Synthesis and Characterization of Temperature- and pH-Responsive PIA-b-PNIPAM@Fe3O4 Nanocomposites
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Synthesis Method | Polymer Used | Functionalization | MNP | Nanocomposite | Intended Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Graft polymerization | Chitosan and PEG | PNIPAM | - | Chitosan films | Medium suppuration wounds | Conzatti et al. [58] |
| One-step precipitation polymerization | PNIPAM | DNAzyme | - | PNIPAM/DNAzyme | Biocatalysts (bioassays and biosensors) | Li et al. [59] |
| Soap-free emulsion polymerization | PNIPAM | Thiol- and carboxyl-functionalization | Bimetallic (Cu/Pd) | PNIPAM-based bimetallic Cu/Pd | Hybrid catalytic materials in the synthesis of nitrogenous compounds with improved optical properties | Kakar et al. [60] |
| Thermal polymerization | Itaconic acid (IA) | Laponite RD | - | IA/Laponite RD hydrogels | Removal of cationic dyes | Huerta-Angeles et al. [61] |
| Radical polymerization | PNIPAM | PIA | Fe3O4-NPs | Folate conjugated Poly(NIPAM-co-IA)@Fe3O4 | Nanocarrier for targeted doxorubicin delivery | Ghorbani et al. [62] |
| Hydrothermal approach | PNIPAM | - | Nickel ion doped iron oxide NPs | NiFe2O4-PNIPAM | Template for the efficient recovery of cefixime and methylene blue | Anushree et al. [63] |
| Free radical polymerization | Poly(NIPAM-co-AA) | APTES and Alanine | Ferrite and Magnetite MNPs | Poly(NIPAM-co-AA) immobilized on MNPs | Comparison between ‘grafting to’ and ‘in situ’ methods | Sakai et al. [64] |
| Copolymerization | PNIPAM | PIA | TiO2@SiO2 | PNIPAM/PIA- TiO2@SiO2 | Investigation in antibacterial activities against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria (S. aureus and E. coli) | Mohamed and Hassabo [65] |
| Surface-initiated ATRP | PNIPAM | 2-bromopropionamidepropyl tri- methoxysilane (BPTMS) | Fe3O4-NPs | SPION-PNIPAM | Contrast generation in MRI | Yar et al. [52] |
| Surface-initiated ATRP | PNIPAM | PIA | Fe3O4-NPs | Fe3O4@PIA-b-PNIPAM | Demonstration of thermo-responsive feature | Eyiler and Walters [57] |
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of APTES-Modified Fe3O4 Nanoparticles
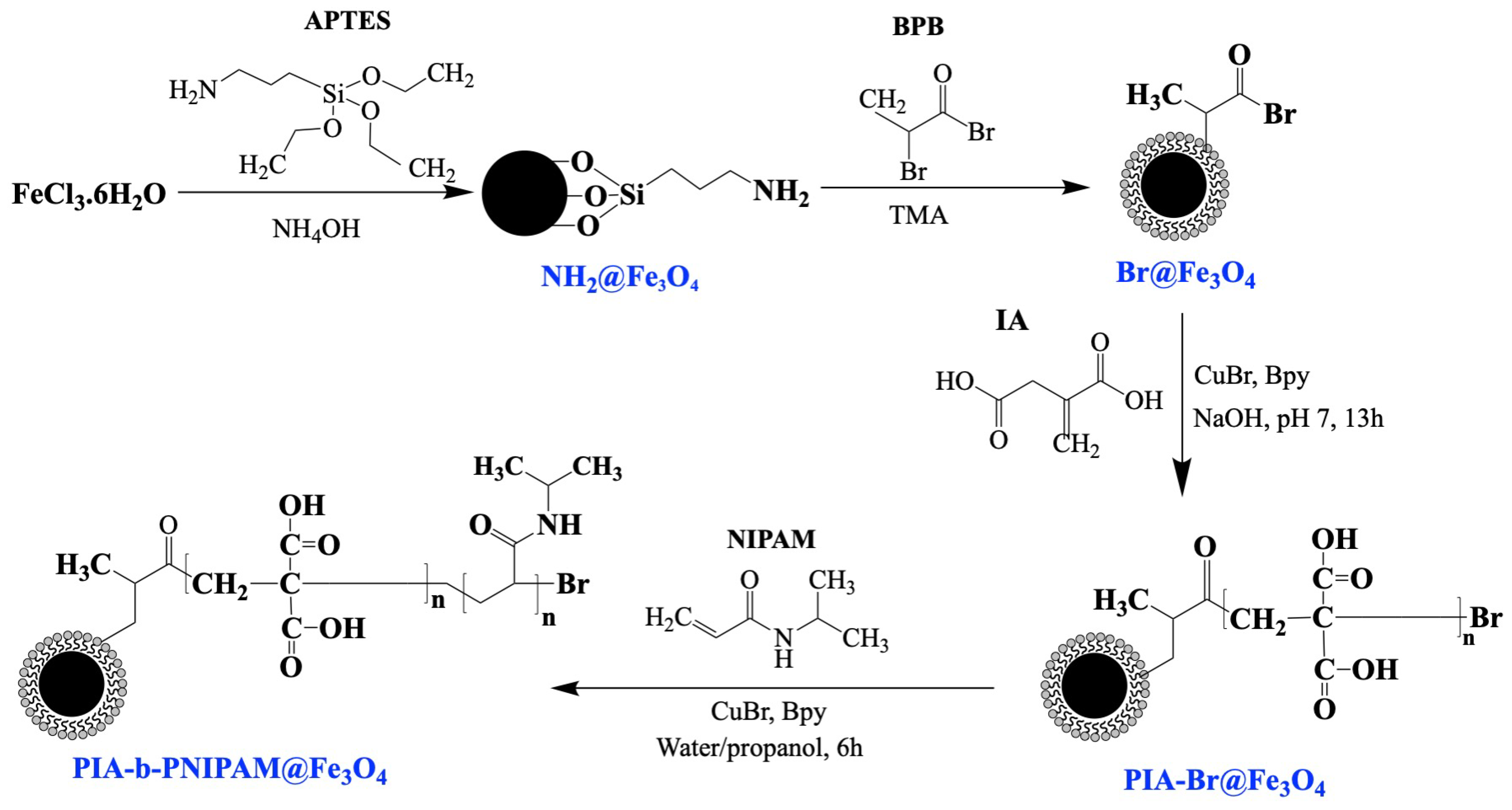
2.3. Surface-Initiated Block Copolymerization of Itaconic Acid (IA) and N-Isopropyl Acrylamide (NIPAM) on Fe3O4 Nanoparticles
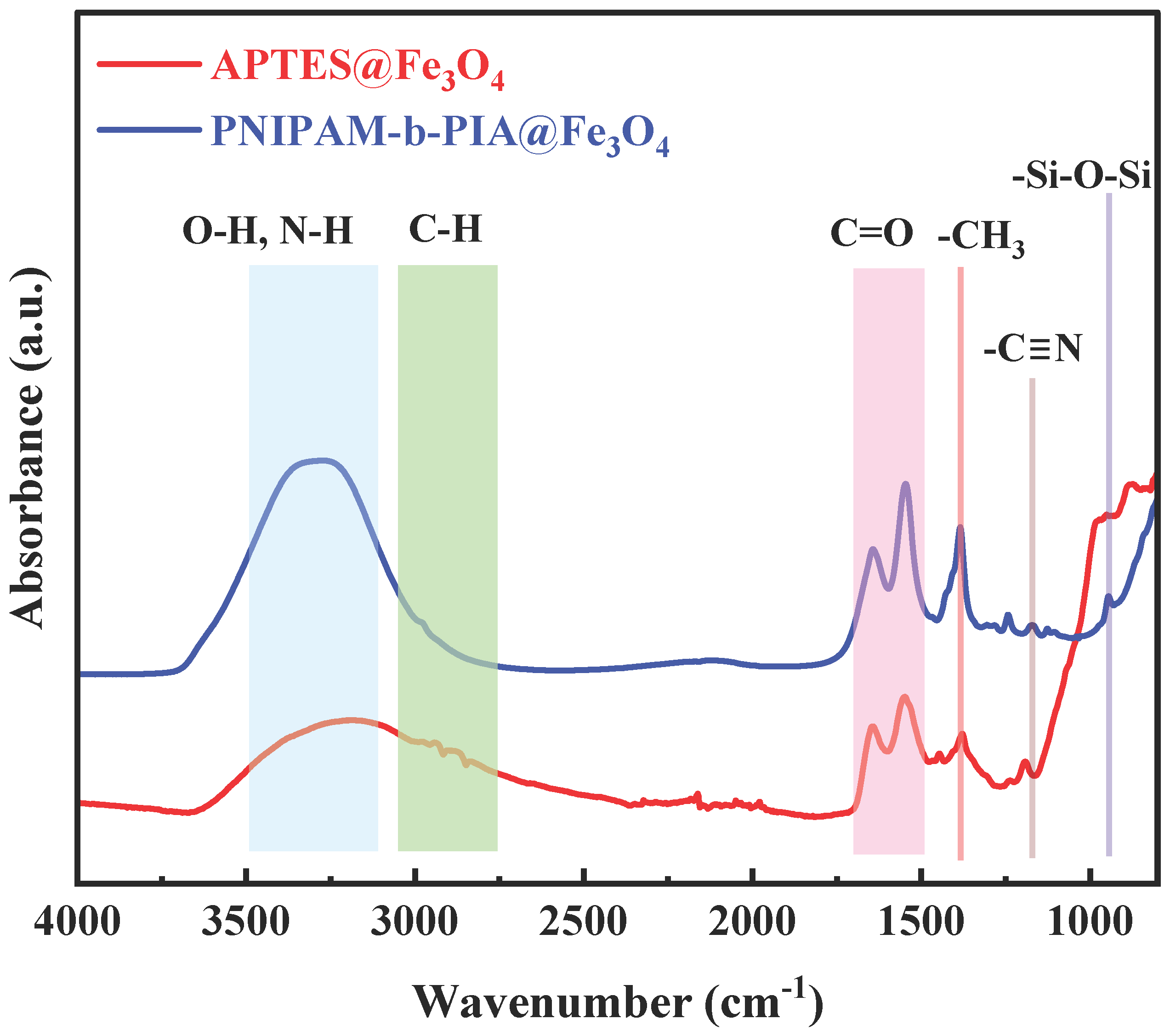
2.4. Characterization
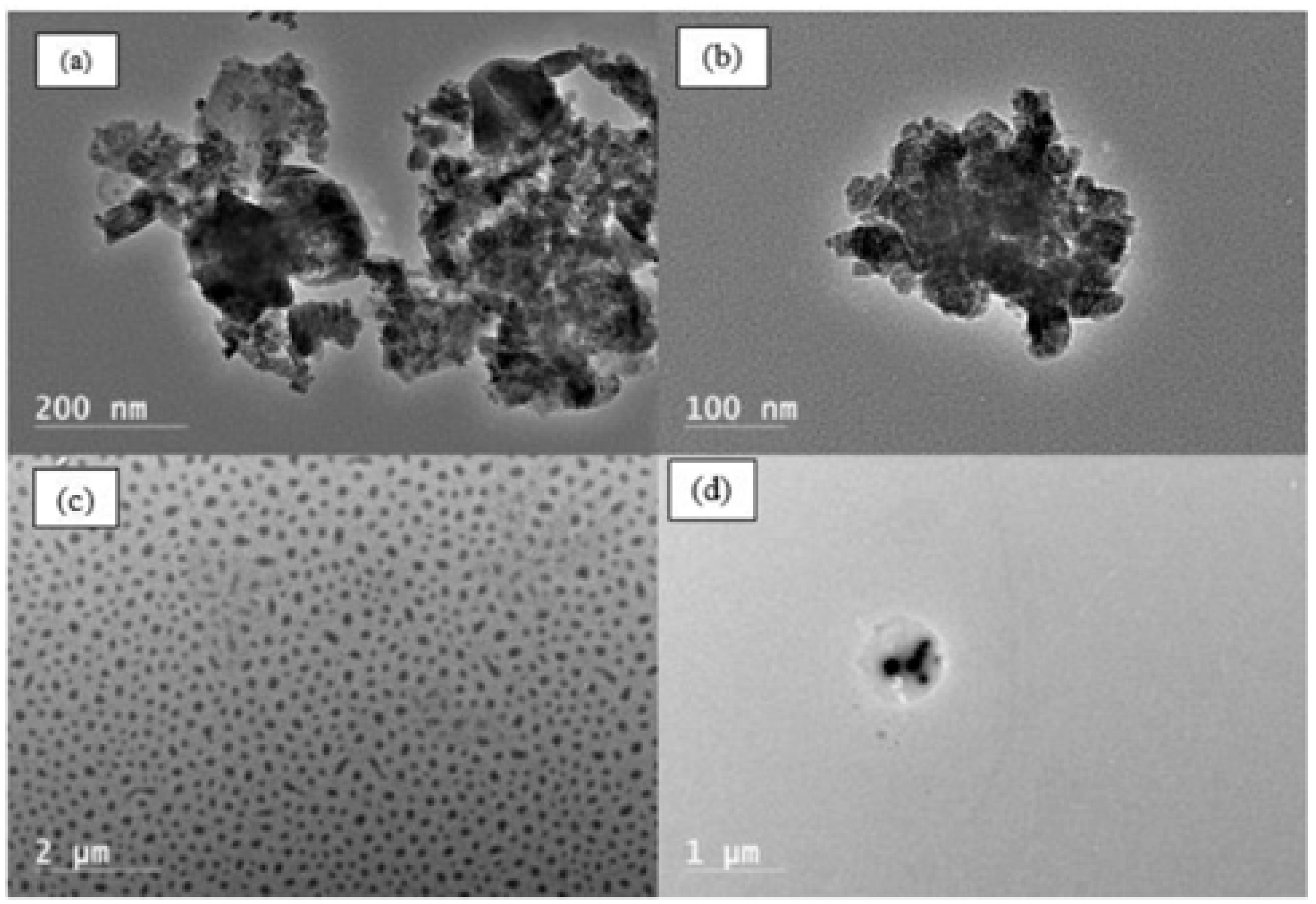
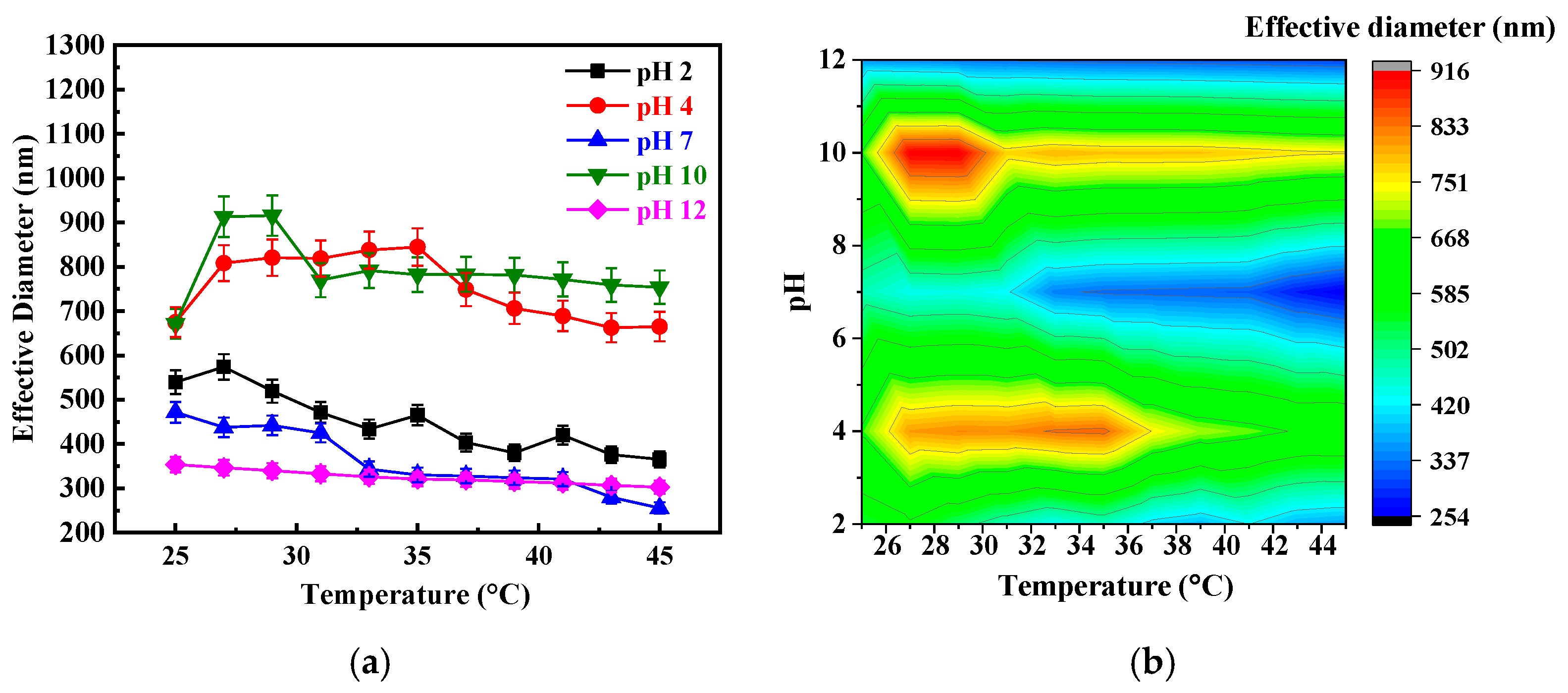
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lochhead, R. The Use of Polymers in Cosmetic Products. Cosmet. Sci. Technol. Theor. Princ. Appl. 2017, 13, 171–221. [Google Scholar]
