Machine Learning Investigation of Ternary-Hybrid Radiative Nanofluid over Stretching and Porous Sheet
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
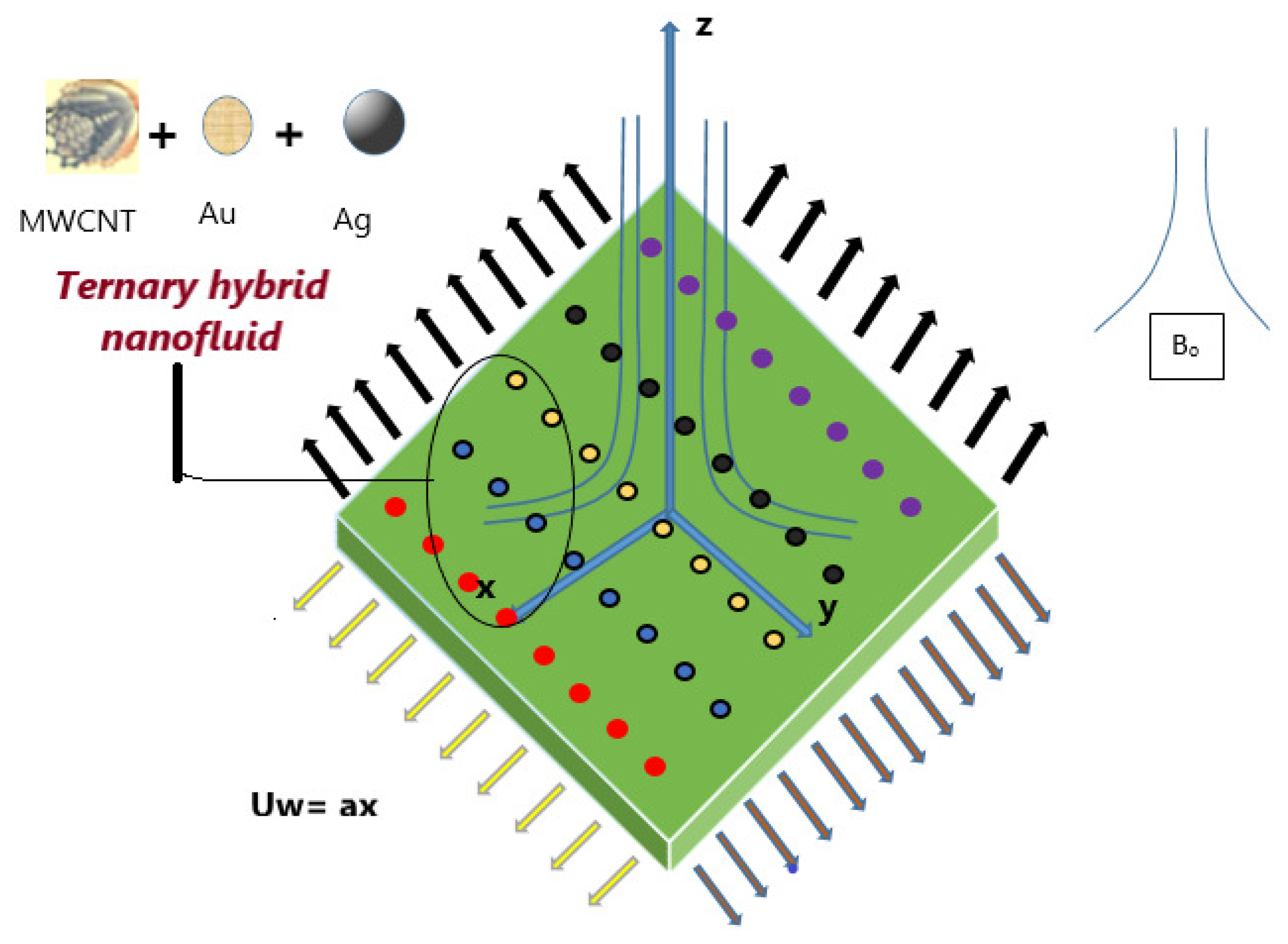
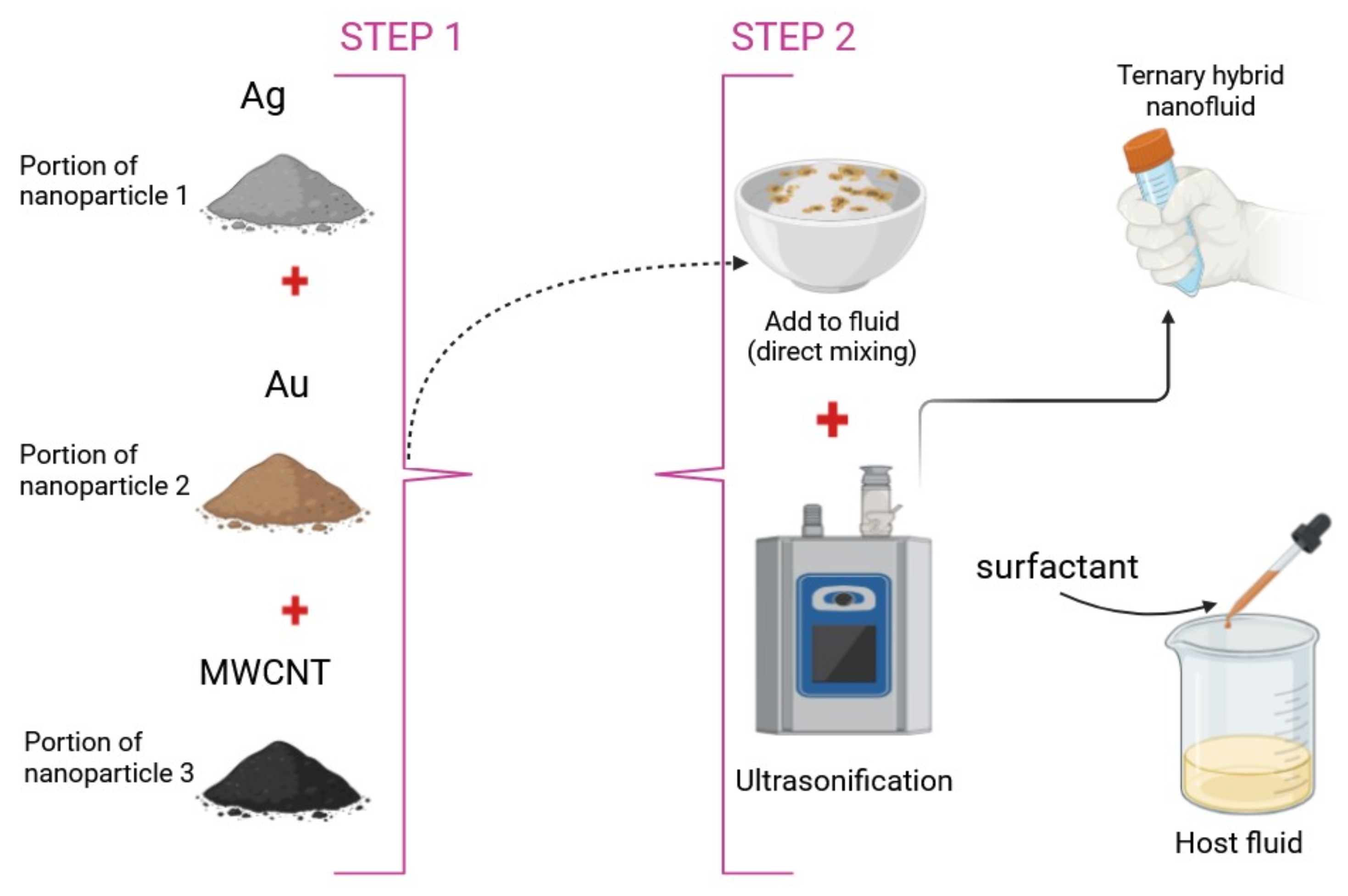
2.1. Model Development
2.2. Expectations and Situations of the Framework
- The substance is considered porous, the single-phase (Tiwari-Das) model is used.
- The nanofluid is treated as a Newtonian fluid, with Boussinesq and boundary layer approximations applied.
- The flow exhibits thermal radiation and heat generation.
- Convective heat boundary conditions are assumed.
- Single and multi-walled Carbon Nanotubes (CNT), along with Silver (Ag) nanoparticles, are combined with plasma as the base liquid.
