Enhancing Nutraceutical Quality and Antioxidant Activity in Chili Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) Fruit by Foliar Application of Green-Synthesized ZnO Nanoparticles (ZnONPs)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Application of Nanoparticles
2.3. Fruit Yield Assessment
2.4. Vitamin C Content
2.5. Chlorophyll and Carotenoid Content
2.6. Bioactive Compounds
2.7. Capsaicin and Dihydrocapsaicin Content
2.8. Enzyme Activity of Catalase
2.9. Nitrogen and Mineral Content in Chili Fruit
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Fruit Yield
3.2. Vitamin C Content
3.3. Bioactive Compounds
3.3.1. Total Phenol Content
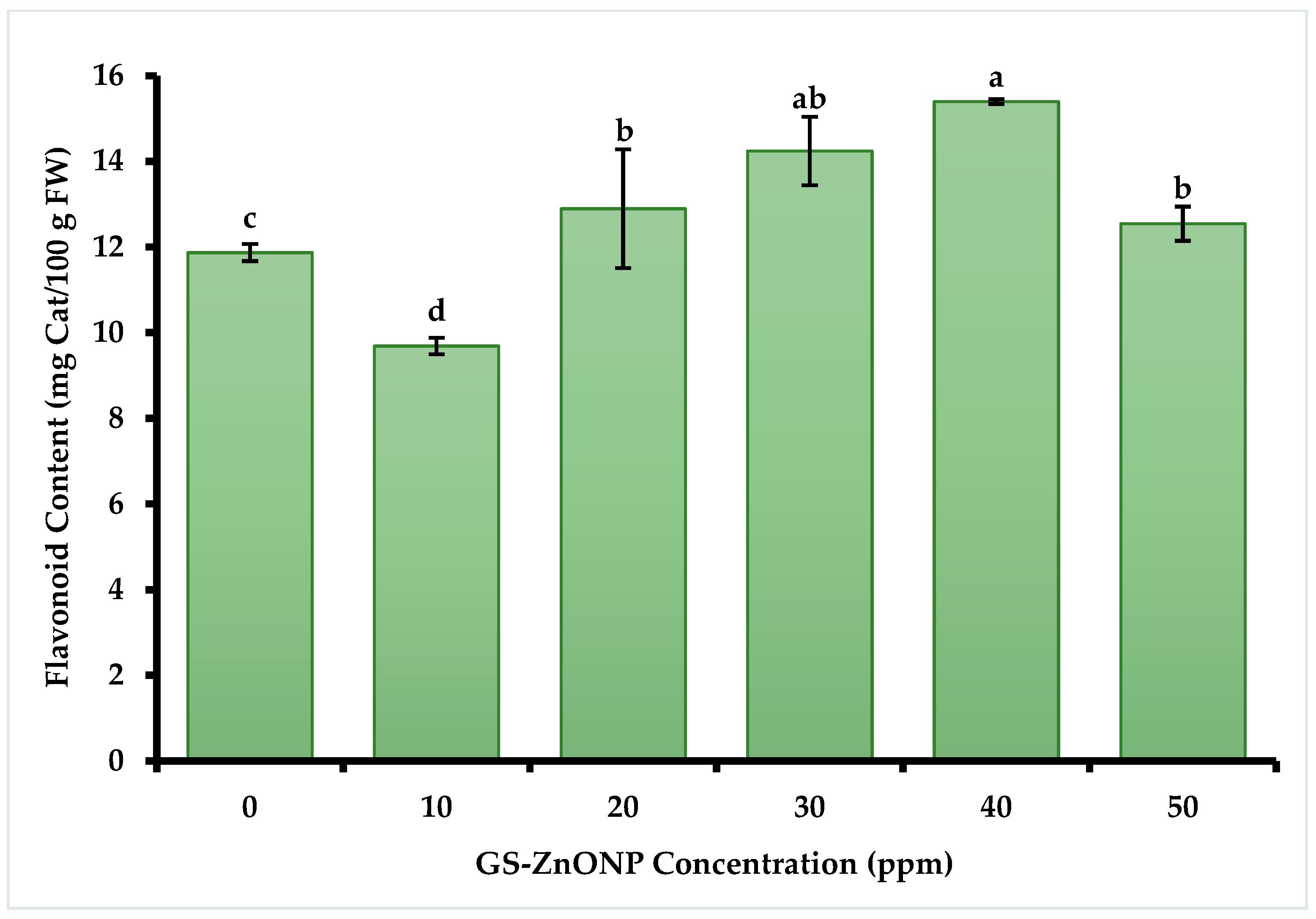
3.3.2. Total Flavonoids
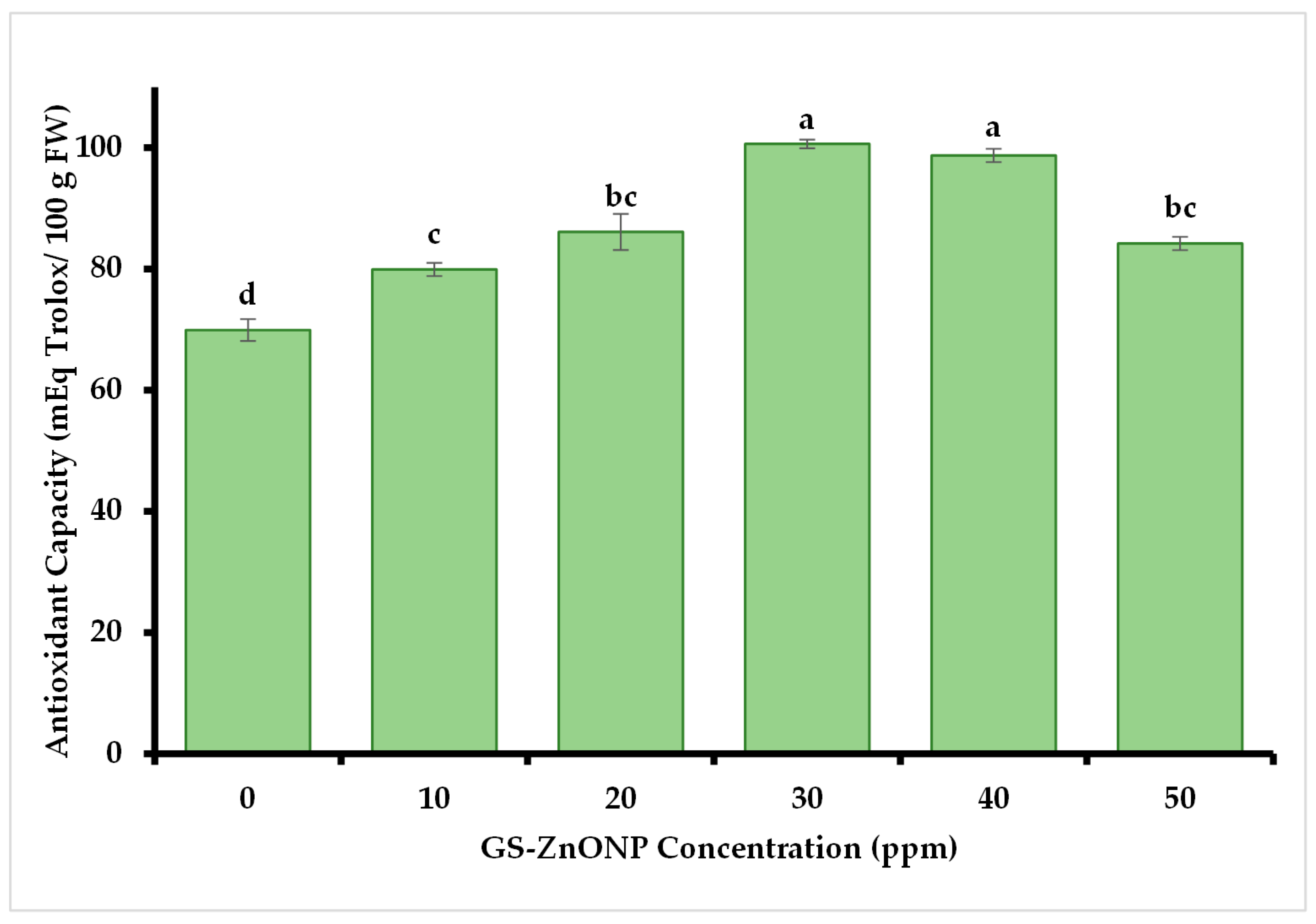
3.3.3. Antioxidant Capacity
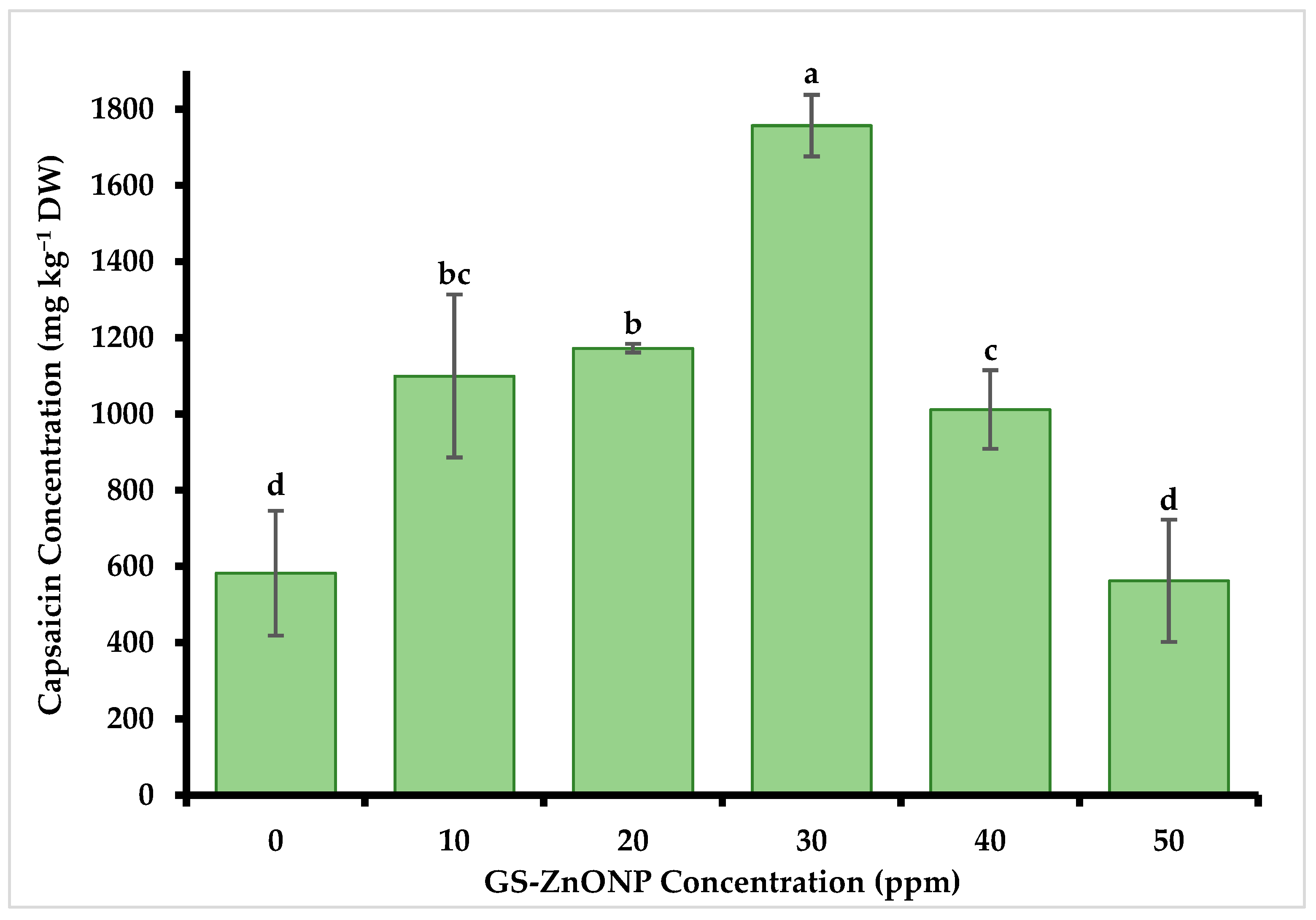
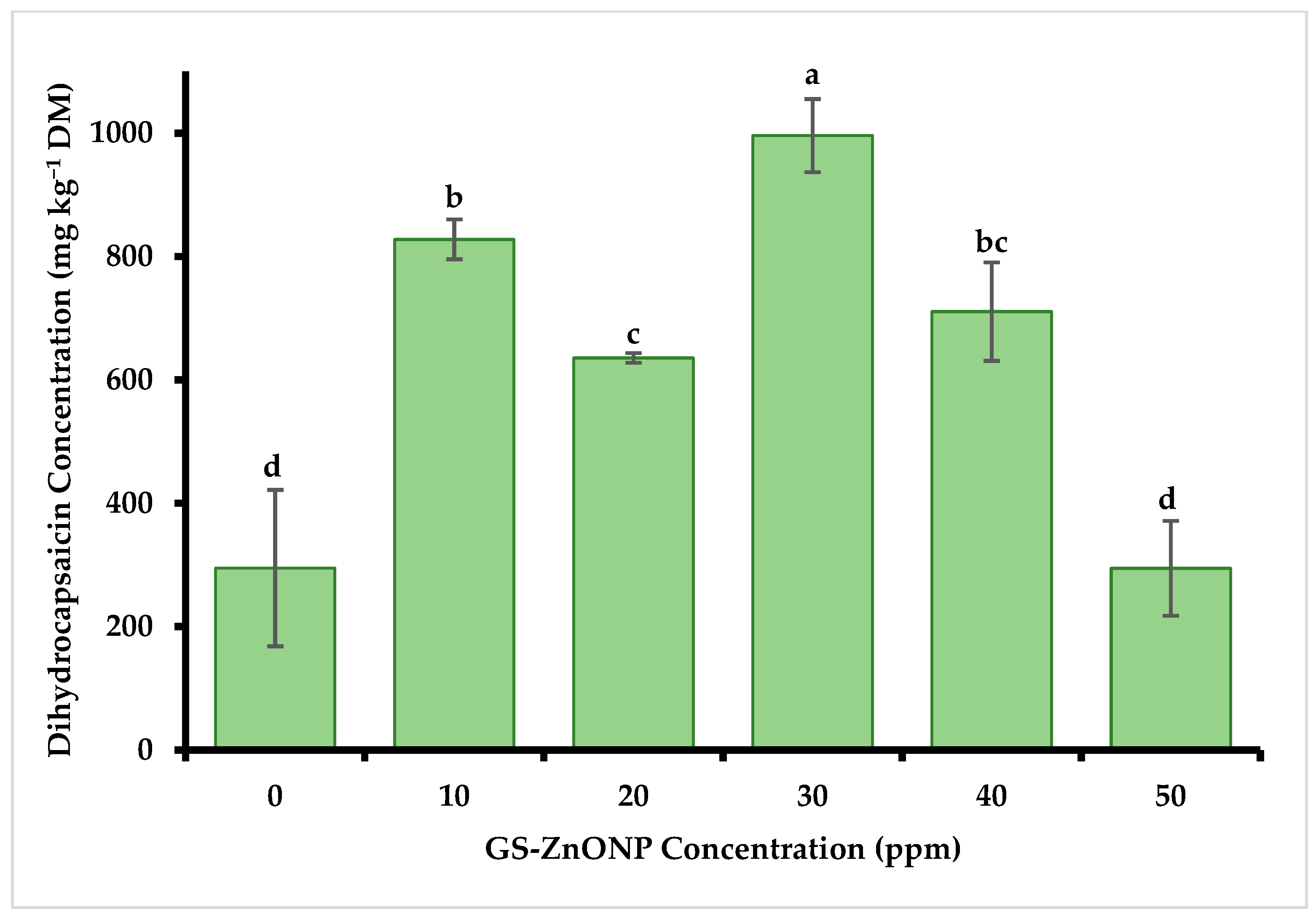
3.4. The Concentration of Capsaicin and Dihydrocapsaicin
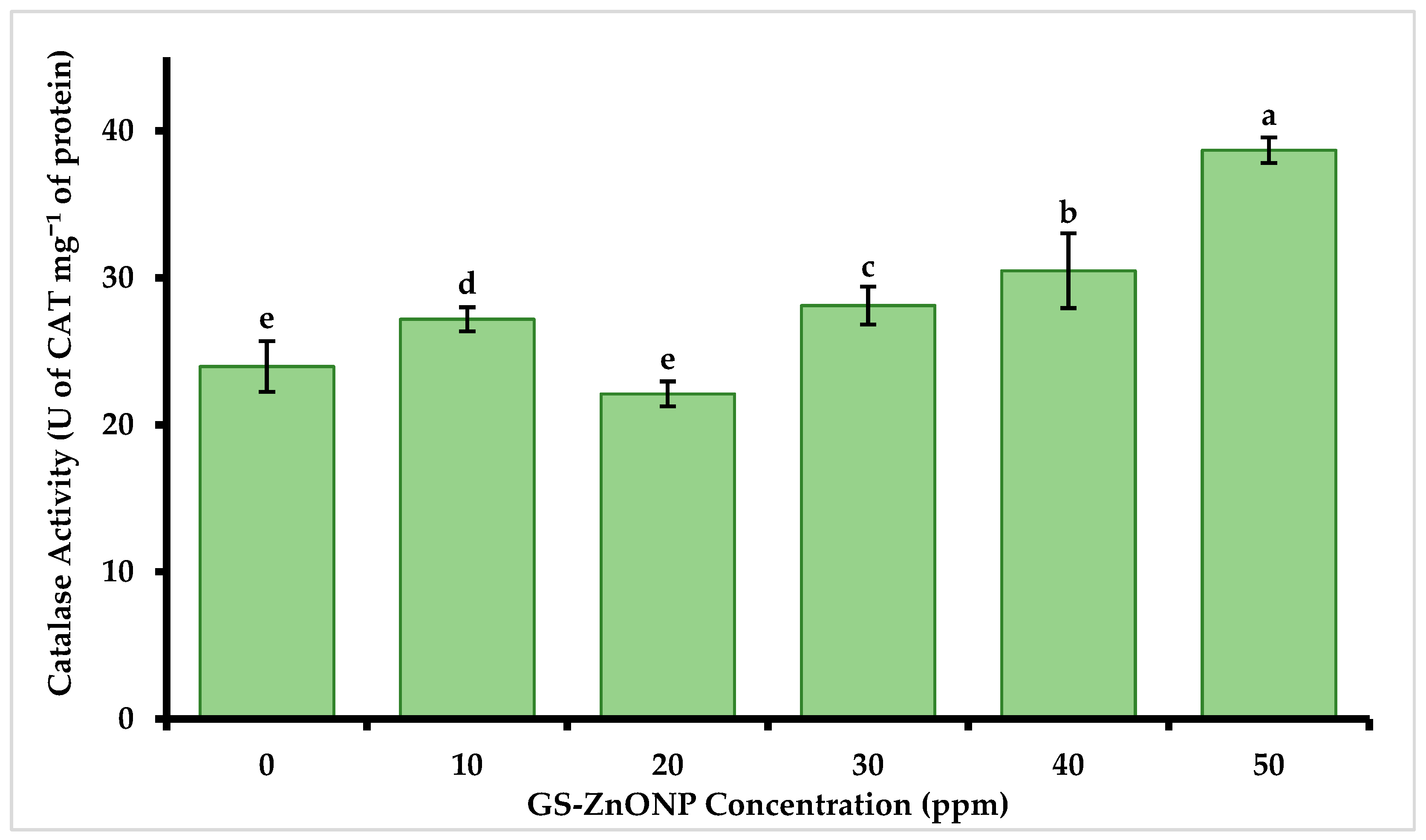
3.5. Catalase
3.6. Nitrogen and Minerals in Fruit
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maurya, A.P.; Chauhan, J.; Yadav, D.K.; Gangwar, R.; Maurya, V.K. Nutraceuticals and Their Impact on Human Health; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; ISBN 9780128202845. [Google Scholar]
- Jędrusek-Golińska, A.; Górecka, D.; Buchowski, M.; Wieczorowska-Tobis, K.; Gramza-Michałowska, A.; Szymandera-Buszka, K. Recent progress in the use of functional foods for older adults: A narrative review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 835–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, B.K.; Omer, A.; Teweldemedhin, B. Medicinal uses and health benefits of chili pepper (Capsicum spp.): A review. MOJ Food Process Technol. 2018, 6, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatunji, T.L.; Afolayan, A.J. Comparison of nutritional, antioxidant vitamins and capsaicin contents in Capsicum annuum and C. frutescens. Int. J. Veg. Sci. 2020, 26, 190–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azlan, A.; Sultana, S.; Huei, C.S.; Razman, M.R. Effects of Different Chili Pepper: A Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, R.; Usman, M.; Yücesan, B.; Zia, M.; Gürel, E. Effect of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles on physiology and steviol glycosides production in micropropagated shoots of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 110, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, M.Â.; Pinheiro, A.C.; Ramos, O.L.; Silva, H.; Bourbon, A.I.; Vicente, A.A. Advances in Food Nanotechnology; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; ISBN 9780323429993. [Google Scholar]
