Surface Modification, Toxicity, and Applications of Carbon Dots to Cancer Theranosis: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
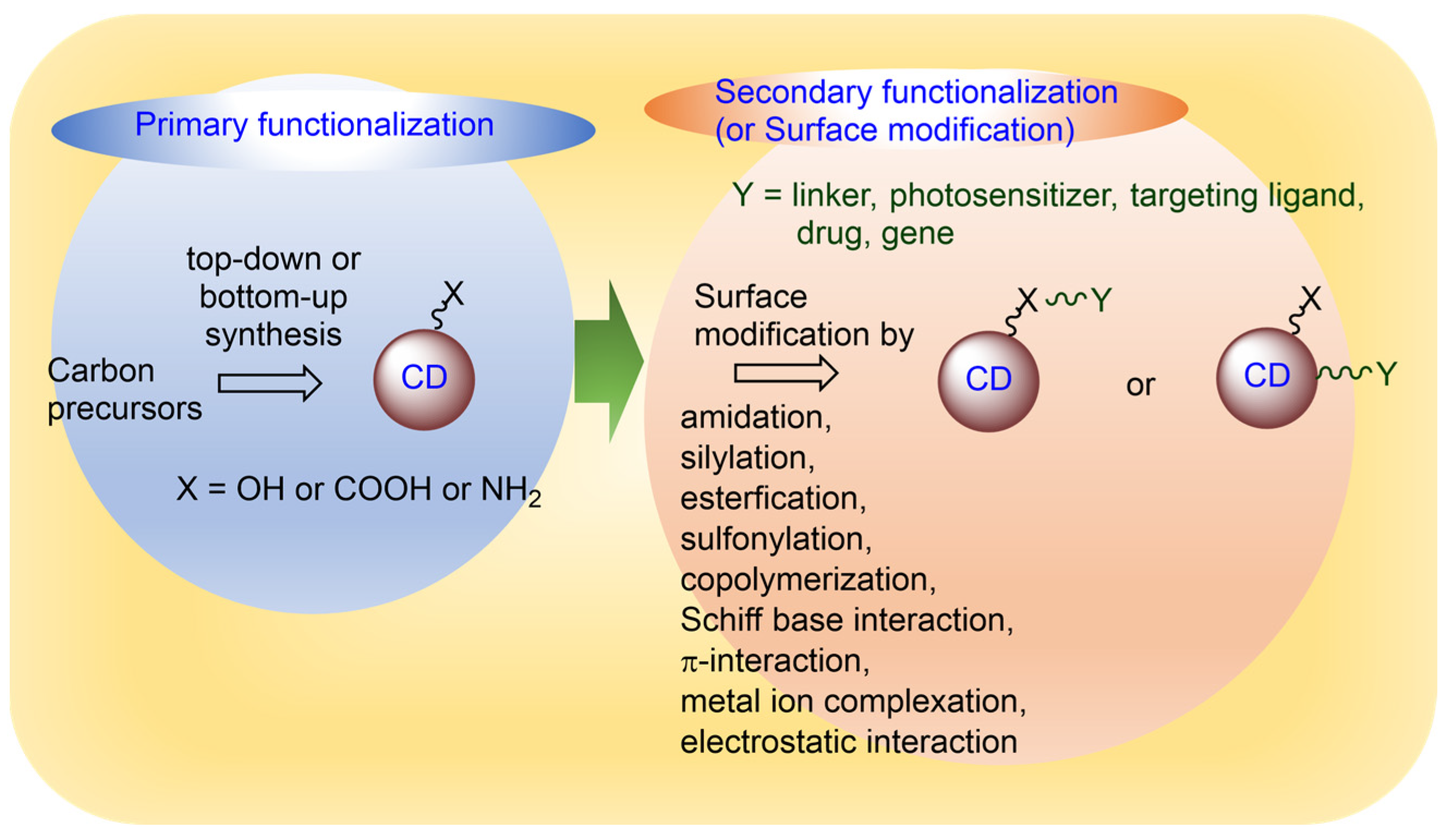
2. Functionalization of CDs
2.1. Primary Functionalization
2.2. Secondary Functionalization or Surface Modification
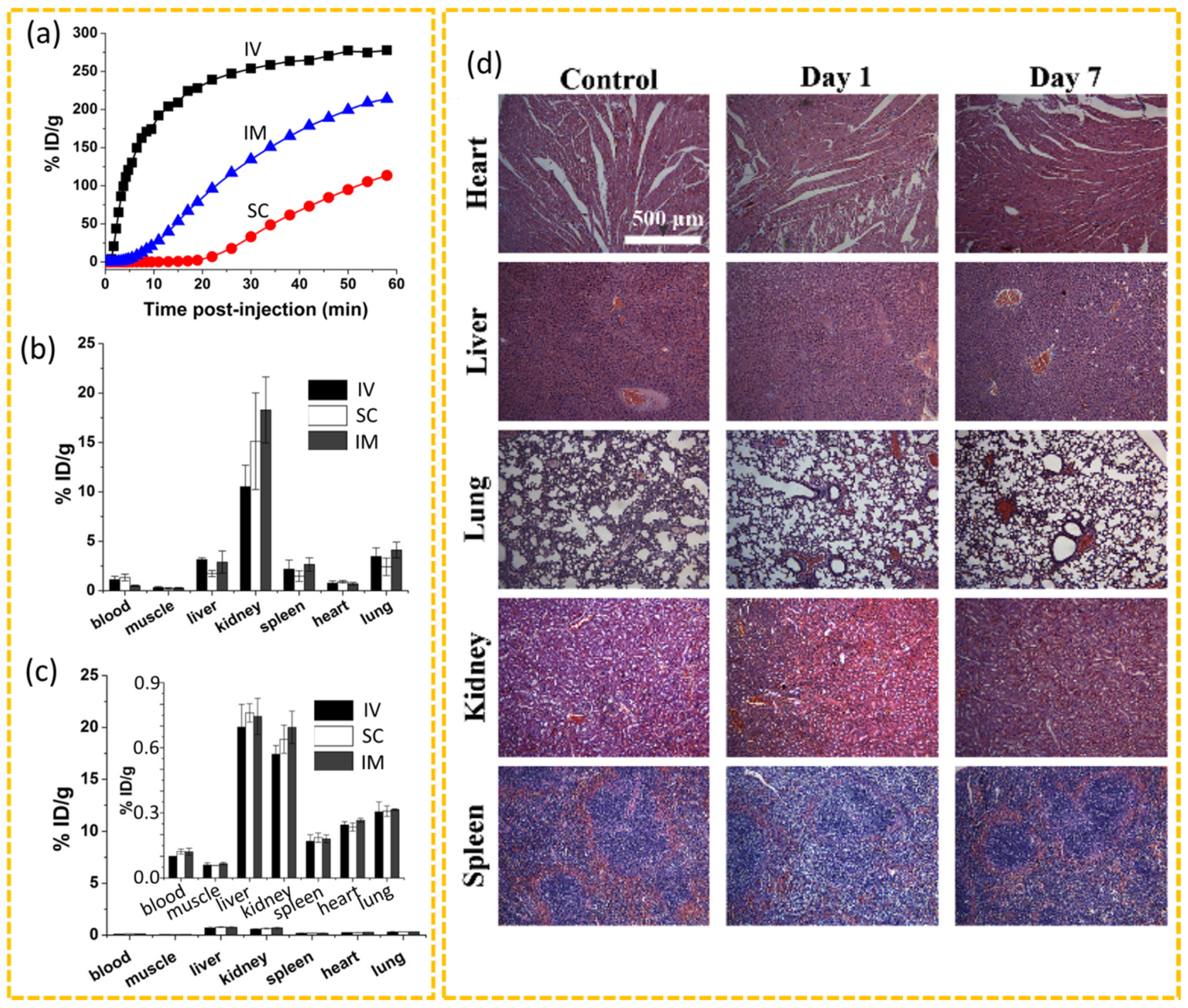
3. In Vitro and In Vivo Toxicity of CDs
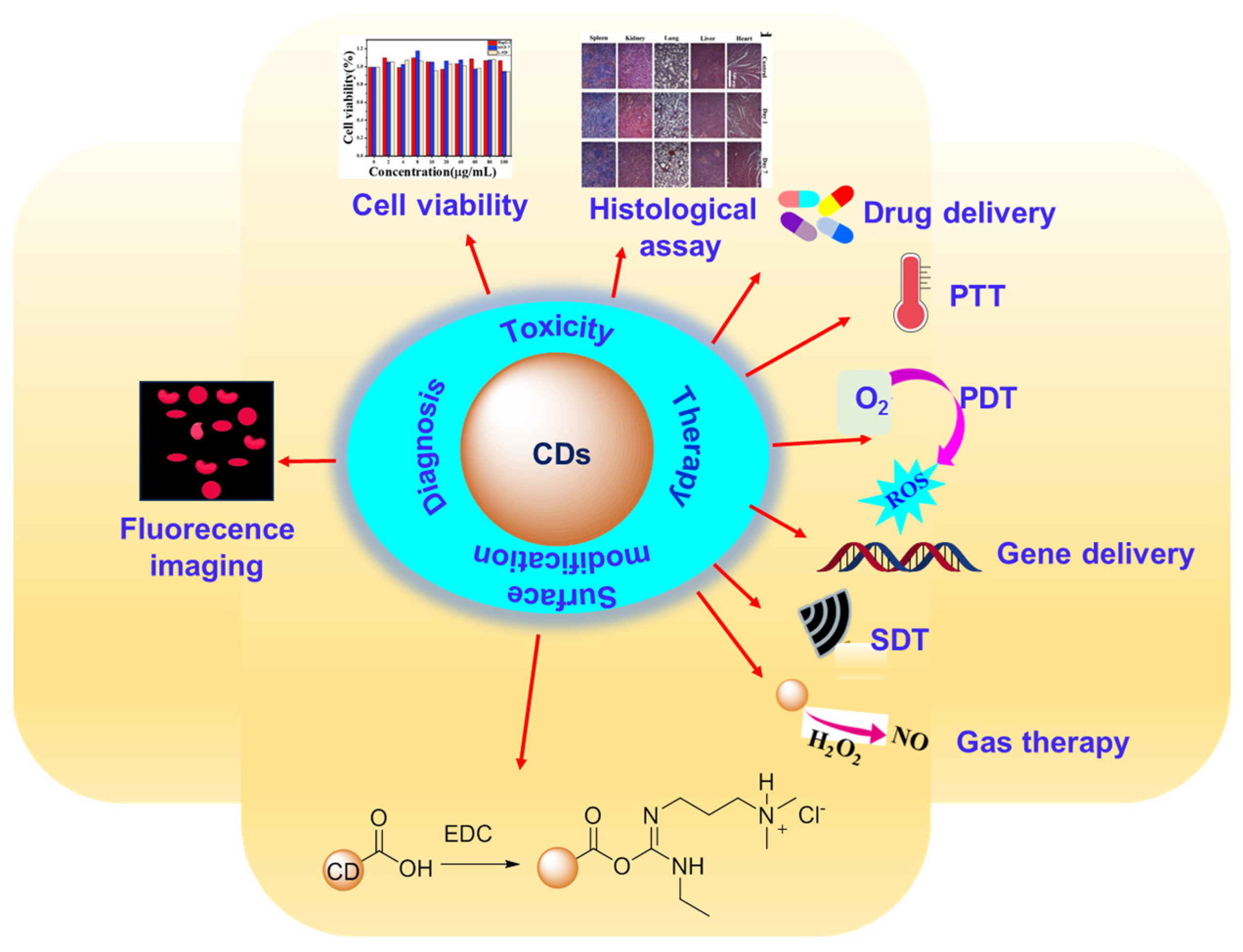
4. Applications of CDs in Cancer Theranosis
4.1. Cancer Diagnosis via Fluorescence Imaging
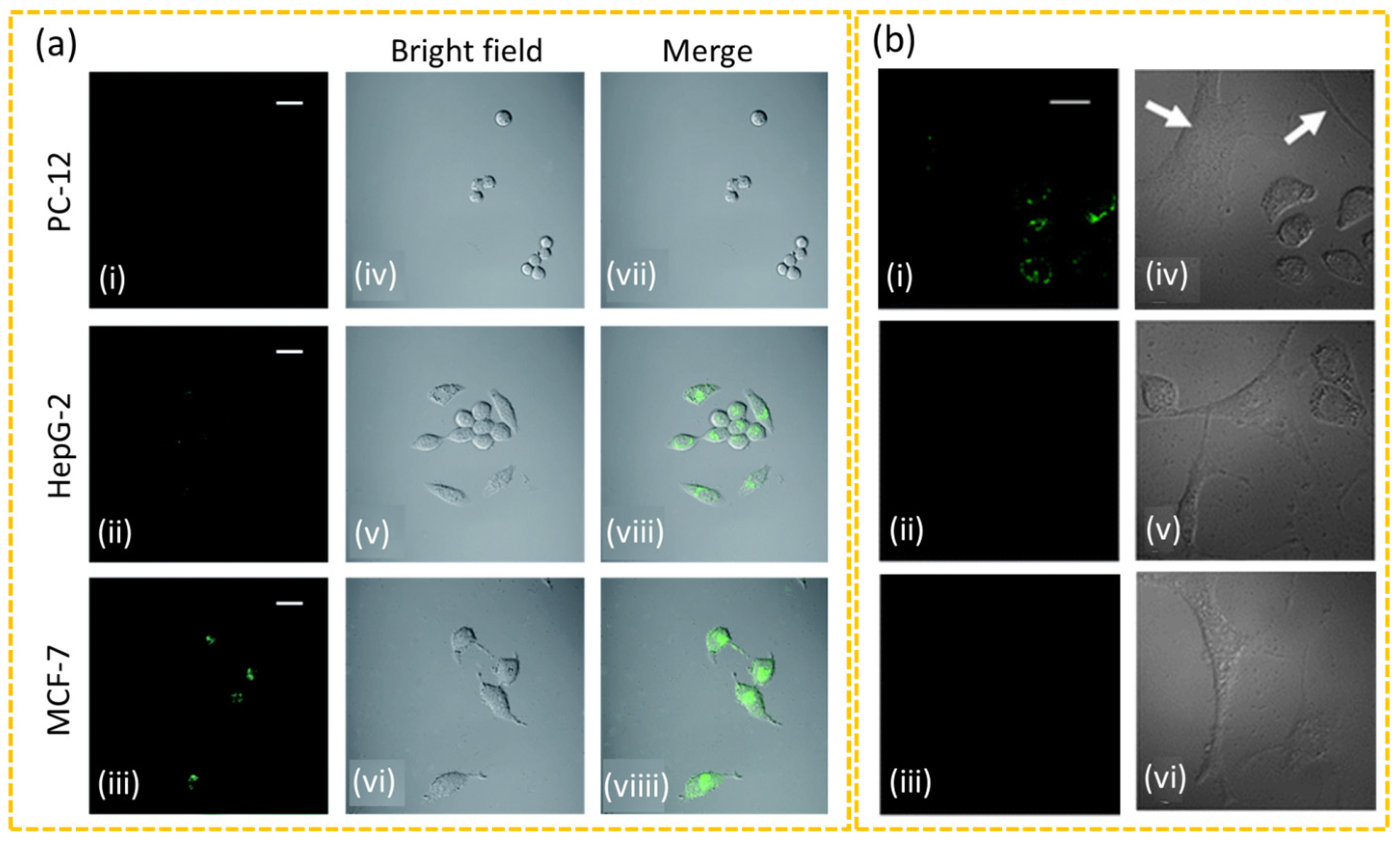
4.1.1. In Vitro Diagnosis
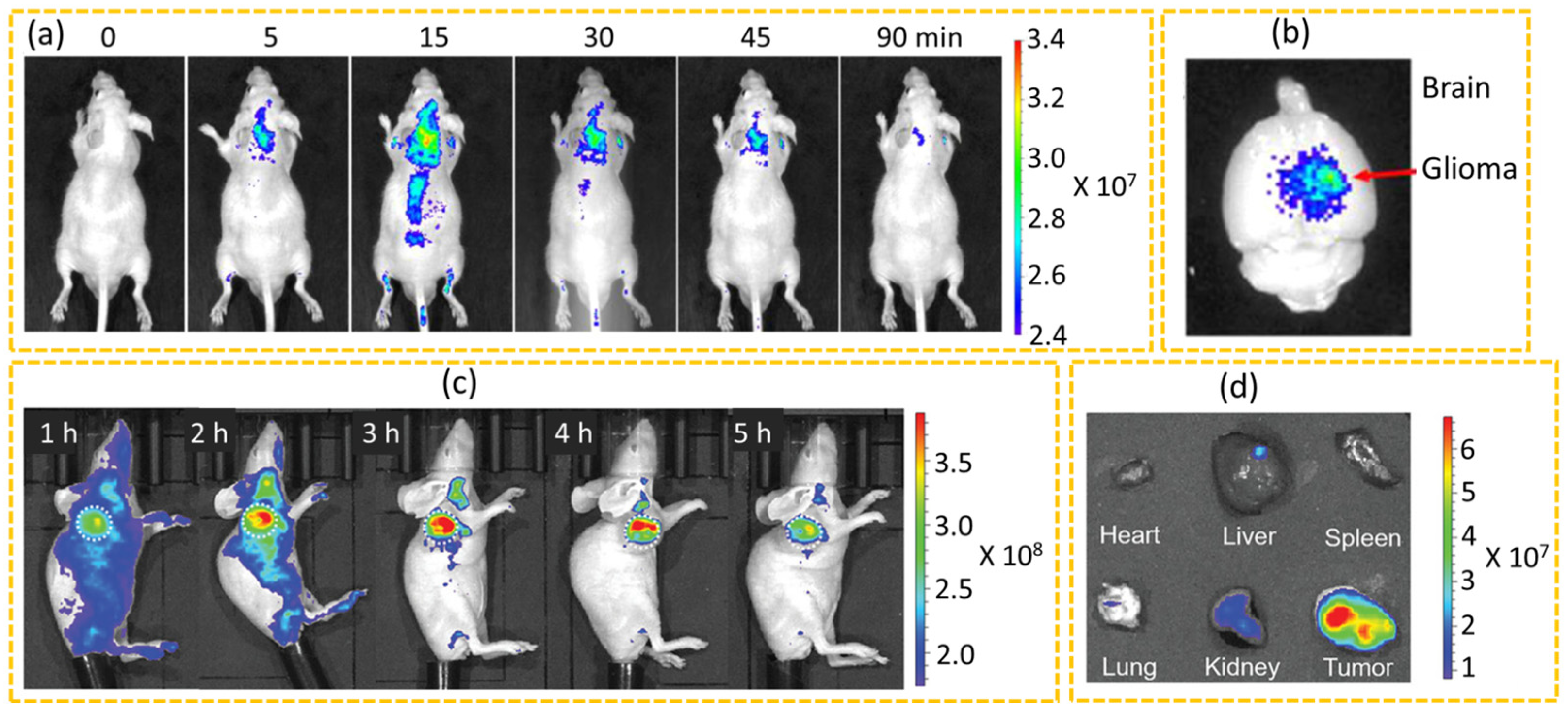
4.1.2. In Vivo Diagnosis
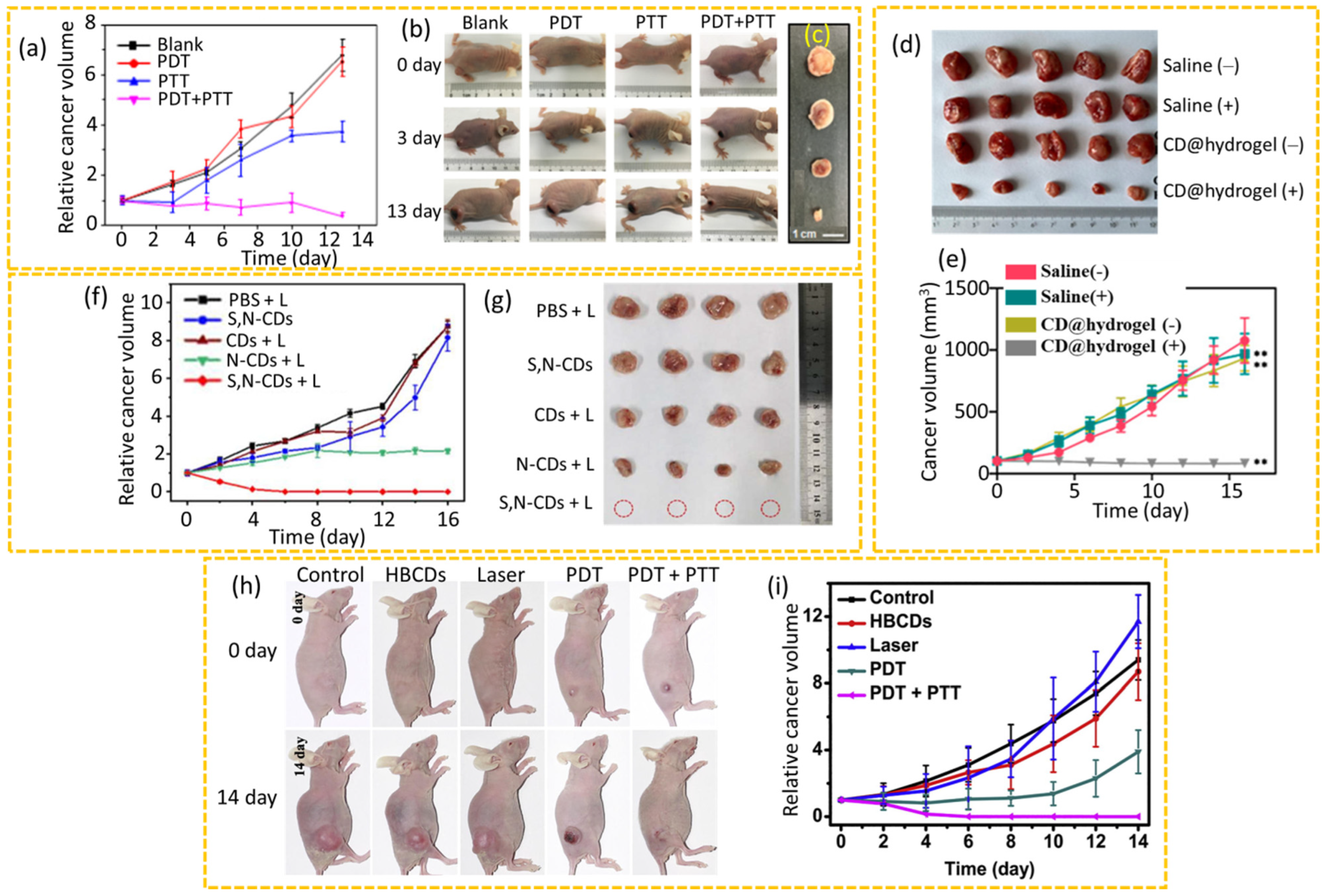
4.2. Cancer Therapy via Drug Delivery, PTT, PDT, PTT+PDT, SiRNA Delivery, SDT, and Gas Therapy
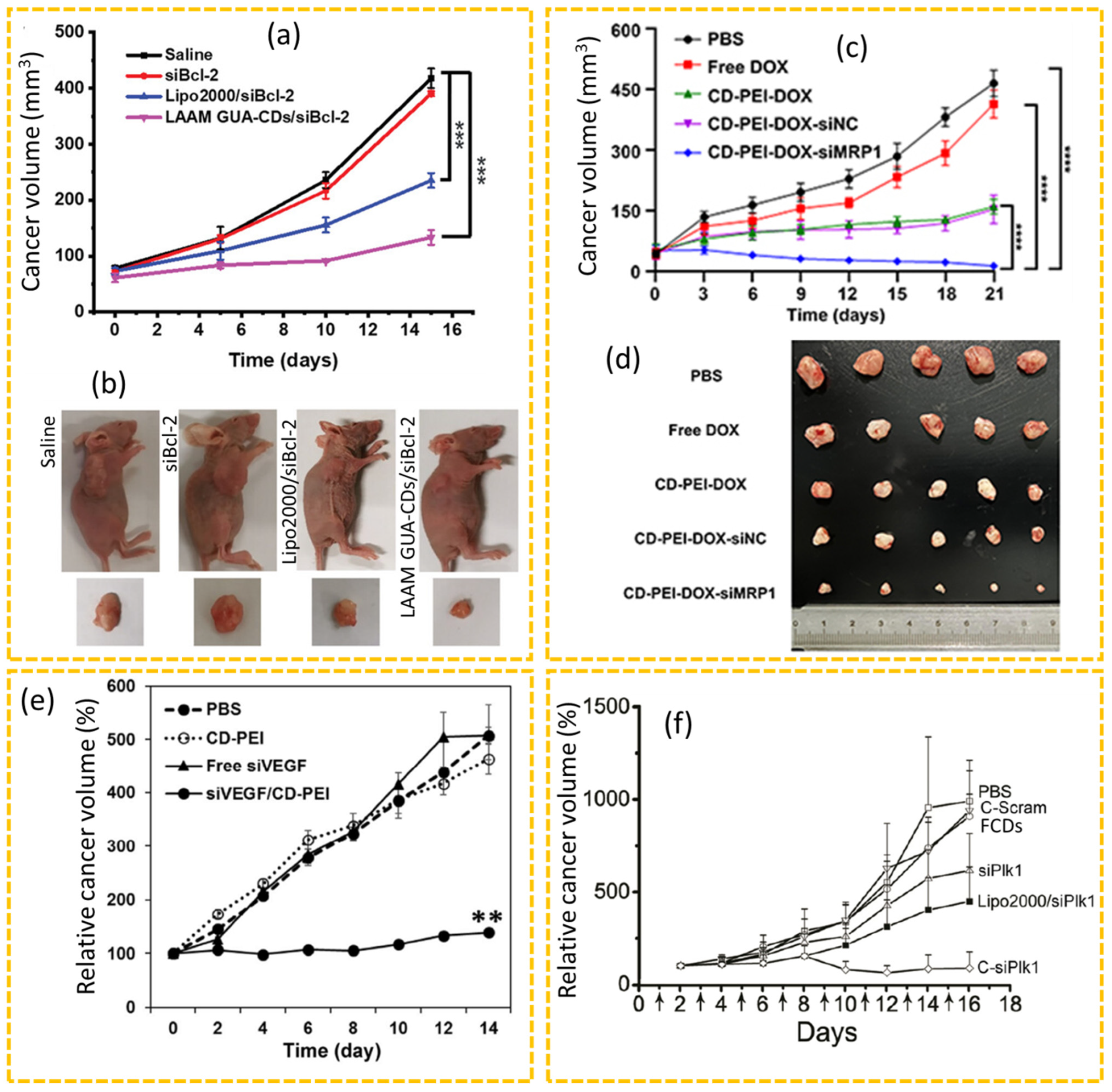
4.2.1. Drug Delivery
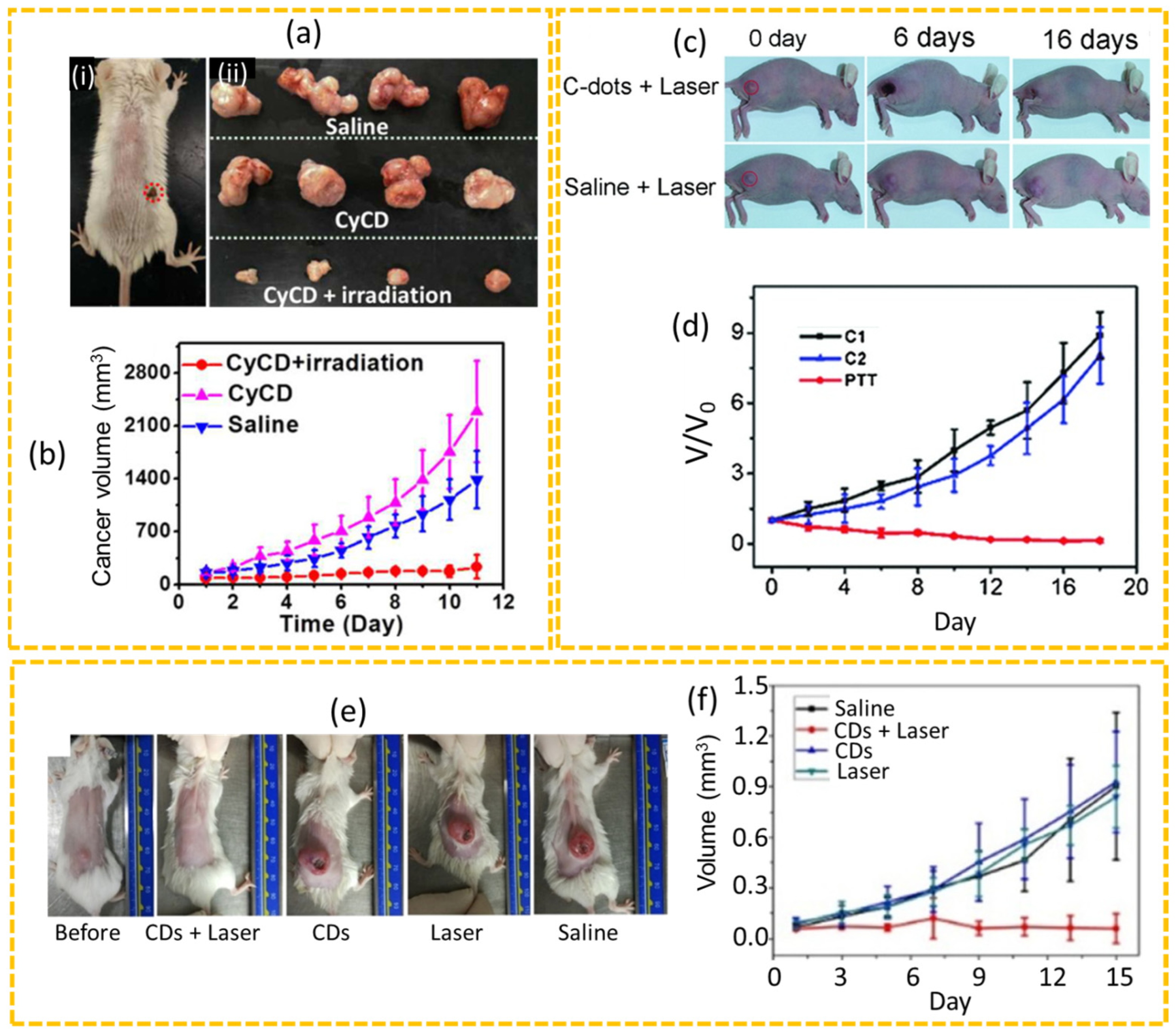
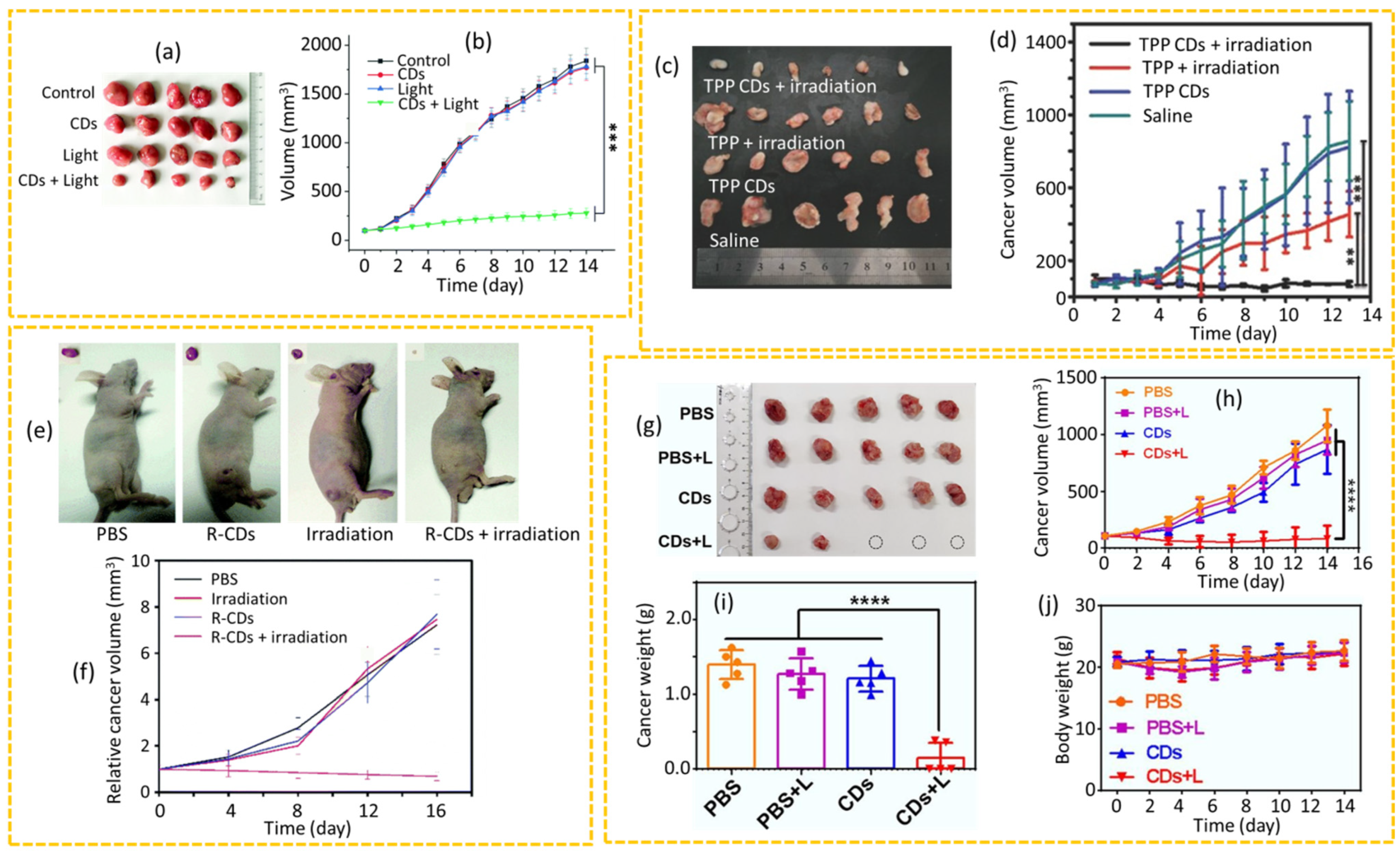
4.2.2. PTT
4.2.3. PDT
4.2.4. Synergistic PDT+PTT
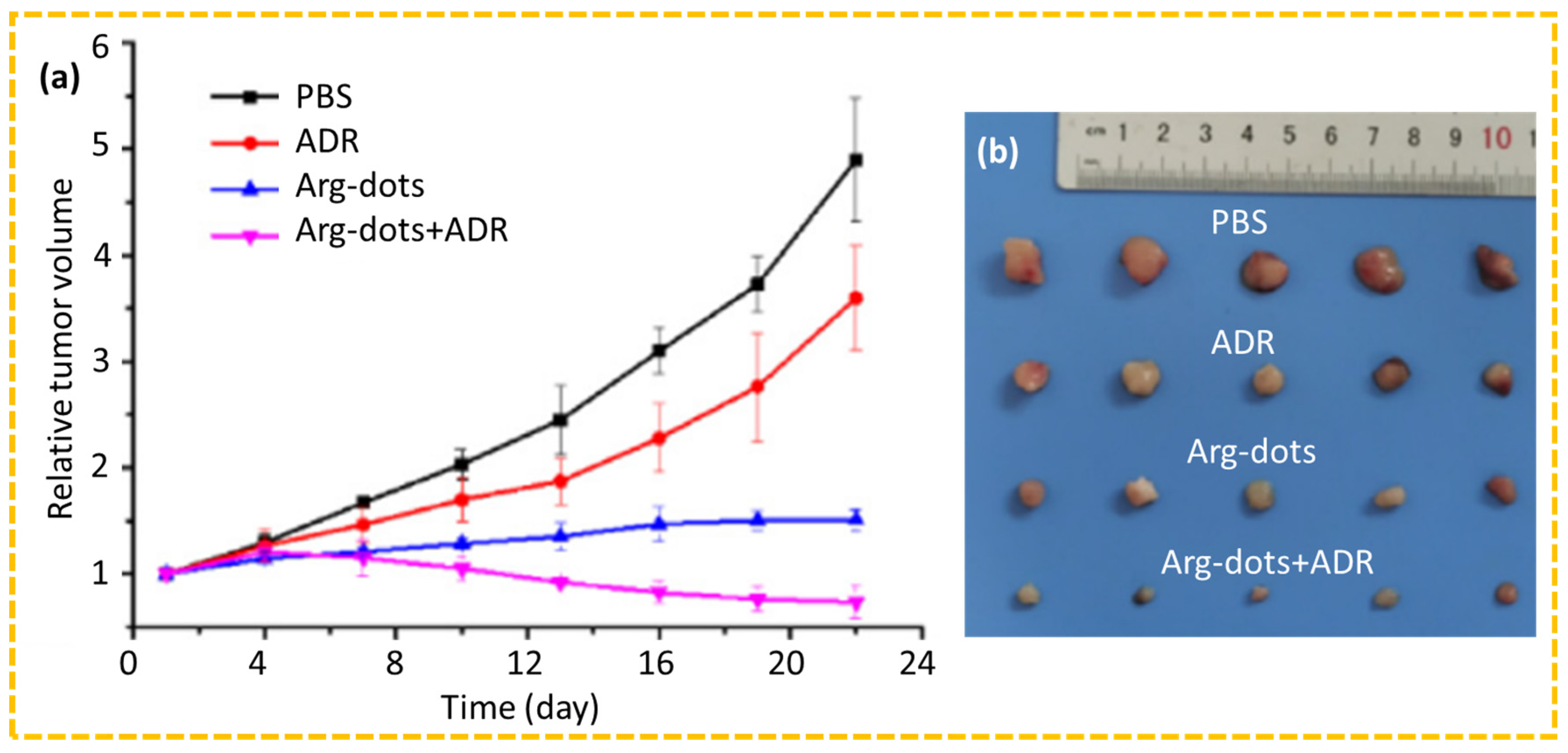
4.2.5. siRNA Therapy
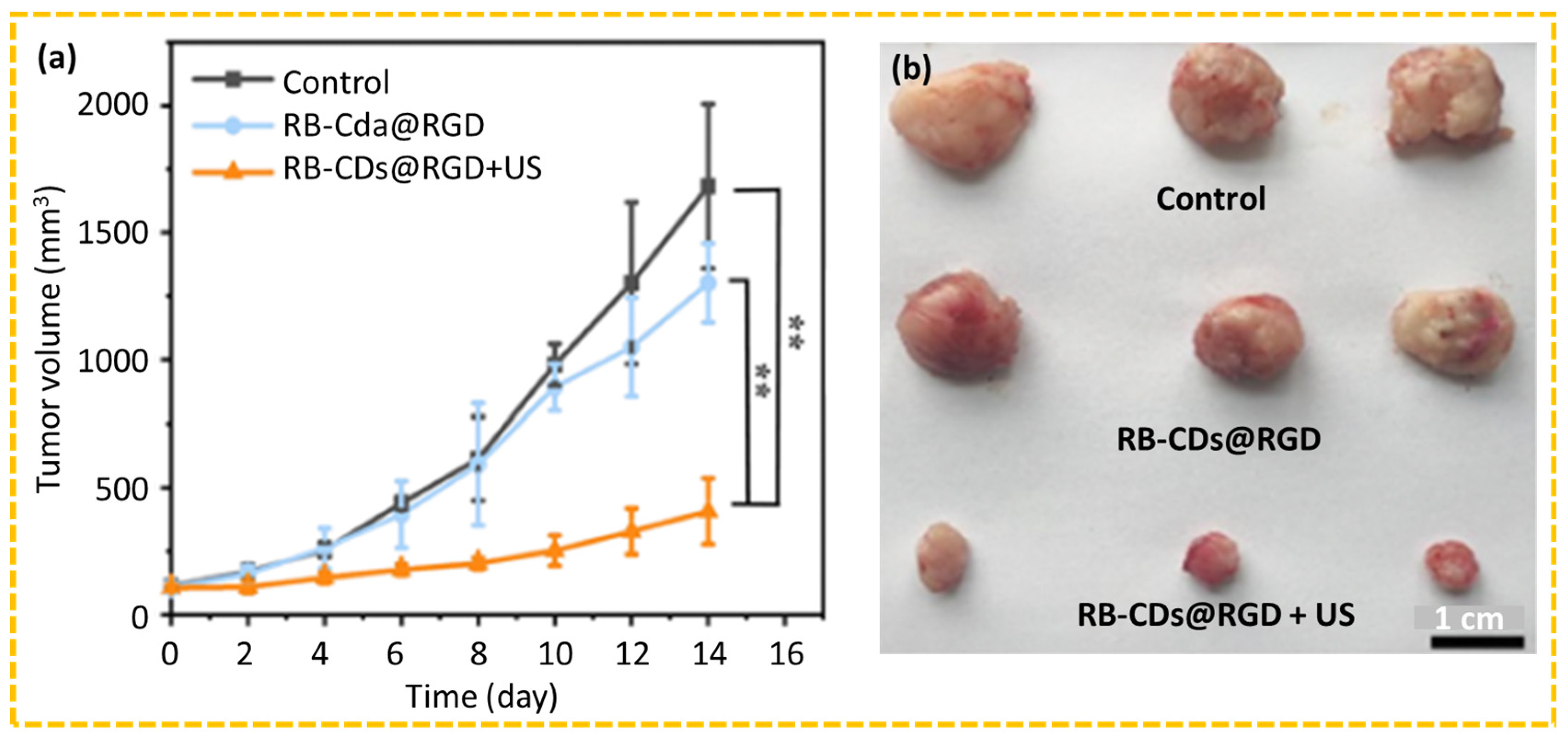
4.2.6. SDT
4.2.7. Gas Therapy
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
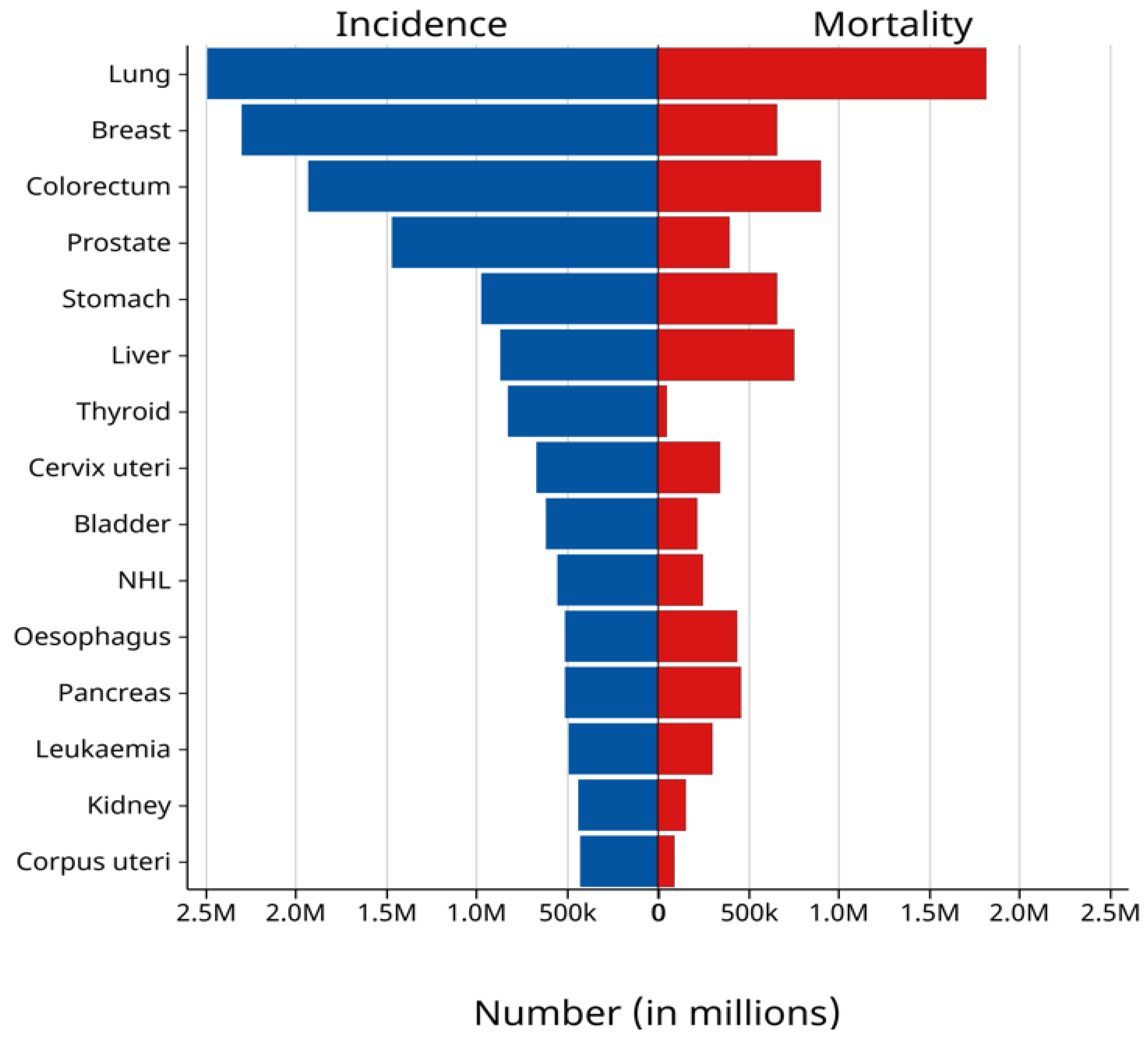
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Data Source from Data from Global Cancer Observatory (GLOBOCAN) 2022, International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), World Health Organization. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/en/dataviz/bars?types=0_1&mode=cancer&group_populations=1&sort_by=value1&key=total (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- Joshi, D.C.; Sharma, A.; Prasad, S.; Singh, K.; Kumar, M.; Sherawat, K.; Tuli, H.S.; Gupta, M. Novel Therapeutic Agents in Clinical Trials: Emerging Approaches in Cancer Therapy. Discov. Oncol. 2024, 15, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Xu, X.; Li, F.; Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, X.; Kong, B.; Hou, H.; Liu, H.; et al. Immunity-Modulating Metal-Based Nanomaterials for Cancer Immunotherapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2502646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Jeong, Y.Y.; Jon, S. A Drug-Loaded Aptamer−Gold Nanoparticle Bioconjugate for Combined CT Imaging and Therapy of Prostate Cancer. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3689–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mieszawska, A.J.; Mulder, W.J.M.; Fayad, Z.A.; Cormode, D.P. Multifunctional Gold Nanoparticles for Diagnosis and Therapy of Disease. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 831–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Liang, H.; Ma, S.; Wang, D.; Huang, J. Gold Nanoparticle Based Photothermal Therapy: Development and Application for Effective Cancer Treatment. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2019, 22, e00109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengan, A.K.; Bukhari, A.B.; Pradhan, A.; Malhotra, R.; Banerjee, R.; Srivastava, R.; De, A. In Vivo Analysis of Biodegradable Liposome Gold Nanoparticles as Efficient Agents for Photothermal Therapy of Cancer. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, P.; Tang, W.; McHugh, K.J.; Kershaw, S.V.; Jiao, M.; Huang, X.; Kalytchuk, S.; Perkinson, C.F.; Yue, S.; et al. Bright, Magnetic NIR-II Quantum Dot Probe for Sensitive Dual-Modality Imaging and Intensive Combination Therapy of Cancer. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 8076–8094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Guo, W.; Guo, C.; Sun, J.; Zheng, N.; Wang, F.; Yan, M.; Liu, S. MoO3−x Quantum Dots for Photoacoustic Imaging Guided Photothermal/Photodynamic Cancer Treatment. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 2020–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, M.; Sarkar, S.; Debnath, S.K.; Dkhar, D.S.; Kumari, R.; Vaskuri, G.S.S.J.; Srivastava, A.; Chandra, P.; Prasad, R.; Srivastava, R. Photothermally Active Quantum Dots in Cancer Imaging and Therapeutics: Nanotheranostics Perspective. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2024, 7, 8126–8148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Liu, M.; You, B.; Luo, G.; Chen, Y.; Liu, B.; Jiang, Z.; Chu, P.K.; Shao, J.; Yu, X.-F. Biodegradable Bi2O2Se Quantum Dots for Photoacoustic Imaging-Guided Cancer Photothermal Therapy. Small 2020, 16, 1905208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Care, A.; Zhang, R.; Lu, Y.; Packer, N.H.; Sunna, A.; Qian, Y.; Zvyagin, A.V. Facile Assembly of Functional Upconversion Nanoparticles for Targeted Cancer Imaging and Photodynamic Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 11945–11953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Cheng, L.; Liu, Z. Drug Delivery with Upconversion Nanoparticles for Multi-Functional Targeted Cancer Cell Imaging and Therapy. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.-H.; Shao, K.; Wu, L.; Hu, J.; Man, M.; Li, X.; Kong, X.-Y.; Shi, J.-S. Upconversion-Nanoparticle-Based Smart Drug-Delivery Platforms for Multimodal Imaging-Guided Cancer Therapies. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 15473–15487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, M.; Dong, H.; Ge, J.; Chen, D.; Sun, L.; Li, S.; Wang, C.; Yan, C.; Wang, P.; Shu, C. Multifunctional Upconversion–Nanoparticles–Trismethylpyridylporphyrin–Fullerene Nanocomposite: A near-Infrared Light-Triggered Theranostic Platform for Imaging-Guided Photodynamic Therapy. NPG Asia Mater. 2015, 7, e205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, M.; Sun, R.; Li, G.; Syeda, M.Z.; Ma, W.; Mai, Z.; Shao, L.; Tang, L.; Yu, Z. NIR-II Emissive Dye Based Polymer Nanoparticle Targeting EGFR for Oral Cancer Theranostics. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 6288–6296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yuan, A.; Sun, M.; Wu, J.; Hu, Y. Self-Assembled IR780-Loaded Transferrin Nanoparticles as an Imaging, Targeting and PDT/PTT Agent for Cancer Therapy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Fernandez-Fernandez, A.; Manchanda, R.; Huang, Y.-C.; McGoron, A.J. Near-infrared dye loaded polymeric nanoparticles for cancer imaging and therapy and cellular response after laser-induced heating. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santra, S.; Kaittanis, C.; Grimm, J.; Perez, J.M. Drug/Dye-Loaded, Multifunctional Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Combined Targeted Cancer Therapy and Dual Optical/Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Small 2009, 5, 1862–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, A.; Yang, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, X. The Glowing Frontier: Carbon Dots’ Journey for Customized Cancer Treatments. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2025, 105, 106658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, T.; Shin, G.H.; Kim, J.T. Carbon Dots: Opportunities and Challenges in Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ray, R.; Gu, Y.; Ploehn, H.J.; Gearheart, L.; Raker, K.; Scrivens, W.A. Electrophoretic Analysis and Purification of Fluorescent Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Fragments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 12736–12737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, T.; Mohiyuddin, S.; Packirisamy, G. Facile and Green Synthesis of Multicolor Fluorescence Carbon Dots from Curcumin: In Vitro and in Vivo Bioimaging and Other Applications. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 831–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Yu, M.; Li, P.; Xu, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Xing, X. Recent Progress on Chiral Carbon Dots: Synthetic Strategies and Biomedical Applications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 9, 5548–5566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, S.; Ding, H.; Xu, M.; Hu, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Jiang, L.; Wang, D.; Dong, C.; et al. Recent Advances in Synthesis, Optical Properties, and Biomedical Applications of Carbon Dots. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 2317–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Han, Y.; Bianco, A.; Ji, D.-K. Recent Progress on Second Near-Infrared Emitting Carbon Dots in Biomedicine. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 11560–11572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegafaw, T.; Oh, I.T.; Cha, H.; Yue, H.; Miao, X.; Ho, S.L.; Ahmad, M.Y.; Marasini, S.; Ghazanfari, A.; Kim, H.-K.; et al. Facile Synthesis of Stable Colloidal Suspension of Amorphous Carbon Nanoparticles in Aqueous Medium and Their Characterization. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2018, 120, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.N.; Baker, G.A. Luminescent Carbon Nanodots: Emergent Nanolights. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6726–6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansuriya, B.D.; Altintas, Z. Carbon Dots: Classification, Properties, Synthesis, Characterization, and Applications in Health Care—An Updated Review (2018–2021). Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Ngashangva, L.; Goswami, P. Carbon Dots: An Emerging Smart Material for Analytical Applications. Micromachines 2021, 12, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, E.R.; Usharani, M.; Usha, A.L. Carbon Dots: An Updated Overview on Their Synthesis, Properties, and Applications in Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Sciences. Thai J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 46, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Zhu, S.; Feng, T.; Yang, M.; Yang, B. Evolution and Synthesis of Carbon Dots: From Carbon Dots to Carbonized Polymer Dots. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1901316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Q.; Ma, Y.; Che, M.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Sang, S. Fluorescent Carbon Dots as Carriers for Intracellular Doxorubicin Delivery and Track. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zheng, S.; Liu, L.; Kong, Y.; Zhang, A.; Xu, K.; Han, C. The Cost-Effective Preparation of Green Fluorescent Carbon Dots for Bioimaging and Enhanced Intracellular Drug Delivery. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Jiang, W.; Jiang, X.; Bai, Z.; He, Y.; Jiang, J.; Wang, D.; Yang, L. Doxorubicin Conjugated Functionalizable Carbon Dots for Nucleus Targeted Delivery and Enhanced Therapeutic Efficacy. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 6801–6809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Yadav, B.; Patil, M.D.; Pujari, A.K.; Singh, U.; Rishi, V.; Bhaumik, J. A Photoarchitectonic Hydrogel for Synergistic in Vitro Chemo–Phototherapy of Breast Cancer. Mater. Adv. 2024, 5, 1903–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, T.; Hao, L.; Wei, Y.; Cai, X.; Zhu, B. Doxorubicin Conjugated Carbon Dots as a Drug Delivery System for Human Breast Cancer Therapy. Cell Prolif. 2018, 51, e12488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Chen, J.; Jiang, K.; Tang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, C.; Wu, A.; Lin, H. Ce6-Modified Carbon Dots for Multimodal-Imaging-Guided and Single-NIR-Laser-Triggered Photothermal/Photodynamic Synergistic Cancer Therapy by Reduced Irradiation Power. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 5791–5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beack, S.; Kong, W.H.; Jung, H.S.; Do, I.H.; Han, S.; Kim, H.; Kim, K.S.; Yun, S.H.; Hahn, S.K. Photodynamic Therapy of Melanoma Skin Cancer Using Carbon Dot–Chlorin e6–Hyaluronate Conjugate. Acta Biomater. 2015, 26, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Yue, L.; Su, H.; Wang, K.; Yang, L.; Zhu, X. Carbon Dots @ Platinum Porphyrin Composite as Theranostic Nanoagent for Efficient Photodynamic Cancer Therapy. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loukanov, A.; Sekiya, R.; Yoshikawa, M.; Kobayashi, N.; Moriyasu, Y.; Nakabayashi, S. Photosensitizer-Conjugated Ultrasmall Carbon Nanodots as Multifunctional Fluorescent Probes for Bioimaging. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 15867–15874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Lin, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; He, M.; Wang, Q.; Chen, F.; Li, Z.; Shen, G.; et al. Light-Triggered Theranostics Based on Photosensitizer-Conjugated Carbon Dots for Simultaneous Enhanced-Fluorescence Imaging and Photodynamic Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 5104–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Solanki, A.; Mandal, S.; Subramanyam, D.; Das, P. Creation of Linear Carbon Dot Array with Improved Optical Properties through Controlled Covalent Conjugation with DNA. Bioconjugate Chem. 2018, 29, 1500–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadinejad, R.; Dadashzadeh, A.; Moghassemi, S.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Dehshahri, A.; Pardakhty, A.; Sassan, H.; Sohrevardi, S.-M.; Mandegary, A. Shedding Light on Gene Therapy: Carbon Dots for the Minimally Invasive Image-Guided Delivery of Plasmids and Noncoding RNAs—A Review. J. Adv. Res. 2019, 18, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-F.; Wu, H.-C.; Kuan, C.-H.; Lin, C.-J.; Wang, L.-W.; Chang, C.-W.; Wang, T.-W. Multi-Functionalized Carbon Dots as Theranostic Nanoagent for Gene Delivery in Lung Cancer Therapy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, A.; Ghosh, A.K.; Chowdhury, M.; Das, P.K. Folic Acid-Functionalized Carbon Dot-Enabled Starvation Therapy in Synergism with Paclitaxel against Breast Cancer. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 2389–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Peng, Z.; Dallman, J.; Baker, J.; Othman, A.M.; Blackwelder, P.L.; Leblanc, R.M. Crossing the Blood–Brain–Barrier with Transferrin Conjugated Carbon Dots: A Zebrafish Model Study. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 145, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strickland, S.; Jorns, M.; Fourroux, L.; Heyd, L.; Pappas, D. Cancer Cell Targeting Via Selective Transferrin Receptor Labeling Using Protein-Derived Carbon Dots. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 2707–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, L.M.T.; Gul, A.R.; Le, T.N.; Kim, M.W.; Kailasa, S.K.; Oh, K.T.; Park, T.J. One-pot synthesis of carbon dots with intrinsic folic acid for synergistic imaging-guided photothermal therapy of prostate cancer cells. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 5187–5196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lin, Z.; Yu, Y.X.; Jiang, B.P.; Shen, X.C. Multifunctional hyaluronic acid-derived carbon dots for self-targeted imaging-guided photodynamic therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 6534–6543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.-H.; Luo, T.-Y.; He, X.; Yu, X.-Q. Hyaluronic Acid-Based Carbon Dots for Efficient Gene Delivery and Cell Imaging. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 15613–15624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Chen, T. A Review of in Vivo Toxicity of Quantum Dots in Animal Models. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 8143–8168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Ding, H.; Xu, M.; Hu, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Lu, S.; Tian, Y.; et al. UV–Vis–NIR Full-Range Responsive Carbon Dots with Large Multiphoton Absorption Cross Sections and Deep-Red Fluorescence at Nucleoli and In Vivo. Small 2020, 16, 2000680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Zhang, B.; Chen, L.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, X.; Ge, D.; Shi, W.; Sun, Y. Facile One-Pot Synthesis of Polydopamine Carbon Dots for Photothermal Therapy. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Tan, Z.; Zhao, T.; Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Jia, Y.; Peng, Z. Indocyanine Green derived Carbon Dots with Significantly Enhanced Properties for Efficient Photothermal Therapy. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 1925–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Cheng, H.; Ren, Z.; Wang, H.; Lu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, S. Red light-emitting carbon dots for reduced phototoxicity and photothermal/photodynamic-enhanced synergistic tumor therapy. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 659, 130763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Qiao, H.; Zhang, Y.; He, Y.; Xie, S.; Gu, Y.; Lin, F. Facile Microwave Hydrothermal Synthesis of Citric Acid-Derived Carbon Dots for Photothermal Therapy of Cancers under NIR Irradiation. Carbon Lett. 2025, 35, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Pei, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Xie, Z.; Zheng, M. Carbon dots for long-term near-infrared afterglow imaging and photodynamic therapy. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 467, 143384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Shen, X.; Su, C.; Yang, J.; Piao, M.; Jia, F.; Gao, G.; Zhang, L.; Lin, Q. One-step synthesis of photoluminescent carbon dots with excitation-independent emission for selective bioimaging and gene delivery. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 492, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Li, Y.; Zhai, X.; Xu, B.; Cao, Z.; Liu, W. Polycation-b-Polyzwitterion Copolymer Grafted Luminescent Carbon Dots as a Multifunctional Platform for Serum-Resistant Gene Delivery and Bioimaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 20487–20497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, J.; Wang, J.; Cheng, H.; Wang, Y.; Qin, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Wu, X.; et al. Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots as a Highly Efficient Photosensitizer for Photodynamic Therapy to Promote Apoptosis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 697, 134409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balou, S.; Shandilya, P.; Priye, A. Carbon Dots for Photothermal Applications. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 1023602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, B.; Hu, J.; Li, Y.; Feng, S.; Pan, D.; Feng, L.; Shen, L. Near-Infrared Phosphorescent Carbon Dots for Sonodynamic Precision Tumor Therapy. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Thakor, A.S.; Kevadiya, B.D.; Cheng, J.; Chen, M.; Li, Y.; Xu, Q.; Wu, Q.; Wu, Y. Endogenous NO-releasing Carbon Nanodots for Tumor-specific Gas Therapy. Acta Biomater. 2021, 136, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.; Lin, S.; Huang, X.; Jin, Y. Synthesis and Properties of Carbon Quantum Dots and Their Research Progress in Cancer Treatment. Dye. Pigment. 2021, 196, 109766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesani, P.; Hadi, A.H.M.; Lu, Z.; Palomba, S.; New, J.E.; Zreiqat, H. Design principles and biological applications of red-emissive two-photon carbon dots. Commun. Mater. 2021, 2, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-L.; Bai, L.-F.; Geng, Z.-R.; Chen, H.; Xu, L.-T.; Xie, Y.-C.; Wang, D.-J.; Gu, H.-W.; Wang, X.-M. Carbon quantum dots: Preparation, optical properties, and biomedical applications. Mater. Today Adv. 2023, 18, 100376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alafeef, M.; Srivastava, I.; Aditya, T.; Pan, D. Carbon Dots: From Synthesis to Unraveling the Fluorescence Mechanism. Small 2024, 20, 2303937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, F.; Karmaker, P.G.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, B.; Yang, X. Preparation and Biomedical Applications of Multicolor Carbon Dots: Recent Advances and Future Challenges. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2020, 37, 1900489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahana, S.; Gautam, A.; Singh, R.; Chandel, S. A Recent Update on Development, Synthesis Methods, Properties and Application of Natural Products Derived Carbon Dots. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2023, 13, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayiloor Rajesh, G.; John, V.L.; Pookunnath Santhosh, A.; Krishnan Nair Ambika, A.; Thavarool Puthiyedath, V. Carbon dots from natural sources for biomedical applications. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2022, 39, 2200017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döring, A.; Ushakova, E.; Rogach, A.L. Chiral Carbon Dots: Synthesis, Optical Properties, and Emerging Applications. Light Sci. Appl. 2022, 11, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khayal, A.; Dawane, V.; Amin, M.A.; Tirth, V.; Yadav, V.K.; Algahtani, A.; Khan, S.H.; Islam, S.; Yadav, K.K.; Jeon, B.