- The THNF is assumed to have uniformly sized, spherical nanoparticles, with no consideration for aggregation effects.
2.3. Mathematical Modeling
- 1.
- Convective BC non-dimensionalization: Starting withUsing similarity transform, it reduces to
- 2.
- Rosseland linearization: Expanding aboutSubstitution yieldsWhich leads to the modified coefficient in the energy Equation (16).
2.4. Investigation of the THNF Model
- Magnetic Parameter:
- Biot value:
- Prandtl ratio:
- Velocity Ratio Parameter:
- Darcy numbers:
- Radiation Parameter:
- x-wall stresses:
- y-wall stresses:
- Nusselt number:
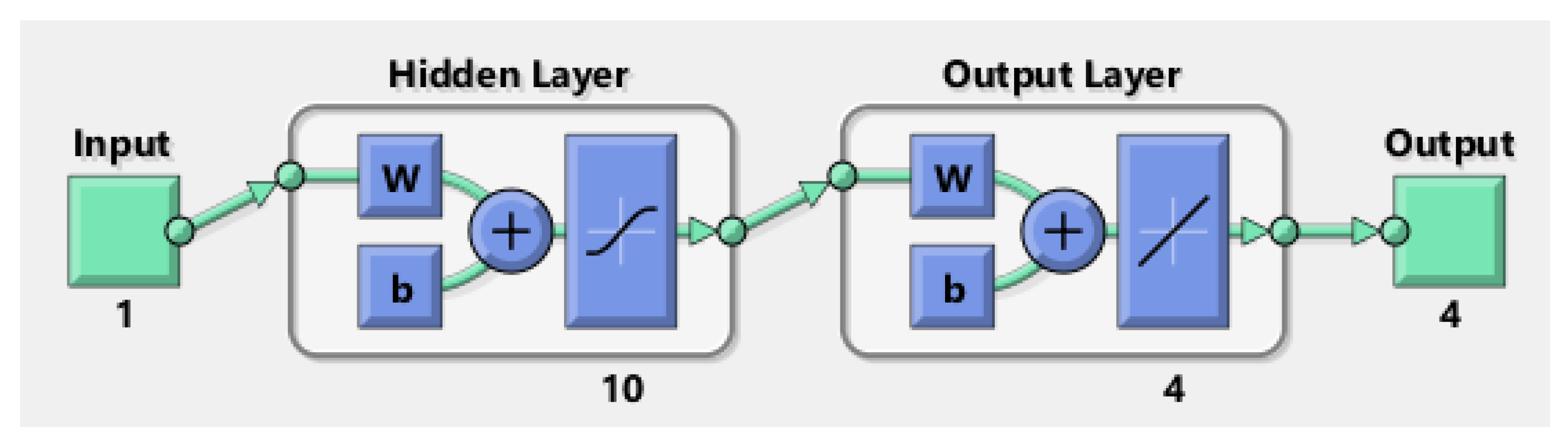
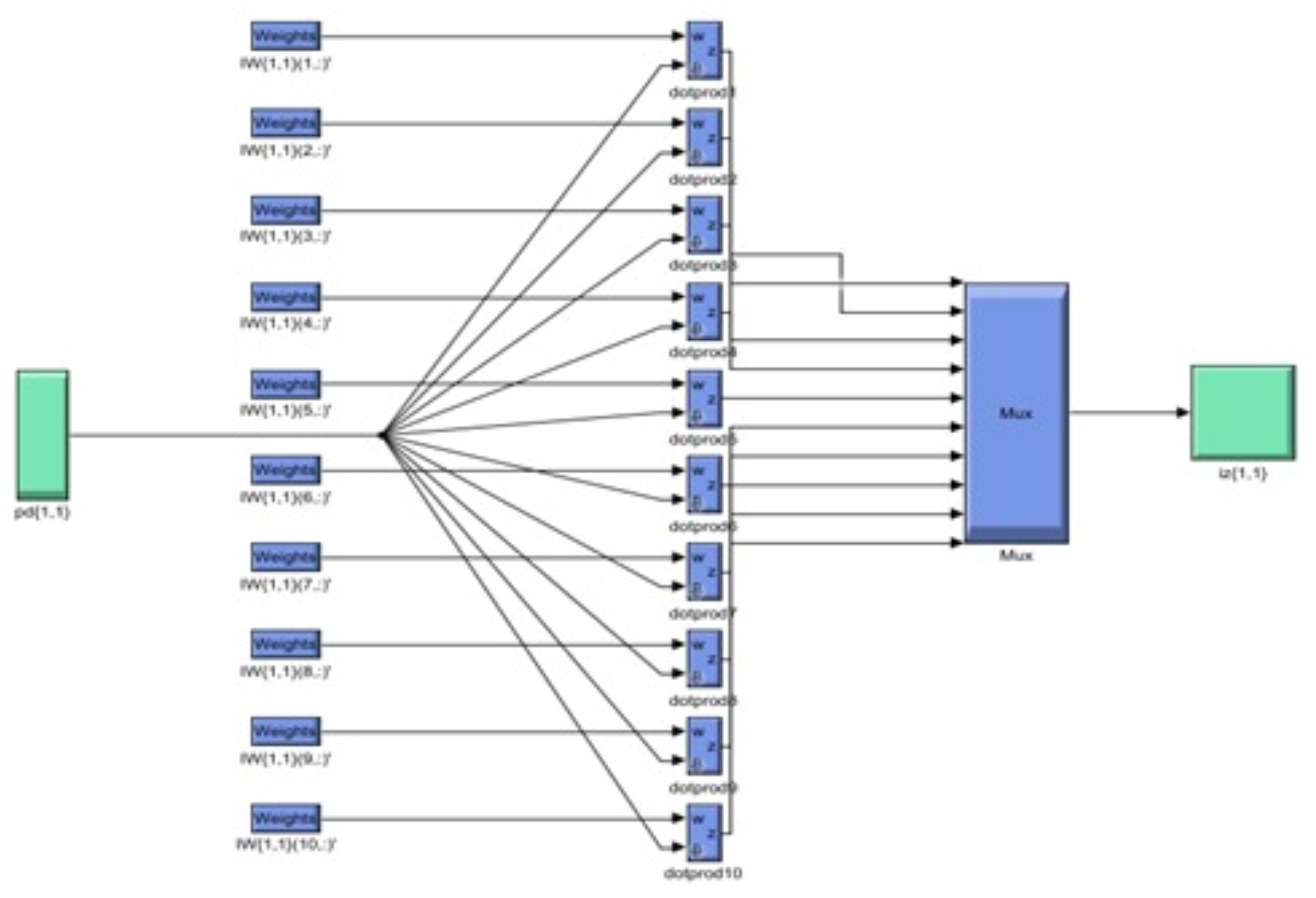
3. Solution Methodology and Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Model Validation
- 1.
- Limiting cases: The model recovers Newtonian single-phase blood when .
- 2.
- Parameter realism: The chosen ranges of Bi, Pr, M, Da, and R align with experimentally and numerically reported values in biomedical and engineering contexts [31].
- 3.
- Domain truncation: Increasing from 10 to 15 did not affect velocity or temperature profiles, confirming domain adequacy.
- 4.
- Dual-solution probe: In our study, we used the Python bvp_solver to test for multiplicity by employing different initial guesses, mesh refinements (200–600 points), and extended computational domains ( to 15). Across all parameter ranges considered (bidirectional stretching, a,b > 0), the solver consistently converged to a unique branch.