- Seleiman, M.F.; Almutairi, K.F.; Alotaibi, M.; Shami, A.; Alhammad, B.A.; Battaglia, M.L. Nano-Fertilization as an Emerging Fertilization Technique: Why Can Modern Agriculture Benefit from Its Use? Plants 2020, 10, 2–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husen, A.; Iqbal, M. Nanomaterials and Plant Potential; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; 605p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Singh, N.B.; Afzal, S.; Singh, T.; Hussain, I. Zinc oxide nanoparticles: A review of their biological synthesis, antimicrobial activity, uptake, translocation and biotransformation in plants. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, M.; Gopinath, V.; Chaurasia, M.K.; Syed, A.; Ameen, F.; Purushothaman, N. Green synthesis of anisotropic zinc oxide nanoparticles with antibacterial and cytofriendly properties. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 115, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, S.; Jia, X.; Huang, Y.; Ji, R.; Zhao, L. Comparation of the phytotoxicity between chemically and green synthesized silver nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 142264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-López, J.I.; Niño-Medina, G.; Olivares-Sáenz, E.; Lira-Saldivar, R.H.; Barriga-Castro, E.D.; Vázquez-Alvarado, R.; Rodríguez-Salinas, P.A.; Zavala-García, F. Foliar application of zinc oxide nanoparticles and zinc sulfate boosts the content of bioactive compounds in habanero peppers. Plants 2019, 8, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Afzal, S.; Singh, N.K. Nanopriming with phytosynthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles for promoting germination and starch metabolism in rice seeds. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 336, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, S.; Saddiq, A.A.; Ashy, R.A.; Baghdadi, A.M.; Alzahrani, A.J.; Mostafa, E.M.; Al Jaouni, S.K.; Elamir, M.Y.M.; Amin, M.A.; Salah, A.M.; et al. Bimetallic selenium/zinc oxide nanoparticles: Biological activity and plant biostimulant properties. AMB Express 2025, 15, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza-Alonso, C.A.; Juárez-Maldonado, A.; González-Morales, S.; Cabrera-De la Fuente, M.; Cadenas-Pliego, G.; Morales-Díaz, A.B.; Trejo-Téllez, L.I.; Tortella, G.; Benavides-Mendoza, A. ZnO nanoparticles as potential fertilizer and biostimulant for lettuce. Heliyon 2023, 9, e12787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.T.; Ahmed, S.; Shah, A.A.; Noor Shah, A.; Tanveer, M.; El-Sheikh, M.A.; Siddiqui, M.H. Influence of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles to Regulate the Antioxidants Enzymes, Some Osmolytes and Agronomic Attributes in Coriandrum sativum L. Grown under Water Stress. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejam, F.; Ardebili, Z.O.; Ladan-Moghadam, A.; Danaee, E. Zinc oxide nanoparticles mediated substantial physiological and molecular changes in tomato. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganya, A.; Saravanan, A.; Manivannan, N. Role of Zinc Nutrition for Increasing Zinc Availability, Uptake, Yield, and Quality of Maize (Zea mays L.) Grains: An Overview. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2020, 51, 2001–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmat-Campos, D.; López-Medina, E.; Montes de Oca-Vásquez, G.; Gil-Rivero, E.; Delfín-Narciso, D.; Juárez-Cortijo, L.; Villena-Zapata, L.; Gurreonero-Fernández, J.; Rafael-Amaya, R. ZnO Nanoparticles Obtained by Green Synthesis as an Alternative to Improve the Germination Characteristics of L. esculentum. Molecules 2022, 27, 2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Gómez, C.; Obrador, A.; González, D.; Babín, M.; Fernández, M.D. Comparative effect of ZnO NPs, ZnO bulk and ZnSO4 in the antioxidant defences of two plant species growing in two agricultural soils under greenhouse conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 589, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Pérez, D.M.; Flores-Loyola, E.; Márquez-Guerrero, S.Y.; Galindo-Guzman, M.; Marszalek, J.E. Green Synthesis and Characterization of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Larrea tridentata Extract and Their Impact on the In-Vitro Germination and Seedling Growth of Capsicum annuum. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faizan, M.; Hayat, S.; Pichtel, J. Effects of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on Crop Plants: A Perspective Analysis. In Sustainable Agriculture Reviews 41; Hayat, S., Pichtel, J., Faizan, M., Fariduddin, Q., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 83–99. ISBN 9783030339968. [Google Scholar]
- Rajput, V.D.; Minkina, T.; Fedorenko, A.; Chernikova, N.; Hassan, T.; Mandzhieva, S.; Sushkova, S.; Lysenko, V.; Soldatov, M.A.; Burachevskaya, M. Effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles on physiological and anatomical indices in spring barley tissues. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratap, V.; Durgesh, K.; Sheo, M.; Devendra, K.; Singh, S. Plant Responses to Nanomaterials, 1st ed.; Singh, V.P., Singh, S., Tripathi, D.K., Prasad, S.M., Chauhan, D.K., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; ISBN 978-3-030-36739-8. [Google Scholar]
- Asghari, M.; Hasanlooe, A.R. Interaction effects of salicylic acid and methyl jasmonate on total antioxidant content, catalase and peroxidase enzymes activity in “Sabrosa” strawberry fruit during storage. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 197, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faizan, M.; Faraz, A.; Hayat, S. Effective use of zinc oxide nanoparticles through root dipping on the performance of growth, quality, photosynthesis and antioxidant system in tomato. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2020, 29, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatunbosun, A.; Nigar, H.; Rovshan, K.; Nurlan, A.; Boyukhanim, J.; Narmina, A.; Ibrahim, A. Comparative impact of nanoparticles on salt resistance of wheat plants. MethodsX 2023, 11, 102371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Tóth, Z.; Decsi, K. The Impact of Salinity on Crop Yields and the Confrontational Behavior of Transcriptional Regulators, Nanoparticles, and Antioxidant Defensive Mechanisms under Stressful Conditions: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Zahoor, M.; Sher Khan, R.; Ikram, M.; Islam, N.U. The impact of silver nanoparticles on the growth of plants: The agriculture applications. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, A.A. A universal method for preparing nutrient solutions of a certain desired composition. Plant Soil 1961, 15, 134–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosen, Z.; Afroz Bipasha, S.; Kamal, S.; Rafique, S.; Islam, B.; Fatema, K. Dietary Supplementation of Citrus limon L. (Lemon) and Evaluation of Its Role to Prevent and Cure of Vitamin C Deficiency Diseases. Int. J. Nutr. Food Sci. 2020, 9, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenthaler, H.K. Chlorophylls and Carotenoids: Pigments of Photosynthetic Biomembranes. Methods Enzymol. 1987, 148, 350–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Pérez, D.M.; Márquez-Guerrero, S.Y.; Ramírez-Moreno, A.; Rodríguez-Sifuentes, L.; Galindo-Guzmán, M.; Flores-Loyola, E.; Marszalek, J.E. Impact of Biologically and Chemically Synthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on Seed Germination and Seedlings’ Growth. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Orthofer, R.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M. Analysis of total phenols and Other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of Folin-Ciocalteu Reagent. Sci. Hortic. 1999, 213, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhishen, J.; Mengcheng, T.; Jianming, W. The determination of flavonoid contents in mulberry and their scavenging effects on superoxide radicals. Food Chem. 1999, 64, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.D.; Wasmund, L.M.; Bosland, P.W. Improved method for quantifying capsaicinoids in Capsicum using high-performance liquid chromatography. HortScience 1995, 30, 137–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, W.K.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, G.D.; Rhee, H.I. Rapid determination of capsaicinoids by colorimetric method. J. Food Drug Anal. 2017, 25, 798–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aebi, H. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1984, 105, 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.P.; Kiesow, L.A. Enthalpy of decomposition of hydrogen peroxide by catalase at 25 °C (with molar extinction coefficients of H2O2 solutions in the UV). Anal. Biochem. 1972, 49, 474–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Bio 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, J.M. Determination of nitrogen in soil by the Kjeldahl method. J. Agric. Sci. 1960, 55, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.P.S.; Silva, F.L.F.; Monte, R.J.G.; Matos, W.O.; Lopes, G.S. A new approach to mineralization of flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum L.) for trace element analysis by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Chem. 2017, 224, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhu, X.; Shen, D. Ecological Risks