Sublethal Toxicity and Gene Expression Changes in Hydra vulgaris Exposed to Polyethylene and Polypropylene Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Nanoplastic Preparation
2.2. Aquatic Toxicity Assessment with Hydra Vulgaris
2.3. Gene Expression Analysis
2.4. Data Analysis
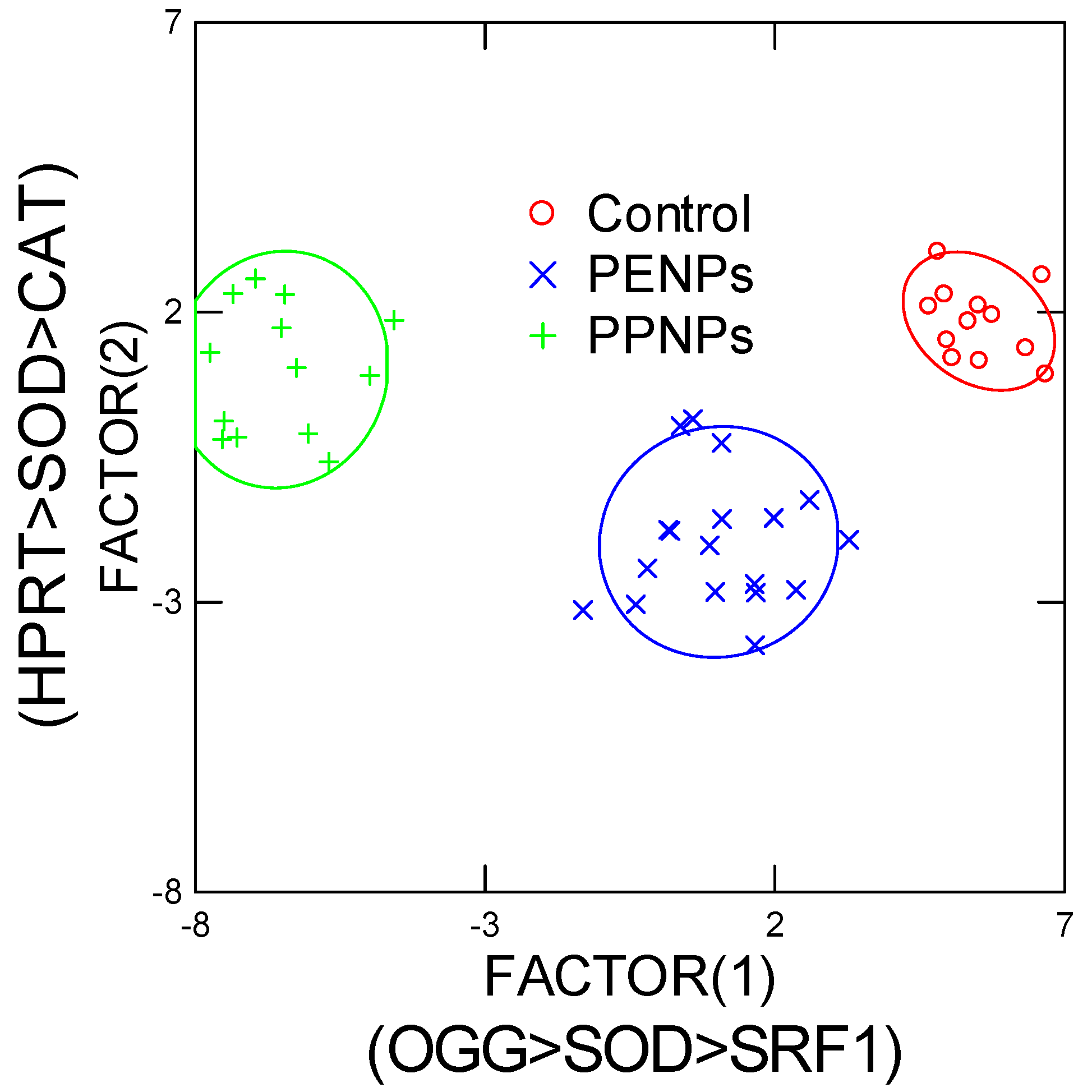
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Atugoda, T.; Piyumali, H.; Wijesekara, C.; Sonne, S.S.; Lam, K. Mahatantila, and M. Vithanage. Nanoplastic Occurrence, Transformation and Toxicity: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 363–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avio, C.G.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. Plastics and Microplastics in the Oceans: From Emerging Pollutants to Emerged Threat. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 128, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD. Global Plastics Outlook—Economic Drivers, Environmental Impacts and Policy Options; OECD: Paris, France, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, L.; Dierkes, G.; Ternes, T.A.; Völker, C.; Wagner, M. Benchmarking the in Vitro Toxicity and Chemical Composition of Plastic Consumer Products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 11467–11477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plastics Europe. Plastics—The Fast Facts; Plastic Europe: Brussels, Belgium, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Argeswara, J.; Hendrawan, I.G.; Dharma, I.G.B.S.; Germanov, E. What’s in the soup? Visual characterization and polymer analysis of microplastics from an Indonesian manta ray feeding ground. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 168, 112427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thacharodi, A.; Meenatchi, R.; Hassan, S.; Hussain, N.; Bhat, M.A.; Arockiaraj, J.; Ngo, H.H.; Le, Q.H.; Pugazhendhi, A. Microplastics in the environment: A critical overview on its fate, toxicity, implications, management, and bioremediation strategies. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 349, 119433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes JCde, S.; Sobral, P.; Branco, V.; Martins, M. Uncovering layer by layer the risk of nanoplastics to the environment and human health. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2025, 28, 63–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junaid, M.; Liu, S.; Liao, H.; Yue, Q.; Wang, J. Environmental nanoplastics quantification by pyrolysis-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry in the Pearl River, China: First insights into spatiotemporal distributions, compositions, sources and risks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 135055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, C.; Smyth, S.A.; Gagné, F. The peroxidase toxicity assay for the rapid evaluation of municipal effluent quality. Water Emerg. Contam. Nanoplastics 2025, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piarulli, S.; Sørensen, L.; Amat, L.M.; Farkas, J.; Khan, E.A.; Arukwe, A.; Gomiero, A.; Booth, A.M.; Gomes, T.; Hansen, B.H. Particles, chemicals or both? Assessing the drivers of the multidimensional toxicity of car tire rubber microplastic on early life stages of Atlantic cod. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 494, 138699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aib, H.; Parvez, M.S.; Czédli, H.M. Pharmaceuticals and Microplastics in Aquatic Environments: A Comprehensive Review of Pathways and Distribution, Toxicological and Ecological Effects. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Xing, T.; Yu, X.; Wu, J.; Li, T.; Xu, S.; Du, T.; Wu, L. Insights into the effects of aging on the combined toxicity of polystyrene nanoplastics and chlordane against Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 156, 794–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, H.; Lee, J.; Oh, J.E.; Song, J.; Jeong, S. Epigenetic and Gene Expression Responses of Daphnia magna to Polyethylene and Polystyrene Microplastics. Molecules 2025, 30, 1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, J.; Vercauteren, M.; Schoenaers, S.; Janssen, C.R.; Blust, R.; Asselman, J.; Town, R.M. Differential sensitivity of hemocyte subpopulations (Mytilus edulis) to aged polyethylene terephthalate micro- and nanoplastic particles. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 286, 117255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cera, A.; Cesarini, G.; Spani, F.; Scalici, M. Hydra vulgaris assay as environmental assessment tool for ecotoxicology in freshwaters: A review. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2020, 72, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farley, G.; Bouchard, P.; Faille, C.; Trottier, S.; Gagné, F. Towards the standardization of Hydra vulgaris bioassay for toxicity assessments of liquid samples. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 290, 117560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auclair, J.; Roubeau-Dumont, E.; Gagné, F. Lethal and Sublethal Toxicity of Nanosilver and Carbon Nanotube Composites to Hydra vulgaris—A Toxicogenomic Approach. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acar, U.; İnanan, B.E.; Zemheri-Navruz, F. Ecotoxicological effects of polystyrene nanoplastics on common carp: Insights into blood parameters, DNA damage, and gene expression. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2024, 44, 1416–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobori, D.; Dimitriadi, A.; Karasiali, S.; Tsoumaki-Tsouroufli, P.; Mastora, M.; Kastrinaki, G.; Feidantsis, K.; Printzim, A.; Koumoundouros, G.; Kaloyianni, M. Common mechanisms activated in the tissues of aquatic and terrestrial animal models after TiO2 nanoparticles exposure. Environ. Int. 2020, 138, 105611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaise, C.; Kusui, T. Acute toxicity assessment of industrial effluents with a microplate-based Hydra attenuata assay. Environ. Toxicol. Water Qual. 1997, 12, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environment and Climate Change Canada. Sublethal and Lethal Evaluation with the Hydra attenuata—Method for Aqueous Solutions; Environment and Climate Change Canada: Gatineau, QC, Canada, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Finney, D.J. Statistical Method in Biological Assay; Hafner Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 1964; 668p. [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrandt, J.; Thünemann, A.F. Aqueous Dispersions of Polypropylene: Toward Reference Materials for Characterizing Nanoplastics. Macromolecular 2022, 44, 2200874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorant, Y.; Quillien, V.; Le Luyer, J.; Ky, C.L. Comparative transcriptomics identifies genes underlying growth performance of the Pacific black-lipped pearl oyster Pinctada margaritifera. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barron, M.R.; Belaguli, N.S.; Zhang, S.X.; Trinh, M.; Iyer, D.; Merlo, X.; Lough, J.W.; Parmacek, M.S.; Bruneau, B.G.; Schwartz, R.J. Serum response factor an enriched cardiac mesoderm obligatory factor is a downstream gene target for Tbx genes. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 11816–11828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaluç, N.; Çötelli, E.L.; Tuncay, S.; Thomas, P.B. Polyethylene terephthalate nanoplastics cause oxidative stress induced cell death in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2024, 59, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Wu, Z.; Lu, Z.; Yan, L.; Dong, X.; Dai, Z.; Sun, R.; Hong, P.; Zhou, C.; Li, C. Differences in toxicity induced by the various polymer types of nanoplastics on HepG2 cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 918, 170664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auclair, J.; Quinn, B.; Peyrot, C.; Wilkinson, K.J.; Gagné, F. Detection, biophysical effects, and toxicity of polystyrene nanoparticles to the cnidarian Hydra attenuata. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 11772–11781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Gupta, I.; Xia, L.; Pitchai, A.; Shannahan, J.; Mitra, S. Generation of Eroded Nanoplastics from Domestic Wastes and Their Impact on Macrophage Cell Viability and Gene Expression. Molecules 2024, 29, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, S.Y.; Bruce, T.F.; Bridges, W.C.; Klaine, S.J. Responses of Hyallela azteca to acute and chronic microplastic exposures. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 2564–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, S.; Oliviero, M.; Chiavarini, S.; Dumontet, S.; Manzo, S. Polyethylene, Polystyrene, and Polypropylene leachate impact upon marine microalgae Dunaliella tertiolecta. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2021, 84, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyavani, J.; Sibiya, A.; Bhavaniramya, S.; Mahboob, S.; Al-Ghanim, K.A.; Nisa, Z.-U.; Riaz, M.N.; Nicoletti, M.; Govindarajan, M.; Vaseeharan, B. Toxicity evaluation of polypropylene microplastic on marine microcrustacean Artemia salina: An analysis of implications and vulnerability. Chemosphere 2022, 296, 133990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasamma, S.; Audira, G.; Siregar, P.; Malhotra, N.; Lai, Y.