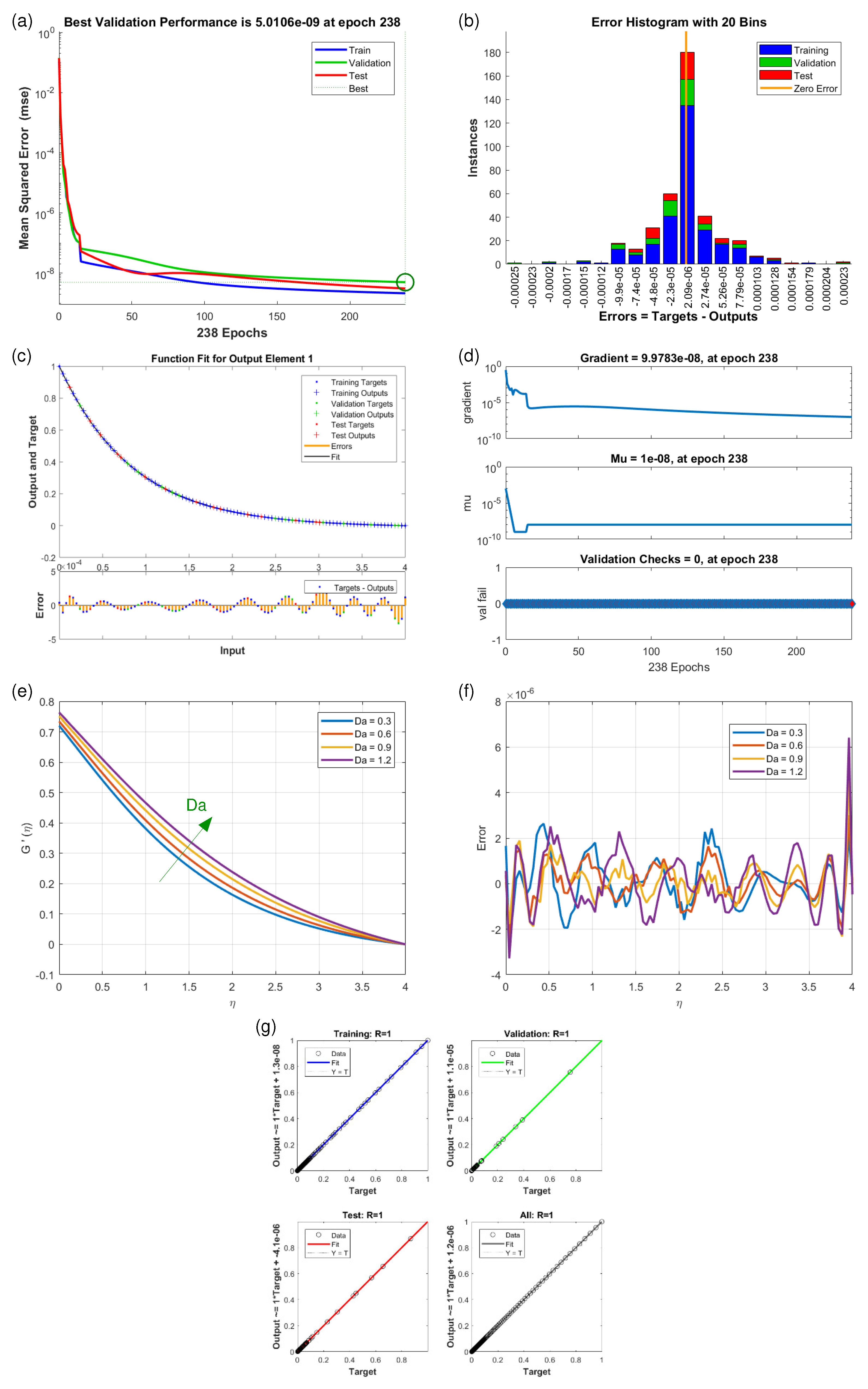
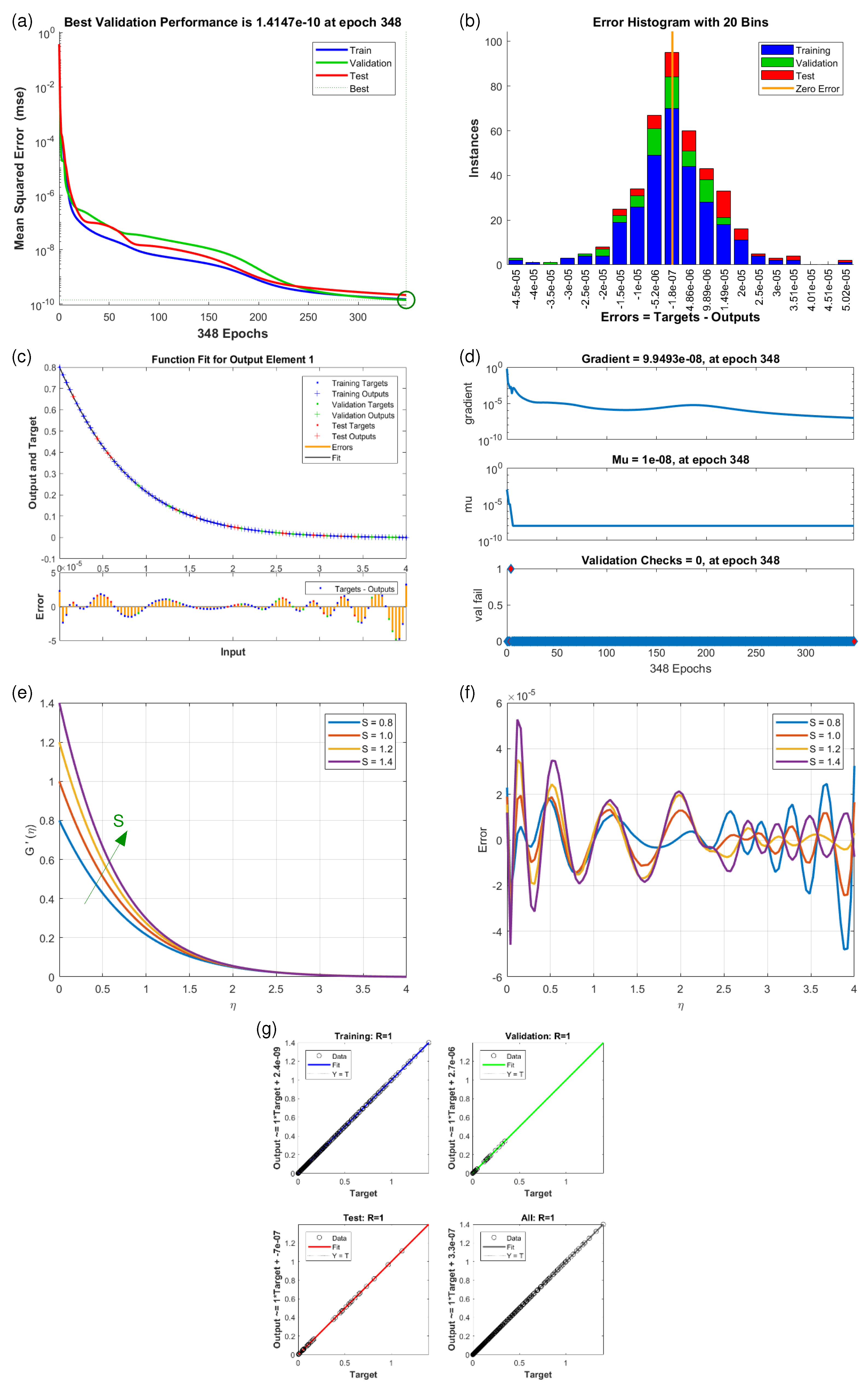
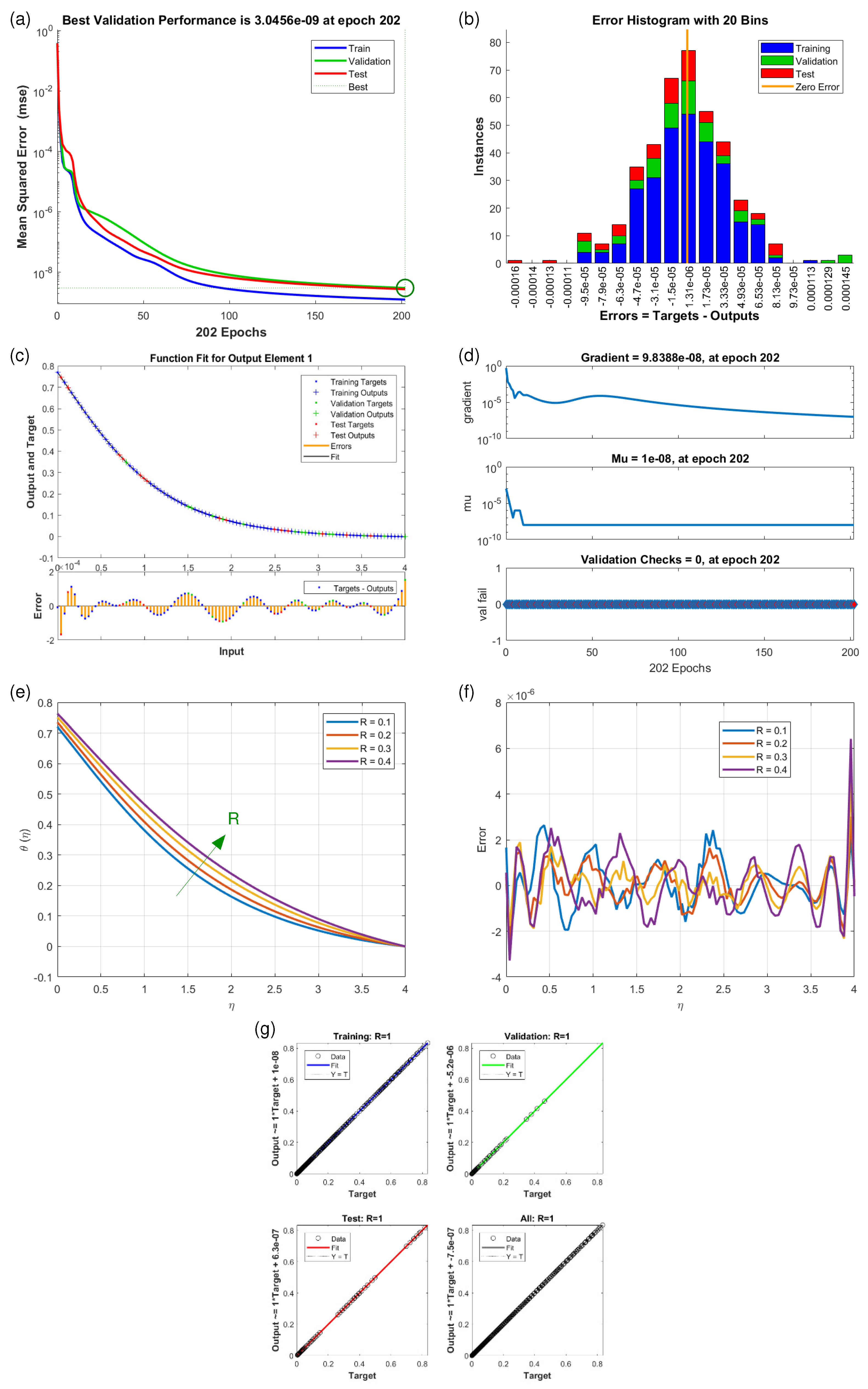
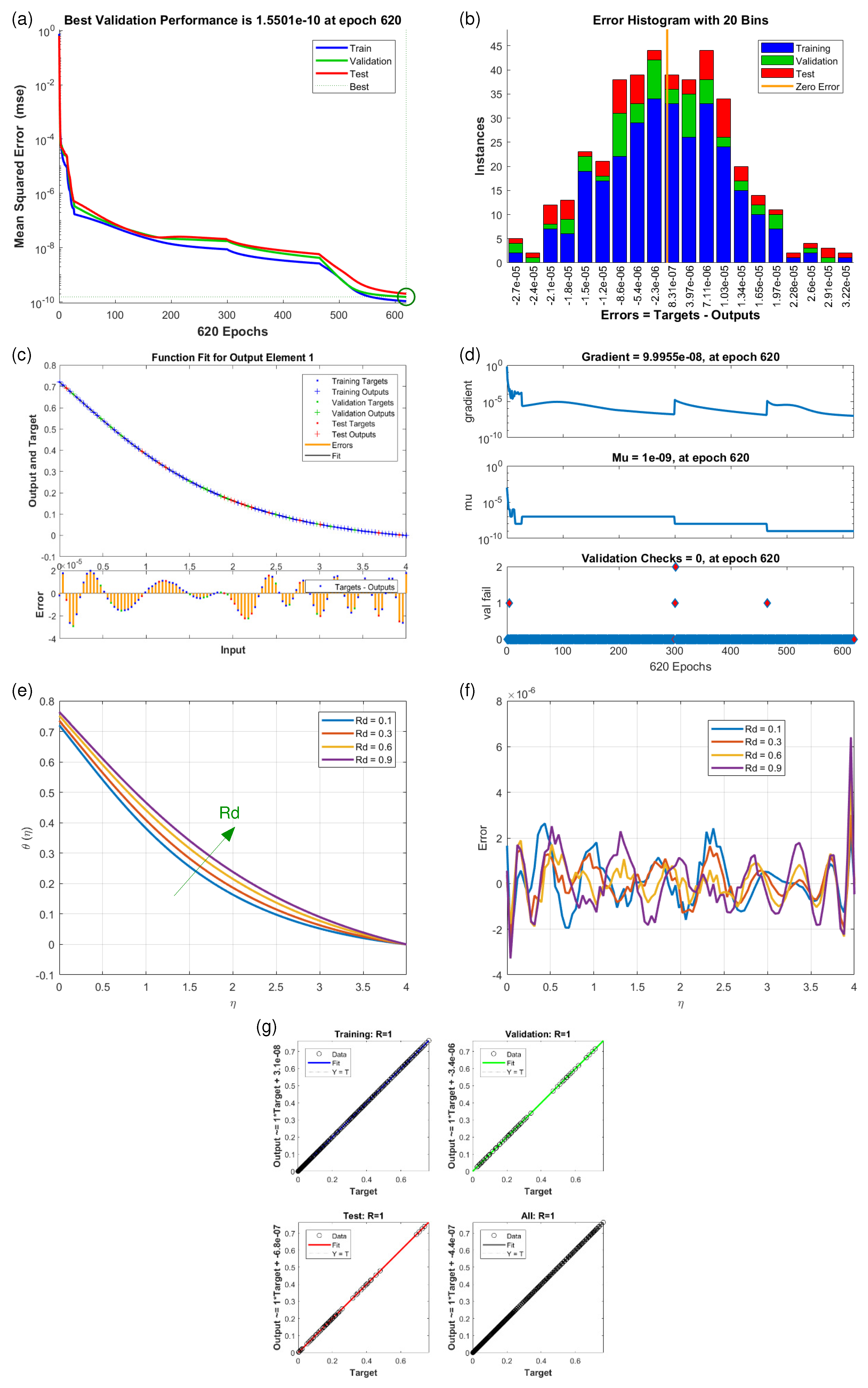
4.2. Velocity Profiles and (Scenario S-1 to S-5)
4.3. Temperature Profiles (Scenario S-6 and S-7)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UCM | Upper-convected Maxwell |
| CNT | Carbon nanotubes |
| MHD | Magnetohydrodynamics |
| ML | Machine learning |
| ODE | Ordinary differential equation |
| PDE | Partial differential equation |
| LMFA | Levenberg-Marquardt Feedforward Algorithm |
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
Nomenclature
| Parameter | Description | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| (x, y) | position coordinate | Bi | Biot value |
| Uw | velocity along x-direction | Pr | Prandtl ratio |
| Vw | velocity along y-direction | S | velocity ratio |
| Tf | temperature of the fluid | Da | porosity characteristics |
| B 0 | Tesla value | R | radiation parameter |
| K* | absorbing medium | Cfx, Cfx | local wall stresses |
| Q 0 | external heat | Nu | Nussel number |
| qr | radial flux | Re | Reynolds number |
| T ∞ | wall temperature | Q | heat source/skin characteristics |
| h | thermal exchange rate | Rd | Retardation factor |
| μ | dynamic viscosity | nf | nanofluid |
| σ | electrical conductivity | hnf | hybrid nanofluid |
| ρcp | heat capacity | thnf | Ternary hybrid nanofluid |
| k | heat conduction rate | M | magnetic parameter |
References
- Adnan; Ashraf, W. Thermal efficiency in hybrid (Al2O3-CuO/H2O) and ternary hybrid nanofluids (Al2O3-CuO-Cu/H2O) by considering the novel effects of imposed magnetic field and convective heat condition. Waves Random Complex Media 2022, 35, 8029–8044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, U.; Zaib, A.; Khan, I.; Nisar, K.S. Insight into the dynamics of transient blood conveying gold nanoparticles when entropy generation and Lorentz force are significant. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 127, 105415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kouz, W.; Abderrahmane, A.; Shamshuddin, M.D.; Younis, O.; Mohammed, S.; Bég, O.A.; Toghraie, D. Heat transfer and entropy generation analysis of water-Fe3O4/CNT hybrid magnetic nanofluid flow in a trapezoidal wavy enclosure containing porous media with the Galerkin finite element method. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2021, 136, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshuddin, M.D.; Eid, M.R. Nth order reactive nanoliquid through convective elongated sheet under mixed convection flow with joule heating effects. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2022, 147, 3853–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salawu, S.O.; Ogunseye, H.A.; Yusuf, T.A.; Lebelo, R.S.; Mustapha, R.A.; Wukair, A. Entropy generation in a magnetohydrodynamic hybrid nanofluid flow over a nonlinear permeable surface with velocity slip effect. WSEAS Trans. Fluid Mech. 2023, 18, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, M.; Swamy, H.A.K.; Do, Y.; Altmeyer, S. Thermal effects of nonuniform heating in a nanofluid filled annulus: Buoyant transport versus entropy generation. Heat Transf. 