of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Early Life Stages of Obscure Puffer (Takifugu obscurus). Toxics 2024, 12, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, L.; Fedenia, L.N.; Sharifan, H.; Ma, X.; Lombardini, L. Effects of foliar application of zinc sulfate and zinc nanoparticles in coffee (Coffea arabica L.) plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 135, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amezcua, J.C.; Lara, M. El Zinc en las Plantas. Ciencia 2017, 68, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Gonmei, G.; Deb, P.; Kumar, P.; Sinha, D.; Halder, A. Zinc Nutrition in Banana (cv. Grand Naine) at Early Growth Stage. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2022, 34, 1648–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaithon, T.; Atichakaro, T.; Phonphoem, W.; T-Thienprasert, J.; Sreewongchai, T.; T-Thienprasert, N.P. Potential usage of biosynthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles from mangosteen peel ethanol extract to inhibit Xanthomonas oryzae and promote rice growth. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, R.; Uddin, M.K.; Quddus, M.A.; Samad, M.Y.A.; Hossain, M.A.M.; Haque, A.N.A. Impact of Foliar Application of Zinc and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on Growth, Yield, Nutrient Uptake and Quality of Tomato. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, Z.A.; Parveen, A.; Ahmad, L.; Hashem, A. Effects of graphene oxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles on growth, chlorophyll, carotenoids, proline contents and diseases of carrot. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 249, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Yin, S.S.; Li, X.L.; Hu, W.J.; Simon, M.; Shen, Z.J.; Xiao, Q.; Chu, C.C.; et al. Nitric oxide ameliorates zinc oxide nanoparticles-induced phytotoxicity in rice seedlings. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 297, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-López, J.; Zavala-García, F.; Olivares-Sáenz, E.; Lira-Saldívar, R.; Díaz Barriga-Castro, E.; Ruiz-Torres, N.; Ramos-Cortez, E.; Vázquez-Alvarado, R.; Niño-Medina, G. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Boosts Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Capsicum annuum L. during Germination. Agronomy 2018, 8, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.; Jiang, J.; Ding, J.; Sheng, G.D. Blocking effect of fullerene nanoparticles (nC60) on the plant cell structure and its phytotoxicity. Chemosphere 2021, 278, 130474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Sun, H.; Du, W.; Li, R.; Mao, H.; Kopittke, P.M. Interaction of different-sized ZnO nanoparticles with maize (Zea mays): Accumulation, biotransformation and phytotoxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 796, 148927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoofs, H.; Schmit, J.; Rink, L. Zinc Toxicity: Understanding the Limits. Molecules 2024, 29, 3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Bhardwaj, R.; Thukral, A.K.; Al-Huqail, A.A.