Rose Bengal–Chitosan Nanocomposites for Oral Administration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Purification of CS
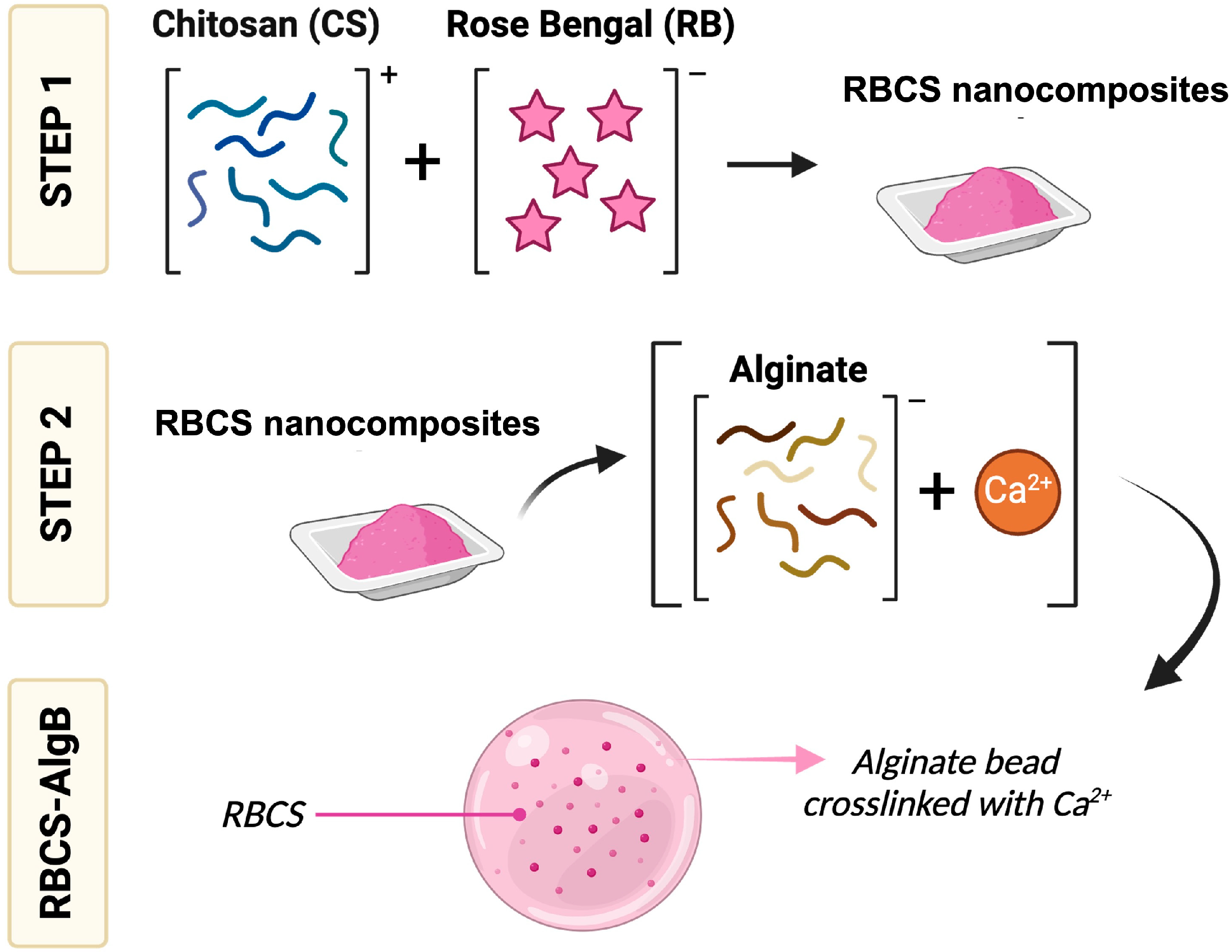
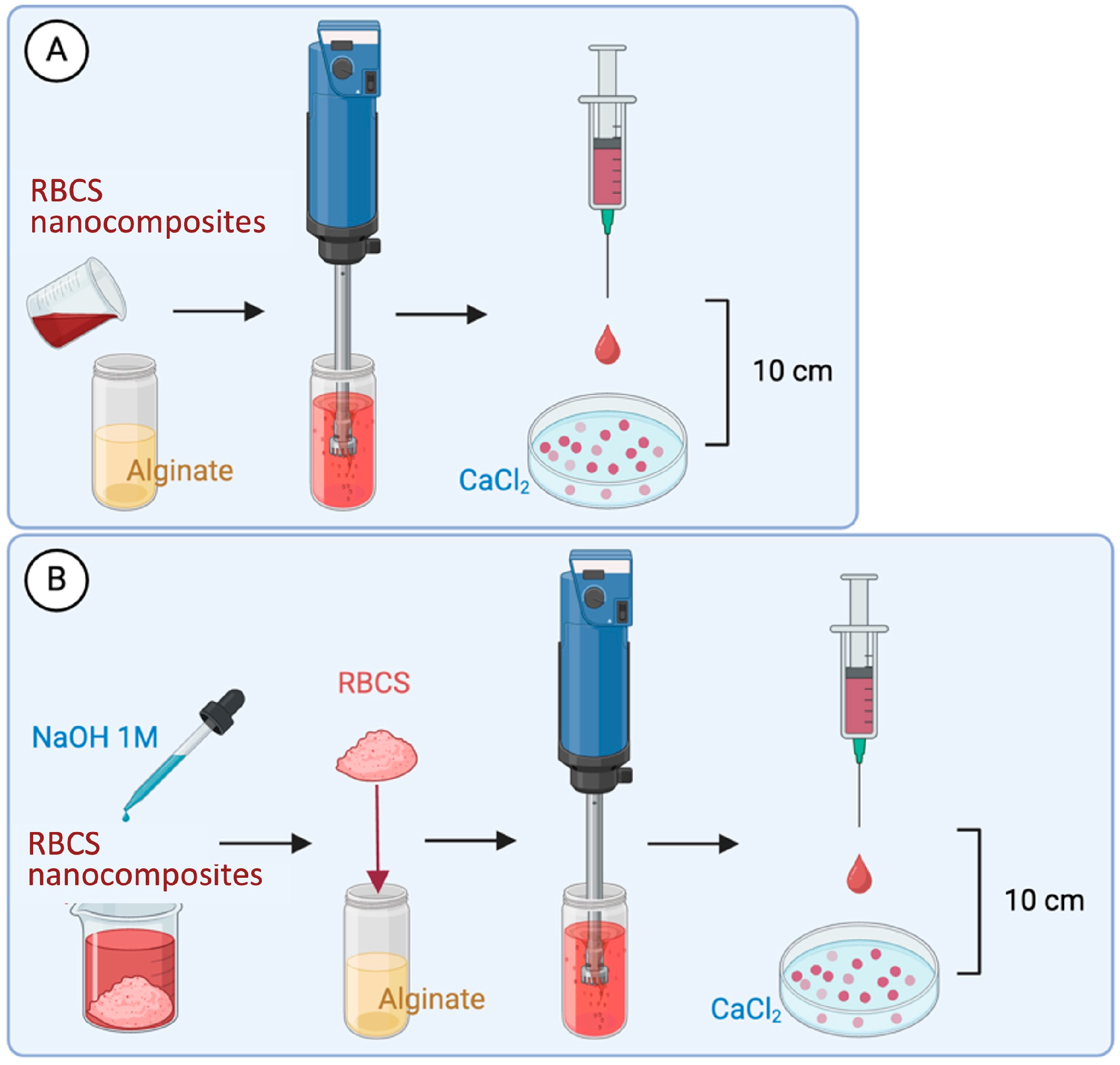
2.3. Formulation of RBCS Nanocomposites
2.4. Formulation of RBCS-Loaded AlgBs (RBCS-AlgBs)
2.5. Characterization of RB Delivery Systems
2.5.1. Drug Content and Drug Loading
2.5.2. Production Yield
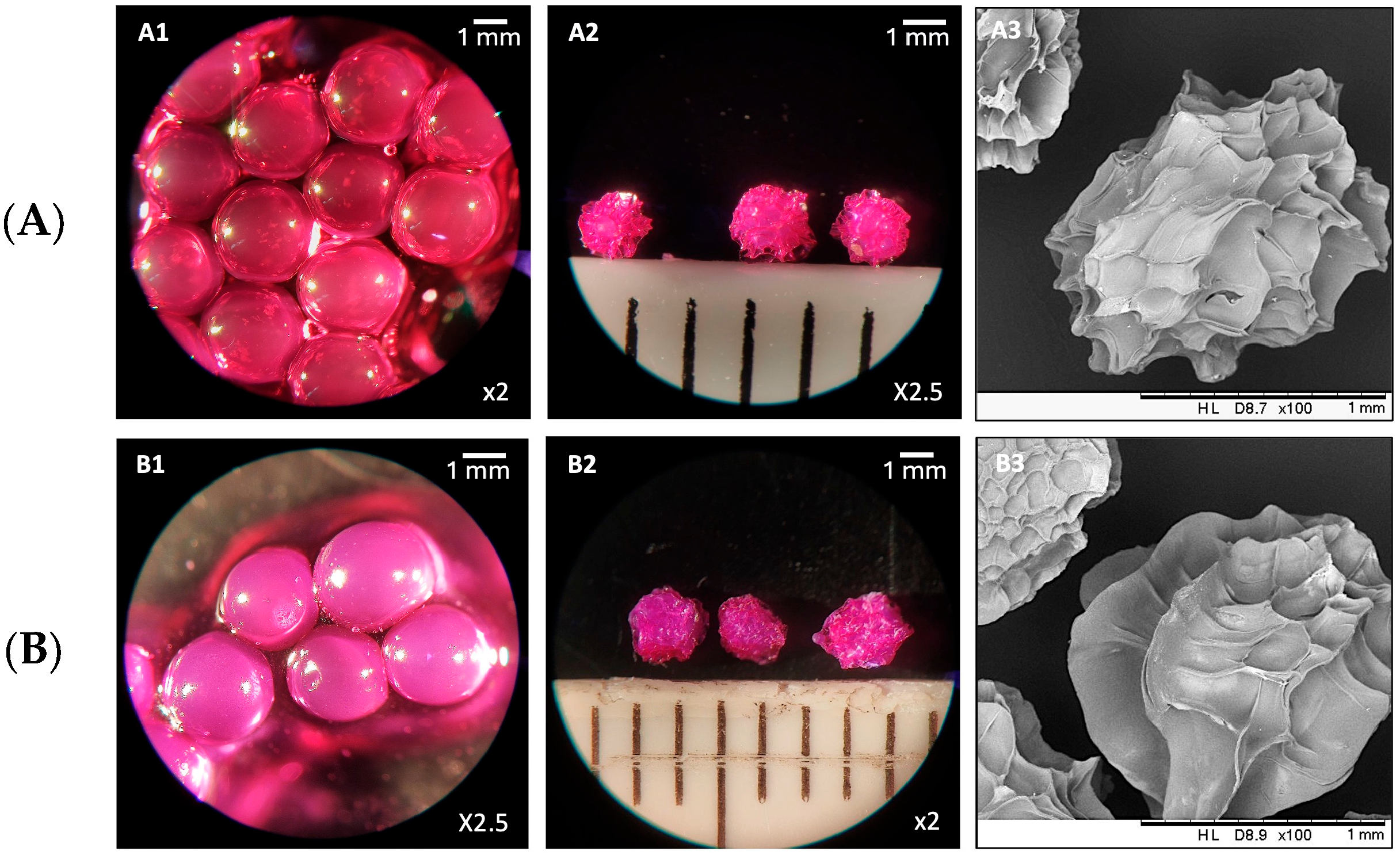
2.5.3. Microscopy-Based Evaluations
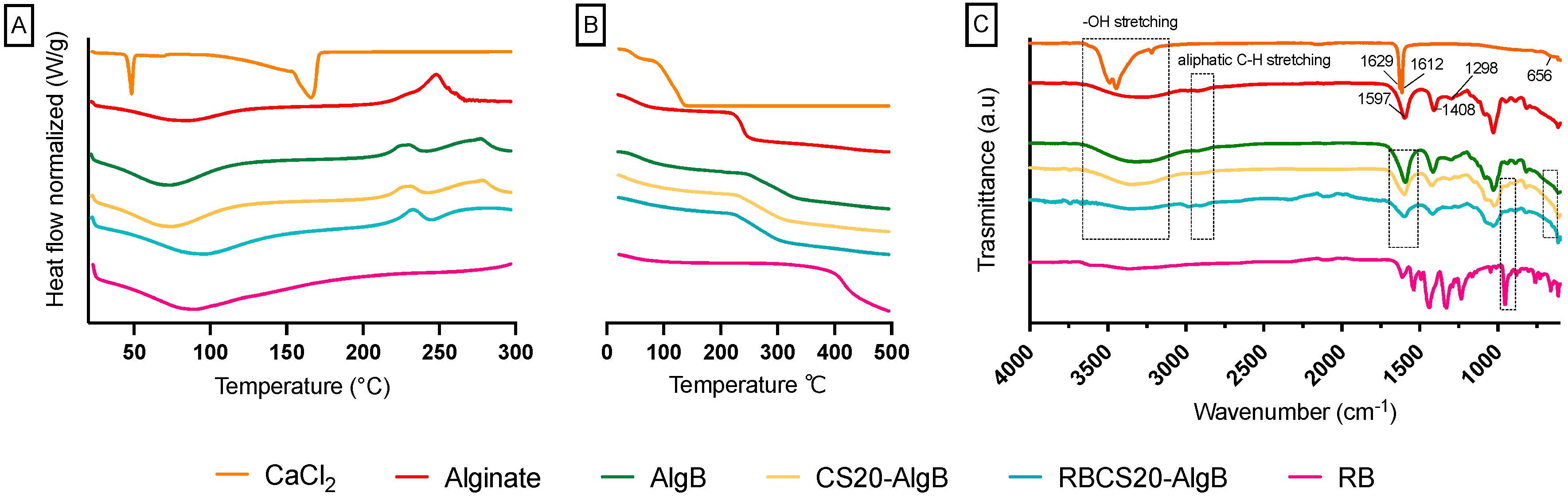
2.5.4. Physicochemical Characterization
2.6. In Vitro Drug Release Studies
2.6.1. Release Study in Buffer Solutions as Acceptor Mediums
2.6.2. Release Study in SGFs as Acceptor Mediums
2.6.3. Data Analysis of In Vitro Release Profiles
2.7. Swelling Studies
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
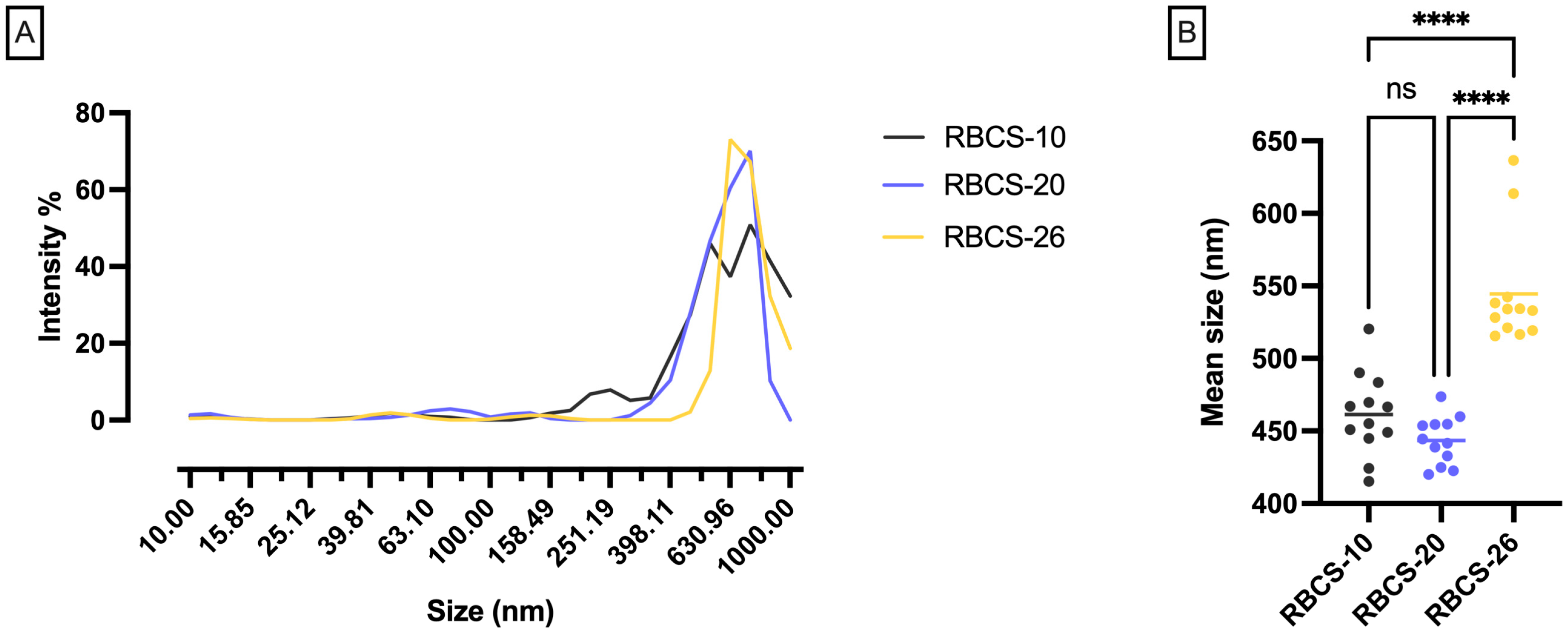
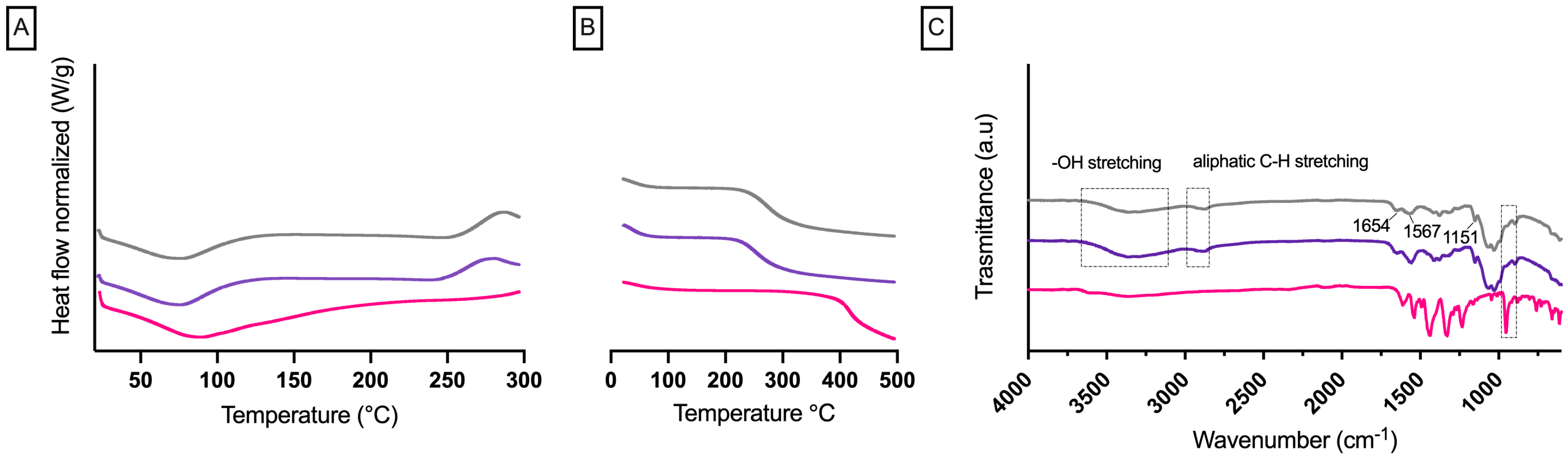
3.1. Formulation and Characterization of RBCS
3.1.1. In Vitro Release Profiles of RBCS-20
3.2. Formulation and Characterization of RBCS-AlgBs
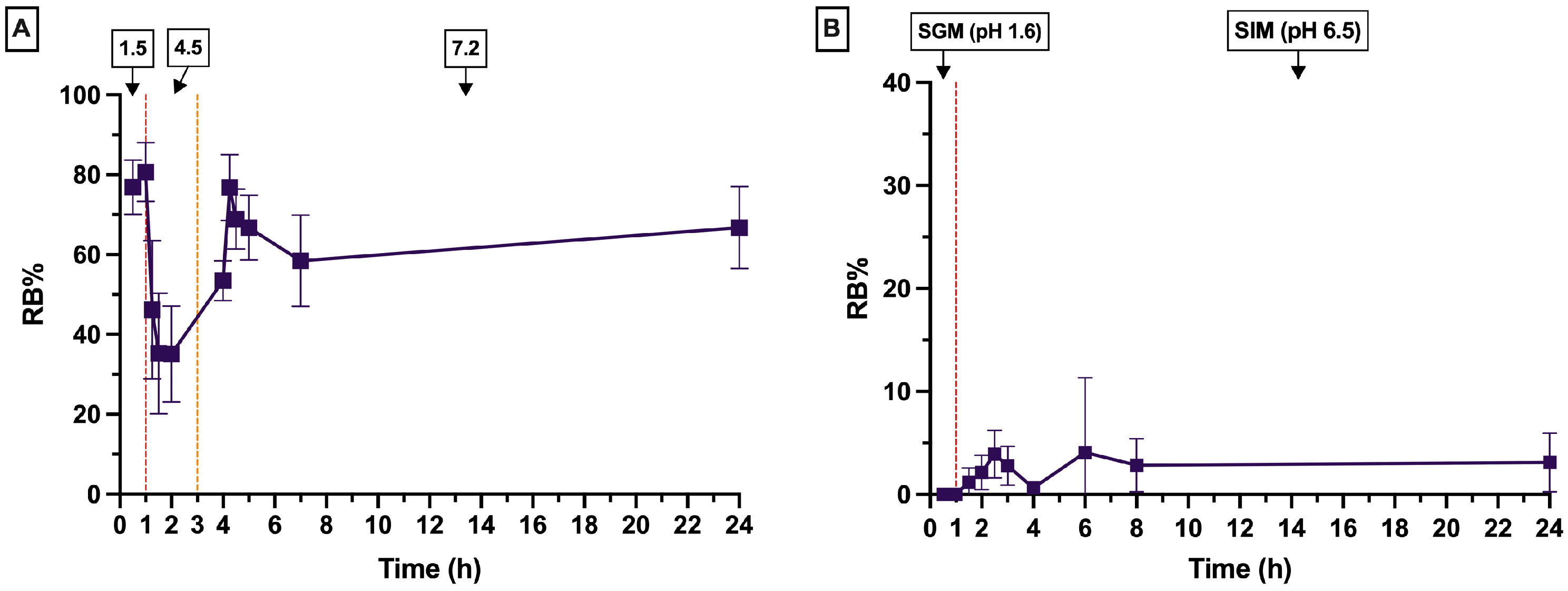
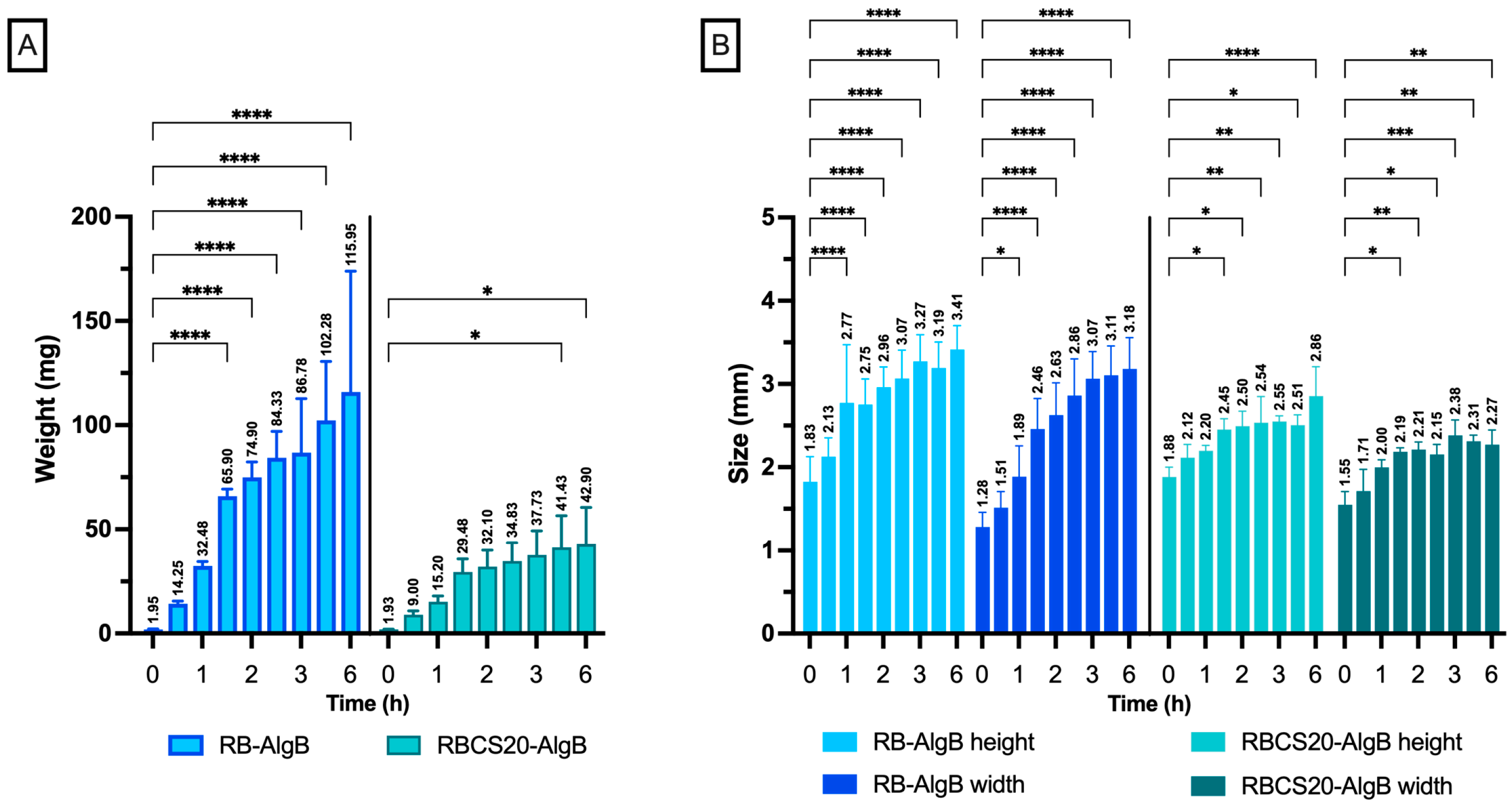
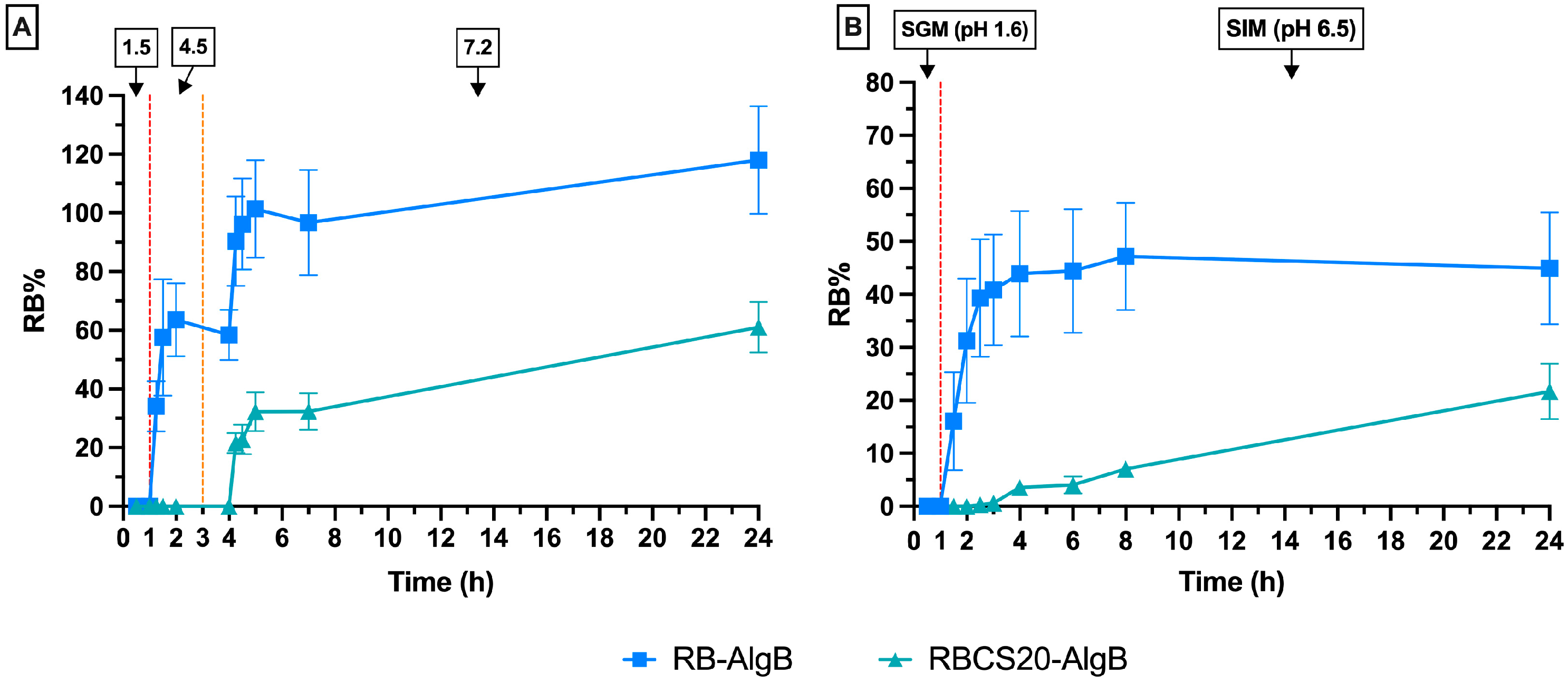
In Vitro Swelling and Release Profiles of RBCS20-AlgBs and RB-AlgBs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yan, E.; Kwek, G.; Qing, N.S.; Lingesh, S.; Xing, B. Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy for the Remote Eradication of Bacteria. ChemPlusChem 2023, 88, e202300009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurosu, M.; Mitachi, K.; Yang, J.; Pershing, E.V.; Horowitz, B.D.; Wachter, E.A.; Lacey, J.W.; Ji, Y.; Rodrigues, D.J. Antibacterial Activity of Pharmaceutical-Grade Rose Bengal: An Application of a Synthetic Dye in Antibacterial Therapies. Molecules 2022, 27, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamblin, M.R.; Hasan, T. Photodynamic Therapy: A New Antimicrobial Approach to Infectious Disease? Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2004, 3, 436–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, C.M.; Tunney, M.M.; McCarron, P.A.; Donnelly, R.F. Drug Delivery Strategies for Photodynamic Antimicrobial Chemotherapy: From Benchtop to Clinical Practice. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2009, 95, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turrini, E.; Ulfo, L.; Costantini, P.E.; Saporetti, R.; Di Giosia, M.; Nigro, M.; Petrosino, A.; Pappagallo, L.; Kaltenbrunner, A.; Cantelli, A.; et al. Molecular Engineering of a Spheroid-Penetrating Phage Nanovector for Photodynamic Treatment of Colon Cancer Cells. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2024, 81, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani Taghizadeh Rabe, S.; Mousavi, S.H.; Tabasi, N.; Rastin, M.; Zamani Taghizadeh Rabe, S.; Siadat, Z.; Mahmoudi, M. Rose Bengal Suppresses Gastric Cancer Cell Proliferation via Apoptosis and Inhibits Nitric Oxide Formation in Macrophages. J. Immunotoxicol. 2014, 11, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Kunda, N.; Qiao, G.; Calata, J.F.; Pardiwala, K.; Prabhakar, B.S.; Maker, A.V. Colon Cancer Cell Treatment with Rose Bengal Generates a Protective Immune Response via Immunogenic Cell Death. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Qiu, T.; Zhou, G. Co-Delivery of Rose Bengal and Doxorubicin Nanoparticles for Combination Photodynamic and Chemo-Therapy. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2019, 15, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshammari, N.D.; Elkanayati, R.; Vemula, S.K.; Al Shawakri, E.; Uttreja, P.; Almutairi, M.; Repka, M.A. Advancements in Colon-Targeted Drug Delivery: A Comprehensive Review on Recent Techniques with Emphasis on Hot-Melt Extrusion and 3D Printing Technologies. AAPS PharmSciTech 2024, 25, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, J.; Duan, H.; Qin, Q.; Teng, Z.; Gan, F.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, X. Advances in Oral Drug Delivery Systems: Challenges and Opportunities. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Sun, Y.; Lu, A.; Wang, X.; Shi, Y. Ionic Liquids: Promising Approach for Oral Drug Delivery. Pharm. Res. 2022, 39, 2353–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jirsa, M.; Raban, P. Metabolism of Rose Bengal. Nature 1962, 195, 1100–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, J.B.; Bauman, M.E.; Beaty, T.M. Effect of Sodium Orthovanadate on the Hepatobiliary Clearance of Rose Bengal in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1993, 46, 2269–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mura, P.; Maestrelli, F.; Cirri, M.; Mennini, N. Multiple Roles of Chitosan in Mucosal Drug Delivery: An Updated Review. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, A. Chitosan-Based Drug Conjugated Nanocomposites: Advances and Innovation in Cancer Therapy. Regen. Eng. Transl. Med. 2024, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; Mondal, S.; Mukherjee, D.; Adhikari, A.; Ahmed, S.A.; Alsantali, R.I.; Khder, A.S.; Altass, H.M.; Moussa, Z.; Das, R.; et al. Oral Drug Delivery Using a Polymeric Nanocarrier: Chitosan Nanoparticles in the Delivery of Rifampicin. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 4622–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.; You, J.; Jin, B.; Mo, F.; Chen, J.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, H. Self-Assembled Chitosan/Rose Bengal Derivative Nanoparticles for Targeted Sonodynamic Therapy: Preparation and Tumor Accumulation. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 17915–17923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekmukhametova, A.; Antony, A.; Halliday, C.; Chen, S.; Ho, C.-H.; Uddin, M.M.N.; Longo, L.; Pedrinazzi, C.; George, L.; Wuhrer, R.; et al. Rose Bengal–Encapsulated Chitosan Nanoparticles for the Photodynamic Treatment of Trichophyton Species. Photochem. Photobiol. 2024, 100, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.; Hamblin, M.R.; Kishen, A. Characterization of a Conjugate between Rose Bengal and Chitosan for Targeted Antibiofilm and Tissue Stabilization Effects as a Potential Treatment of Infected Dentin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 4876–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.M.N.; Bekmukhametova, A.; Antony, A.; Barman, S.K.; Houang, J.; Wu, M.J.; Hook, J.M.; George, L.; Wuhrer, R.; Mawad, D.; et al. Encapsulated Rose Bengal Enhances the Photodynamic Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Molecules 2024, 29, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.M.N.; Bekmukhametova, A.; Antony, A.; Barman, S.K.; Houang, J.; Wu, M.J.; Hook, J.; George, L.; Wuhrer, R.; Mawad, D.; et