Slip Boundary-Enabled Multiscale Modeling for Sound Absorption Coefficient of Nanofiber Porous Media with High Fidelity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Measuring Equipment
3. Theory and Methods
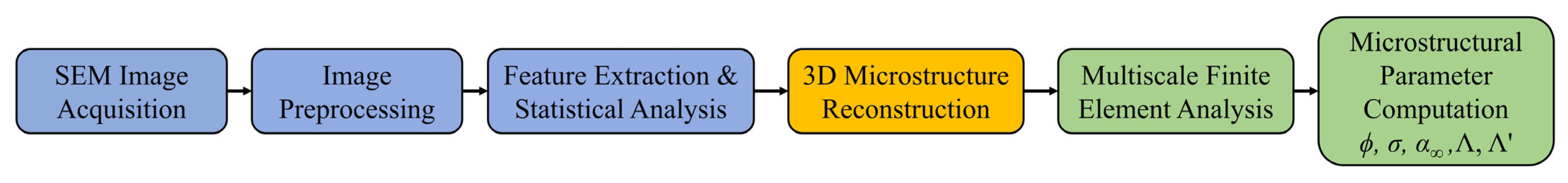
3.1. Characterization and Modeling
3.2. MFEA Model
3.3. Acoustic Characterization of Nanofibers
4. Results and Discussion
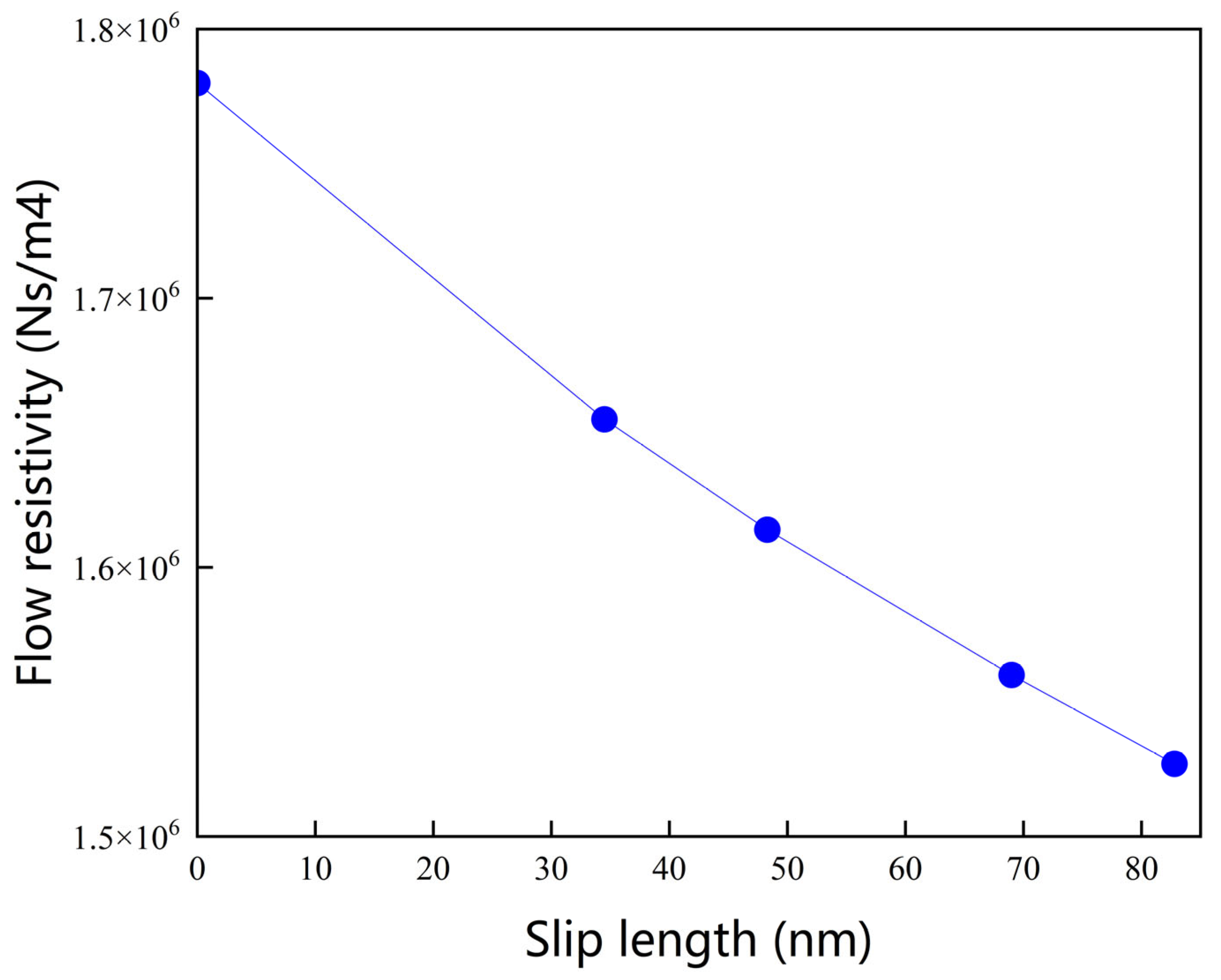
4.1. Microstructural Parameter Analysis
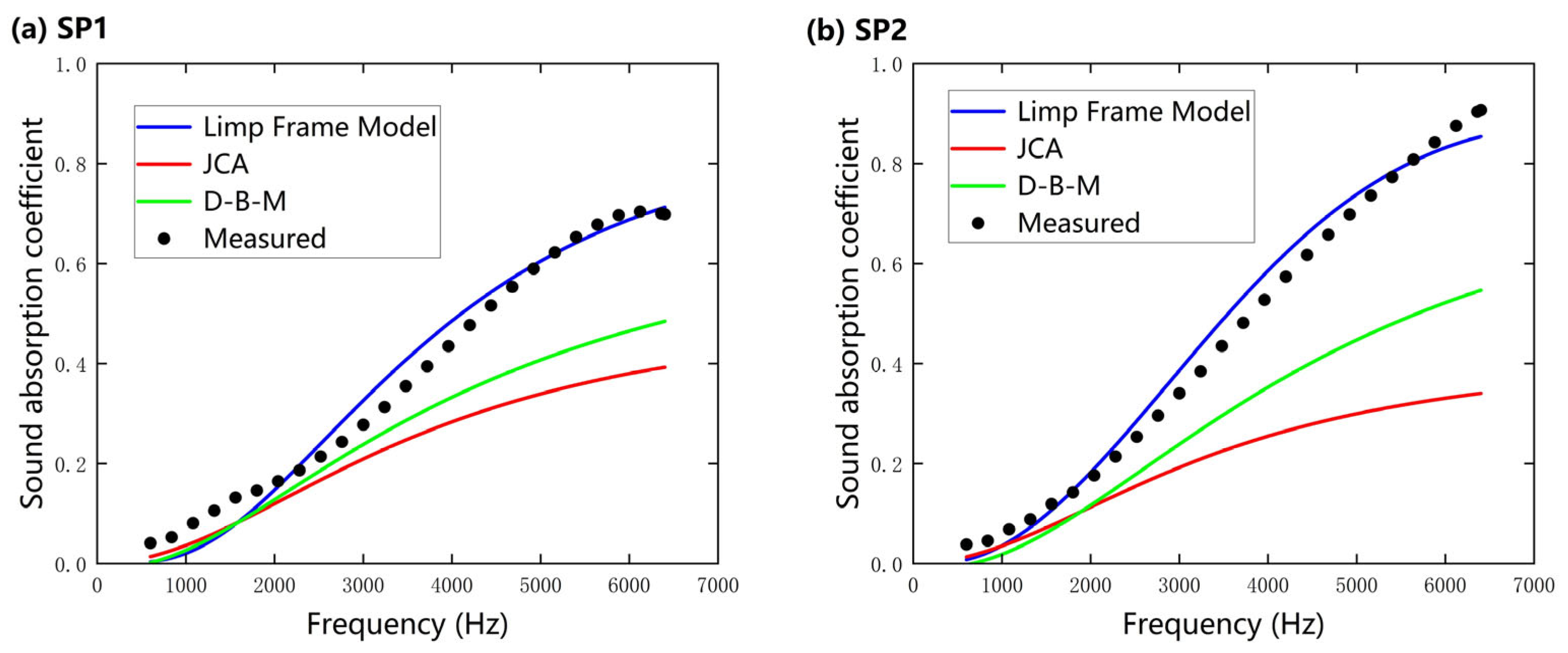
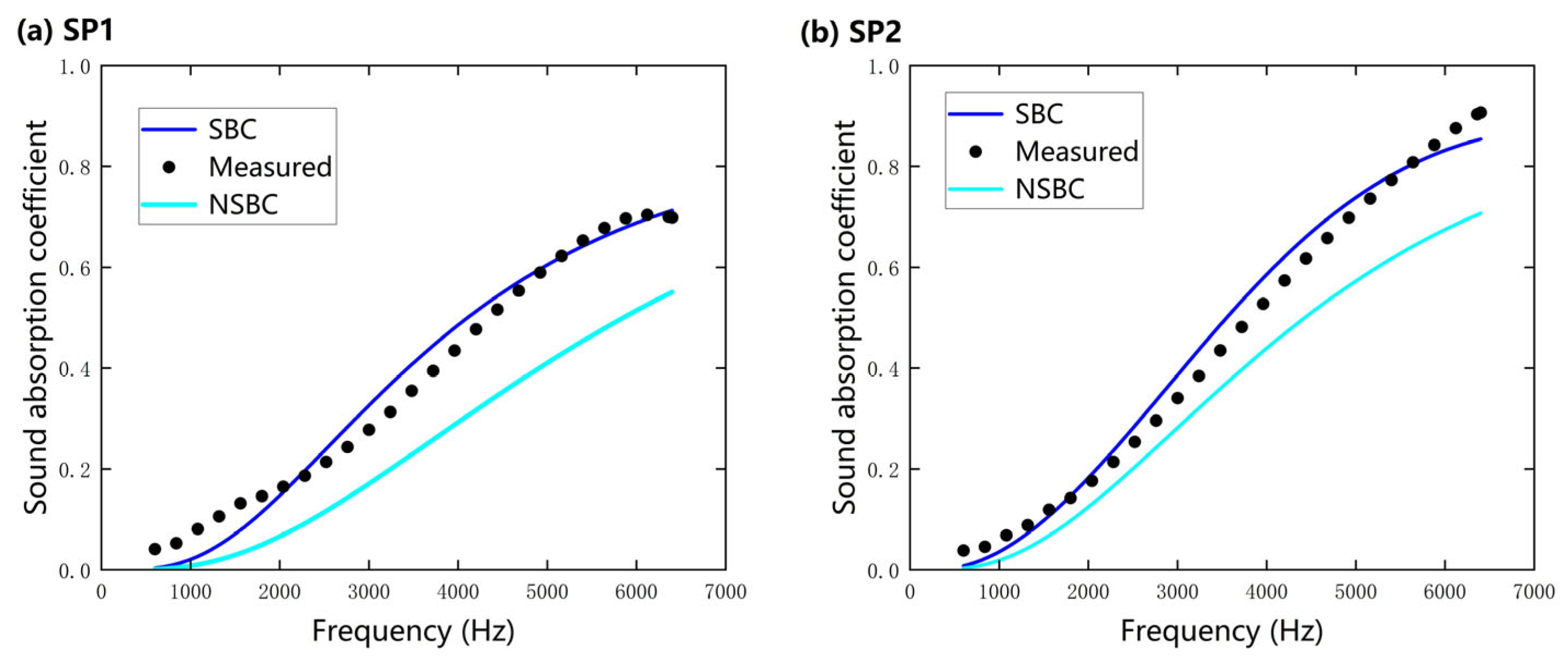
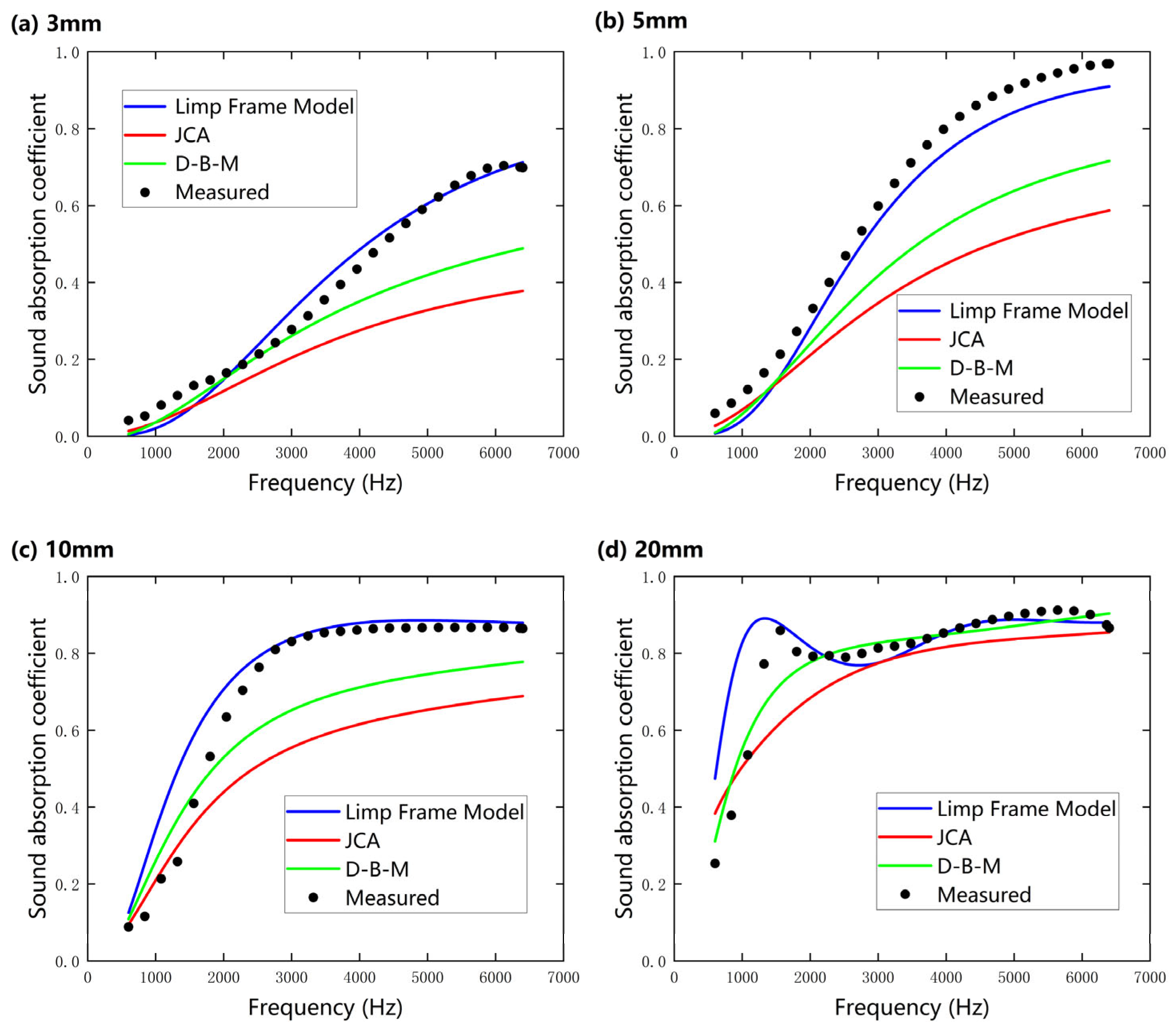
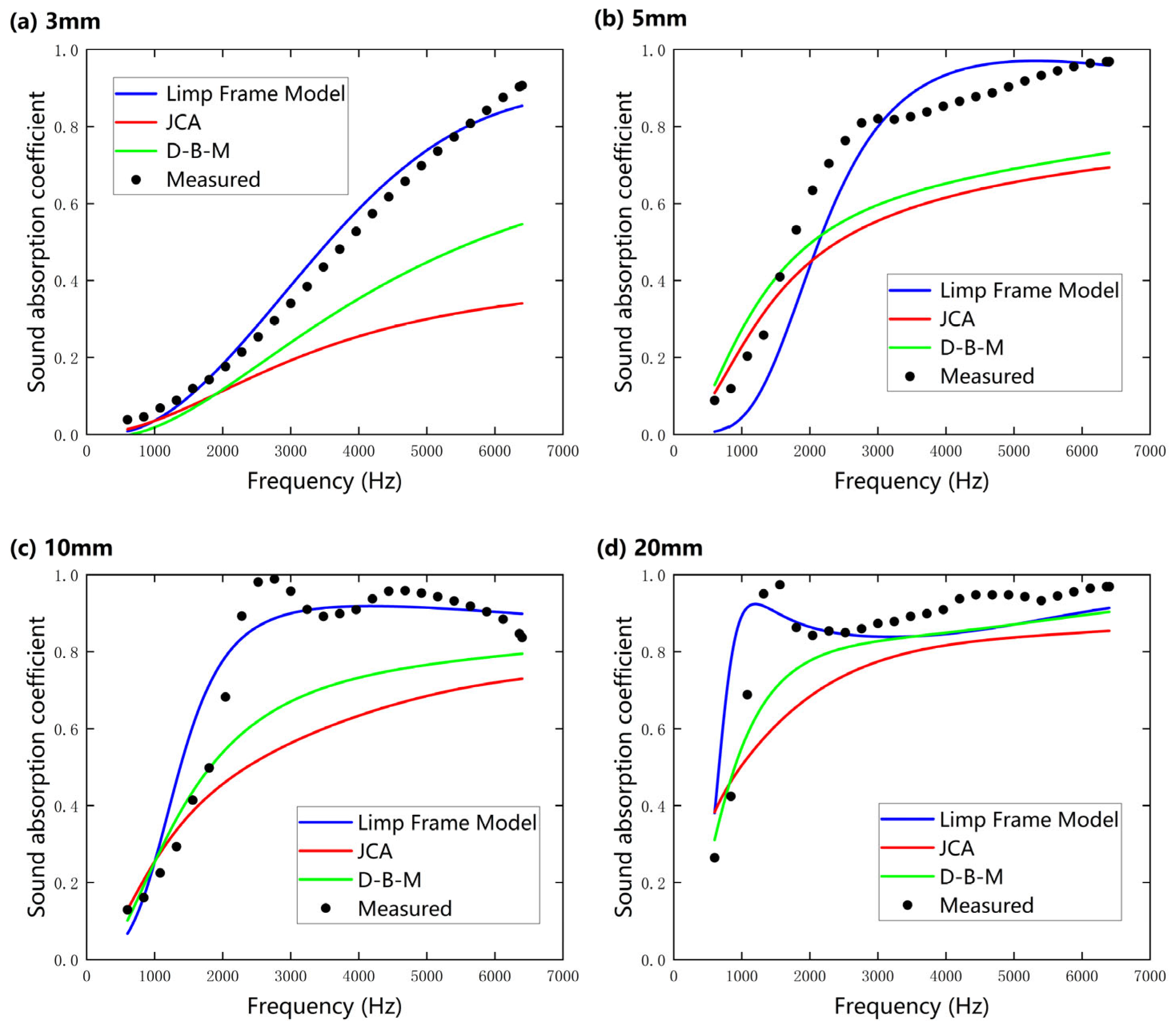
4.2. Prediction and Experimental Comparison
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
| Symbol | Unit | Physical Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| μ | Pa·s | Dynamic viscosity of air |
| Ls | nm | Slip length |
| σv | — | Momentum accommodation coefficient |
| Kn | — | Knudsen number |
| λ | nm | Gas mean free path |
| df | nm | fiber diameter |
| Δp | Pa | Pressure drop across the sample |
| u | m/s | periodic velocity |
| h | m | Sample thickness |
| σ | Ns/m4 | Flow resistivity; resistance to airflow through porous media |
| α∞ | — | Tortuosity; ratio of effective to straight acoustic path length |
| ϕ | — | Porosity; fraction of void volume in the total volume |
| Λ | μm | Viscous characteristic length; controls viscous dissipation scale |
| Λ′ | μm | Thermal characteristic length; controls heat exchange scale |
| Vp | M3 | Pore volume |
| Sp | M2 | Effective surface area of pores |
| ρf | kg/m3 | Air density |