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Ahmad, P. Oxidative stress mitigation and initiation of antioxidant and osmoprotectant responses mediated by ascorbic acid in Brassica juncea L. subjected to copper (II) stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 182, 109436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mieszczakowska-Frąc, M.; Celejewska, K.; Płocharski, W. Impact of innovative technologies on the content of vitamin C and its bioavailability from processed fruit and vegetable products. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevinho, B.N.; Carlan, I.; Blaga, A.; Rocha, F. Soluble vitamins (vitamin B12 and vitamin C) microencapsulated with different biopolymers by a spray drying process. Powder Technol. 2016, 289, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davarpanah, S.; Tehranifar, A.; Davarynejad, G.; Abadía, J.; Khorasani, R. Effects of foliar applications of zinc and boron nano-fertilizers on pomegranate (Punica granatum cv. Ardestani) fruit yield and quality. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 210, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Kambe, T. The functions of metallothionein and ZIP and ZnT transporters: An overview and perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balážová, Ľ.; Babula, P.; Baláž, M.; Bačkorová, M.; Bujňáková, Z.; Briančin, J.; Kurmanbayeva, A.; Sagi, M. Zinc oxide nanoparticles phytotoxicity on halophyte from genus Salicornia. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 130, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendra, S.; Zhu, H.; Colvin, V.L.; Alvarez, P.J. Quantum dot weathering results in microbial toxicity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 9424–9430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tariverdizadeh, N.; Mohebodini, M.; Chamani, E.; Ebadi, A. Iron and zinc oxide nanoparticles: An efficient elicitor to enhance trigonelline alkaloid production in hairy roots of fenugreek. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 162, 113240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinedo-Guerrero, Z.H.; Delia Hernández-Fuentes, A.; Ortega-Ortiz, H.; Benavides-Mendoza, A.; Cadenas-Pliego, G.; Juárez-Maldonado, A. Cu nanoparticles in hydrogels of chitosan-PVA affects the characteristics of post-harvest and bioactive compounds of jalapeño pepper. Molecules 2017, 22, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Parrilla, E.; De La Rosa, L.A.; Amarowicz, R.; Shahidi, F. Antioxidant activity of fresh and processed Jalapeño and Serrano peppers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Perez, D.M.; Flores-Loyola, E.; Orozco-Vidal, J.A.; Yescas-Coronado, P.; Rodriguez-Beltran, R.I.; Puente-Valenzuela, C.O.; Marszalek, J.E.; Marquez-Guerrero, S.Y. The application of biosynthesized ZnO nanoparticles enhances the morphological and physiological indices of serrano pepper plants. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. 