High Anti-Swelling Zwitterion-Based Hydrogel with Merit Stretchability and Conductivity for Motion Detection and Information Transmission
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experiment Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of PVA/PSBMA-PA Hydrogel
3. Results and Discussion
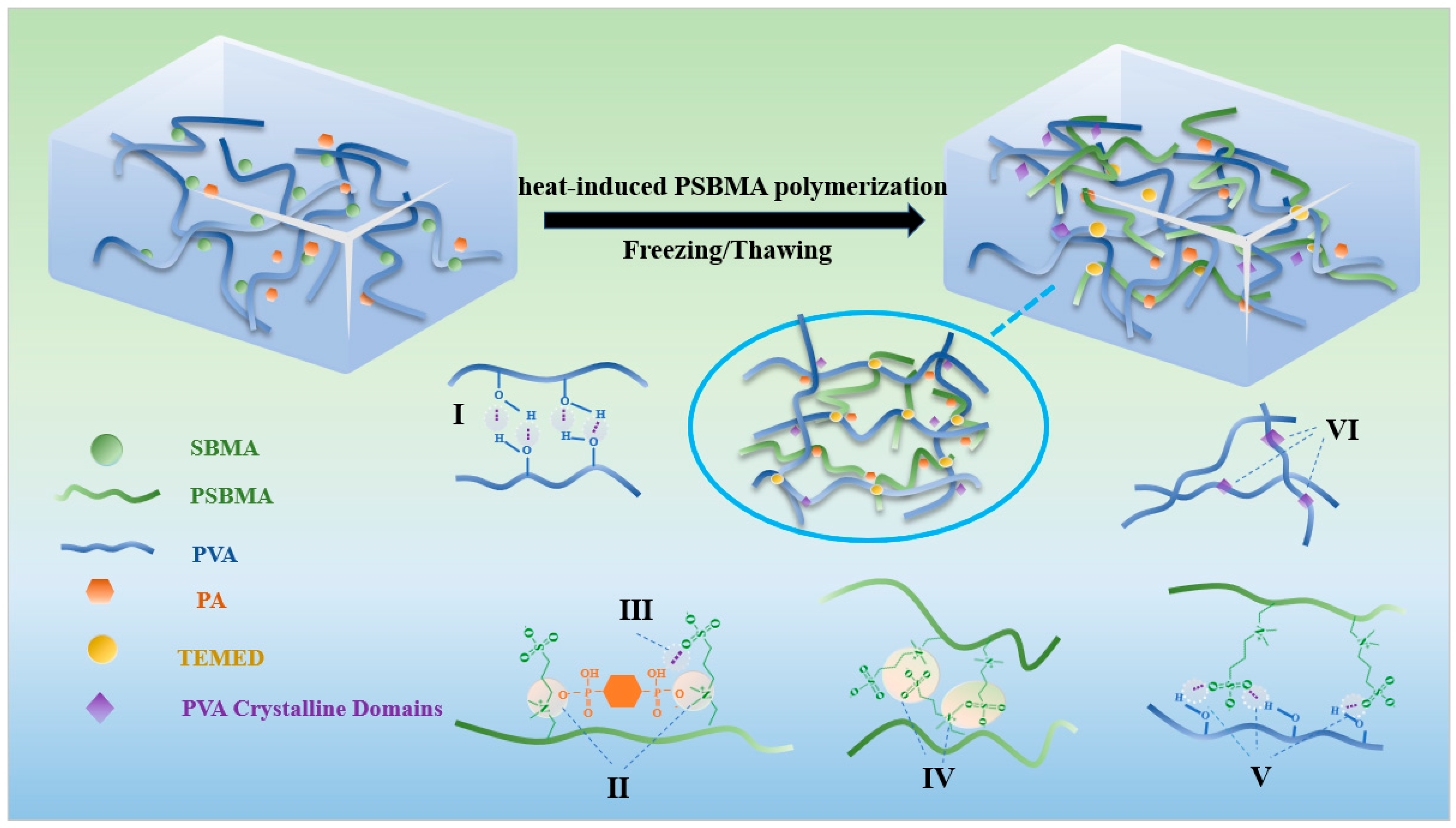
3.1. Characterization of Hydrogel
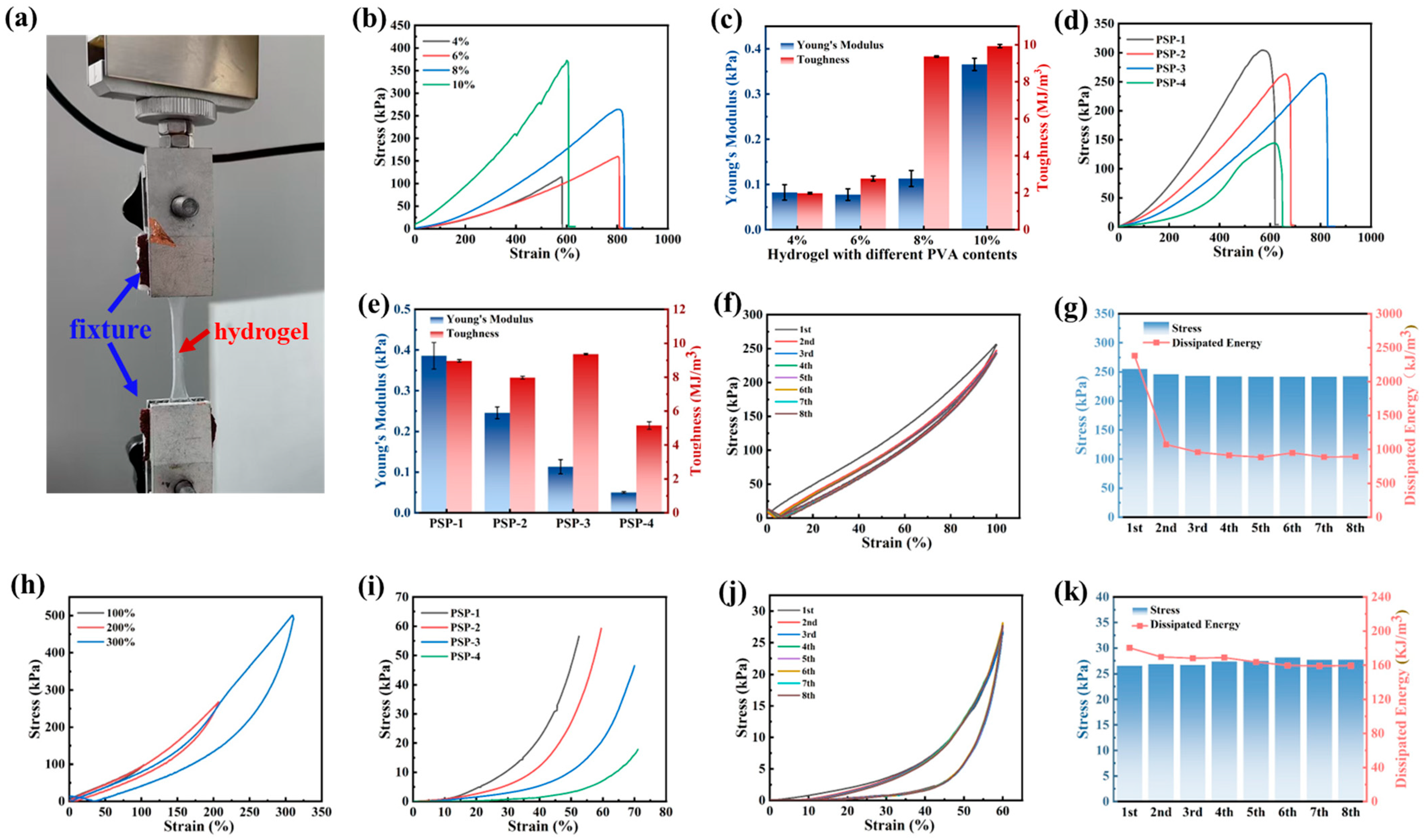
3.2. Mechanical Properties of PVA/PSBMA-PA Hydrogel
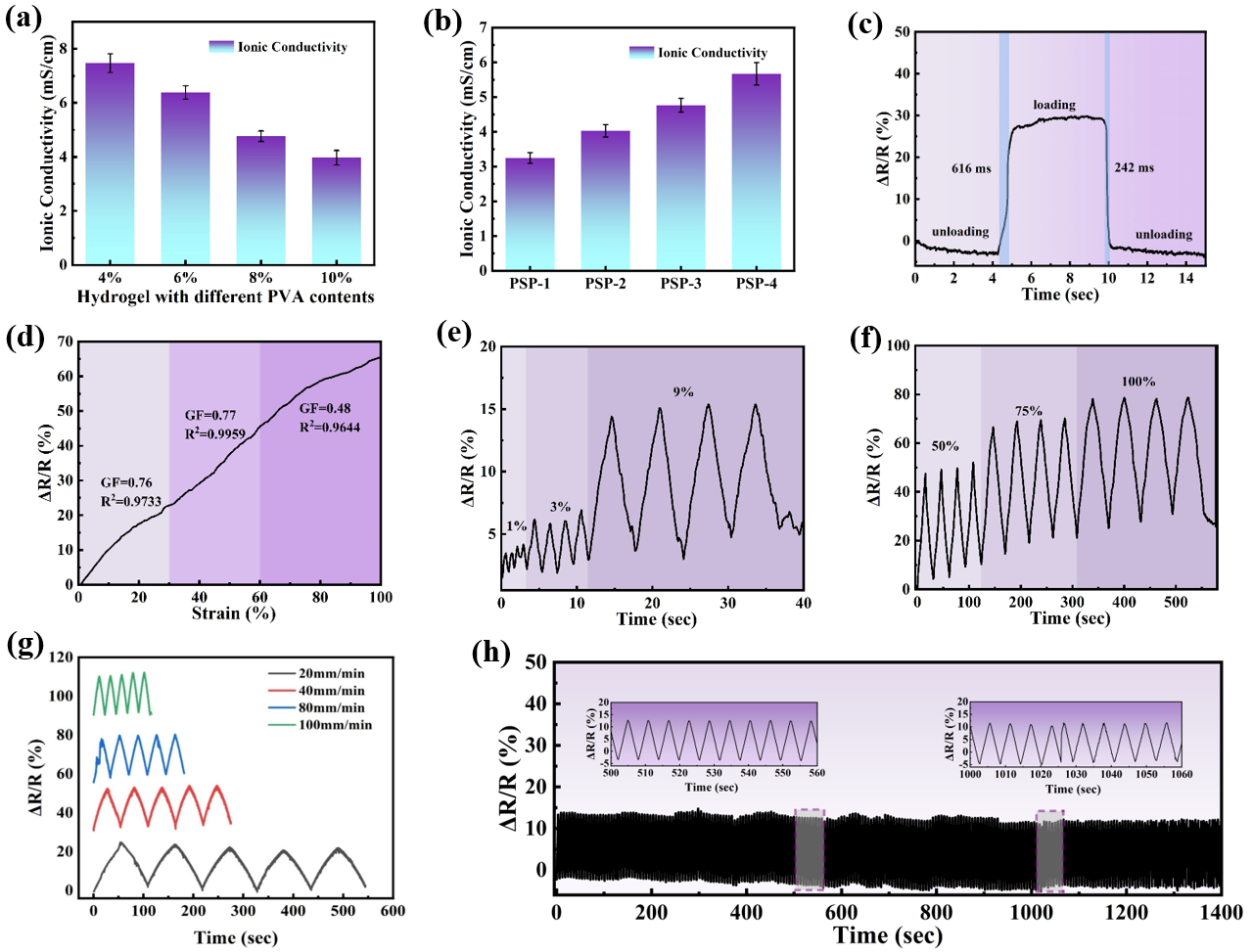
3.3. Electrical Properties of PVA/PSBMA-PA Hydrogel
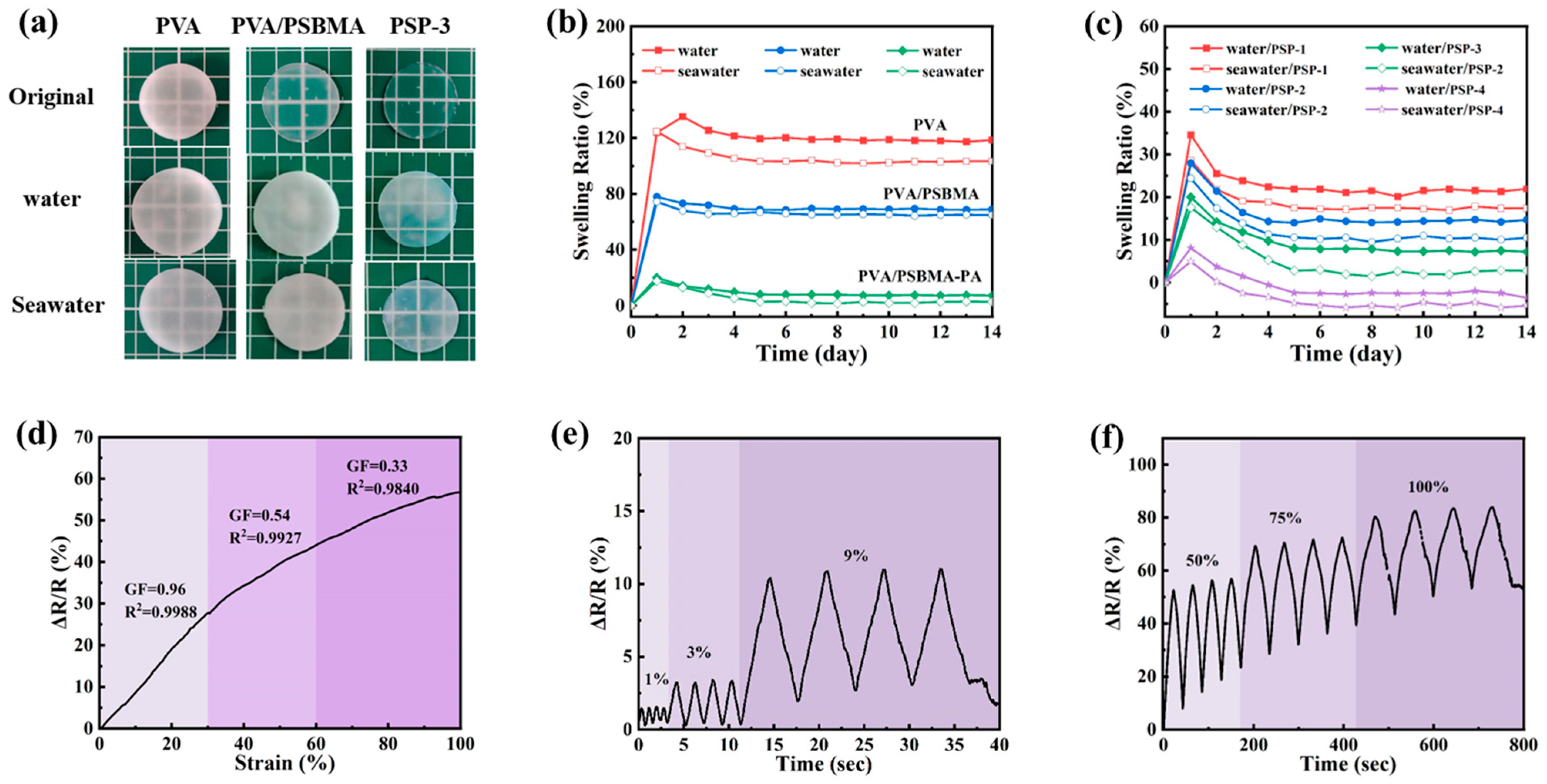
3.4. Anti-Swelling Properties
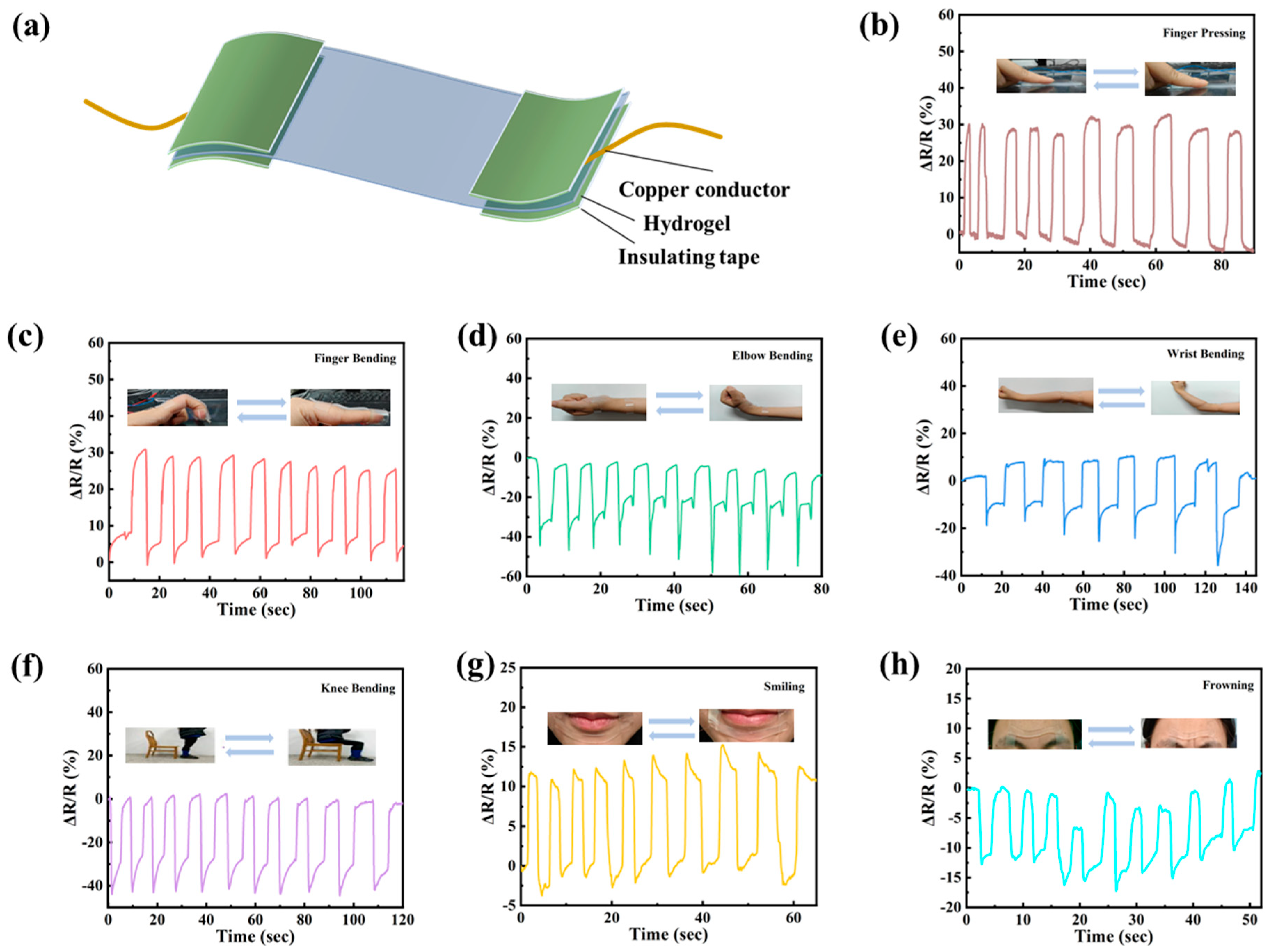
3.5. Human Motion Sensing of PVA/PSBMA-PA Hydrogel
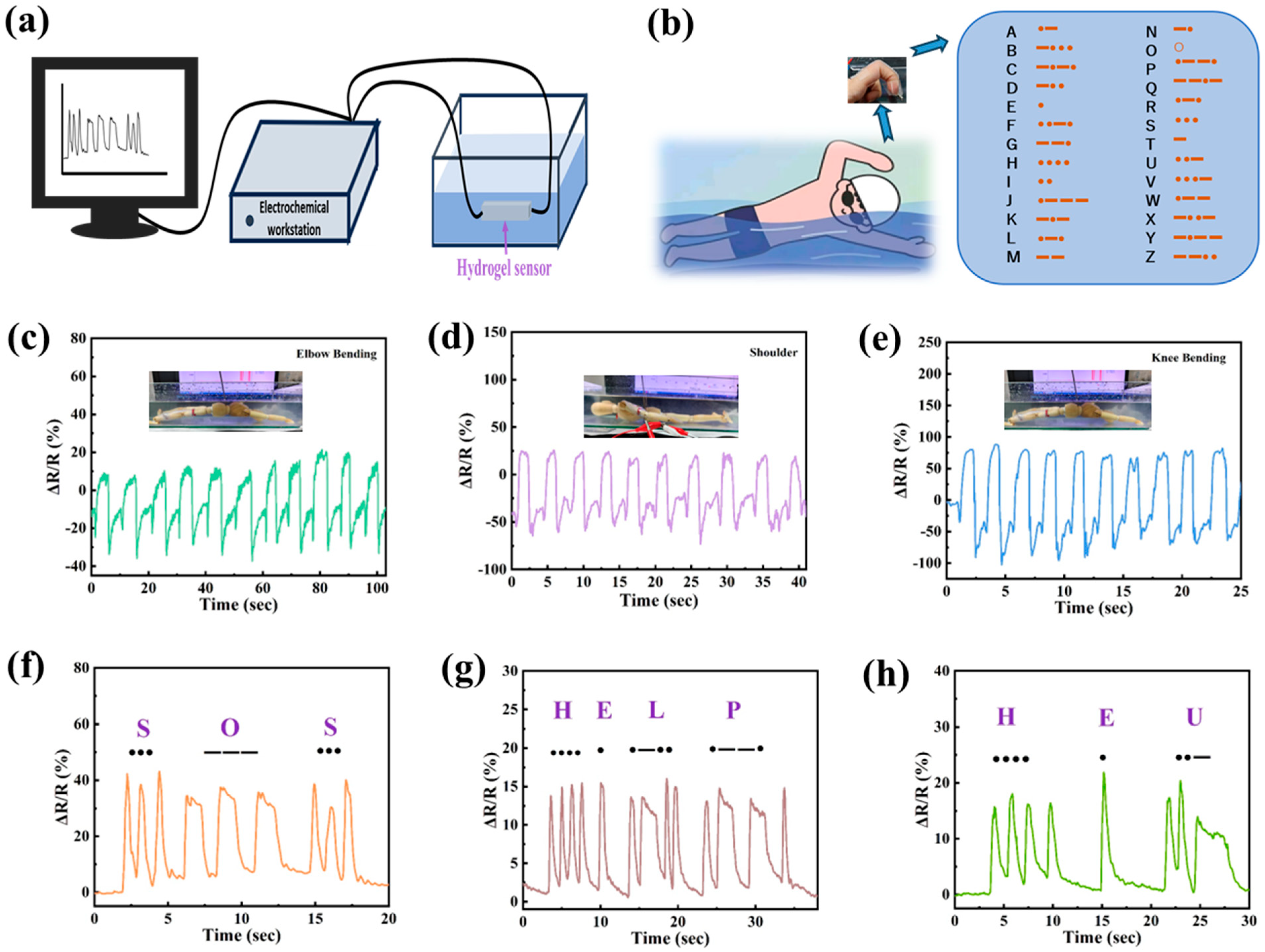
3.6. Underwater Motion Sensing of PVA/PSBMA-PA Hydrogel
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Z.; Qin, X.; Cao, L.; Li, J.; Wei, Y. Chitosan-enhanced nonswelling hydrogel with stable mechanical properties for long-lasting underwater sensing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 212, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, F.; Ge, G.; Qian, J.; Lin, J.; Chen, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhai, J. Gradient-Structured Ceramics with High Energy Storage Performance and Excellent Stability. Small 2023, 19, 2206125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Yu, J.X.; Guo, H.; Tian, S.; Long, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, L. Force-induced ion generation in zwitterionic hydrogels for a sensitive silent-speech sensor. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Duan, X.; Zhao, H.; Ma, S.; Ma, X.; Wang, N.; Zhang, A.L.; Wan, A.; Xia, Z.; Shou, W.; et al. A multifunctional flexible wearable hydrogel sensors with anti-swelling via supramolecular interactions for underwater motion detection and information transmission. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 504, 158700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wei, Q.; Wei, S.; Zhang, J.; Jin, Q.; Wang, G.; Hu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Kong, Y.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Acrylamide Hydrogel-Modified Silicon Nanowire Field-Effect Transistors for pH Sensing. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, B.; Yin, M.; Yang, K.; Wang, S.; Pei, Y.; Luo, R.; Zhou, S.; Li, H. Ultrafast Polymerization of a Self-Adhesive and Strain Sensitive Hydrogel-Based Flexible Sensor for Human Motion Monitoring and Handwriting Recognition. Polymers 2024, 16, 1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, K.; Ma, C.; Zhou, W.; Lin, T.; Xu, T.; Liu, X. Self-Healable PEDOT:PSS-PVA Nanocomposite Hydrogel Strain Sensor for Human Motion Monitoring. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Du, S.; Guo, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Tian, Y.; Sun, R.; Yang, P.; Wu, D.; Zhou, Z.; Li, R. Hydrogel Strain Sensors Based on Ordered Iron Nanowires for Human-Machine Interaction. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 38835–38842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.; Chen, O.; Edmunds, J.L.; Piech, D.K.; Maharbiz, M.M. Translational opportunities and challenges of invasive electrodes for neural interfaces. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 7, 424–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.B.; Zhu, K.H.; Ye, S.F.; Wang, Y.; Guo, L.; Tao, X.Y.; Guo, L.-T.; Fan, H.-L.; Liu, Z.-S.; Zhu, X.-B.; et al. A self-healing hydrogel electrolyte towards all-in-one flexible supercapacitors. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 20445–20460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ding, Q.; Wang, H.; Wu, Z.; Gui, X.; Li, C.; Hu, N.; Tao, K.; Wu, J. Engineering Smart Composite Hydrogels for Wearable Disease Monitoring. Nano-Micro Lett. 2023, 15, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, S.; Wan, C.; Wang, T.; Li, Q.; Chen, G.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Yang, H.; Liu, X.; Chen, X. Water-Resistant Conformal Hybrid Electrodes for Aquatic Endurable Electrocardiographic Monitoring. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2001496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Xu, B.; Feng, H.; Luo, Z.; Weng, M. PVA-based Hydrogel Materials for Underwater Energy Storage and Underwater Sensing. Chem. Asian J. 2024, 19, e202401109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Liao, Z.; Zhang, R.; Song, S.; Yang, Y.; Xie, D.; Liu, X.; Wei, L.; Liu, Y.; Song, Y. Cellulose nanofibers/liquid metal hydrogels with high tensile strength, environmental adaptability and electromagnetic shielding for temperature monitoring and strain sensors. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 348, 122788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Li, M.; Liu, C.