Influences of Initial Stresses on Formation of Shear Bands and Mechanical Properties in Binodal Decomposed Metallic Glass Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
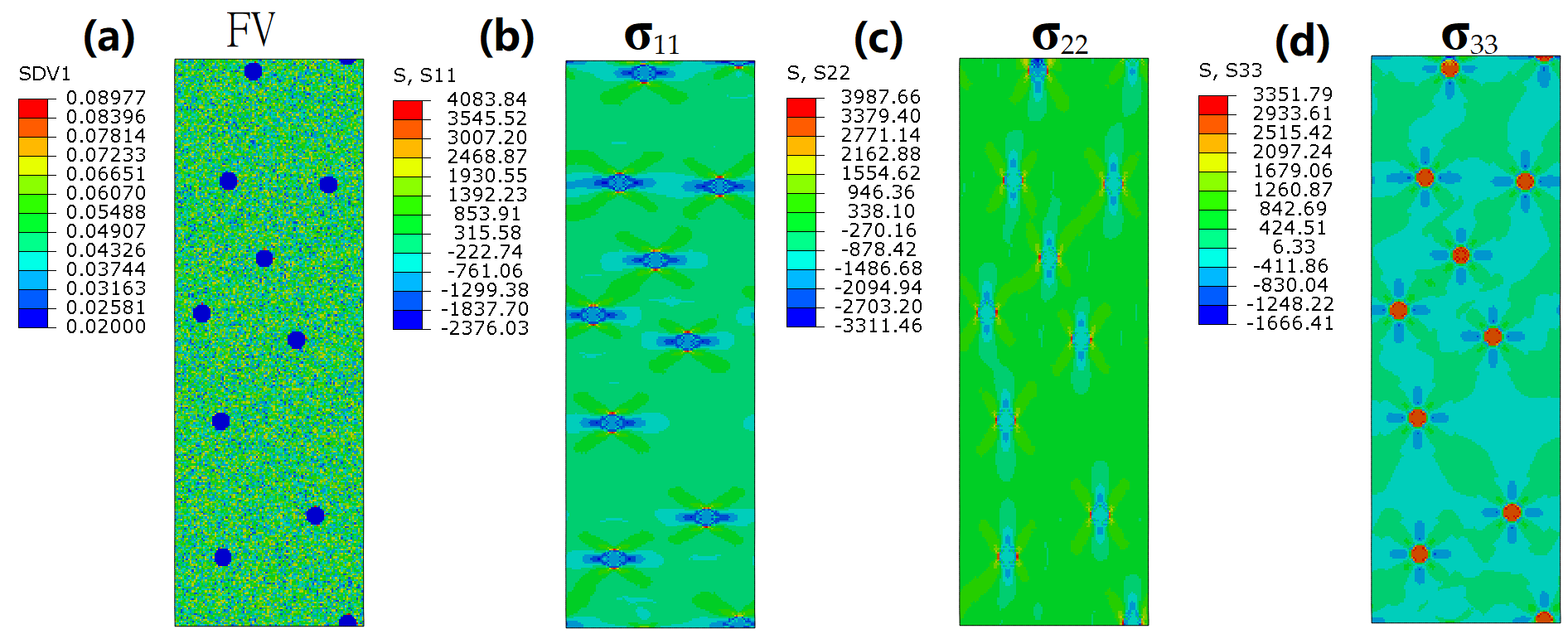
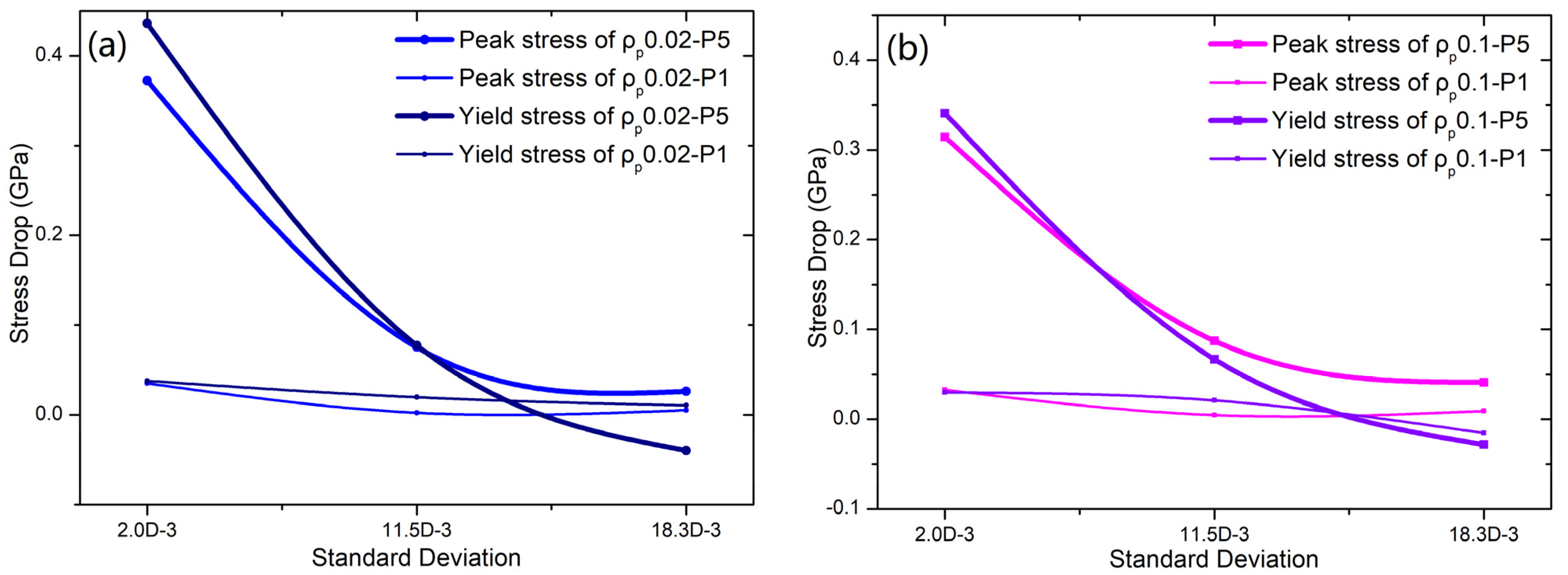
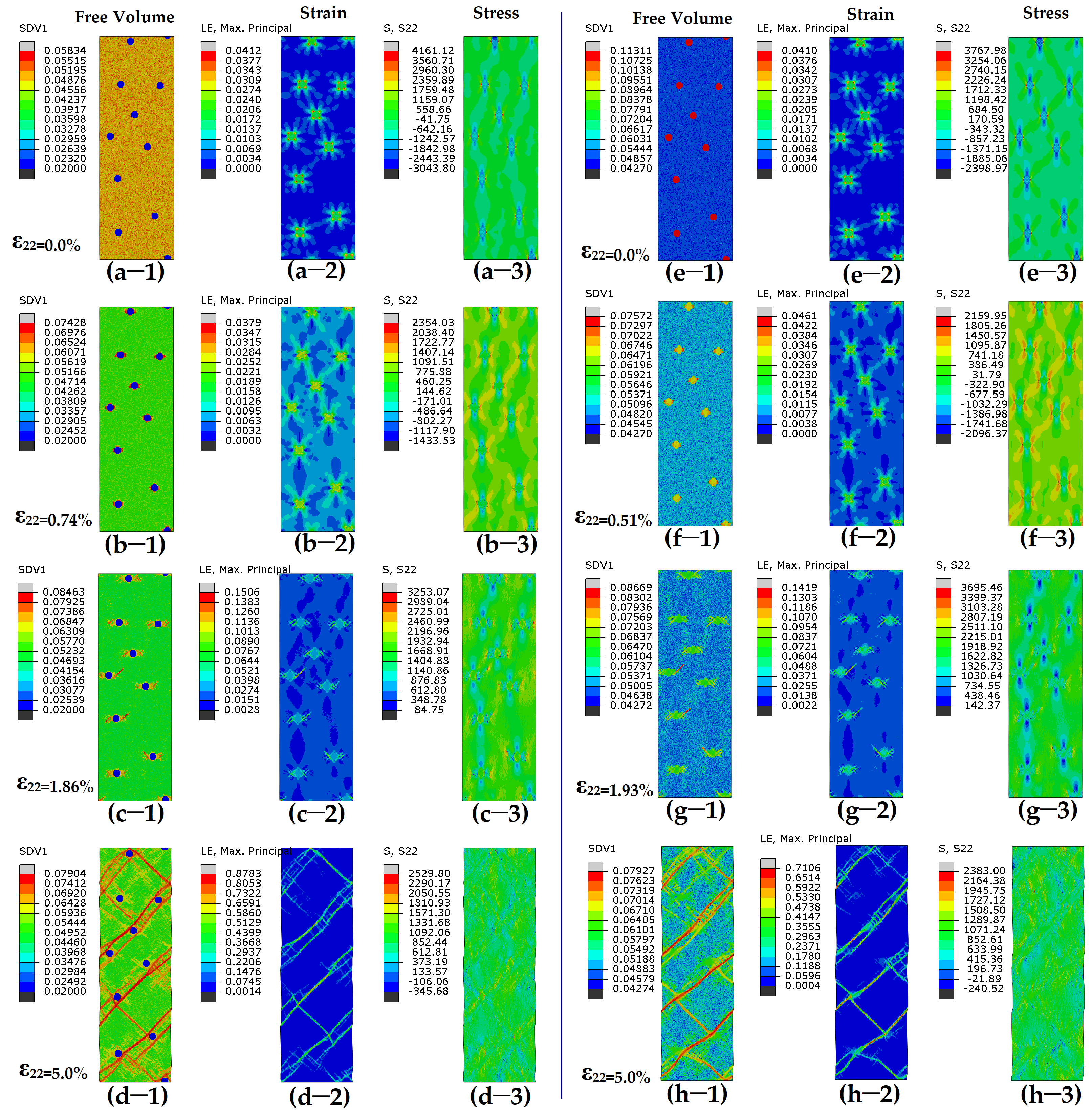
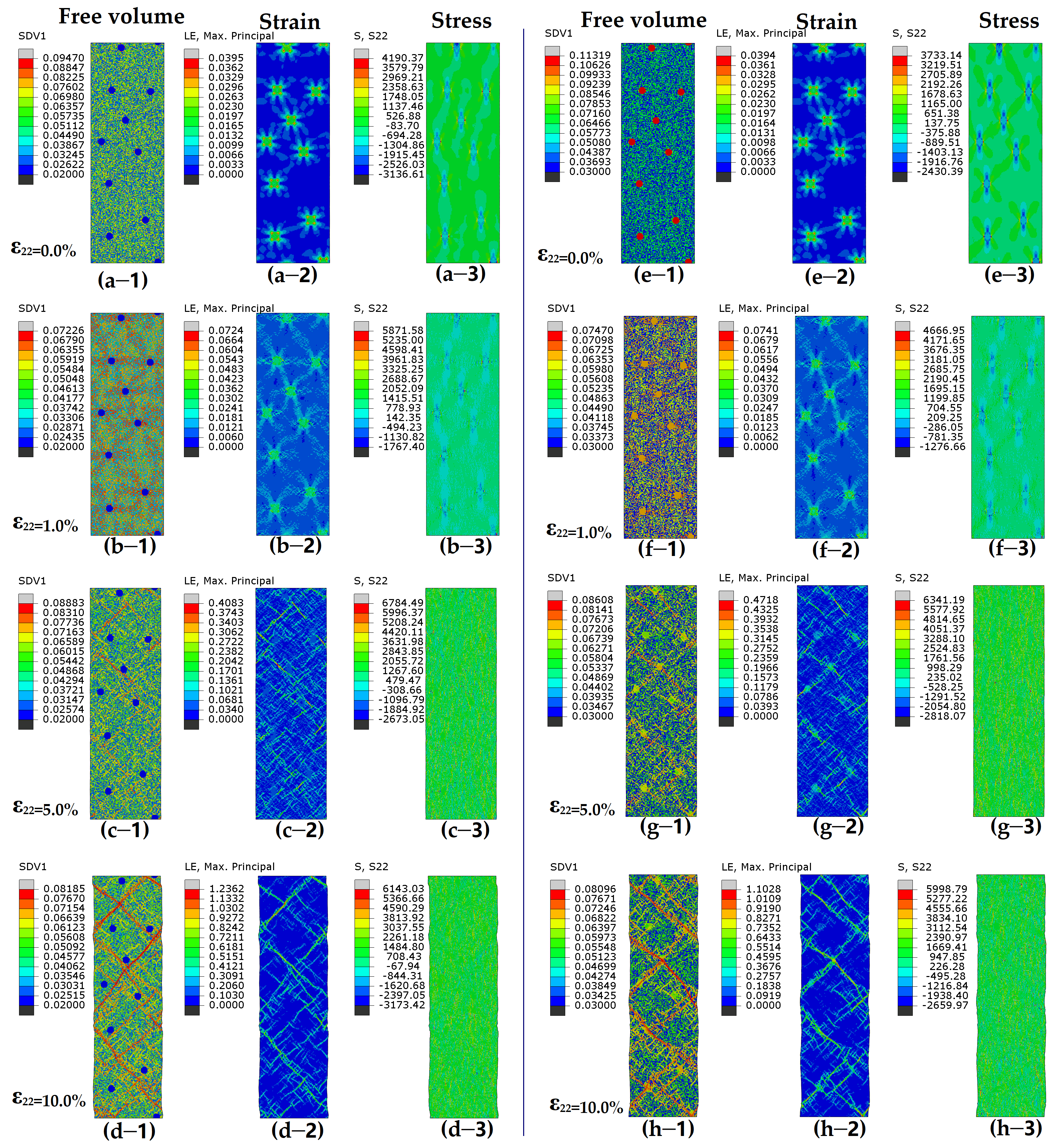
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klement, W.I.; Willens, R.H.; Duwez, P. Non-crystalline structure in solidified gold-silicon alloys. Nature 1960, 187, 869–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Rector, D.; Conner, R.D.; Schroers, J. Embrittlement of Zr-based bulk metallic glasses. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scudino, S.; Jerliu, B.; Pauly, S. Ductile bulk metallic glasses produced through designed heterogeneities. Scr. Mater. 2011, 65, 815–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetriou, M.D.; Launey, M.E.; Garrett, G.; Schramm, G.P.; Hofmann, D.C.; Johnson, W.L.; Ritchie, R.O. A damage-tolerant glass. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Shang, J.K.; Ma, E.; Xu, J. Crack-resistance curve of a Zr-Ti-Cu-Al bulk metallic glass with extraordinary fracture toughness. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 4940–4949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi-Yima, H.; Johnson, W.L. Bulk metallic glass matrix composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1997, 71, 3808–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, D.C.; Suh, J.Y.; Wiest, A.; Duan, G.; Lind, M.L.; Demetriou, M.D.; Johnson, W.L. Designing metallic glass matrix composites with high toughness and tensile ductility. Nature 2008, 451, 1085–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, C.C.; Kim, C.P.; Johnson, W.L. Microstructure Controlled Shear Band Pattern Formation and Enhanced Plasticity of Bulk Metallic Glasses Containing in situ Formed Ductile Phase Dendrite Dispersions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 84, 2901–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conner, R.D.; Dandliker, R.B.; Johnson, W.L. Mechanical properties of tungsten and steel fiber reinforced Zr41.25Ti13.75Cu12.5Ni10Be22.5 metallic glass matrix composites. Acta Mater. 