2025, 53, 14103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai-Kalal, P.; Jajoo, A. Priming with zinc oxide nanoparticles improve germination and photosynthetic performance in wheat. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 160, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Torres, N.; Flores-Naveda, A.; Barriga-Castro, E.D.; Camposeco-Montejo, N.; Ramírez-Barrón, S.; Borrego-Escalante, F.; Niño-Medina, G.; Hernández-Juárez, A.; Garza-Alonso, C.; Rodríguez-Salinas, P.; et al. Zinc oxide nanoparticles and zinc sulfate impact physiological parameters and boosts lipid peroxidation in soil grown coriander plants (Coriandrum sativum). Molecules 2021, 26, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehzadi, N.; Mahmood, A.; Kaleem, M.; Chishti, M.S.; Bashir, H.; Hashem, A.; Fathi, E.; Allah, A.; Shahid, H.; Ishtiaq, A. Zinc and nitrogen mediate the regulation of growth, leading to the upregulation of antioxidant aptitude, physio-biochemical traits, and yield in wheat plants. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naziębło, A.; Bemowska-Kałabun, O.; Wierzbicka, M.; Zienkiewicz, M. Foliar application of nitrates limits lead uptake by Cucumis sativus L. plants. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2025, 87, 127592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Pérez, T.; Gómez-García, M.R.; Valverde, M.E.; Paredes-López, O. Capsicum annuum (hot pepper): An ancient Latin-American crop with outstanding bioactive compounds and nutraceutical potential. A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2972–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| GS-ZnONP Concentration (ppm) | Fruit Diameter (cm) | Fruit Length (cm) | Fresh Fruit Mass (g) | Number of Fruit per Plant | Total Mass of Fruit (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.79 ± 0.17 d | 8.97 ± 0.15 d | 4.12 ± 0.17 c | 292.75 ± 5.32 c | 1047.65 ± 52 c |
| 10 | 0.82 ± 0.05 c | 9.52 ± 0.52 bc | 4.76 ± 0.18 b | 295.75 ± 22.14 b | 1456.85 ± 29 b |
| 20 | 0.87 ± 0.09 c | 9.02 ± 0.73 c | 5.06 ± 0.05 a | 297.75 ± 2.31 bc | 1486.01 ± 10 b |
| 30 | 1.07 ± 0.14 b | 10.42 ± 0.40 b | 5.31 ± 0.33 a | 347.50 ± 26.12 ab | 1502.28 ± 48 b |
| 40 | 1.22 ± 0.02 a | 11.45 ± 0.17 a | 5.35 ± 0.23 a | 396.23 ± 5.20 a | 2056.41 ± 31 a |
| 50 | 1.12 ± 0.17 b | 12.41 ± 0.35 a | 4.01 ± 0.12 b | 383.51 ± 13.21 a | 1680.08 ± 15 ab |
| GS-ZnONP Concentration (ppm) | Vitamin C (mg 100 g−1 FW) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 128.07 ± 4.15 c |
| 10 | 131.21 ± 2.52 c |
| 20 | 129.25 ± 3.73 c |
| 30 | 141.42 ± 4.40 b |
| 40 | 151.65 ± 3.17 a |
| 50 | 112.41 ± 2.35 d |
| GS-ZnONPs (ppm) | Macro Minerals (g kg−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P | K | Ca | Na | Mg | |
| 0 | 13.44 ± 1.35 d | 5.35 ± 0.11 d | 4.28 ± 0.39 d | 2.71 ± 0.18 b | 0.13 ± 0.01 d | 1.78 ± 0.01 c |
| 10 | 14.54 ± 2.04 c | 6.41 ± 0.12 b | 6.98 ± 0.42 a | 3.73 ± 0.19 a | 0.18 ± 0.01 c | 1.87 ± 0.03 b |