-H. Advances in the Methods for the Synthesis of Carbon Dots and Their Emerging Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Liccardo, L.; Moretti, E.; Zhao, H.; Vomiero, A. Synthesis, optical properties and applications of red/near-infrared carbon dots. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 11827–11847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shafey, A.M. Carbon dots: Discovery, structure, fluorescent properties, and applications. Green Process. Synth. 2021, 10, 134–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pundi, A.; Chang, C.-J. Recent Advances in Synthesis, Modification, Characterization, and Applications of Carbon Dots. Polymers 2022, 14, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorns, M.; Pappas, D. A Review of Fluorescent Carbon Dots, Their Synthesis, Physical and Chemical Characteristics, and Applications. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, G.; Li, L.; Wang, D.; Chen, M.; Zeng, Z.; Xiong, W.; Wu, X.; Guo, C. Carbon dots: Synthesis, properties and biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 6553–6575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.H.; Bardakci, F.; Akgöl, S.; Kusat, K.; Adnan, M.; Alam, M.J.; Gupta, R.; Sahreen, S.; Chen, Y.; Gopinath, S.C. Green Carbon Dots: Synthesis, Characterization, Properties and Biomedical Applications. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, V.M.; Bhosale, S.V.; Kolekar, G.B. A brief review on the synthesis, characterisation and analytical applications of nitrogen doped carbon dots. Anal. Methods 2022, 14, 877–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Ren, X.; Sun, M.; Liu, H.; Xia, L. Carbon Dots: Synthesis, Properties and Applications. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Choi, Y.; Kwon, O.-H.; Kim, B.-S. Carbon Dots: Bottom-Up Syntheses, Properties, and Light-Harvesting Applications. Chem. Asian J. 2018, 13, 586–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, X.; Bai, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X. Surface Modification and Chemical Functionalization of Carbon Dots: A Review. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Ai, L.; Song, Z.; Nie, M.; Xiao, J.; Li, G.; Lu, S. Surface Modification Functionalized Carbon Dots. Chem. Eur. J. 2023, 29, e202302383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benner, D.; Yadav, P.; Bhatia, D. Red emitting carbon dots: Surface modifications and bioapplications. Nanoscale Adv. 2023, 5, 4337–4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hetty, H.R.A.K.; Jalil, A.T.; Al-Tamimi, J.H.Z.; Shakier, H.G.; Kandeel, M.; Saleh, M.M.; Naderifar, M. Engineering and surface modification of carbon quantum dots for cancer bioimaging. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 149, 110433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Ragib, A.; Al Amin, A.; Alanazi, Y.M.; Kormoker, T.; Uddin, M.; Siddique, M.A.B.; Barai, H.R. Multifunctional carbon dots in nanomaterial surface modification: A descriptive review. Carbon Res. 2023, 2, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Deng, D.; Xing, Y.; Li, S.; Yuan, B.; Chen, J.; Xia, N. Activity analysis of the carbodiimide-mediated amine coupling reaction on self-assembled monolayers by cyclic voltammetry. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 89, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramathilaka, M.P.; Tao, B.Y. Characterization of covalent crosslinking strategies for synthesizing DNA-based bioconjugates. J. Biol. Eng. 2019, 13, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Amat, D.; Peng, Z.; Vanni, S.; Raskin, S.; De Angulo, G.; Othman, A.M.; Graham, R.M.; Leblanc, R.M. Transferrin conjugated nontoxic carbon dots for doxorubicin delivery to target pediatric brain tumor cells. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 16662–16669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, W.-J.; Shan, D.; Zhu, R.-H.; Deng, S.-Y.; Cosnier, S.; Zhang, X.-J. Dumbbell-Shaped Carbon Quantum Dots/AuNCs Nanohybrid as an Efficient Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe for Sensing Cadmium (II) Ions and l-Ascorbic Acid. Carbon 2016, 96, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, A.S.; Radhakumary, C.; Priya, S.S.; Ramesan, R.M.; Sreenivasan, K. Methotrexate Anchored Carbon Dots as Theranostic Probes: Digitonin Conjugation Enhances Cellular Uptake and Cytotoxicity. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 56313–56318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algarra, M.; Campos, B.B.; Radotić, K.; Mutavdžić, D.; Bandosz, T.; Jiménez-Jiménez, J.; Rodriguez-Castellón, E.; da Silva, J.C.G.E. Luminescent Carbon Nanoparticles: Effects of Chemical Functionalization, and Evaluation of Ag+ Sensing Properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 8342–8351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Zhong, Y.; Yang, X.-F.; Li, Z.; Li, H. Preparation of yellow-green-emissive carbon dots and their application in constructing a fluorescent turn-on nanoprobe for imaging of selenol in living cells. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 1734–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Guo, Z.; Feng, R.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, W.; Liu, Z. Hyperbranched polyglycerol conjugated fluorescent carbon dots with improved in vitro toxicity and red blood cell compatibility for bioimaging. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 4975–4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Ye, Z.; Kang, J.; Wang, X.; Han, Z. Synthesis of carbon dot based Schiff bases and selective anticancer activity in glioma cells. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 1952–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajani, A.A.; Rafiee, L.; Javanmard, S.H.; Dana, N.; Jandaghian, S. Carbon dot incorporated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy and fluorescence imaging. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 9491–9500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Yin, G.; Song, Z.; Yu, J.; Yong, X.; Zhang, B.; Ai, L.; Lu, S. Solid-State Luminescence in Self-Assembled Chlorosalicylaldehyde-Modified Carbon Dots. ACS Mater. Lett. 2023, 5, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Xu, C.; Guo, Y.; Bao, X.; Guan, S.; Liu, H.; Zhang, T. Nucleus-Targeting Carbon Quantum Dots Assembled with Gambogic Acid via π–π Stacking for Cancer Therapy. Adv. Therap. 2023, 6, 2200201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Dai, Z. Preparation of Silicon-Carbon-Based Dots@Dopamine and Its Application in Intracellular Ag+ Detection and Cell Imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 3644–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.B.; Liu, M.L.; Zhan, L.; Li, C.M.; Huang, C.Z. Terbium (III) Modified Fluorescent Carbon Dots for Highly Selective and Sensitive Ratiometry of Stringent. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 4003–4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Gui, R.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J. Carrot-derived carbon dots modified with polyethyleneimine and nile blue for ratiometric two-photon fluorescence turn-on sensing of sulfide anion in biological fluids. Talanta 2017, 169, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Claudel, M.; Ronzani, C.; Arezki, Y.; Lebeau, L.; Pons, F. Physicochemical Characteristics That Affect Carbon Dot Safety: Lessons from A Comprehensive Study on A Nanoparticle Library. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 569, 118521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havrdova, M.; Hola, K.; Skopalik, J.; Tomankova, K.; Petr, M.; Cepe, K.; Polakova, K.; Tucek, J.; Bourlinos, A.B.; Zboril, R. Toxicity of Carbon Dots – Effect of Surface Functionalization on the Cell Viability, Reactive Oxygen Species Generation and Cell Cycle. Carbon 2016, 99, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznietsova, H.; Géloën, A.; Dziubenko, N.; Zaderko, A.; Alekseev, S.; Lysenko, V.; Skryshevsky, V. In Vitro and in Vivo Toxicity of Carbon Dots with Different Chemical Compositions. Discover Nano 2023, 18, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, N.; Valenzuela, S.; Segura, C.; Osorio-Roman, I.; Arrázola, M.S.; Panadero-Medianero, C.; Santana, P.A.; Ahumada, M. Poly(Ethylene Imine)-Chitosan Carbon Dots: Study of Its Physical–Chemical Properties and Biological in Vitro Performance. Discover Nano 2023, 18, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, M.; Fan, J.; Claudel, M.; Sonntag, T.; Didier, P.; Ronzani, C.; Lebeau, L.; Pons, F. Density of Surface Charge Is a More Predictive Factor of the Toxicity of Cationic Carbon Nanoparticles than Zeta Potential. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Sun, H.; Ruan, S.; Wang, Y.; Shen, S.; Xu, W.; He, Q.; Gao, H. In Vitro and in Vivo Toxicology of Bare and PEGylated Fluorescent Carbonaceous Nanodots in Mice and Zebrafish: The Potential Relationship with Autophagy. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 38547–38557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Wu, X.; Liang, Q.; Yu, F.; Xu, J.; Li, Z.; Bi, H. Aptamer-Modified Carbon Dots for Enhancement of Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer Cells. Talanta Open 2022, 6, 100161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getachew, G.; Korupalli, C.; Rasal, A.S.; Chang, J.-Y. ROS generation/scavenging modulation of carbon dots as phototherapeutic candidates and peroxidase mimetics to integrate with polydopamine nanoparticles/GOx towards cooperative cancer therapy. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 226, 109364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehvari, K.; Liu, K.Y.; Tseng, P.-J.; Gedda, G.; Girma, W.M.; Chang, J.-Y. Sonochemical-assisted green synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon dots from crab shell as targeted nanoprobes for cell imaging. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2019, 95, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, K.; Wang, L.; Lee, C.-S. Oxygen/Nitrogen-Related Surface States Controlled Carbon Nanodots with Tunable Full-Color Luminescence: Mechanism and Bio-Imaging. Carbon 2020, 160, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, B.; Xu, F.; Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wei, D.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jia, D.; Zhou, Y. Visual in Vivo Degradation of Injectable Hydrogel by Real-Time and Non-Invasive Tracking Using Carbon Nanodots as Fluorescent Indicator. Biomaterials 2017, 145, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Xue, W.; Huang, S. Functionalized Green Carbon Dots for Specific Detection of Copper in Human Serum Samples and Living Cells. J. Fluoresc. 2025, 35, 1637–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Yao, Y.; Lee, C.-H.; Wu, Y.; Li, P. In Vivo Biodistribution, Clearance, and Biocompatibility of Multiple Carbon Dots Containing Nanoparticles for Biomedical Application. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, L.; Choi, K.Y.; Guo, N.; Guo, J.; Tackett, K.; Anilkumar, P.; Liu, G.; Quan, Q.; et al. Effect of Injection Routes on the Biodistribution, Clearance, and Tumor Uptake of Carbon Dots. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 5684–5693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, B.; Li, D.; Zhou, D.; Jing, P.; Xu, G.; Wang, Y.; Holá, K.; et al. In Vivo Theranostics with Near-Infrared-Emitting Carbon Dots—Highly Efficient Photothermal Therapy Based on Passive Targeting after Intravenous Administration. Light Sci. Appl. 2018, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Yang, K.; Ma, Z.; Wan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, Z.; Liu, Z. In Vivo NIR Fluorescence Imaging, Biodistribution, and Toxicology of Photoluminescent Carbon Dots Produced from Carbon Nanotubes and Graphite. Small 2012, 8, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Shao, D.; Li, J.; Song, Y.; Chen, Y.; Pan, Y.; Zhu, S.; Yang, B.; Chen, L. Single and repeated dose toxicity of citric acid-based carbon dots and a derivative in mice. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 91398–91406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Shen, G.; Zhao, X.; Dong, N.; Jia, P.; Wu, J.; Cui, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. Carbon dots: A safe nanoscale substance for the immunologic system of mice. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, M.; Valizadeh, H.; Shahgolzari, M.; Talebi, M.; Baybordi, E.; Dadpour, M.R.; Salehi, R.; Mehrmohammadi, M. Synthesis of Self-Targeted Carbon Dot with Ultrahigh Quantum Yield for Detection and Therapy of Cancer. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 24628–24638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Su, W.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Fan, L. Applications of Carbon Dots on Tumour Theranostics. VIEW 2021, 2, 20200061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zhao, J.; Fu, J.; Cai, J.; Zhang, P. Recent advances of biomimetic nano-systems in the diagnosis and treatment of tumor. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 16, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sigdel, G.; Mintz, K.J.; Seven, E.S.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Wang, C.Y.; Leblanc, R.M. Carbon dots: A future blood-brain barrier penetrating nanomedicine and drug nanocarrier. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 5003–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oerlemans, C.; Bult, W.; Bos, M.; Storm, G.; Nijsen, J.F.W.; Hennink, W.E. Polymeric Micelles in Anticancer Therapy: Targeting, Imaging and Triggered Release. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 2569–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotta, S.; Aldawsari, H.M.; Badr-Eldin, S.M.; Nair, A.B.; Yt, K. Progress in Polymeric Micelles for Drug Delivery Applications. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perumal, S.; Atchudan, R.; Lee, W. A Review of Polymeric Micelles and Their Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolova, M.P.; Kumar, E.M.; Chavali, M.S. Updates on Responsive Drug Delivery Based on Liposome Vehicles for Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senjab, R.; Alsawaftah, N.M.; AbuWatfa, W.; Husseini, G. Advances in liposomal nanotechnology: From concept to clinics. RSC Pharm. 2024, 1, 928–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manimaran, V.; Nivetha, R.P.; Tamilanban, T.; Narayanan, J.; Vetriselvan, S.; Fuloria, N.K.; Chinni, S.V.; Sekar, M.; Fuloria, S.; Wong, L.S.; et al. Nanogels as Novel Drug Nanocarriers for CNS Drug Delivery. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1232109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panta, P.; Kim, D.Y.; Kwon, J.S.; Son, A.R.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, M.S. Protein drug-loaded polymeric nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 2014, 7, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltaib, L. Polymeric Nanoparticles in Targeted Drug Delivery: Unveiling the Impact of Polymer Characterization and Fabrication. Polymers 2025, 17, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Ruan, S.; Liu, S.; Sun, T.; Qu, D.; Zhao, H.; Xie, Z.; Gao, H.; Jing, X.; Sun, Z. Self-Targeting Fluorescent Carbon Dots for Diagnosis of Brain Cancer Cells. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 11455–11461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Jiang, J.; Yan, Y.; Wang, P.; Huang, G.; Kim, N.H.; Lee, J.H.; He, D. Red, Green, and Blue Fluorescent Folate-Receptor-Targeting Carbon Dots for Cervical Cancer Cellular and Tissue Imaging. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 93, 1054–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Dong, H.; Su, Y.; Wu, Y.; Narron, R.; Yong, Q. Synthesis of Carbon Quantum Dot Nanoparticles Derived from Byproducts in Bio-Refinery Process for Cell Imaging and In Vivo Bioimaging. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakocak, B.B.; Laradji, A.; Primeau, T.; Berezin, M.Y.; Li, S.; Ravi, N. Hyaluronan-Conjugated Carbon Quantum Dots for Bioimaging Use. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.-W.; Bao, Y.-W.; Zeng, J.; Wu, F.-G. Nucleolus-Targeted Red Emissive Carbon Dots with Polarity-Sensitive and Excitation-Independent Fluorescence Emission: High-Resolution Cell Imaging and in Vivo Tracking. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 32647–32658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Yuan, T.; Sui, L.; Wang, Z.; Xi, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Fan, L.; Tan, Z.; Chen, A.; et al. Engineering Triangular Carbon Quantum Dots with Unprecedented Narrow Bandwidth Emission for Multicolored LEDs. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, R.; Feng, B.; Zhong, X.; Ostrikov, K. Photoluminescence mechanism of carbon dots: Triggering high-color-purity red fluorescence emission through edge amino protonation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, R.; Basavegowda, N.; Jena, S.; Jayakodi, S.; Elumalai, P.; Chaitanyakumar, A.; Somu, P.; Baek, K.-H. Recent Developments in Heteroatom/Metal-Doped Carbon Dot-Based Image-Guided Photodynamic Therapy for Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, P.; Moitra, P.; McDonald, M.M.; Esch, M.B.; Pan, D. Near-Infrared Emitting Dual-Stimuli-Responsive Carbon Dots from Endogenous Bile Pigments. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 13487–13496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G.-S.; Shen, C.-L.; Niu, C.-Y.; Lou, Q.; Jiang, T.-C.; Li, P.-F.; Shi, X.-J.; Song, R.-W.; Deng, Y.; Lv, C.-F.; et al. Photooxidation triggered ultralong afterglow in carbon nanodots. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Huang, J.; Yuan, L.; Xie, W.; Ying, Y.; Li, C.; Yu, Y.; Pan, Y.; Qu, W.; Hao, H.; et al. Recent Progress of Emitting Long-Wavelength Carbon Dots and Their Merits for Visualization Tracking, Target Delivery and Theranostics. Theranostics 2023, 13, 3064–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Lee, S.H.; Kwon, H.-Y.; Ciaramicoli, L.M.; Jo, E.; Yu, Y.H.; Li, F.; Kim, B.; Hong, K.; Lee, J.-S.; et al. A Pair of Fluorescent Probes Enabling Precise Diagnosis of Liver Cancer by Complementary Imaging. ACS Cent. Sci. 2025, 11, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Liu, M.; Zhang, H.; Guo, W. High-Contrast Fluorescence Diagnosis of Cancer Cells/Tissues Based on β-Lapachone-Triggered ROS Amplification Specific in Cancer Cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2021, 60, 12992–12998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Guo, W. Discrimination between cancerous and normal cells/tissues enabled by a near-infrared fluorescent HClO probe. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 334, 129602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, N.; Ramteke, S.; Jain, N.K.; Dutta, T.; Lal Koner, A. Folate-Receptor-Mediated Uptake of Carbon Dots as a pH-Responsive Carrier for Chemotherapy. ChemistrySelect 2022, 7, e202201604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhunia, S.K.; Maity, A.R.; Nandi, S.; Stepensky, D.; Jelinek, R. Imaging Cancer Cells Expressing the Folate Receptor with Carbon Dots Produced from Folic Acid. ChemBioChem 2016, 17, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, X.; Xian, M.; Dong, C.; Shuang, S. Folic Acid-Conjugated Green Luminescent Carbon Dots as a Nanoprobe for Identifying Folate Receptor-Positive Cancer Cells. Talanta 2018, 183, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.W.; Zhang, J.L.; Shi, L.H.; Xian, M.; Dong, C.; Shuang, S.M. Folic acid-conjugated carbon dots as green fluorescent probes based on cellular targeting imaging for recognizing cancer cells. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 42159–42167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Shi, W.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Ma, H. Fluorescent Carbon Nanodots Conjugated with Folic Acid for Distinguishing Folate-Receptor-Positive Cancer Cells from Normal Cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 12568–12573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Chang, J.; Wu, H.; Wang, H.; Xie, W.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, L. Carbon Dots with Guanidinium and Amino Acid Functional Groups for Targeted Small Interfering RNA Delivery toward Tumor Gene Therapy. Small 2023, 19, 2207204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Guo, R.; Yuan, F.