Novel Terpineol-Based Silver Nanoparticle Ink with High Stability for Inkjet Printing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
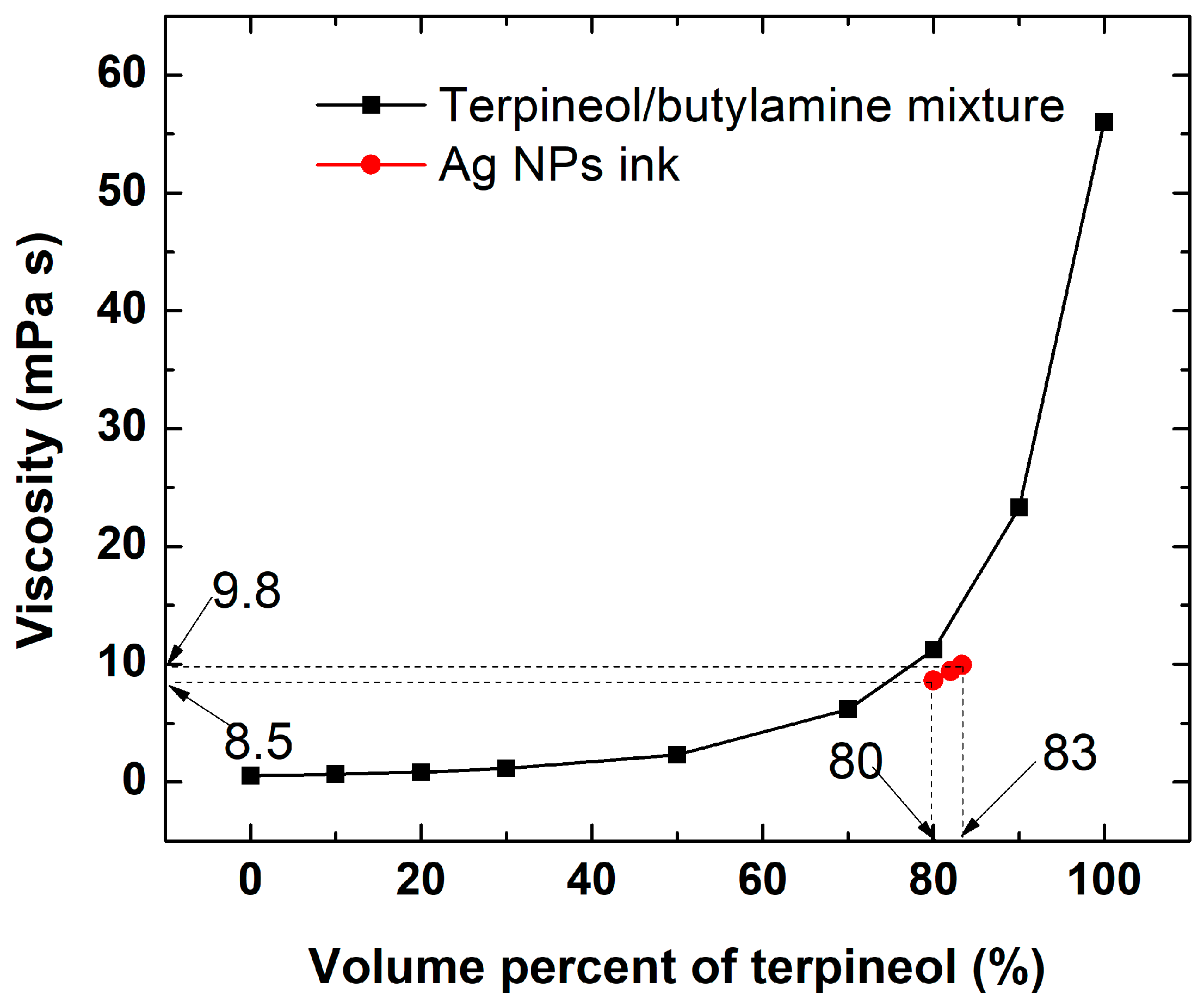
2.2.1. Preparation of Silver Nanoparticles and Conductive Inks
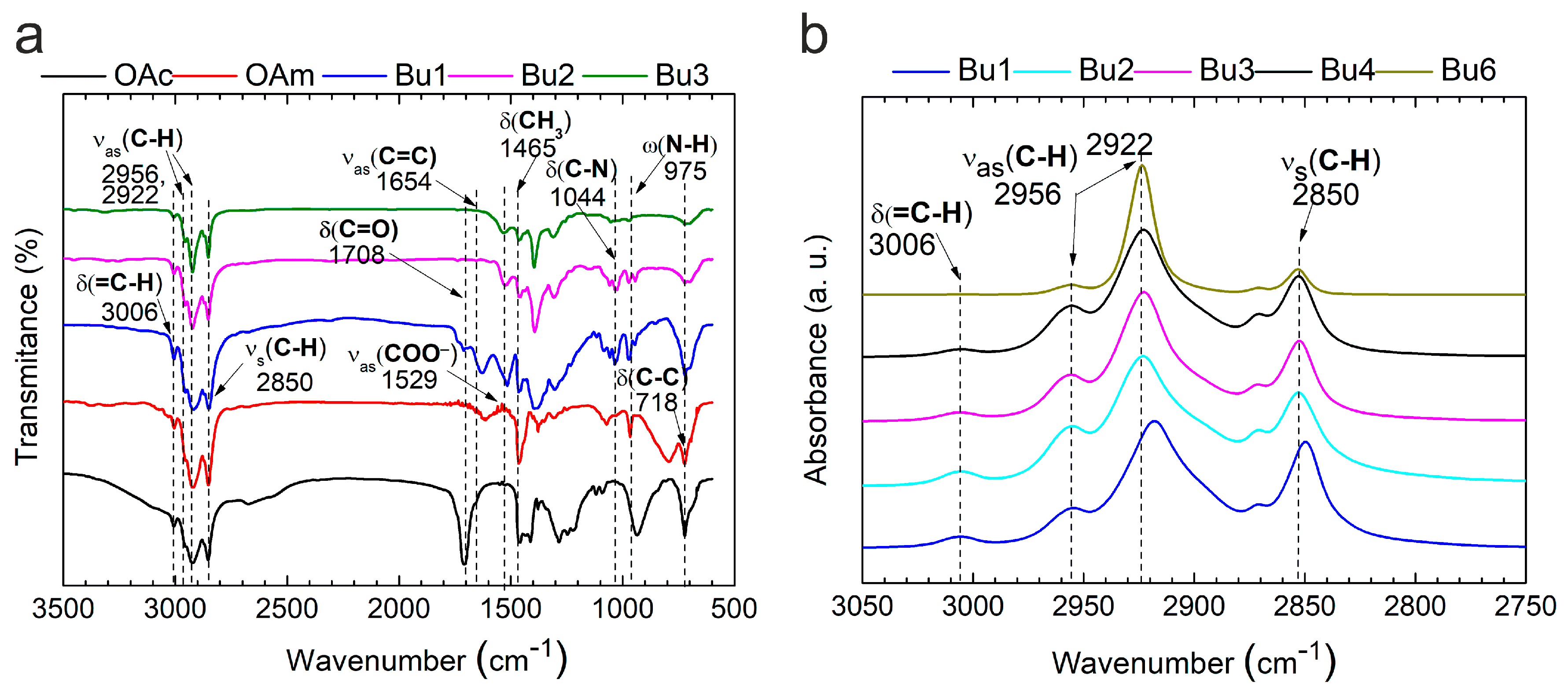
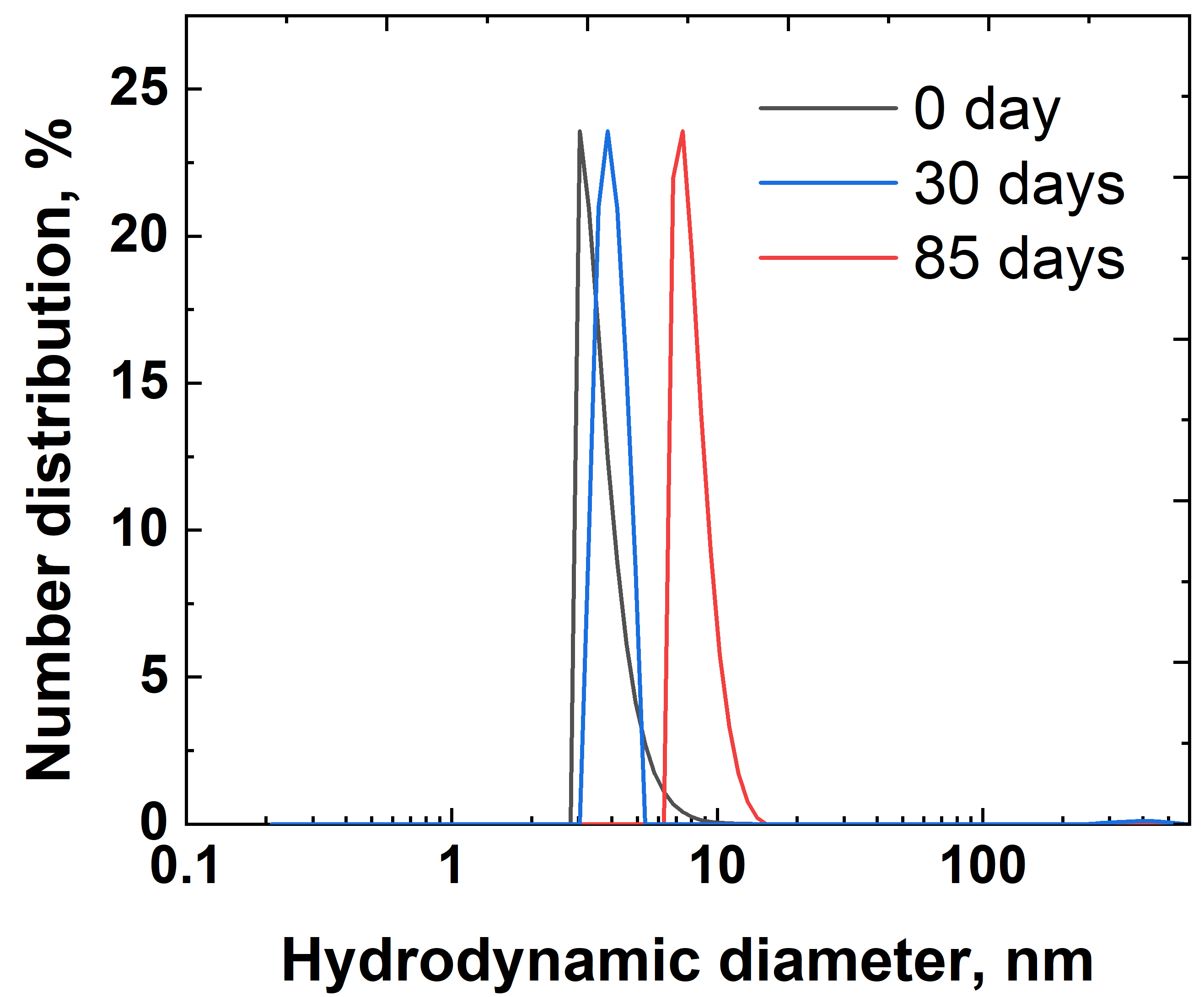
2.2.2. Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles and Inks
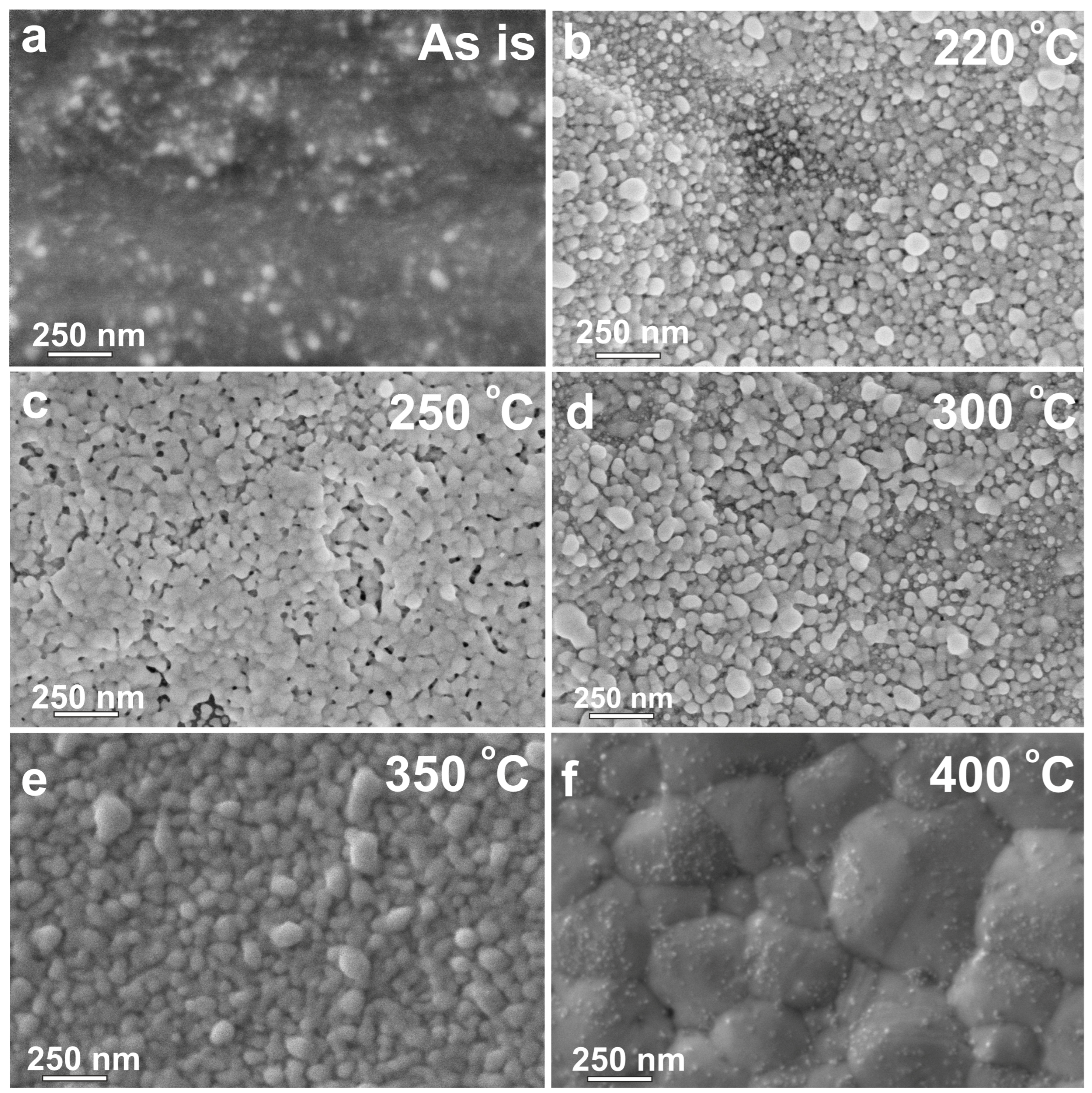
2.2.3. Printing of Silver Conductive Inks, Their Thermal Treatment, and Characteristics of Printed Samples
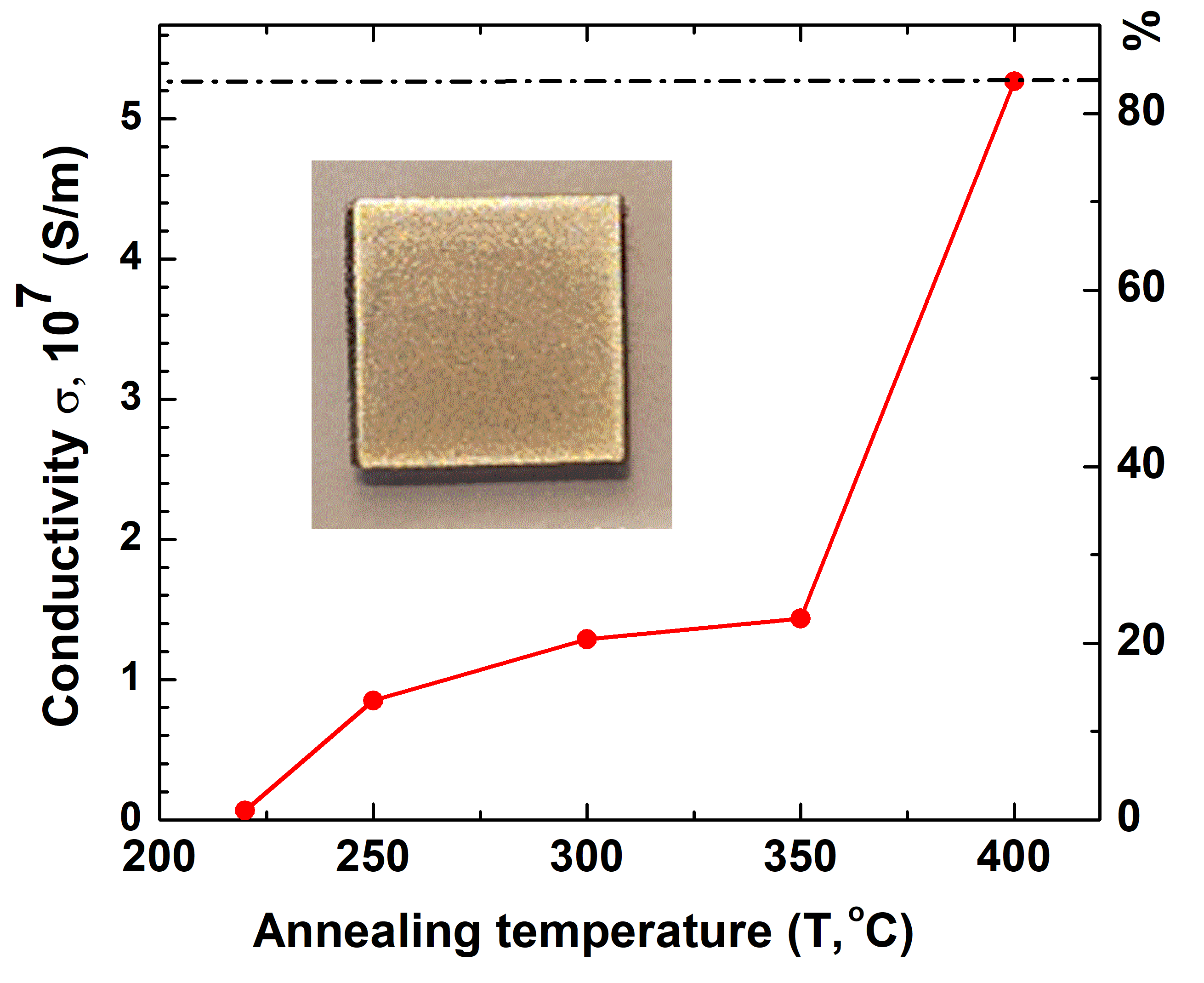
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATR | Attenuated Total Reflectance |
| DLS | Dynamic Light Scattering |
| DSA | Drop Shape Analyzer |
| DSC | Differential Scanning Calorimetry |
| FTIR | Fourier Transform Infrared |
| JCPDS | Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards |
| LED | Light-Emitting Diode |
| NPs | Nanoparticles |
| OA | Oleylamine |
| OAc | Oleic Acid |
| PEG | Polyethylene Glycol |
| PVP | Polyvinylpyrrolidone |
| RFID | Radio Frequency Identification |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| SPR | Surface Plasmon Resonance |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric Analysis |
| TFT | Thin-Film Transistor |
| UV-Vis | Ultraviolet–Visible Spectroscopy |
| XRD | X-Ray Diffraction |
| wt% | Weight Percent |
References
