Numerical Investigation of Enhanced High-Intensity Laser–Matter Interactions in Nanowire-Coated Conical Targets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
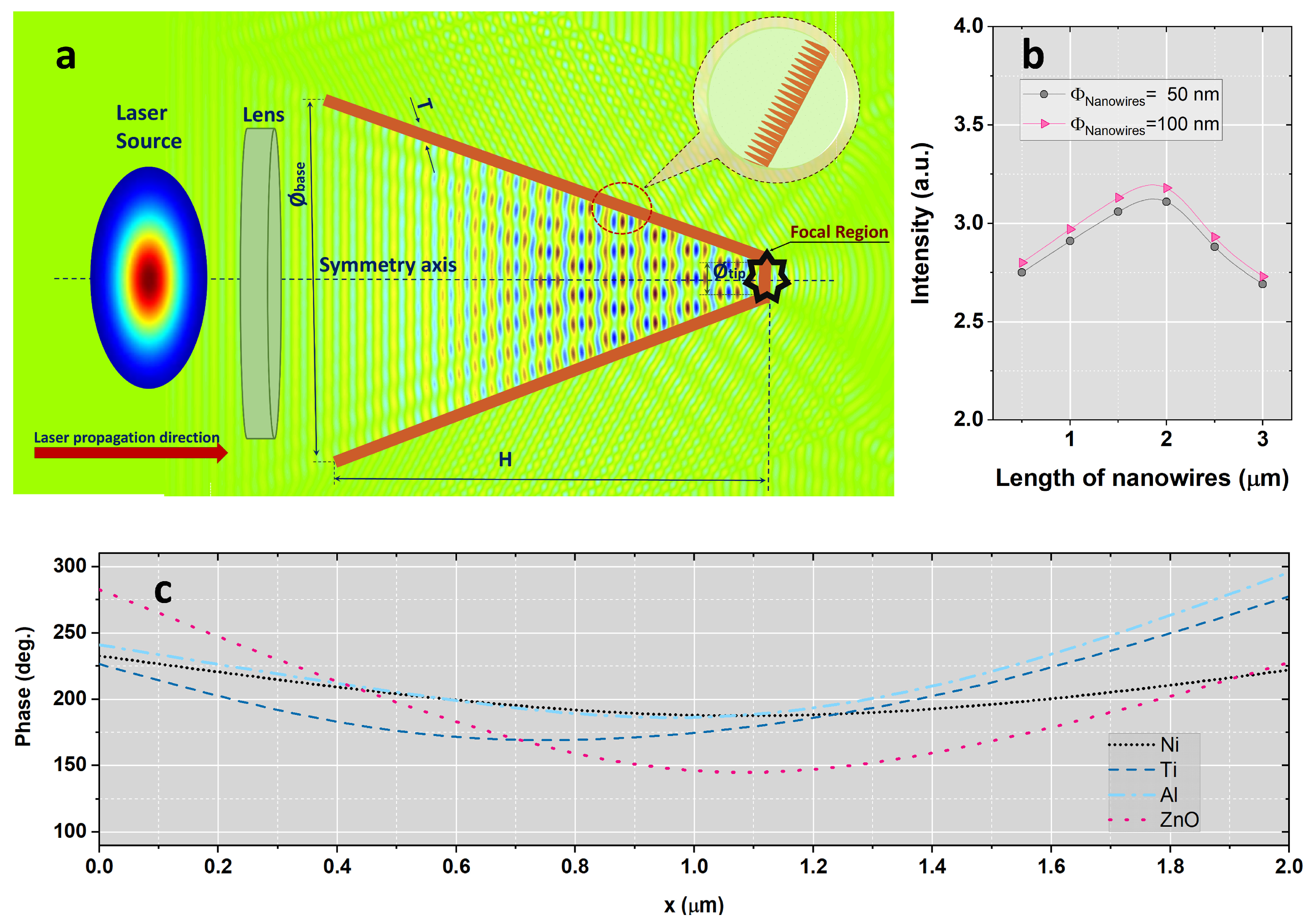
2.1. Numerical Model and Setup
2.2. Determination of Optimal Geometrical Parameters
3. Results and Discussions
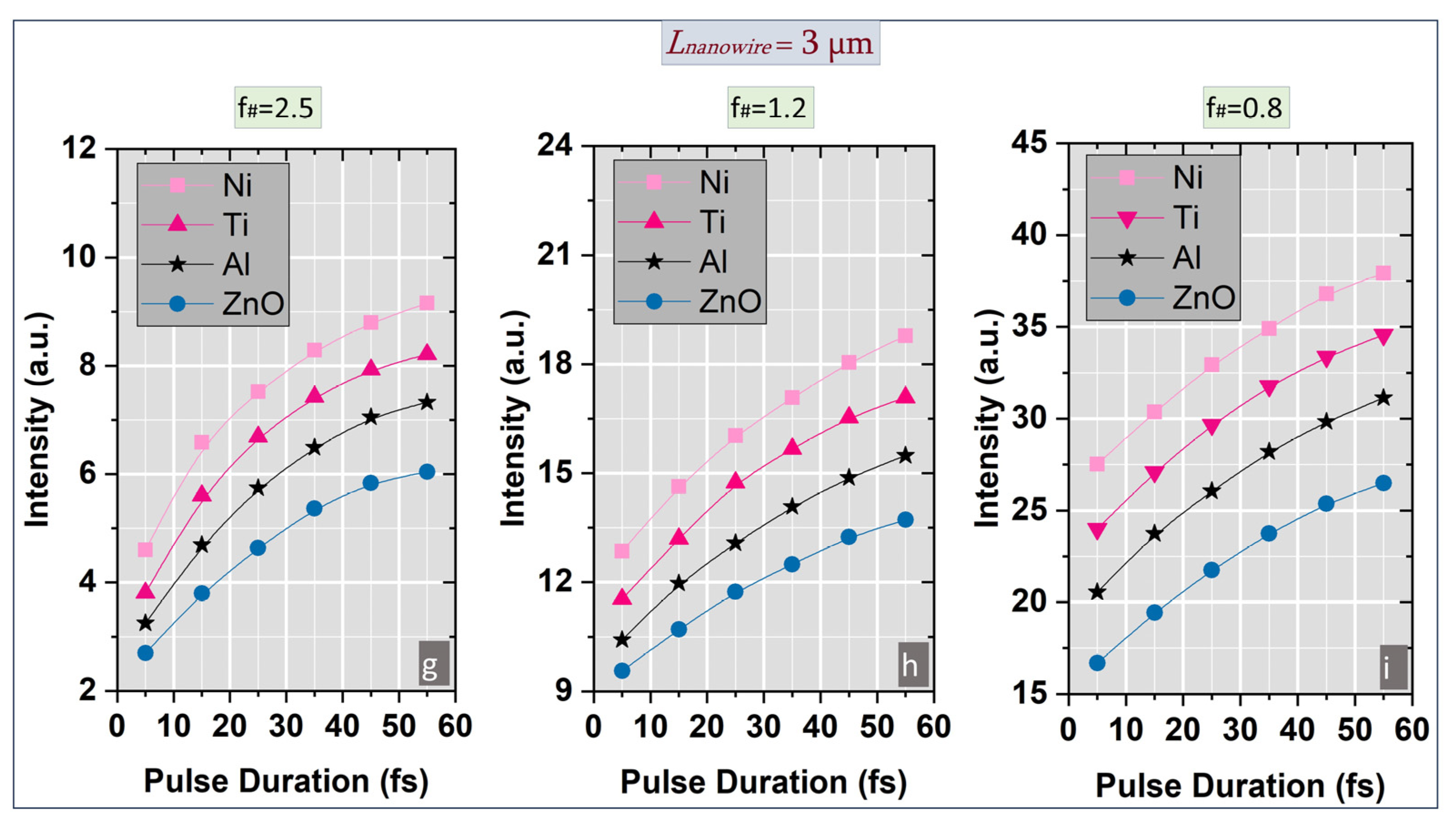
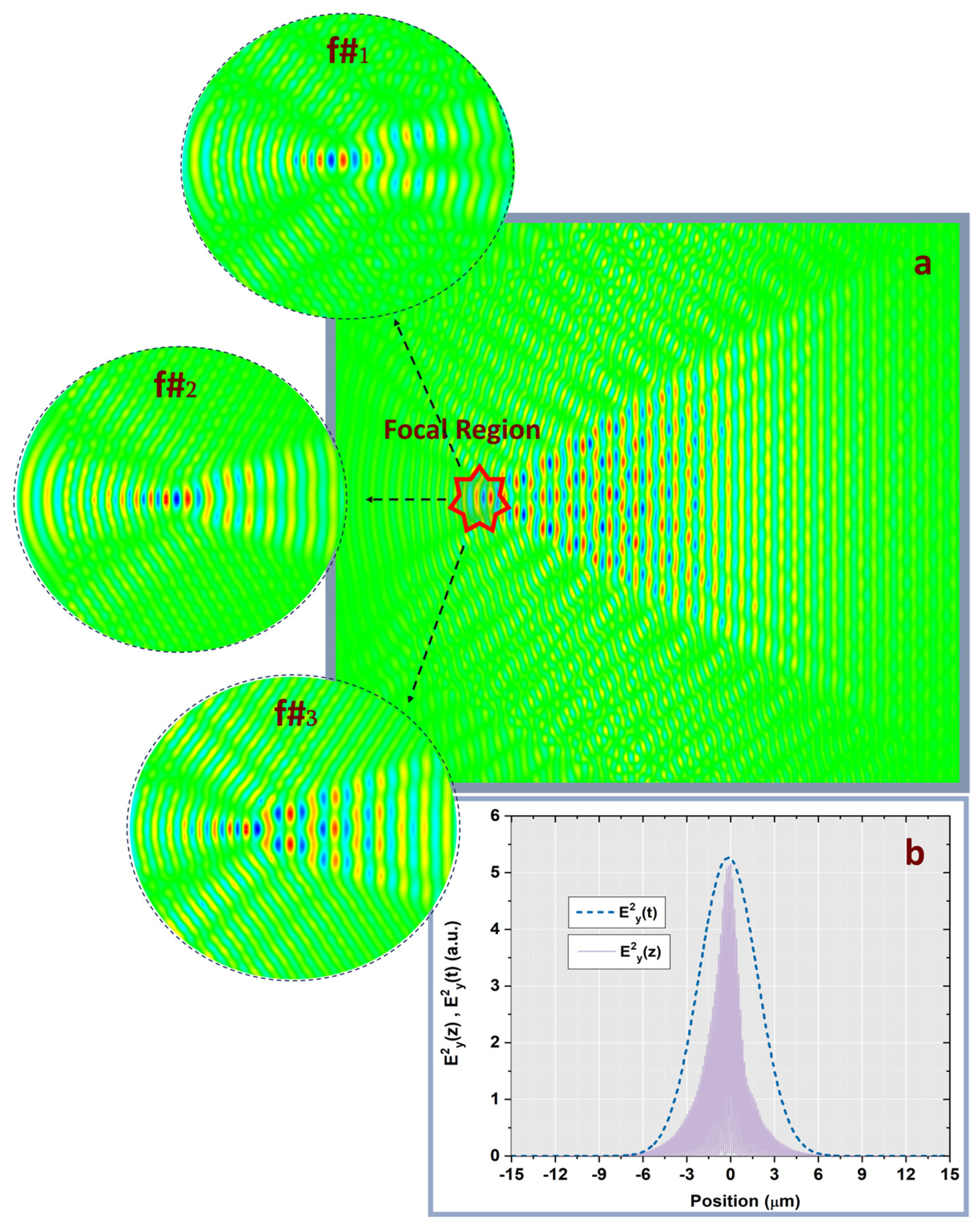
3.1. Spatial Distribution and Laser Intensity Evolution
3.2. Temporal Field Dynamics
3.3. Spatio-Temporal Analogy
3.4. Benchmarking with Published Experiments (Scope and Comparability)
- (i)
- Increasing f/# leads to smoother focusing and a larger effective Rayleigh range, producing a monotonic rise in on-axis intensity and relative spatial extension (RSE);
- (ii)
- Decreasing f/# results in stronger geometrical confinement and phase curvature, which enhances peak intensity but reduces RSE, indicative of tighter spatio-temporal coupling;
- (iii)
- Material-dependent dispersion, represented by ε(ω), modulates the enhancement in a manner consistent with experimental findings on metallic and semiconductor nanowires.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weber, S.; Bechet, S.; Borneis, S.; Brabec, L.; Bučka, M.; Chacon, E.; Golcher, M.; Ciappina, M.; DeMarco, M.; Fajstavr, A.; et al. An installation for high-energy density plasma physics and ultra-high intensity laser–matter interaction at ELI-Beamlines. Matter. Radiat. Extrem. 2017, 2, 149–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Lei, G. Research of interaction between ultra-short ultra-intense laser pulses and multiple plasma layers. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Kato, Y.; Kawanaka, J. Simulating an ultra-broadband concept for Exawatt-class lasers. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margarone, D.; Klimo, O.; Kim, I.J.; Prokůpek, J.; Limpouch, J.; Jeong, T.M.; Mocek, T.; Pšikal, J.; Kim, H.T.; Proška, J.; et al. Laser-driven proton acceleration enhancement by nanostructured foils. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 234801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehret, M.; Vladisavlevici, I.-M.; Bradford, P.W.; Cikhardt, J.; Filippov, E.; Henares, J.L.; Hernández Martín, R.; de Luis, D.; Pérez-Hernández, J.A.; Vicente, P.; et al. Currents from relativistic laser–plasma interaction as a novel metrology for the system stability of high-repetition-rate laser secondary sources. Matter Radiat. Extremes 2025, 10, 027203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassuchine, J.; D’Humières, E.; Baton, S.D.; Cowan, T.E. Enhanced hot-electron localization and heating in high-contrast ultraintense laser irradiation of microcone targets. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 79 Pt 2, 036408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, Y.; Kong, D.; Wang, P.; Mei, Z.; Cao, Z.; Pan, Z.; Li, Y.; Xu, S.; Qi, G.; Chen, S.; et al. High-efficiency water-window X-ray generation from nanowire array targets irradiated with femtosecond laser pulses. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftekhari-Zadeh, E.; Blümcke, M.S.; Samsonova, Z.; Loetzsch, R.; Uschmann, I.; Zapf, M.; Ronning, C.; Rosmej, O.N.; Kartashov, D.; Spielmann, C. Laser energy absorption and X-ray generation in nanowire arrays irradiated by relativistically intense ultra-high contrast femtosecond laser pulses. Phys. Plasmas 2022, 29, 013301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, T.; Heber, R.; Abel, T.; Bieker, J.; Schaumann, G.; Roth, M. Targets with cone-shaped microstructures from various materials for enhanced high-intensity laser–matter interaction. High Power Laser Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calestani, D.; Villani, M.; Cristoforetti, G.; Brandi, F.; Koester, P.; Labate, L.; Gizzi, L.A. Fabrication