Charging and Aggregation of Nano-Clay Na-Montmorillonite in the Presence of Ciprofloxacin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Electrophoretic Mobility
2.3. Dynamic Lighting Scattering
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Electrophoretic Mobility and Hydrodynamic Diameter of Na-Montmorillonite
3.2. The Stability Ratio of Na-Montmorillonite
3.3. The Relationship Between Critical Coagulation Ionic Strength and Surface Charge Density Based on the DLVO Theory
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thiele-Bruhn, S. Pharmaceutical Antibiotic Compounds in Soils—A Review. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2003, 166, 145–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golet, E.M.; Strehler, A.; Alder, A.C.; Giger, W. Determination of Fluoroquinolone Antibacterial Agents in Sewage Sludge and Sludge-Treated Soil Using Accelerated Solvent Extraction Followed by Solid-Phase Extraction. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 5455–5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andras, P.; Lazarus, J.; Roberts, G.; Lynden, S.J. Environmental Risk. In Proceedings of the Joint Symposium on Socially Inspired Computing; The Society for the Study of Artificial Intelligence and the Simulation of Behaviour: Bath, UK, 2005; ISBN 1-902956-48-4. [Google Scholar]
- Katsikaros, A.G.; Chrysikopoulos, C.V. Estimation of Urine Volume in Municipal Sewage Originating from Patients Receiving Antibiotics at a Private Clinic in Crete, Greece. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 134858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, D.G.J. Antibiotics in the Environment. Ups. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 119, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rooklidge, S.J. Environmental Antimicrobial Contamination from Terraccumulation and Diffuse Pollution Pathways. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 325, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halling-Sorensen, B.; Holten Lutzhoft, H.C.; Andersen, H.R.; Ingerslev, F. Environmental Risk Assessment of Antibiotics: Comparison of Mecillinam, Trimethoprim and Ciprofloxacin. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2000, 46, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggen, T.; Vogelsang, C. Occurrence and Fate of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Wastewater. Compr. Anal. Chem. 2015, 67, 245–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudevan, D.; Bruland, G.L.; Torrance, B.S.; Upchurch, V.G.; MacKay, A.A. pH-Dependent Ciprofloxacin Sorption to Soils: Interaction Mechanisms and Soil Factors Influencing Sorption. Geoderma 2009, 151, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Gao, B.; Li, H.; Ma, L.Q. Effects of H and Ionic Strength on Sulfamethoxazole and Ciprofloxacin Transport in Saturated Porous Media. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2011, 126, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ma, L.Q.; Gao, B.; Gu, C. Effects of Cu and Ca Cations and Fe/Al Coating on Ciprofloxacin Sorption onto Sand Media. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 252–253, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, J.L. The Role of Natural Environments in the Evolution of Resistance Traits in Pathogenic Bacteria. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 276, 2521–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, D.; Hilton, M.; Thomas, K.V. Investigating the Environmental Transport of Human Pharmaceuticals to Streams in the United Kingdom. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 333, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picó, Y.; Andreu, V. Fluoroquinolones in Soil—Risks and Challenges. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 1287–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, C.H. Adsorption and Oxidation of Fluoroquinolone Antibacterial Agents and Structurally Related Amines with Goethite. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 1502–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.-L.; Tan, M.; Qiu, A.-M.; Tao, Z.; Wang, C.-H. Antibiotics for Treatment of Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Network Meta-Analysis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2017, 17, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verderosa, A.D.; de la Fuente-Núñez, C.; Mansour, S.C.; Cao, J.; Lu, T.K.; Hancock, R.E.W.; Fairfull-Smith, K.E. Ciprofloxacin-Nitroxide Hybrids with Potential for Biofilm Control. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 138, 590–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.T.; Dao, T.H.; Truong, T.T.; Nguyen, T.M.T.; Pham, T.D. Adsorption Characteristic of Ciprofloxacin Antibiotic onto Synthesized Alpha Alumina Nanoparticles with Surface Modification by Polyanion. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thai, T.; Salisbury, B.H.; Zito, P.M. Ciprofloxacin. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, A.Q.; Nguyen, T.T.M.; Phan, D.T.; Nguyen, N.T.M.; Nguyen-Thanh, L.; Nguyen, D.N.; Nguyen, A.D.; Pham, T.D.; Nguyen, M.N. Antibiotics Can Alter the Dispersibility and Reroute the Transport of Microsized Colloids. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashiq, A.; Sarkar, B.; Adassooriya, N.; Walpita, J.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Ok, Y.S.; Vithanage, M. Sorption Process of Municipal Solid Waste Biochar-Montmorillonite Composite for Ciprofloxacin Removal in Aqueous Media. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Karthikeyan, K.G. Sorption of the Antimicrobial Ciprofloxacin to Aluminum and Iron Hydrous Oxides. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 9166–9173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Li, Z.; Hong, H. Influence of Types and Charges of Exchangeable Cations on Ciprofloxacin Sorption by Montmorillonite. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2012, 27, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmosini, N.; Lee, L.S. Ciprofloxacin Sorption by Dissolved Organic Carbon from Reference and Bio-Waste Materials. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szilágyi, I.; Labádi, I.; Hernádi, K.; Kiss, T.; Pálinkó, I. Montmorillonite Intercalated Cu (II)-Histidine Complex—Synthesis, Characterisation and Superoxide Dismutase Activity. In Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 158, pp. 1011–1018. ISBN 0167-2991. [Google Scholar]
- Segad, M.; Jonsson, B.; Åkesson, T.; Cabane, B. Ca/Na Montmorillonite: Structure, Forces and Swelling Properties. Langmuir 2010, 26, 5782–5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigatti, M.F.; Galán, E.; Theng, B.K.G. Structure and Mineralogy of Clay Minerals. In Developments in Clay Science; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 5, pp. 21–81. ISBN 9780080982588. [Google Scholar]