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, L.; Li, J. Study on characteristics of the electric-field-sensitive hydrogel inspired by jelly in the ampullae of Lorenzini of elasmobranchs. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2022, 33, 3681–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Hsiao, L.Y.; Li, S.; Yang, H.; Ng, P.L.P.; Ding, M.; Truong, T.V.; Gao, S.-P.; Li, K.; Guo, Y.-X.; et al. 2D-Material-integrated hydrogels as multifunctional protective skins for soft robots. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 2065–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Xin, Z.; Yang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Xia, K.; Wang, B.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; et al. Ultrasensitive, Low-Voltage Operational, and Asymmetric Ionic Sensing Hydrogel for Multipurpose Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; He, R.; Liu, X.; Blennow, A.; Ye, Q.; Hong, B.; Li, X.; Lu, L.; Cui, B. “Soaking-in-water” strategy stimulated starch/poly(vinyl alcohol)-based flexible hydrogel with heterogeneous network for highly sensitive underwater wearable sensor. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2024, 41, e01049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.M.; Wu, B.H.; Sun, S.T.; Wu, P.Y. Interface Deformable, Thermally Sensitive Hydrogel-Elastomer Hybrid Fiber for Versatile Underwater Sensing. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 2000515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhao, C.; Guo, M.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, Z.; Xiang, D.; Li, H.; Wang, L. Underwater sensors based on dual dynamically crosslinked hydrogels with excellent anti-swelling and adhesive properties. Polymer 2024, 305, 127160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Hu, J.; Liu, L.; Wu, S.; Pan, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, P.; Zhang, Q.; Qiu, W.; et al. An underwater vest containing an antioxidant MXene hydrogel for sensitive recognition of fish locomotion. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2024, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; He, S.; Qin, Z.; Li, J.; Yao, F. Fast self-healing zwitterion nanocomposite hydrogel for underwater sensing. Compos. Commun. 