-H.; Liang, S.-T.; Chen, J.R.; Chen, K.H.-C.; Hsiao, C.D. Nanoplastics Cause Neurobehavioral Impairments, Reproductive and Oxidative Damages, and Biomarker Responses in Zebrafish: Throwing up Alarms of Wide Spread Health Risk of Exposure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaya, H.J.; Park, S.; Kim, J.-H.; Kusumi, J.; Krenenou, S.; Sawatari, E.; Sato, A.; Lee, J.; Bang, H.; Kobayakawa, Y.; et al. A sleep-like state in Hydra unravels conserved sleep mechanisms during the evolutionary development of the central nervous system. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabb9415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omond, S.E.T.; Hale, M.W.; Lesku, J.A. Neurotransmitters of sleep and wakefulness in flatworms. Sleep 2022, 45, zsac053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, U.; Kroiher, M. A Possible Role for the Cnidarian Homologue of Serum Response Factor in Decision Making by Undifferentiated Cells. Dev. Biol. 2001, 236, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
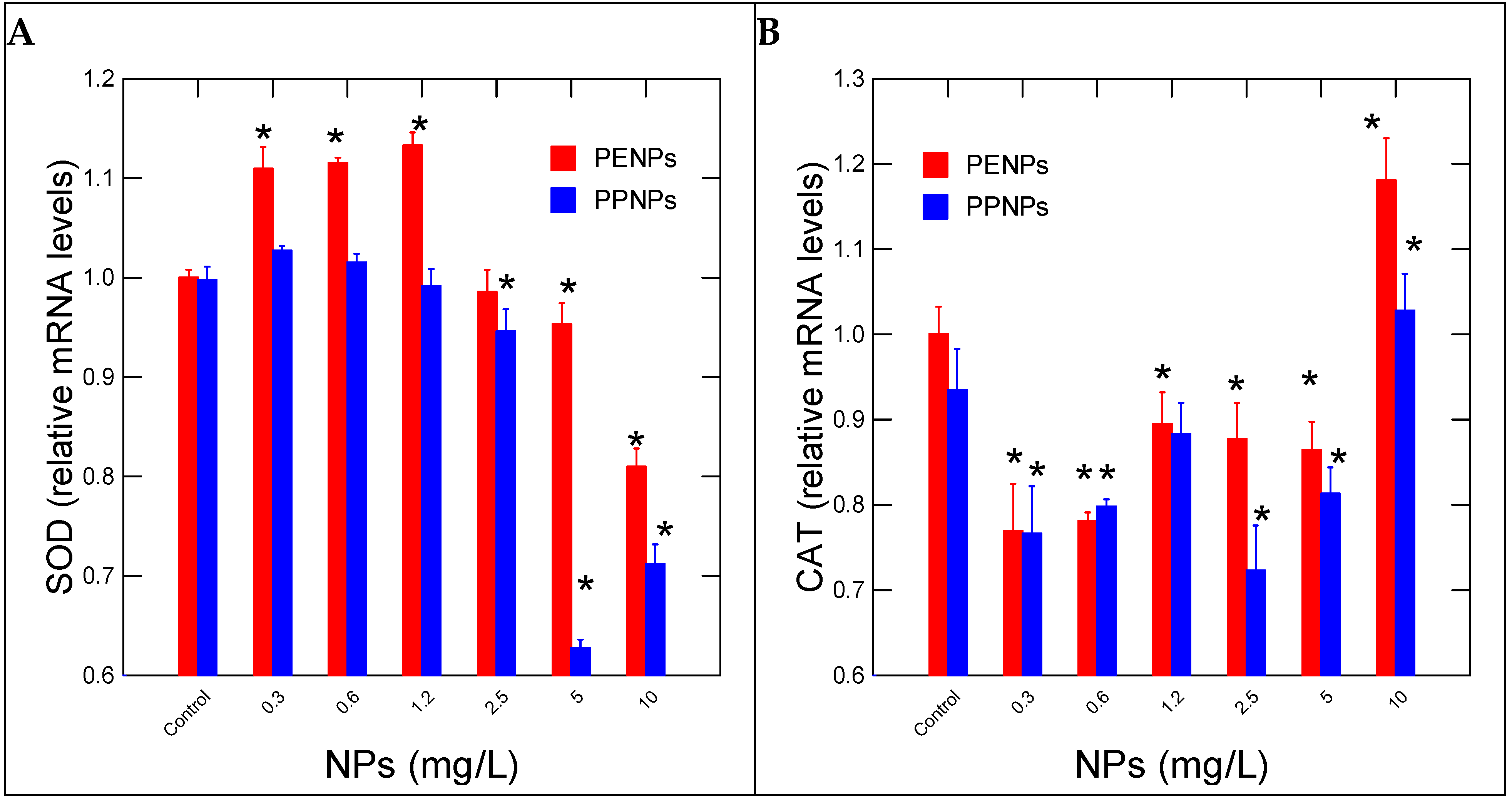
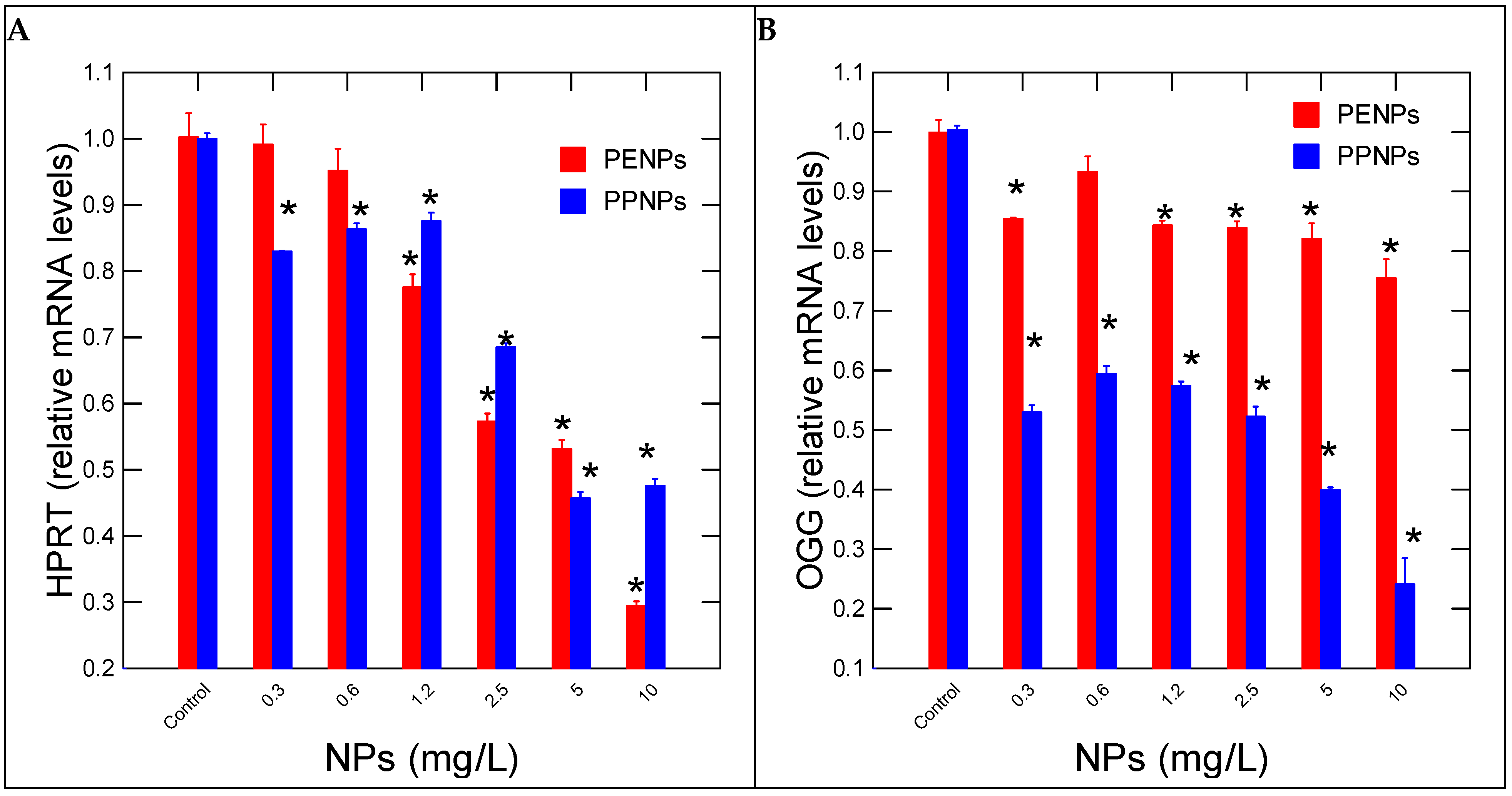
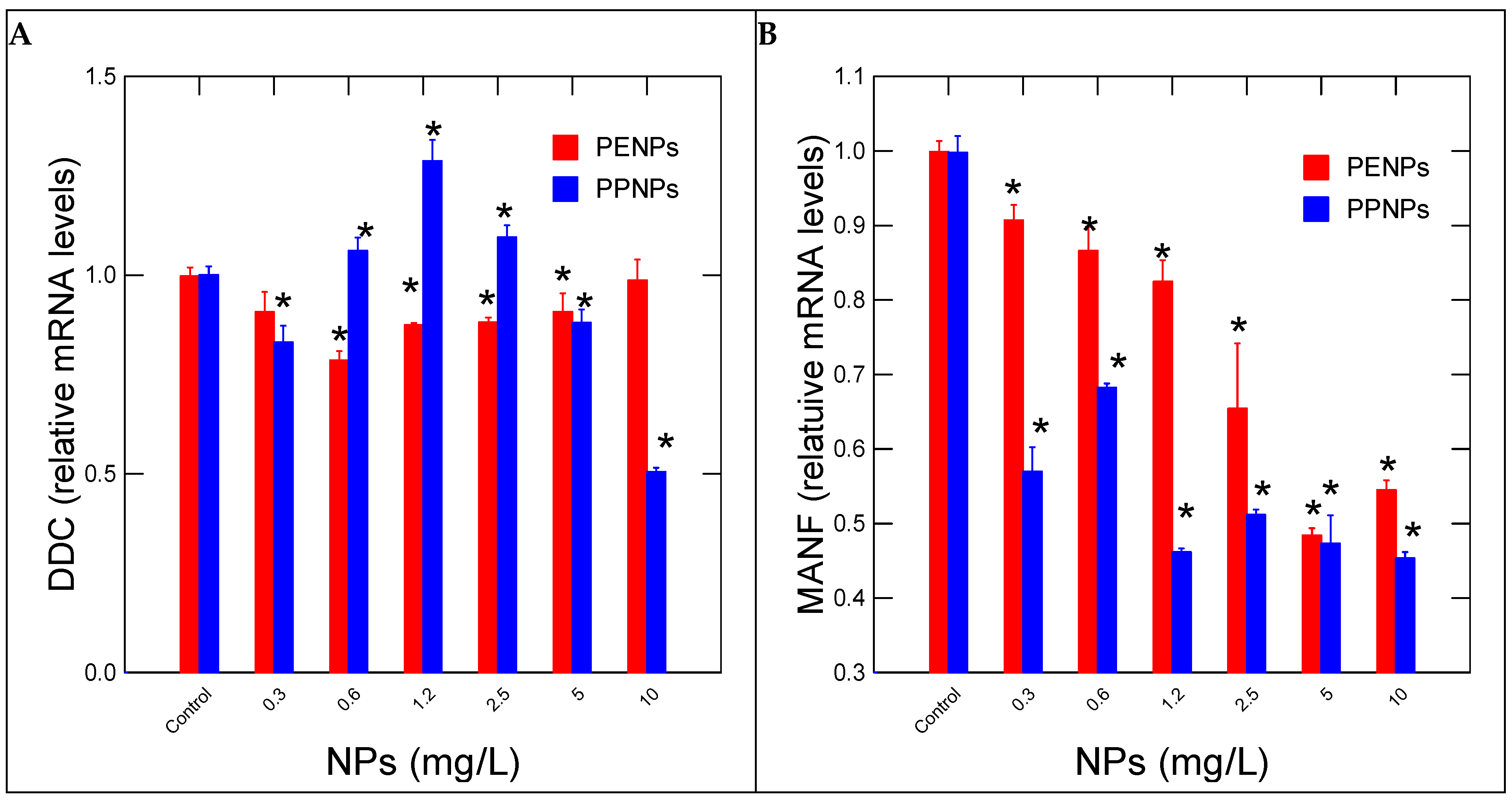
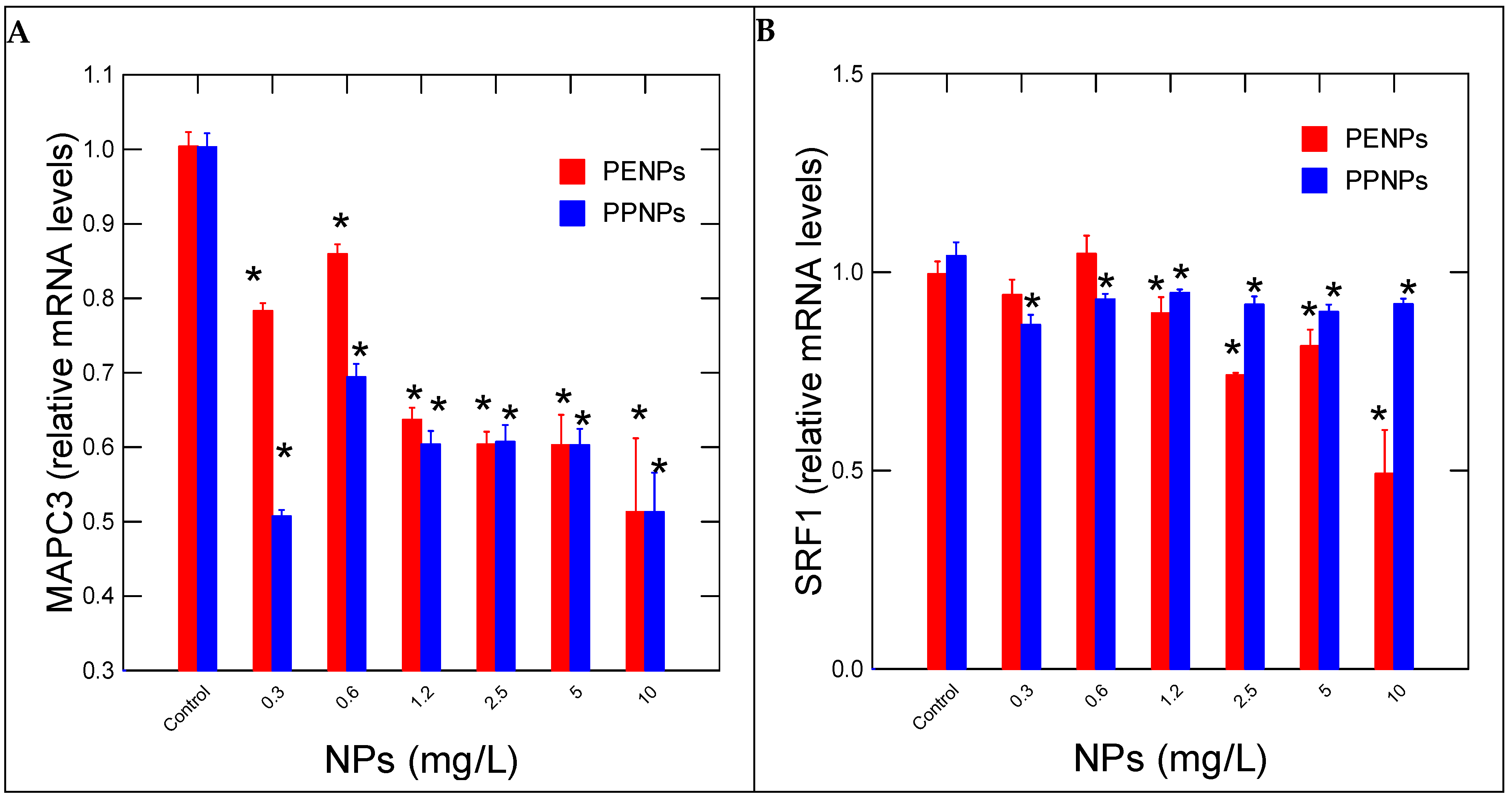
| Function | Gene Name | Forward/Reverse (5’---->3’) | Amplicon (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Housekeeping genes | 60S acidic ribosomal protein P0-like Rplp0-1 | CTG AGG CTG CTC TTC TTG CT/ GGA CTG AAA ATG CTT CCG TTG T | 94 |
| Housekeeping genes | Elongation factor-1 alpha EL1 | TGC TCC TGG ACA TCG TGA CT/ CAA CGA TGA GTA CGG CAC AAT C | 77 |
| Autophagy and Ub-pathway | (Microtubule-associated protein 1 chain 3 light) MAPC3l | CCA GAG AAA GCG AGA ATC CGA/ TGG AGA GCA TAC CAA CTG TCA T | 152 |
| Oxidative stress | Superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn]-like SOD | ACC TGG TAA GCA CGG TTT TCA/ TGC ACC ACT CCA TCT TTA CCA | 171 |