2021, 51, 1062–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatunmbi, E.O.; Adigun, A.J.; Salawu, S.O. Dual stratification mechanism for nonlinear mixed convective magneto-tangent hyperbolic fluid over a stretchable device with activation energy. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math. 2023, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshuddin, M.D.; Salawu, S.O.; Ogunseye, H.A.; Mabood, F. Dissipative Power-law fluid flow using spectral quasi linearization method over an exponentially stretchable surface with Hall current and power-law slip velocity. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 119, 104933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, G.K.; Prasannakumara, B.C.; Gireesha, B.J.; Shehzad, S.A.; Abbasi, F.M. Three-dimensional flow of Maxwell fluid with suspended nanoparticles past a bidirectional porous stretching surface with thermal radiation. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2017, 1, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, A.; Mustafa, M.; Hayat, T.; Alsaedi, A. A numerical study for three-dimensional viscoelastic flow inspired by non-linear radiative heat flux. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 2016, 79, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, I.C.; Andersson, H.I. Heat transfer over a bidirectional stretching sheet with variable thermal conditions. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2008, 51, 4018–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalkilic, A.S. Parametric study of energy, exergy and thermoeconomic analyses on vapor-compression system cascaded with libr/water and nh3/water absorbtion cascade refrigeration cycle. Anadolu Univ. J. Sci. Technol. A Appl. Sci. Eng. 2017, 18, 78–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalkılıç, A.S. A review of flow boiling in mini and microchannel for enhanced geometries. J. Therm. Eng. 2018, 4, 2037–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.R.; Pattnaik, P.K.; Ontela, S.; Panda, S. Characterization of shape factor with multi slip and inclined magnetized radiative Casson hybrid nanofluid transport in an expanding/contracting convective sheet. Partial. Differ. Equ. Appl. Math. 2023, 8, 100570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, K.; Mahmood, Z.; Khan, U.; Eldin, S.M.; Alzubaidi, A.M. Mathematical analysis of radius and length of CNTs on flow of nanofluid over surface with variable viscosity and joule heating. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, U.; Maatki, C.; Kriaa, K.; Hadrich, B.; Imran, M.; Noreen, S.; Waqas, H.; Akgül, A. Characteristics of sodium alginate-based hybrid nanofluid and Darcy-forchheimer flow induced by stretching surface with thermal radiation and Cattaneo? Christov heat flux model. J. Comput. Sci. 2024, 76, 102209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattnaik, P.K.; Mishra, S.R.; Panda, S.; Syed, S.A.; Muduli, K. Hybrid methodology for the computational behaviour of thermal radiation and chemical reaction on viscoelastic nanofluid flow. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 2227811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.R.; Panda, S.; Vignesh, S.; Pattnaik, P.K.; Govindan, V.; Tawade, J.V.; Khan, M.I.; Abduvalieva, D.; Bouazzi, I.R. Radiative heat transfer on the peristaltic flow of an electrically conducting nanofluid through wavy walls of a tapered channel. Results Phys. 2023, 52, 106898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshuddin, M.D.; Panda, S.; Pattnaik, P.K.; Mishra, S.R. Ferromagnetic and Ohmic heating effects on nanofluid flow via permeability rotative disk: Significant interparticle radial and nanoparticle radius. Phys. Scr. 2024, 99, 055206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, R.R.; Kumar, V. Impact of Novel Dissimilar Shape Ternary Composition-Based Hybrid Nanofluids on the Thermal Performance Analysis of Radiator. J. Therm. Sci. Eng. Appl. 2021, 13, 041002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Farooq, U.; Waqas, H.; Muhammad, T.; Khan, S.A.; Hendy, A.S.; Ali, M.R. Numerical solution of entropy generation in nanofluid flow through a surface with thermal radiation applications. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 54, 103967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, L.A.; Asghar, A.; Rasool, G.; Yashkun, U. Magnetized casson SA-hybrid nanofluid flow over a permeable moving surface with thermal radiation and Joule heating effect. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2023, 50, 103510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, T.; Hasnain, J.; Abid, N.; Abbas, Z. Entropy generation for mixed convection flow in vertical annulus with two regions hydromagnetic viscous and Cu-Ag water hybrid nanofluid through porous zone: A comparative numerical study. Propuls. Power Res. 2022, 11, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.U.; Abbas, Z.; Hasnain, J. Prediction of heat and mass transfer in radiative hybrid nanofluid with chemical reaction using the least square method: A stability analysis of dual solution. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A Appl. 2023, 83, 958–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Z.; Rahim, T.; Hasnain, J.; Abid, N.; Shah, Z.M. Entropy generation analysis of multi-mass diffusion in a nanofluid interfaced three-phase viscous fluid in an inclined channel. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2023, 49, 103368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnain, J.; Abid, N. Numerical investigation for thermal growth in water and engine oil-based ternary nanofluid using three different shaped nanoparticles over a linear and nonlinear stretching sheet. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A Appl. 2022, 83, 1365–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.U.; Abbas, Z.; Hussain, Z.; Hasnain, J.; Asma, M. Integration of statistical and simulation analyses for ternary hybrid nanofluid over a moving surface with melting heat transfer. Nanotechnology 2024, 35, 265401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, H.A.; Hossen Siam, M.M.; Ghosh, A.; Hasan Mamun, M.A. Application of Artificial Intelligence on Predicting the Effects of Buoyancy Ratio on Magnetohydrodynamics Double-Diffusive Mixed Convection and Entropy Generation in Different Nanofluids and Hybrid Nanofluids. J. Therm. Sci. Eng. Appl. 2023, 15, 091008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabassum, F.; Hajimirza, S. Enhancing Computational Efficiency in Porous Media Analysis: Integrating Machine Learning with Monte