- Naderi-Samani, E.; Razavi, R.S.; Nekouee, K.; Naderi-Samani, H. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles for Use in Conductive Inks by Chemical Reduction Method. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajan, K.; Roppolo, I.; Chiappone, A.; Bocchini, S.; Perrone, D.; Chiolerio, A. Silver nanoparticle ink technology: State of the art. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2016, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.K.; El-Sayed, I.H.; El-Sayed, M.A. Au nanoparticles target cancer. Nano Today 2007, 2, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Vaseem, M.; Yang, S.; Shamim, A. Flexible and Reconfigurable Radio Frequency Electronics Realized by High-Throughput Screen Printing of Vanadium Dioxide Switches. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2020, 6, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Naiini, J.; Vaziri, M.M.; Lemme, S.; Östling, M. Inkjet Printing of MoS2. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 6524–6531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Lim, J.; Lee, S.; Kang, M.H.; Song, W.; Lim, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, E.K.; Park, E.K.; Myung, S. Flexible Hybrid Photodetector Based on Silver Sulfide Nanoparticles and Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 22625–22632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhu, X.; Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Lan, H. Preparation of Nano Silver Paste and Applications in Transparent Electrodes via Electric-Field Driven Micro-Scale 3D Printing. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khondoker, M.A.H.; Mun, S.C.; Kim, J. Synthesis and Characterization of Conductive Silver Ink for Electrode Printing on Cellulose Film. Appl. Phys. A 2013, 112, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.Y.; Cha, H.C.; Chuang, C.M.; Tsao, C.S.; Glowienka, D.; Wang, Y.H.; Wu, H.