Nanovesicles and Human Skin Interaction: A Comparative Ex-Vivo Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Nanovesicular Systems
2.2.1. Microfluidic Approach
2.2.2. Bulk Approach
2.3. Vesicle Characterization
2.3.1. Photon Correlation Spectroscopy (PCS)
2.3.2. Cryogenic Electron Microscopy (Cryo-EM)
2.3.3. Small Angle X-Ray Scattering (SAXS)
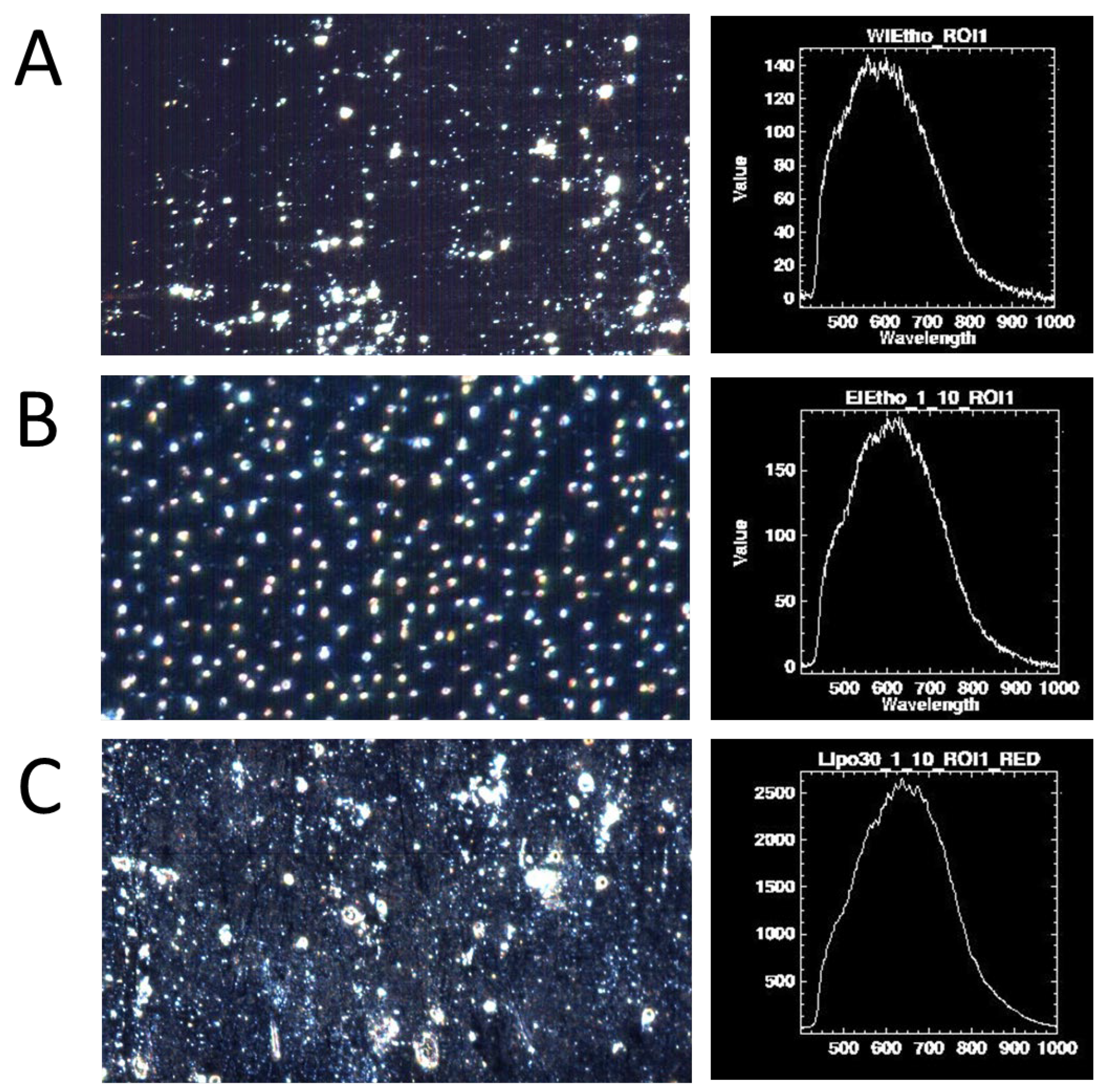
2.3.4. Hyperspectral Dark-Field Microscopy
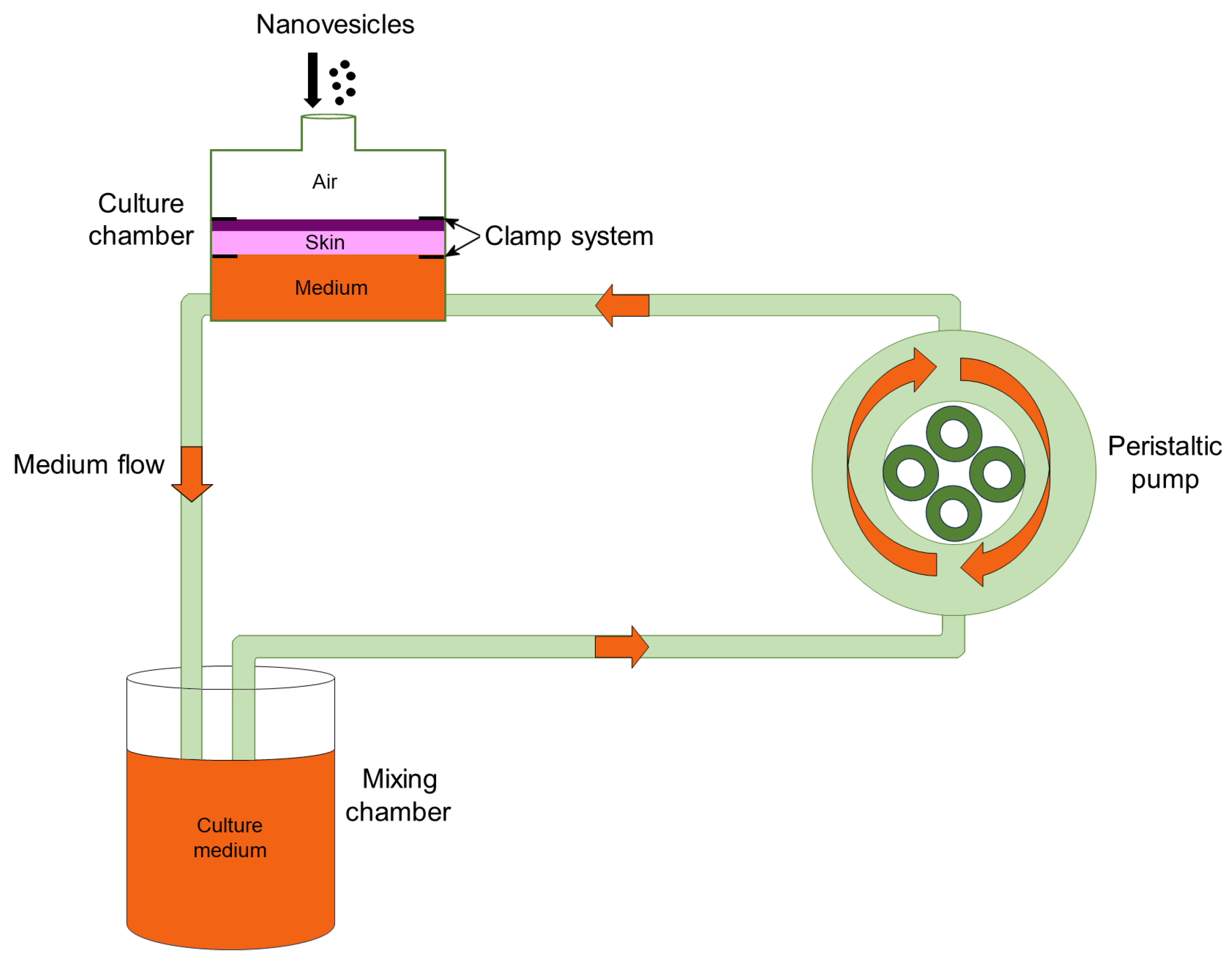
2.4. Human Skin Sampling
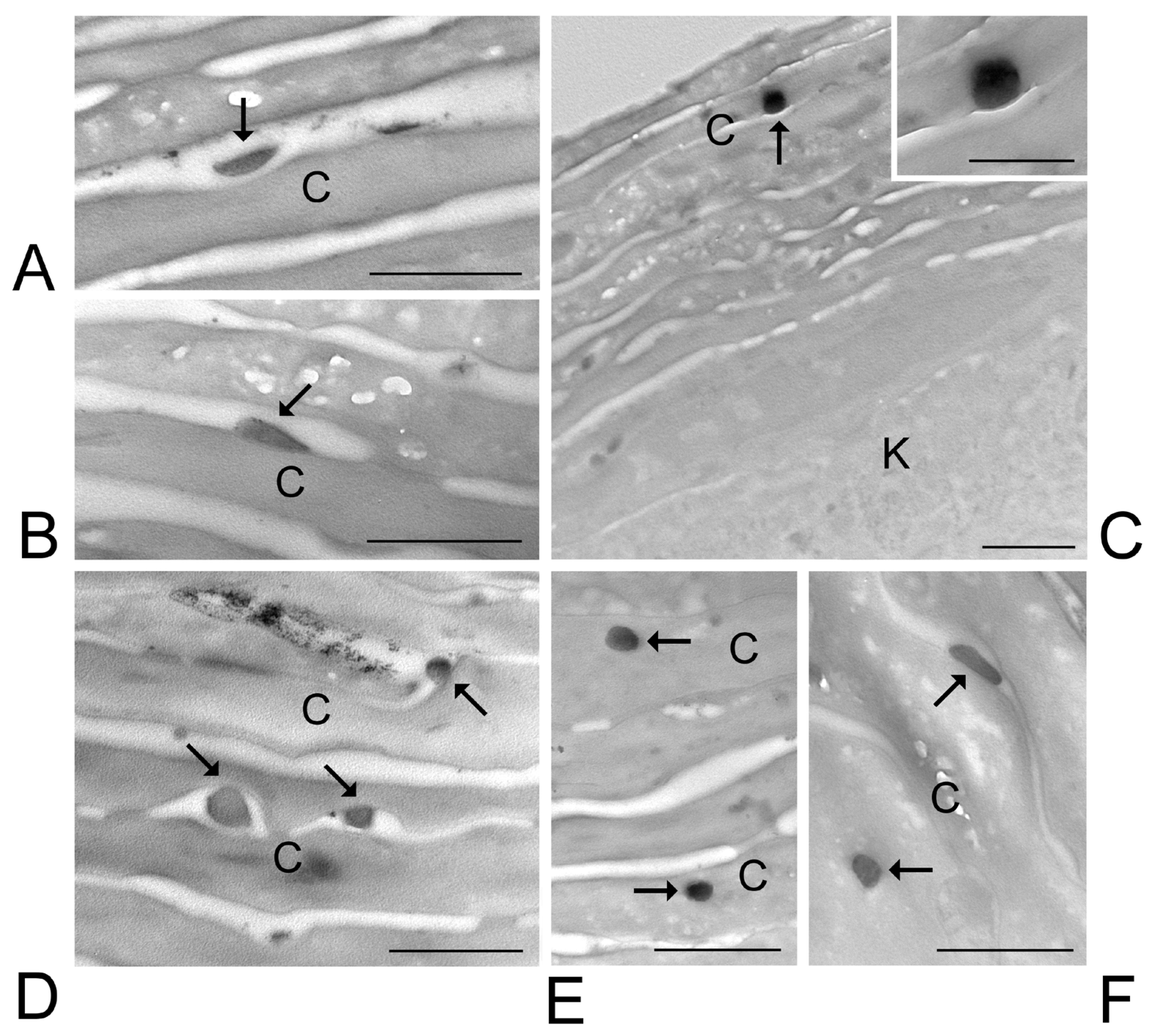
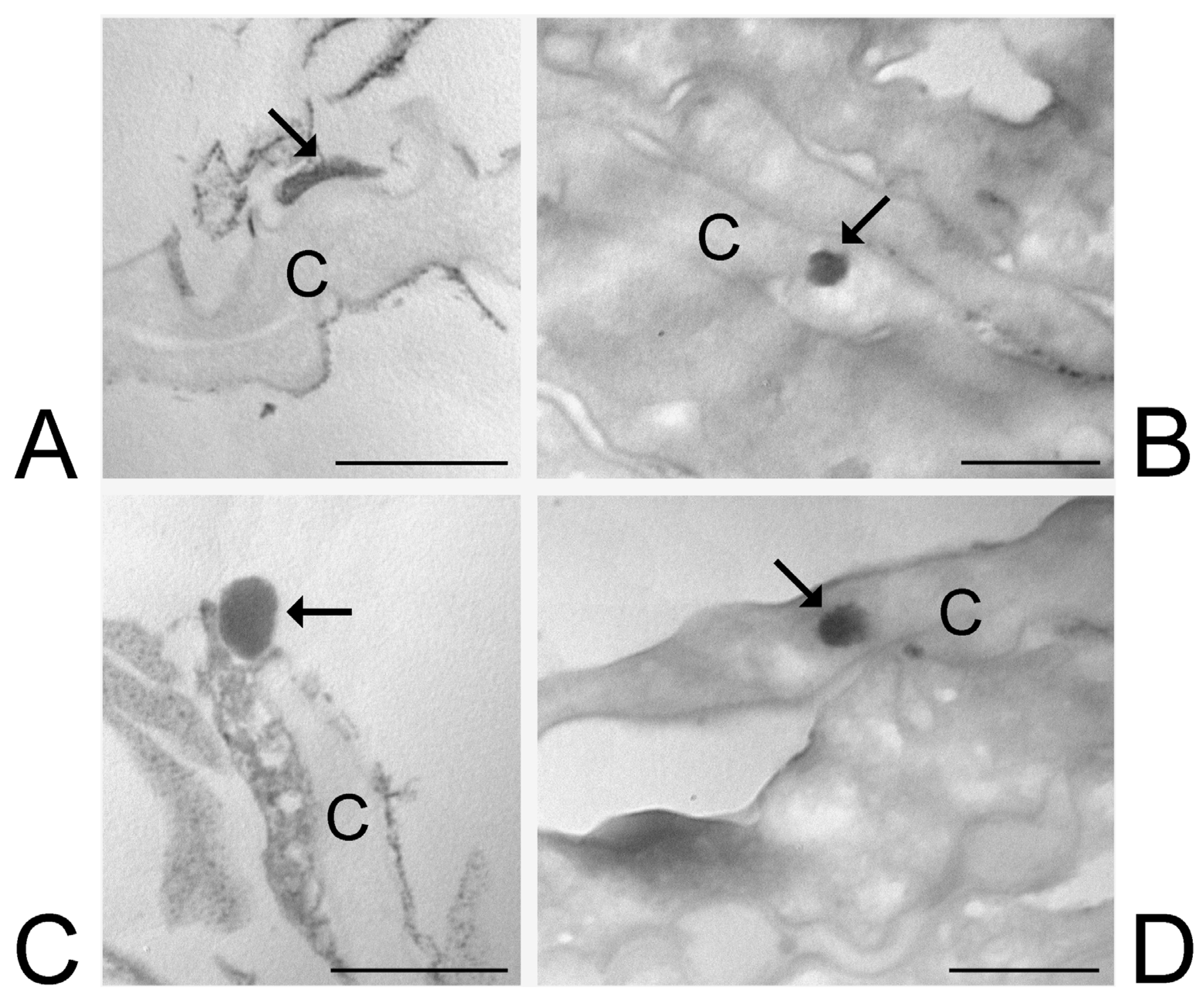
2.5. Skin Treatment and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Preparation of Nanovesicles
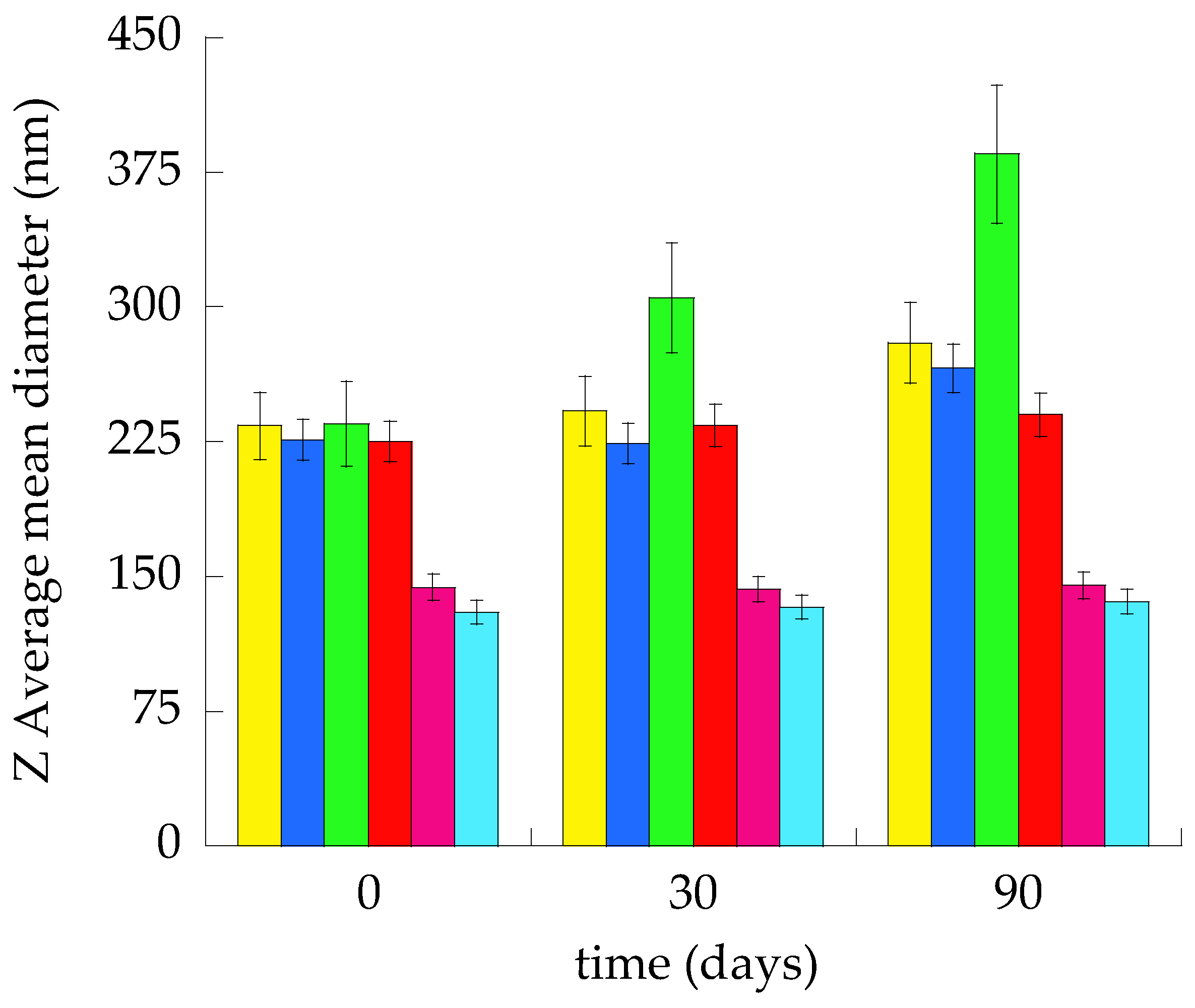
3.2. Size Distribution
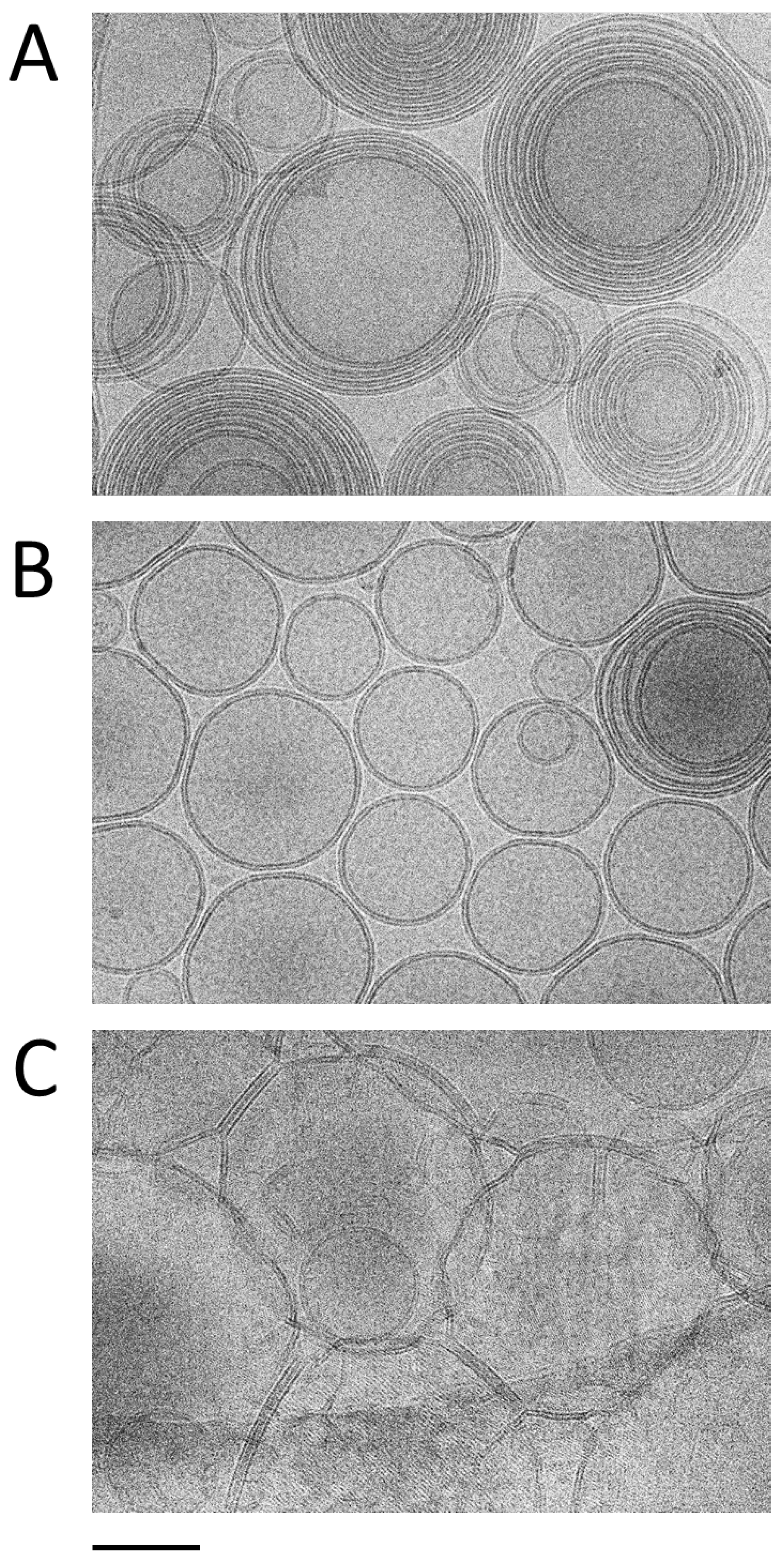
3.3. Morphological Characterization
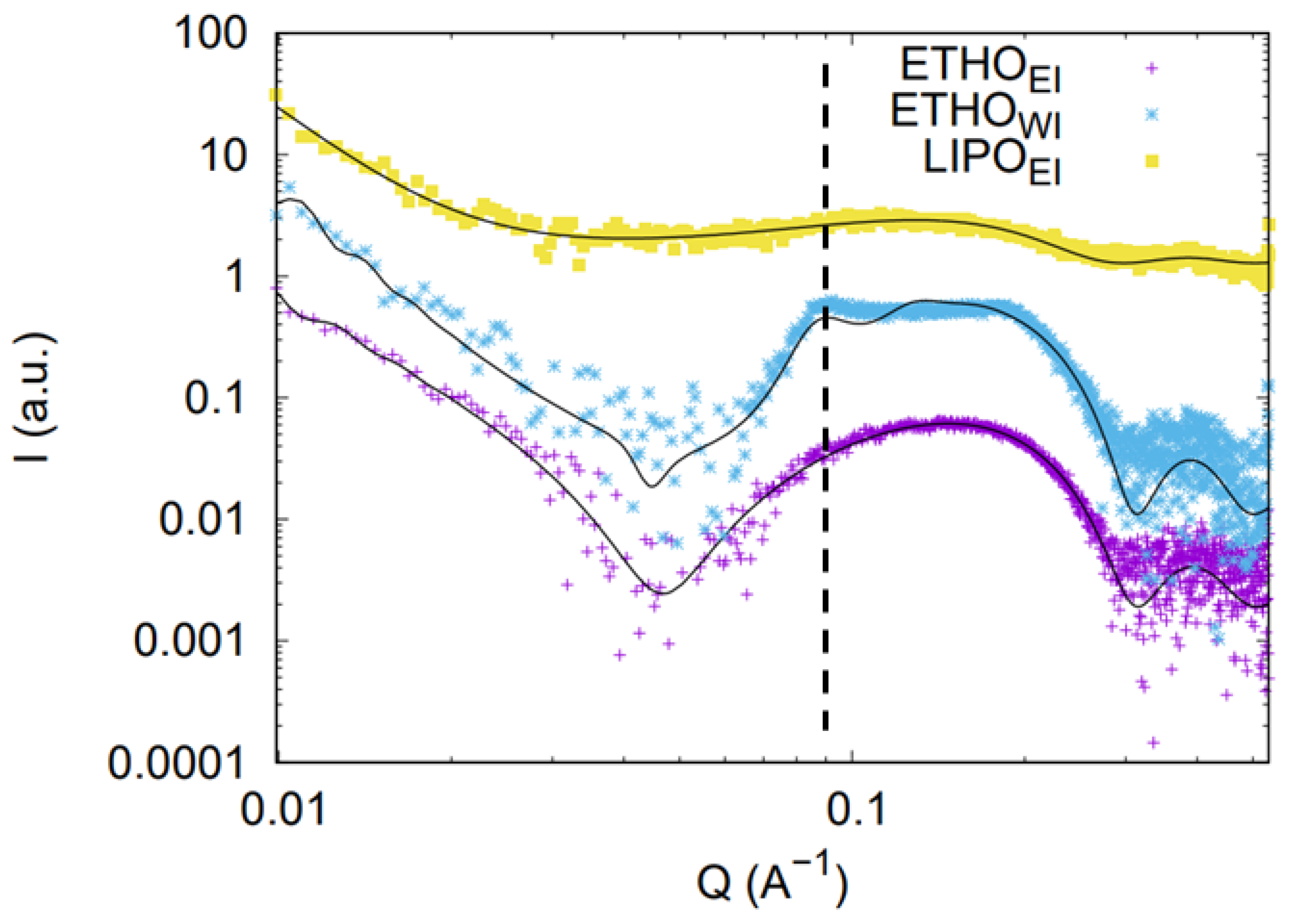
3.4. SAXS Study
3.5. Hyperspectral Dark-Field Microscopy Study
3.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy Analysis of Skin Treated with ETHO and LIPO
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LIPO | Liposomes |
| ETHO | Ethosomes |
| WI | Water injection |
| EI | Ethanol injection |
| PC | Phosphatidylcholine |
| PCS | Photon Correlation Spectroscopy |
| Cryo-EM | Cryogenic Electron Microscopy |
| SAXS | Small Angle X-Ray Scattering |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| AP | Aqueous Phase |
| LP | Lipid Phase |
| TFR | Total Flow Rate |
| FRR | Flow Rate Ratio |
References
- Valacchi, G.; Sticozzi, C.; Pecorelli, A.; Cervellati, F.; Cervellati, C.; Maioli, E. Cutaneous Responses to Environmental Stressors. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1271, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravitz, L. Skin. Nature 2018, 563, S83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, A.; Guttman-Yassky, E. Topical Agents for the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 15, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambunlertchai, S.; Geary, S.M.; Salem, A.K. Skin Penetration Enhancement Strategies Used in the Development of Melanoma Topical Treatments. AAPS J. 2021, 23, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Zaafarany, G.M.; Nasr, M. Insightful Exploring of Advanced Nanocarriers for the Topical/Transdermal Treatment of Skin Diseases. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2021, 26, 1136–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacko, I.A.; Ghate, V.M.; Dsouza, L.; Lewis, S.A. Lipid Vesicles: A Versatile Drug Delivery Platform for Dermal and Transdermal Applications. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 195, 111262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhwa, S.; Garg, V.; Gulati, M.; Kapoor, B.; Singh, S.K.; Mittal, N. Nanovesicles for Nanomedicine: Theory and Practices. In Pharmaceutical Nanotechnology; Methods in Molecular Biology Volume 2000; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kuhad, A.; Bhandari, R. Novel Nanotechnological Approaches for Treatment of Skin-Aging. J. Tissue Viability 2022, 31, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, U.; Jain, K. Dermal and Transdermal Drug Delivery through Vesicles and Particles: Preparation and Applications. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2022, 12, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arana-Linares, A.C.; Barrera-Ocampo, A.; Salamanca, C.H. Determination of the Critical Aggregation Concentration of Phospholipids Widely Used in Nanoliposomal Development from Different Experimental Methodologies. J. Mol. Liq. 2025, 417, 126677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touitou, E.; Dayan, N.; Bergelson, L.; Godin, B.; Eliaz, M. Ethosomes—Novel Vesicular Carriers for Enhanced Delivery: Characterization and Skin Penetration Properties. J. Control. Release 2000, 65, 403–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Altamimi, M.A.; Afzal, O.; Altamimi, A.S.A.; Ramzan, M.; Khuroo, T. Mechanistic of Vesicular Ethosomes and Elastic Liposomes on Permeation Profiles of Acyclovir across Artificial Membrane, Human Cultured EpiDerm, and Rat Skin: In Vitro-Ex Vivo Study. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asadi, P.; Mehravaran, A.; Soltanloo, N.; Abastabar, M.; Akhtari, J. Nanoliposome-Loaded Antifungal Drugs for Dermal Administration: A Review. Curr. Med. Mycol. 2021, 7, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhou, J.; Cheng, H.W.; Liu, Y.Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Novel Colchicine Ethosomes Cataplasm for the Treatment of Acute Gouty Arthritis. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2025, 254, 114776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragicevic, N.; Maibach, H.I. Liposomes and Other Nanocarriers for the Treatment of Acne Vulgaris: Improved Therapeutic Efficacy and Skin Tolerability. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musielak, E.; Krajka-Kuźniak, V. Liposomes and Ethosomes: Comparative Potential in Enhancing Skin Permeability for Therapeutic and Cosmetic Applications. Cosmetics 2024, 11, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, M.Y.; Kong, Y.L.; Burgess, K.; Wong, W.F.; Sethi, G.; Looi, C.Y. Recent Development of Nanomaterials for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari, A.; Daneshamouz, S.; Ghasemiyeh, P.; Mohammadi-Samani, S. Ethosomes as Dermal/Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems: Applications, Preparation and Characterization. J. Liposome Res. 2023, 33, 34–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natsheh, H.; Vettorato, E.; Touitou, E. Ethosomes for Dermal Administration of Natural Active Molecules. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 2338–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godin, B.; Touitou, E. Ethosomes: New Prospects in Transdermal Delivery. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carrier Syst. 2003, 20, 63–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva-Santos, A.C.; Silva, A.L.; Guerra, C.; Peixoto, D.; Pereira-Silva, M.; Zeinali, M.; Mascarenhas-Melo, F.; Castro, R.; Veiga, F. Ethosomes as Nanocarriers for the Development of Skin Delivery Formulations. Pharm. Res. 2021, 38, 947–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nainwal, N.; Jawla, S.; Singh, R.; Saharan, V.A. Transdermal Applications of Ethosomes—A Detailed Review. J. Liposome Res. 2019, 29, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, B.; Nag, O.K.; Rogers, K.E.; Delehanty, J.B. Recent Progress in Bioconjugation Strategies for Liposome-Mediated Drug Delivery. Molecules 2020, 25, 5672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyarzún, P.; Gallardo-Toledo, E.; Morales, J.; Arriagada, F. Transfersomes as Alternative Topical Nanodosage Forms for The Treatment of Skin Disorders. Nanomedicine 2021, 16, 2465–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.B.; Macedo, A.S.; Dias-Ferreira, J.; Cano, A.; Zielińska, A.; Matos, C.M. Elastic and Ultradeformable Liposomes for Transdermal Delivery