Carlo Ray Tracing. J. Therm. Sci. Eng. Appl. 2024, 16, 101003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, H.; Shah, Z.; Raja, M.A.Z.; Khan, W.A. Machine learning investigation for tri-magnetized Sutterby nanofluidic model with Joule heating in agrivoltaics technology. Nano 2024, 2450058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, H.; Pasha, A.A.; Shah, Z.; Raja, M.A.Z.; Algarni, S.; Alqahtani, T.; Irshad, K.; Khan, W.A. Application of machine learning for thermal exchange of dissipative ternary nanofluid over a stretchable Wavy cylinder with thermal slip. Case Stud. Therm. 2024, 60, 104599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, H.; Shah, Z.; Raja, M.A.Z.; Shoaib, M.; Khan, W.A. Supervised machine learning computing paradigm to measure melting and dissipative effects in entropy induced Darcy-Forchheimer flow with ternary-hybrid nanofluids. Numer. Heat Transf. Part B Fundam. 2024, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, H.; Altmeyer, S. A Numerical Investigation of Marangoni convective flow in nanofluids and hybrid nanofluids in a Darcy-Forchheimer porous medium. J. Appl. Mater. Sci. Eng. Res. 2024, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, H.; Shah, Z.; Raja, M.A.Z.; Alshahrani, M.Y.; Khan, W.A.; Shoaib, M. Machine Learning Investigation of Tuberculosis with Medicine Immunity Impact. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2024, 110, 116472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, H.; Shah, Z.; Altmeyer, S. A Numerical Analysis of Tetra-Hybrid Nanofluid Flow to classify the thermal performance of solar-powered Photovoltaic Panels. Numer. Heat Transf. Part B Fundam. 2024, accepted and in print. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, H.; Raja, M.; Altmeyer, S. Machine Learning Investigation of Thermal Case Classification Using Tetra-hybrid Nanofluid. Numer. Heat Transf. Part B Fundam. 2024, accepted and in print. [Google Scholar]
- Shamshuddin, M.D.; Salawu, S.O.; Panda, S.; Mishra, S.R.; Alanazy, A.; Eid, M.R. Thermal case exploration of electromagnetic radiative trihybrid nanofluid flow in Bi-directional stretching device in absorbent medium: SQLM analysis. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 60, 04734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, H. Zenodo Data Base. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/17246057 (accessed on 1 October 2025).




| Physical Properties | Blood | MWCNT | Gold | Silver |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (J/kg K) | 3617 | 796 | 129.1 | 235 |
| (kg/m3) | 1050 | 1600 | 19,300 | 10,500 |
| (W/mK) | 0.52 | 3000 | 318 | 429 |
| (S/m) | 1090 | 105 | 4.52 × 107 | 3.6 × 107 |
| 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.04 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| 0.0045 | |
| 1608.4272 | |
| 1247.1246 | |
| 2305.4235 | |
| 0.6206 |
| Scenarios | Cases | Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S-1 | 1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| Variation | 2 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| of M for | 3 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| 4 | 1.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.5 | |
