The Dose-Dependent Effect of Carbon Quantum Dots as a Photosynthesis Enhancer on Soybean Plant Growth
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
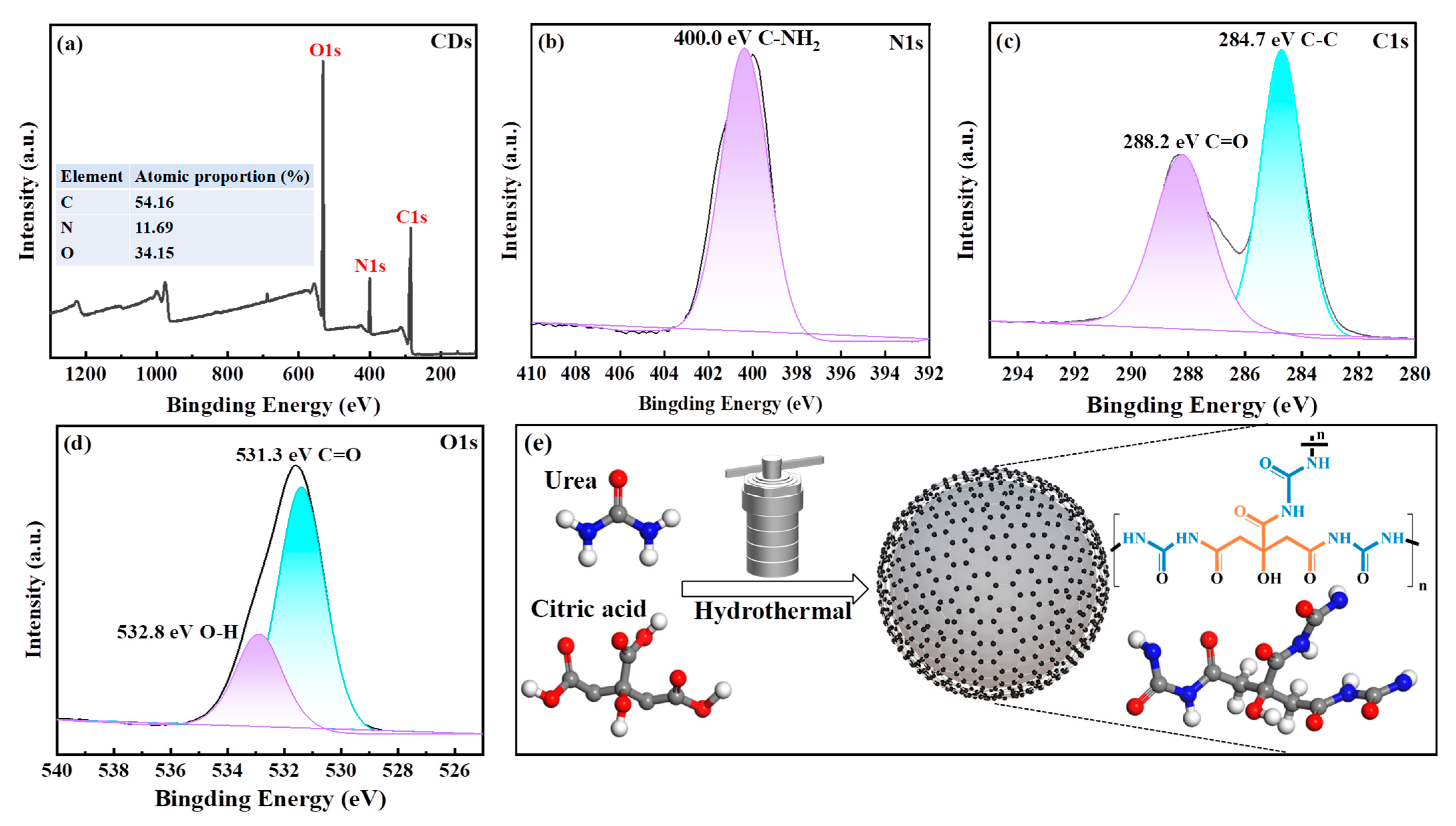
2.2. Synthesis of CDs
2.3. Characterization Methosds of CDs
2.4. Cultivation Experiment
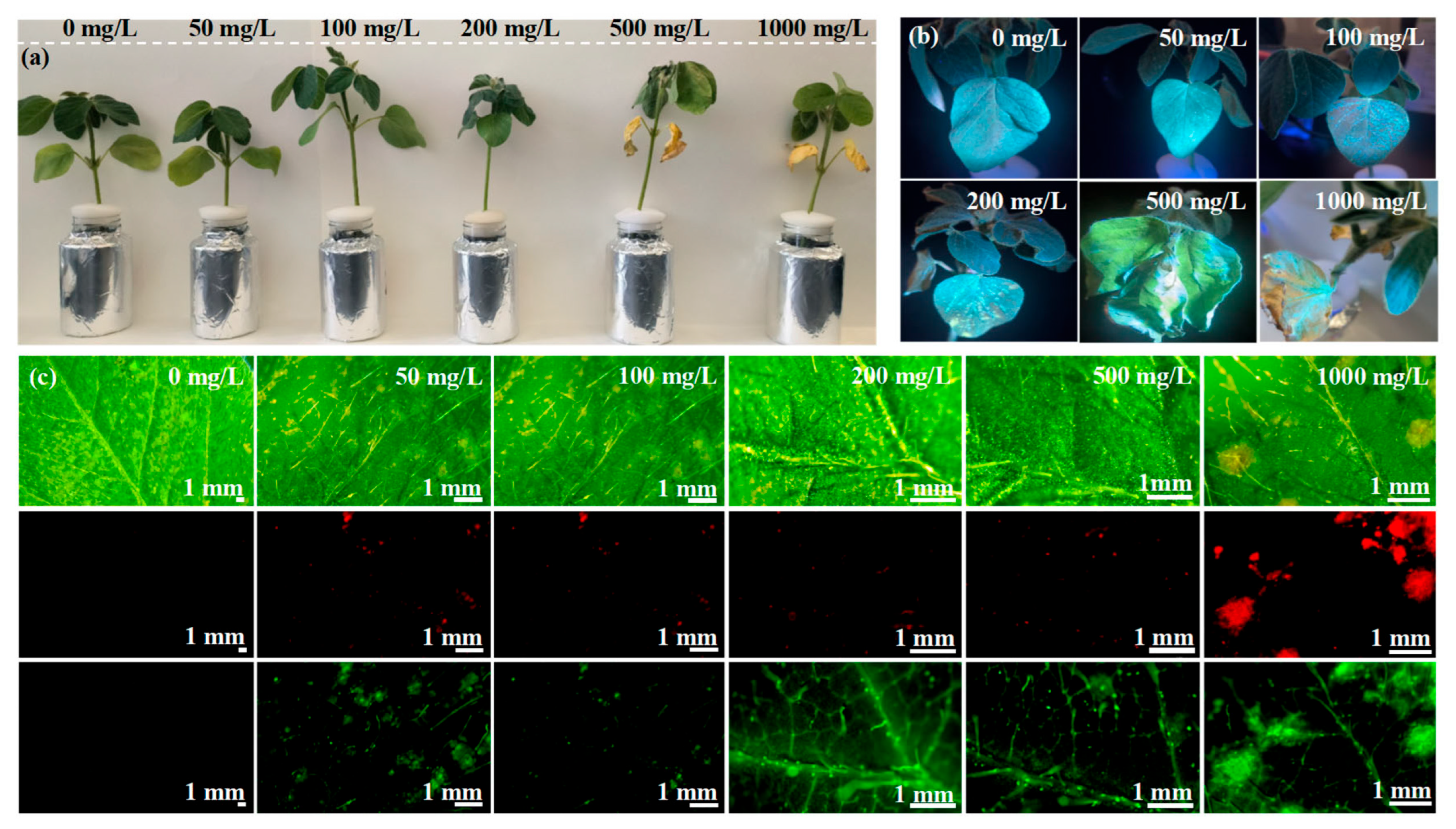
2.4.1. Soybean Cultivation and Phytotoxicity Testing
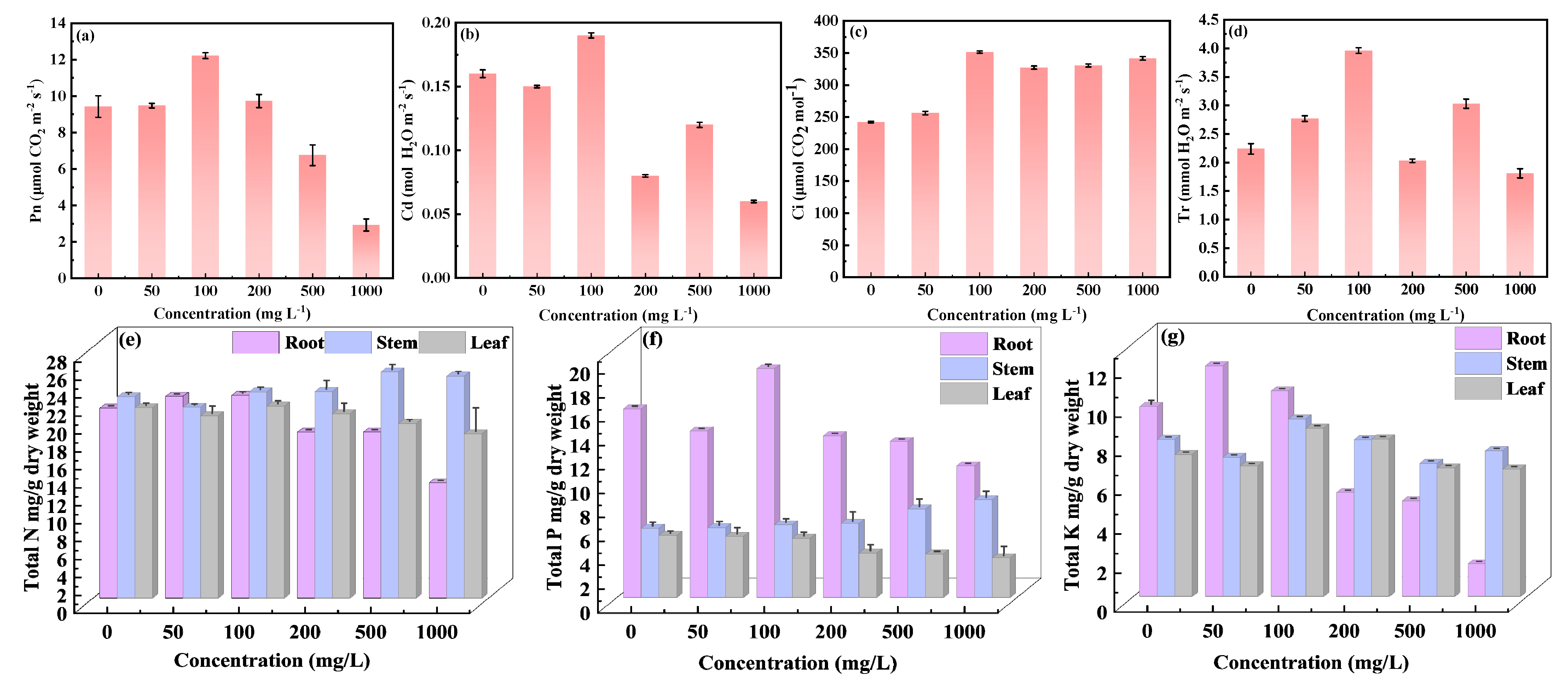
2.4.2. Assessment of Photosynthetic and Growth Indexes
2.4.3. Analysis of Metabolites and Transcriptome of Soybean Leaves
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of CDs
3.2. Effect of CDs on Soybean Growth
3.3. Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Profiles of Soybean Leaves After Exposure to CDs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guirguis, A.; Yang, W.R.; Conlan, X.A.; Kong, L.X.; Cahill, D.M.; Wang, Y.C. Boosting Plant Photosynthesis with Carbon Dots: A Critical Review of Performance and Prospects. Small 2023, 19, 2300671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.X.; Yang, Z.L.; Chen, F.R.; Yue, L.; Cao, X.S.; Li, J.; Qian, H.L.; Yan, X.P.; Wang, C.X.; Wang, Z.Y. Biomass-Derived Carbon Dots with Light Conversion and Nutrient Provisioning Capabilities Facilitate Plant Photosynthesis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 901, 165973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, X.N.; Kah, M.; Yue, L.; Cheng, B.X.; Wang, C.X.; Wang, Z.Y.; Xing, B.S. Unlocking the Potential of Carbon Dots in Agriculture Using Data-Driven Approaches. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 944, 173605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhong, Y.; Fu, G.; Lai, W.; Pan, Z.; Yang, Y.; Chen, F.; Yan, H. Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Luminescent Carbonaceous Nanoparticles as Silkworm Feed for Fabricating Fluorescent Silkworm Silk. Coatings 2023, 13, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhu, Q. Low Cu(II) Concentration Detection Based on Fluorescent Detector Made from Citric Acid and Urea. J. Fluoresc. 