of ZnO-nanowire-coated thin foil targets for ultra-high intensity laser interaction experiments. Matter Radiat. Extremes 2021, 6, 046903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargsten, C.; Hollinger, R.; Capeluto, M.G.; Kaymak, V.; Pukhov, A.; Wang, S.; Rockwood, A.; Wang, Y.; Keiss, D.; Rocca, J.J. Energy penetration into arrays of aligned nanowires irradiated with relativistic intensities: Scaling to terabar pressures. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1601558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.B.; Pukhov, A.; Yi, L.Q.; Zhuo, H.B.; Yu, T.P.; Yin, Y.; Shao, F.Q. Laser-driven ion acceleration from plasma micro-channel targets. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42666. [Google Scholar]
- Kamboj, O.; Ghotra, H.; Thakur, V.; Kant, N. Optimizing laser focal spot size using self-focusing in a cone-guided fast-ignition ICF target. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2021, 136, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierwage, A.; Esirkepov, T.Z.; Koga, J.K.; Pirozhkov, A.S.; Aiba, N.; Huang, K.; Kando, M.; Kiriyama, H.; Matsuyama, A.; Shinohara, K.; et al. Evolution of a laser wake cavity in a MCF plasma. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Synopsys. RSoft Photonic Device Tools. Available online: https://www.synopsys.com/photonic-solutions/rsoft-photonic-device-tools/rsoft-products.html (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Radu, B.; Egger, H. A Yee-like finite-element scheme for Maxwell’s equations on unstructured grids. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 2025, 45, 1028–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chern, A. A reflectionless discrete perfectly matched layer. J. Comput. Phys. 2019, 381, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionel, L. Spatio-temporal analysis of high-power laser micro-structured targets interaction. Phys. Scr. 2020, 95, 105501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionel, L. Numerical analysis of non-collinear coherently combined laser beams interaction with micro-structured targets. Opt. Commun. 