| Catalase-like CAT | ACA GCC TCA ATG ACT GTT GGG/ CCA CTC CAT TCA GAG CAG CC | 196 | |
| DNA damage and repair | 8-Oxoguanine DNA Glycosylase OGG | TGT GAC TGG AGT TGA AGA TGC T/ ACT CCA GGC AAT GAG CAA AGA | 174 |
| Purine salvage pathway | Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase-like HPRT | GAA TTG AAC GCA TGG CTC GT/ GTC TTG GCT GAA CCG AAA ACC | 98 |
| Regeneration and stem factor | Serum Response Factor SRF1 | CTT GTG GCA TCG GAA ACA GG/ TGC TTT GCC ACT TTC AGA GGT A | 84 |
| Neural activity | Dopa Decarboxylase DDC | GCC CCA GTT GAG CCA GAT AA/CAG TGA GTG ACA CCT GGC AT | 77 |
| Mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor homolog (Reparation of damaged dopaminergic nerve cells) MANF | CCA CTC GCA TAC TAC AAG CCT/ACA ACC ACT ACA AGT CTC ACC C | 180 |
| Pe CAT | Pp CAT | Pe DDC | Pp DDC | Pe HPRT | Pp HPRT | Pe MANF | Pp MANF | Pe MAPC | Pp MAPC | Pe OGG | Pp OGG | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PE CAT | 1 | |||||||||||
| PP CAT | 0.82 | 1 | ||||||||||
| PE DDC | 0.52 | 0.45 | 1 | |||||||||
| PP DDC | −0.58 | −0.45 | −0.33 | 1 | ||||||||
| PE HPRT | −0.45 | −0.13 | −0.04 | 0.46 | 1 | |||||||
| PP HPRT | −0.23 | −0.01 | 0.08 | 0.53 | 0.90 | 1 | ||||||
| PE MANF | −0.29 | −0.12 | −0.03 | 0.50 | 0.86 | 0.94 | 1 | |||||
| PP MANF | 0.11 | 0.24 | 0.30 | 0.17 | 0.75 | 0.82 | 0.76 | 1 | ||||
| PE MAPC | −0.09 | 0.13 | 0.08 | 0.28 | 0.87 | 0.85 | 0.80 | 0.92 | 1 | |||
| PP MAPC | 0.23 | 0.28 | 0.23 | 0.28 | 0.57 | 0.69 | 0.59 | 0.90 | 0.84 | 1 | ||
| PE OGG | −0.07 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.34 | 0.72 | 0.78 | 0.68 | 0.81 | 0.86 | 0.81 | 1 | |
| PP OGG | −0.04 | 0.09 | 0.25 | 0.47 | 0.77 | 0.89 | 0.81 | 0.93 | 0.87 | 0.89 | 0.82 | 1 |
| PE SOD | −0.71 | −0.46 | −0.49 | 0.66 | 0.71 | 0.57 | 0.56 | 0.16 | 0.41 | 0.07 | 0.33 | 0.31 |