- Yusuf, M.; Eskandarinezhad, S. An overview of materials, processing, and applications for wearable electronics. J. Compos. Compd. 2021, 3, 275–290. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; Sudhakara, P.; Omran, A.A.B.; Singh, J.; Ilyas, R. Recent Trends and Developments in Conducting Polymer Nanocomposites for Multifunctional Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadasivuni, K.K.; Hegazy, S.M.; Aly, A.A.M.A.; Waseem, S.; Karthik, K. Polymers in Electronics. In Polymer Science and Innovative Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 365–392. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, C.; Zhang, W.; Li, R.-W.; Wang, L. Polymer Memristor for Information Storage and Neuromorphic Applications. Mater. Horiz. 2014, 1, 489–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikada, Y. Surface Modification of Polymers for Medical Applications. Biomaterials 1994, 15, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moinudeen, G.; Ahmad, F.; Kumar, D.; Al-Douri, Y.; Ahmad, S. IoT Applications in Future Foreseen Guided by Engineered Nanomaterials and Printed Intelligence Technologies a Technology Review. Int. J. Internet Things 2017, 6, 106–148. [Google Scholar]
- Png, Z.M.; Wang, C.G.; Yeo, J.C.C.; Lee, J.J.C.; Surat’man, N.E.; Tan, Y.L.; Liu, H.; Wang, P.; Tan, B.H.; Xu, J.W.; et al. Stimuli-Responsive Structure–Property Switchable Polymer Materials. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2023, 8, 1097–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiruta, Y. Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide)-Based Temperature- and pH-Responsive Polymer Materials for Application in Biomedical Fields. Polym. J. 2022, 54, 1419–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.E.; Macdonald, M.; Nie, J.; Bowman, C.N. Structure and Swelling of Poly(Acrylic Acid) Hydrogels: Effect of pH, Ionic Strength, and Dilution on the Crosslinked Polymer Structure. Polymer 2004, 45, 1503–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, T.; Swanson, L.; Geoghegan, M.; Rimmer, S. The pH-Responsive Behaviour of Poly(Acrylic Acid) in Aqueous Solution Is Dependent on Molar Mass. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 2542–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Li, N.; Chen, K.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y. A Solid–Liquid Composite Lubricating “Nano-snowboard” for Long-acting Treatment of Osteoarthritis. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2208189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Liu, J.; Gong, P.; Li, Z.; Ke, C.; Qian, Y.; Luo, H.; Xiao, L.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. Construction of Core-Shell NanoMOFs@ Microgel for Aqueous Lubrication and Thermal-Responsive Drug Release. Small 2022, 18, 2202510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, T.; Hu, L.; Shen, Q.