-C.; Huang, Y.C. Developing Screen-Printing Processes for Silver Electrodes Towards All-Solution Coating Processes for Solar Cells. Polymers 2024, 16, 3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Matteini, P.; Hwang, B. Effect of the Blade-Coating Conditions on the Electrical and Optical Properties of Transparent Ag Nanowire Electrodes. Micromachines 2022, 14, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, D.; Zhou, W.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Mi, B.; Wang, L.; Ma, Y. Order-Enhanced Silver Nanowire Networks Fabricated by Two-Step Dip-Coating as Polymer Solar Cell Electrodes. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 100725–100729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, I.; Sartale, S. Spin Coated Ag NPs SERS Substrate: Trace Detection Study of Methylene Blue and Melamine. Appl. Phys. A 2023, 129, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, N.C.; Al-Shamery, K. Inkjet Printing Metals on Flexible Materials for Plastic and Paper Electronics. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 1618–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, D.J.; Lotya, M.; Coleman, J.N. Inkjet Printing of Silver Nanowire Networks. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 9254–9261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, I.J.; Aroche, A.F.; Schuck, A.; Lamberty, P.; Peter, C.R.; Hasenkamp, W.; Rocha, T.L. Silver Nanoparticle Conductive Inks: Synthesis, Characterization, and Fabrication of Inkjet-Printed Flexible