| c0 | m/s | Speed of sound in air |
| Zc | Pa·s/m | Characteristic acoustic impedance |
| k | m−1 | Complex wave number |
| ρ(ω) | kg/m3 | Effective density |
| K(ω) | Pa | Effective bulk modulus |
| γ | — | Ratio of specific heats of air |
| pA | Pa | Standard atmospheric pressure |
| ω | rad/s | Angular frequency |
| f | Hz | Acoustic frequency |
| Pr | — | Prandtl number |
| ρ | kg/m3 | Bulk density of the material |
| Pin | Pa | Inlet pressures of the nanofiber |
| Pout | Pa | Outlet pressures of the nanofiber |
| c | Pa | Constant pressure drop |
| ϕm | — | Measured porosity |
| ρfiber | kg/m3 | Intrinsic density of the nanofiber |
| Vt | m3 | Total volume of the domain |
References
- Cao, L.T.; Fu, Q.X.; Si, Y.; Ding, B.; Yu, J.Y. Porous materials for sound absorption. Compos. Commun. 2018, 10, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenry; Lim, C.T. Nanofiber technology: Current status and emerging developments. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2017, 70, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.N.; Li, Z.W.; Wu, H. Blowspinning: A New Choice for Nanofibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 33447–33464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelegrinis, M.T.; Horoshenkov, K.V.; Burnett, A. An application of Kozeny-Carman flow resistivity model to predict the acoustical properties of polyester fibre. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 101, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akasaka, S.; Kato, T.; Azuma, K.; Konosu, Y.; Matsumoto, H.; Asai, S. Structure-sound absorption property relationships of electrospun thin silica fiber sheets: Quantitative analysis based on acoustic models. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 152, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurrell, A.; Horoshenkov, K.V.; King, S.G.; Stolojon, V. On the relationship of the observed acoustical and related non-acoustical behaviours of nanofibers membranes using Biot- and Darcy-type models. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 179, 108075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, T.; Arenas, J.P. Sound Absorption of Sustainable Polymer Nanofibrous Thin Membranes Bonded to a Bulk Porous Material. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, V.; Pablos, I.P.; Chen, J.M. Acoustic characterization of nanofibers for optimization with porous substrate. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2023, 153, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venegas, R.; Boutin, C.; Umnova, O. Acoustics of multiscale sorptive porous materials. Phys. Fluids 2017, 29, 082006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayrault, C.; Moussatov, A.; Castagnède, B.; Lafarge, D. Ultrasonic characterization of plastic foams via measurements with static pressure variations. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1999, 74, 3224–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, H.T.; Perrot, C.; Monchiet, V.; Panneton, R. Three-dimensional reconstruction of a random fibrous medium: Geometry, transport, and sound absorbing properties. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2017, 141, 4768–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Perrot, C.; Guilleminot, J.; Leroy, P.; Jacqus, G. Multiscale prediction of acoustic properties for glass wools: Computational study and experimental validation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2018, 143, 3283–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.Z.; Chen, F.; Fei, Y.P.; Jin, J.M.; Li, P.F.; Kuang, T.R.; Xiao, Y.P.; Ruan, S.L.; Lu, H.C. High sound insulation property of prepared polypropylene/polyolefin elastomer blends by combining pressure-induced-flow processing and supercritical CO2 foaming. Compos. Commun. 2021, 28, 100958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peta, K.; Stemp, W.J.; Stocking, T.; Chen, R.C.; Love, G.; Gleason, M.A.; Houk, B.A.; Brown, C.A. Multiscale Geometric Characterization and Discrimination of Dermatoglyphs (Fingerprints) on Hardened Clay-A Novel Archaeological Application of the GelSight Max. Materials 2025, 18, 2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.A.; Tafreshi, H.V. Modeling permeability of 3-D nanofiber media in slip flow regime. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 2249–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimian, M.; Naderi, M.; Soltani, P.; Cheng, L.P.; Naderi, K.; Linden, S.; Wiegmann, A. Experimental and CFD analysis of fluid flow through nanofiber filter media. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 42697-2023; Textiles—Test Method for Porosity of Nonwoven Fabrics. Standardization Administration of China (SAC): Beijing, China, 2023.