2023, 33, 2391–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoes, E.F.C.; Leitao, J.M.M.; da Silva, J.C.G.E. Carbon Dots Prepared from Citric Acid and Urea as Fluorescent Probes for Hypochlorite and Peroxynitrite. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 1769–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunelli, A.; Cazzagon, V.; Faraggiana, E.; Bettiol, C.; Picone, M.; Marcomini, A.; Badetti, E. An Overview on Dispersion Procedures and Testing Methods for the Ecotoxicity Testing of Nanomaterials in the Marine Environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 921, 171132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.H.; Jiang, M.; Wang, M.; Ren, K.W.; Luo, X.; Luo, Y.; Chen, Q.; Lu, C.A.; Huang, C.Z.; Liu, Q.Q. Synergistic Mitochondrial Genotoxicity of Carbon Dots and Arsenate in Earthworms Eisenia fetida Across Generations: The Critical Role of Binding. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 16750–16761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, T.N.V.K.V.; Swethasree, M.; Satisha, G.C.; Nirmal Kumar, A.R.; Sudhakar, P.; Ravindra Reddy, B.; Saritha, M.; Sabitha, N.; Bhaskar Reddy, B.V.; Rajasekhar, P.; et al. Nanoparticulate Silica Internalization and Its Effect on the Growth and Yield of Groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 5881–5890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, G.; Gualtieri, M.; Bengalli, R.; Saibene, M.; Belosi, F.; Nicosia, A.; Cabellos, J.; Mantecca, P. An Integrated New Approach Methodology for Inhalation Risk Assessment of Safe and Sustainable by Design Nanomaterials. Environ. Int. 2024, 183, 108420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Q.; Chen, L.A.; Xu, J.K.; Zhang, L.L.; Yang, X.Q.; Zhang, X.K.; Zhang, C.; Gao, P.; Zhu, L.S. Environmental Behaviors and Toxic Mechanisms of Engineered Nanomaterials in Soil. Environ. Res. 2024, 242, 117820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.D.; Jin, Q.J.; Xu, X.; Miao, A.J.; White, J.C.