| 20 | 15.72 ± 1.82 b | 6.97 ± 0.09 a | 5.35 ± 0.29 c | 3.81 ± 0.23 a | 0.20 ± 0.01 b | 1.89 ± 0.01 b |
| 30 | 16.79 ± 1.72 a | 6.95 ± 0.04 a | 5.98 ± 0.33 bc | 3.99 ± 0.21 a | 0.20 ± 0.01 b | 1.94 ± 0.01 a |
| 40 | 14.28 ± 1.10 c | 5.90 ± 0.08 c | 6.86 ± 0.32 b | 3.51 ± 0.20 a | 0.23 ± 0.02 a | 1.92 ± 0.02 a |
| 50 | 14.02 ± 0.93 cd | 5.76 ± 0.17 c | 5.32 ± 0.46 c | 3.22 ± 0.10 ab | 0.22 ± 0.03 a | 1.71 ± 0.04 d |
| GS-ZnONPs (ppm) | Micro Minerals (mg kg−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | Fe | Zn | Mn | |
| 0 | 13.01 ± 0.43 c | 178.13 ± 1.21 d | 25.27 ± 0.19 d | 24.03 ± 0.12 c |
| 10 | 12.21 ± 0.12 d | 223.41 ± 1.26 c | 85.21 ± 0.23 c | 36.23 ± 0.38 bc |
| 20 | 15.52 ± 0.23 a | 248.45 ± 1.14 c | 95.25 ± 0.45 b | 40.78 ± 0.28 b |
| 30 | 15.68 ± 0.31 a | 779.67 ± 4.21 b | 122.21 ± 1.02 a | 41.02 ± 0.31 b |
| 40 | 14.34 ± 0.25 b | 825.62 ± 2.56 b | 123.12 ± 1.02 a | 52.34 ± 0.24 a |
| 50 | 14.27 ± 0.19 b | 1054.21 ± 2.23 a | 97.12 ± 0.98 b | 51.21 ± 0.32 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sánchez-Pérez, D.M.; Marszalek, J.E.; Meza-Velázquez, J.A.; Lafuente-Rincon, D.F.; Salazar-Ramírez, M.T.; Márquez-Guerrero, S.Y.; Pineda-Escareño, M.G.; Moreno, A.R.; Flores-Loyola, E. Enhancing Nutraceutical Quality and Antioxidant Activity in Chili Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) Fruit by Foliar Application of Green-Synthesized ZnO Nanoparticles (ZnONPs). Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15181440
Sánchez-Pérez DM, Marszalek JE, Meza-Velázquez JA, Lafuente-Rincon DF, Salazar-Ramírez MT, Márquez-Guerrero SY, Pineda-Escareño MG, Moreno AR, Flores-Loyola E. Enhancing Nutraceutical Quality and Antioxidant Activity in Chili Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) Fruit by Foliar Application of Green-Synthesized ZnO Nanoparticles (ZnONPs). Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(18):1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15181440
Chicago/Turabian StyleSánchez-Pérez, Daniela Monserrat, Jolanta E. Marszalek, Jorge Armando Meza-Velázquez, David Francisco Lafuente-Rincon, Maria Teresa Salazar-Ramírez, Selenne Yuridia Márquez-Guerrero, Maria Guadalupe Pineda-Escareño, Agustina Ramírez Moreno, and Erika Flores-Loyola. 2025. "Enhancing Nutraceutical Quality and Antioxidant Activity in Chili Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) Fruit by Foliar Application of Green-Synthesized ZnO Nanoparticles (ZnONPs)" Nanomaterials 15, no. 18: 1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15181440
APA StyleSánchez-Pérez, D. M., Marszalek, J. E., Meza-Velázquez, J. A., Lafuente-Rincon, D. F., Salazar-Ramírez, M. T., Márquez-Guerrero, S. Y., Pineda-Escareño, M. G., Moreno, A. R., & Flores-Loyola, E. (2025). Enhancing Nutraceutical Quality and Antioxidant Activity in Chili Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) Fruit by Foliar Application of Green-Synthesized ZnO Nanoparticles (ZnONPs). Nanomaterials, 15(18), 1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15181440






