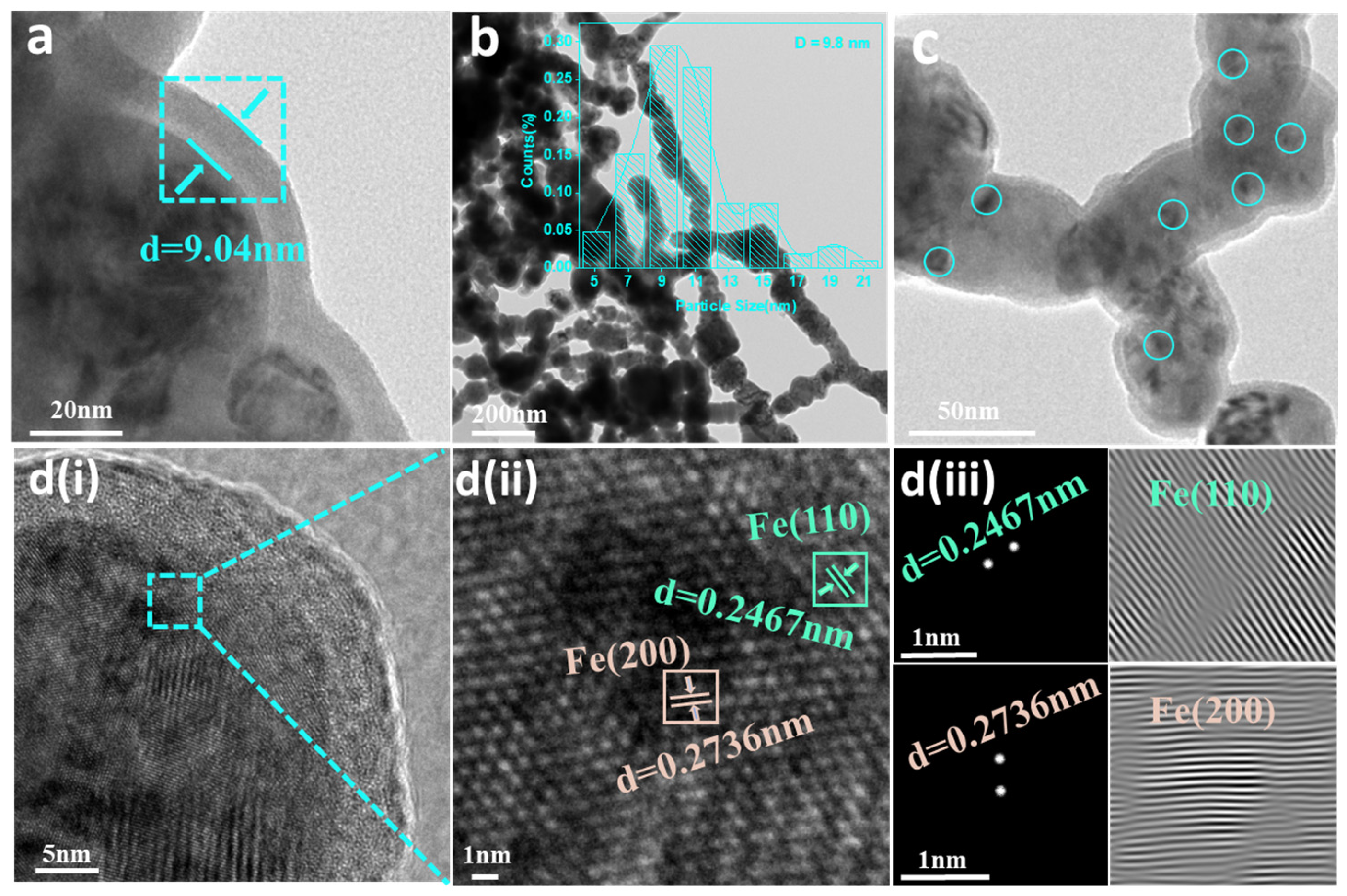
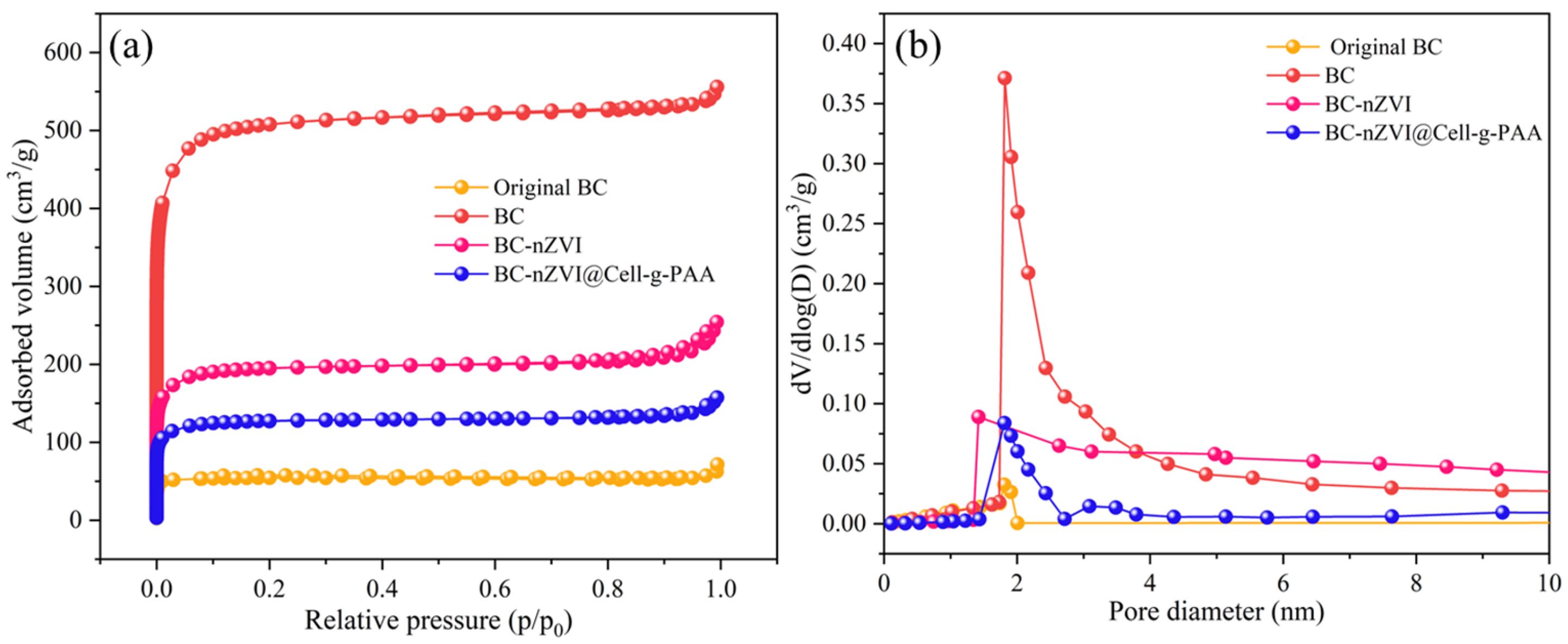
3.1. Characterization of Samples
3.2. Optimal Conditions for Cr(VI) Reduction
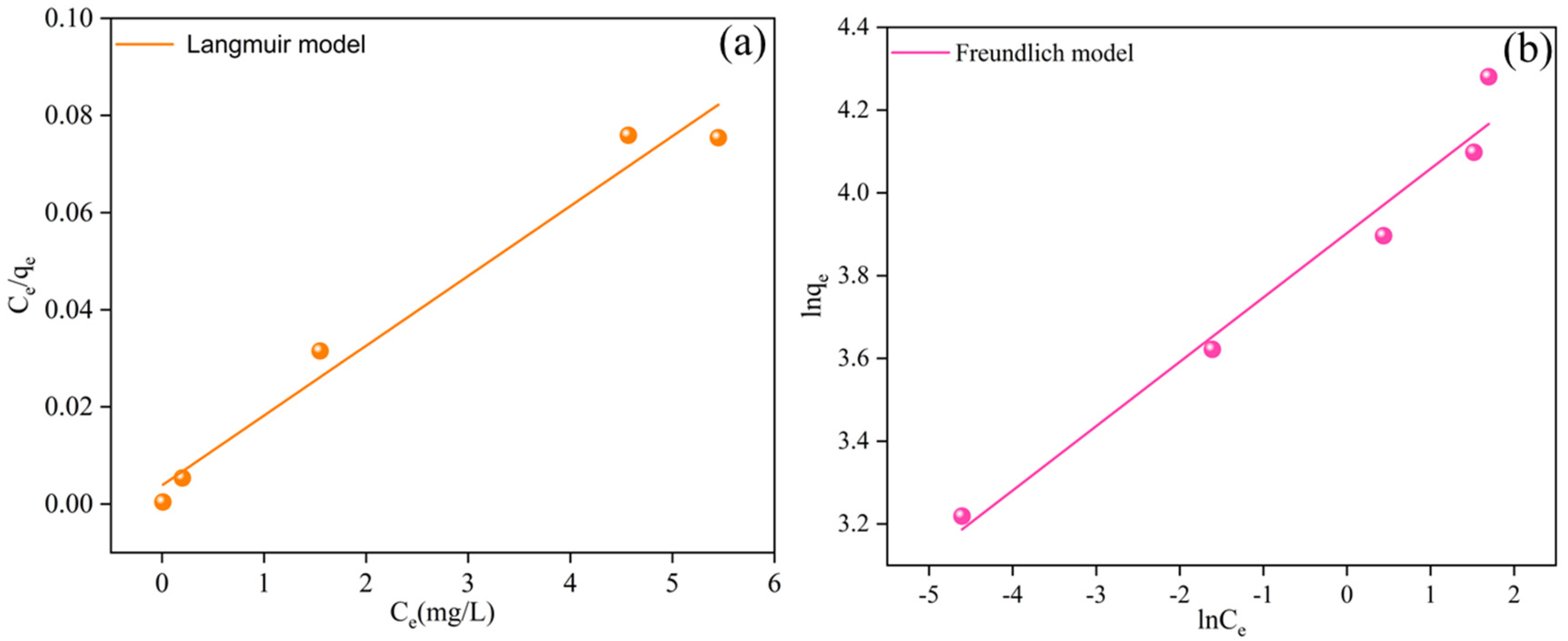
3.3. Cr(VI) Adsorption Isotherms
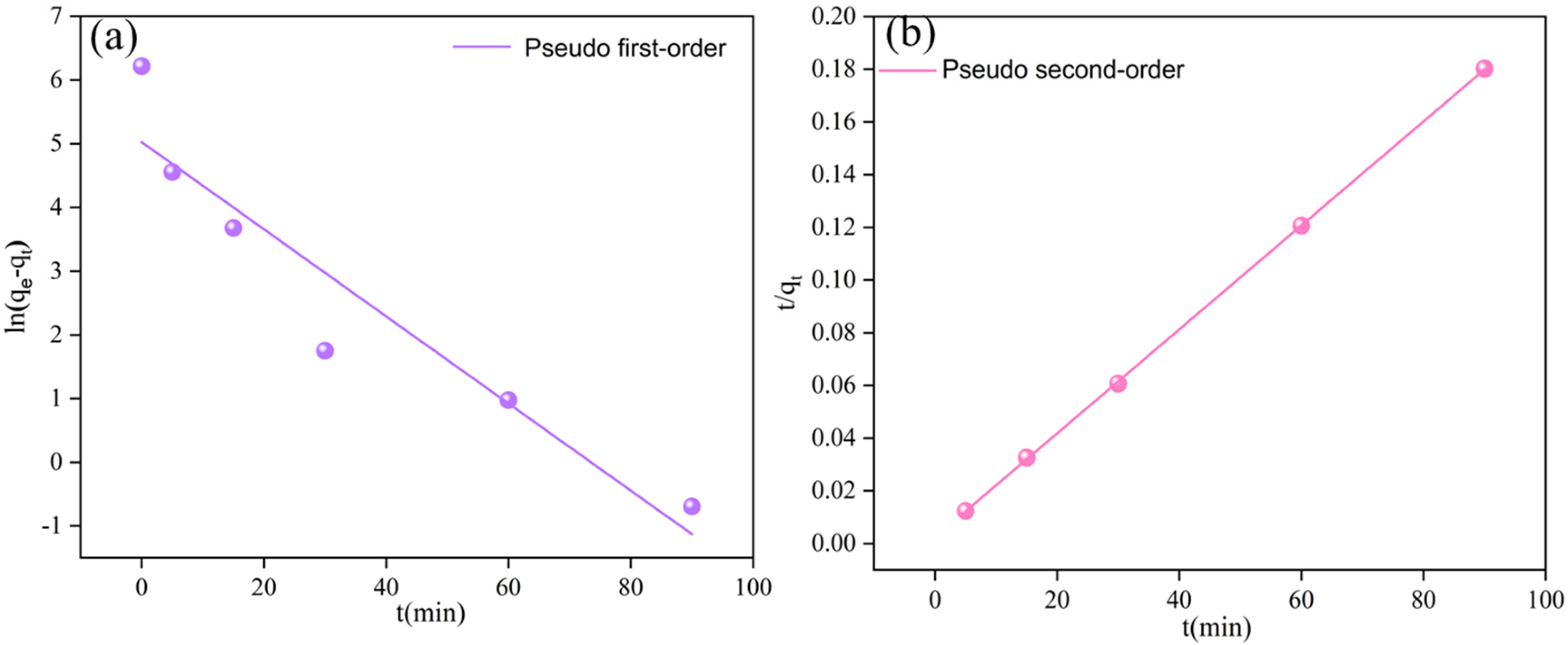
3.4. Cr(VI) Adsorption Kinetics
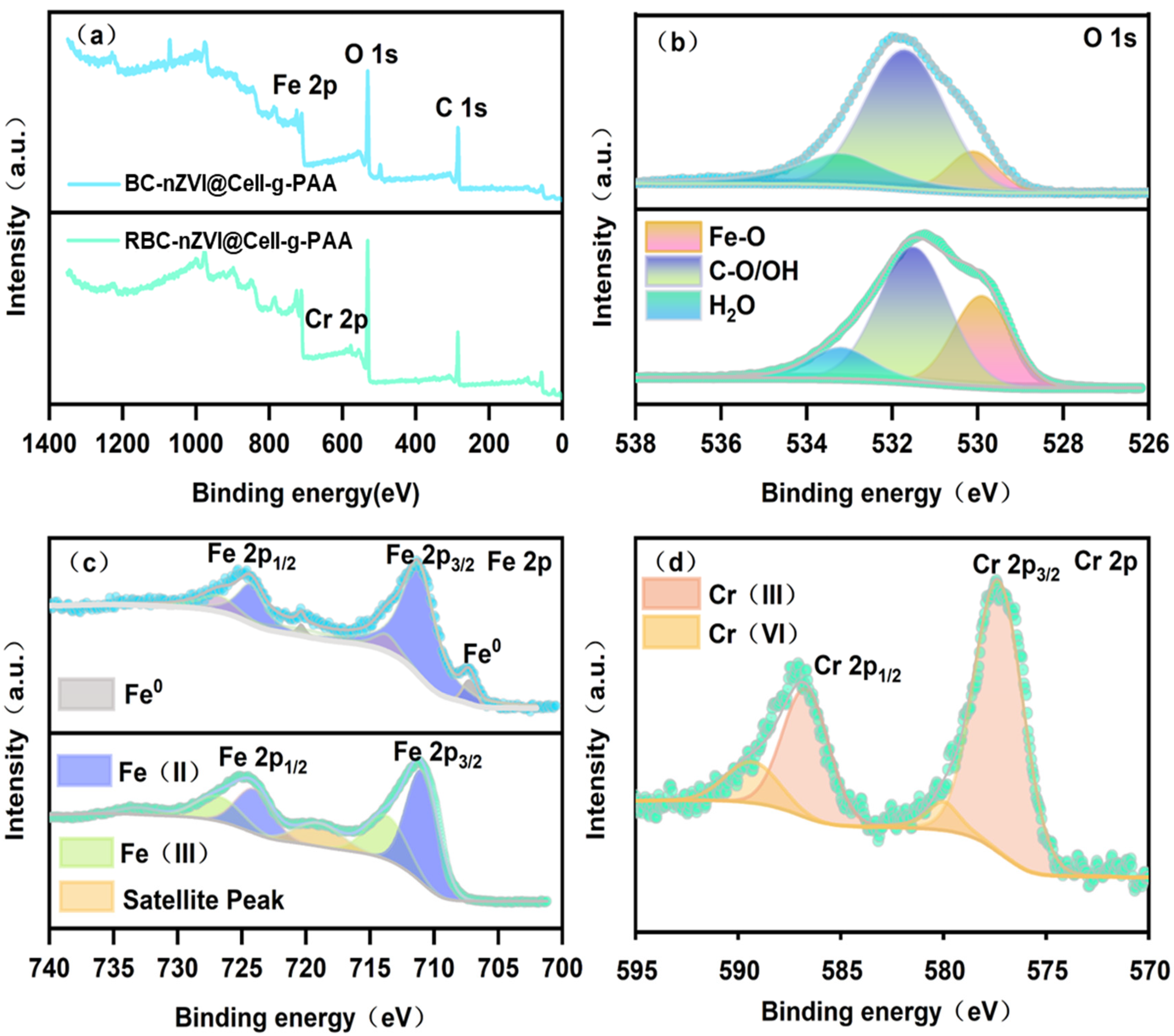
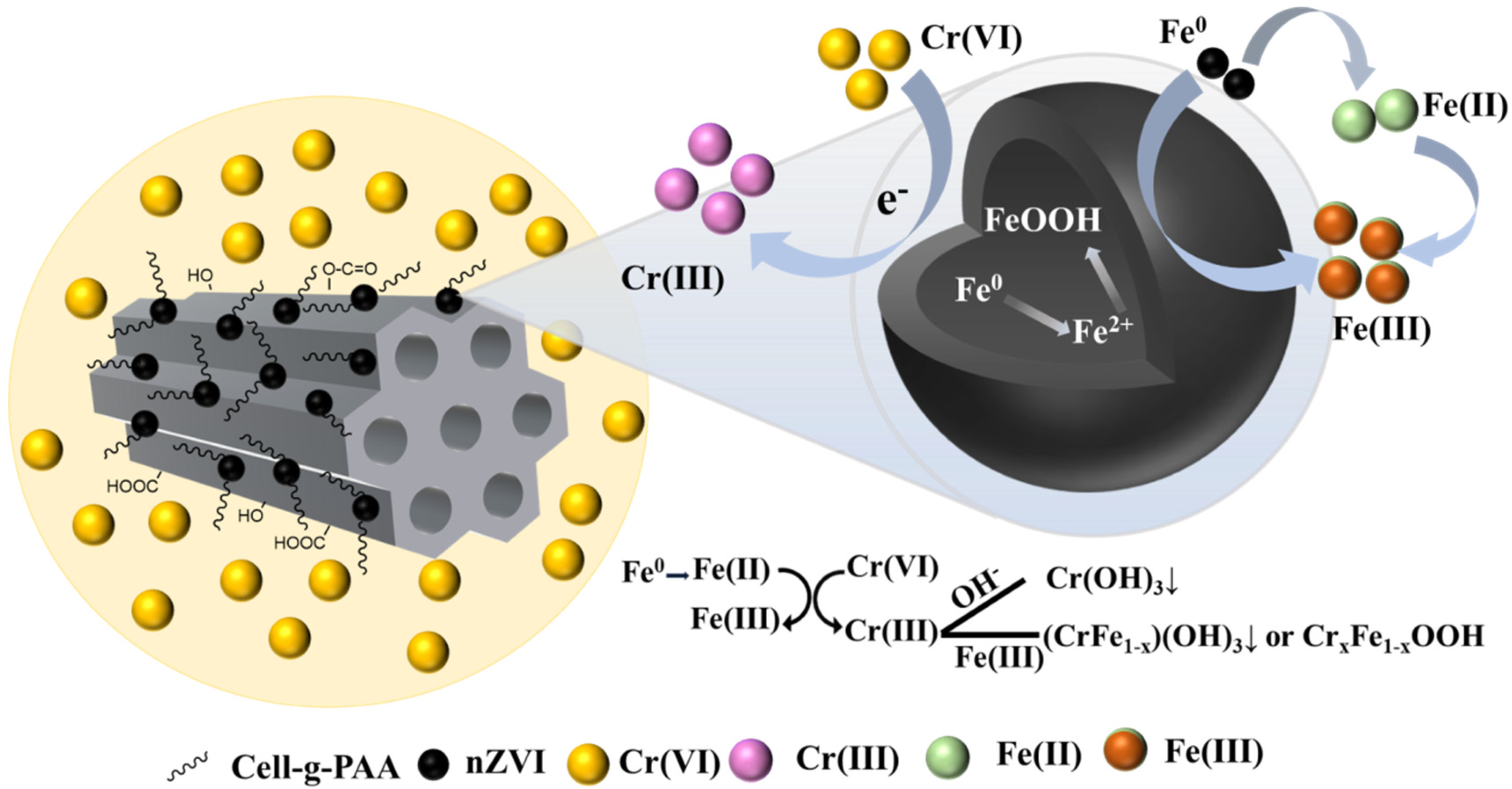
3.5. Cr(VI) Reduction Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hashim, M.A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Sahu, J.N.; Sengupta, B. Remediation technologies for heavy metal contaminated groundwater. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 2355–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.; Avasarala, S.; Liu, H. Hexavalent chromium release in drinking water distribution systems: New insights into zerovalent chromium in iron corrosion scales. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 13036–13045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, M. Toxicity and carcinogenicity of Cr(VI) in animal models and humans. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 1997, 27, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karn, B.; Kuiken, T.; Otto, M. Nanotechnology and in situ remediation: A review of the benefits and potential risks. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 1813–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.; Xu, S.; Zhao, C.; Lv, F.; Liu, H. Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions by sodium dodecyl sulfate stabilized nano zero-valent iron: A kinetics, equilibrium, thermodynamics study. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 1729–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Wan, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Lin, K.; Peng, C. Removal of decabromodiphenyl ethane (DBDPE) by BC/nZVI in the soil: Kinetics, pathways and mechanisms. J. Environ. 