al. Photodynamic Treatment of Human Breast and Prostate Cancer Cells Using Rose Bengal-Encapsulated Nanoparticles. Molecules 2023, 28, 6901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rassu, G.; Porcu, E.; Fancello, S.; Obinu, A.; Senes, N.; Galleri, G.; Migheli, R.; Gavini, E.; Giunchedi, P. Intranasal Delivery of Genistein-Loaded Nanoparticles as a Potential Preventive System against Neurodegenerative Disorders. Pharmaceutics 2018, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, M.R.C.; Loebenberg, R.; Almukainzi, M. Simulated Biological Fluids with Possible Application in Dissolution Testing. Dissolution Technol. 2011, 18, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demartis, S.; Obinu, A.; Gavini, E.; Giunchedi, P.; Rassu, G. Nanotechnology-Based Rose Bengal: A Broad-Spectrum Biomedical Tool. Dyes Pigments 2021, 188, 109236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.; Sousa Lobo, J.M. Evaluation of Mathematical Models Describing Drug Release from Estradiol Transdermal Systems. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2003, 29, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritger, P.L.; Peppas, N.A. A Simple Equation for Description of Solute Release II. Fickian and Anomalous Release from Swellable Devices. J. Control. Release 1987, 5, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafernik, K.; Ładniak, A.; Blicharska, E.; Czarnek, K.; Ekiert, H.; Wiącek, A.E.; Szopa, A. Chitosan-Based Nanoparticles as Effective Drug Delivery Systems—A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baharlouei, P.; Rahman, A. Chitin and Chitosan: Prospective Biomedical Applications in Drug Delivery, Cancer Treatment, and Wound Healing. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, R.S.; Ferreira, A.P.G.; Venâncio, T.; Cavalheiro, É.T.G. Preparation, Characterization and Study of the Dissociation of Naproxen from Its Chitosan Salt. Molecules 2022, 27, 5801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhail, L.; Aleksandr, K.; Aleksandr, P. Study of the Influence of the Composition and pH of the Solution on the Structure and Morphology of Particle Dispersions of a (Bio)Polyelectrolyte Complex between Chitosan and Gelatin. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2024, 303, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Huang, Y. Ionically Crosslinked Polyelectrolyte Nanoparticle Formation Mechanisms: The Significance of Mixing. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 9871–9880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demartis, S.; Picco, C.J.; Larrañeta, E.; Korelidou, A.; Islam, R.; Coulter, J.A.; Giunchedi, P.; Donnelly, R.F.; Rassu, G.; Gavini, E. Evaluating the Efficacy of Rose Bengal-PVA Combinations within PCL/PLA Implants for Sustained Cancer Treatment. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2024, 15, 1770–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, S.; Rath, P.; Sri Hari Kumar, A.; Tiwari, T.N. Extraction and Characterization of Chitin and Chitosan from Fishery Waste by Chemical Method. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2015, 3, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Reddy, C.S.K.; Swami, R.; Kushwah, V. Amphotericin B Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles: Implication of Bile Salt Stabilization on Gastrointestinal Stability, Permeability and Oral Bioavailability. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 3152–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, D.; Rathnanand, M.; Tippavajhala, V.K. Unlocking the Potential of Bilosomes and Modified Bilosomes: A Comprehensive Journey into Advanced Drug Delivery Trends. AAPS PharmSciTech 2023, 24, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-Y.; Oh, H.; Wang, T.-Y.; Raghavan, S.R.; Tung, S.-H. Mixtures of Lecithin and Bile Salt Can Form Highly Viscous Wormlike Micellar Solutions in Water. Langmuir 2014, 30, 10221–10230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennacef, C.; Desobry, S.; Jasniewski, J.; Leclerc, S.; Probst, L.; Desobry-Banon, S. Influence of Alginate Properties and Calcium Chloride Concentration on Alginate Bead Reticulation and Size: A Phenomenological Approach. Polymers 2023, 15, 4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malektaj, H.; Drozdov, A.D.; deClaville Christiansen, J. Mechanical Properties of