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Serpe, M.J. Stimuli-Responsive Polymer-Based Systems for Diagnostic Applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 7042–7061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trehan, K.; Saini, M.; Thakur, S. Stimuli-Responsive Material in Controlled Release of Drug. In Engineered Biomaterials: Synthesis and Applications; Malviya, R., Sundram, S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2023; pp. 535–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagay, Z.A.; Rongpi, S. Stimuli-Responsive In-Situ Gelling Systems: Smart Polymers for Enhanced Drug Delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Ahadi, F.; Bahmanpour, A.H.; Mozafari, M. 14-Stimuli-Responsive Polymers for Biomedical Applications. In Handbook of Polymers in Medicine; Woodhead Publishing Series in Biomaterials; Mozafari, M., Singh Chauhan, N.P., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2023; pp. 401–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Jung, K.; Li, A.; Liu, J.; Boyer, C. Recent Advances in Stimuli-Responsive Polymer Systems for Remotely Controlled Drug Release. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 99, 101164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Municoy, S.; Álvarez Echazú, M.I.; Antezana, P.E.; Galdopórpora, J.M.; Olivetti, C.; Mebert, A.M.; Foglia, M.L.; Tuttolomondo, M.V.; Alvarez, G.S.; Hardy, J.G.; et al. Stimuli-Responsive Materials for Tissue Engineering and Drug Delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Yu, L.; Ding, J. PEG-Based Thermosensitive and Biodegradable Hydrogels. Acta Biomater. 2021, 128, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, A.; Khan, J.; Saraf, S.; Saraf, S. Polyethylene Glycol (PEG)–Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAAm) Based Thermosensitive Injectable Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 88, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawan, S.; Dhawan, K.; Varma, M.; Sinha, V. Applications of Poly(ethylene oxide) in Drug Delivery Systems. Pharm. Technol. 2005, 29, 82–96. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, H.C.; Hsiue, G.H.; Lee, Y.P.; Huang, L.W. Synthesis and Characterization of pH-Sensitive Dextran Hydrogels as a Potential Colon-Specific Drug Delivery System. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 1999, 10, 591–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Sun, J.; Bai, S.; Wu, X. pH-Sensitive Performance of Dextran–Poly(Acrylic Acid) Copolymer and Its Application in Controlled in Vitro Release of Ibuprofen. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2017, 66, 900–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardajee, G.R.; Hooshyar, Z.; Rastgo, F. Kappa Carrageenan-g-Poly(Acrylic Acid)/SPION Nanocomposite as a Novel Stimuli-Sensitive Drug Delivery System. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2013, 291, 2791–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Lin, S.; Xie, R.; Ju, X.