Electrodes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamyshny, A.; Sowade, E.; Magdassi, S. Inkjet Ink Formulations: Overview and Fundamentals. In Inkjet Printing in Industry: Materials, Technologies, Systems, and Applications; Zapka, W., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 93–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Q. Significant Parameters in the Optimization of Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles by Chemical Reduction Method. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2010, 19, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvítek, L.; Panáček, A.; Soukupová, J.; Kolář, M.; Večeřová, R.; Prucek, R.; Holecová, M.; Zbořil, R. Effect of Surfactants and Polymers on Stability and Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles (NPs). J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 5825–5834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereshteh, Z.; Rojaee, R.; Sharifnabi, A. Effect of Different Polymers on Morphology and Particle Size of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Modified Polyol Method. Superlattices Microstruct. 2016, 98, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, N.; Khanal, S.; Pudasaini, P.R.; Pahl, S.; Romero-Urbina, D. Citrate stabilized silver nanoparticles: Study of crystallography and surface properties. Int. J. Nanotechnol. Mol. Comput. (IJNMC) 2011, 3, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battocchio, C.; Meneghini, C.; Fratoddi, I.; Venditti, I.; Russo, M.V.; Aquilanti, G.; Maurizio, C.; Bondino, F.; Matassa, R.; Rossi, M.; et al. Silver nanoparticles stabilized with thiols: A close look at the local chemistry and chemical structure. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 19571–19578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charan, K.P.; Pothanagandhi, N.; Vijayakrishna, K.; Sivaramakrishna, A.; Mecerreyes, D.; Sreedhar, B. Poly(Ionic Liquids) as “Smart” Stabilizers for Metal Nanoparticles. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 60, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, C.M.; Huynh, K.K.; Dang, D.M.T. Influence of Solvents on Characteristics of Inkjet Printing Conductive Ink Based on Nano Silver Particles. Biol. Chem. Res. 2019, 6, 126–134. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, C.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cai, K. Scalable Printing High-Performance and Self-Healable Ag2Se/Terpineol Nanocomposite Film for Flexible Thermoelectric Device. Energy 2024, 296, 131232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, M.; Biswas, C.; Kaul, A.B. High-Performance Ink-Jet Printed Graphene Resistors Formed with Environmentally-Friendly Surfactant-Free Inks for Extreme Thermal Environments. Appl. Mater. Today 2017, 6, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.R.; Mirihanage, W.; Potluri, P.; Fernando, A. Highly Stable Graphene Inks Based on Organic Binary Solvents. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2023, 40, 2200153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molesa, S.; Redinger, D.; Huang, D.; Subramanian, V. High-Quality Inkjet-Printed Multilevel Interconnects and Inductive Components on Plastic for Ultra-Low-Cost RFID Applications. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 2003, 769, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sels, A.; Subramanian, V. Printed Platinum Nanoparticle Thin-Film Structures for Use in Biology and Catalysis: Synthesis, Printing, and Application Demonstration. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 1929–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, S.B.; Wilhelm, E.J.; Jacobson, J.M. Ink-Jet Printed Nanoparticle Microelectromechanical Systems. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2002, 11, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, M.; Lee, S.W.; Joh, H.; Lee, W.S.; Paik, T.; Oh, S.J. Designing Highly Conductive and Stable Silver Nanocrystal Thin Films with Tunable Work Functions through Solution-Based Surface Engineering with Gold Coating Process. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 698, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourdikoudis, S.; Menelaou, M.; Fiuza-Maneiro, N.; Zheng, G.; Wei, S.; Pérez-Juste, J.; Polavarapu, L.; Sofer, Z. Oleic Acid/Oleylamine Ligand Pair: A Versatile Combination in the Synthesis of Colloidal Nanoparticles. Nanoscale Horiz. 2022, 7, 941–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyhan, M.; Kucharczyk, W.; Yarar, U.E.; Rickard, K.; Rende, D.; Baysal, N.; Bucak, S.; Ozisik, R. Interfacial surfactant competition and its impact on poly(ethylene oxide)/Au and poly(ethylene oxide)/Ag nanocomposite properties. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2017, 10, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.J.; Kim, N.R.; Lee, C.; Lee, H.M. Uniform thin film electrode made of low-temperature-sinterable silver nanoparticles: Optimized extent of ligand exchange from oleylamine to acrylic acid. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2017, 19, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourdikoudis, S.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Oleylamine in nanoparticle synthesis. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 1465–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelaer, J.; de Laat, A.W.M.; Hendriks, C.E.; Schubert, U.S. Inkjet-Printed Silver Tracks: Low Temperature Curing and Thermal Stability Investigation. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 3209–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Osch, T.H.J.; Perelaer, J.; de Laat, A.W.M.; Schubert, U.S. Inkjet Printing of Narrow Conductive Tracks on Untreated Polymeric Substrates. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 343–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Larson, R.G. Marangoni Effect Reverses Coffee-Ring Depositions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 7090–7094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ider, M.; Abderrafi, K.; Eddahbi, A.; Ouaskit, S.; Kassiba, A. Silver Metallic Nanoparticles with Surface Plasmon Resonance: Synthesis and Characterizations. J. Clust. Sci. 2017, 28, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FUJIFILM. FUJIFILM Dimatix Ink Tutorial. Available online: https://www.cnfusers.cornell.edu/sites/default/files/Equipment-Resources/Ink%20formulation%20tutorial.pdf (accessed on 11 June 2025).
