Improving Nanosilica Fluidization by Premixing with Geldart A and B Particles: A Detailed Region-Wise Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Set-Up
2.2. Pressure Drop Measurements
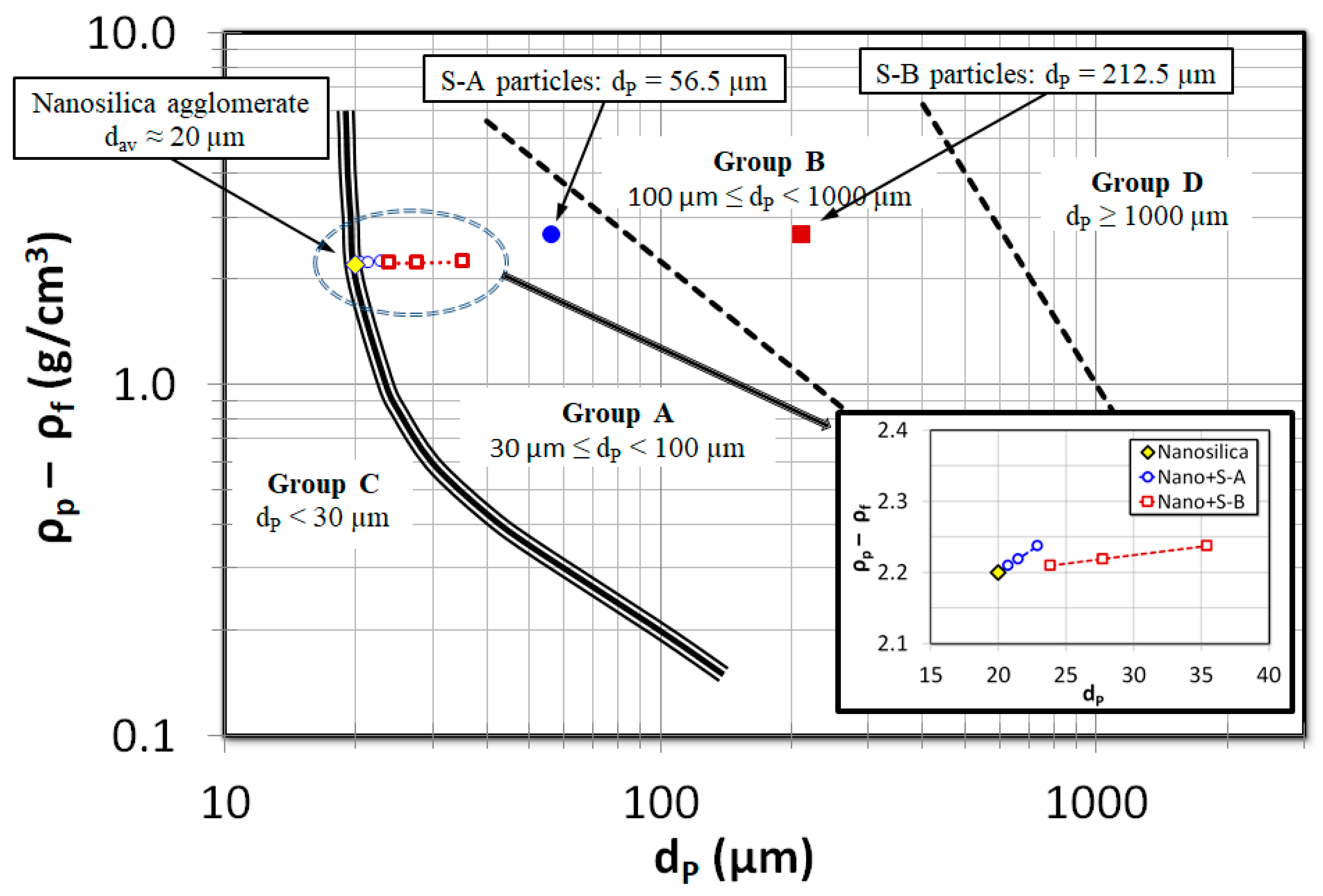
2.3. Solid Particles
2.4. Methodology
3. Result and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| A | cross-sectional area of the bed |
| m | mass of the particles in the bed |
| average pressure drop (Pa) | |
| volume change of mixing for two component mixture (m3/kg) | |
| specific volume of the mixture (m3/kg) | |
| specific volume of component (m3/kg) | |
| initial volume fraction (-/-) | |
| Greek symbols | |
| ε | bed porosity (-/-) |
| air density (kg/m3) | |
| true solid density (kg/m3) |
References
- Asif, M.; Ali, S.S. Bed collapse dynamics of fluidized beds of nano-powder. Adv. Powder Technol. 2013, 24, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shao, Y.; Zhu, J. Improving flow and fluidization quality of fine and ultrafine particles via nanoparticle modulation. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 12013–12025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Kamphorst, R.; van der Sande, P.C.; Wagner, E.C.; Meesters, G.M.H.; van Ommen, J.R. Gas pulsation-assisted fluidization of cohesive micron powder: An X-ray imaging study. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2025, 310, 121529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M. Development of Functional Nanomaterials for Applications in Chemical Engineering. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedi, N.; Esfahany, M.N. Elutriation of fine particles in a pulsed fluidized bed. Powder Technol. 2024, 434, 119355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, S.; Shakaib, M.; Allauddin, U. A CFD and experimental study of hydrodynamic and heat transfer behavior in ribbed fluidized beds. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 2024, 22, 1039–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neogi, A.; Mohanta, H.K.; Sharma, A.K.; Sande, P.C. PIV investigation on the effect of gas distributor design for fluidization of Geldart A spherical particles. Powder Technol. 2024, 442, 119872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Francia, V.; Jiang, S.; Coppens, M.