-J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, W.; Mou, C.-L.; Zhao, C.; Chen, Q.; Chu, L.-Y. pH-Responsive Poly(Ether Sulfone) Composite Membranes Blended with Amphiphilic Polystyrene-Block-Poly(Acrylic Acid) Copolymers. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 450, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Li, D.; Jin, S.; Ding, J.; Guo, J.; Shi, W.; Wang, C. Stimuli-Responsive Biodegradable Poly(Methacrylic Acid) Based Nanocapsules for Ultrasound Traced and Triggered Drug Delivery System. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 2079–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Zhang, D.; Han, L.; Tejada, J.; Ortiz, C. Synthesis, Preparation, and Conformation of Stimulus-Responsive End-Grafted Poly(Methacrylic Acid-g-Ethylene Glycol) Layers. Soft Matter 2006, 2, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kim, I.; Lu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yu, D.-G.; Song, W. Intelligent Poly(l-Histidine)-Based Nanovehicles for Controlled Drug Delivery. J. Control. Release 2022, 349, 963–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, M.; Fernandez-Rodriguez, M.A.; Karg, M.; Isa, L.; Vogel, N. Poly-N-Isopropylacrylamide Nanogels and Microgels at Fluid Interfaces. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, M.; Hebels, E.; Hennink, W.E.; Vermonden, T. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide): Physicochemical Properties and Biomedical Applications. Temp. Polym. Chem. Prop. Appl. 2018, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Shaibie, N.A.; Ramli, N.A.; Mohammad Faizal, N.D.F.; Srichana, T.; Mohd Amin, M.C.I. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-Based Polymers: Recent Overview for the Development of Temperature-Responsive Drug Delivery and Biomedical Applications. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2023, 224, 2300157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toma, M.; Jonas, U.; Mateescu, A.; Knoll, W.; Dostalek, J. Active Control of SPR by Thermoresponsive Hydrogels for Biosensor Applications. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 11705–11712. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/jp400255u (accessed on 10 May 2025). [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Feng, Y.; Li, Y.; Feng, W. Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide)-Based Smart Hydrogels: Design, Properties and Applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 115, 100702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekin, H.; Sanchez, J.G.; Tsinman, T.; Langer, R.; Khademhosseini, A. Thermoresponsive Platforms for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. AIChE J. Am. Inst. Chem. Eng. 2011, 57, 3249–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasef, H.; Saidi, H.; Uthman, H.; Sithambaranathan, P. Advances in Membranes for High Temperature Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. Adv. Funct. Polym. Compos. Mater. Devices Allied Appl. 2013, 1, 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Vince, M.; Augustyniak, A.; Durant, Y.; Shaw, J. Soluble Aqueous Compositions of Selected Polyitaconic Acid Polymers. WO2015100412A1, 2 July 2015. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2015100412A1/en (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Lanzalaco, S.; Armelin, E. Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide) and Copolymers: A Review on Recent Progresses in Biomedical Applications. Gels 2017, 3, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khabibullin, A.; Mastan, E.; Matyjaszewski, K.; Zhu, S. Surface-Initiated Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization. In Controlled Radical Polymerization at and from Solid Surfaces; Vana, P., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 29–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Chen, Z. Function-Driven Design of Stimuli-Responsive Polymer Composites: Recent Progress and Challenges. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 11817–11834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.-Z.; Hong, C.-Y.; Pan, C.-Y. Preparation of Smart Polymer/Carbon Nanotube Conjugates via Stimuli-Responsive Linkages. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 2470–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, J.; Minko, T. Multifunctional and Stimuli-Responsive Nanocarriers for Targeted Therapeutic Delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2021, 18, 205–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakpour, E.; Salehi, S.; Naghib, S.M.; Ghorbanzadeh, S.; Zhang, W. Graphene-Based Nanomaterials for Stimuli-Sensitive Controlled Delivery of Therapeutic Molecules. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1129768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, L.T.; Rodriguez-Lorenzo, L.; Hirsch, V.; Balog, S.; Urban, D.; Jud, C.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Lattuada, M.; Petri-Fink, A. Nanoparticle Colloidal Stability in Cell Culture Media and Impact on Cellular Interactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 6287–6305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, X.-M.; He, T. Kinetics of (3-Aminopropyl)Triethoxylsilane (APTES) Silanization of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2013, 29, 15275–15282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Yan, Y.; Roberts, C.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y. The Role of Dipole Interactions in Hyperthermia Heating Colloidal Clusters of Densely-Packed Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, S.; Mahmoudi, M. Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Promises for Diagnosis and Treatment of Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Genet. 2011, 2, 367–390. [Google Scholar]