of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Zaafarany, G.M.; Awad, G.A.S.; Holayel, S.M.; Mortada, N.D. Role of Edge Activators and Surface Charge in Developing Ultradeformable Vesicles with Enhanced Skin Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 397, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhigaltsev, I.V.; Tam, Y.K.; Leung, A.K.K.; Cullis, P.R. Production of Limit Size Nanoliposomal Systems with Potential Utility as Ultra-Small Drug Delivery Agents. J. Liposome Res. 2016, 26, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardo, D.; Kiselev, M.A. Methods of Liposomes Preparation: Formation and Control Factors of Versatile Nanocarriers for Biomedical and Nanomedicine Application. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Large, D.E.; Abdelmessih, R.G.; Fink, E.A.; Auguste, D.T. Liposome Composition in Drug Delivery Design, Synthesis, Characterization, and Clinical Application. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 176, 113851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Marioli, M.; Zhang, K. Analytical Characterization of Liposomes and Other Lipid Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 192, 113642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzyhovskyi, V.; Romani, A.; Pula, W.; Bondi, A.; Ferrara, F.; Melloni, E.; Gonelli, A.; Pozza, E.; Voltan, R.; Sguizzato, M.; et al. Characterization Methods for Nanoparticle-Skin Interactions: An Overview. Life 2024, 14, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendas, E.R.; Tadros, M.I. Enhanced Transdermal Delivery of Salbutamol Sulfate via Ethosomes. AAPS PharmSciTech 2007, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soni, K.; Mujtaba, A.; Akhter, M.H.; Zafar, A.; Kohli, K. Optimisation of Ethosomal Nanogel for Topical Nano-CUR and Sulphoraphane Delivery in Effective Skin Cancer Therapy. J. Microencapsul. 2020, 37, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Tiwary, A.K.; Sapra, B.; Jain, N.K. Formulation and Evaluation of Ethosomes for Transdermal Delivery of Lamivudine. AAPS PharmSciTech 2007, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, V.; Mishra, D.; Jain, N.K. Melatonin Loaded Ethanolic Liposomes: Physicochemical Characterization and Enhanced Transdermal Delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 67, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, E.; Calderan, L.; Galvan, A.; Cappellozza, E.; Drechsler, M.; Mariani, P.; Pepe, A.; Sguizzato, M.; Vigato, E.; Dalla Pozza, E.; et al. Ex Vivo Evaluation of Ethosomes and Transethosomes Applied on Human Skin: A Comparative Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulbaqi, I.M.; Darwis, Y.; Khan, N.A.K.; Assi, R.A.; Khan, A.A. Ethosomal Nanocarriers: The Impact of Constituents and Formulation Techniques on Ethosomal Properties, in Vivo Studies, and Clinical Trials. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 2279–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappellozza, E.; Zanzoni, S.; Malatesta, M.; Calderan, L. Integrated Microscopy and Metabolomics to Test an Innovative Fluid Dynamic System for Skin Explants In Vitro. Microsc. Microanal. 2021, 27, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, M.; Esposito, E.; Sguizzato, M.; Lacavalla, M.A.; Drechsler, M.; Valacchi, G.; Zancanaro, C.; Malatesta, M. Formulative Study and Intracellular Fate Evaluation of Ethosomes and Transethosomes for Vitamin D3 Delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecora, R. Dynamic Light Scattering Measurement of Nanometer Particles in Liquids. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2000, 2, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amenitsch, H.; Bernstorff, S.; Kriechbaum, M.; Lombardo, D.; Mio, H.; Rappolt, M.; Laggner, P. Performance and First Results of the ELETTRA High-Flux Beamline for Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1997, 30, 872–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallan, S.S.; Sguizzato, M.; Mariani, P.; Cortesi, R.; Huang, N.; Simelière, F.; Marchetti, N.; Drechsler, M.; Ruzgas, T.; Esposito, E. Design and Characterization of Ethosomes for Transdermal Delivery of Caffeic Acid. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sguizzato, M.; Mariani, P.; Spinozzi, F.; Benedusi, M.; Cervellati, F.; Cortesi, R.; Drechsler, M.; Prieux, R.; Valacchi, G.; Esposito, E. Ethosomes for Coenzyme Q10 Cutaneous Administration: From Design to 3D Skin Tissue Evaluation. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sguizzato, M.; Ferrara, F.; Hallan, S.S.; Baldisserotto, A.; Drechsler, M.; Malatesta, M.; Costanzo, M.; Cortesi, R.; Puglia, C.; Valacchi, G.; et al. Ethosomes and Transethosomes for Mangiferin Transdermal Delivery. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsairat, H.; Khater, D.; Sayed, U.; Odeh, F.; Al Bawab, A.; Alshaer, W. Liposomes: Structure, Composition, Types, and Clinical Applications. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Kang, B.; Yang, E.; Kim, K.; Kwak, M.K.; Chang, P.S.; Jung, H.S. Precise Control of Liposome Size Using Characteristic Time Depends on Solvent Type and Membrane Properties. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, K.; Fan, Z.H. Mixing in Microfluidic Devices and Enhancement Methods. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2015, 25, 094001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, E.; Pozza, E.; Contado, C.; Pula, W.; Bortolini, O.; Ragno, D.; Toldo, S.; Casciano, F.; Bondi, A.; Zauli, E.; et al. Microfluidic Fabricated Liposomes for Nutlin-3a Ocular Delivery as Potential Candidate for Proliferative Vitreoretinal Diseases Treatment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 3513–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondi, A.; Pula, W.; Benedusi, M.; Trinchera, G.; Baldisserotto, A.; Manfredini, S.; Ortore, M.G.; Pepe, A.; Mariani, P.; Stuart, M.C.A.; et al. Gossypin-Loaded Ethosome Gel for Cutaneous Administration: A Preliminary Study on Melanoma Cells. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Păvăloiu, R.D.; Sha’at, F.; Bubueanu, C.; Deaconu, M.; Neagu, G.; Sha’at, M.; Anastasescu, M.; Mihailescu, M.; Matei, C.; Nechifor, G.; et al. Polyphenolic Extract from Sambucus ebulus L. Leaves Free and Loaded into Lipid Vesicles. Nanomaterials 2019, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, R.P.; Kappes, M.; Cicha, I.; Tietze, R.; Braun, C.; Schneider-Stock, R.; Nagy, R.; Alexiou, C.; Janko, C. Optical Microscopy Systems for the Detection of Unlabeled Nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 2139–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhrullin, R.; Nigamatzyanova, L.; Fakhrullina, G. Dark-Field/Hyperspectral Microscopy for Detecting Nanoscale Particles in Environmental Nanotoxicology Research. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittiu, A.; Pannuzzo, M.; Casula, L.; Pireddu, R.; Valenti, D.; Cardia, M.C.; Lai, F.; Rosa, A.; Sinico, C.; Schlich, M. Production of Liposomes by Microfluidics: The Impact of Post-Manufacturing Dilution on Drug Encapsulation and Lipid Loss. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 664, 124641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carugo, D.; Bottaro, E.; Owen, J.; Stride, E.; Nastruzzi, C. Liposome Production by Microfluidics: Potential and Limiting Factors. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, C.; Cristóvão, J.; Silvério, V.; Lino, P.R.; Fonte, P. Microfluidic Production of MRNA-Loaded Lipid Nanoparticles for Vaccine Applications. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2022, 19, 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebollo, R.; Oyoun, F.; Corvis, Y.; El-Hammadi, M.M.; Saubamea, B.; Andrieux, K.; Mignet, N.; Alhareth, K. Microfluidic Manufacturing of Liposomes: Development and Optimization by Design of Experiment and Machine Learning. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 39736–39745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdallah, S.I.; Zoqlam, R.; Erfle, P.; Blyth, M.; Alkilany, A.M.; Dietzel, A.; Qi, S. Microfluidics for Pharmaceutical Nanoparticle Fabrication: The Truth and the Myth. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 584, 119408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elizondo, E.; Moreno, E.; Cabrera, I.; Córdoba, A.; Sala, S.; Veciana, J.; Ventosa, N. Liposomes and Other Vesicular Systems: Structural Characteristics, Methods of Preparation, and Use in Nanomedicine. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2011, 104, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliano, C.B.; Cvjetan, N.; Ayache, J.; Walde, P. Multivesicular Vesicles: Preparation and Applications. ChemSystemsChem 2021, 3, e2000049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Nanovesicular System | TFR a (μL/min) | FRR b | FAP c (μL/min) | FLP d (μL/min) | PC e (%, w/w) | Ethanol (%, w/w) | Water (%, w/w) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LIPOMF | 55 | 10:1 | 25 + 25 | 5 | 0.9 | 9.1 | 90 |
| ETHOMF | 90 | 2:1 | 30 + 30 | 30 | 0.9 | 29.1 | 70 |
| LIPOWI | - | - | 1500 | - | 0.9 | 9.1 | 90 |
| ETHOWI | - | - | 1500 | - | 0.9 | 29.1 | 70 |
| LIPOEI | - | - | - | 1500 | 0.9 | 9.1 | 90 |
| ETHOEI | - | - | - | 1500 | 0.9 | 29.1 | 70 |
| Nanovesicular System | Z-Average (nm) ± s.d. | Dispersity Index ± s.d. | Typical Intensity Distribution (nm) | Macroscopic Aspect |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LIPOMF | 234 ± 10 | 0.24 ± 0.01 | 233.02 (91%) | milky, homogeneous |