2022, 10, 107004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Velducea, H.A.; Moreno-Vásquez, M.J.; Guzmán, H.; Esquer, J.; Rodríguez-Félix, F.; Graciano-Verdugo, A.Z.; Santos-Sauceda, I.; Quintero-Reyes, I.E.; Barreras-Urbina, C.G.; Vásquez-López, C.; et al. Valorization of Agave angustifolia Bagasse Biomass from the Bacanora Industry in Sonora, Mexico as a Biochar Material: Preparation, Characterization, and Potential Application in Ibuprofen Removal. Sustain. Chem. 2024, 5, 196–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Gao, B. Removal of arsenic, methylene blue, and phosphate by biochar/AlOOH nanocomposite. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 226, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazycki, M.A.; Godinho, M.; Perondi, D.; Foletto, E.L.; Collazzo, G.C.; Dotto, G.L. New biochar from pecan nutshells as an alternative adsorbent for removing reactive red 141 from aqueous solutions. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhong, D.; Xu, Y.; Chang, H.; Shen, H.; Xu, C.; Mou, J.; Zhong, N. Enhanced removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by nano- zero-valent iron supported by KOH activated sludge-based biochar. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 651, 129697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maduabuchi, M.N. Agricultural Waste Materials as a Potential Adsorbent for Removal of Heavy Metals in Waste Water. Open Access J. Waste Manag. Xenobiotics 2018, 1, 000104. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, M.; Chai, Y.; Chen, A.; Yuan, J.; Shang, C.; Peng, L.; Peng, C. Enhancing cadmium removal efficiency through spinel ferrites modified biochar derived from agricultural waste straw. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109027–109037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, B.; Li, M.; Liu, C.; Qiu, Y. Removal of hexavalent chromium by biochar supported nZVI composite: Batch and fixed-bed column evaluations, mechanisms, and secondary contamination prevention. Chemosphere 2019, 217, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, M.; Zhou, M.; Li, Y.C.; Wang, J.; Gao, B.; Sato, S.; Feng, K.; Yin, W. Biochar-supported nZVI (nZVI/BC) for contaminant removal from soil and water: A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 820–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, X.; Lynch, I.