- Nosrati, A.; Addai-Mensah, J.; Skinner, W. pH-Mediated Interfacial Chemistry and Particle Interactions in Aqueous Muscovite Dispersions. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 152, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aristilde, L.; Lanson, B.; Miéhé-Brendlé, J.; Marichal, C.; Charlet, L. Enhanced Interlayer Trapping of a Tetracycline Antibiotic within Montmorillonite Layers in the Presence of Ca and Mg. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 464, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avena, M.J.; De Pauli, C.P. Proton Adsorption and Electrokinetics of an Argentinean Montmorillonite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 202, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimoto, Y.; Chassagne, C.; Adachi, Y. Dielectric and Electrophoretic Response of Montmorillonite Particles as Function of Ionic Strength. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 404, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, J.D.G.; Ramos-Tejada, M.M.; Arroyo, F.J.; González-Caballero, F. Rheological and Electrokinetic Properties of Sodium Montmorillonite Suspensions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 229, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, A.; González-Caballero, F.; Bruque, J.M. On the Zeta Potential and Surface Charge Density of Montmorillonite in Aqueous Electrolyte Solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1986, 113, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombácz, E.; Szekeres, M. Surface Charge Heterogeneity of Kaolinite in Aqueous Suspension in Comparison with Montmorillonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2006, 34, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishijima, H.; Kudo, M.; Masuko, T. Effect of pH on Rheological Properties of Synthetic Hectorite/Water Suspensions. Nihon Reoroji Gakkaishi 2000, 28, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michot, L.J.; Bihannic, I.; Thomas, F.; Lartiges, B.S.; Waldvogel, Y.; Caillet, C.; Thieme, J.; Funari, S.S.; Levitz, P. Coagulation of Na-Montmorillonite by Inorganic Cations at Neutral pH. A Combined Transmission X-Ray Microscopy, Small Angle and Wide Angle X-Ray Scattering Study. Langmuir 2013, 29, 3500–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, R.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Xi, Y.; Zhu, J.; He, H. Adsorbents Based on Montmorillonite for Contaminant Removal from Water: A Review. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 123, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majzik, A.; Tombácz, E. Interaction between Humic Acid and Montmorillonite in the Presence of Calcium Ions II. Colloidal Interactions: Charge State, Dispersing and/or Aggregation of Particles in Suspension. Org. Geochem. 