| S-2 | 1 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| Variation | 2 | 0.9 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| of M for | 3 | 1.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| 4 | 1.3 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.5 | |
| S-3 | 1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| Variation | 2 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| of for | 3 | 0.2 | 0.9 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| 4 | 0.2 | 1.2 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.5 | |
| S-4 | 1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| Variation | 2 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| of for | 3 | 0.2 | 0.9 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| 4 | 0.2 | 1.2 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.5 | |
| S-5 | 1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| Variation | 2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| of S for | 3 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 1.2 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| 4 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 1.4 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.5 | |
| S-6 | 1 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.1 | 2.5 | 0.9 |
| Variation | 2 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 2.5 | 0.9 |
| of R for | 3 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 2.5 | 0.9 |
| 4 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 2.5 | 0.9 | |
| S-7 | 1 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 1.0 | 0.1 |
| Variation | 2 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 1.0 | 0.3 |
| of for | 3 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 1.0 | 0.6 |
| 4 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 1.0 | 0.9 | |
| Scenarios | M.S.E. Data | Grids | Gradient | Mu | Closing | T/s | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trainung | Validation | Testing | Grids | Epoch | ||||
| S1 | 1 | 432 | 0.1 | |||||
| S2 | 24 | 0.0 | ||||||
| S3 | 1 | 411 | 0.1 | |||||
| S4 | 1 | 238 | 0.1 | |||||
| S5 | 1 | 208 | 0.1 | |||||
| S6 | 1 | 202 | 0.0 | |||||
| S7 | 10 | 620 | 0.1 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qureshi, H.; Zubair, M.; Altmeyer, S.A. Machine Learning Investigation of Ternary-Hybrid Radiative Nanofluid over Stretching and Porous Sheet. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1525. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15191525
Qureshi H, Zubair M, Altmeyer SA. Machine Learning Investigation of Ternary-Hybrid Radiative Nanofluid over Stretching and Porous Sheet. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(19):1525. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15191525
Chicago/Turabian StyleQureshi, Hamid, Muhammad Zubair, and Sebastian Andreas Altmeyer. 2025. "Machine Learning Investigation of Ternary-Hybrid Radiative Nanofluid over Stretching and Porous Sheet" Nanomaterials 15, no. 19: 1525. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15191525
APA StyleQureshi, H., Zubair, M., & Altmeyer, S. A. (2025). Machine Learning Investigation of Ternary-Hybrid Radiative Nanofluid over Stretching and Porous Sheet. Nanomaterials, 15(19), 1525. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15191525