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, P.; Wu, L.; Wu, X.; Li, T. Homogeneous dispersion of amorphous nanoscale zero-valent iron supported on chlorella-derived biochar: In-situ synthesis and application mechanism for Cr(VI) removal over a wide pH range. Sep. Purif. 2024, 330, 125207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Han, B.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Wu, P.; Liu, T.; Li, J.; Han, B.; Deng, N. The link between deacetylation and hepatotoxicity induced by exposure to hexavalent chromium. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 35, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Lyu, H.; Tang, J.; Song, B.; Zhen, M.; Liu, X. A novel biochar supported CMC stabilized nano zero-valent iron composite for hexavalent chromium removal from water. Chemosphere 2019, 217, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.M.; Ruan, Y.; Liang, A.P.; Shih, K.M.; Diao, Z.H.; Su, M.H.; Hou, L.A.; Chen, D.Y. Carbothermal reduction for preparing nZVI/BC to extract uranium: Insight into the iron species dependent uranium adsorption behavior. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 239, 117873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.W.; Tan, X.P.; Shaaban, M.; Cai, Y.J.; Wang, B.Y.; Peng, Q.A. Remediation of Cr(VI)-Contaminated Soil by Biochar-Supported Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron and the Consequences for Indigenous Microbial Communities. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.N.; Lin, Y.M.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.L. Synthesis, characterization and kinetics of bentonite supported nZVI for the removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Zeng, Y.; Zeng, G.; Huang, D.; Liang, J.; Zhao, F.; He, Q.; Xie, Y.; Wu, Y. EDDS-assisted reduction of Cr(VI) by nanoscale zero-valentiron. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 165, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Ren, H.; Ma, X.; Zhou, S.; Huang, J.; Jiao, W.; Qi, G.; Liu, Y. High-gravity continuous preparation of chitosan-stabilized nanoscale zero-valent iron towards Cr(VI) removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 390, 124–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Lv, B.; Zhou, Z.; Li, W.; Jing, G. Evaluation of highly active nanoscale zero-valent iron coupled with ultrasound for chromium(VI) removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 281, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z. Removal of chromium(VI) from wastewater using bentonite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron. Water Res. 2011, 45, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Cao, S.; Zhang, L.; Peng, X.; Wang, X.; Ai, Z.; Zhang, L. Structural dependent Cr(VI) adsorption and reduction of biochar: Hydrochar versus pyrochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 783, 147–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.G.; Zong, M.Z.; Yu, Y.; Kong, X.R.; Du, Q.; Liao, J.H. Removal of chromium(VI) from water using nanoscalezerovalent iron particles supported on herb-residue biochar. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 97, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wang, X.; Ma, J.; Liu, H.; Ning, P. Highly efficient immobilization of NZVI onto bio-inspired reagents functionalized polyacrylonitrile membrane for Cr(VI) reduction. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 1003–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurshid, H.; Mustafa, M.R.U.; Isa, M.H. Adsorption of chromium, copper, lead and mercury ions from aqueous solution using bio and nano adsorbents: A review of recent trends in the application of AC, BC, nZVI and MXene. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Ge, C.Z.; Li, X.L.; Li, L.; Wang, B.; Lin, A.J.; Yang, W.J. Does soluble starch improve the removal of Cr(VI) by nZVI loaded on biochar? Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsamhary, K.E. Moringa oleifera seed based green synthesis of copper nanoparticles: Characterization, environmental remediation and antimicrobial activity. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 11, 103820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Sun, Y.; Bai, L.; Han, C.; Sun, X. Ultrafast removal of Cr(VI) by chitosan coated biochar-supported nano zero-valent iron aerogel from aqueous solution: Application performance and reaction mechanism. Sep. Purif. 