2021, 26, 100784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Liu, D.; Chen, X.; Wang, D.; Dai, S.; Chen, F.; Xu, B.B. A Structural Gel Composite Enabled Robust Underwater Mechanosensing Strategy with High Sensitivity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2201396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Dong, Z.; Huang, Y.; Xu, J.; Lei, C. Tough, Anti-Swelling Supramolecular Hydrogels Mediated by Surfactant-Polymer Interactions for Underwater Sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 30385–30397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.K.; Lee, D.S.; Na, Y.H. Relationship between crosslinking structure and tensile properties of a double network nano-composite hydrogel. J. Polym. Res. 2023, 30, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Geng, L.; Wu, J.; Huang, A.; Peng, X. Highly strong and sensitive bilayer hydrogel actuators enhanced by cross-oriented nanocellulose networks. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 225, 109494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Kong, Y.; Han, K.; Hao, H.; Shi, B. A physically cross-linked self-healable double-network polymer hydrogel as a framework for nanomaterial. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 15127–15135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.; Babhadiashar, N.; Barrett-Catton, E.; Asuri, P. Role of Nanoparticle-Polymer Interactions on the Development of Double-Network Hydrogel Nanocomposites with High Mechanical Strength. Polymers 2020, 12, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. Preparation of Nanocellulose Whisker/Polyacrylamide/Xanthan Gum Double Network Conductive Hydrogels. Coatings 2023, 13, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, F.; Shen, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, D. One-Step Soaking Strategy toward Anti-Swelling Hydrogels with a Stiff “Armor”. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2206242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, M.; Du, Y.; Ding, X.; Xiao, C.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhuo, Y.; Zheng, K.; Liu, X.; et al. Self-healing liquid metal hydrogel for human-computer interaction and infrared camouflage. Mater. Horiz. 2023, 10, 2945–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elessawy, N.A.; Alhamzani, A.G.; Almahmoud, S.A.; Hsiao, B.S. Evaluation, optimization study, and life cycle assessment of novel eco-friendly PVA-based nanocomposite hydrogel adsorbents for methylene blue and paracetamol removal. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 285, 117123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, H.Y.; Bei, H.P.; Zhao, X. Underwater and wet adhesion strategies for hydrogels in biomedical applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 133372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, K.; Rajhans, A.; Kandasubramanian, B. Starch/PVA hydrogels for oil/water separation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 32013–32028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Qiu, J.; Yang, C.; Zang, L.; Zhang, G.; Sakai, E. High-Performance PVA/PEDOT:PSS Hydrogel Electrode for All-Gel-State Flexible Supercapacitors. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2000919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yan, Z.; Yang, L.; Meng, L. Mechanical and electrical properties of a modified carbon nanotube-mediated hydrogel as a strain sensor. New J. Chem. 2023, 47, 10409–10414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.J.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Q. Covalent/crystallite cross-linked co-network hydrogels: An efficient and simple strategy for mechanically strong and tough hydrogels. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 301, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Zhang, E.; Shi, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhu, H.; Gallagher, S.J.; Fischer, S.; Rigney, J.; Kim, E.; Cao, Z. Hydrogel Coating with Antisediment Properties for Marine Antifouling Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 27908–27916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wang, S.; Mao, J.; Guo, Z.; Hu, Y. Dual network zwitterionic hydrogels with excellent mechanical properties, anti-swelling, and shape memory behaviors. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 197, 112373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z.; Song, L.; Niu, L.; Wang, R. Self-adhesive, ionic conductive, environmentally tolerant, and antibacterial phytic acid-reinforced zwitterionic hydrogels as flexible sensor applications. Appl. Mater. Today 2024, 37, 102147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, P.; Kan, L.; Wang, G.; Ma, N. One-Step Preparation of a Highly Stretchable, Conductive, and Transparent Poly(vinyl alcohol)-Phytic Acid Hydrogel for Casual Writing Circuits. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 32441–32448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agudelo, J.I.D.; Badano, J.M.; Rintoul, I. Kinetics and thermodynamics of swelling and dissolution of PVA gels obtained by freeze-thaw technique. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 216, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Han, H.; Xu, L.; Gao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Jiang, Z.; De Schutter, G. The improvement of freezing-thawing resistance of concrete by cellulose/polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 291, 123274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, J.L.; Lowman, A.M.; Palmese, G.R. The role of crystallization and phase separation in the formation of physically cross-linked PVA hydrogels. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J.; Ng, P.F.; Fei, B. High-strength hydrogels: Microstructure design, characterization and applications. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2018, 56, 1325–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, J.; Luo, J.; Gao, Q.; Mao, A.; Li, J. Research progress on double-network hydrogels. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 29, 102757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelnia, H.; Ensandoost, R.; Moonshi, S.S.; Gavgani, J.N.; Vasafi, E.I.; Ta, H.T. Freeze/thawed polyvinyl alcohol hydrogels: Present, past and future. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 164, 110974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, S.; Ma, Y.; Wei, H.; Lü, S. An Anti-Swellable Hydrogel Strain Sensor for Underwater Motion Detection. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2107404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, C.; Yang, X.; Wei, J.; Xia, Y.; Gong, X.; Suo, Z. Hydrogel Paint. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1903062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xie, Q.; Pan, J.; Ma, C.; Zhang, G. Strong-adhesion and nonfouling self-generating zwitterionic Janus hydrogel paint. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 485, 149959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Li, J.; Ding, Q.; Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Wu, J. Functionalized Hydrogel-Based Wearable Gas and Humidity Sensors. Nano-Micro Lett. 2023, 15, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Luo, B.; Sun, Z.; Ren, X.; Xu, J. Anti-swelling hydrogel with three-dimensional print for underwater communication. Mater. Today Commun. 