1998, 46, 6089–6102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.F.; Li, H.; Wang, A.M.; Fu, H.M.; Ding, B.Z.; Hu, Z.Q. Synthesis and characteristics of 80vol.% tungsten (W) fibre/Zr based metallic glass composite. Intermetallics 2009, 17, 1070–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, J.; Tang, M.B.; Kim, K.B.; Theissmann, R.; Baier, F.; Wang, W.H.; Eckert, J. “Work-hardenable” ductile bulk metallic glass. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 205501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.F.; Wei, B.C.; Wang, Y.R.; Li, W.H.; Cheung, T.L.; Shek, C.H. Plasticity-improved Zr-Cu-Al bulk metallic glass matrix composites containing martensite phase. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 051905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, D.C. Shape memory bulk metallic glass composites. Science 2010, 329, 1294–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, J.; Jia, H.; Liaw, P.K. Metallic glass matrix composites. Mat. Sci. Eng. R 2016, 100, 1–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trexler, M.M.; Thadhani, N.N. Mechanical properties of bulk metallic glasses. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2010, 55, 759–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, G.; Ma, J.; Cao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ming, W. Progress in the preparation, forming and machining of metallic glasses. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 117, 244–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi, S.; Fu, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, F.; Ma, J.; Wang, W.H. Manufacturing of metallic glass components: Processes, structures, and properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2024, 144, 101283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Du, C.; Cheng, C.; Xu, L.; Du, Z.; Gao, G.; Liu, A.; Fu, H. Penetration performance and fragmentation mechanism behind target of tungsten fibre/zirconium-based bulk metallic glass matrix composite rod. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2023, 112, 106160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, H. Unravelling the relation between free volume gradient and shear band deflection induced extra plasticity in metallic glasses. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2024, 192, 105806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.J.; Yook, W.; Park, E.S.; Kyeong, J.S.; Kim, D.H. Synthesis of metallic glass composites using phase separation phenomena. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 2483–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.W.; Zheng, G.P.; Li, M. Orientation effects on strengthening mechanism of network-structured metallic glass composites and nanoglasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2025, 666, 123702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.W.; Zheng, G.P.; Li, M. Extraordinary enhancement of the toughness and plasticity of multilayered metallic glass composites with gradient heterogeneous interfaces. Philos. Mag. Lett. 2025, 105, 2544113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, H.B.; Zeng, J.F.; Liu, C.T.; Yang, Y. Structure heterogeneity in metallic glass: Modeling and experiment. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2014, 30, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, A.L.; Cheng, Y.Q.; Ma, E. Shear bands in metallic glasses. Mat. Sci. Eng. R 2013, 74, 71–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mear, F.; Vaughan, G.; Yavari, A.; Greer, A.L. Residual-stress distribution in shot-peened metallic-glass plate. Philos. Mag. Lett. 2008, 88, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Pang, S.; Chen, C.; Zhang, T. Tailoring residual stress to achieve large plasticity in Zr55Al10Ni5Cu30 bulk metallic glass. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 690, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Ravichandrana, G. Pressure-dependent flow behavior of Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10Be22.5 bulk metallic glass. J. Mater. Res. 2003, 18, 2039–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wu, H.; Lü, Z.P. Effects of cooling rates on the mechanical properties of a Ti-based bulk metallic glass. Sci. China 2010, 53, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scudino, S.; Surreddi, K.; Khoshkhoo, M.; Sakaliyska, M.; Wang, G.; Eckert, J. Improved Room Temperature Plasticity of Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10Be22.5 Bulk Metallic Glass by Channel-Die Compression. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2010, 12, 1123–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, K.M.; Dauskardt, R.H. Mean stress effects on flow localization and failure in a bulk metallic glass. Acta Mater. 2001, 49, 2527–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aben, H.; Anton, J.; Ois, M.; Viswanathan, K.; Chandrasekar, S.; Chaudhri, M.M. On the extraordinary strength of Prince Rupert’s drops. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 231903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Launey, M.E.; Busch, R.; Kruzic, J.J. Effects of free volume changes and residual stresses on the fatigue and fracture behavior of a Zr-Ti-Ni-Cu-Be bulk metallic glass. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, H.; Fu, H.; Wang, Z.; Nie, Z.; Wang, L. Thermal Residual Stresses in W Fibers/Zr-based Metallic Glass Composites by High-energy Synchrotron X-ray Diffraction. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2015, 31, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.B.; Barkey, M. FE-simulation of the effects of machining-induced residual stress profile on rolling contact of hard machined components. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2004, 46, 371–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majzoobi, G.H.; Azizi, R.; Nia, A. A three-dimensional simulation of shot peening process using multiple shot impacts. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2005, 164, 1226–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.H.; Greer, A.L. Making metallic glasses plastic by control of residual stress. Nature 2006, 5, 857–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scudino, S.; Surreddi, K.B.; Eckert, J. Mechanical properties of cold-rolled Zr60Ti5Ag5Cu12.5Ni10Al7.5 metallic glass. Phys. Status Solidi A 2010, 207, 1118–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.; Pi, D.; Setyawan, A.; Kato, H.; Janecek, M.; Kim, Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, H. Work-Hardening Induced Tensile Ductility of Bulk Metallic Glasses via High-Pressure Torsion. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Huang, J.C.; Wang, L.; Nieh, T.G. Effect of residual stresses on nanoindentation creep behavior of Zr-based bulk metallic glasses. Intermetallics 2013, 41, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieh, T.G.; Yang, Y.; Lu, J.; Liu, C.T. Effect of surface modifications on shear banding and plasticity in metallic glasses: An overview. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2012, 22, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Zheng, W.; Guo, W.; Lü, S.; Wu, S. In situ Fe-rich particle reinforced Mg-based metallic glass matrix composites via dealloying in metallic melt. Mater. Lett. 2021, 285, 129165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Jiang, M.Q.; Dai, L.H. Intrinsic correlation between dilatation and pressure sensitivity of plastic flow in metallic glasses. Scr. Mater. 2010, 63, 945–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.P.; Shen, Y. Simulation of shear banding and crack propagation in bulk metallic glass matrix composites. J. Alloys Comp. 2011, 509, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Kim, W.T.; Park, E.S.; Mattern, N.; Eckert, J. Phase separation in metallic glasses. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2013, 58, 1103–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaepen, F. A microscopic mechanism for steady state inhomogeneous flow in metallic glasses. Acta Metall. 1977, 25, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argon, A. Plastic deformation in metallic glasses. Acta Metall. 1979, 27, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.F. An implicit finite element method for simulating inhomogeneous deformation and shear bands of amorphous alloys based on the free-volume model. Modell. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2006, 14, 1329–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Li, M. Interpreting the change in shear band inclination angle in metallic glasses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 241906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.W.; Li, M.; Xu, J.W. Toughen and harden metallic glass through designing statistical heterogeneity. Scr. Mater. 2016, 113, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.W.; Li, M.; Xu, J.W. Free volume gradient effect on mechanical properties of metallic glasses. Scr. Mater. 2017, 130, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.W.; Gleiter, H.; Li, M. From patterning heterogeneity to nanoglass: A new approach to harden and toughen metallic glasses. MRS Bull. 2023, 48, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.W.; Zheng, G.P.; Li, M. Manage local deformation by patterning structural heterogeneity: Controlling toughness in honeycomb patterned metallic glass composites. Mater. Des. 2025, 253, 113846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bower, A.F. Applied Mechanics of Solids, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 213–229. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Zheng, G.; Li, M. Influences of Initial Stresses on Formation of Shear Bands and Mechanical Properties in Binodal Decomposed Metallic Glass Composites. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15221725
Wang Y, Zheng G, Li M. Influences of Initial Stresses on Formation of Shear Bands and Mechanical Properties in Binodal Decomposed Metallic Glass Composites. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(22):1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15221725
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yongwei, Guangping Zheng, and Mo Li. 2025. "Influences of Initial Stresses on Formation of Shear Bands and Mechanical Properties in Binodal Decomposed Metallic Glass Composites" Nanomaterials 15, no. 22: 1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15221725
APA StyleWang, Y., Zheng, G., & Li, M. (2025). Influences of Initial Stresses on Formation of Shear Bands and Mechanical Properties in Binodal Decomposed Metallic Glass Composites. Nanomaterials, 15(22), 1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15221725