- ISO 10534-2; Acoustics—Determination of Sound Absorption Coefficient and Impedance in Impedance Tubes—Part 2: Transfer-Function Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998.
- Soltani, P.; Taban, E.; Faridan, M.; Samaei, S.E.; Amininasab, S. Experimental and computational investigation of sound absorption performance of sustainable porous material: Yucca Gloriosa fiber. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 157, 106999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babanezhad, M.; Behroyan, I.; Nakhjiri, A.T.; Marjani, A.; Shirazian, S. Simulation of liquid flow with a combination artificial intelligence flow field and Adams-Bashforth method. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcato, A.; Boccardo, G.; Marchisio, D. A computational workflow to study particle transport and filtration in porous media: Coupling CFD and deep learning. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 128936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.J.; Kumita, M.; Seto, T.; Inui, Y.; Bao, L.; Fujimoto, T.; Otani, Y. Effect of slip flow on pressure drop of nanofiber filters. J. Aerosol. Sci. 2017, 114, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.Y.; Ou, Q.S.; Romay, F.J.; Chen, W.Q.; Liang, Y.; Pui, D.Y.H. Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Slip Effect on Nanofiber Filter Performance at Low Pressures. Small 2024, 20, e2406619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsalikis, D.G.; Mavrantzas, V.G.; Pratsinis, S.E. Dynamics of molecular collisions in air and its mean free path. Phys. Fluids 2023, 35, 097131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsalikis, D.G.; Mavrantzas, V.G.; Pratsinis, S.E. A new equation for the mean free path of air. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 930–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, J.F.; Castagnede, B.; Henry, M.; Lauriks, W. Evaluation of tortuosity in acoustic porous materials saturated by air. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1994, 65, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linton Johnson, D.; Koplik, J.; Dashen, R. Theory of dynamic permeability and tortuosity in fluid-saturated porous media. J. Fluid Mech. 1987, 176, 379–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delany, M.E.; Bazley, E.N. Acoustical properties of fibrous absorbent materials. Appl. Acoust. 1970, 3, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, Y. Acoustical properties of porous materials-Modifications of Delany-Bazley models. J. Acoust. Soc. Jpn. (E) 1990, 11, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, J.F.; Champoux, Y. New empirical equations for sound propagation in rigid frame fibrous materials. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1992, 91, 3346–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panneton, R. Comments on the limp frame equivalent fluid model for porous media. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2007, 122, EL217–EL222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, S.; Shintani, T.; Hasegawa, T. Simplified Limp Frame Model for Application to Nanofiber Nonwovens (Selection of Dominant Biot Parameters). Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, Y.; Agnhage, T.; Cho, G. Sound Absorption of Multiple Layers of Nanofiber Webs and the Comparison of Measuring Methods for Sound Absorption Coefficients. Fibers Polym. 2012, 13, 1348–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Zuo, L.Y.; Zuo, B.Q. Sound absorption properties of spiral vane electrospun PVA/nano particle nanofiber membrane and non-woven composite material. Fibers Polym. 2016, 17, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avossa, J.; Branda, F.; Marulo, F.; Petrone, G.; Guido, S.; Tomaiuolo, G.; Costantini, A. Light Electrospun Polyvinylpyrrolidone Blanket for Low Frequencies Sound Absorption. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2018, 36, 1368–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
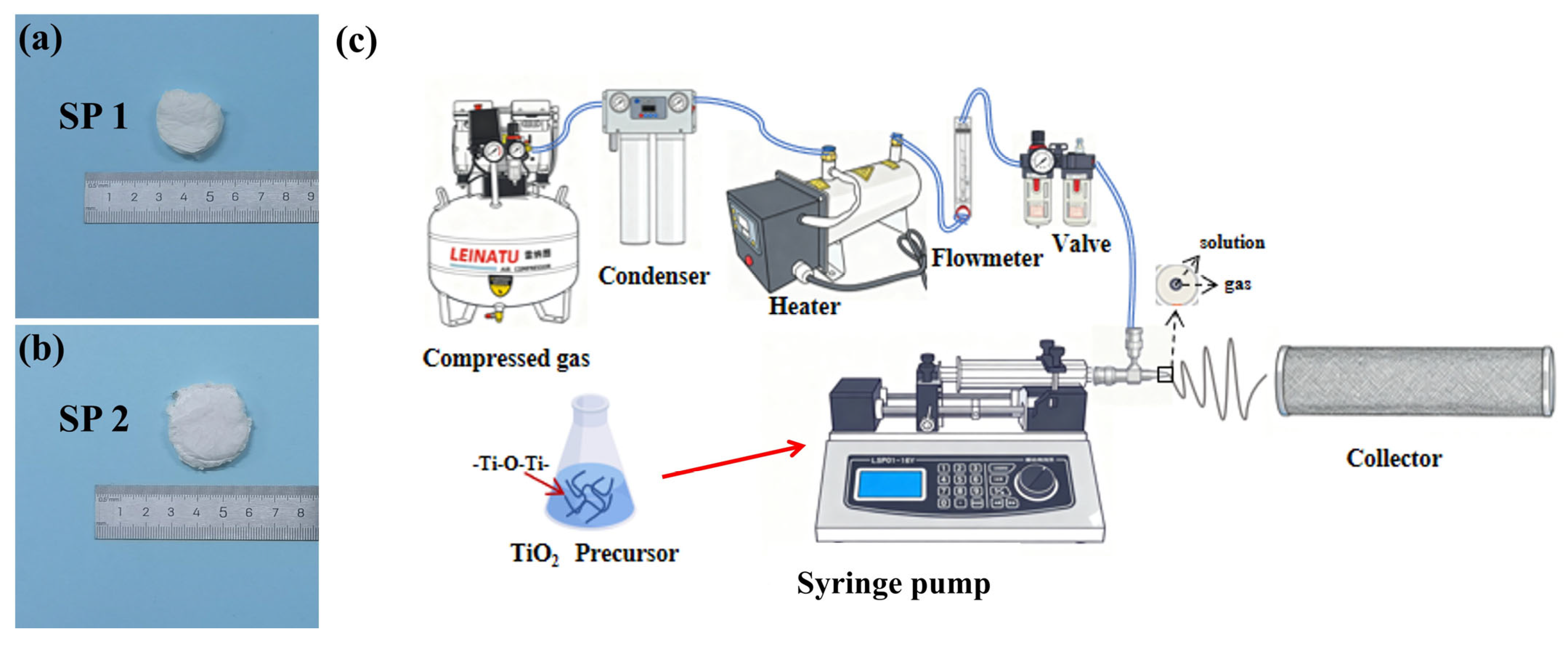
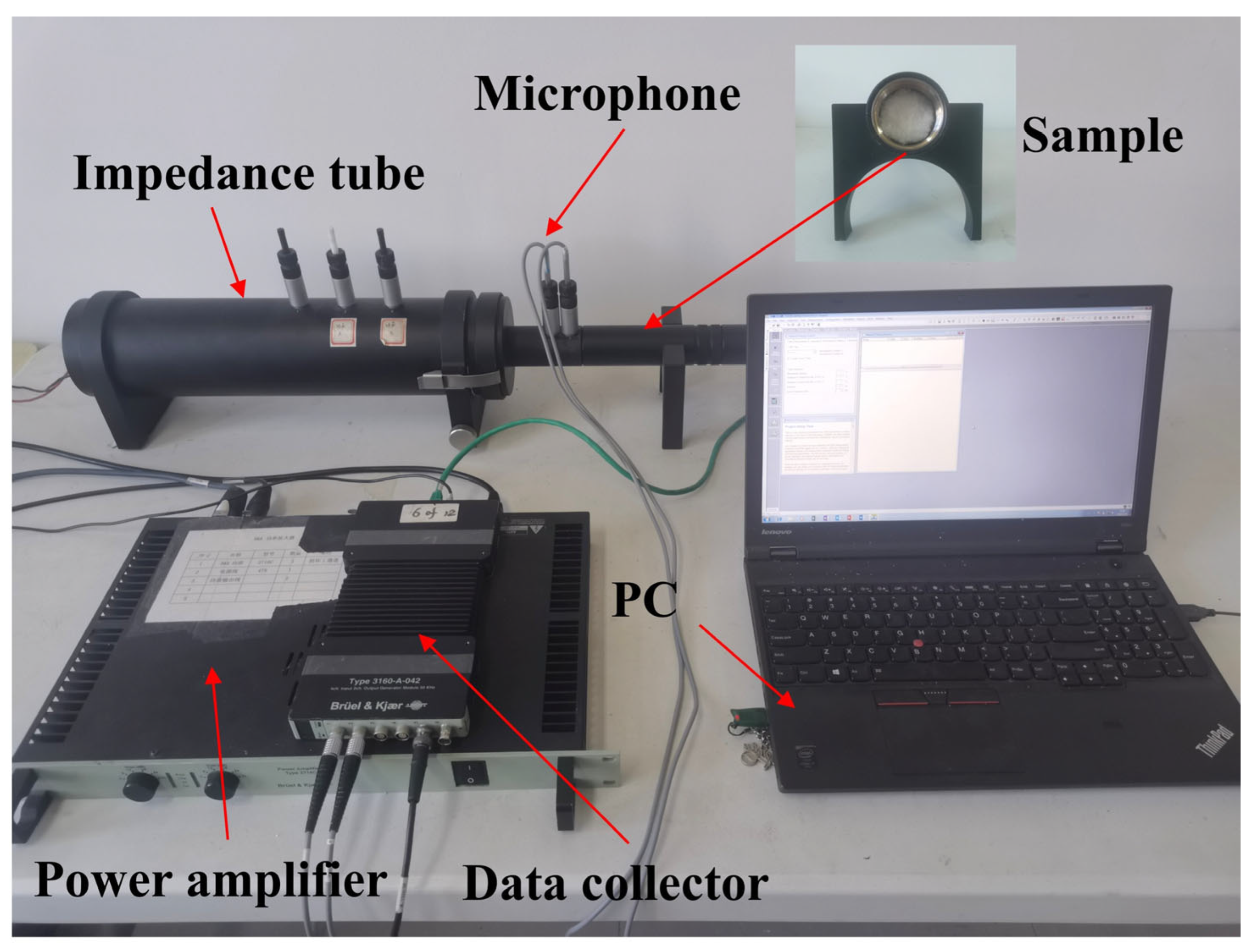
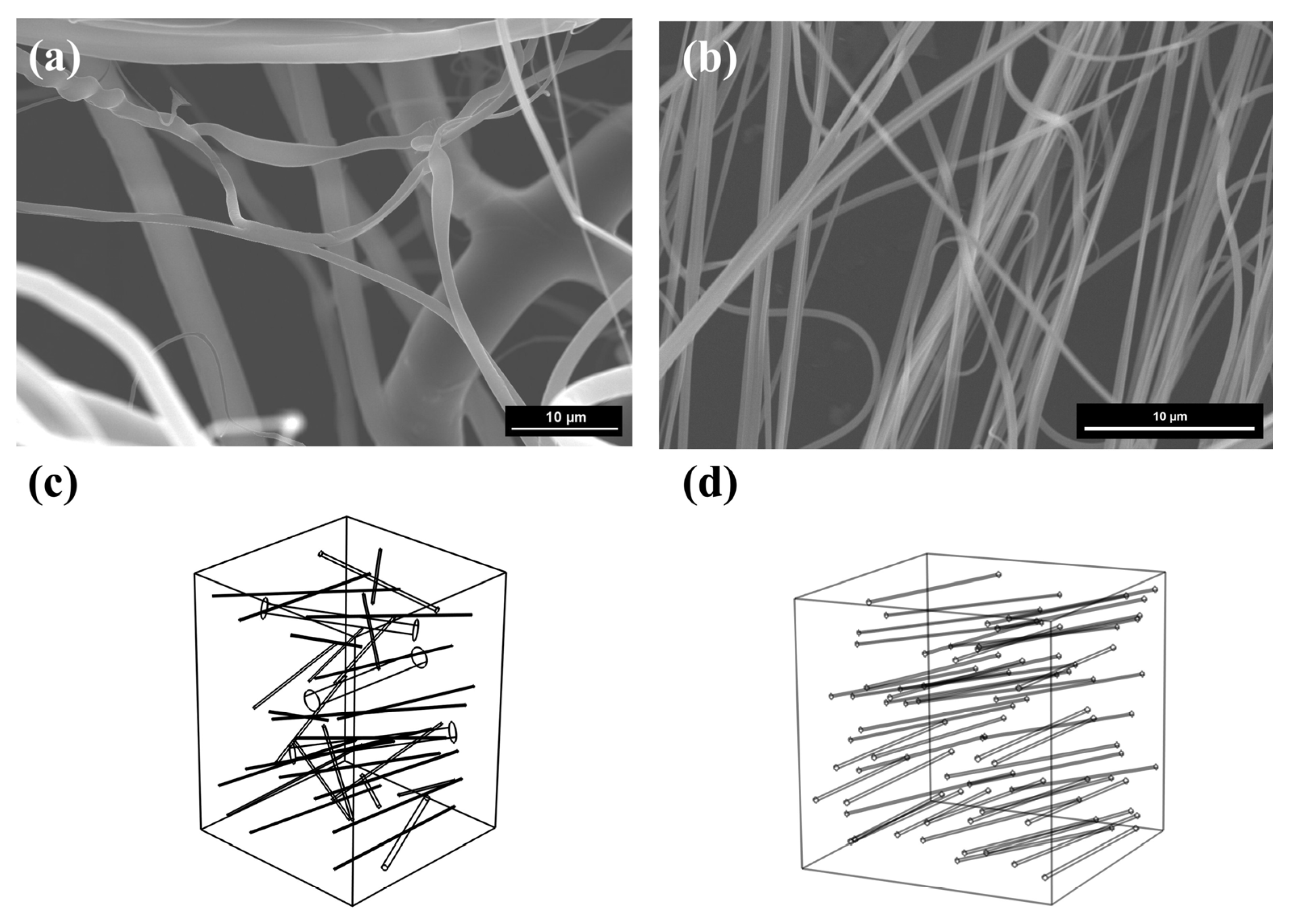
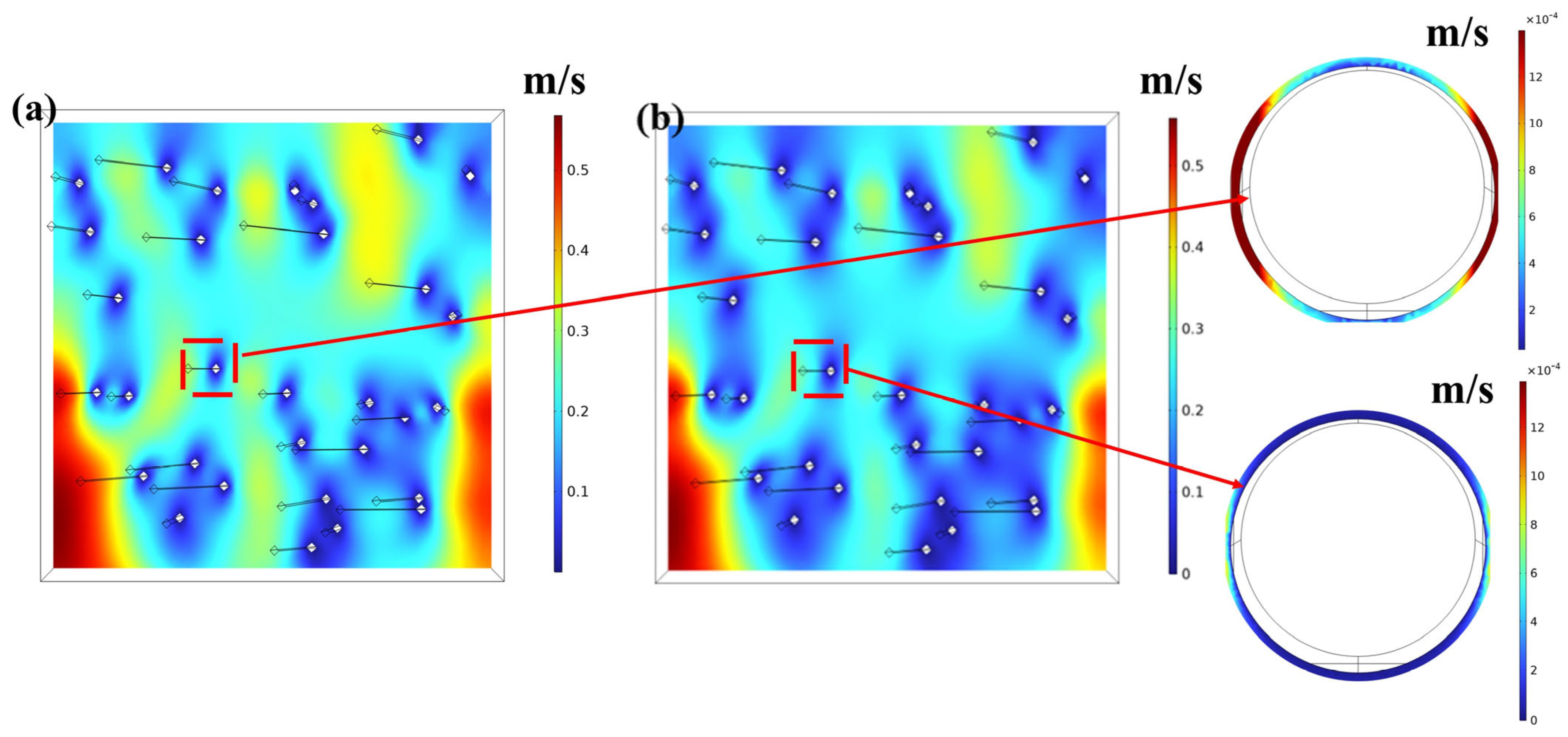
| Sample | Bulk Density ρ (kg/m3) | Measured Porosity ϕm |
|---|---|---|
| SP 1 | 47.8 | 0.956 |
| SP 2 | 11.2 | 0.987 |
| Porosity ϕ | Flow Resistivity σ (Ns/m4) | Tortuosity α∞ | Vicious Characteristic Length Λ (µm) | Thermal Characteristic Length Λ’ (µm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBC | SP 1 | 0.96 | 1.22 × 106 | 1.05 | 3.64 | 8.24 |
| SP 2 | 0.98 | 1.56 × 106 | 1.10 | 3.32 | 9.81 | |
| NSBC | SP 1 | 0.96 | 1.38 × 106 | 1.05 | 3.64 | 8.24 |
| SP 2 | 0.98 | 1.78 × 106 | 1.10 | 3.32 | 9.81 | |
| Porosity ϕ | Flow Resistivity σ (Ns/m4) | Tortuosity α∞ | Vicious Characteristic Length Λ (µm) | Thermal Characteristic Length Λ’ (µm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Akasaka et al. [5] | SF 1 | 0.972 | 1.35 × 106 | 2.25 | 2 | 7.8 |
| SF 2 | 0.969 | 1.02 × 106 | 2 | 4.6 | 9.1 | |
| SF 3 | 0.973 | 7.65 × 105 | 1.5 | 10.4 | 21.5 | |
| Sakamoto et al. [32] | SF 1 | 0.78 | 5.26 × 106 | 1.1 | 4.8 | 5.5 |
| Authors | SP 1 | 0.96 | 1.22 × 106 | 1.05 | 3.64 | 8.24 |
| SP 2 | 0.98 | 1.56 × 106 | 1.10 | 3.32 | 9.81 | |