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Fan, L. Red-Emissive Carbon Quantum Dots for Nuclear Drug Delivery in Cancer Stem Cells. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 1357–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manhas, P.; Cokca, C.; Sharma, R.; Peneva, K.; Wangoo, N.; Sharma, D.; Sharma, R.K. Chitosan Functionalized Doxorubicin Loaded Poly(Methacrylamide) Based Copolymeric Nanoparticles for Enhanced Cellular Internalization and in Vitro Anticancer Evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 129242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, M.; Tian, L.; Qiu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Wang, X.; Guo, R.; He, Q. Facile strategy by hyaluronic acid functional carbon dot-doxorubicin nanoparticles for CD44 targeted drug delivery and enhanced breast cancer therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 578, 119122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailing, Y.; Xiufang, L.; Lili, W.; Baoqiang, L.; Kaichen, H.; Yongquan, H.; Qianqian, Z.; Chaoming, M.; Xiaoshuai, R.; Rui, Z.; et al. Doxorubicin-Loaded Fluorescent Carbon Dots with PEI Passivation as a Drug Delivery System for Cancer Therapy. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 17222–17237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Tian, Y.; Kang, Y.; Ren, G.; Liu, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, B.; Yan, L.; et al. Targeted Delivery of Doxorubicin Using Transferrin-Conjugated Carbon Dots for Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 7280–7289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, B.; Yang, D.; Pan, D.; Wang, L.; Zheng, F.; Shen, W.; Zhang, C.; Li, X. NIR-Responsive Carbon Dots for Efficient Photothermal Cancer Therapy at Low Power Densities. Carbon 2018, 134, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudjedi, F.; Kirk, A.G. Near-Infrared Nanoparticle-Mediated Photothermal Cancer Therapy: A Comprehensive Review of Advances in Monitoring and Controlling Thermal Effects for Effective Cancer Treatment. Nano Select 2025, 6, e202400107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Li, H.; Yin, X.; Yang, Q.; Chen, A.; Li, R.; Wang, J.; Yang, R. Revealing Graphitic Nitrogen Participating in p–π Conjugated Domain as Emissive Center of Red Carbon Dots and Applied to Red Room-Temperature Phosphorescence. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 22335–22343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, W.Q.; Xie, Z.G.; Jing, X.B. One-Pot to Synthesize Multifunctional Carbon Dots for Near Infrared Fluorescence Imaging and Photothermal Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 23533–23541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Jia, Q.; Liu, W.; Guo, L.; Liu, Q.; Lan, M.; Zhang, H.; Meng, X.; Wang, P. Red-Emissive Carbon Dots for Fluorescent, Photoacoustic, and Thermal Theranostics in Living Mice. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4169–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yan, L.; Cao, M.; Huang, L.; Yang, K.; Wu, S.; Lan, M.; Niu, G.; Zhang, W. Near-Infrared Light-Triggered Lysosome-Targetable Carbon Dots for Photothermal Therapy of Cancer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 53610–53617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, F.; Zhang, S.; An, Y.; Sun, S. Preparation of N-Doped Yellow Carbon Dots and N, P Co-Doped Red Carbon Dots for Bioimaging and Photodynamic Therapy of Tumors. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 6332–6342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillar-Little, T.J.; Wanninayake, N.; Nease, L.; Heidary, D.K.; Glazer, E.C.; Kim, D.Y. Superior Photodynamic Effect of Carbon Quantum Dots through Both Type I and Type II Pathways: Detailed Comparison Study of Top-down-Synthesized and Bottom-up-Synthesized Carbon Quantum Dots. Carbon 2018, 140, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ding, H.; Li, Z.; Tedesco, A.C.; Bi, H. Carbon Dots Derived from Tea Polyphenols as Photosensitizers for Photodynamic Therapy. Molecules 2022, 27, 8627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Pei, Q.; Zheng, M.; Xie, Z. Porphyrin-based carbon dots for photodynamic therapy of hepatoma. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1600924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boidin, L.; Moinard, M.; Moussaron, A.; Merlier, M.; Moralès, O.; Grolez, G.P.; Baydoun, M.; Mohd-Gazzali, A.; Tazizi, M.H.D.M.; Allah, H.H.A.; et al. Targeted Photodynamic Therapy Using a Vectorized Photosensitizer Coupled to Folic Acid Analog Induces Ovarian Tumor Cell Death and Inhibits IL-6-Mediated Inflammation. J. Control. Rel. 2024, 371, 351–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Kim, S.; Choi, M.H.; Ryoo, S.-R.; Park, J.; Min, D.-M.; Kim, B.-S. Highly biocompatible carbon nanodots for simultaneous bioimaging and targeted photodynamic therapy in vitro and in vivo. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 5781–5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; Li, L.; Jiang, C.; Mei, Q.; Dong, W.-F.; Yan, R. Riboflavin-based carbon dots with high singlet oxygen generation for photodynamic therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 7972–7978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.; Xu, B.; Qiu, G.; Wei, M.; Zhang, M.; Bao, S.; Tang, J.; Li, L.; Liu, J. Multifunctional Nanoparticles-Mediated PTT/PDT Synergistic Immune Activation and Antitumor Activity Combined with Anti-PD-L1 Immunotherapy for Breast Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 5391–5411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, M.; Guo, L.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, Q.; Yan, L.; Xia, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, P.; Zhang, W. Carbon Dots as Multifunctional Phototheranostic Agents for Photoacoustic/Fluorescence Imaging and Photothermal/Photodynamic Synergistic Cancer Therapy. Adv. Ther. 2018, 1, 1800077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wu, S.; Jia, Q.; Huang, L.; Lan, M.; Wang, P.; Zhang, W. Lysosome-targetable carbon dots for highly efficient photothermal/photodynamic synergistic cancer therapy and photoacoustic/two-photon excited fluorescence imaging. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 388, 124212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Sun, S.; Li, S.; Lv, A.; Chen, Q.; Jiang, K.; Jiang, Z.; Li, Z.; Wu, A.; Lin, H. Programmed Stimuli-Responsive Carbon Dot-Nanogel Hybrids for Imaging-Guided Enhanced Tumor Phototherapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 10142–10153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Zheng, X.; Ge, J.; Liu, W.; Ren, H.; Chen, S.