Alginate Hydrogels Cross-Linked with Multivalent Cations. Polymers 2023, 15, 3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekalska, M.; Sosnowska, K.; Czajkowska-Kośnik, A.; Winnicka, K. Calcium Chloride Modified Alginate Microparticles Formulated by the Spray Drying Process: A Strategy to Prolong the Release of Freely Soluble Drugs. Materials 2018, 11, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekalska, M.; Sosnowska, K.; Zakrzeska, A.; Kasacka, I.; Lewandowska, A.; Winnicka, K. The Influence of Chitosan Cross-Linking on the Properties of Alginate Microparticles with Metformin Hydrochloride—In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. Molecules 2017, 22, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, M.T.P.; Kishima, J.O.F.; Silva, J.B.M.D.; Mantovan, J.; Colodi, F.G.; Mali, S. Crosslinking Methods in Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogels for Drug Delivery Systems. Biomed. Mater. Devices 2024, 2, 288–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herdiana, Y.; Febrina, E.; Nurhasanah, S.; Gozali, D.; Elamin, K.M.; Wathoni, N. Drug Loading in Chitosan-Based Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, S.; Wang, K.; Guo, D.-S.; Liu, Y. Supramolecular Polymeric Vesicles Formed by p -Sulfonatocalix[4]Arene and Chitosan with Multistimuli Responses. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekin, S.; Sarmad, S.; Gürkan, K.; Yenici, G.; Keçeli, G.; Gürdağ, G. Dielectric, Thermal, and Swelling Properties of Calcium Ion-Crosslinked Sodium Alginate Film. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2014, 54, 1372–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushak, S.; Suárez, M.; Véliz, S.; Fernández, A.G.; Flores, E.; Galleguillos, H.R. Characterization of Calcium Chloride Tetrahydrate as a Phase Change Material and Thermodynamic Analysis of the Results. Renew. Energy 2016, 95, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurić, S.; Đermić, E.; Topolovec-Pintarić, S.; Bedek, M.; Vinceković, M. Physicochemical Properties and Release Characteristics of Calcium Alginate Microspheres Loaded with Trichoderma Viride Spores. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 2534–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, J.A.; Cortese, Y.J.; Mojicevic, M.; Brennan Fournet, M.; Chen, Y. Composite Films of Thermoplastic Starch and CaCl2 Extracted from Eggshells for Extending Food Shelf-Life. Polysaccharides 2021, 2, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Yu, S.; Lin, D.; Wu, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Ding, Z.; Miao, Y.; Liu, T.; Chen, T.; et al. Preparation, Characterization, and Release Behavior of Doxorubicin Hydrochloride from Dual Cross-Linked Chitosan/Alginate Hydrogel Beads. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 3057–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Choi, D.; Heo, J.; Jung, S.Y.; Hong, J. Studies on the Drug Loading and Release Profiles of Degradable Chitosan-Based Multilayer Films for Anticancer Treatment. Cancers 2020, 12, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovidendra, K.; Deepti, C.; Himanshu, C.; Santosh, K.M.; Peeyush, B. Development and Characterization of Floating Alginate Beads for Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System. Acta Pharm. Sci. 2011, 53, 551–562. [Google Scholar]
- Sipos, B.; Benei, M.; Katona, G.; Csóka, I. Optimization and Characterization of Sodium Alginate Beads Providing Extended Release for Antidiabetic Drugs. Molecules 2023, 28, 6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | RB Solution (mg/mL) | CS Solution (mg/mL) | CS/RB Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| RBCS-10 | 1.5 | 15 | 10:1 |
| RBCS-20 | 0.75 | 15 | 20:1 |
| RBCS-26 | 0.75 | 20 | 26.6:1 |
| Sample | CaCl2 Solution (mg/mL) | CaCl2/Alginate Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| AlgB-1.8 | 5 | 1.8:1 |
| AlgB-3.75 | 10 | 3.75:1 |
| AlgB-5.6 | 15 | 5.6:1 |
| Parameter | Condition 1 Buffer Solutions 1 | Condition 2 Simulated Gastrointestinal Fluids 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Amount of RB | 0.5 mg | 0.1 mg |
| Volume of Release Medium | 200 mL | 10 mL |
| Temperature | 37 °C | 37 °C |
| Agitation Speed | 100 rpm | 100 rpm |
| Apparatus | USP dissolution apparatus (paddles) | Incubator |
| pH Conditions | 1.5 (1 h), 4.5 (2 h), 7.2 (21 h) | 1.6 (1 h), 6.5 (23 h) |