2023, 306, 122631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Ma, Q.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Guo, P.; Zhang, J.; Duan, G.; Lin, A.; Zhang, T.; Li, S. Efficient remediation of different concentrations of Cr-contaminated soils by nano zero-valent iron modified with carboxymethyl cellulose and biochar. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 147, 474–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.P.; Shaaban, M.; Yang, J.W.; Cai, Y.J.; Wang, B.Y.; Peng, Q.A. Biochar supported modified nZVI for effective remediation of hexavalent chromium: Enhanced performance and remediation mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114410. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Yang, X.; Lu, X.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y. Kinetics and Mechanisms of Cr(VI) Removal by nZVI: Influencing Parameters and Modification. Catalysts 2022, 12, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Wang, Z.Q.; An, S.W.; Zhao, J.; Yan, Y.C.; Zhang, D.J.; Wu, Z.N. Biochar-supported nZVI for the removal of Cr(VI) from soil and water: Advances in experimental research and engineering applications. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 316, 115211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.L.; Xiong, C.M.; Wang, W.; Tan, F.T.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Qiao, X.L. Facile modification of nanoscale zero-valent iron with high stability for Cr(VI) remediation. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 596, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.L.; Ren, L. Preparation and evaluation of activated carbon-based iron-containing adsorbents for enhanced Cr(VI) removal: Mechanism study. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 189, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Wang, X.; Du, K.; Mao, Y.; Han, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, X.; Wen, G. Hierarchical Lotus-Seedpod-Derived Porous Activated Carbon Encapsulated with NiCo2S4 for a High-Performance All-Solid-State Asymmetric Supercapacitor. Molecules 2023, 28, 5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhao, L.; Yang, X. Enhanced chitosan/Fe0-nanoparticles beads for hexavalent chromium removal from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 189, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.Y.; Zhao, L.; Sun, D.S.; Tan, X. Entrapment of nanoscale zero-valent iron in chitosan beads for hexavalent chromium removal from wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 184, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.K.; Li, J.X.; Huang, T.L.; Guan, X.H. The influences of iron characteristics, operating conditions and solution chemistry on contaminants removal by zero-valent iron: A review. Water Res. 2016, 100, 277–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.B.; Wang, Y.X.; Liu, H.L.; Zhang, Y.N.; Fan, Y.M.; Mo, S.P.; Li, H.X. Novel amino-modified bamboo-derived biochar-supported nano-zero-valent iron (AMBBC-nZVI) composite for efficient Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. 2023, 30, 119935–119946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.C.; Li, Y.H.; Qian, J.; Liu, S.N.; Wang, J.X. Remediation of Cr(VI)-contaminated soil by double-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron: Performance and mechanism. J. Soils Sediments 2024, 24, 1724–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.Y.; Shan, R.; Lu, L.L.; Yuan, H.R.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Chen, Y. High-efficiency removal of Cr(VI) by modified biochar derived from glue residue. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 254, 119935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, H.Y.; Hu, J.; Xu, H.C.; Zhao, Y.S. Study of the nano zero-valent iron stabilized by carboxymethyl cellulose loaded on biochar for remediation of Cr(VI)-contaminated groundwater. Sep. Purif. 