2025, 46, 112605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Lin, X.; Yu, M.; Mondal, A.K.; Huang, L.; Chen, L.; Wu, H. Antiswellable, Conductive, and Recyclable Coacervate Polyacrylamide/Tannic Acid Composite Hydrogel for Underwater Wearable Sensors. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 6, 806–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Guan, Y.; Xiao, C.; Fan, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Yu, P.; Tu, L.; Tan, G.; Zhai, J.; et al. Tough and Highly Efficient Underwater Self-Repairing Hydrogels for Soft Electronics. Small Methods 2022, 6, 2101513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhou, G.; Peng, M. Superhydrophobic, Anti-Freezing and Multi-Cross-Linked Wearable Hydrogel Strain Sensor for Underwater Gesture Recognition. ACS Sens. 2024, 9, 4617–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yang, L.; Dou, B.; Lan, J.; Shang, J.; Lin, S. Zwitterionic hydrogel-coated cotton fabrics with underwater superoleophobic, self-healing and anti-fouling performances for oil-water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 279, 119789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, H.Q.; Liu, C.L.; Bao, W.; Hu, Y.J.; Maimaitiyiming, X. High toughness, high stability and low hysteresis PVA/HPMC/PA/SBMA/ZnCl2 conductive hydrogels for wearable flexible electronics for multifunctional sensors and supercapacitors. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 361, 123644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.X.; Zheng, D.Y.; Long, B.C.; Chen, Z.W.; Zhu, J.D.; Gao, Q. Anti-swelling and adhesive γ-PGA/PVA/PEDOT:PSS/TA composite conductive hydrogels for underwater wearable sensors. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 201, 122590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.L.; Liu, L.R.; Ge, Z.; Ren, H.Y.; Wang, W.T.; Zhu, M.Y.; Luo, C.H. Coordination hydrogel enables an extremely stable, highly sensitive, self-healable and robust underwater sensor. Eur. Polym. J. 2025, 233, 114010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.L.; Zheng, Y.; Feng, Y.Q.; Yang, W.H.; Pu, J.J.; Ren, T.; Hu, S.C.; Wu, Y.P. Anti-freezing and conductive hydrogel with water-resistant properties for flexible underwater sensors. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 702, 135000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.D.; Wang, Y.M.; Li, H.; Hou, Z.Q.; Miao, X.; Miao, G.; Li, F.C.; Lu, J.W.; Ren, G.A.; Zhu, X.T. Janus Hydrogel with Both Sticky Adhesion and Slippery Antifouling Properties for Strain Sensing. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2024, 6, 2339–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, K.J.; Xiang, J.; Liu, Y.; Song, C.L.; Mu, Y.T.; Yao, T.; Zhao, K.; Gu, T.F.; Jia, P.X.; Zhang, W.Y. Fabrication of a high strength, swelling resistance, and conductive hydrogel for flexible underwater sensor via ketalization. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 511, 161885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Sha, D.; Sun, L.; Chen, L.; Xu, J.D.; Shi, K.; Yu, C.; Wang, B.L.; Ji, X.L. Charged group-modified poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels: Preparation and antibacterial property. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 154, 104635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Q.; Liu, J.; Chen, R.; Liu, Q.; Yu, J.; Zhu, J.; Liu, P. High Anti-Swelling Zwitterion-Based Hydrogel with Merit Stretchability and Conductivity for Motion Detection and Information Transmission. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15131027
Zheng Q, Liu J, Chen R, Liu Q, Yu J, Zhu J, Liu P. High Anti-Swelling Zwitterion-Based Hydrogel with Merit Stretchability and Conductivity for Motion Detection and Information Transmission. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(13):1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15131027
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Qingyun, Jingyuan Liu, Rongrong Chen, Qi Liu, Jing Yu, Jiahui Zhu, and Peili Liu. 2025. "High Anti-Swelling Zwitterion-Based Hydrogel with Merit Stretchability and Conductivity for Motion Detection and Information Transmission" Nanomaterials 15, no. 13: 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15131027
APA StyleZheng, Q., Liu, J., Chen, R., Liu, Q., Yu, J., Zhu, J., & Liu, P. (2025). High Anti-Swelling Zwitterion-Based Hydrogel with Merit Stretchability and Conductivity for Motion Detection and Information Transmission. Nanomaterials, 15(13), 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15131027







