Evaluating the In Situ Effects of Whole Protein Coronas on the Biosensing of Antibody-Immobilized Nanoparticles Using Two-Color Fluorescence Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Fluorescently Labeled IgG and Anti-IgG
2.3. Preparation of IgG-AuNPs
2.4. Incubation of Protein Coronas and Biosensing of Anti-IgG
2.5. NTA Measurement
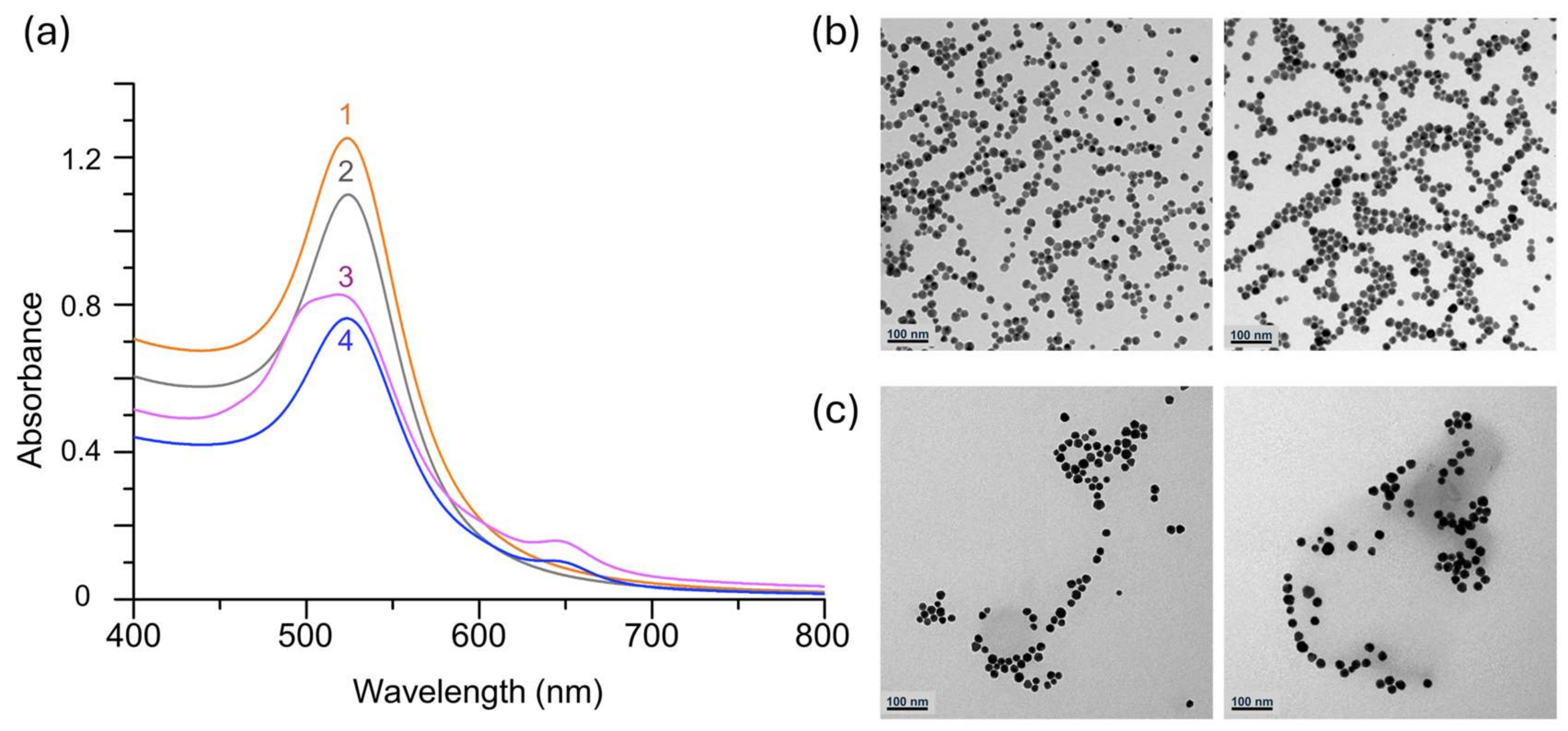
2.6. Characterization by UV–VIS Spectrophotometry and TEM
3. Data and Results
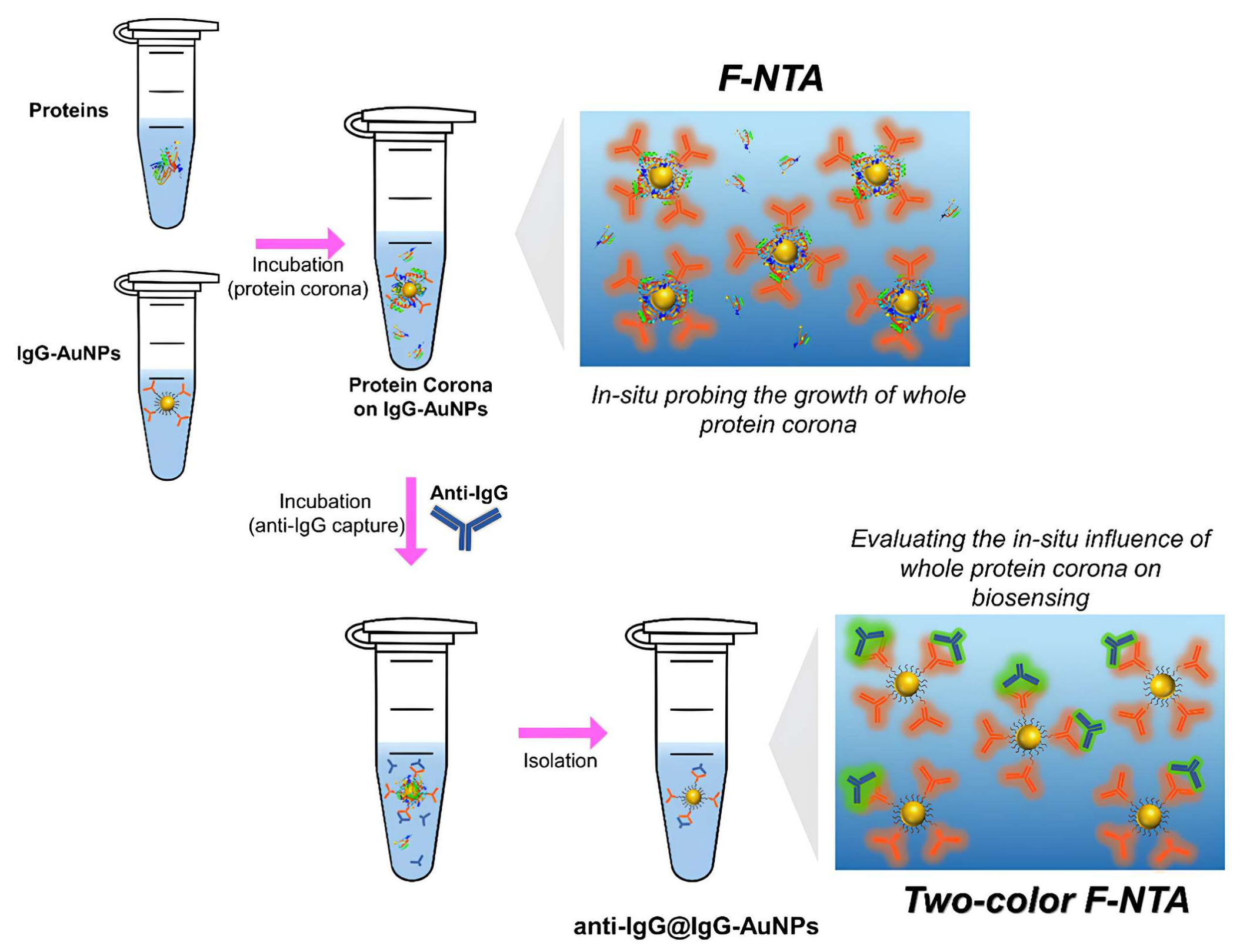
3.1. Assement Strategy
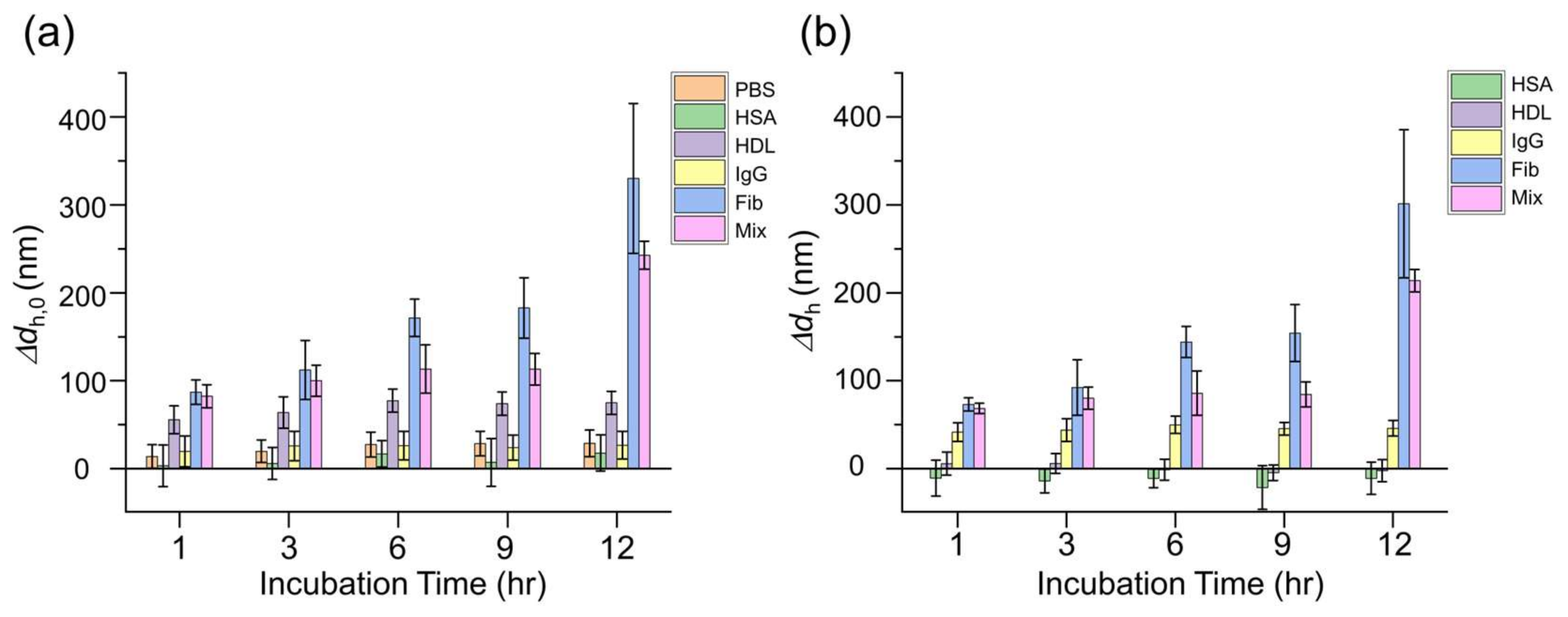
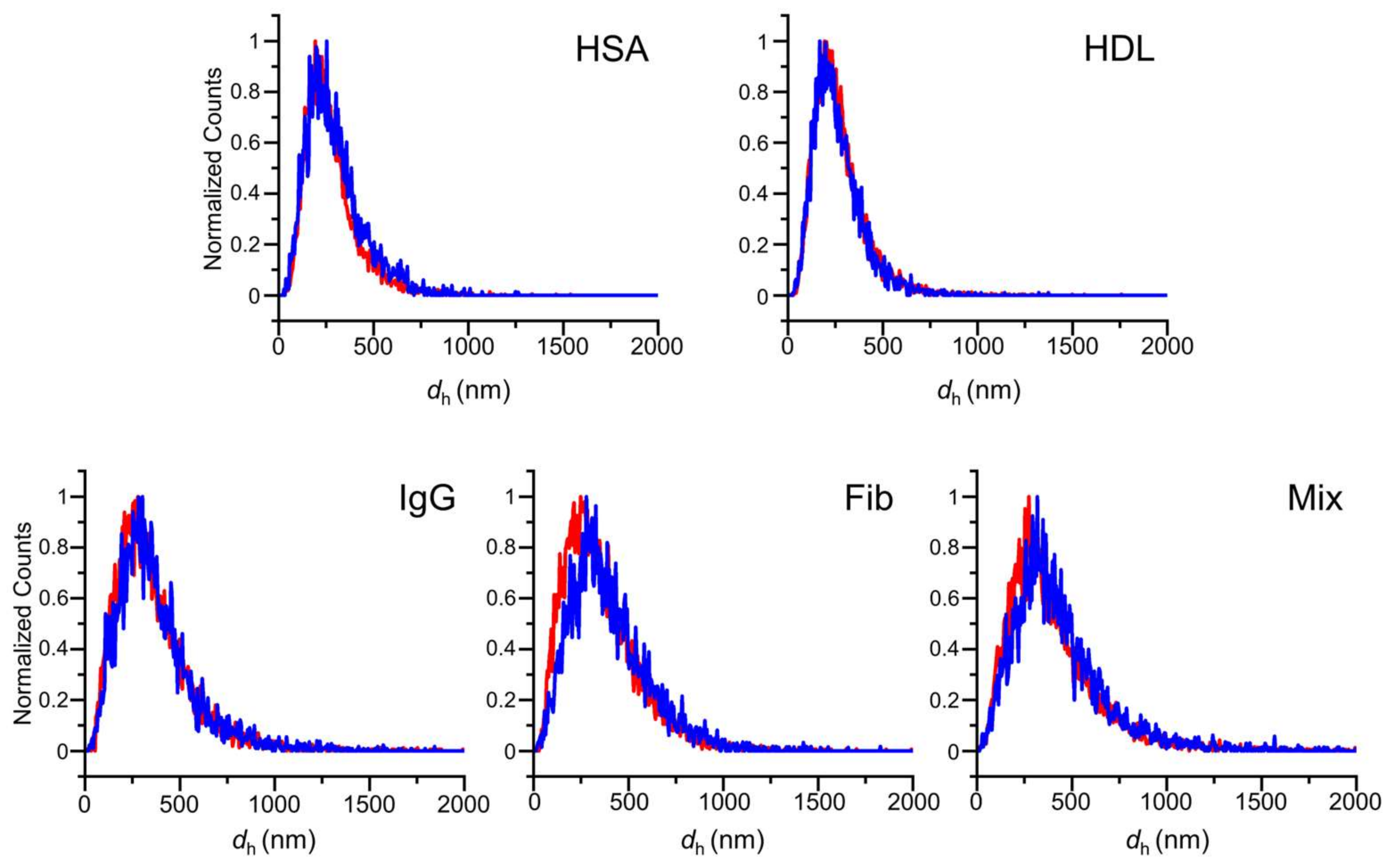
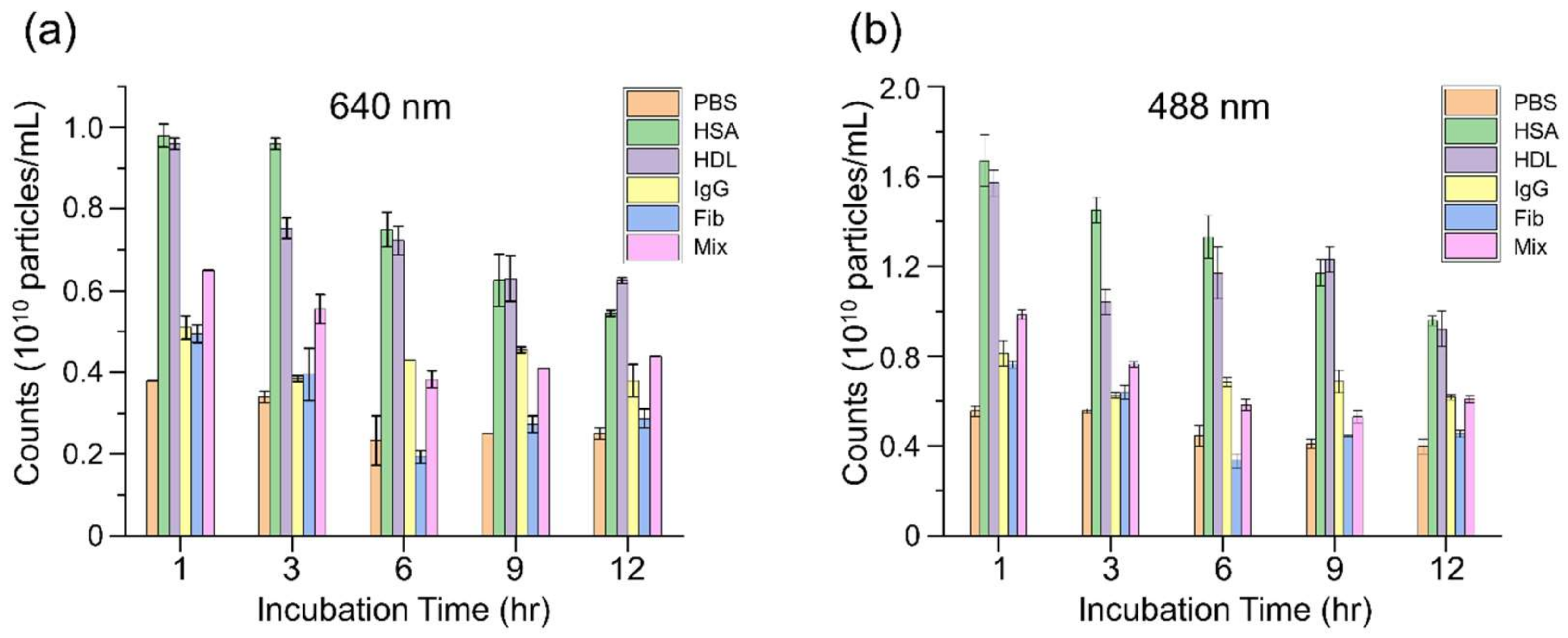
3.2. In Situ Time-Dependent Growth of Whole Protein Coronas on IgG-AuNPs Probed by F-NTA
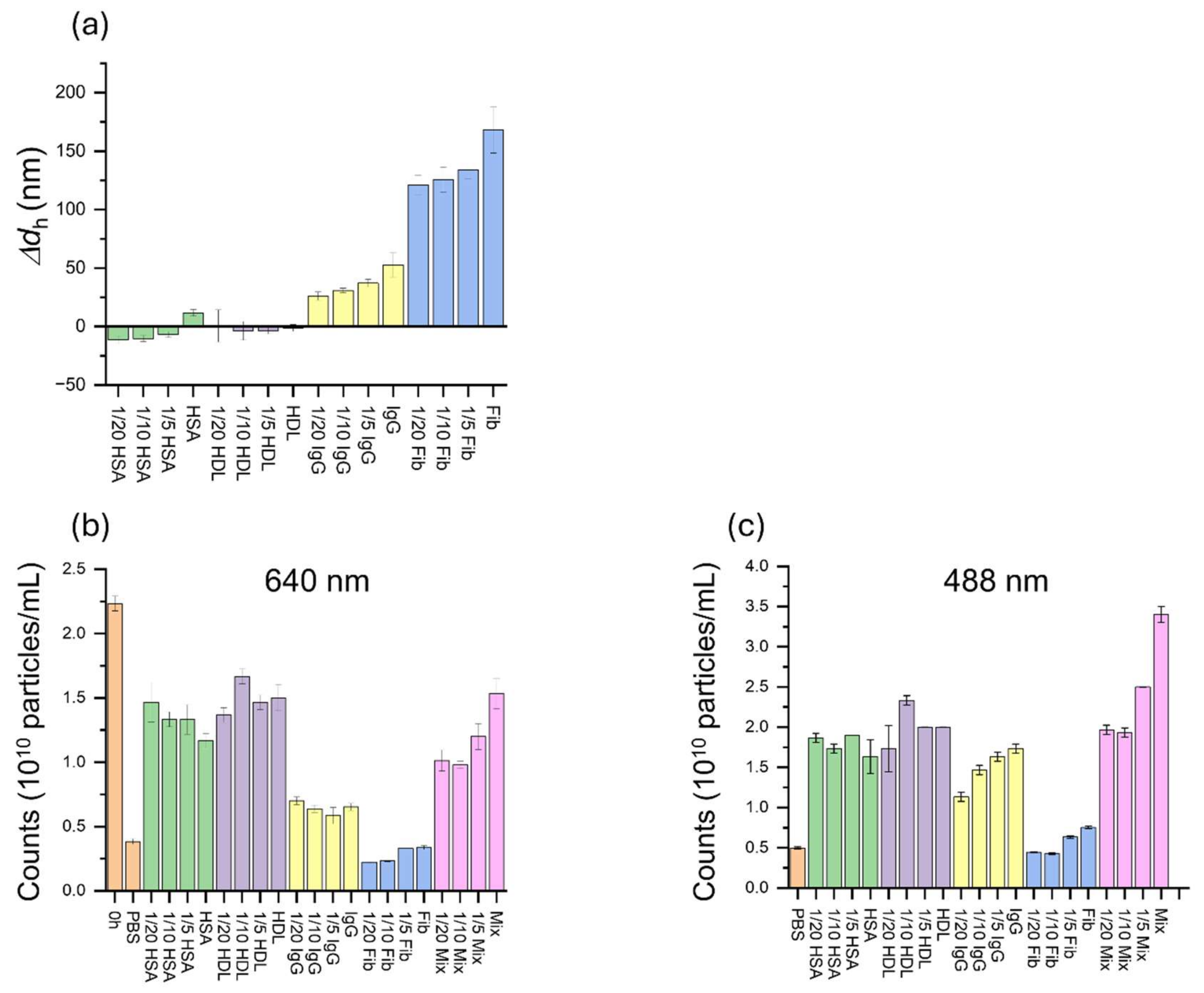
3.3. Assessment of the In Situ Influence of Whole Protein Coronas on the Biosensing of Anti-IgG Using Two-Color F-NTA
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ENPs | Engineered nanoparticles |
| IgG-AuNPs | IgG (mouse)-conjugated PEGylated gold nanoparticles |
| F-NTA | Fluorescence nanoparticle tracking analysis |
| HC | Hard corona |
| SC | Soft corona |
| Cryo-EM | Cryo-electron microscopy |
| Cryo-ET | Cryo-electron tomography |
| AF4 | Asymmetric flow field-flow fractionation |
| MS | Mass spectrometry |
| PEG-scFv | PEG single-chain variable fragment |
| AfC | Affinity chromatography |
| MP-SPR | Multi-parametric surface plasmon resonance |
| BLI | Bio-layer interferometry |
| FCS | Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy |
| ARMES | Anisotropy-resolved multi-dimensional emission spectroscopy |
| DLS | Dynamic light scattering |
| NTA | Nanoparticle tracking analysis |
| HSA | Human serum albumin |