- Wahajuddin, N.; Arora, S. Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Magnetic Nanoplatforms as Drug Carriers. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 3445–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucci, C.; Degl’Innocenti, A.; Gümüş, M.B.; Ciofani, G. Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Magnetic Hyperthermia: Recent Advancements, Molecular Effects, and Future Directions in the Omics Era. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 2103–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M. Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Iron-Oxide Nanoparticles in the Era of Personalized Medicine. Nanotheranostics 2023, 7, 424–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.I.; Miranda, M.S.; Rodrigues, M.T.; Reis, R.L.; Gomes, M.E. Magnetic Responsive Cell-Based Strategies for Diagnostics and Therapeutics. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 13, 054001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yar, Y.; Khodadust, R.; Akkoc, Y.; Utkur, M.; Saritas, E.U.; Gozuacik, D.; Acar, H.Y. Development of Tailored SPION-PNIPAM Nanoparticles by ATRP for Dually Responsive Doxorubicin Delivery and MR Imaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Han, S.; Wu, W.; Li, Z.; He, Z.; Liu, C.; Xue, H.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W.; Liu, J. Dose-Effect Relationship of Copolymer on Enhancing Aqueous Lubrication of a Hybrid Osteoarthritis Drug Delivery Nanocarrier. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 679, 788–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Liu, J.; Tian, L.; Lin, X.; Xue, H.; Gong, P.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. Polyelectrolyte-Functionalized NanoMOFs for Highly Efficient Aqueous Lubrication and Sustained Drug Release. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2023, 44, 2300089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanujan, R.V.; Ang, K.L.; Venkatraman, S. Magnet–PNIPA Hydrogels for Bioengineering Applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthika, V.; AlSalhi, M.S.; Devanesan, S.; Gopinath, K.; Arumugam, A.; Govindarajan, M. Chitosan Overlaid Fe3O4/rGO Nanocomposite for Targeted Drug Delivery, Imaging, and Biomedical Applications. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyiler, E.; Walters, K.B. Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Grafted with Poly(Itaconic Acid)-Block-Poly (N-Isopropylacrylamide). Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 444, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conzatti, G.; Chamary, S.; De Geyter, N.; Cavalie, S.; Morent, R.; Tourrette, A. Surface Functionalization of Plasticized Chitosan Films through PNIPAM Grafting via UV and Plasma Graft Polymerization. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 105, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, C.; Guo, W. Multifunctional poly-N-isopropylacrylamide/DNAzyme microgels as highly efficient and recyclable catalysts for biosensing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705876. [Google Scholar]
