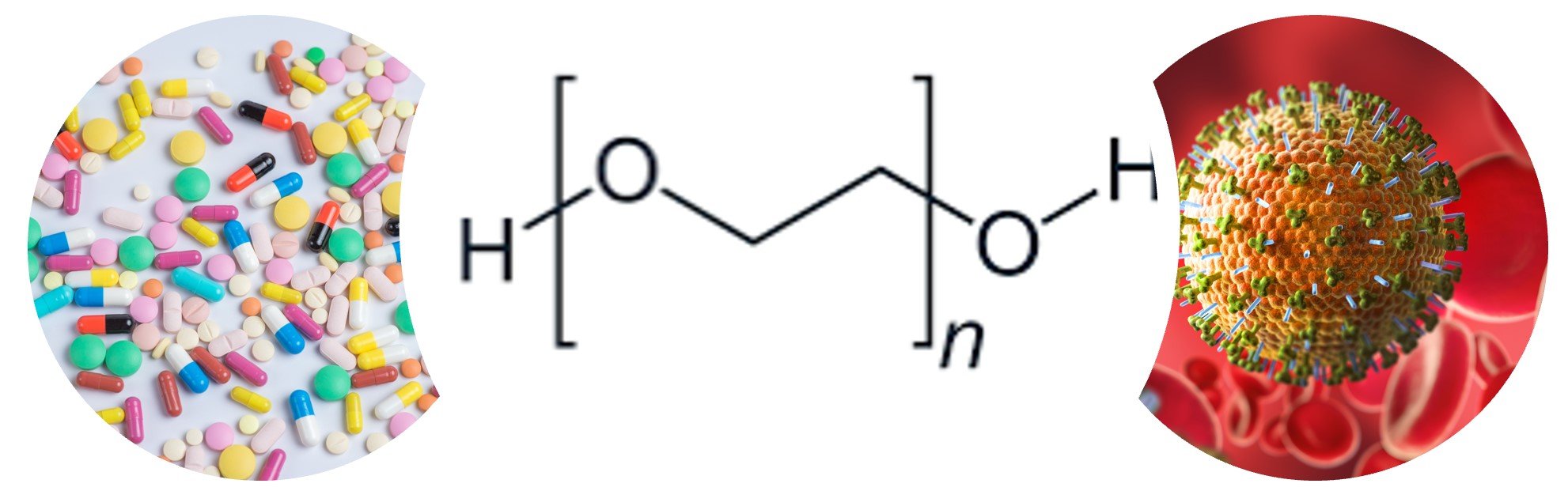
The Ubiquitous Use of Polyethylene Glycol in Pharmaceutical Design and Development: Technological Aspects and Future Perspectives
Abstract
Share and Cite
Christoforou, I.; Kalatzis, A.; Siamidi, A.; Vlachou, M.; Pispas, S.; Pippa, N. The Ubiquitous Use of Polyethylene Glycol in Pharmaceutical Design and Development: Technological Aspects and Future Perspectives. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15231762
Christoforou I, Kalatzis A, Siamidi A, Vlachou M, Pispas S, Pippa N. The Ubiquitous Use of Polyethylene Glycol in Pharmaceutical Design and Development: Technological Aspects and Future Perspectives. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(23):1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15231762
Chicago/Turabian StyleChristoforou, Iliana, Anastasios Kalatzis, Angeliki Siamidi, Marilena Vlachou, Stergios Pispas, and Natassa Pippa. 2025. "The Ubiquitous Use of Polyethylene Glycol in Pharmaceutical Design and Development: Technological Aspects and Future Perspectives" Nanomaterials 15, no. 23: 1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15231762
APA StyleChristoforou, I., Kalatzis, A., Siamidi, A., Vlachou, M., Pispas, S., & Pippa, N. (2025). The Ubiquitous Use of Polyethylene Glycol in Pharmaceutical Design and Development: Technological Aspects and Future Perspectives. Nanomaterials, 15(23), 1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15231762