2021, 498, 127234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionel, L. Characterising spatio-temporal coupling of tightly focused femtosecond laser pulses in micro-structured dispersive materials. Photonics 2024, 11, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionel, L. Piston error effect on intensity at the interaction of coherently combined femtosecond laser beams with cone targets. UPB Sci. Bull. Ser. A 2024, 86, 179–190. [Google Scholar]
- Ionel, L.; Ursescu, D. Spatial extension of the electromagnetic field from tightly focused ultrashort laser pulses. Laser Part. Beams 2014, 32, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ionel, L.; Viespe, C. Numerical Investigation of Enhanced High-Intensity Laser–Matter Interactions in Nanowire-Coated Conical Targets. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1763. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15231763
Ionel L, Viespe C. Numerical Investigation of Enhanced High-Intensity Laser–Matter Interactions in Nanowire-Coated Conical Targets. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(23):1763. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15231763
Chicago/Turabian StyleIonel, Laura, and Cristian Viespe. 2025. "Numerical Investigation of Enhanced High-Intensity Laser–Matter Interactions in Nanowire-Coated Conical Targets" Nanomaterials 15, no. 23: 1763. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15231763
APA StyleIonel, L., & Viespe, C. (2025). Numerical Investigation of Enhanced High-Intensity Laser–Matter Interactions in Nanowire-Coated Conical Targets. Nanomaterials, 15(23), 1763. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15231763