| HDL | High-density lipoproteins |
| IgG | IgG (human) |
| Fib | Fibrinogen |
| Mix | Mixture of HSA, HDL, IgG, and Fib |
| anti-IgG | Anti-IgG (mouse) |
References
- Afzal, O.; Altamimi, A.S.; Nadeem, M.S.; Alzarea, S.I.; Almalki, W.H.; Tariq, A.; Mubeen, B.; Murtaza, B.N.; Iftikhar, S.; Riaz, N. Nanoparticles in drug delivery: From history to therapeutic applications. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 4494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albalawi, F.; Hussein, M.Z.; Fakurazi, S.; Masarudin, M.J. Engineered nanomaterials: The challenges and opportunities for nanomedicines. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 161–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irvine, D.J.; Dane, E.L. Enhancing cancer immunotherapy with nanomedicine. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.J.; Billingsley, M.M.; Haley, R.M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Peppas, N.A.; Langer, R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrakala, V.; Aruna, V.; Angajala, G. Review on metal nanoparticles as nanocarriers: Current challenges and perspectives in drug delivery systems. Emergent Mater. 2022, 5, 1593–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopac, T. Protein corona, understanding the nanoparticle–protein interactions and future perspectives: A critical review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 169, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Yin, D.; Tang, C.; He, E.; Zou, L.; Peng, Q. The protein corona and its effects on nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems. Acta Biomater. 