| Sample | Thickness (mm) | Experimental | D–B–M | JCA | Limp Frame Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SP 1 | 3 | 0.376 | 0.283 | 0.222 | 0.379 |
| 5 | 0.596 | 0.435 | 0.362 | 0.583 | |
| 10 | 0.748 | 0.615 | 0.528 | 0.760 | |
| 20 | 0.815 | 0.796 | 0.746 | 0.834 | |
| SP 2 | 3 | 0.447 | 0.293 | 0.235 | 0.461 |
| 5 | 0.716 | 0.573 | 0.533 | 0.698 | |
| 10 | 0.775 | 0.628 | 0.554 | 0.787 | |
| 20 | 0.871 | 0.815 | 0.765 | 0.857 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, J.; Cao, B.; Huang, J.; Jiang, L.; Liu, Z.; Kuang, T.; Wu, W.; Chen, F.; Fei, Y. Slip Boundary-Enabled Multiscale Modeling for Sound Absorption Coefficient of Nanofiber Porous Media with High Fidelity. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1696. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15221696
Jin J, Cao B, Huang J, Jiang L, Liu Z, Kuang T, Wu W, Chen F, Fei Y. Slip Boundary-Enabled Multiscale Modeling for Sound Absorption Coefficient of Nanofiber Porous Media with High Fidelity. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(22):1696. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15221696
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Jiangming, Bohan Cao, Jietao Huang, Liyang Jiang, Ziyi Liu, Tairong Kuang, Wei Wu, Feng Chen, and Yanpei Fei. 2025. "Slip Boundary-Enabled Multiscale Modeling for Sound Absorption Coefficient of Nanofiber Porous Media with High Fidelity" Nanomaterials 15, no. 22: 1696. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15221696
APA StyleJin, J., Cao, B., Huang, J., Jiang, L., Liu, Z., Kuang, T., Wu, W., Chen, F., & Fei, Y. (2025). Slip Boundary-Enabled Multiscale Modeling for Sound Absorption Coefficient of Nanofiber Porous Media with High Fidelity. Nanomaterials, 15(22), 1696. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15221696