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, J.; Wang, P. Synthesis of carbon dots from Hypocrella bambusae for bimodel fluorescence/photoacoustic imaging-guided synergistic photodynamic/photothermal therapy of cancer. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 526, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; Miao, P.; Li, L.; Yan, R.; Dong, W.-F.; Mei, Q. Injectable Carbon Dots-Based Hydrogel for Combined Photothermal Therapy and Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 49582–49591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Yao, T.; Peng, H.; Whittaker, A.K.; Li, Y.; Zhu, S.; Wang, Z. An Injectable Hydrogel for Simultaneous Photothermal Therapy and Photodynamic Therapy with Ultrahigh Efficiency Based on Carbon Dots and Modified Cellulose Nanocrystals. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2106079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, S.; Lin, T.; Ye, F.; Zhao, S. Carbon Dots with Absorption Red-Shifting for Two-Photon Fluorescence Imaging of Tumor Tissue pH and Synergistic Phototherapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 35365–35375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, R.; Singh, A.; Singh, S.; Navneesh; Rawal, R.K. Emerging Trends in Nano-Carrier Based Gene Delivery Systems for Targeted Cancer Therapy. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 95, 105546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, S.; Mozaffarian, M.; Pazuki, G.; Hadidi, N.; Villate-Beitia, I.; Zárate, J.; Puras, G.; Pedraz, J.L. Carbon-Based Nanostructures as Emerging Materials for Gene Delivery Applications. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Raut, J.; Sahoo, P. Gene Silencing and Gene Delivery in Therapeutics: Insights Using Quantum Dots. Front. Biosci. Landmark Ed. 2023, 28, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zheng, W.; Tang, R.; Wang, N.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, X. Gene Regulation with Carbon-Based siRNA Conjugates for Cancer Therapy. Biomaterials 2016, 104, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, M.; Gao, F.; Yu, C.; Zeng, M.; He, G.; Wu, Y.; Su, Y.; Hu, N.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, Z.; et al. Dual-Targeted Therapy in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Cells with the Combination of Carbon Dots/HER3 siRNA and Trastuzumab. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 335102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Choi, Y.; Park, G.; Won, C.; Park, Y.-J.; Lee, Y.; Kim, B.-S.; Min, D.-H. Highly Efficient Gene Silencing and Bioimaging Based on Fluorescent Carbon Dots in Vitro and in Vivo. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 503–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, X.; Fang, Z.; Niu, Y.; Lou, J.; Wu, Y.; Zou, S.; Xia, S.; Sun, M.; Du, F. Fabrication of HA/PEI-Functionalized Carbon Dots for Tumor Targeting, Intracellular Imaging and Gene Delivery. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 3369–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Ghosal, K.; Mohammad, S.A.; Sarkar, K. Dendrimer functionalized carbon quantum dot for selective detection of breast cancer and gene therapy. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 373, 468–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Tang, K.; Cai, Z.; Lin, X.; Huang, Y.; Yu, T.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wu, L.; Yang, L.; et al. Carbon Dots-Based Nanozyme for Drug-Resistant Lung Cancer Therapy by Encapsulated Doxorubicin/siRNA Cocktail. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 933–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Shen, G.; Liu, H.; Fu, H.; Cui, D. Fluorescent carbon dots as an efficient siRNA nanocarrier for its interference therapy in gastric cancer cells. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2014, 12, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Shao, Z.; Zhao, Y. Development of porphyrin and titanium dioxide sonosensitizers for sonodynamic cancer therapy. Biomater. Transl. 2021, 2, 72–85. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, W.; Wang, H.; Chang, Q.; Li, N.; Yang, J.; Hu, S. Origin of sonocatalytic activity of fluorescent carbon dots. Carbon 2021, 184, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Shi, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z. Integrin αvβ3-targeted engineered carbon dots for efficacious sonodynamic therapy and fluorescence navigation surgery against gliomas. Mater. Chem. Front. 2024, 8, 2511–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Peng, Y.; Lu, L.; Peng, S.; Chen, T.; Zhan, M. Near-infrared light-triggered nano-prodrug for cancer gas therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Cao, X.; Wen, H.; Shubhra, Q.T.; Hu, X.; He, X.; Cai, X. Integrative gas-based therapeutics for cancer treatment: Recent advances and multi-therapy innovations. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2025, 539, 216746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Cai, S.; Wang, M.; Chen, Z.; Lu, C.; Yang, H. Photogenerated Holes Mediated Nitric Oxide Production for Hypoxic Tumor Treatment. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 7046–7050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Nanocarrier | Size (nm) | Advantage | Limitation | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD | <10 |
|
| [30,125] |
| Micelle | 5–100 |
|
| [126,127,128] |
| Liposome | 50–150 |
|
| [129,130] |
| Nanogel | <200 |
|
| [131] |
| Polymeric nanoparticle | 10–1000 |
|
| [132,133] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tegafaw, T.; Mulugeta, E.; Zhao, D.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Baek, A.; Kim, J.; Chang, Y.; Lee, G.H. Surface Modification, Toxicity, and Applications of Carbon Dots to Cancer Theranosis: A Review. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 781. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110781
Tegafaw T, Mulugeta E, Zhao D, Liu Y, Chen X, Baek A, Kim J, Chang Y, Lee GH. Surface Modification, Toxicity, and Applications of Carbon Dots to Cancer Theranosis: A Review. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(11):781. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110781
Chicago/Turabian StyleTegafaw, Tirusew, Endale Mulugeta, Dejun Zhao, Ying Liu, Xiaoran Chen, Ahrum Baek, Jihyun Kim, Yongmin Chang, and Gang Ho Lee. 2025. "Surface Modification, Toxicity, and Applications of Carbon Dots to Cancer Theranosis: A Review" Nanomaterials 15, no. 11: 781. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110781
APA StyleTegafaw, T., Mulugeta, E., Zhao, D., Liu, Y., Chen, X., Baek, A., Kim, J., Chang, Y., & Lee, G. H. (2025). Surface Modification, Toxicity, and Applications of Carbon Dots to Cancer Theranosis: A Review. Nanomaterials, 15(11), 781. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110781









