Highly Wear-Resistant Triboelectric Nanogenerators Based on Fluorocarbon-Graphene Hybrids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Material
2.2. Preparation of 3D HPG-FEVE Complex
2.3. Preparation of Contact-Separation TENG and Sliding TENG
2.4. Characterization Methods
3. Result and Discussion
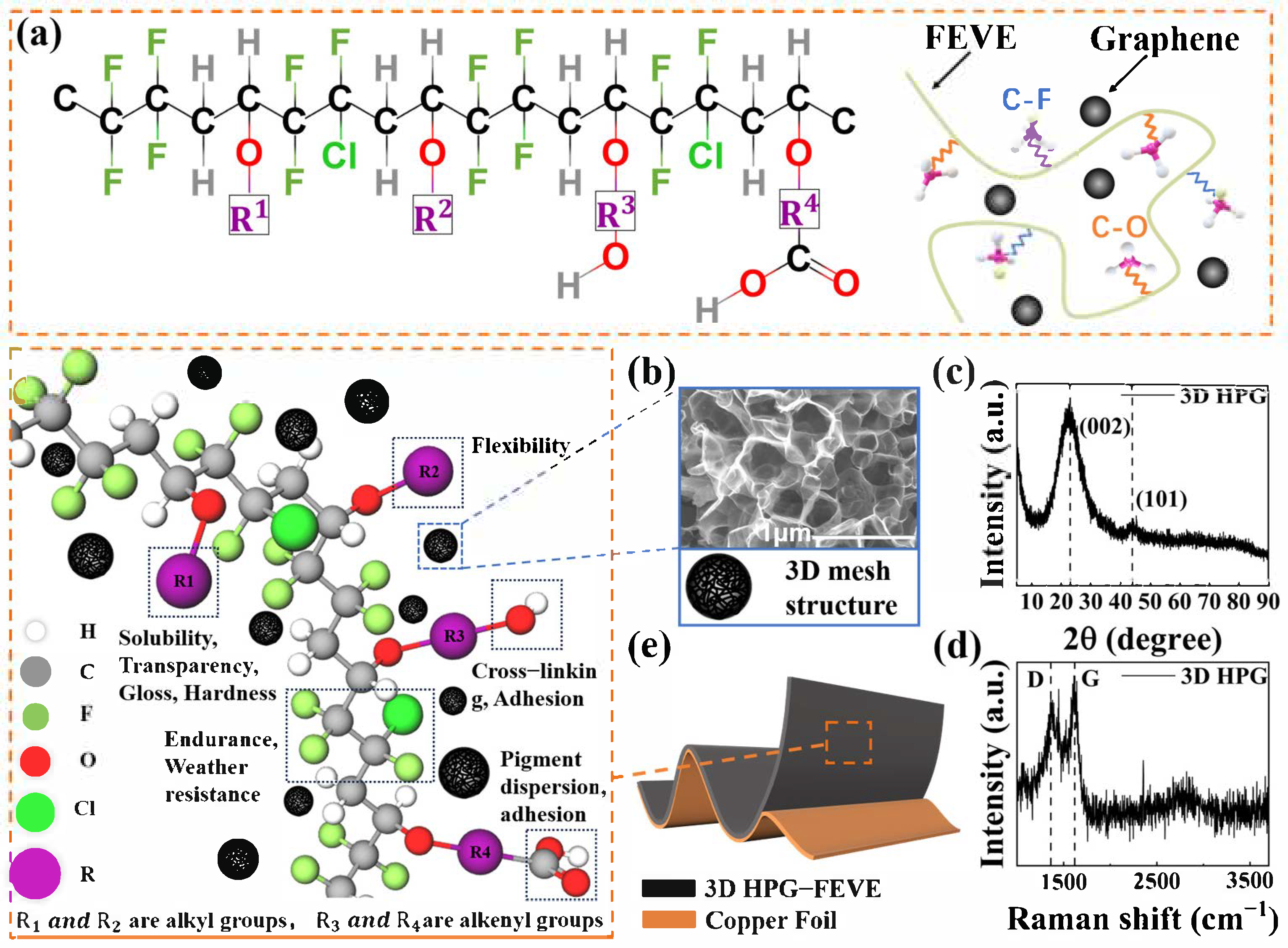
3.1. Fabrication of 3D HPG-FEVE Triboelectric Layers
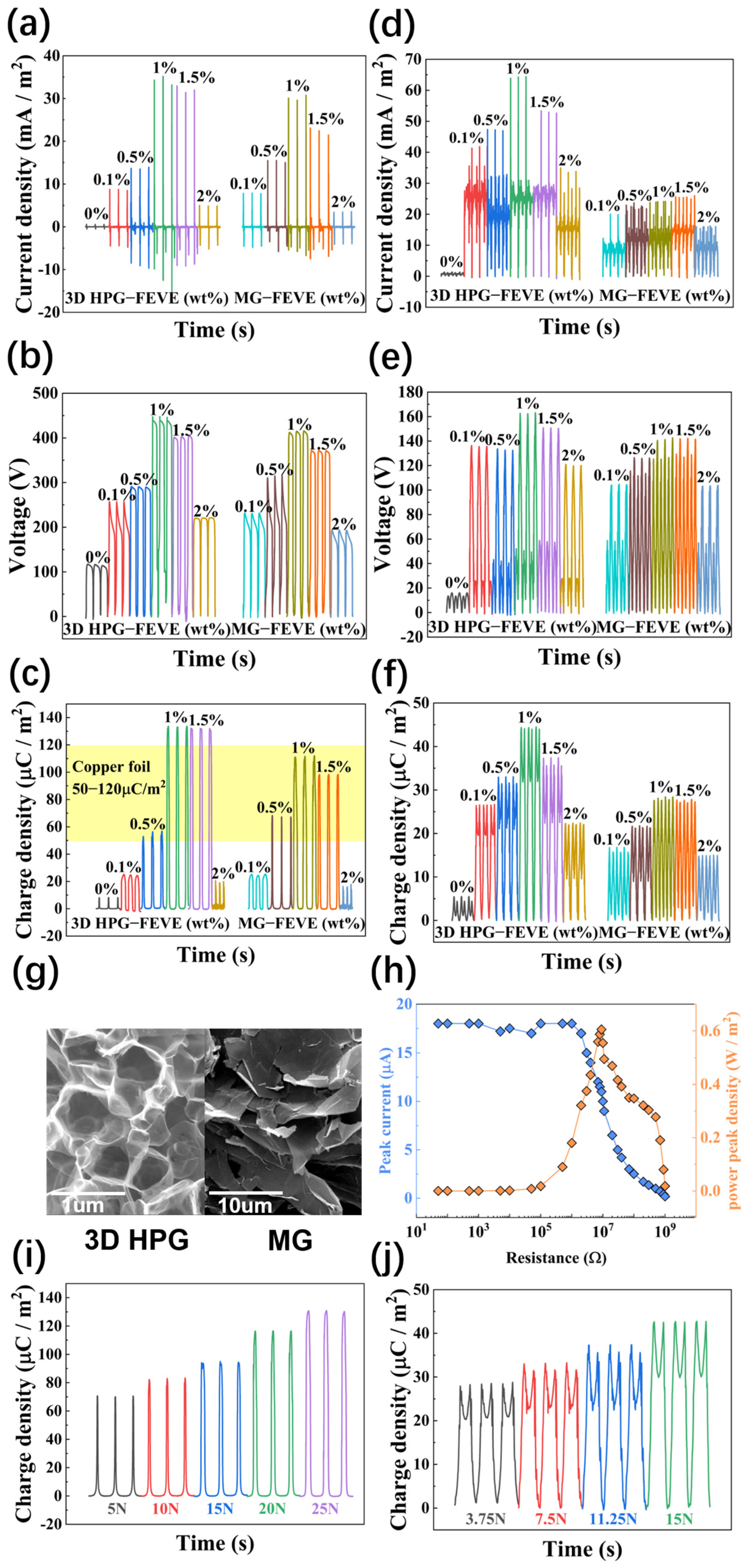
3.2. Triboelectric Performance of 3D HPG-FEVE Layers
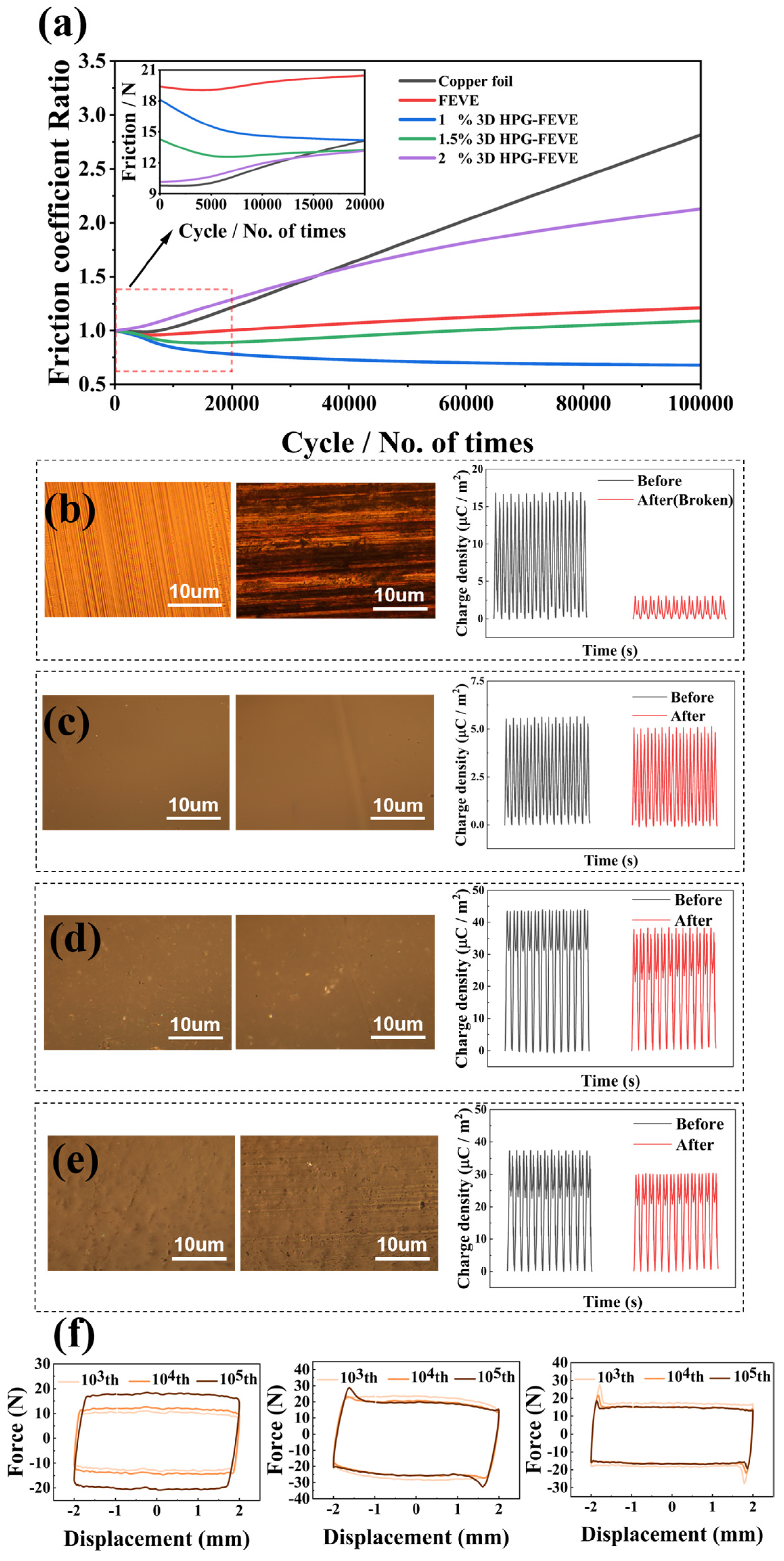
3.3. Wear Resistance of 3D HPG-FEVE Triboelectric Layer
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shan, C.; Li, K.; Cheng, Y.; Hu, C. Harvesting Environment Mechanical Energy by Direct Current Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Nano-Micro Lett. 2023, 15, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.; He, W.; Wu, H.; Shan, C.; Du, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, P.; Guo, H.; Chen, J.; Hu, C. High Output Performance and Ultra-Durable DC Output for Triboelectric Nanogenerator Inspired by Primary Cell. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Iwamoto, M.; Chen, X. A Review of Contact Electrification at Diversified Interfaces and Related Applications on Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Nano-Micro Lett. 2024, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.-R.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Wang, Z.L. Flexible triboelectric generator! Nano Energy 2012, 1, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerators as self-powered active sensors. Nano Energy 2015, 11, 436–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Zhou, L.; Gao, Y.; Xiao, J.; Liu, D.; Zhao, Z.; Qiao, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, J. Achieving High-Performance Triboelectric Nanogenerator by DC Pump Strategy. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2201957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Bai, P.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Ultrathin, Rollable, Paper-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Acoustic Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Sound Recording. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 4236–4243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, Y.; Lin, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Fan, X.; Yang, P.-K.; Yi, F.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric-Pyroelectric-Piezoelectric Hybrid Cell for High-Efficiency Energy-Harvesting and Self-Powered Sensing. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2340–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.L. Recent advances in high-performance triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 11698–11717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhou, L.; Liu, D.; Li, S.; Chen, S.; Dai, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.L. Improved Output Performance of Triboelectric Nanogenerator by Fast Accumulation Process of Surface Charges. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2100050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Diao, D.; Sun, K.; Fan, X.; Wang, P. Study on friction-electrification coupling in sliding-mode triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2018, 48, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhou, L.; Li, S.; Liu, D.; Li, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Dai, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.L. Selection rules of triboelectric materials for direct-current triboelectric nanogenerator. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoller, M.D.; Park, S.; Zhu, Y.; An, J.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene-Based Ultracapacitors. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 3498–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankovich, S.; Dikin, D.A.; Dommett, G.H.B.; Kohlhaas, K.M.; Zimney, E.J.; Stach, E.A.; Piner, R.D.; Nguyen, S.T.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene-based composite materials. Nature 2006, 442, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kady, M.F.; Strong, V.; Dubin, S.; Kaner, R.B. Laser Scribing of High-Performance and Flexible Graphene-Based Electrochemical Capacitors. Science 2012, 335, 1326–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shi, G. Preparation of Highly Conductive Graphene Hydrogels for Fabricating Supercapacitors with High Rate Capability. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 17206–17212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Scharstein, R.W. Electrostatics of graphene: Charge distribution and capacitance. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2010, 489, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yu, Z.; Neff, D.; Zhamu, A.; Jang, B.Z. Graphene-Based Supercapacitor with an Ultrahigh Energy Density. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 4863–4868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Lin, D.; Xu, F.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, H.; Gong, J.; Wang, T. Highly orientated graphene/epoxy coating with exceptional anti-corrosion performance for harsh oxygen environments. Corros. Sci. 2020, 176, 109049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatta, F.F.; Mohammad Haniff, M.A.S.; Mohamed, M.A. A review on applications of graphene in triboelectric nanogenerators. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022, 46, 544–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Gupta, M.K.; Lee, K.Y.; Sohn, A.; Kim, T.Y.; Shin, K.