2025, 353, 128494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.C.; Zhong, D.J.; Xu, Y.L.; Zhong, N.B. A novel superparamagnetic micro-nano-bio-adsorbent PDA/Fe3O4/BC for removal of hexavalent chromium ions from simulated and electroplating wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 23981–23993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.R.; Deng, J.M. Stabilization of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) with modified biochar for Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 332, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, M.; Wang, H.; Qi, L.; Cui, L.Q.; Quan, G.X.; Yan, J.L. Production of activated biochar via a self-blowing strategy-supported sulfidated nanoscale zerovalent iron with enhanced reactivity and stability for Cr(VI) reduction. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 315, 28108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.G.; Liu, D.; Chen, C.T.; Sun, B.J. In situ carbothermal synthesis of carbonized bacterial cellulose embedded with nano zero-valent iron for removal of Cr(VI). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 267, 131445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Yang, K.N.; Ma, J.; Ning, P. Formation and mechanism of nanoscale zerovalent iron supported by phosphoric acid modified biochar for highly efficient removal of Cr(VI). Adv. Powder Technol. 2023, 34, 103826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Yang, X.N.; Sun, R.H.; Wang, X.Z.; Yin, W.Q.; Wang, S.S.; Wang, J. The contribution of lignocellulosic constituents to Cr(VI) reduction capacity of biochar-supported zerovalent iron. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Chemical Component | C | H | O | N | Other Metals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (%) | 47.21 | 5.90 | 41.35 | 0.42 | 5.10 |
| Species BE (eV) | FWHM(eV) a | Area (%) | Species | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | A | B | A | |||
| 530.1 | 1.3 | 1.5 | 11.8 | 30.2 | Fe-O | |
| O 1s | 531.7 | 2.2 | 1.9 | 65.7 | 55.7 | C-O/OH |
| 533.2 | 2.3 | 1.7 | 22.5 | 14.1 | H2O | |
| 707.3/720.3 | 1.2/0.7 | / | 5.1 | 0.0 | Fe0 | |
| Fe 2p | 711.2/724.3 | 3.1/2.6 | 2.9/3.3 | 78.2 | 64.1 | Fe(II) |
| 713.7/726.8 | 2.3/3.5 | 3.7/4.2 | 16.7 | 35.9 | Fe(III) | |
| 577.3/586.7 | / | 2.8/3.7 | / | 85.1 | Cr(III) | |