-O. An experimental flow regime map to dynamically structure gas–solid bubbling fluidized beds. AIChE J. 2025, 71, e18681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Zhang, H.; Hu, C.; Li, S.; Xiang, M.; Lv, P.; Zhu, Q. Efficient fluidization intensification process to fabricate in-situ dispersed (SiO+G)/CNTs composites for high-performance lithium-ion battery anode applications. Particuology 2021, 56, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Sande, P.C.; Wu, K.; Kamphorst, R.; Wagner, E.C.; Meesters, G.M.H.; van Ommen, J.R. On the inherent correlation between the fluidization and flow properties of cohesive powders. AIChE J. 2025, 71, e18706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, L.F.; Portman, J.L.; Casper, M.D.; Weimer, A.W. Aggregation behavior of nanoparticles in fluidized beds. Powder Technol. 2005, 160, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Yu, Q.; Dave, R.N.; Pfeffer, R. Gas fluidization characteristics of nanoparticle agglomerates. AIChE J. 2005, 51, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geldart, D. Types of gas fluidization. Powder Technol. 1973, 7, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raganati, F.; Chirone, R.; Ammendola, P. Gas–solid fluidization of cohesive powders. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 133, 347–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhu, J. A review on fluidization of Geldart Group C powders through nanoparticle modulation. Powder Technol. 2021, 381, 698–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogre, C.; Thakurdesai, A.U.; van Ommen, J.R.; Salameh, S. Long-term fluidization of titania nanoparticle agglomerates. Powder Technol. 2017, 316, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Arsad, A.; Roberts, K.L.; Asif, M. Effect of Voidage on the Collapsing Bed Dynamics of Fine Particles: A Detailed Region-Wise Study. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Hu, X.; Liu, N.; Liu, H. Flow Behavior of Nanoparticle Agglomerates in a Fluidized Bed Simulated with Porous-Structure-Based Drag Laws. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Arsad, A.; Roberts, K.L.; Asif, M. Effect of Inlet Flow Strategies on the Dynamics of Pulsed Fluidized Bed of Nanopowder. Nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, D.; Ma, J.; Chen, X. Fluidization of nanoparticle agglomerates assisted by combining vibration and stirring methods. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 388, 124213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Halim, L.; Basrawi, F.; Md Yudin, A.S.; Mohd Azman, N.A.; Oumer, A.N.; Abd Razak, S.B. Pulsation-assisted fluidised bed drying of heat-sensitive and sticky materials: Effect of basic parameter, and pulsation-specific parameter. Part. Sci. Technol. 2023, 41, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghurabi, E.H.; Ali, S.S.; Alfadul, S.M.; Shahabuddin, M.; Asif, M. Experimental investigation of fluidized bed dynamics under resonant frequency of sound waves. Adv. Powder Technol. 2019, 30, 2812–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Arsad, A.; Hossain, S.S.; Asif, M. A Detailed Insight into Acoustic Attenuation in a Static Bed of Hydrophilic Nanosilica. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Fu, Y.; Song, S.; Dong, L.; Lv, B.; Chen, Z.; Tian, Y.; Chen, J. Fluidization and separation characteristics of a gas–solid separation fluidized bed in the presence of an acoustic field. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2021, 169, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Xi, T.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Song, S.; Dong, L. Propagation and attenuation of acoustic in gas-solid fluidized beds of group B particles. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2024, 201, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirone, R.; Raganati, F.; Ammendola, P.; Barletta, D.; Lettieri, P.; Poletto, M. A comparison between interparticle forces estimated with direct powder shear testing and with sound assisted fluidization. Powder Technol. 2018, 323, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Dave, R.N.; Zhu, C.; Quevedo, J.A.; Pfeffer, R. Enhanced fluidization of nanoparticles in an oscillating magnetic field. AIChE J. 2005, 51, 1971–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yang, L.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Song, S.; Dong, L. Enhanced fluidization of solid particles in an oscillating acoustic field. Adv. Powder Technol. 2022, 33, 103875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barletta, D.; Poletto, M. Aggregation phenomena in fluidization of cohesive powders assisted by mechanical vibrations. Powder Technol. 