| Gastric Medium Composition | NaCl, HCl | STC 3, Lecithin, Pepsin, NaCl, pH 1.6 |
| Intestinal Medium Composition | NaCl, HCl, Trizma base, sodium acetate | STC, Lecithin, Maleic acid, NaOH, NaCl, pH 6.5 |
| Sample Volume Collected | 1 mL | 0.5 mL |
| Sample | PY% (Mean ± SD) | CV% |
|---|---|---|
| AlgB-1.8 | 44 ± 3 ° * | 6.42 |
| AlgB-3.75 | 31 ± 3 ° # | 9.11 |
| AlgB-5.6 | 17 ± 2 * # | 10.56 |
| Sample | PY% (Mean ± SD) | Theor. DC% (Mean ± SD) | Exp. DC% (Mean ± SD) | DL% (Mean ± SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AlgB | 44.0 ± 3.0 | - | - | - |
| RB-AlgB | 37.0 ± 2.0 * | 2.6 ± 0.2 ° | 1.3 ± 0.4 ° | 47.0 ± 12.0 # |
| CS20-AlgB | 68.0 ± 4.0 | - | - | - |
| RBCS20-AlgB | 73.0 ± 11.0 * | 2.5 ± 0.3 | 2.4 ± 0.3 | 96.0 ± 1.0 # |
| Zero Order | Korsmeyer–Peppas | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | KZO (h−1) | R2 | KKP (h−n) | n | |
| RB-AlgBs (all curve) | 0.213 | 0.010 | 0.842 | 0.327 | 0.149 |
| RB-AlgBs (linear section) | 0.980 | 0.266 | 0.994 | 0.294 | 0.769 |
| RBCS20-AlgBs (all curve) | 0.991 | 0.010 | 0.988 | 0.008 | 1.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Demartis, S.; Picco, C.J.; Fandiño, O.E.; Larrañeta, E.; Donnelly, R.F.; Giunchedi, P.; Rassu, G.; Gavini, E. Rose Bengal–Chitosan Nanocomposites for Oral Administration. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15100706
Demartis S, Picco CJ, Fandiño OE, Larrañeta E, Donnelly RF, Giunchedi P, Rassu G, Gavini E. Rose Bengal–Chitosan Nanocomposites for Oral Administration. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(10):706. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15100706
Chicago/Turabian StyleDemartis, Sara, Camila J. Picco, Octavio E. Fandiño, Eneko Larrañeta, Ryan F. Donnelly, Paolo Giunchedi, Giovanna Rassu, and Elisabetta Gavini. 2025. "Rose Bengal–Chitosan Nanocomposites for Oral Administration" Nanomaterials 15, no. 10: 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15100706
APA StyleDemartis, S., Picco, C. J., Fandiño, O. E., Larrañeta, E., Donnelly, R. F., Giunchedi, P., Rassu, G., & Gavini, E. (2025). Rose Bengal–Chitosan Nanocomposites for Oral Administration. Nanomaterials, 15(10), 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15100706