2021, 129, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epanchintseva, A.V.; Baranova, S.V.; Poletaeva, J.E.; Bakhno, I.A.; Ryabchikova, E.I.; Dovydenko, I.S. Study of Hard Protein Corona on Lipid Surface of Composite Nanoconstruction. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Önal Acet, B.; Gül, D.; Stauber, R.H.; Odabaşı, M.; Acet, Ö. A Review for Uncovering the “Protein-Nanoparticle Alliance”: Implications of the Protein Corona for Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epanchintseva, A.V.; Poletaeva, J.E.; Bakhno, I.A.; Belov, V.V.; Grigor’eva, A.E.; Baranova, S.V.; Ryabchikova, E.I.; Dovydenko, I.S. Fixation and Visualization of Full Protein Corona on Lipid Surface of Composite Nanoconstruction. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajipour, M.J.; Safavi-Sohi, R.; Sharifi, S.; Mahmoud, N.; Ashkarran, A.A.; Voke, E.; Serpooshan, V.; Ramezankhani, M.; Milani, A.S.; Landry, M.P. An overview of nanoparticle protein corona literature. Small 2023, 19, 2301838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Álvarez, R.; Vallet-Regí, M. Hard and soft protein corona of nanomaterials: Analysis and relevance. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, P.C.; Lin, S.; Parak, W.J.; Davis, T.P.; Caruso, F. A decade of the protein corona. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 11773–11776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winzen, S.; Schoettler, S.; Baier, G.; Rosenauer, C.; Mailaender, V.; Landfester, K.; Mohr, K. Complementary analysis of the hard and soft protein corona: Sample preparation critically effects corona composition. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 2992–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheibani, S.; Basu, K.; Farnudi, A.; Ashkarran, A.; Ichikawa, M.; Presley, J.F.; Bui, K.H.; Ejtehadi, M.R.; Vali, H.; Mahmoudi, M. Nanoscale characterization of the biomolecular corona by cryo-electron microscopy, cryo-electron tomography, and image simulation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.; Simon, J.; Mailänder, V.; Morsbach, S.; Landfester, K. Preservation of the soft protein corona in distinct flow allows identification of weakly bound proteins. Acta Biomater. 2018, 76, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Tang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C.; Qian, J.; Wei, X.; Ying, T.; Lu, W.; Zhan, C. Deciphering protein corona by scFv-based affinity chromatography. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 2124–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad-Beigi, H.; Hayashi, Y.; Zeuthen, C.M.; Eskandari, H.; Scavenius, C.; Juul-Madsen, K.; Vorup-Jensen, T.; Enghild, J.J.; Sutherland, D.S. Mapping and identification of soft corona proteins at nanoparticles and their impact on cellular association. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kari, O.K.; Ndika, J.; Parkkila, P.; Louna, A.; Lajunen, T.; Puustinen, A.; Viitala, T.; Alenius, H.; Urtti, A. In situ analysis of liposome hard and soft protein corona structure and composition in a single label-free workflow. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 1728–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baimanov, D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, K.; Cong, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Qiao, R. In situ analysis of nanoparticle soft corona and dynamic evolution. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Nilsson, R.; Lázaro-Ibáñez, E.; Duàn, H.; Miliotis, T.; Strimfors, M.; Lerche, M.; Salgado Ribeiro, A.R.; Ulander, J.; Lindén, D. Multiomics analysis of naturally efficacious lipid nanoparticle coronas reveals high-density lipoprotein is necessary for their function. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, K.; Urquhart, A.J.; Thormann, E.; Andresen, T.L. Binding of human serum albumin to PEGylated liposomes: Insights into binding numbers and dynamics by fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 19726–19736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, F.; Casamayou-Boucau, Y.; Ryder, A.G. Evaluating the interaction of human serum albumin (HSA) and 1, 2-dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DMPC) liposomes in different aqueous environments using anisotropy resolved multi-dimensional emission spectroscopy (ARMES). Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 211, 112310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Welsher, K. Particle-by-Particle In situ Characterization of the Protein Corona via Real-Time 3D Single-Particle-Tracking Spectroscopy. Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 22533–22541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S. DLS and zeta potential–What they are and what they are not? J. Control. Release 2016, 235, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowkabany, G.; Bao, Y. Nanoparticle tracking analysis: An effective tool to characterize extracellular vesicles. Molecules 2024, 29, 4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yáñez-Mó, M.; Siljander, P.R.-M.; Andreu, Z.; Bedina Zavec, A.; Borràs, F.E.; Buzas, E.I.; Buzas, K.; Casal, E.