2012, 225, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, K.; Andino, J.M. Enhanced fluidization of nanosized TiO2 by a microjet and vibration assisted (MVA) method. Powder Technol. 2019, 356, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, D.; Wu, X.; Zhang, W.; Feng, H. Enhancing fluidization quality of nanoparticle agglomerates by combining vibration, stirring and jet assistances. Powder Technol. 2023, 430, 118996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Baeyens, J.; Yang, M.; Li, Z.; Deng, Y. Vibro-fluidization of cohesive particles. Powder Technol. 2024, 432, 119107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, P.; Orwa, M.G.; Pacek, A.W. De-agglomeration of hydrophobic and hydrophilic silica nano-powders in a high shear mixer. Powder Technol. 2009, 195, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, P.; Pacek, A.W. De-agglomeration of goethite nano-particles using ultrasonic comminution device. Powder Technol. 2008, 187, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, H.; Hong, K.; Dong, L. Prediction and Interpretative Analysis of Bed Expansion Ratio in Pulsed Fluidized Beds. Separations 2025, 12, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Hossain, S.K.S.; Asif, M. Dynamics of partially collapsing pulsed fluidized bed. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 99, 2333–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Asif, M. Fluidization of nano-powders: Effect of flow pulsation. Powder Technol. 2012, 225, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, A.; Rahman, F.; Wang, S.; Rhodes, M. Enhanced fluidization of nanoparticles with gas phase pulsation assistance. Powder Technol. 2015, 284, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Lin, W.; Dam-Johansen, K.; Wu, H. Application of pulse flow to a fluidized bed for combustion and gasification of wheat straw—A possible way to mitigate agglomeration. Fuel 2025, 379, 132955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, W.C.; Jung, H.S.; Bae, J.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, D.H. Segregation phenomena of binary solids in a pulsed fluidized bed. Powder Technol. 2022, 410, 117881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajbar, A.; Alhumazi, K.; Asif, M. Improvement of the Fluidizability of Cohesive Powders through Mixing with Small Proportions of Group A Particles. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2005, 83, 930–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamranian Marnani, A.; Bück, A.; Antonyuk, S.; van Wachem, B.; Thévenin, D.; Tomas, J. The Effect of the Presence of Very Cohesive Geldart C Ultra-Fine Particles on the Fluidization of Geldart A Fine Particle Beds. Processes 2019, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, H.; Xu, B.; Luo, C.; Zhou, T.; Kong, J. Aggregation and fragmentation of agglomerates in a fluidized bed of mixed nanoparticles by adding FCC coarse particles. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 26, 2531–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghurabi, E.; Ajbar, A.; Asif, M. Improving Fluidization Hydrodynamics of Group C Particles by Mixing with Group B Particles. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghurabi, E.; Ajbar, A.; Asif, M. Enhancement of CO2 Removal Efficacy of Fluidized Bed Using Particle Mixing. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Zhou, T.; Yang, J. Fluidization behavior of nano-particles by adding coarse particles. Adv. Powder Technol. 2009, 20, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Liang, X.; Zhou, T.; Wang, J.; Tang, W. Fluidization of mixed SiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles by adding coarse particles. Powder Technol. 2014, 267, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Basu, A.; Alfadul, S.M.; Asif, M. Nanopowder Fluidization Using the Combined Assisted Fluidization Techniques of Particle Mixing and Flow Pulsation. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Asif, M. Effect of particle mixing on the hydrodynamics of fluidized bed of nanoparticles. Powder Technol. 2017, 310, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Al-Ghurabi, E.H.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Asif, M. Effect of adding Geldart group A particles on the collapse of fluidized bed of hydrophilic nanoparticles. Powder Technol. 2018, 330, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Al-Ghurabi, E.H.; Ajbar, A.; Mohammed, Y.A.; Boumaza, M.; Asif, M. Effect of Frequency on Pulsed Fluidized Beds of Ultrafine Powders. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 4592501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Arsad, A.; Asif, M. Effect of modified inlet flow strategy on the segregation phenomenon in pulsed fluidized bed of ultrafine particles: A collapse bed study. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2020, 159, 108243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M. Volume-change of mixing at incipient fluidization of binary-solid mixtures: Experimental data and predictive models. Powder Technol. 2012, 217, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