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L.; Ji, R.; Zhao, L.J. High-Throughput Screening for Engineered Nanoparticles That Enhance Photosynthesis Using Mesophyll Protoplasts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 3382–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govorov, A.O.; Carmeli, I. Hybrid Structures Composed of Photosynthetic System and Metal Nanoparticles: Plasmon Enhancement Effect. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.N.; Li, W.; Zhang, H.R.; Zhang, X.J.; Zhuang, J.L.; Liu, Y.L.; Hu, C.F.; Lei, B.F. Far-Red Carbon Dots as Efficient Light—Harvesting Agents for Enhanced Photosynthesis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 21009–21019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.C.; Lin, Y.; Wang, W.C.; Min, K.; Ling, W.B.; Ma, W.D.; Zhang, W.C.; Hou, X.W.; Wei, L.F.; Liu, Q.; et al. Dose-Dependent Effect on Plant Growth of Exposure to Metal-Organic Framework MIL-101(Cr). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 8009–8019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.P.; He, Y.Z.; Ye, W.B.; Lao, J.Y.; Guan, D.X.; Dong, S.P.; Liu, G.G.; Mao, L. Mechanistic Insights into the Biodegradation of Carbon Dots by Fungal Laccase. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 11977–11987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarac, V.; Milic, D.; Vukelic, N.; Novakovic, T.; Novakovic, D.; Ljubojevic, M.; Rodic, V. Assessment of Beef Manure Economic Value by the Method of Equivalent Green and Mineral Fertilizer Substitution. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.C.; Lv, K.; Yu, J.T.; Que, X.Y.; Liu, J.L.; Ouyang, X.N.; Li, M.Y.; Tian, Y.R.; Song, J.; Wang, J.X.; et al. Electron-beam radiation-induced ultrafast synthesis of highly conjugated carbon quantum dots with excellent fluorescence intensity. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2025, 45, e01448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.Y.; Qiu, L.X.; Zhang, X.H.; Yi, T.H.; Jing, J.; Sami, R.; Alanazi, S.F.; Alqahtani, Z.; Aljabri, M.D.; Rahman, M.M. Novel N-doped carbon dots derived from citric acid and urea: Fluorescent sensing for determination of metronidazole and cytotoxicity studies. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajid, M.; Stone, S.R.; Kaur, P. Phylogenetic Analysis and Protein Modelling of Isoflavonoid Synthase Highlights Key Catalytic Sites Towards Realizing New Bioengineering Endeavours. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.L.; Zheng, H.; Li, X.Y.; Li, N.N.; Liu, Y.F.; Li, T.; Wang, Y.; Xing, B.S. Direct Spectroscopic Evidence for Charge-Assisted Hydrogen-Bond Formation Between Ionizable Organic Chemicals and Carbonaceous Materials. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 9356–9366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mintz, K.J.; Bartoli, M.; Rovere, M.; Zhou, Y.; Hettiarachchi, S.D.; Paudyal, S.; Chen, J.Y.; Domena, J.B.; Liyanage, P.Y.; Sampson, R.; et al. A Deep Investigation into the Structure of Carbon Dots. Carbon 2021, 173, 433–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.K.; Shi, L.J.; Liu, Y.Q.; Meng, X.R.; Xu, H.; Xu, Y.Q.; Liu, B.Y.; Fang, X.M.; Li, H.B.; Ding, T. Supramolecular Interactions via Hydrogen Bonding Contributing to Citric-Acid Derived Carbon Dots with High Quantum Yield and Sensitive Photoluminescence. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 20345–20352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.Y.; Hsieh, C.T.; Gandomi, Y.A.; Chang, J.K.; Li, J.; Li, J.L.; Zhang, H.A.; Guo, Q.; Lau, K.C.; Pandey, R. Microwave Growth and Tunable Photoluminescence of Nitrogen-Doped Graphene and Carbon Nitride Quantum Dots. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 5468–5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.F.; Liu, C.; He, H.; Li, J.F.; Wang, L.; Long, Q.; Zhang, P.C.; Huang, Y. Hydrothermal Synthesis and Characterization of Nitrogen-Doped Fluorescent Carbon Quantum Dots from Citric Acid and Urea. Ferroelectrics 2020, 566, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.Y.; Sun, H.D.; Du, W.; Li, R.Y.; Mao, H.; Kopittke, P.M. Interaction of Different-Sized ZnO Nanoparticles with Maize (Zea mays): Accumulation, Biotransformation and Phytotoxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 796, 148927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.D.; Pan, X.Q.; Xu, X.K.; Wu, Y.; Zhuang, J.L.; Zhang, X.J.; Zhang, H.R.; Lei, B.F.; Hu, C.F.; Liu, Y.L. Carbon Dots as Light Converter for Plant Photosynthesis: Augmenting Light Coverage and Quantum Yield Effect. J. Hazard Mater. 2021, 410, 124534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Cho, K.H.; Tucker, E.; Yoo, C.Y.; Kim, J. Identification of Tomato F-Box Proteins Functioning in Phenylpropanoid Metabolism. Plant Mol. Biol. 2024, 114, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporali, S.; Stefano, A.D.; Calabrese, C.; Giovannelli, A.; Pieri, M.; Savini, I.; Tesauro, M.; Bernardini, S.; Minieri, M.; Terrinoni, A. Anti-Inflammatory and Active Biological Properties of the Plant-Derived Bioactive Compounds Luteolin and Luteolin 7-Glucoside. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlovskaya, E.P.; Popov, A.M.; Styshova, O.N.; Vakhrushev, A.I.; Rutckova, T.A.; Podvolotskaya, A.B.; Tekutyeva, L.A. Comparative Study of the Pharmacological Properties of Luteolin and Its 7,3-Disulfate. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.W.; Liu, T.; Yang, R.W.; Fan, H.Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Xuan, Y.H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Chen, L.J.; Duan, Y.X.; Zhu, X.F. Overexpression of GmPAL Genes Enhances Soybean Resistance Against Heterodera glycines. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2024, 37, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.F.; Chen, Y.Q.; Chen, J.H.; Shen, C.W. Flavonoid Metabolites in Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis) Stress Response: Insights from Bibliometric Analysis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 202, 107934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, A.T.; Tran, L.H.; Jung, S.Y. Salt Stress-Induced Modulation of Porphyrin Biosynthesis, Photoprotection, and Antioxidant Properties in Rice Plants (Oryza sativa). Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| CD Concentration (mg L−1) | Fv/Fm |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0.725 ± 0.008 c |
| 50 | 0.728 ± 0.004 c |
| 100 | 0.808 ± 0.011 a |
| 200 | 0.748 ± 0.009 b |
| 500 | 0.693 ± 0.006 d |
| 1000 | 0.697 ± 0.004 d |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; Lv, K.; Song, J.; Li, M.; Ouyang, X.; Liu, C.; Gong, S.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z. The Dose-Dependent Effect of Carbon Quantum Dots as a Photosynthesis Enhancer on Soybean Plant Growth. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15201603
Wang Q, Lv K, Song J, Li M, Ouyang X, Liu C, Gong S, Wang J, Li J, Zhang Z. The Dose-Dependent Effect of Carbon Quantum Dots as a Photosynthesis Enhancer on Soybean Plant Growth. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(20):1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15201603
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qianyuyue, Kun Lv, Jian Song, Moyan Li, Xingnan Ouyang, Chengcheng Liu, Shuang Gong, Jinxing Wang, Jianming Li, and Zhe Zhang. 2025. "The Dose-Dependent Effect of Carbon Quantum Dots as a Photosynthesis Enhancer on Soybean Plant Growth" Nanomaterials 15, no. 20: 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15201603
APA StyleWang, Q., Lv, K., Song, J., Li, M., Ouyang, X., Liu, C., Gong, S., Wang, J., Li, J., & Zhang, Z. (2025). The Dose-Dependent Effect of Carbon Quantum Dots as a Photosynthesis Enhancer on Soybean Plant Growth. Nanomaterials, 15(20), 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15201603