2007, 38, 1330–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.J.; Li, Z.; Jiang, W.T.; Jean, J.S.; Liu, C.C. Cation Exchange Interaction between Antibiotic Ciprofloxacin and Montmorillonite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 183, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, E.; Duan, W.; Wang, A.; Zheng, Y. Oriented Growth of Poly (m-Phenylenediamine) on Calotropis Gigantea Fiber for Rapid Adsorption of Ciprofloxacin. Chemosphere 2017, 171, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.D.; Vu, T.N.; Nguyen, H.L.; Le, P.H.P.; Hoang, T.S. Adsorptive Removal of Antibiotic Ciprofloxacin from Aqueous Solution Using Protein-Modified Nanosilica. Polymers 2020, 12, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, T.H.; Tran, T.T.; Nguyen, V.R.; Pham, T.N.M.; Vu, C.M.; Pham, T.D. Removal of Antibiotic from Aqueous Solution Using Synthesized TiO2 Nanoparticles: Characteristics and Mechanisms. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.J.; Li, Z.; Jiang, W.T. Adsorption of Ciprofloxacin on 2:1 Dioctahedral Clay Minerals. Appl. Clay Sci. 2011, 53, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.T.; Wang, C.J.; Li, Z. Intercalation of Ciprofloxacin Accompanied by Dehydration in Rectorite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 74, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Li, Z.; Hong, H.; Yin, K.; Tie, L. Adsorption and Intercalation of Ciprofloxacin on Montmorillonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 50, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagaly, G.; Ziesmer, S. Colloid Chemistry of Clay Minerals: The Coagulation of Montmorillonite Dispersions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 100–102, 105–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Ookawa, M.; Yamada, S. The Effects of Surface Charging Properties on Colloid Transport in Porous Media. J. Jpn. Soc. Civ. Eng. Ser. A2 (Appl. Mech. (AM)) 2014, 70, I_743–I_752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Nanaumi, H.; Muto, Y. Initial Deposition Rate of Latex Particles in the Packed Bed of Zirconia Beads. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 347, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, Y.; Kobayashi, M. Transport of Colloidal Silica in Unsaturated Sand: Effect of Charging Properties of Sand and Silica Particles. Chemosphere 2016, 154, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Sugimoto, T.; Yamashita, Y.; Kobayashi, M. Aggregation and Charging of Natural Allophane Particles in the Presence of Oxyanions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 649, 129413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, C.; Masuda, K.; Kobayashi, M. The Effect of Monovalent Anion Species on the Aggregation and Charging of Allophane Clay Nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 577, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombácz, E.; Szekeres, M. Colloidal Behavior of Aqueous Montmorillonite Suspensions: The Specific Role of pH in the Presence of Indifferent Electrolytes. Appl. Clay Sci. 2004, 27, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, A.; Suzuki, T.; Kobayashi, M. Strength of Humic Acid Aggregates: Effects of Divalent Cations and Solution pH. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 8559–8567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missana, T.; Adell, A. On the Applicability of DLVO Theory to the Prediction of Clay Colloids Stability. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 230, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derjaguin, B.; Landau, L. Theory of the Stability of Strongly Charged Lyophobic Sols and of the Adhesion of Strongly Charged Particles in Solutions of Electrolytes. Prog. Surf. Sci. 1993, 43, 30–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohshima, H. Electrical Phenomena at Interfaces and Biointerfaces: Fundamentals and Applications in Nano-, Bio-, and Environmental Sciences; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; ISBN 1118135423. [Google Scholar]