- Kakar, M.U.; Khan, K.; Akram, M.; Sami, R.; Khojah, E.; Iqbal, I.; Helal, M.; Hakeem, A.; Deng, Y.; Dai, R. Synthesis of Bimetallic Nanoparticles Loaded on to PNIPAM Hybrid Microgel and Their Catalytic Activity. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta-Ángeles, G.; Kanizsová, L.; Mielczarek, K.; Konefał, M.; Konefał, R.; Hodan, J.; Kočková, O.; Bednarz, S.; Beneš, H. Sustainable Aerogels Based on Biobased Poly(Itaconic Acid) for Adsorption of Cationic Dyes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 129727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, M.; Hamishehkar, H.; Arsalani, N.; Entezami, A.A. Surface Decoration of Magnetic Nanoparticles with Folate-Conjugated Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide-Co-Itaconic Acid): A Facial Synthesis of Dual-Responsive Nanocarrier for Targeted Delivery of Doxorubicin. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2016, 65, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anushree, C.; Krishna, D.N.G.; Philip, J. Synthesis of Ni Doped Iron Oxide Colloidal Nanocrystal Clusters Using Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide) Templates for Efficient Recovery of Cefixime and Methylene Blue. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 650, 129616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, R.; Matsuyama, T.; Ida, J. Effect of Immobilization Method and Particle Size on Heavy Metal Ion Recovery of Thermoresponsive Polymer/Magnetic Particle Composites. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 590, 124499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.L.; Hassabo, A.G. Core–Shell Titanium@ Silica Nanoparticles Impregnating in Poly(Itaconic Acid)/Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide) Microgel for Multifunctional Cellulosic Fabrics. J. Polym. Res. 2022, 29, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobeze, H.B.; Ma, J.; Leonik, F.M.; Kuroda, D.G. Bottom-up Approach to Assess the Molecular Structure of Aqueous Poly (N-Isopropylacrylamide) at Room Temperature via Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 11699–11710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saif, B.; Wang, C.; Chuan, D.; Shuang, S. Synthesis and Characterization of Fe3O4 Coated on APTES as Carriers for Morin-Anticancer Drug. J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 6, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Téllez, C.N.; Luque-Alcaraz, A.G.; Plascencia-Jatomea, M.; Higuera-Valenzuela, H.J.; Burgos-Hernández, M.; García-Flores, N.; Álvarez-Ramos, M.E.; Iriqui-Razcon, J.L.; Gonzalez, R.E.; Hernández-Abril, P.A. Synthesis and Characterization of a Fe3O4@PNIPAM-Chitosan Nanocomposite and Its Potential Application in Vincristine Delivery. Polymers 2021, 13, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, H.; Lin, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Ding, X. Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide) Modified Fe3O4@Au Nanoparticles with Magnetic and Temperature Responsive Properties. Mater. Lett. 2016, 169, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, P. Infrared and Raman spectroscopy: Principles and spectral interpretation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Interpreting Infrared Spectra. Specac Ltd. Available online: https://specac.com/theory-articles/interpreting-infra-red-spectroscopy/ (accessed on 17 June 2025).
- Gao, G.; Wang, L.; Cong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, R.; Chen, J.; Fu, J. Synergistic pH and Temperature-Driven Actuation of Poly(NIPAM-Co-DMAPMA)/Clay Nanocomposite Hydrogel Bilayers. Acs Omega 2018, 3, 17914–17921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deloney, M.A.; Smart, K.; Christiansen, B.; Panitch, A. 4260 Hollow, Degradable Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide) Derived Nanoparticles for the Delivery of Anti-Inflammatory Peptides for the Treatment and Prevention of Post-Traumatic Osteoarthritis. J. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2020, 4, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumari, S.; Cook, C.; Tarannum, F.; Vasquez-Guardado, E.S.; Ogunjimi, O.; Walters, K.B. Synthesis and Characterization of Temperature- and pH-Responsive PIA-b-PNIPAM@Fe3O4 Nanocomposites. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15131041
Kumari S, Cook C, Tarannum F, Vasquez-Guardado ES, Ogunjimi O, Walters KB. Synthesis and Characterization of Temperature- and pH-Responsive PIA-b-PNIPAM@Fe3O4 Nanocomposites. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(13):1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15131041
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumari, Swati, Cayla Cook, Fatema Tarannum, Erick S. Vasquez-Guardado, Olufemi Ogunjimi, and Keisha B. Walters. 2025. "Synthesis and Characterization of Temperature- and pH-Responsive PIA-b-PNIPAM@Fe3O4 Nanocomposites" Nanomaterials 15, no. 13: 1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15131041
APA StyleKumari, S., Cook, C., Tarannum, F., Vasquez-Guardado, E. S., Ogunjimi, O., & Walters, K. B. (2025). Synthesis and Characterization of Temperature- and pH-Responsive PIA-b-PNIPAM@Fe3O4 Nanocomposites. Nanomaterials, 15(13), 1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15131041