-S.; Kim, D.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, K.H.; Shin, H.-J.; et al. Transparent Flexible Graphene Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3918–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xie, B.; Long, J.; Kuang, Y.; Chen, X.; Hou, M.; Gao, J.; Zhou, S.; Fan, B.; He, Y.; et al. Interfacial Laser-Induced Graphene Enabling High-Performance Liquid-Solid Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2104290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrashekar, B.N.; Deng, B.; Smitha, A.S.; Chen, Y.; Tan, C.; Zhang, H.; Peng, H.; Liu, Z. Roll-to-Roll Green Transfer of CVD Graphene onto Plastic for a Transparent and Flexible Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 5210–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Jang, H.; Lee, Y.; Chae, Y.; Ahn, J.-H. Conformal, graphene-based triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered wearable electronics. Nano Energy 2016, 27, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Xu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Song, X. High-performance flexible self-powered tin disulfide nanoflowers/reduced graphene oxide nanohybrid-based humidity sensor driven by triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2020, 67, 104251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keel, E.; Ejaz, A.; McKinlay, M.; Garcia, M.P.; Caffio, M.; Gibson, D.; Nunez, C.G. Three-dimensional graphene foam based triboelectric nanogenerators for energy systems and autonomous sensors. Nano Energy 2023, 112, 108475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lin, X.; Gao, G.; Yu, J.; Wei, Y.; Gong, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z.L.; Sun, Q. Tribotronic Vertical Field-Effect Transistor Based on van der Waals Heterostructures. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2313210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Fang, L.; Qu, H.; Zhou, T.; Chen, C.; Wei, Q.; Shen, P.K.; Wan, L.; Tian, Z.Q. A wave-powered capacitive deionization system with in-situ blue energy harvester. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 498, 155530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, G.; Javed, M.S.; Wang, X.; Hu, C. Aligning graphene sheets in PDMS for improving output performance of triboelectric nanogenerator. Carbon 2017, 111, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnchana, V.; Huynh Van, N.; He, W.; Rasheed, A.; Park, H.; Amornkitbamrung, V.; Kang, D.J. Enhanced Power Output of a Triboelectric Nanogenerator using Poly(dimethylsiloxane) Modified with Graphene Oxide and Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 25263–25272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, G.; Bu, T.; Liu, Y.; Qi, Y.; Xie, Y.; Xu, S.; Deng, W.; Yang, W.; Zhang, C. MXene