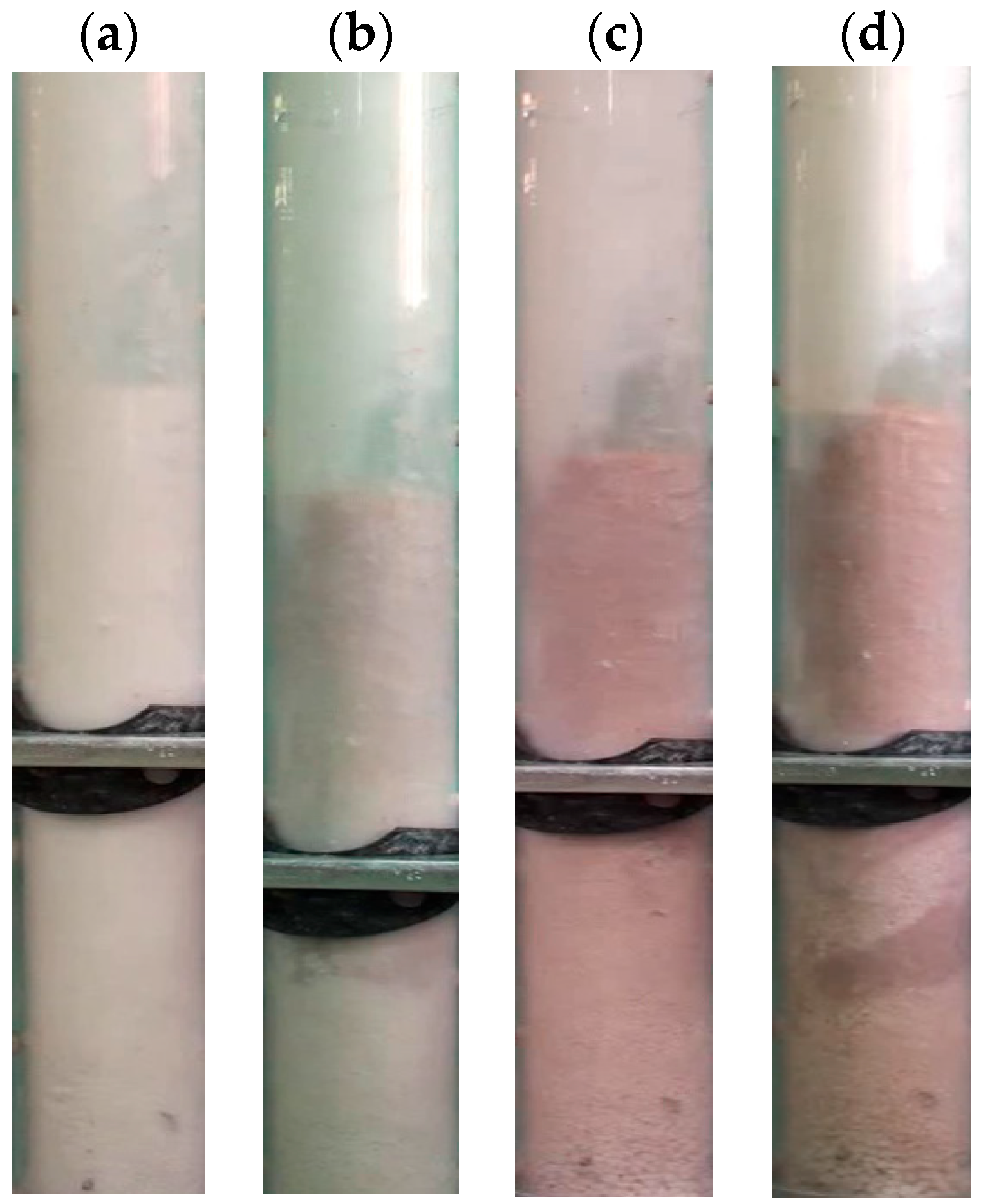



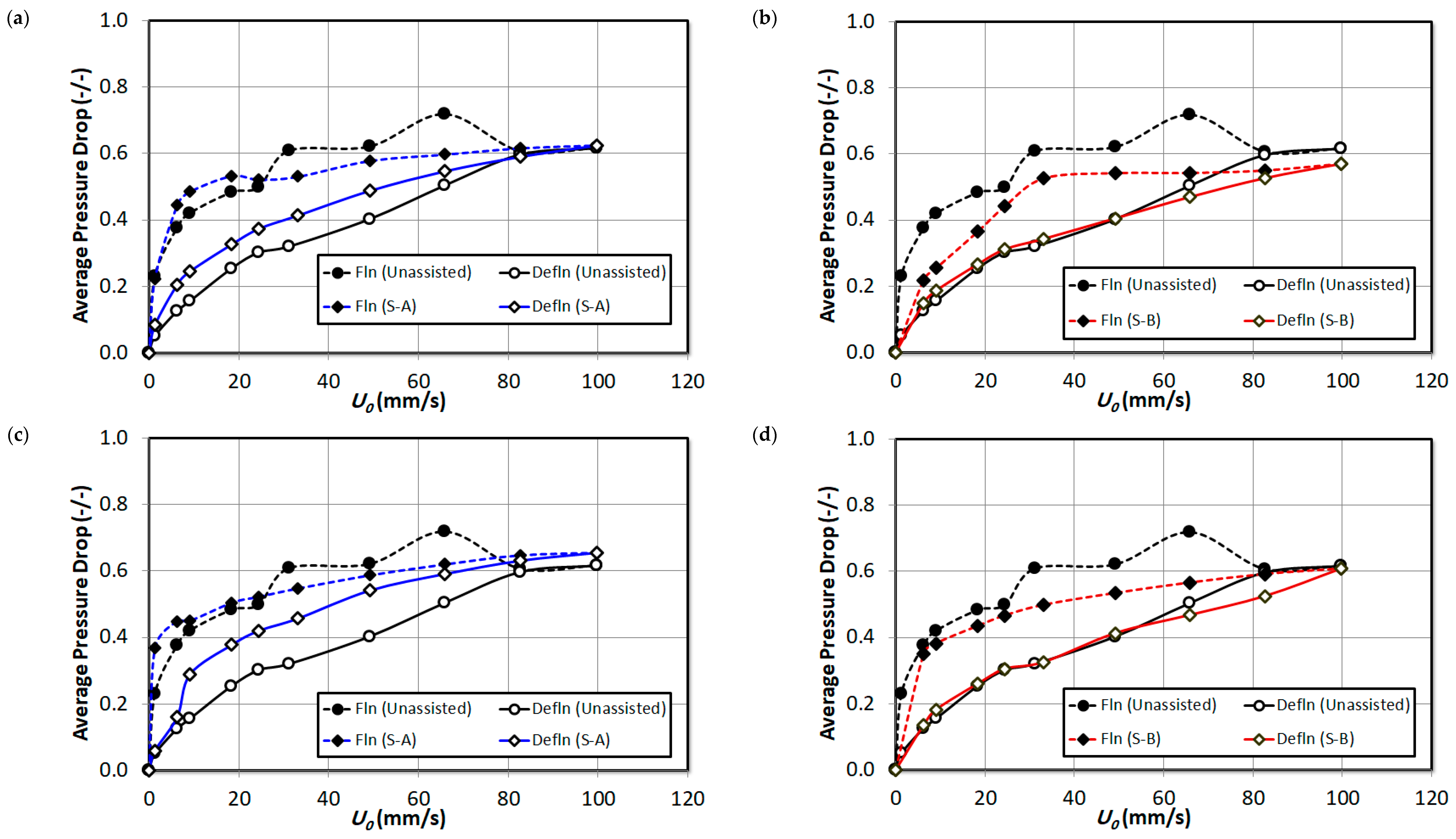
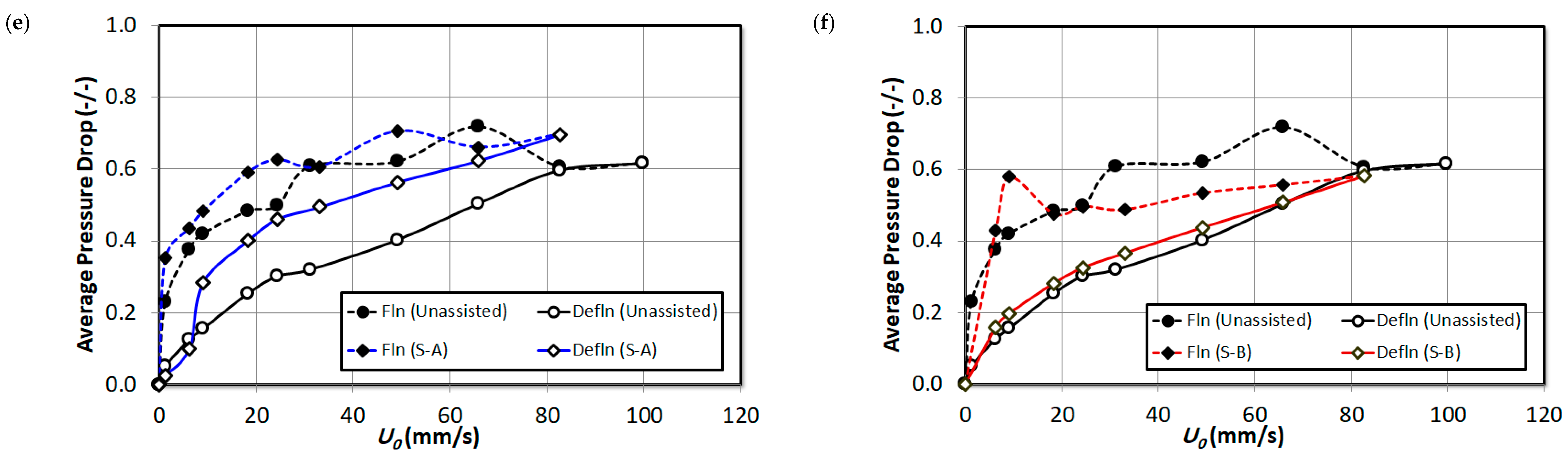










| Pressure Drop | Pressure Tap Positions (from the Distributor) | Bed Region |
|---|---|---|
| 0.05 m–open | Overall | |
| 0.3 m–open | Upper | |
| 0.2 m–0.3 m | Upper–middle | |
| 0.1 m–0.2 m | Lower–middle | |
| 0.05 m–0.1 m | Lower |
| Particles’ Name | Chemical Formula | Primary Size | Sauter Mean Diameter (μm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nanosilica | SiO2 | 12 nm | 20 μm | 2200 |
| S-A | SiO2 | 38–75 μm | 56.5 μm | 2664 |
| S-B | SiO2 | 125–300 μm | 212.5 μm | 2664 |
| Vol. % | (mm/s) | F.I. (Dimensionless) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unassisted | 33.0 | 0.62 | |
| S-A | 2% | 22.0 | 0.57 |
| 4% | 19.0 | 0.58 | |
| 8% | 26.0 | 0.65 | |
| S-B | 2% | 32.5 | 0.55 |
| 4% | 22.0 | 0.56 | |
| 8% | 19.0 | 0.54 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, S.S.; Hossain, S.S.; Mohsin, M.E.A.; Asif, M. Improving Nanosilica Fluidization by Premixing with Geldart A and B Particles: A Detailed Region-Wise Study. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110822
Ali SS, Hossain SS, Mohsin MEA, Asif M. Improving Nanosilica Fluidization by Premixing with Geldart A and B Particles: A Detailed Region-Wise Study. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(11):822. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110822
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Syed Sadiq, SK Safdar Hossain, Mohammad E. Ali Mohsin, and Mohammad Asif. 2025. "Improving Nanosilica Fluidization by Premixing with Geldart A and B Particles: A Detailed Region-Wise Study" Nanomaterials 15, no. 11: 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110822
APA StyleAli, S. S., Hossain, S. S., Mohsin, M. E. A., & Asif, M. (2025). Improving Nanosilica Fluidization by Premixing with Geldart A and B Particles: A Detailed Region-Wise Study. Nanomaterials, 15(11), 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110822