| ETHOMF | 226 ± 7 | 0.26 ± 0.03 | 238.21 (90%) | milky, homogeneous |
| LIPOWI | 235 ± 14 | 0.27 ± 0.02 | 226.61 (97%) | phase separation |
| ETHOWI | 225 ± 9 | 0.20 ± 0.01 | 225.11 (95%) | milky, homogeneous |
| LIPOEI | 144 ± 3 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 143.21 (98%) | milky, homogeneous |
| ETHOEI | 130 ± 13 | 0.15 ± 0.02 | 138.40 (100%) | milky, homogeneous |
| LIPOEI | ETHOWI | ETHOEI | |
|---|---|---|---|
| R1 (nm) | 0.49 ± 0.07 | 0.66 ± 0.04 | 0.64 ± 0.02 |
| R2 (nm) | 1.19 ± 0.02 | 1.03 ± 0.06 | 1.04 ± 0.02 |
| R3 (nm) | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 0.16 ± 0.05 | 0.14 ± 0.02 |
| N | 6 ± 2 | 5 ± 2 | 2 ± 4 |
| c (nm) | 17 ± 10 | 14 ± 1 | 35 ± 9 |
| gc | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 0.5 ± 0.2 |
| R0 (nm) | 500 ± 100 | 488 ± 85 | 500 ± 90 |
| ξRo | 0.1 ± 0:2 | 0.01 ± 0.06 | 0.0 ± 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Esposito, E.; Dzyhovski, V.; Santamaria, F.; Contado, C.; Brenna, C.; Neri, L.M.; Secchiero, P.; Spinozzi, F.; Pepe, A.; Rawski, M.; et al. Nanovesicles and Human Skin Interaction: A Comparative Ex-Vivo Study. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 937. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15120937
Esposito E, Dzyhovski V, Santamaria F, Contado C, Brenna C, Neri LM, Secchiero P, Spinozzi F, Pepe A, Rawski M, et al. Nanovesicles and Human Skin Interaction: A Comparative Ex-Vivo Study. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(12):937. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15120937
Chicago/Turabian StyleEsposito, Elisabetta, Valentyn Dzyhovski, Federico Santamaria, Catia Contado, Cinzia Brenna, Luca Maria Neri, Paola Secchiero, Francesco Spinozzi, Alessia Pepe, Michał Rawski, and et al. 2025. "Nanovesicles and Human Skin Interaction: A Comparative Ex-Vivo Study" Nanomaterials 15, no. 12: 937. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15120937
APA StyleEsposito, E., Dzyhovski, V., Santamaria, F., Contado, C., Brenna, C., Neri, L. M., Secchiero, P., Spinozzi, F., Pepe, A., Rawski, M., Ortore, M. G., Mariani, P., Galvan, A., Calderan, L., & Malatesta, M. (2025). Nanovesicles and Human Skin Interaction: A Comparative Ex-Vivo Study. Nanomaterials, 15(12), 937. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15120937