| PP SOD | −0.42 | −0.18 | −0.16 | 0.53 | 0.81 | 0.88 | 0.93 | 0.56 | 0.63 | 0.36 | 0.55 | 0.64 |
| PES RF1 | −0.43 | −0.13 | −0.29 | 0.54 | 0.82 | 0.73 | 0.67 | 0.56 | 0.77 | 0.53 | 0.77 | 0.61 |
| PP SRF1 | 0.27 | 0.28 | 0.27 | 0.28 | 0.32 | 0.54 | 0.43 | 0.63 | 0.58 | 0.72 | 0.56 | 0.67 |
| PE SOD | PP SOD | PE SRF1 | ||||||||||
| PE CAT | ||||||||||||
| PP CAT | ||||||||||||
| PE DDC | ||||||||||||
| PP DDC | ||||||||||||
| PE HPRT | ||||||||||||
| PP HPRT | ||||||||||||
| PE MANF | ||||||||||||
| PP MANF | ||||||||||||
| PE MAPC | ||||||||||||
| PP MAPC | ||||||||||||
| PE OGG | ||||||||||||
| PP OGG | ||||||||||||
| PE SOD | 1 | |||||||||||
| PP SOD | 0.68 | 1 | ||||||||||
| PE SRF1 | 0.74 | 0.64 | 1 | |||||||||
| PP SRF1 | −0.12 | 0.25 | 0.33 | |||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Auclair, J.; André, C.; Gagné, F. Sublethal Toxicity and Gene Expression Changes in Hydra vulgaris Exposed to Polyethylene and Polypropylene Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15130954
Auclair J, André C, Gagné F. Sublethal Toxicity and Gene Expression Changes in Hydra vulgaris Exposed to Polyethylene and Polypropylene Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(13):954. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15130954
Chicago/Turabian StyleAuclair, Joelle, Chantale André, and François Gagné. 2025. "Sublethal Toxicity and Gene Expression Changes in Hydra vulgaris Exposed to Polyethylene and Polypropylene Nanoparticles" Nanomaterials 15, no. 13: 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15130954
APA StyleAuclair, J., André, C., & Gagné, F. (2025). Sublethal Toxicity and Gene Expression Changes in Hydra vulgaris Exposed to Polyethylene and Polypropylene Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials, 15(13), 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15130954