- Moon, K.S.; Dong, H.; Maric, R.; Pothukuchi, S.; Hunt, A.; Li, Y.I.; Wong, C.P. Thermal Behavior of Silver Nanoparticles for Low-Temperature Interconnect Applications. J. Electron. Mater. 2005, 34, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiruvengadam, V.; Bansod, A.V. Characterization of silver nanoparticles synthesized using chemical method and its antibacterial property. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2020, 10, 7257–7264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döbelin, N.; Kleeberg, R. Profex: A graphical user interface for the Rietveld refinement program BGMN. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2015, 48, 1573–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lide, D.R. (Ed.) Electrical Resistivity of Pure Metals. In CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 86th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]





| Physical Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Average size of nanoparticles (nm) (according to TEM and DLS data) | ≤10 |
| Viscosity (mPa·s) | ~10 |
| Density (g/mL) | 0.98–1.03 |
| Surface tension (mN/m) | 27 |
| Contact angle on washed glass substrates (degrees) | 18.0–21.5° |
| Drop Spacing (µm) | Print Height (mm) | Cartridge Temperature (°C) | Substrate Temperature (°C) | Firing Voltage (V) | Jetting Frequency (kHz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 1.35 | 38 | 38 | 35 | 1.5 |
| Sample | Annealing Temp. (°C) | Lattice Parameter (nm) | Crystallite Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | 0.4092 ± 0.0001 | 2 ± 1 |
| 2 | 220 | 0.4090 ± 0.0001 | 21 ± 1 |
| 3 | 250 | 0.4090 ± 0.0001 | 33 ± 1 |
| 4 | 300 | 0.4089 ± 0.0001 | 27 ± 1 |
| 5 | 350 | 0.4089 ± 0.0001 | 32 ± 1 |
| 6 | 400 | 0.4088 ± 0.0001 | 85 ± 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Novikovs, A.; Tsebriienko, T.; Trausa, A.; Berzina, A.; Chikvaidze, G.; Bocharov, D.; Mulla, M.Y.; Purans, J.; Polyakov, B. Novel Terpineol-Based Silver Nanoparticle Ink with High Stability for Inkjet Printing. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15130955
Novikovs A, Tsebriienko T, Trausa A, Berzina A, Chikvaidze G, Bocharov D, Mulla MY, Purans J, Polyakov B. Novel Terpineol-Based Silver Nanoparticle Ink with High Stability for Inkjet Printing. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(13):955. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15130955
Chicago/Turabian StyleNovikovs, Aleksandrs, Tamara Tsebriienko, Annamarija Trausa, Anete Berzina, George Chikvaidze, Dmitry Bocharov, Mohammad Yusuf Mulla, Juris Purans, and Boris Polyakov. 2025. "Novel Terpineol-Based Silver Nanoparticle Ink with High Stability for Inkjet Printing" Nanomaterials 15, no. 13: 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15130955
APA StyleNovikovs, A., Tsebriienko, T., Trausa, A., Berzina, A., Chikvaidze, G., Bocharov, D., Mulla, M. Y., Purans, J., & Polyakov, B. (2025). Novel Terpineol-Based Silver Nanoparticle Ink with High Stability for Inkjet Printing. Nanomaterials, 15(13), 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15130955