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Pol, E.; Hoekstra, A.; Sturk, A.; Otto, C.; Van Leeuwen, T.; Nieuwland, R. Optical and non-optical methods for detection and characterization of microparticles and exosomes. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 2596–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, D.; Mladenović, D.; Criscuoli, M.; Loria, F.; Veiman, K.-L.; Zocco, D.; Koort, K.; Zarovni, N. Opportunities and pitfalls of fluorescent labeling methodologies for extracellular vesicle profiling on high-resolution single-particle platforms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koksal, A.R.; Ekmen, N.; Aydin, Y.; Nunez, K.; Sandow, T.; Delk, M.; Moehlen, M.; Thevenot, P.; Cohen, A.; Dash, S. A single-step immunocapture assay to quantify HCC exosomes using the highly sensitive fluorescence nanoparticle-tracking analysis. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2023, 10, 1935–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannon, M.S.; López Ruiz, A.; Corrotea Reyes, K.; Marquez, M.; Wallizadeh, Z.; Savarmand, M.; LaPres, C.A.; Lahann, J.; McEnnis, K. Nanoparticle tracking analysis of polymer nanoparticles in blood plasma. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2021, 38, 2100016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.Y.; Joung, H.; Jang, G.J.; Han, S.Y. Probing emergence of biomolecular coronas around drug-loaded liposomal nanoparticles in the solution by using nanoparticle tracking analysis. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2023, 44, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Mazouzi, Y.; Salmain, M.; Liedberg, B.; Boujday, S. Antibody-gold nanoparticle bioconjugates for biosensors: Synthesis, characterization and selected applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 165, 112370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llevot, A.; Astruc, D. Applications of vectorized gold nanoparticles to the diagnosis and therapy of cancer. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadkhoda, J.; Akrami-Hasan-Kohal, M.; Tohidkia, M.R.; Khaledi, S.; Davaran, S.; Aghanejad, A. Advances in antibody nanoconjugates for diagnosis and therapy: A review of recent studies and trends. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 185, 664–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anaraki, N.I.; Liebi, M.; Iranshahi, K.; Blanchet, C.; Wick, P.; Neels, A. Time-resolved study on self-assembling behavior of PEGylated gold nanoparticles in the presence of human serum albumin: A system for nanomedical applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 18921–18929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, H.; Yang, W. Gold nanoparticle-based facile detection of human serum albumin and its application as an INHIBIT logic gate. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 8990–8998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, G.J.; Jeong, J.Y.; Kang, J.; Cho, W.; Han, S.Y. Size dependence unveiling the adsorption interaction of high-density lipoprotein particles with PEGylated gold nanoparticles in biomolecular corona formation. Langmuir 2021, 37, 9755–9763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Lee, C.; Jang, G.J.; Yoo, S.; Lee, S.; Han, S.Y. Understanding the biomolecular coronas of high-density lipoproteins on PEGylated Au nanoparticles: Implication for lipid corona formation in the blood. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 2018–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haller, E.; Lindner, W.; Lämmerhofer, M. Gold nanoparticle–antibody conjugates for specific extraction and subsequent analysis by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry of malondialdehyde-modified low density lipoprotein as biomarker for cardiovascular risk. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 857, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Joung, H.; Jang, G.J.; Jeong, J.Y.; Lim, G.; Han, S.Y. Evaluating the In Situ Effects of Whole Protein Coronas on the Biosensing of Antibody-Immobilized Nanoparticles Using Two-Color Fluorescence Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15030220
Joung H, Jang GJ, Jeong JY, Lim G, Han SY. Evaluating the In Situ Effects of Whole Protein Coronas on the Biosensing of Antibody-Immobilized Nanoparticles Using Two-Color Fluorescence Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(3):220. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15030220
Chicago/Turabian StyleJoung, Heeju, Gwi Ju Jang, Ji Yeon Jeong, Goeun Lim, and Sang Yun Han. 2025. "Evaluating the In Situ Effects of Whole Protein Coronas on the Biosensing of Antibody-Immobilized Nanoparticles Using Two-Color Fluorescence Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis" Nanomaterials 15, no. 3: 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15030220
APA StyleJoung, H., Jang, G. J., Jeong, J. Y., Lim, G., & Han, S. Y. (2025). Evaluating the In Situ Effects of Whole Protein Coronas on the Biosensing of Antibody-Immobilized Nanoparticles Using Two-Color Fluorescence Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis. Nanomaterials, 15(3), 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15030220