| Cr 2p | 580/589.3 | / | 1.8/3.1 | / | 14.9 | Cr(VI) |
| Sample | SSA (m2 g−1) | Pore Volume (m3 g−1) | Average Pore Size (nm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vtotal | Vmic | |||
| Original BC | 220.87 | 0.1 | 0.08 | 1.79 |
| BC | 1987.6 | 0.86 | 0.66 | 1.72 |
| BC-nZVI | 735.6 | 0.39 | 0.25 | 2.23 |
| BC-nZVI@Cell-g-PAA | 142.3 | 0.07 | 0.12 | 2.38 |
| Sample | Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | R2 | KF (mg/g) | 1/n | R2 | |
| BC-nZVI@Cell-g-PAA | 69.54 | 3.75 | 0.96 | 49.50 | 0.15 | 0.95 |
| Model | Parameter | Sample |
|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order | K1 (min−1) | 0.06 |
| R2 | 0.87 | |
| Pseudo-second-order | K2·(g·mg−1·min−1) | 0.01 |
| R2 | 0.99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Tan, Z.; Shi, S.; Zhang, S.; Yang, S.; Zhang, X.; Gao, P.; Zhang, Y. Preparation of Cellulose-Grafted Acrylic Acid Stabilized Jujube Branch Biochar-Supported Nano Zero-Valent Iron Composite for Cr(VI) Removal from Water. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15060441
Wang X, Tan Z, Shi S, Zhang S, Yang S, Zhang X, Gao P, Zhang Y. Preparation of Cellulose-Grafted Acrylic Acid Stabilized Jujube Branch Biochar-Supported Nano Zero-Valent Iron Composite for Cr(VI) Removal from Water. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(6):441. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15060441
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaoxue, Zhe Tan, Shuang Shi, Shanyuan Zhang, Shuang Yang, Xingyu Zhang, Pingqiang Gao, and Yan Zhang. 2025. "Preparation of Cellulose-Grafted Acrylic Acid Stabilized Jujube Branch Biochar-Supported Nano Zero-Valent Iron Composite for Cr(VI) Removal from Water" Nanomaterials 15, no. 6: 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15060441
APA StyleWang, X., Tan, Z., Shi, S., Zhang, S., Yang, S., Zhang, X., Gao, P., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Preparation of Cellulose-Grafted Acrylic Acid Stabilized Jujube Branch Biochar-Supported Nano Zero-Valent Iron Composite for Cr(VI) Removal from Water. Nanomaterials, 15(6), 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15060441