- Hakim, A.; Kobayashi, M. Charging, Aggregation, and Aggregate Strength of Humic Substances in the Presence of Cationic Surfactants: Effects of Humic Substances Hydrophobicity and Surfactant Tail Length. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 577, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohshima, H.; Furusawa, K. Electrical Phenomena at Interfaces: Fundamentals: Measurements, and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998; Volume 76, ISBN 0824790391. [Google Scholar]
- Trefalt, G.; Szilagyi, I.; Borkovec, M. Poisson–Boltzmann Description of Interaction Forces and Aggregation Rates Involving Charged Colloidal Particles in Asymmetric Electrolytes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 406, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, A.; Tanu, F.Z.; Alam, S.S. Interaction, Adhesion and Aggregation of Microplastic/Nanoplastic Particles: Effects of Plastic Polymer Type. Asian J. Water Environ. Pollut. 2023, 20, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Elimelech, M. Colloidal Stability of Cellulose Nanocrystals in Aqueous Solutions Containing Monovalent, Divalent, and Trivalent Inorganic Salts. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 584, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, T.; Szilagyi, I.; Oncsik, T.; Borkovec, M.; Trefalt, G. Aggregation of Colloidal Particles in the Presence of Multivalent Co-Ions: The Inverse Schulze-Hardy Rule. Langmuir 2015, 31, 6610–6614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, Y.; Watkins, J.L.; Kim, J.; Curry, K.J.; Bennett, R.H. Aggregation of Montmorillonite and Organic Matter in Aqueous Media Containing Artificial Seawater. Geochem. Trans. 2009, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Tian, R.; Liu, X.; Zhu, H.; Tang, Y.; Xu, C.; Shah, G.M.; Li, H. Specific Ion Effects of Cu2+, Ca2+ and Mg2+ on Montmorillonite Aggregation. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 179, 105154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimoto, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Adachi, Y. Viscosity of Dilute Na-Montmorillonite Suspensions in Electrostatically Stable Condition under Low Shear Stress. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 440, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, K.S. Introduction to Dynamic Light Scattering by Macromolecules; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; ISBN 0323140351. [Google Scholar]
- Kretzschmar, R.; Holthoff, H.; Sticher, H. Influence of pH and Humic Acid on Coagulation Kinetics of Kaolinite: A Dynamic Light Scattering Study. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 202, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, C.M.; Rösslein, M.; Wick, P.; Prina-Mello, A. Characterisation of Particles in Solution–a Perspective on Light Scattering and Comparative Technologies. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2018, 19, 732–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambinossi, F.; Mylon, S.E.; Ferri, J.K. Aggregation Kinetics and Colloidal Stability of Functionalized Nanoparticles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 222, 332–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, Y.; Katoh, Y.; Ohshima, H. Colloidal Stability of Aqueous Polymeric Dispersions: Effect of pH and Salt Concentration. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2005, 42, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrens, S.H.; Borkovec, M.; Semmler, M. Aggregation in Sulfate Latex Suspensions: The Role of Charge for Stability Predictions. In Trends in Colloid and Interface Science XII; Steinkopff: Dresden, Germany, 1998; pp. 66–69. [Google Scholar]
- Grolimund, D.; Elimelech, M.; Borkovec, M. Aggregation and Deposition Kinetics of Mobile Colloidal Particles in Natural Porous Media. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2001, 191, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, Y.; Koga, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Inada, M. Study of Colloidal Stability of Allophane Dispersion by Dynamic Light Scattering. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2005, 265, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordillo-Galeano, A.; Mora-Huertas, C.E. Hydrodynamic Diameter and Zeta Potential of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: Emphasizing Some Parameters for Correct Measurements. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 620, 126610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trefalt, G.; Szilagyi, I.; Téllez, G.; Borkovec, M. Colloidal Stability in Asymmetric Electrolytes: Modifications of the Schulze-Hardy Rule. Langmuir 2017, 33, 1695–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.; Kaufhold, S. Hamaker Functions for Kaolinite and Montmorillonite. Colloids Interface Sci. Commun. 2021, 43, 100442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Gao, B.; Yang, L.Y.; Ma, L.Q. Montmorillonite Enhanced Ciprofloxacin Transport in Saturated Porous Media with Sorbed Ciprofloxacin Showing Antibiotic Activity. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2015, 173, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


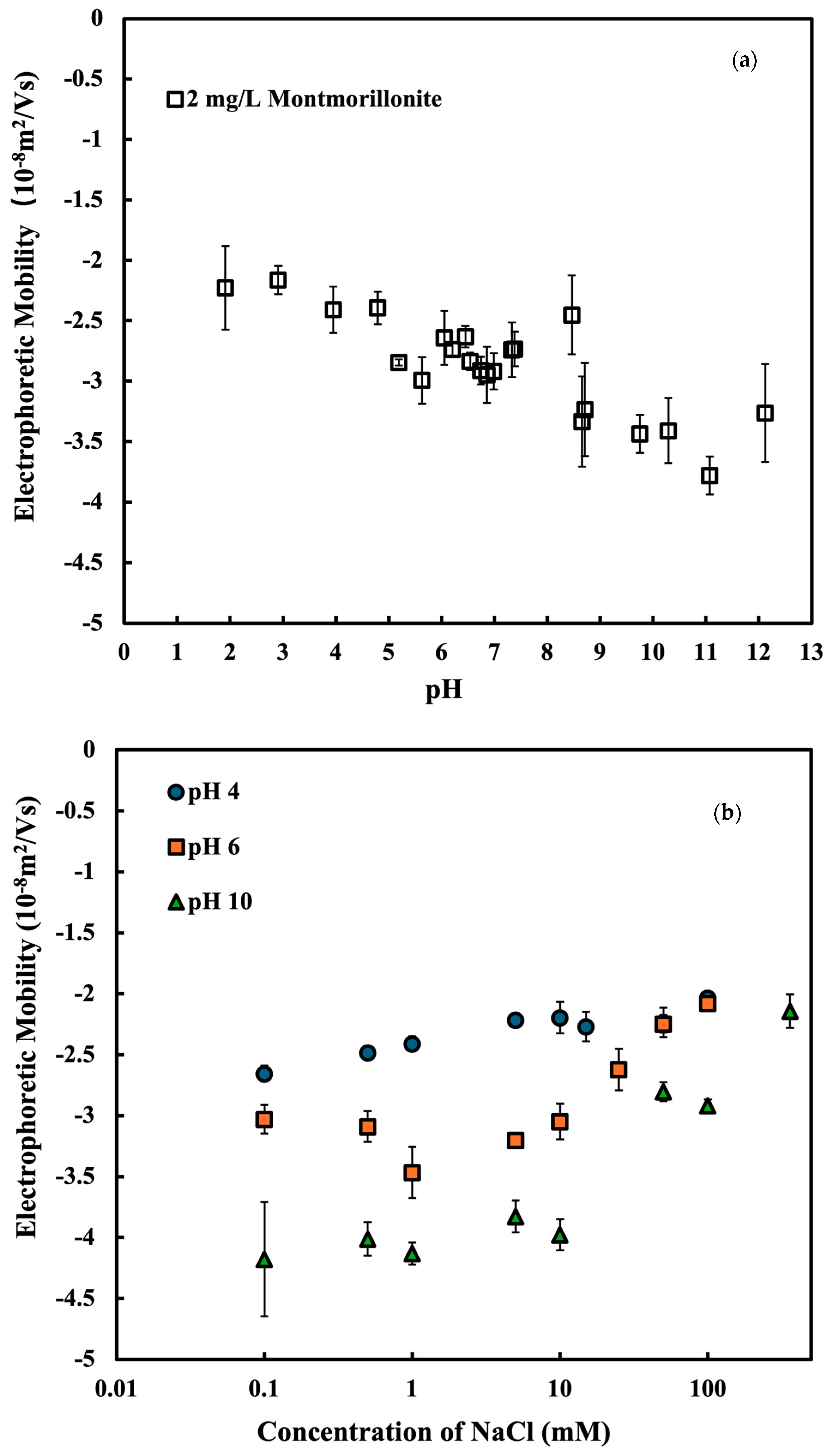







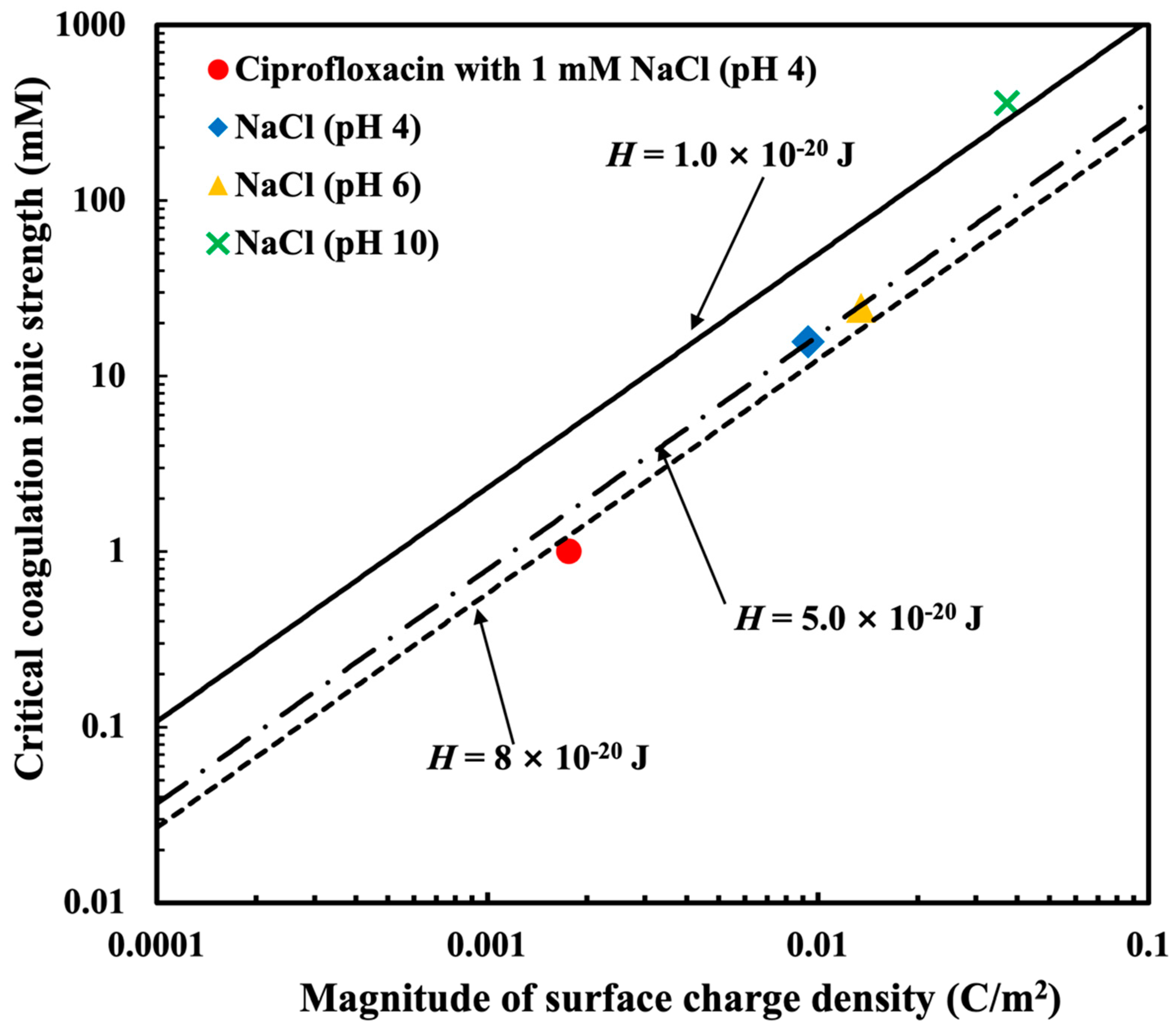

| Ciprofloxacin (pH 4) | NaCl (pH 4) | NaCl (pH 6) | NaCl (pH 10) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCC (mM) | 0.034 | 15.69 | 24.54 | 360.19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, C.; Kobayashi, M. Charging and Aggregation of Nano-Clay Na-Montmorillonite in the Presence of Ciprofloxacin. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15050389
Zeng C, Kobayashi M. Charging and Aggregation of Nano-Clay Na-Montmorillonite in the Presence of Ciprofloxacin. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(5):389. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15050389
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Chuanzi, and Motoyoshi Kobayashi. 2025. "Charging and Aggregation of Nano-Clay Na-Montmorillonite in the Presence of Ciprofloxacin" Nanomaterials 15, no. 5: 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15050389
APA StyleZeng, C., & Kobayashi, M. (2025). Charging and Aggregation of Nano-Clay Na-Montmorillonite in the Presence of Ciprofloxacin. Nanomaterials, 15(5), 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15050389