based mechanically and electrically enhanced film for triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 4833–4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Tian, G.; Xiong, D.; Yang, T.; Chun, F.; Zhong, S.; Lin, Z.; Li, W.; Yang, W. Understanding the Percolation Effect in Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Conductive Intermediate Layer. Research 2021, 2021, 7189376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Li, X.; Yao, Y.; Lan, L.; Shao, Y.; Zhao, F.; Ying, Y.; Ping, J. A multifunctional and highly flexible triboelectric nanogenerator based on MXene-enabled porous film integrated with laser-induced graphene electrode. Nano Energy 2019, 66, 104121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, Z.; Hu, C. Advanced designs for output improvement of triboelectric nanogenerator system. Mater. Today 2021, 45, 93–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Kim, S.-W.; Kar-Narayan, S. Materials-Related Strategies for Highly Efficient Triboelectric Energy Generators. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2003802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Olin, H. Material choices for triboelectric nanogenerators: A critical review. Ecomat 2020, 2, e12062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Hassan, I.; Pourrahimi, A.M.; Helal, A.S.; El-Kady, M.F.; Khassaf, H.; Kaner, R.B. Toward High-Performance Triboelectric Nanogenerators by Engineering Interfaces at the Nanoscale: Looking into the Future Research Roadmap. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 2000520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, G.; Wang, Z.L. Polymer Materials for High-Performance Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2000186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, C.; Zhao, F.; Shao, Y.; Ying, Y.; Ping, J. A self-charging device with bionic self-cleaning interface for energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2020, 73, 104738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xie, G.; Xu, W.; Guo, D.; Luo, J.; Prakash, B. Mechanical and tribological properties of nanocomposites incorporated with two-dimensional materials. Friction 2020, 8, 813–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, G.; Raj, N.P.M.J.; Kim, S.-J. Materials Beyond Conventional Triboelectric Series for Fabrication and Applications of Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2101170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wu, M.; Chen, H.; Hang, W.; Wang, X.; Han, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, P.; Beri, T.H.; Luo, L.; et al. Damage evolution and plastic deformation mechanism of passivation layer during shear rheological polishing of polycrystalline tungsten. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 28, 1584–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Peng, F.; Xu, Q.; Xiong, Y.; Zhao, S.; Tokunaga, K.; Wu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Chen, P.; et al. Hydrogen retention and affecting factors in rolled tungsten: Thermal desorption spectra and molecular dynamics simulations. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 30522–30531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penkov, O.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, D.-E. Tribology of Graphene: A Review. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2014, 15, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Du, S. Application of graphene derivatives and their nanocomposites in tribology and lubrication: A review. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 40642–40661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Sohn, M.; He, W.; Park, H.; Subramanian, K.R.V.; Kang, D.J. A high-output flexible triboelectric nanogenerator based on polydimethylsiloxane/three-dimensional bilayer graphene/carbon cloth composites. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 17150–17155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, G.-J.; Baek, S.-H.; Lee, S.-S.; Khan, F.; Kim, J.H.; Park, I.-K. Performance enhancement of triboelectric nanogenerators based on polyvinylidene fluoride/graphene quantum dot composite nanofibers. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 797, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menge, H.G.; Kim, J.O.; Park, Y.T. Enhanced Triboelectric Performance of Modified PDMS Nanocomposite Multilayered Nanogenerators. Materials 2020, 13, 4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wu, C.; Ruan, L.; Wang, J.; Qiu, Z.; Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, T.; Lin, J.; et al. Electron-transfer mechanisms for confirmation of contact-electrification in ZnO/polyimide-based triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2020, 75, 104818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wu, C.; Li, F.; Chen, W.; Guo, T.; Kim, T.W. Triboelectric electronic-skin based on graphene quantum dots for application in self-powered, smart, artificial fingers. Nano Energy 2018, 49, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Kim, T.W.; Choi, H.Y. Reduced graphene-oxide acting as electron-trapping sites in the friction layer for giant triboelectric enhancement. Nano Energy 2017, 32, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Wang, P.; Diao, D. Graphene Nanosheets Enhanced Triboelectric Output Performances of PTFE Films. Acs Appl. Electron. Mater. 2022, 4, 2839–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhou, F.; Zhan, S.; Tian, Y.; He, Q. Study on the bactericidal performance of graphene/TiO2 composite photocatalyst in the coating of PEVE. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 430, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shen, L.; Bao, N. Tribological and corrosion behaviors of fluorocarbon coating reinforced with sodium iron titanate platelets and whiskers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Bi, Z.; Zhang, R.; Liu, J.; Yu, X.; Li, Z. A comprehensive review on graphene-based anti-corrosive coatings. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 373, 104–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, S.; Hu, C. Charge Generation and Enhancement of Key Components of Triboelectric Nanogenerators: A Review. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, e2409833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Shen, P.K. Simultaneous Formation of Ultrahigh Surface Area and Three-Dimensional Hierarchical Porous Graphene-Like Networks for Fast and Highly Stable Supercapacitors. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2474–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical study of contact-mode triboelectric nanogenerators as an effective power source. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 3576–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, C.; Dai, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, A.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Z.L. Achieving ultrahigh triboelectric charge density for efficient energy harvesting. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Chen, Y.; Chi, H.; Qiu, H.; Xue, H.; Bai, H. 3D Printing of a Polydimethylsiloxane/Polytetrafluoroethylene Composite Elastomer and its Application in a Triboelectric Nanogenerator. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 57441–57449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wen, Z.; Zi, Y.; Zhou, P.; Lin, J.; Guo, H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. All-Plastic-Materials Based Self-Charging Power System Composed of Triboelectric Nanogenerators and Supercapacitors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 1070–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zi, Y.; Zhou, Y.S.; Li, S.; Fan, F.; Lin, L.; Wang, Z.L. Molecular surface functionalization to enhance the power output of triboelectric nanogenerators. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 3728–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, Y.; Wu, C.; Ding, W.; Wang, Z.L. Maximized Effective Energy Output of Contact-SeparationTriggered Triboelectric Nanogenerators as Limited by Air Breakdown. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1700049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soin, N.; Zhao, P.; Prashanthi, K.; Chen, J.; Ding, P.; Zhou, E.; Shab, T.; Ray, S.C.; Tsonos, C.; Thundat, T.; et al. High performance triboelectric nanogenerators based on phase-inversion piezoelectric membranes of poly(vinylidene fluoride)-zinc stannate (PVDF-ZnSnO₃) and polyamide-6 (PA6). Nano Energy 2016, 30, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Jin, H.; Ma, M.; Quan, L.; Chen, J.; Dong, S.; Zhang, H.; Lv, C.; Fu, Y.; Luo, J. Significantly Enhanced Performance of Triboelectric Nanogenerator by Incorporating BaTiO3 Nanoparticles in Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Film. Phys. Status Solidi A-Appl. Mater. Sci. 2019, 216, 1900068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, M.M.; Saqib, Q.M.; Noman, M.; Sheeraz, M.; Rasheed, A.; Yousuf, M.; Lee, E.; Kim, J.; Ko, Y.; Patil, C.S.; et al. Novel Intercalation Approach in MXene Using Modified Silica Nanospheres to Enhance the Surface Charge Density for Superior Triboelectric Performance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2408271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekhar, R.; Reza, M.S.; Kim, K.J.; Prabu, A.A.; Kim, H. Electrospun PVDF/aromatic HBP of 4th gen based flexible and self-powered TENG for wearable energy harvesting and health monitoring. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 50231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Chen, H.; Wu, M.; Sun, Z.; Gao, M.; Li, W.; Li, C.; Yu, H.; Zhang, C.; Xu, Y.; et al. A Flexible Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on Cellulose-Reinforced MXene Composite Film. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 9, 2102124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, K.; Zhang, L.; Ren, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, Z.; Shan, K.; Zhang, L.; Wan, L.; Lin, T. Highly Wear-Resistant Triboelectric Nanogenerators Based on Fluorocarbon-Graphene Hybrids. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15100763
Zhang K, Zhang L, Ren J, Li Y, Wu Z, Shan K, Zhang L, Wan L, Lin T. Highly Wear-Resistant Triboelectric Nanogenerators Based on Fluorocarbon-Graphene Hybrids. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(10):763. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15100763
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ke, Liang Zhang, Jinlong Ren, Yubin Li, Zaibang Wu, Kaihan Shan, Lin Zhang, Lingyu Wan, and Tao Lin. 2025. "Highly Wear-Resistant Triboelectric Nanogenerators Based on Fluorocarbon-Graphene Hybrids" Nanomaterials 15, no. 10: 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15100763
APA StyleZhang, K., Zhang, L., Ren, J., Li, Y., Wu, Z., Shan, K., Zhang, L., Wan, L., & Lin, T. (2025). Highly Wear-Resistant Triboelectric Nanogenerators Based on Fluorocarbon-Graphene Hybrids. Nanomaterials, 15(10), 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15100763





